a08ccd4ddd2ccfd46e27ba3b5c5dc6c4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Memory
Memory
 Considering memory… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Be prepared to interpret, or share your perspectives on the following quotes. “Whereas all living species have a past, only humans have a history. ” “One never steps into the same stream of consciousness twice. ” “Most of our memories are really about the future. ” “We are the sum of our memories…Change your memory and change your identity. ” “A memory is more atmospheric than accurate, more an evolving fiction than a sacred text. ”
Considering memory… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Be prepared to interpret, or share your perspectives on the following quotes. “Whereas all living species have a past, only humans have a history. ” “One never steps into the same stream of consciousness twice. ” “Most of our memories are really about the future. ” “We are the sum of our memories…Change your memory and change your identity. ” “A memory is more atmospheric than accurate, more an evolving fiction than a sacred text. ”
 The Memory Process Three Steps § Encoding § Processing of info into memory system (typing on a computer) § Storage § Retention of encoded material over time (to hit save) § Retrieval § Getting the info out of storage (opening a file)
The Memory Process Three Steps § Encoding § Processing of info into memory system (typing on a computer) § Storage § Retention of encoded material over time (to hit save) § Retrieval § Getting the info out of storage (opening a file)
 Encoding, storage or retrieval? ? § Continuing to pronounce nuclear as nucular… § A failure of which?
Encoding, storage or retrieval? ? § Continuing to pronounce nuclear as nucular… § A failure of which?
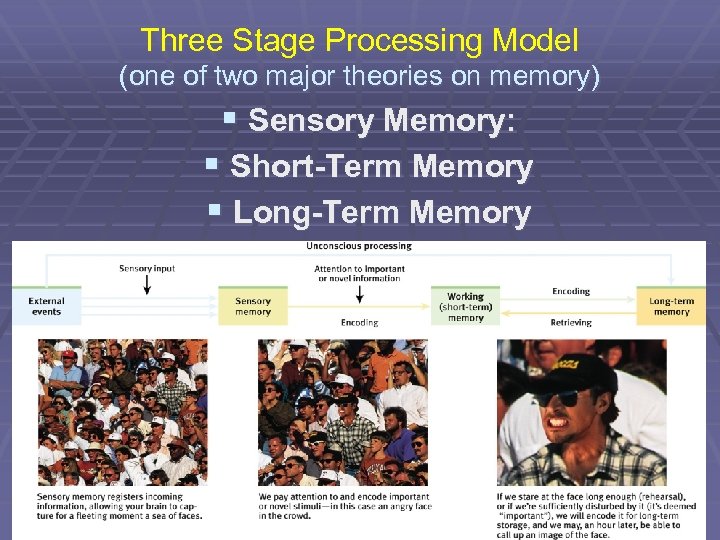 Three Stage Processing Model (one of two major theories on memory) § Sensory Memory: § Short-Term Memory § Long-Term Memory
Three Stage Processing Model (one of two major theories on memory) § Sensory Memory: § Short-Term Memory § Long-Term Memory
 Sensory Memory § Immediate recording of sensory info § “Split second holding tank” § Most stimulus not encoded- Why? § Selective Attention § Sensory Memory registered as: § Iconic (split second vanishing photograph) § Echoic (4 second sounds)
Sensory Memory § Immediate recording of sensory info § “Split second holding tank” § Most stimulus not encoded- Why? § Selective Attention § Sensory Memory registered as: § Iconic (split second vanishing photograph) § Echoic (4 second sounds)
 Short-Term Memory AKA Working Memory § § Memory that holds a few items briefly. Limit: Seven digits/ items (plus or minus 2) Info is stored into long-term, or forgotten. Lasts 3 -12 seconds § Short-Term, or Working Memory has 3 parts: § Acoustic codes § Visual Codes § Semantic Codes
Short-Term Memory AKA Working Memory § § Memory that holds a few items briefly. Limit: Seven digits/ items (plus or minus 2) Info is stored into long-term, or forgotten. Lasts 3 -12 seconds § Short-Term, or Working Memory has 3 parts: § Acoustic codes § Visual Codes § Semantic Codes
 Long-Term Memory § The relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system.
Long-Term Memory § The relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system.
 Flashbulb Memory Exception to 3 Stage theory § An extreme emotional moment or event § Somehow branded into Long-Term Memory § § Where were you when? 1. You heard about 9/11? 2. You had your first kiss? 3. You had your first car accident?
Flashbulb Memory Exception to 3 Stage theory § An extreme emotional moment or event § Somehow branded into Long-Term Memory § § Where were you when? 1. You heard about 9/11? 2. You had your first kiss? 3. You had your first car accident?
 Encoding § We encode info in two ways: § Automatic Processing § Effortful Processing
Encoding § We encode info in two ways: § Automatic Processing § Effortful Processing
 Encoding § Automatic Processing § Unconscious encoding § Location, time and frequency § Retracing steps to find your keys… § Also becomes automatic with practice § Driving to a friends house…
Encoding § Automatic Processing § Unconscious encoding § Location, time and frequency § Retracing steps to find your keys… § Also becomes automatic with practice § Driving to a friends house…
 Encoding § Effortful Processing § Attention / conscious effort § Studying for a test § Through rehearsal, Effortful can become automatic
Encoding § Effortful Processing § Attention / conscious effort § Studying for a test § Through rehearsal, Effortful can become automatic
 Ways of Encoding (activity 9. 3) § Semantic: § encoding of meaning § Acoustic § Encoding of sound § Visual § Encoding of picture images
Ways of Encoding (activity 9. 3) § Semantic: § encoding of meaning § Acoustic § Encoding of sound § Visual § Encoding of picture images
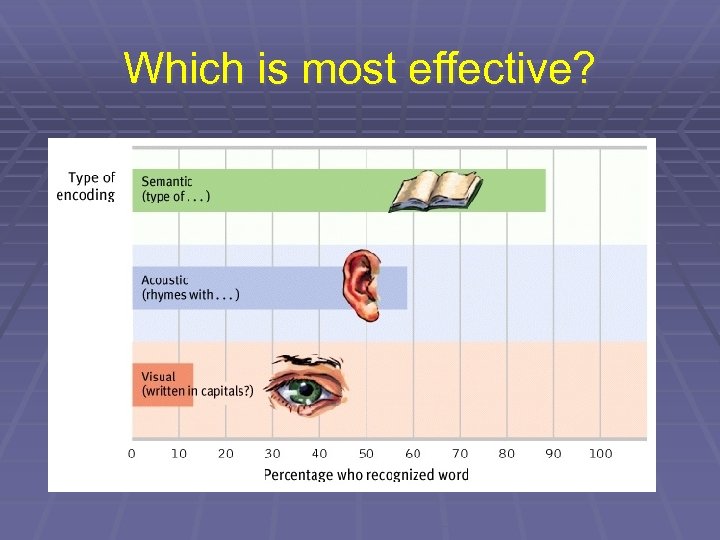 Which is most effective?
Which is most effective?
 Factors that Influence Encoding § Spacing Effect § Encode info better if in increments over time § Serial Positioning Effect § Tendency to recall best the first and last items in a list. § Primacy Effect: Remember first words, items § Recency Effect: Remember last items, words § Next-In-Line Effect § Don’t remember what someone has said if we are next… § Self-Reference Effect § We encode better when issue relates to us
Factors that Influence Encoding § Spacing Effect § Encode info better if in increments over time § Serial Positioning Effect § Tendency to recall best the first and last items in a list. § Primacy Effect: Remember first words, items § Recency Effect: Remember last items, words § Next-In-Line Effect § Don’t remember what someone has said if we are next… § Self-Reference Effect § We encode better when issue relates to us
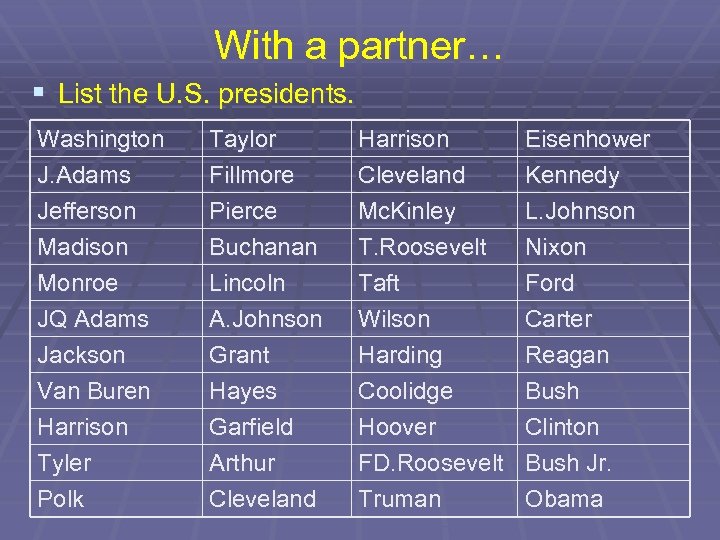 With a partner… § List the U. S. presidents. Washington J. Adams Jefferson Madison Taylor Fillmore Pierce Buchanan Harrison Cleveland Mc. Kinley T. Roosevelt Eisenhower Kennedy L. Johnson Nixon Monroe JQ Adams Jackson Van Buren Harrison Tyler Polk Lincoln A. Johnson Grant Hayes Garfield Arthur Cleveland Taft Wilson Harding Coolidge Hoover FD. Roosevelt Truman Ford Carter Reagan Bush Clinton Bush Jr. Obama
With a partner… § List the U. S. presidents. Washington J. Adams Jefferson Madison Taylor Fillmore Pierce Buchanan Harrison Cleveland Mc. Kinley T. Roosevelt Eisenhower Kennedy L. Johnson Nixon Monroe JQ Adams Jackson Van Buren Harrison Tyler Polk Lincoln A. Johnson Grant Hayes Garfield Arthur Cleveland Taft Wilson Harding Coolidge Hoover FD. Roosevelt Truman Ford Carter Reagan Bush Clinton Bush Jr. Obama
 Encoding Strategies Can enhance memory… § Mnemonic Devices: § Any learning technique that aids memory § uses imagery, semantics to remember… § Acronyms: § Parentheses, exponents, multiplication, division, addition, subtraction “Please excuse my dear aunt Sally. ”
Encoding Strategies Can enhance memory… § Mnemonic Devices: § Any learning technique that aids memory § uses imagery, semantics to remember… § Acronyms: § Parentheses, exponents, multiplication, division, addition, subtraction “Please excuse my dear aunt Sally. ”
 Mnemonic Devices § Peg-Word System § Assign each item to a number or… § Weave a story matching each item / word to a number. (Rhyming also helpful)
Mnemonic Devices § Peg-Word System § Assign each item to a number or… § Weave a story matching each item / word to a number. (Rhyming also helpful)
 Mnemonic Devices Chunking § Organizing items into familiar, manageable units. § Memorize these numbers§ 1 -4 -9 -2 -1 -7 -7 -6 -1 -8 -1 -2 -1 -9 -4 -1 § How bout now? § 1492, 1776, 1812, 1941
Mnemonic Devices Chunking § Organizing items into familiar, manageable units. § Memorize these numbers§ 1 -4 -9 -2 -1 -7 -7 -6 -1 -8 -1 -2 -1 -9 -4 -1 § How bout now? § 1492, 1776, 1812, 1941
 Mnemonic Devices § Key Word System Term Key Word Broca’s Area Tom Brokaw Mental Picture Parietal Lobe Paraná biting your toe Amygdala Old Psycho girlfriend = Fear Amy Hippocampus ? ? News cast (talking) ? ? ?
Mnemonic Devices § Key Word System Term Key Word Broca’s Area Tom Brokaw Mental Picture Parietal Lobe Paraná biting your toe Amygdala Old Psycho girlfriend = Fear Amy Hippocampus ? ? News cast (talking) ? ? ?
 Mnemonic Devices § Loci (Location) 500 BC. - Simonides § Imagine a location (house etc. ) § Imaginary tour: each location paired with specific item
Mnemonic Devices § Loci (Location) 500 BC. - Simonides § Imagine a location (house etc. ) § Imaginary tour: each location paired with specific item
 Choose any mnemonic device (60 seconds) § § § § Ham Pencil turkey pen Check book detergent football glasses globe Brother Laundry Map Scrabble Jeopardy pizza
Choose any mnemonic device (60 seconds) § § § § Ham Pencil turkey pen Check book detergent football glasses globe Brother Laundry Map Scrabble Jeopardy pizza
 Storage and Long-Term Memory § long-term memory: no known limits § Rajan: recited 31, 811 digits of pi. (3 hrs. 49 min. / or 3. 5/second!) § How? Rhythmic memory: “melodic or jarring”- taps feet, sways right / left § At 5 years old, memorized the license plates of parents’ guests (about 75 cars in ten minutes). He still remembers the plates to this day. § Numbers only: average with names, words
Storage and Long-Term Memory § long-term memory: no known limits § Rajan: recited 31, 811 digits of pi. (3 hrs. 49 min. / or 3. 5/second!) § How? Rhythmic memory: “melodic or jarring”- taps feet, sways right / left § At 5 years old, memorized the license plates of parents’ guests (about 75 cars in ten minutes). He still remembers the plates to this day. § Numbers only: average with names, words
 Shereshevskii: 1920’s § Short term memory: 70 items § Forward / Backward / 15 years § Asylum: went mad: 15 minutes / 5 years: all memories ran together
Shereshevskii: 1920’s § Short term memory: 70 items § Forward / Backward / 15 years § Asylum: went mad: 15 minutes / 5 years: all memories ran together
 Long-Term Memory § Remember: There is no one single compartment for memory in our brain. § Long Term-Potentiation (LTP) § Leading Theory for LTM § Neural networks strengthen memory § Neural connections gradually strengthen through rehearsal over time (memory strengthened) • Nerve cell’s genes produce synapse strengthening proteins /enabling LTM formation
Long-Term Memory § Remember: There is no one single compartment for memory in our brain. § Long Term-Potentiation (LTP) § Leading Theory for LTM § Neural networks strengthen memory § Neural connections gradually strengthen through rehearsal over time (memory strengthened) • Nerve cell’s genes produce synapse strengthening proteins /enabling LTM formation
 Stress and Memory § Stress can release hormones that assist in LTM § Stress can also inhibit effective encoding for memory…
Stress and Memory § Stress can release hormones that assist in LTM § Stress can also inhibit effective encoding for memory…
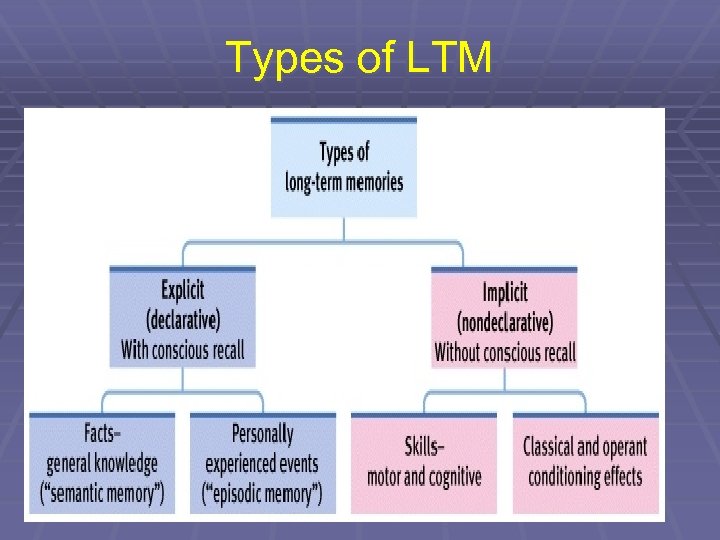 Types of LTM
Types of LTM
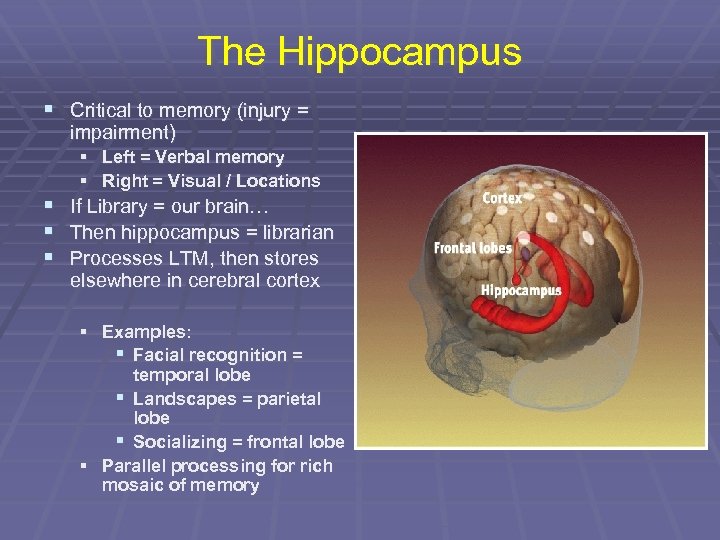 The Hippocampus § Critical to memory (injury = impairment) § Left = Verbal memory § Right = Visual / Locations § If Library = our brain… § Then hippocampus = librarian § Processes LTM, then stores elsewhere in cerebral cortex § Examples: § Facial recognition = temporal lobe § Landscapes = parietal lobe § Socializing = frontal lobe § Parallel processing for rich mosaic of memory
The Hippocampus § Critical to memory (injury = impairment) § Left = Verbal memory § Right = Visual / Locations § If Library = our brain… § Then hippocampus = librarian § Processes LTM, then stores elsewhere in cerebral cortex § Examples: § Facial recognition = temporal lobe § Landscapes = parietal lobe § Socializing = frontal lobe § Parallel processing for rich mosaic of memory
 Amygdala § Emotional memories § Images, smells, sounds § Examples? § Hippocampus and Amygdala work together to form LTM § Hippo = conscious memory of event § Amygdala = emotional memory from the senses
Amygdala § Emotional memories § Images, smells, sounds § Examples? § Hippocampus and Amygdala work together to form LTM § Hippo = conscious memory of event § Amygdala = emotional memory from the senses
 Retrieval Recall Versus Recognition What’s the Difference?
Retrieval Recall Versus Recognition What’s the Difference?
 Retrieval Cues (Aid memory. . ) § Memory = web of associations § Priming: “strand or web of associations that leads to a specific memory”
Retrieval Cues (Aid memory. . ) § Memory = web of associations § Priming: “strand or web of associations that leads to a specific memory”
 Priming Effect (2 types) § Repetition Priming § Semantic Priming A house divided against itself cannot stand. . Those who deny freedom to others, deserve it not for themselves… With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in…
Priming Effect (2 types) § Repetition Priming § Semantic Priming A house divided against itself cannot stand. . Those who deny freedom to others, deserve it not for themselves… With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in…
 Factors that Influence Retrieval § Context effect § Retrieval is more effective when retrieving it in same location as experienced it… § Tip-Of-the-Tongue Effect (TOT) ØTemporary inability to retrieve specific name or information. ØUsually remedied by semantic cues…
Factors that Influence Retrieval § Context effect § Retrieval is more effective when retrieving it in same location as experienced it… § Tip-Of-the-Tongue Effect (TOT) ØTemporary inability to retrieve specific name or information. ØUsually remedied by semantic cues…
 Conditions that Affect Memory § Mood-Congruent Theory § The tendency to recall memories consistent with our current mood § State-Dependent Theory § Recalling events encoded while in a particular state of consciousness. § Example: If you hide money while your drunk, you are more likely to remember where you hid it when you are intoxicated.
Conditions that Affect Memory § Mood-Congruent Theory § The tendency to recall memories consistent with our current mood § State-Dependent Theory § Recalling events encoded while in a particular state of consciousness. § Example: If you hide money while your drunk, you are more likely to remember where you hid it when you are intoxicated.
 Conditions that Affect Memory § Pollyanna Principle § We tend to remember pleasant experiences over negative ones § Before, more efficiently, more accurately § Why? ØWe seek out positive experiences § Faster fading of negative experiences = healthy coping processes in memory § Mild depression = negative and positive experiences fade evenly
Conditions that Affect Memory § Pollyanna Principle § We tend to remember pleasant experiences over negative ones § Before, more efficiently, more accurately § Why? ØWe seek out positive experiences § Faster fading of negative experiences = healthy coping processes in memory § Mild depression = negative and positive experiences fade evenly
 Forgetting… § “Forgetting isn’t the absence of remembering: it’s memory’s ally, a device that allows the brain to stay agile and engaged. ” § Diane Ackerman, An Alchemy of Mind, p. 89
Forgetting… § “Forgetting isn’t the absence of remembering: it’s memory’s ally, a device that allows the brain to stay agile and engaged. ” § Diane Ackerman, An Alchemy of Mind, p. 89
 Three ways we forget… Encoding Failure Storage Decay Retrieval Failure
Three ways we forget… Encoding Failure Storage Decay Retrieval Failure
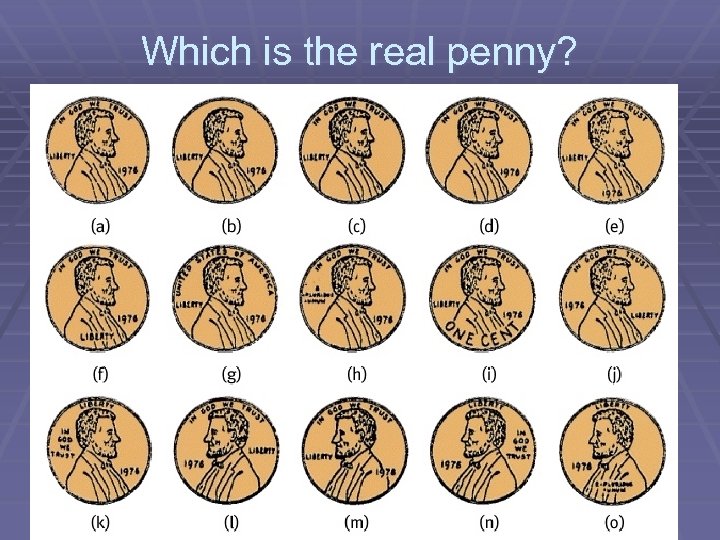 Which is the real penny?
Which is the real penny?
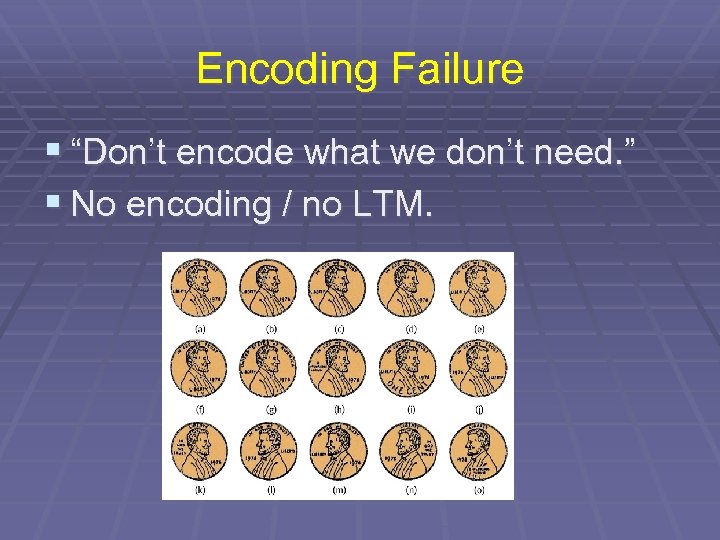 Encoding Failure § “Don’t encode what we don’t need. ” § No encoding / no LTM.
Encoding Failure § “Don’t encode what we don’t need. ” § No encoding / no LTM.
 Storage Decay § Memory storage decays over time § Lack of rehearsal accelerates decay § Ebbinghaus’s forgetting curve ØSteep decline of retention over first three days, then levels off…
Storage Decay § Memory storage decays over time § Lack of rehearsal accelerates decay § Ebbinghaus’s forgetting curve ØSteep decline of retention over first three days, then levels off…
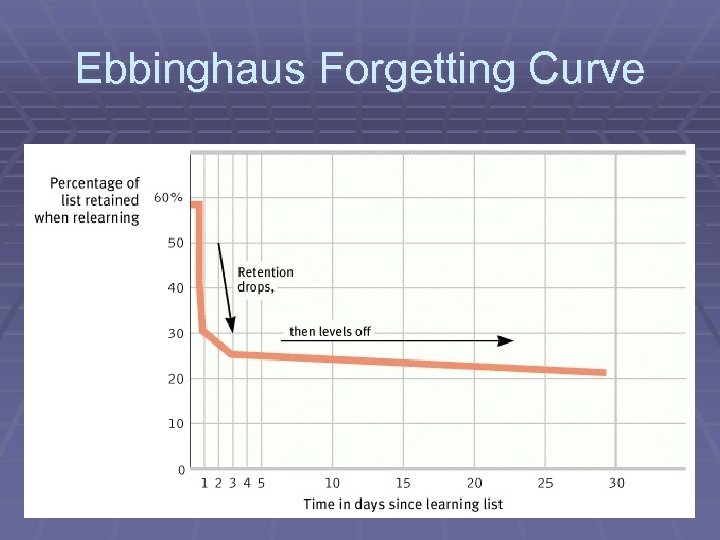 Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve
Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve
 Retrieval Failure § 2 Types (Be careful here…its tricky. . ) § Proactive Interference § New info is messed up by the old info vs. § Retroactive Interference § Old info is messed up by new learning
Retrieval Failure § 2 Types (Be careful here…its tricky. . ) § Proactive Interference § New info is messed up by the old info vs. § Retroactive Interference § Old info is messed up by new learning
 Which type of retrieval failure? If you call your new girlfriend your old girlfriend’s name. When you finally remember this years locker combination, you forget last years.
Which type of retrieval failure? If you call your new girlfriend your old girlfriend’s name. When you finally remember this years locker combination, you forget last years.
 Retrieval Failure REPRESSION: § psychoanalytic theory- Freud’s theory of repression § We push away uncomfortable memories § Contradicts theory that emotions / stress hormones strengthen memories
Retrieval Failure REPRESSION: § psychoanalytic theory- Freud’s theory of repression § We push away uncomfortable memories § Contradicts theory that emotions / stress hormones strengthen memories
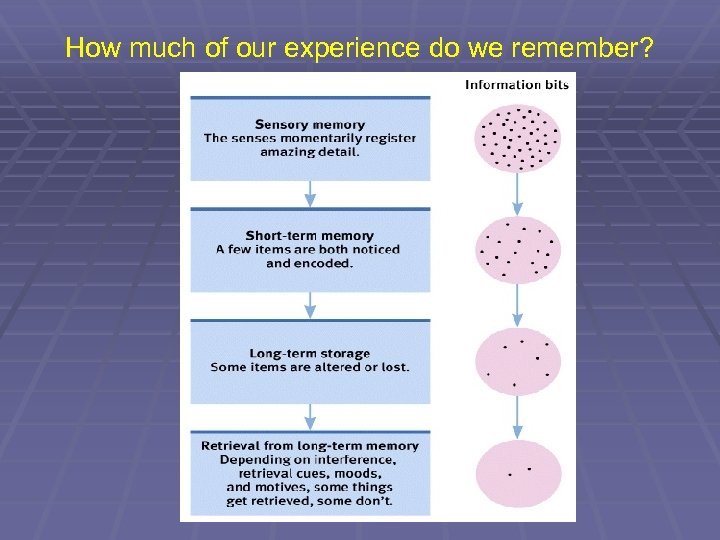 How much of our experience do we remember?
How much of our experience do we remember?
 The truth about memory. . § Memories bend and change over time, and are often inaccurate!! § Youngest and oldest (around 5 and 75) are most susceptible § (Frontal lobe: matures slowly and decays quickly) § § Research studies Elizabeth Loftus (over 200 experiments) § How wording influences our memory § Cornell University- Space Shuttle Disaster § Recollections on day after and three years later § 2/3 were totally wrong as to who with, where etc. .
The truth about memory. . § Memories bend and change over time, and are often inaccurate!! § Youngest and oldest (around 5 and 75) are most susceptible § (Frontal lobe: matures slowly and decays quickly) § § Research studies Elizabeth Loftus (over 200 experiments) § How wording influences our memory § Cornell University- Space Shuttle Disaster § Recollections on day after and three years later § 2/3 were totally wrong as to who with, where etc. .
 Misinformation Effect… Wording affects our memory § About how fast were the vehicles going when they smashed into each other? Or § When they ran into each other?
Misinformation Effect… Wording affects our memory § About how fast were the vehicles going when they smashed into each other? Or § When they ran into each other?
 Source Amnesia § Forgetting the source of a memory § (Where did I hear that…? ) § One of the frailest parts of our memory
Source Amnesia § Forgetting the source of a memory § (Where did I hear that…? ) § One of the frailest parts of our memory
 Types of Amnesia § Anterograde Amnesia ØRemember everything before the accident, but not after. ØOften TBI (part of brain? ) § Retrograde Amnesia § Remember everything after the incident, but not before.
Types of Amnesia § Anterograde Amnesia ØRemember everything before the accident, but not after. ØOften TBI (part of brain? ) § Retrograde Amnesia § Remember everything after the incident, but not before.
 Which type of amnesia?
Which type of amnesia?


