Lecture_3 (Albedo).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
Melting + + Lower albedo Absorbed sunlight +
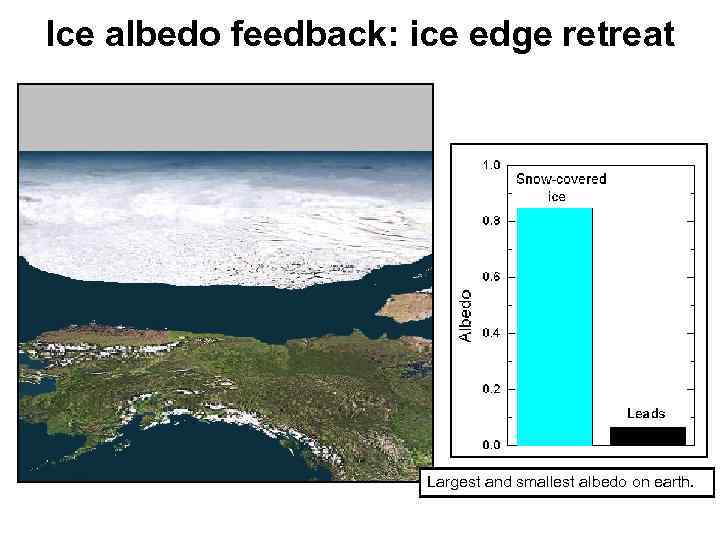
Ice albedo feedback: ice edge retreat Largest and smallest albedo on earth.

Ice albedo feedback April 17 Spring · Uniform appearance · Snow-covered ice ·Large albedo (~ 0. 8) August 8 Summer · Variegated appearance · Bare ice, ponds, and leads · More open water · Reduced albedo (~ 0. 5)

Ice-albedo feedback: seasonal evolution April May June July August September The main surface types: snow, bare ice, melt ponds, and leads

Surface physical properties June-July Regenerating surface scattering layer August-September Deepening ponds
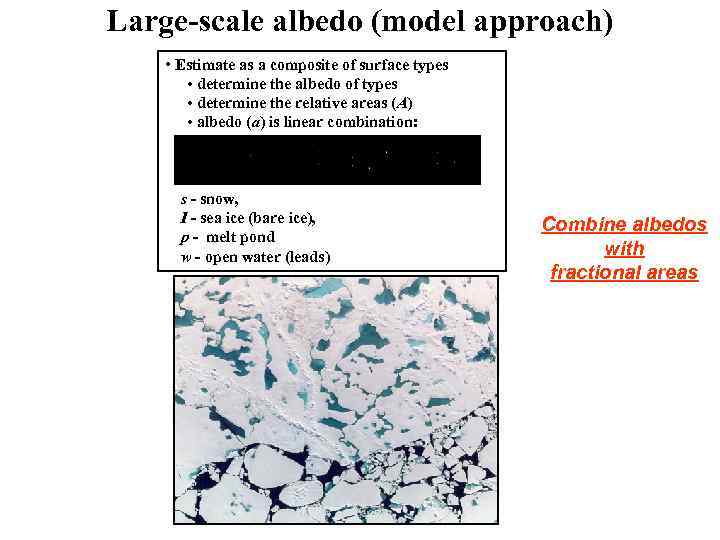
Large-scale albedo (model approach) • Estimate as a composite of surface types • determine the albedo of types • determine the relative areas (A) • albedo (a) is linear combination: s - snow, I - sea ice (bare ice), p - melt pond w - open water (leads) Combine albedos with fractional areas
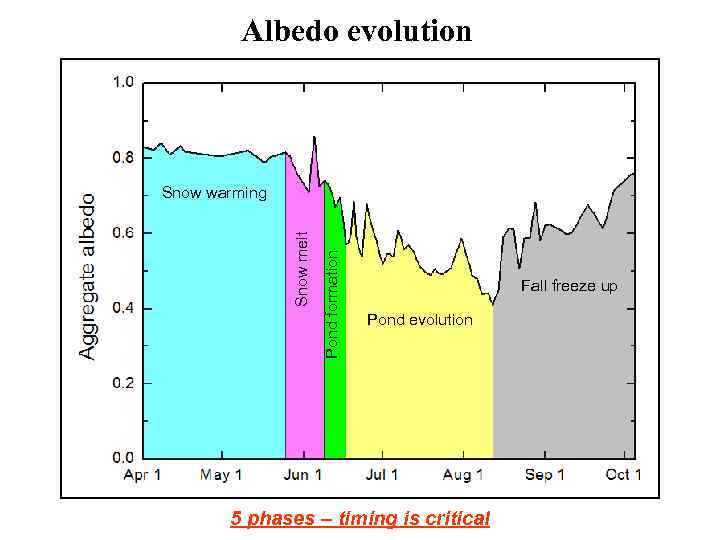
Albedo evolution Pond formation Snow melt Snow warming Fall freeze up Pond evolution 5 phases – timing is critical

«Dramatic» changes …… Multiyear First year Not a minor correction – it’s a new regime
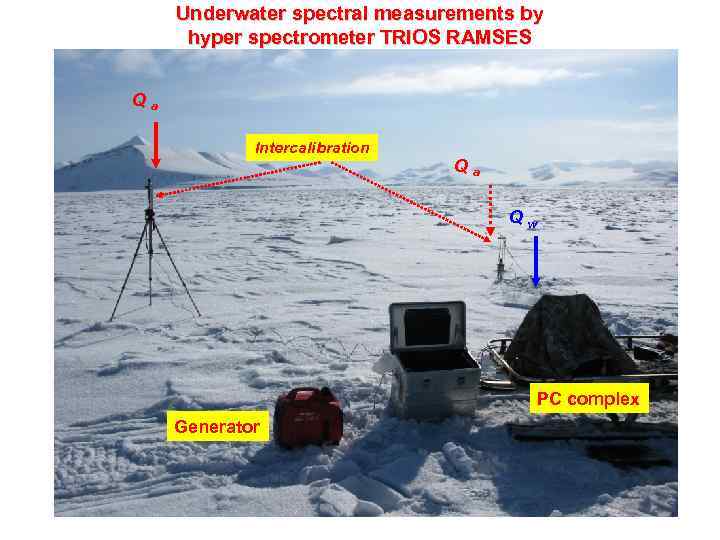

Underwater spectral measurements by hyper spectrometer TRIOS RAMSES Qa Intercalibration Qа Qw PC complex Generator
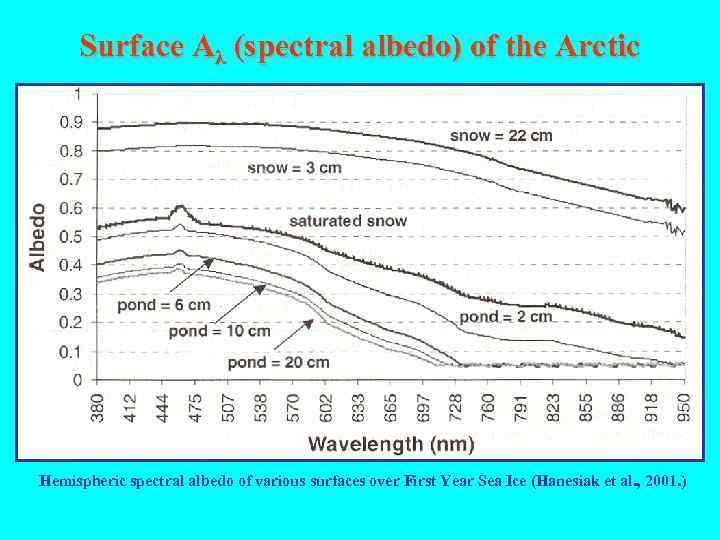
Surface Aλ (spectral albedo) of the Arctic Hemispheric spectral albedo of various surfaces over First Year Sea Ice (Hanesiak et al. , 2001. )
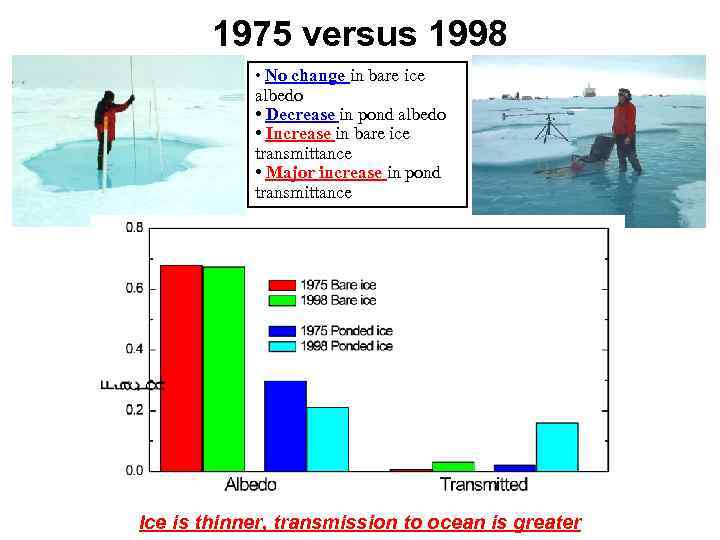
1975 versus 1998 • No change in bare ice albedo • Decrease in pond albedo • Increase in bare ice transmittance • Major increase in pond transmittance Ice is thinner, transmission to ocean is greater


Anthropogenic contamination 2009 -2010, up to 60 mg/l 2011, no more then 6 mg/l

Relationship spectral albedo – contamination (snow surface layer, Barentsburg, 2011)
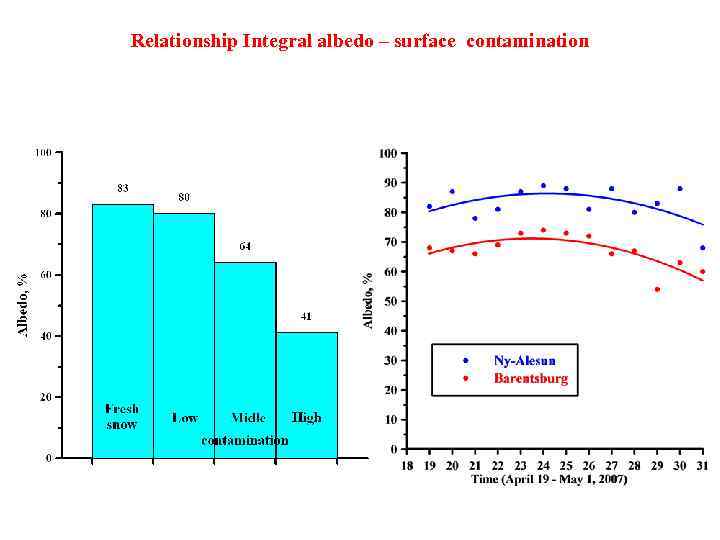
Relationship Integral albedo – surface contamination

Lecture_3 (Albedo).ppt