4d8c9993a83cc7328c5630026285d61e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69

Mehdi Merzougui Alexandre Mylle Thomas Duterte Mohamed Bouras March 2009 1

This is an independent study performed by students from the Faculté des Sciences Pharmaceutiques of Lille. The opinions expressed are our own and not necessarily those of Novo Nordisk. 2
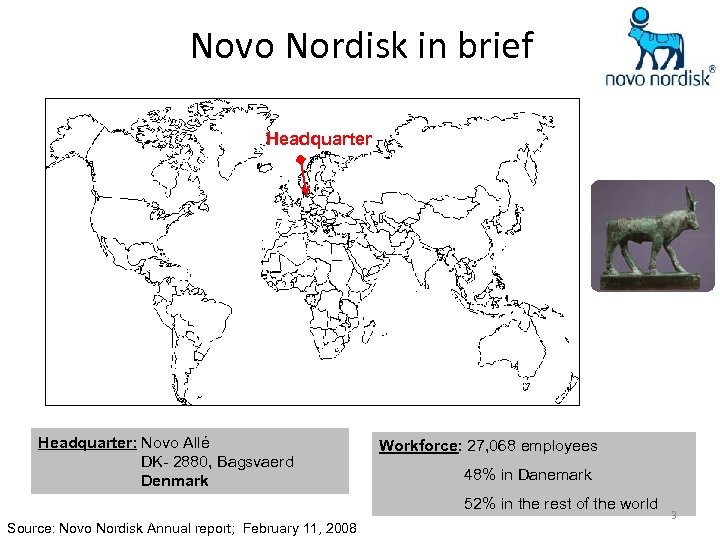
Novo Nordisk in brief Headquarter: Novo Allé DK- 2880, Bagsvaerd Denmark Workforce: 27, 068 employees 48% in Danemark 52% in the rest of the world Source: Novo Nordisk Annual report; February 11, 2008 3
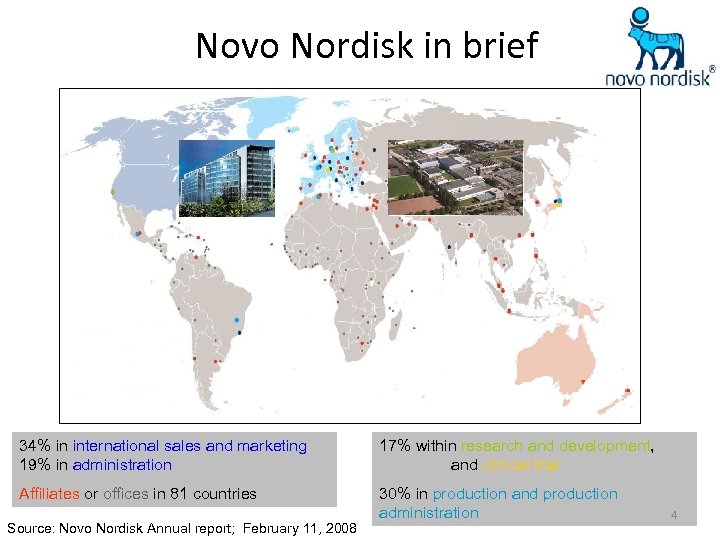
Novo Nordisk in brief 34% in international sales and marketing 19% in administration 17% within research and development, and clinical trial Affiliates or offices in 81 countries 30% in production and production administration Source: Novo Nordisk Annual report; February 11, 2008 4
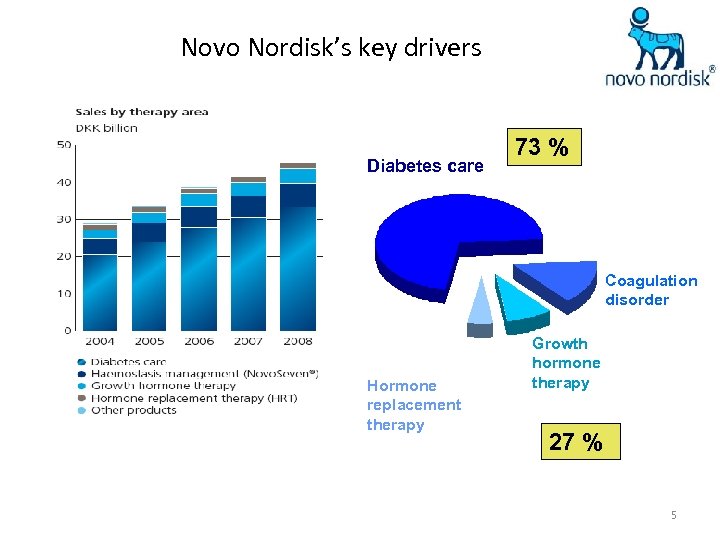
Novo Nordisk’s key drivers Diabetes care 73 % Coagulation disorder Hormone replacement therapy Growth hormone therapy 27 % 5
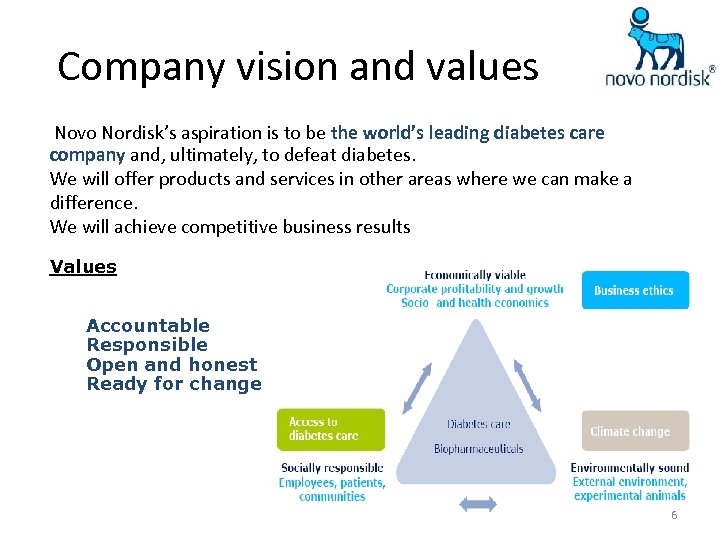
Company vision and values Novo Nordisk’s aspiration is to be the world’s leading diabetes care company and, ultimately, to defeat diabetes. We will offer products and services in other areas where we can make a difference. We will achieve competitive business results Values Accountable Responsible Open and honest Ready for change 6
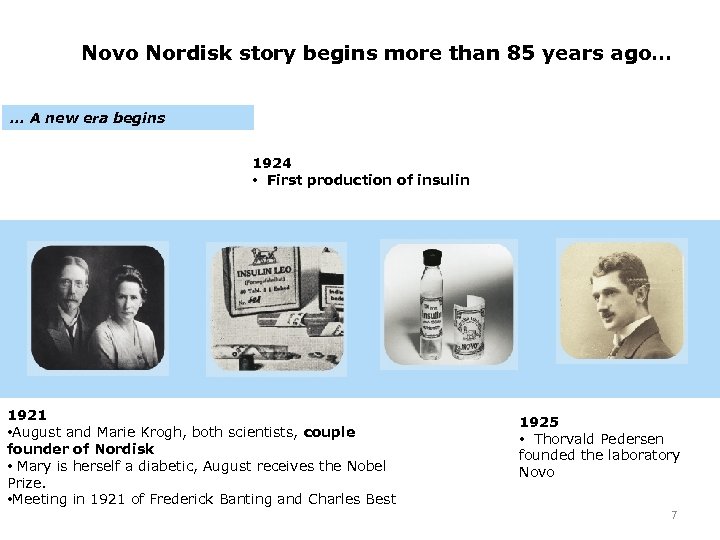
Novo Nordisk story begins more than 85 years ago…. . . A new era begins 1924 • First production of insulin 1921 • August and Marie Krogh, both scientists, couple founder of Nordisk • Mary is herself a diabetic, August receives the Nobel Prize. • Meeting in 1921 of Frederick Banting and Charles Best 1925 • Thorvald Pedersen founded the laboratory Novo 7
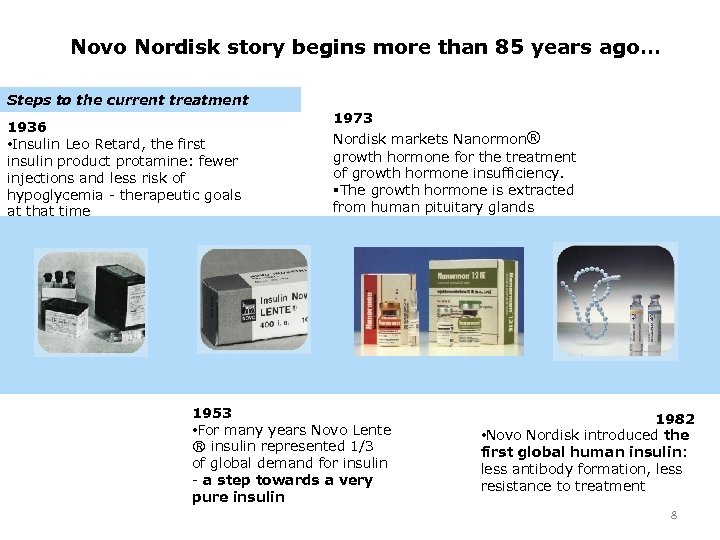
Novo Nordisk story begins more than 85 years ago… Steps to the current treatment 1936 • Insulin Leo Retard, the first insulin product protamine: fewer injections and less risk of hypoglycemia - therapeutic goals at that time 1973 Nordisk markets Nanormon® growth hormone for the treatment of growth hormone insufficiency. §The growth hormone is extracted from human pituitary glands 1953 • For many years Novo Lente ® insulin represented 1/3 of global demand for insulin - a step towards a very pure insulin 1982 • Novo Nordisk introduced the first global human insulin: less antibody formation, less resistance to treatment 8
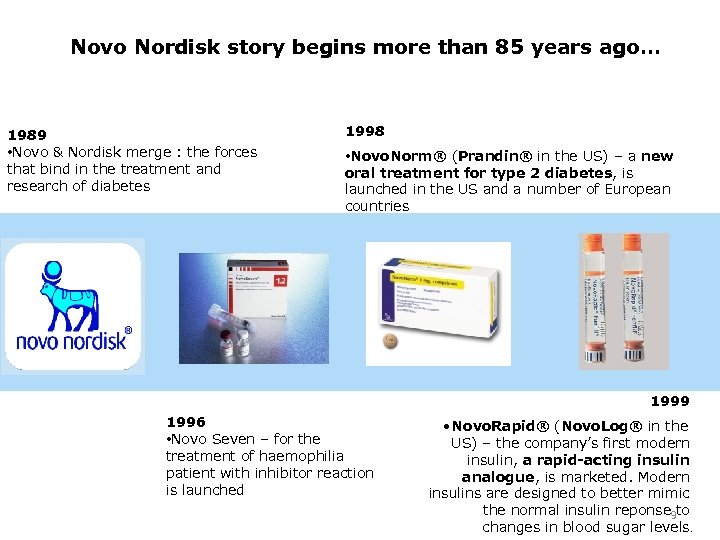
Novo Nordisk story begins more than 85 years ago… 1989 • Novo & Nordisk merge : the forces that bind in the treatment and research of diabetes 1998 • Novo. Norm® (Prandin® in the US) – a new oral treatment for type 2 diabetes, is launched in the US and a number of European countries 1999 1996 • Novo Seven – for the treatment of haemophilia patient with inhibitor reaction is launched • Novo. Rapid® (Novo. Log® in the US) – the company’s first modern insulin, a rapid-acting insulin analogue, is marketed. Modern insulins are designed to better mimic the normal insulin reponse 9 to changes in blood sugar levels.
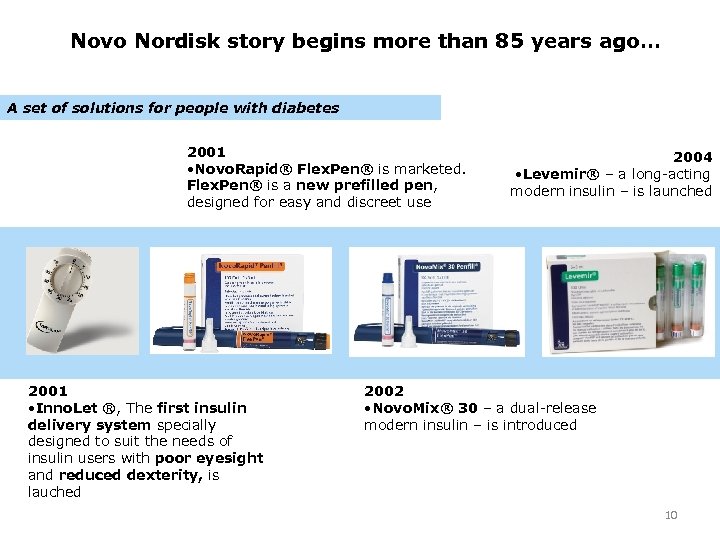
Novo Nordisk story begins more than 85 years ago… A set of solutions for people with diabetes 2001 • Novo. Rapid® Flex. Pen® is marketed. Flex. Pen® is a new prefilled pen, designed for easy and discreet use 2001 • Inno. Let ®, The first insulin delivery system specially designed to suit the needs of insulin users with poor eyesight and reduced dexterity, is lauched 2004 • Levemir® – a long-acting modern insulin – is launched 2002 • Novo. Mix® 30 – a dual-release modern insulin – is introduced 10
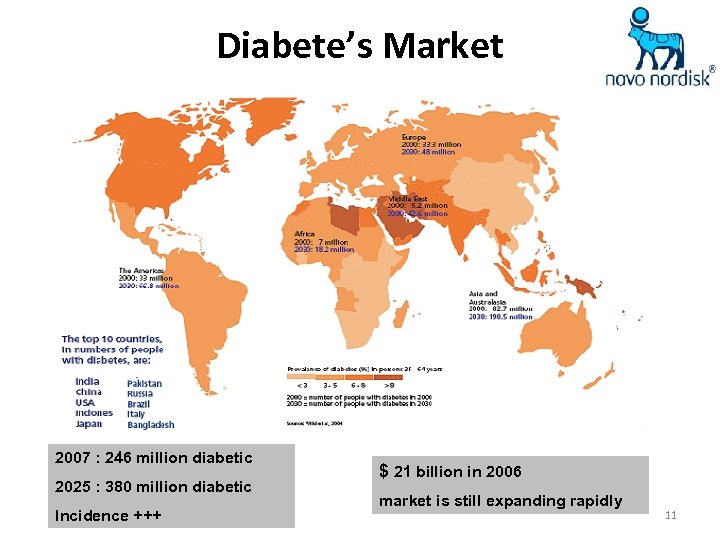
Diabete’s Market 2007 : 246 million diabetic 2025 : 380 million diabetic Incidence +++ $ 21 billion in 2006 market is still expanding rapidly 11
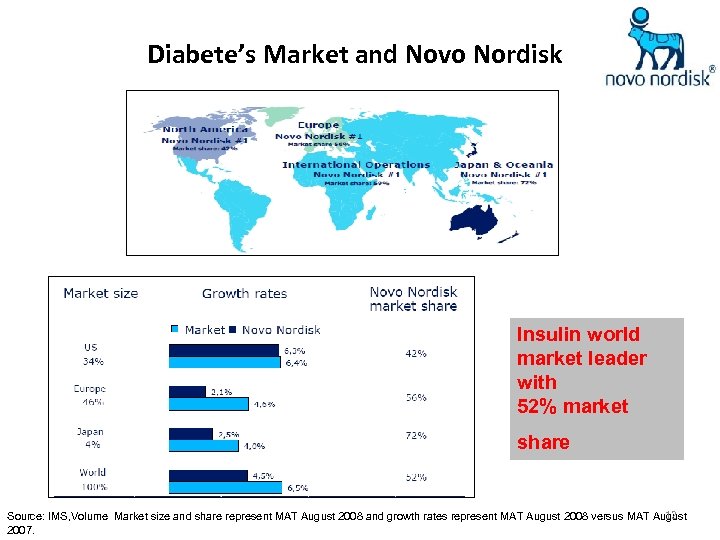
Diabete’s Market and Novo Nordisk Insulin world market leader with 52% market share 12 Source: IMS, Volume Market size and share represent MAT August 2008 and growth rates represent MAT August 2008 versus MAT August 2007.
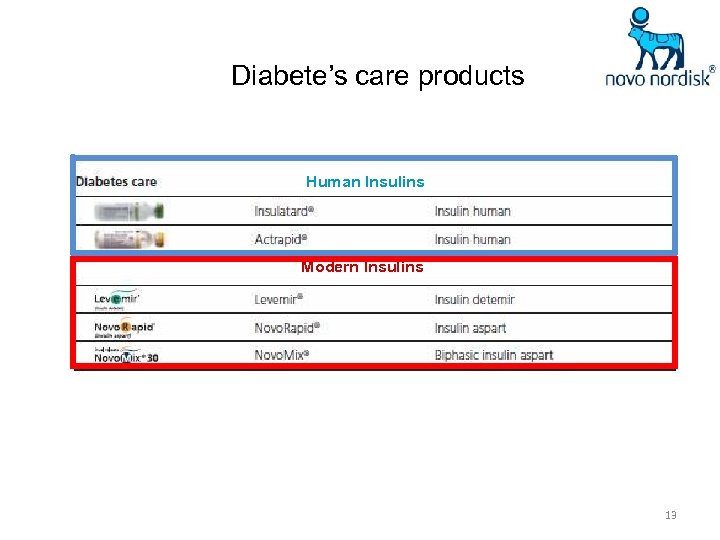
Diabete’s care products Human Insulins Modern Insulins 13
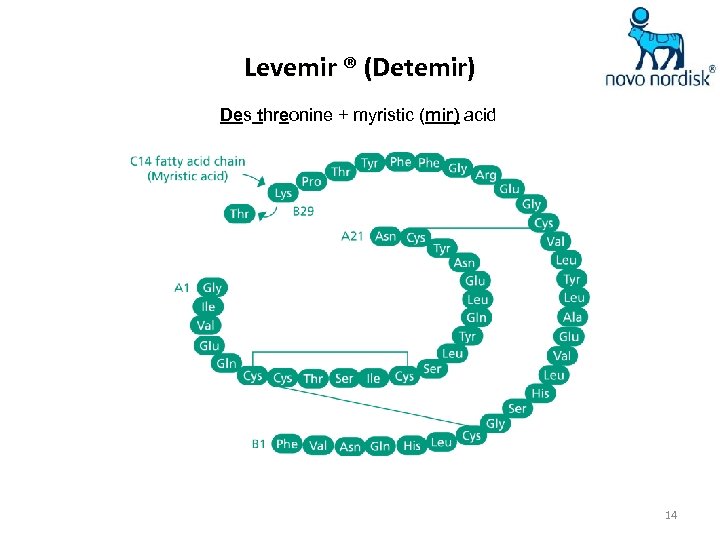
Levemir ® (Detemir) Des threonine + myristic (mir) acid 14
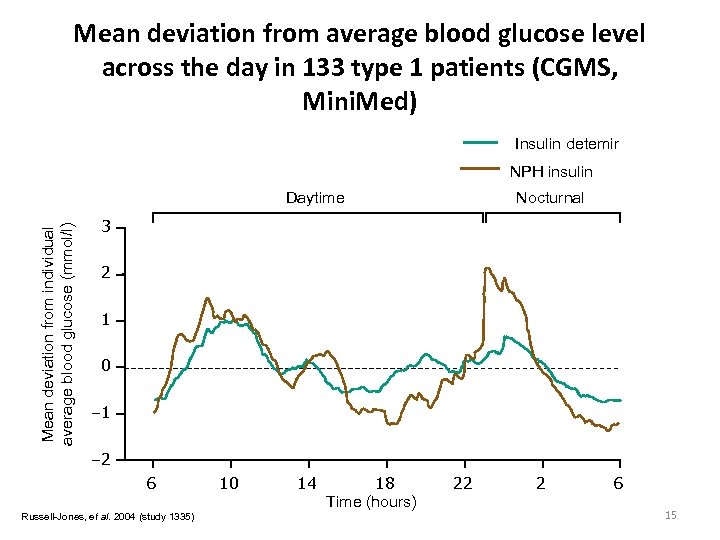
Mean deviation from average blood glucose level across the day in 133 type 1 patients (CGMS, Mini. Med) Insulin detemir NPH insulin Mean deviation from individual average blood glucose (mmol/l) Daytime Nocturnal 3 2 1 0 – 1 – 2 6 Russell-Jones, et al. 2004 (study 1335) 10 14 18 Time (hours) 22 2 6 15
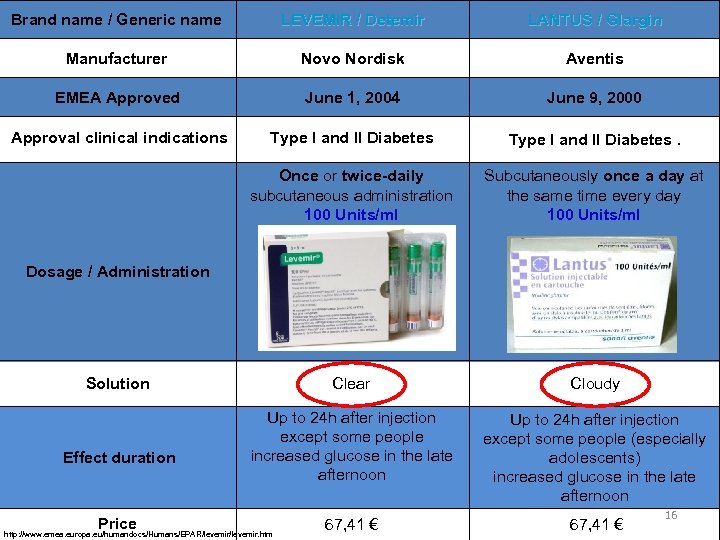
Brand name / Generic name LEVEMIR / Detemir LANTUS / Glargin Manufacturer Novo Nordisk Aventis EMEA Approved June 1, 2004 June 9, 2000 Approval clinical indications Type I and II Diabetes. Once or twice-daily subcutaneous administration 100 Units/ml Subcutaneously once a day at the same time every day 100 Units/ml Clear Cloudy Up to 24 h after injection except some people increased glucose in the late afternoon Up to 24 h after injection except some people (especially adolescents) increased glucose in the late afternoon Dosage / Administration Solution Effect duration Price http: //www. emea. europa. eu/humandocs/Humans/EPAR/levemir. htm 67, 41 € 16
Different people – different insulin needs Convenience Long-acting Low-mix Bolus High-mix Basal-bolus Pump Meeting physiological need for control 17
The only company with a full range of analogues Convenience Analogues supported by strong device portfolio Meeting physiological need for control 18
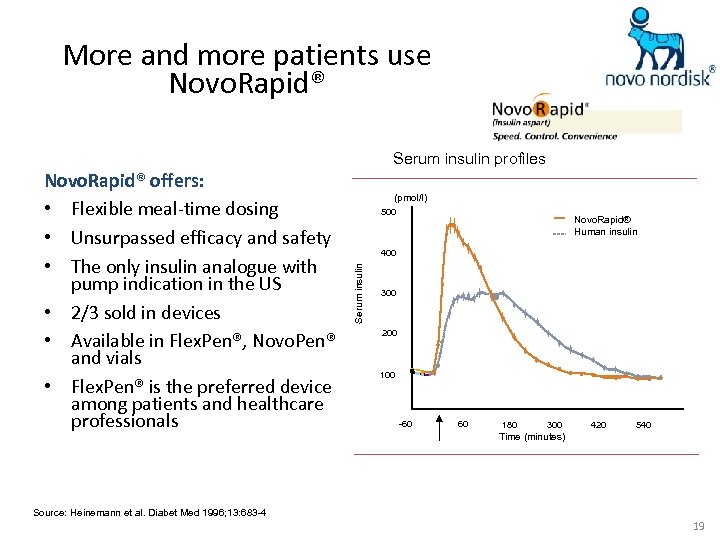
More and more patients use Novo. Rapid® Serum insulin profiles (pmol/l) 500 Novo. Rapid® Human insulin 400 Serum insulin Novo. Rapid® offers: • Flexible meal-time dosing • Unsurpassed efficacy and safety • The only insulin analogue with pump indication in the US • 2/3 sold in devices • Available in Flex. Pen®, Novo. Pen® and vials • Flex. Pen® is the preferred device among patients and healthcare professionals 300 200 100 -60 60 180 300 420 540 Time (minutes) Source: Heinemann et al. Diabet Med 1996; 13: 683 -4 19
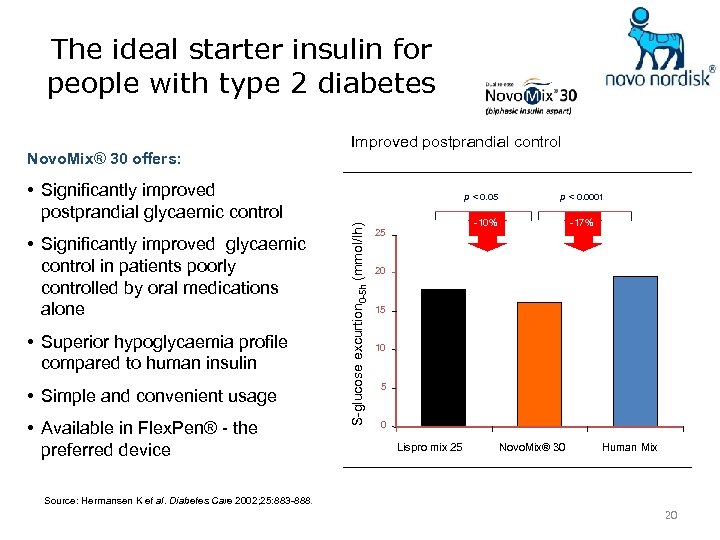
The ideal starter insulin for people with type 2 diabetes Novo. Mix® 30 offers: Improved postprandial control • Significantly improved postprandial glycaemic control • Superior hypoglycaemia profile compared to human insulin • Simple and convenient usage • Available in Flex. Pen® - the preferred device S-glucose excurtion 0 -5 h (mmol/lh) • Significantly improved glycaemic control in patients poorly controlled by oral medications alone p < 0. 05 p < 0. 0001 -10% 25 -17% 20 15 10 5 0 Lispro mix 25 Novo. Mix® 30 Human Mix Source: Hermansen K et al. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 883 -888. 20
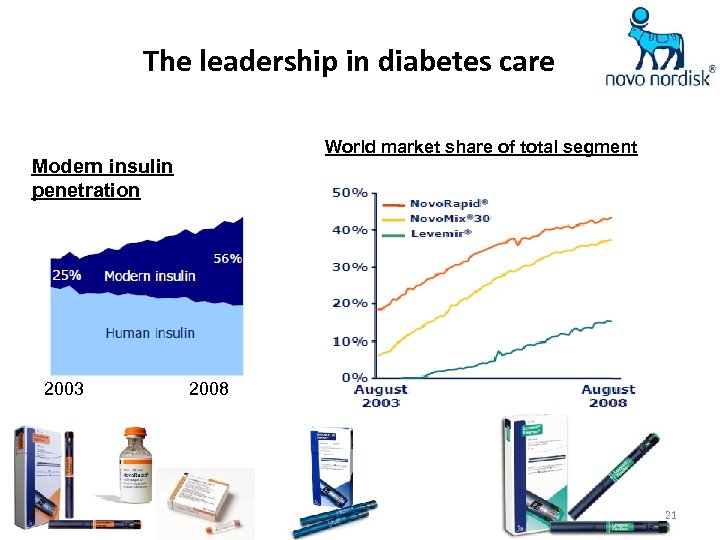
The leadership in diabetes care World market share of total segment Modern insulin penetration 2003 2008 21
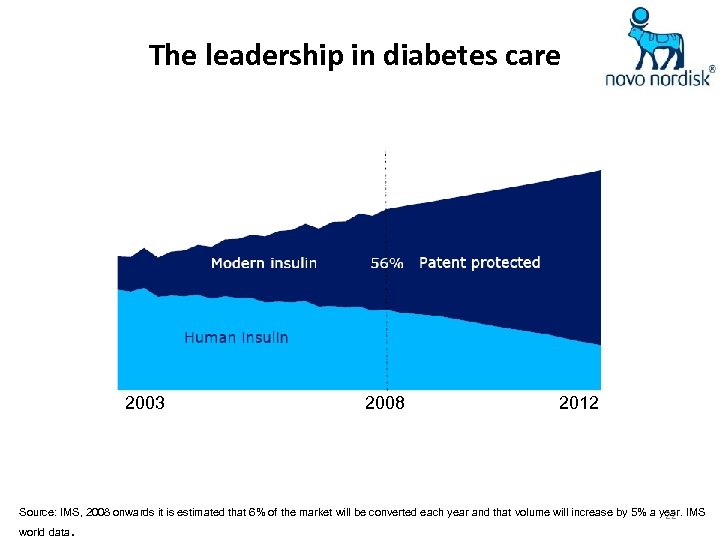
The leadership in diabetes care 2003 2008 2012 Source: IMS, 2008 onwards it is estimated that 6% of the market will be converted each year and that volume will increase by 5% a year. IMS 22 world data .
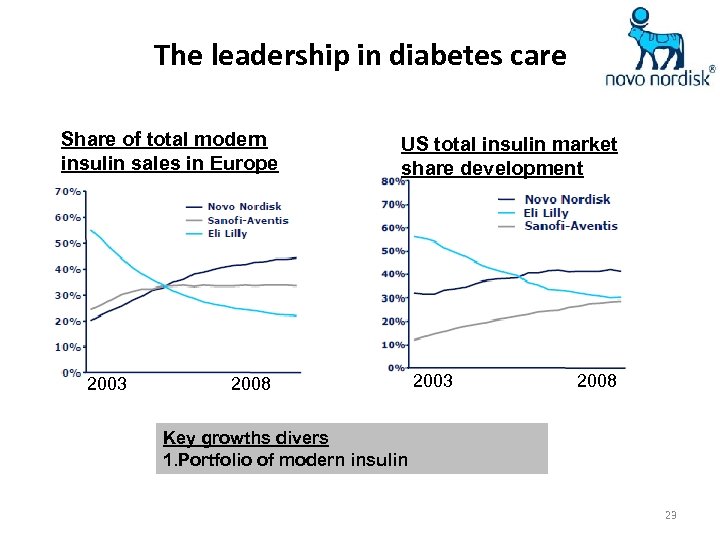
The leadership in diabetes care Share of total modern insulin sales in Europe 2003 US total insulin market share development 2008 2003 2008 Key growths divers 1. Portfolio of modern insulin 23
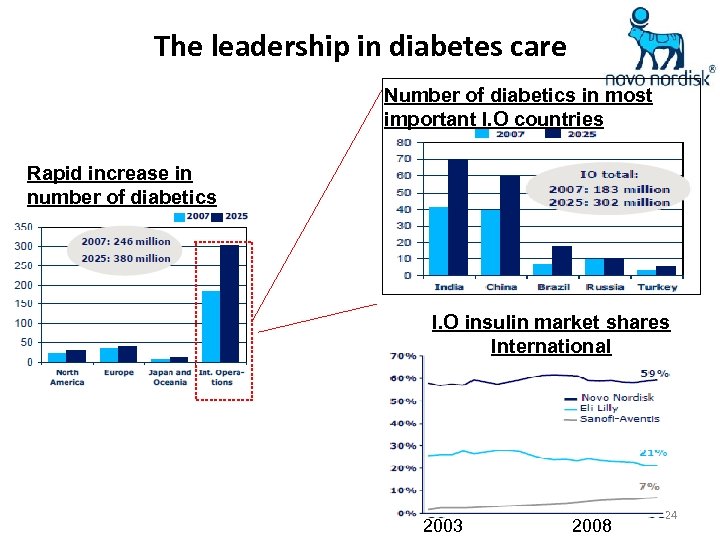
The leadership in diabetes care Number of diabetics in most important I. O countries Rapid increase in number of diabetics I. O insulin market shares International 2003 2008 24
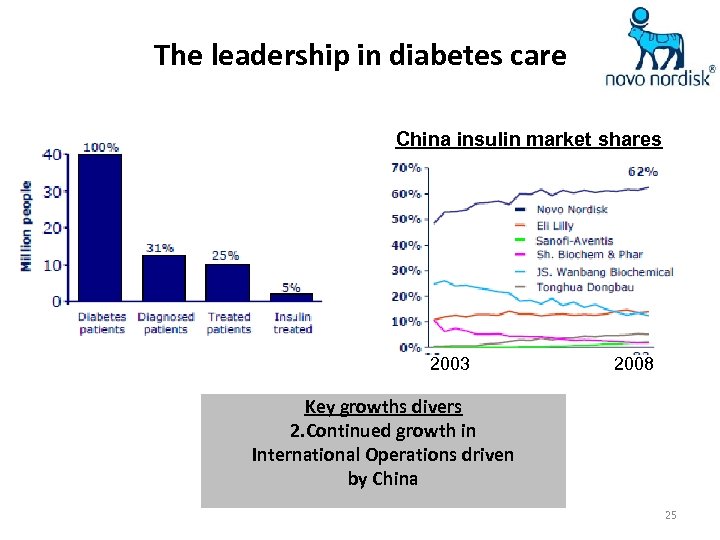
The leadership in diabetes care China insulin market shares 2003 2008 Key growths divers 2. Continued growth in International Operations driven by China 25
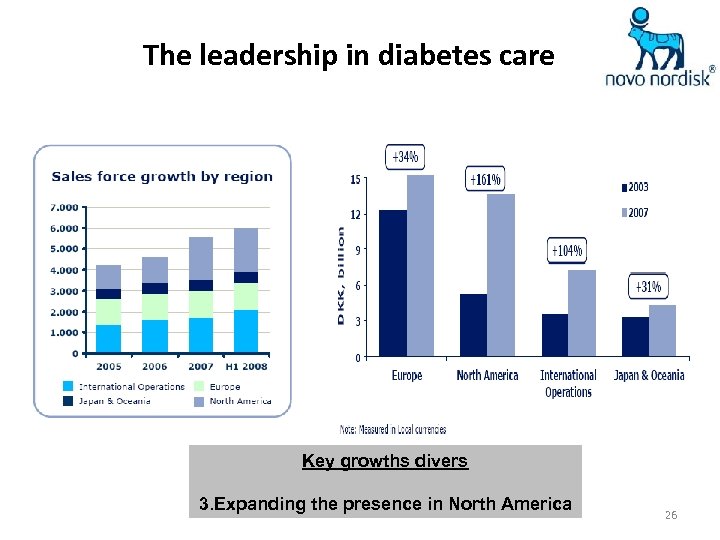
The leadership in diabetes care Key growths divers 3. Expanding the presence in North America 26
The leadership in diabetes care Key growths divers 4. Promising GLP-1 compound 27
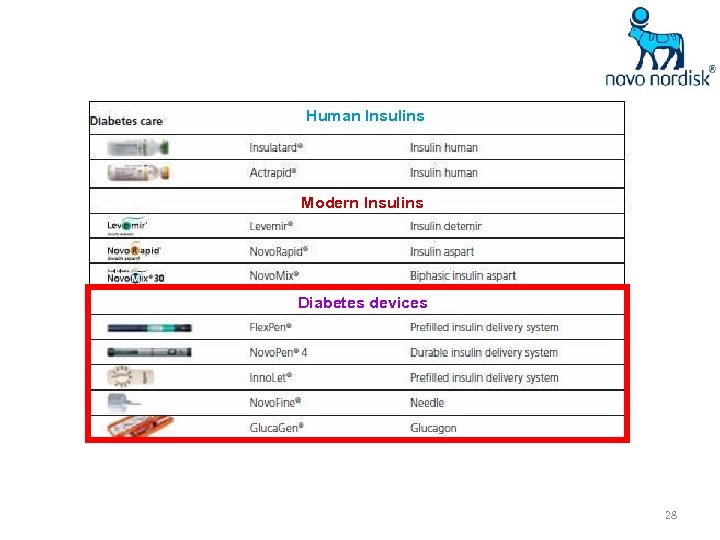
Human Insulins Modern Insulins Diabetes devices 28

Protein Delivery Systems ”Eliminating the barrier to insulin treatment” 29
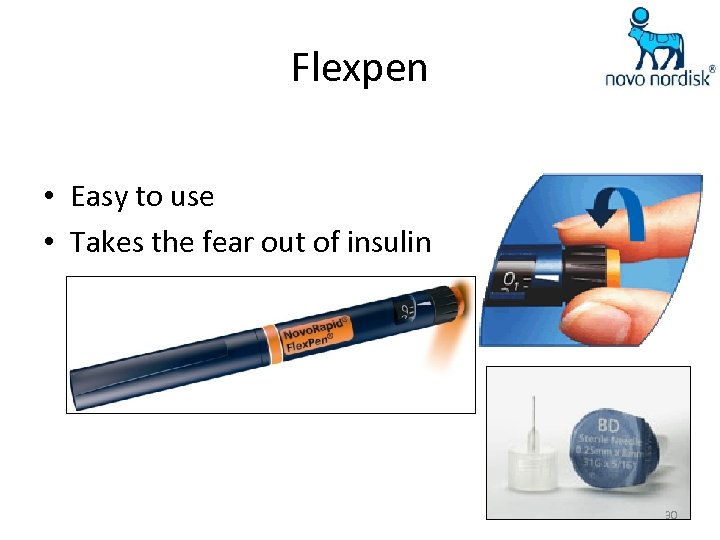
Flexpen • Easy to use • Takes the fear out of insulin 30

Why We Should Use Inhaled Insulin? • Noninvasive, portable, no increased cost. • Combined insulin action profiles of regular and rapid-acting insulin. • Novo-Nordisk / Aradigm AERx System – Heater unit – Liquid blisters – Can titrate in 1 U increments 31

The Exubera case… Exubera would generate annual sales of more than $1. 5 billion in 2010. • In October 2007, Pfizer announced it was ending production of the inhaled insulin, and taking a $2. 8 billion charge. • 32
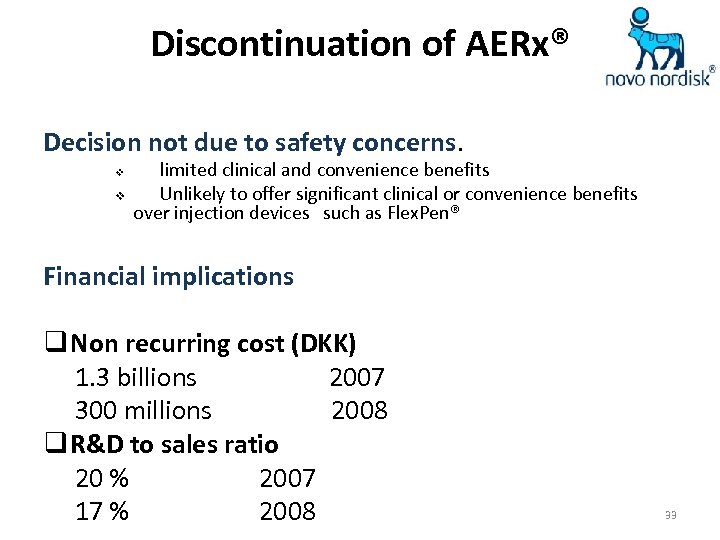
Discontinuation of AERx® Decision not due to safety concerns. v v limited clinical and convenience benefits Unlikely to offer significant clinical or convenience benefits over injection devices such as Flex. Pen® Financial implications q Non recurring cost (DKK) 1. 3 billions 2007 300 millions 2008 q R&D to sales ratio 20 % 2007 17 % 2008 33
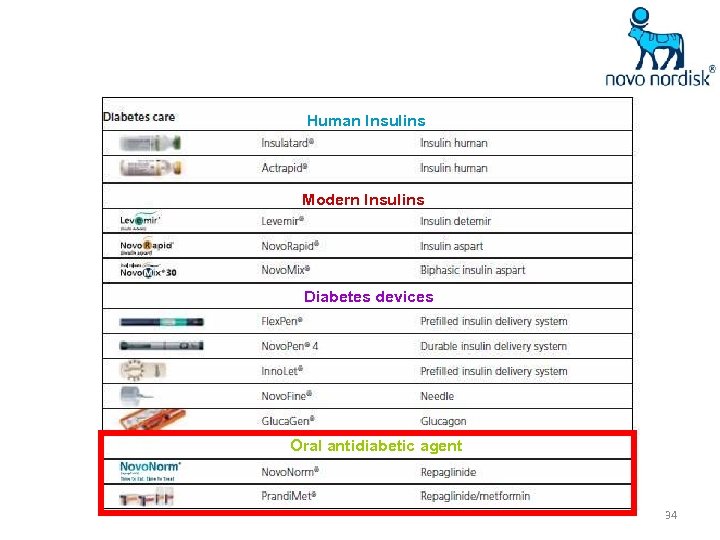
Human Insulins Modern Insulins Diabetes devices Oral antidiabetic agent 34
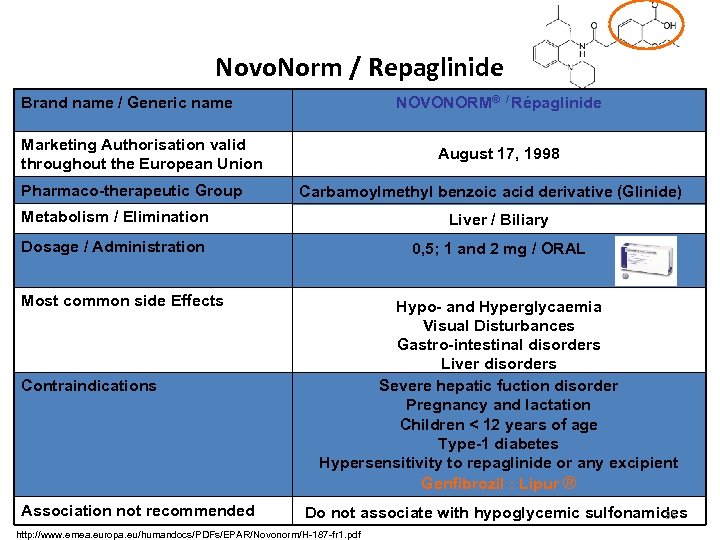
Novo. Norm / Repaglinide Brand name / Generic name NOVONORM® / Répaglinide Marketing Authorisation valid throughout the European Union Pharmaco-therapeutic Group August 17, 1998 Carbamoylmethyl benzoic acid derivative (Glinide) Metabolism / Elimination Liver / Biliary Dosage / Administration 0, 5; 1 and 2 mg / ORAL Most common side Effects Contraindications Association not recommended Hypo- and Hyperglycaemia Visual Disturbances Gastro-intestinal disorders Liver disorders Severe hepatic fuction disorder Pregnancy and lactation Children < 12 years of age Type-1 diabetes Hypersensitivity to repaglinide or any excipient Genfibrozil : Lipur ® Do not associate with hypoglycemic sulfonamides 35 http: //www. emea. europa. eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/Novonorm/H-187 -fr 1. pdf
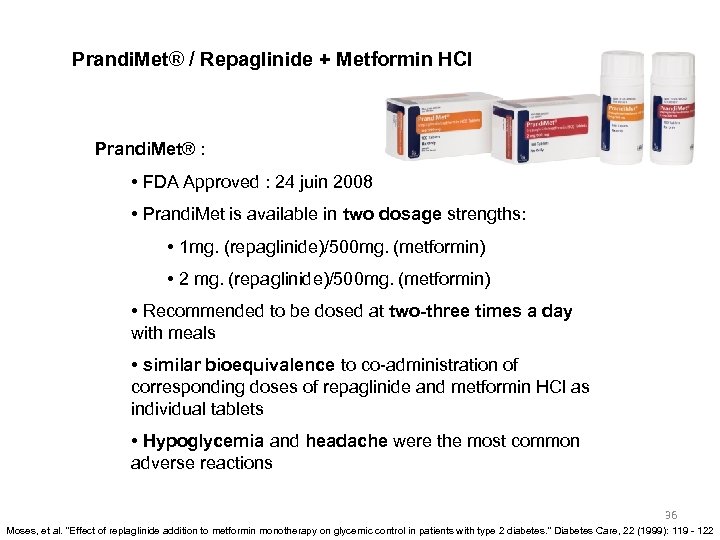
Prandi. Met® / Repaglinide + Metformin HCl Prandi. Met® : • FDA Approved : 24 juin 2008 • Prandi. Met is available in two dosage strengths: • 1 mg. (repaglinide)/500 mg. (metformin) • 2 mg. (repaglinide)/500 mg. (metformin) • Recommended to be dosed at two-three times a day with meals • similar bioequivalence to co-administration of corresponding doses of repaglinide and metformin HCl as individual tablets • Hypoglycemia and headache were the most common adverse reactions 36 Moses, et al. "Effect of replaglinide addition to metformin monotherapy on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. " Diabetes Care, 22 (1999): 119 - 122
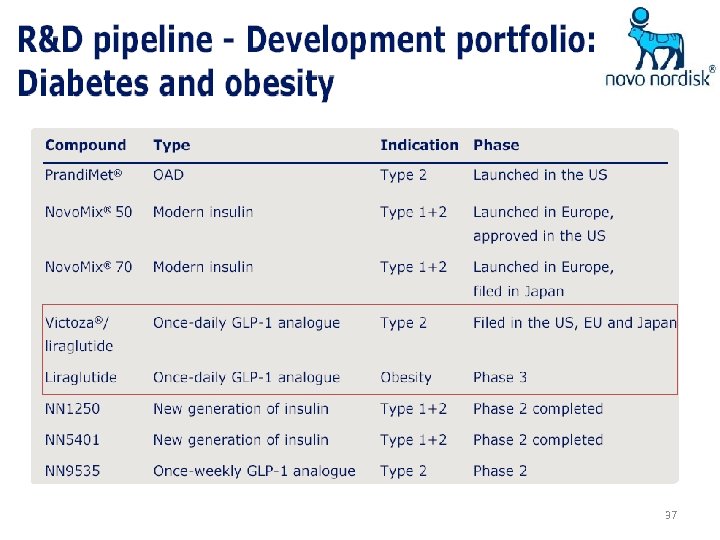
37
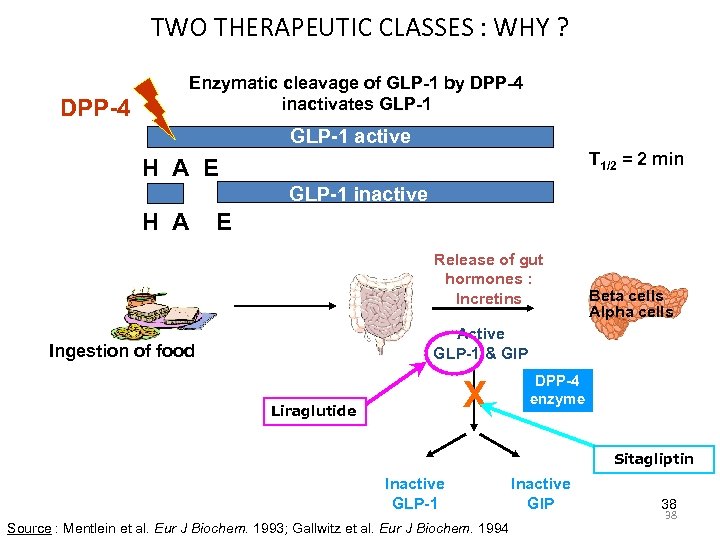
TWO THERAPEUTIC CLASSES : WHY ? DPP-4 Enzymatic cleavage of GLP-1 by DPP-4 inactivates GLP-1 active T 1/2 = 2 min H A E GLP-1 inactive H A E Release of gut hormones : Incretins Beta cells Alpha cells Active GLP-1 & GIP Ingestion of food X Liraglutide DPP-4 enzyme Sitagliptin Inactive GLP-1 Source : Mentlein et al. Eur J Biochem. 1993; Gallwitz et al. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Inactive GIP 38 38
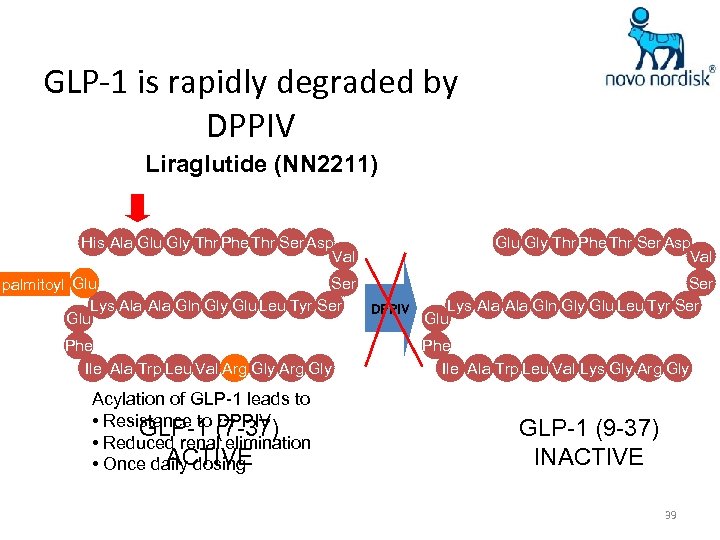
GLP-1 is rapidly degraded by DPPIV Liraglutide (NN 2211) His Ala Glu Gly Thr Phe Thr Ser Asp Val Ser palmitoyl Glu Lys Ala Ala Gln Gly Glu Leu Tyr Ser DPPIV Glu Phe Arg Ile Ala Trp Leu Val Lys Gly Arg Gly Acylation of GLP-1 leads to • Resistance to (7 -37) GLP-1 DPPIV • Reduced renal elimination ACTIVE • Once daily dosing Phe Ile Ala Trp Leu Val Lys Gly Arg Gly GLP-1 (9 -37) INACTIVE 39
40
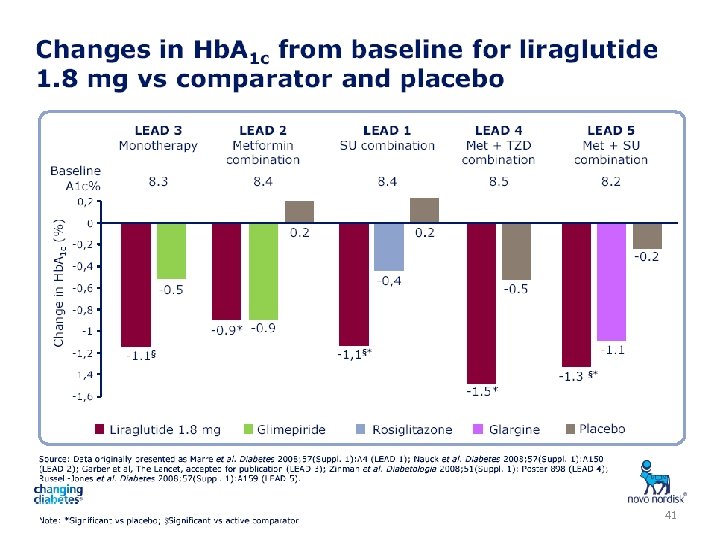
41

43
44
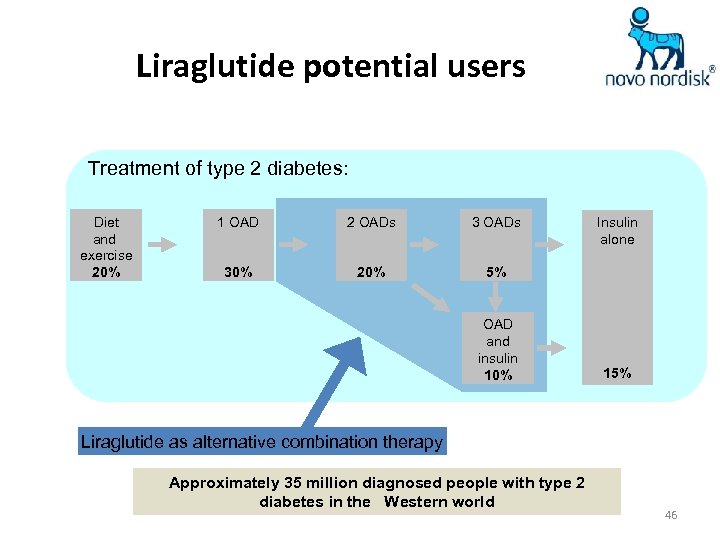
Liraglutide potential users Treatment of type 2 diabetes: Diet and exercise 20% 1 OAD 2 OADs 30% 20% 5% OAD and insulin 10% Insulin alone 15% Liraglutide as alternative combination therapy Approximately 35 million diagnosed people with type 2 diabetes in the Western world 46
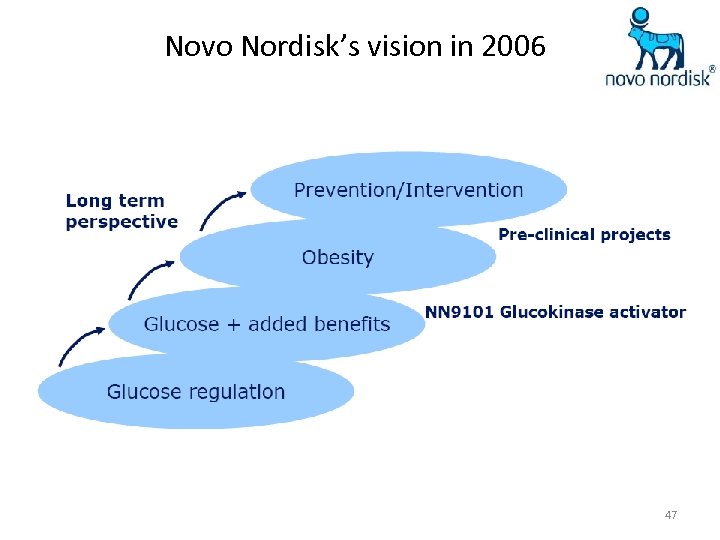
Novo Nordisk’s vision in 2006 47
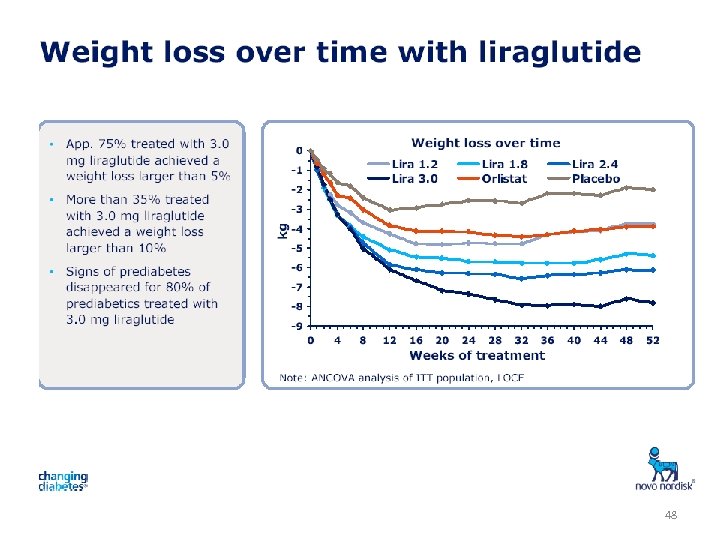
48
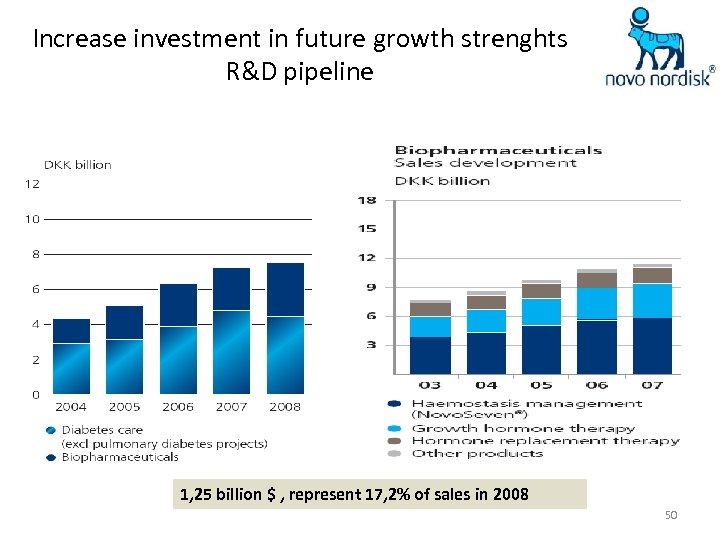
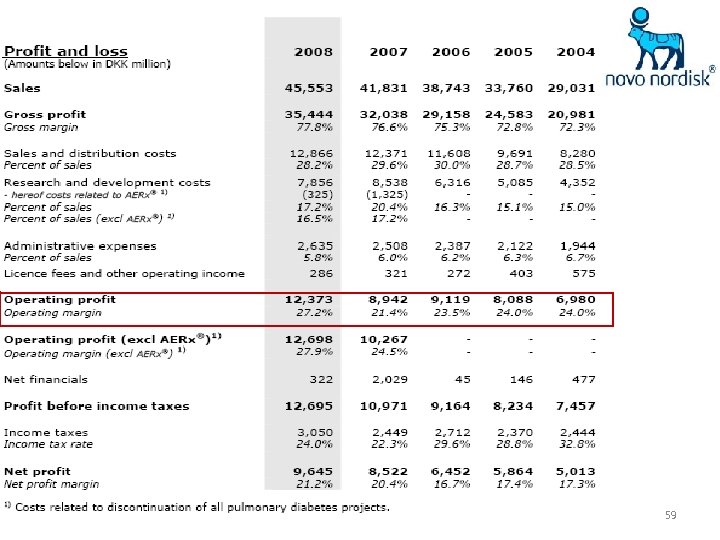
Increase investment in future growth strenghts R&D pipeline 1, 25 billion $ , represent 17, 2% of sales in 2008 50

Novo Nordisk is also exploring potential new therapies in areas where significant medical needs exist Haemostasis/Human Growth Hormon Pros Cons Poor competition between companies Limited number of patients Therapeutic advantage of protein over NCE Conducing clinical trials is cumbersome and time-consuming Disease severity allows for injection acceptance No guarantee of commercially viability Long-term growth outlook must be attractive 51
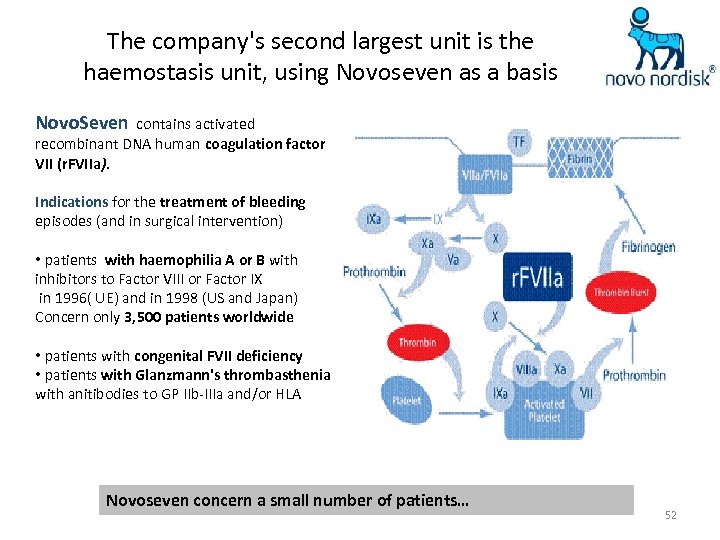
The company's second largest unit is the haemostasis unit, using Novoseven as a basis Novo. Seven contains activated recombinant DNA human coagulation factor VII (r. FVIIa). Indications for the treatment of bleeding episodes (and in surgical intervention) • patients with haemophilia A or B with inhibitors to Factor VIII or Factor IX in 1996( UE) and in 1998 (US and Japan) Concern only 3, 500 patients worldwide • patients with congenital FVII deficiency • patients with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia with anitibodies to GP IIb-IIIa and/or HLA Novoseven concern a small number of patients… 52
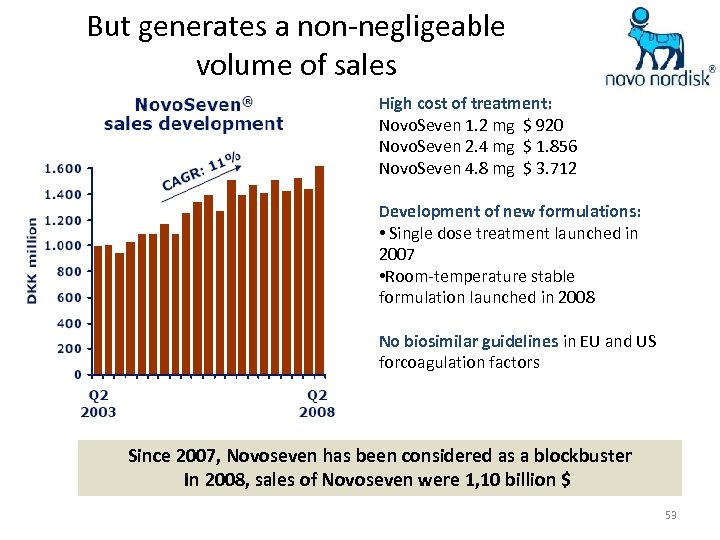
But generates a non-negligeable volume of sales High cost of treatment: Novo. Seven 1. 2 mg $ 920 Novo. Seven 2. 4 mg $ 1. 856 Novo. Seven 4. 8 mg $ 3. 712 Development of new formulations: • Single dose treatment launched in 2007 • Room-temperature stable formulation launched in 2008 No biosimilar guidelines in EU and US forcoagulation factors Since 2007, Novoseven has been considered as a blockbuster In 2008, sales of Novoseven were 1, 10 billion $ 53
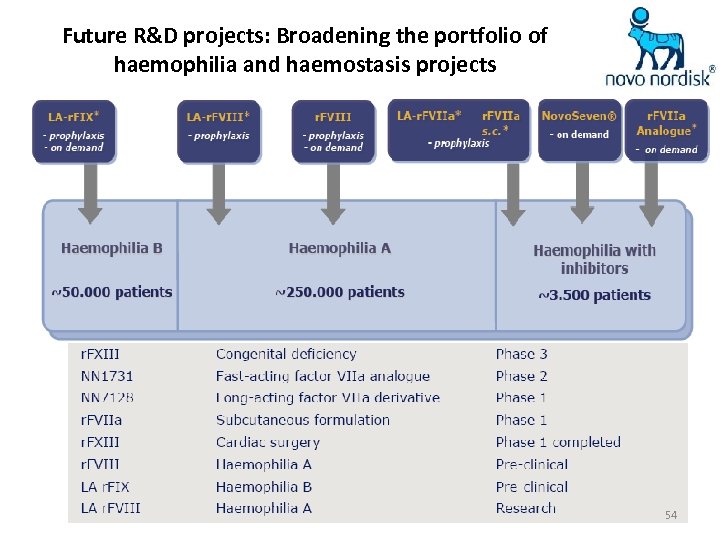
Future R&D projects: Broadening the portfolio of haemophilia and haemostasis projects 54
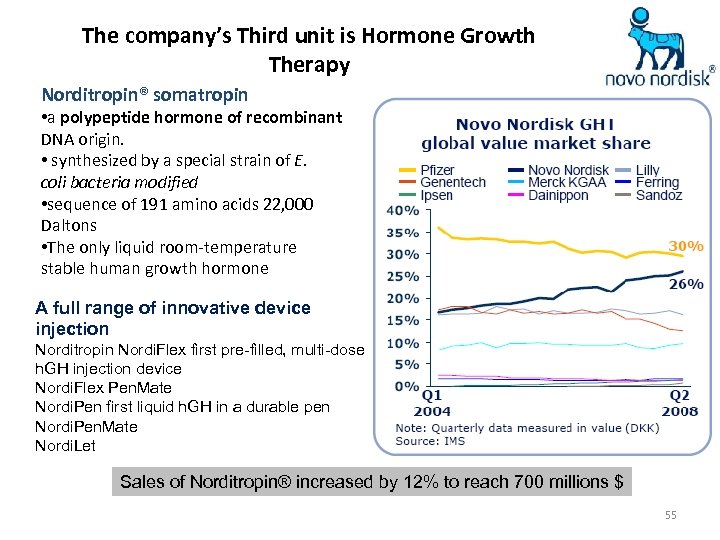
The company’s Third unit is Hormone Growth Therapy Norditropin® somatropin • a polypeptide hormone of recombinant DNA origin. • synthesized by a special strain of E. coli bacteria modified • sequence of 191 amino acids 22, 000 Daltons • The only liquid room-temperature stable human growth hormone A full range of innovative device injection Norditropin Nordi. Flex first pre-filled, multi-dose h. GH injection device Nordi. Flex Pen. Mate Nordi. Pen first liquid h. GH in a durable pen Nordi. Pen. Mate Nordi. Let Sales of Norditropin® increased by 12% to reach 700 millions $ 55
The company’s Third unit is Hormone Growth Therapy Low serum albumin in dialysis Novo Nordisk has initiated a phase 2 clinical study with a long-acting human growth hormone analogue designed for once-weekly treatment 56

SWOT ANALYSIS 57

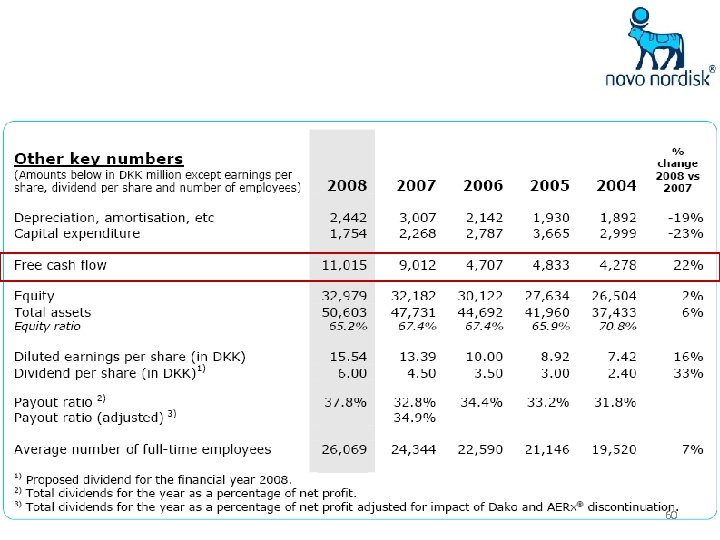
Strenghts • Leadership worldwide on diabetes care especially in insulin’s area Weaknesses • Over 95% of sales were derived from therapeutic proteins • Low exposure to patent expirations • Sales force developed around the world • Good financial handling • Strong R&D performances in devices innovations Opportunities Threats 58
59
60
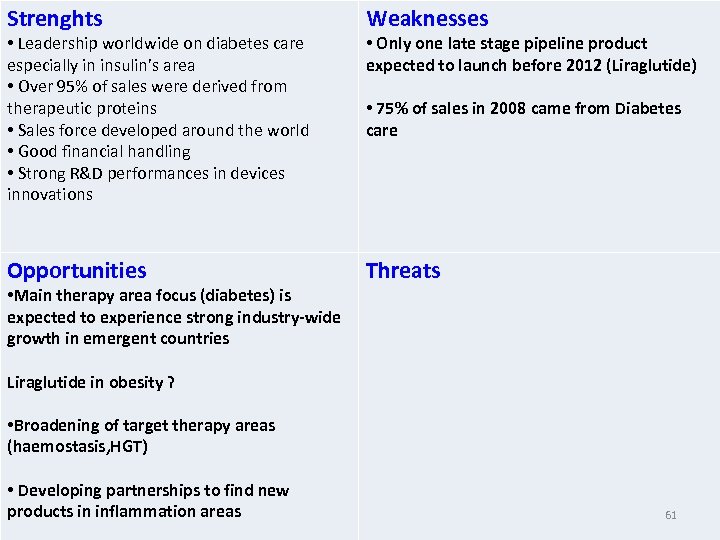
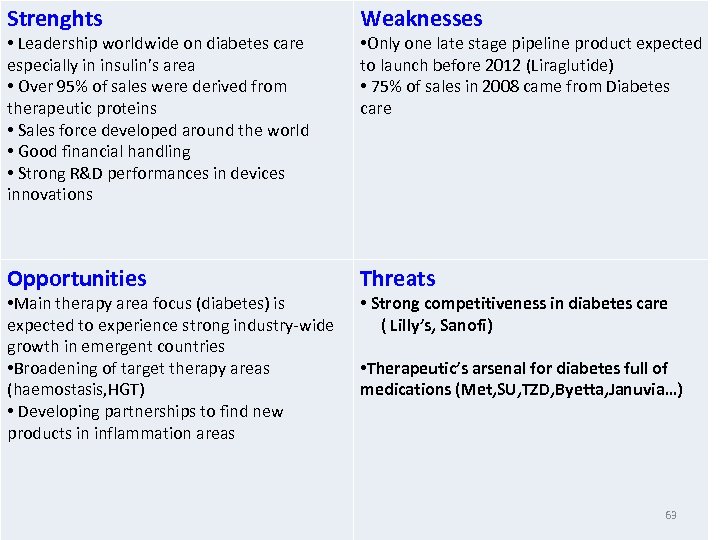
Strenghts • Leadership worldwide on diabetes care especially in insulin’s area • Over 95% of sales were derived from therapeutic proteins • Sales force developed around the world • Good financial handling • Strong R&D performances in devices innovations Opportunities • Main therapy area focus (diabetes) is expected to experience strong industry-wide growth in emergent countries Weaknesses • Only one late stage pipeline product expected to launch before 2012 (Liraglutide) • 75% of sales in 2008 came from Diabetes care Threats Liraglutide in obesity ? • Broadening of target therapy areas (haemostasis, HGT) • Developing partnerships to find new products in inflammation areas 61
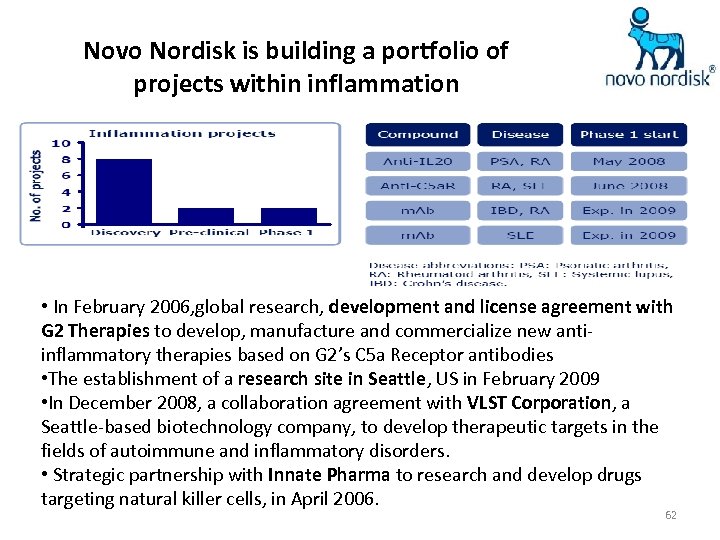
Novo Nordisk is building a portfolio of projects within inflammation • In February 2006, global research, development and license agreement with G 2 Therapies to develop, manufacture and commercialize new antiinflammatory therapies based on G 2’s C 5 a Receptor antibodies • The establishment of a research site in Seattle, US in February 2009 • In December 2008, a collaboration agreement with VLST Corporation, a Seattle-based biotechnology company, to develop therapeutic targets in the fields of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. • Strategic partnership with Innate Pharma to research and develop drugs targeting natural killer cells, in April 2006. 62
Strenghts Weaknesses Opportunities Threats • Leadership worldwide on diabetes care especially in insulin’s area • Over 95% of sales were derived from therapeutic proteins • Sales force developed around the world • Good financial handling • Strong R&D performances in devices innovations • Main therapy area focus (diabetes) is expected to experience strong industry-wide growth in emergent countries • Broadening of target therapy areas (haemostasis, HGT) • Developing partnerships to find new products in inflammation areas • Only one late stage pipeline product expected to launch before 2012 (Liraglutide) • 75% of sales in 2008 came from Diabetes care • Strong competitiveness in diabetes care ( Lilly’s, Sanofi) • Therapeutic’s arsenal for diabetes full of medications (Met, SU, TZD, Byetta, Januvia…) 63
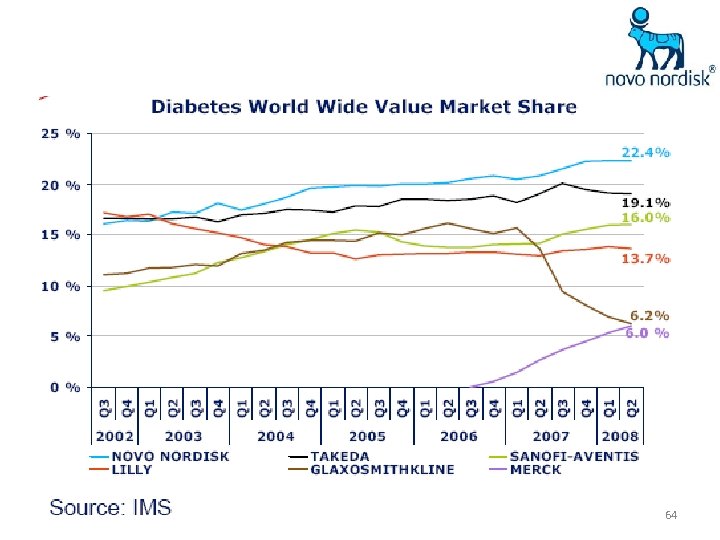
64

GLP-1 me too Coming soon … COMPANY PRODUCT STATUS Sanofi-Aventis / Zealand AVE 0010 Ph IIb Human Genome / Glaxo. Smith. Kline Albiglutide Ph II Ipsen / Roche BIM 51077 Ph II Amylin / Eli Lilly / Nastech Exenatide Nasal Ph I Emisphere GLP-1 Ph I 65 65

THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION ANY QUESTIONS ? 66
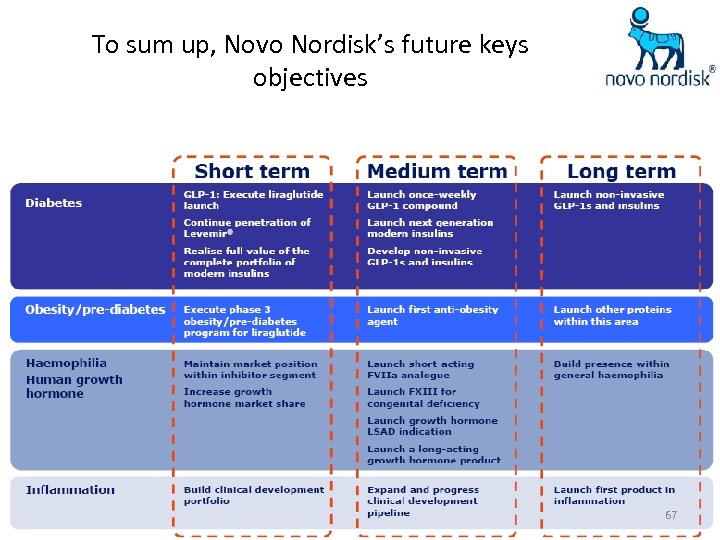
To sum up, Novo Nordisk’s future keys objectives 67
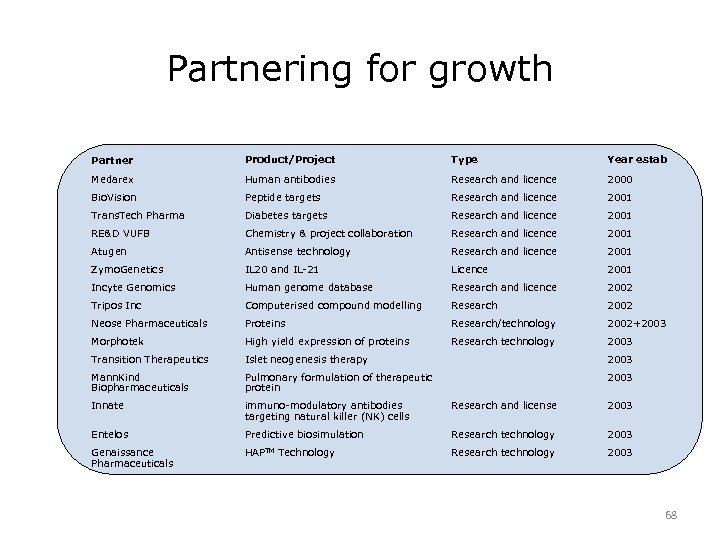
Partnering for growth Partner Product/Project Type Year estab Medarex Human antibodies Research and licence 2000 Bio. Vision Peptide targets Research and licence 2001 Trans. Tech Pharma Diabetes targets Research and licence 2001 RE&D VUFB Chemistry & project collaboration Research and licence 2001 Atugen Antisense technology Research and licence 2001 Zymo. Genetics IL 20 and IL-21 Licence 2001 Incyte Genomics Human genome database Research and licence 2002 Tripos Inc Computerised compound modelling Research 2002 Neose Pharmaceuticals Proteins Research/technology 2002+2003 Morphotek High yield expression of proteins Research technology 2003 Transition Therapeutics Islet neogenesis therapy 2003 Mann. Kind Biopharmaceuticals Pulmonary formulation of therapeutic protein 2003 Innate immuno-modulatory antibodies targeting natural killer (NK) cells Research and license 2003 Entelos Predictive biosimulation Research technology 2003 Genaissance Pharmaceuticals HAPTM Technology Research technology 2003 68
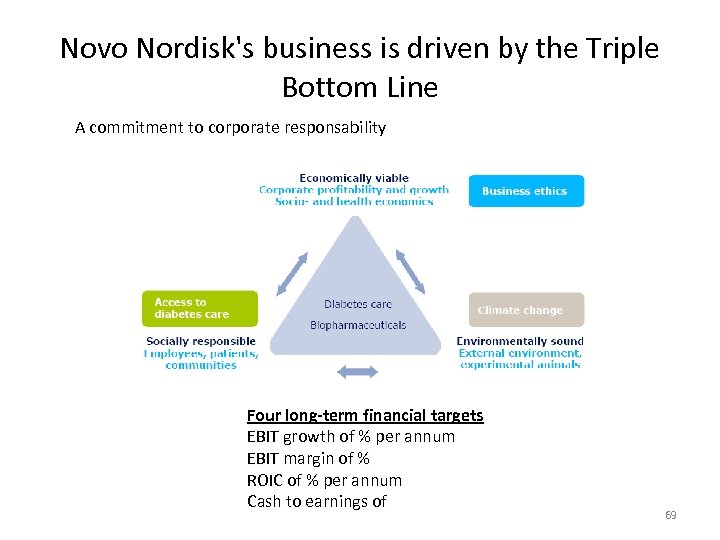
Novo Nordisk's business is driven by the Triple Bottom Line A commitment to corporate responsability Four long-term financial targets EBIT growth of % per annum EBIT margin of % ROIC of % per annum Cash to earnings of 69
4d8c9993a83cc7328c5630026285d61e.ppt