f8f0926911e8091ad95fbd48c2d4ad0b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Meeting the requirements of the ELV Directive: Measurement of Substances of Concern (SOCs) Maré Linsky and Retha Rossouw National Metrology Laboratory Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Meeting the requirements of the ELV Directive: Measurement of Substances of Concern (SOCs) Maré Linsky and Retha Rossouw National Metrology Laboratory Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 Overview Ø European Union Directives Ø Analytical Techniques Ø Developing an In-house Analyses Method Ø Outsourcing Analyses Ø National Metrology Laboratory Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Overview Ø European Union Directives Ø Analytical Techniques Ø Developing an In-house Analyses Method Ø Outsourcing Analyses Ø National Metrology Laboratory Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 European Union Directives Ø End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directive 2000/53 EC Goal: Reduce waste generated by vehicles at the end of their lives, though the collection, re-use and recycling of vehicle components. - Production and Design should facilitate dismantling, re-use, recovery and recycling - Increase the use of recycled material - Reduce the use of hazardous substances - Maximum allowable levels of heavy metals e. g. Cd, Cr(VI), Hg and Pb Ø Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE) 2002/96/EC Ø Restrictions on Hazardous Substances Directive (Ro. HS) 2002/95/EC - Also similar directives being proposed in China, Australia & California Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
European Union Directives Ø End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directive 2000/53 EC Goal: Reduce waste generated by vehicles at the end of their lives, though the collection, re-use and recycling of vehicle components. - Production and Design should facilitate dismantling, re-use, recovery and recycling - Increase the use of recycled material - Reduce the use of hazardous substances - Maximum allowable levels of heavy metals e. g. Cd, Cr(VI), Hg and Pb Ø Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE) 2002/96/EC Ø Restrictions on Hazardous Substances Directive (Ro. HS) 2002/95/EC - Also similar directives being proposed in China, Australia & California Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
![Typical applications of SOCs (functional vs contaminant) • Cadmium [Cd]: • Mercury [Hg]: - Typical applications of SOCs (functional vs contaminant) • Cadmium [Cd]: • Mercury [Hg]: -](https://present5.com/presentation/f8f0926911e8091ad95fbd48c2d4ad0b/image-4.jpg) Typical applications of SOCs (functional vs contaminant) • Cadmium [Cd]: • Mercury [Hg]: - Pigments and stabilizers in plastics - Batteries - Ni. Cd Batteries (exempt until Dec ‘ 08) - Relay-contacts, micro-switches - Fluorescent lamps (to be labeled) • Hexavalent Chromium [Cr(VI)]: - Anti-corrosive coatings (exempt until July ‘ 07) - Anti-corrosive coatings – Nut and Bolt assemblies (exempt until July ‘ 08) - Plasticizers Copyright © CSIR • Lead [Pb]: - Pigments in paint - Minor element in steels, aluminium - Stabilizers and pigments in PVC - Batteries (to be labeled) 2005 www. csir. co. za
Typical applications of SOCs (functional vs contaminant) • Cadmium [Cd]: • Mercury [Hg]: - Pigments and stabilizers in plastics - Batteries - Ni. Cd Batteries (exempt until Dec ‘ 08) - Relay-contacts, micro-switches - Fluorescent lamps (to be labeled) • Hexavalent Chromium [Cr(VI)]: - Anti-corrosive coatings (exempt until July ‘ 07) - Anti-corrosive coatings – Nut and Bolt assemblies (exempt until July ‘ 08) - Plasticizers Copyright © CSIR • Lead [Pb]: - Pigments in paint - Minor element in steels, aluminium - Stabilizers and pigments in PVC - Batteries (to be labeled) 2005 www. csir. co. za
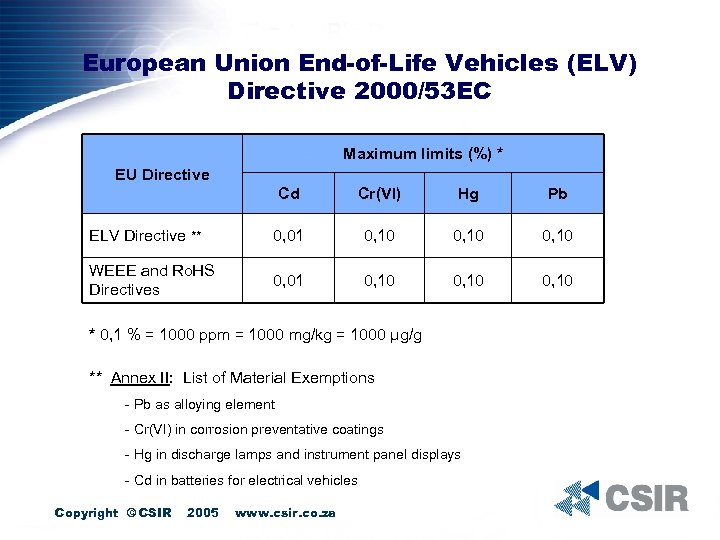 European Union End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directive 2000/53 EC Maximum limits (%) * EU Directive Cd Cr(VI) Hg Pb ELV Directive ** 0, 01 0, 10 WEEE and Ro. HS Directives 0, 01 0, 10 * 0, 1 % = 1000 ppm = 1000 mg/kg = 1000 µg/g ** Annex II: List of Material Exemptions - Pb as alloying element - Cr(VI) in corrosion preventative coatings - Hg in discharge lamps and instrument panel displays - Cd in batteries for electrical vehicles Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
European Union End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directive 2000/53 EC Maximum limits (%) * EU Directive Cd Cr(VI) Hg Pb ELV Directive ** 0, 01 0, 10 WEEE and Ro. HS Directives 0, 01 0, 10 * 0, 1 % = 1000 ppm = 1000 mg/kg = 1000 µg/g ** Annex II: List of Material Exemptions - Pb as alloying element - Cr(VI) in corrosion preventative coatings - Hg in discharge lamps and instrument panel displays - Cd in batteries for electrical vehicles Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
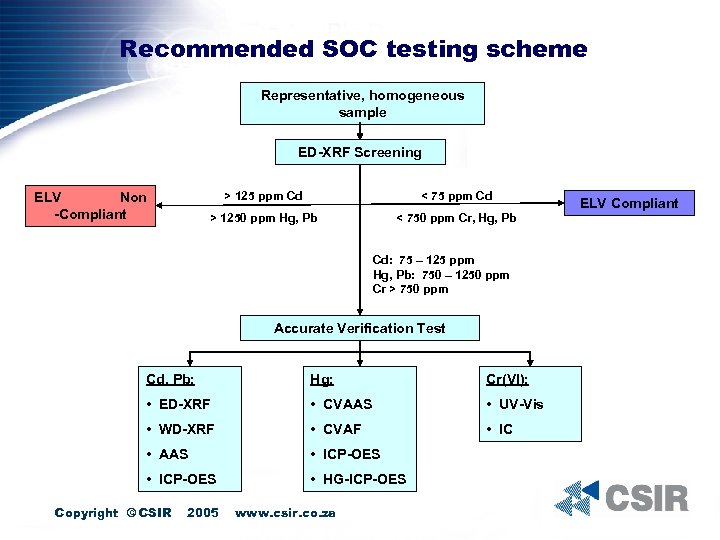 Recommended SOC testing scheme Representative, homogeneous sample ED-XRF Screening > 125 ppm Cd < 75 ppm Cd > 1250 ppm Hg, Pb ELV Non -Compliant < 750 ppm Cr, Hg, Pb Cd: 75 – 125 ppm Hg, Pb: 750 – 1250 ppm Cr > 750 ppm Accurate Verification Test Cd, Pb: Hg: Cr(VI): • ED-XRF • CVAAS • UV-Vis • WD-XRF • CVAF • IC • AAS • ICP-OES • HG-ICP-OES Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za ELV Compliant
Recommended SOC testing scheme Representative, homogeneous sample ED-XRF Screening > 125 ppm Cd < 75 ppm Cd > 1250 ppm Hg, Pb ELV Non -Compliant < 750 ppm Cr, Hg, Pb Cd: 75 – 125 ppm Hg, Pb: 750 – 1250 ppm Cr > 750 ppm Accurate Verification Test Cd, Pb: Hg: Cr(VI): • ED-XRF • CVAAS • UV-Vis • WD-XRF • CVAF • IC • AAS • ICP-OES • HG-ICP-OES Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za ELV Compliant
 WDXRF (Solid with sample preparation) ü (Non)-destructive ü High accuracy ü Excellent precision & long term stability ü Good resolution & sensitivity ü Multi-element analysis ü Well-established technique û Some sample preparation û Qualified, experience staff û Expensive û Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials (CRM) Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
WDXRF (Solid with sample preparation) ü (Non)-destructive ü High accuracy ü Excellent precision & long term stability ü Good resolution & sensitivity ü Multi-element analysis ü Well-established technique û Some sample preparation û Qualified, experience staff û Expensive û Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials (CRM) Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 EDXRF (Solid with sample preparation) ü Fast û Generally not portable ü (Non)-destructive û Some sample preparation required ü Sample Area û Experienced staff ü Good precision, accuracy û Moderately expensive ü Fair sensitivity û Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials (CRM) ü Multi-element analysis Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
EDXRF (Solid with sample preparation) ü Fast û Generally not portable ü (Non)-destructive û Some sample preparation required ü Sample Area û Experienced staff ü Good precision, accuracy û Moderately expensive ü Fair sensitivity û Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials (CRM) ü Multi-element analysis Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 EDXRF (Solid – Minimal preparation) ü Simple, fast û Generally not portable ü Non-destructive û Fair sensitivity (poor excitation due to low tube voltage) ü No sample preparation ü Sample Area (some control) ü Good precision, accuracy ü Multi-element analyses Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za û Moderately expensive û Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials (CRM)
EDXRF (Solid – Minimal preparation) ü Simple, fast û Generally not portable ü Non-destructive û Fair sensitivity (poor excitation due to low tube voltage) ü No sample preparation ü Sample Area (some control) ü Good precision, accuracy ü Multi-element analyses Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za û Moderately expensive û Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials (CRM)
 Handheld EDXRF – Instruments (Solid – No preparation) ü Portable, flexible û Sample Area (large, difficult to control) ü Simple, fast û Poor reproducibility, accuracy ü Non-destructive û Poor sensitivity (poor excitation due to low tube voltage) ü No sample preparation ü Multi-element analysis ü Inexpensive Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za û Instrument Calibration û Safety
Handheld EDXRF – Instruments (Solid – No preparation) ü Portable, flexible û Sample Area (large, difficult to control) ü Simple, fast û Poor reproducibility, accuracy ü Non-destructive û Poor sensitivity (poor excitation due to low tube voltage) ü No sample preparation ü Multi-element analysis ü Inexpensive Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za û Instrument Calibration û Safety
 GDOES (Solid with minimal preparation) û Only conducting samples ü Small sample area ü Analysis of sample layers ü Good precision and long term stability ü Good sensitivity and accuracy ü Multi-element analysis û Flat surface areas û Some sample preparation û Qualified, experienced staff û Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials (CRM) û Expensive Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
GDOES (Solid with minimal preparation) û Only conducting samples ü Small sample area ü Analysis of sample layers ü Good precision and long term stability ü Good sensitivity and accuracy ü Multi-element analysis û Flat surface areas û Some sample preparation û Qualified, experienced staff û Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials (CRM) û Expensive Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 AAS (Solution based analysis) ü Simple, well established technique ü Not expensive û Sample Preparation required (destructive) û Dedicated laboratory ü Matrix tolerant ü Traceable, certified solution standards available û Qualified, experienced staff û Sequential technique (mostly) û Narrow working range û LODs Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
AAS (Solution based analysis) ü Simple, well established technique ü Not expensive û Sample Preparation required (destructive) û Dedicated laboratory ü Matrix tolerant ü Traceable, certified solution standards available û Qualified, experienced staff û Sequential technique (mostly) û Narrow working range û LODs Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 ICP-OES (Solution based analysis) ü Excellent Accuracy, Precision ü Excellent Sensitivity (low LOD) û Dedicated laboratory ü Matrix tolerant ü Traceable, certified standard solutions available ü Multi-element analysis Copyright © CSIR 2005 û Sample Preparation required (destructive and time consuming) www. csir. co. za û Qualified, experienced staff û Expensive
ICP-OES (Solution based analysis) ü Excellent Accuracy, Precision ü Excellent Sensitivity (low LOD) û Dedicated laboratory ü Matrix tolerant ü Traceable, certified standard solutions available ü Multi-element analysis Copyright © CSIR 2005 û Sample Preparation required (destructive and time consuming) www. csir. co. za û Qualified, experienced staff û Expensive
 UV Vis – Spectroscopy Cr(VI) analysis - Solution based analysis ü Simple, well established technique ü Not expensive ü Traceable, certified solution standards available ü IEC recommended technique (Ro. HS Directive) û Sample Preparation required (destructive and time consuming) û Unstable analyte û Matrix tolerance û Dedicated laboratory û Qualified, experienced staff Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
UV Vis – Spectroscopy Cr(VI) analysis - Solution based analysis ü Simple, well established technique ü Not expensive ü Traceable, certified solution standards available ü IEC recommended technique (Ro. HS Directive) û Sample Preparation required (destructive and time consuming) û Unstable analyte û Matrix tolerance û Dedicated laboratory û Qualified, experienced staff Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
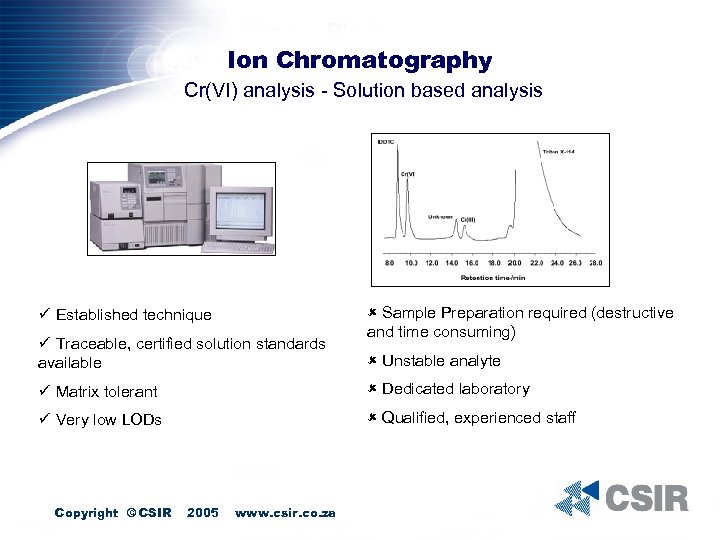 Ion Chromatography Cr(VI) analysis - Solution based analysis ü Established technique ü Traceable, certified solution standards available û Sample Preparation required (destructive and time consuming) û Unstable analyte ü Matrix tolerant û Dedicated laboratory ü Very low LODs û Qualified, experienced staff Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Ion Chromatography Cr(VI) analysis - Solution based analysis ü Established technique ü Traceable, certified solution standards available û Sample Preparation required (destructive and time consuming) û Unstable analyte ü Matrix tolerant û Dedicated laboratory ü Very low LODs û Qualified, experienced staff Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 Hg analysis (Solution based analysis) • Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption (CVAAS) • Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence (CVAF) • Hydride Generation ICP-OES • Direct Mercury Analyzer (DMA) ü Excellent sensitivity ü Traceable, certified solution standards available ü Established techniques û Sample preparation generally required (destructive and time consuming) û Dedicated laboratory û Specialized technique û Qualified, experienced staff Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Hg analysis (Solution based analysis) • Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption (CVAAS) • Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence (CVAF) • Hydride Generation ICP-OES • Direct Mercury Analyzer (DMA) ü Excellent sensitivity ü Traceable, certified solution standards available ü Established techniques û Sample preparation generally required (destructive and time consuming) û Dedicated laboratory û Specialized technique û Qualified, experienced staff Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 Typical Equipment employed for SOC Testing Solid sample analysis: - Minimal sample preparation required: ED-XRF Energy Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy - Some sample preparation required: WD-XRF Wavelength Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy GD-OES Glow Discharge Optical Emission Spectroscopy Solution based analysis: AAS Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy ICP-OES Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy UV-Vis Ultra-Violet Visible Spectroscopy IC Ion Chromatography CV-AAS Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy HG-ICPOES Copyright © CSIR Hydride Generation ICP-OES 2005 www. csir. co. za
Typical Equipment employed for SOC Testing Solid sample analysis: - Minimal sample preparation required: ED-XRF Energy Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy - Some sample preparation required: WD-XRF Wavelength Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy GD-OES Glow Discharge Optical Emission Spectroscopy Solution based analysis: AAS Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy ICP-OES Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy UV-Vis Ultra-Violet Visible Spectroscopy IC Ion Chromatography CV-AAS Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy HG-ICPOES Copyright © CSIR Hydride Generation ICP-OES 2005 www. csir. co. za
 Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials Requirements: - Accredited or reputable manufacturer - SI traceable (mole, gram) - Uncertainty of measurement - Matrix (e. g. plastic, metal) - Concentration levels Examples of Reference Materials’ Suppliers: - Industrial Analytical (local) - Merck (local) - JFJ Industries (local) - COMAR (European Database) - NIST (USA) - Equipment Suppliers (traceablity) Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Calibration Standards and Certified Reference Materials Requirements: - Accredited or reputable manufacturer - SI traceable (mole, gram) - Uncertainty of measurement - Matrix (e. g. plastic, metal) - Concentration levels Examples of Reference Materials’ Suppliers: - Industrial Analytical (local) - Merck (local) - JFJ Industries (local) - COMAR (European Database) - NIST (USA) - Equipment Suppliers (traceablity) Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
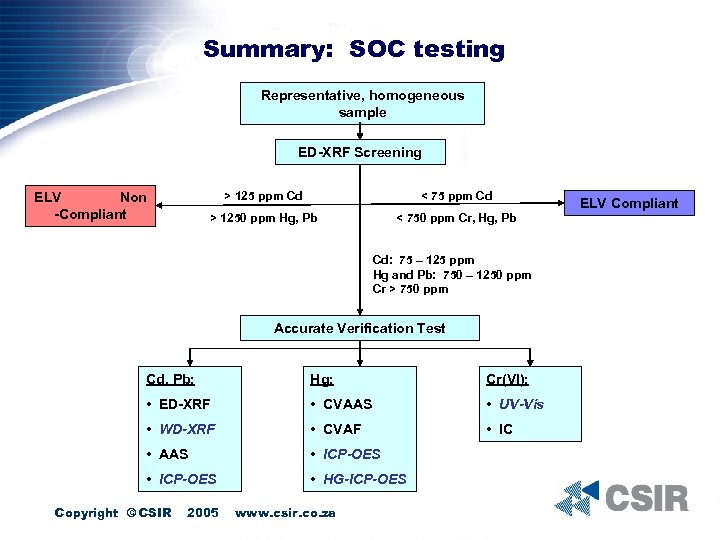 Summary: SOC testing Representative, homogeneous sample ED-XRF Screening > 125 ppm Cd < 75 ppm Cd > 1250 ppm Hg, Pb ELV Non -Compliant < 750 ppm Cr, Hg, Pb Cd: 75 – 125 ppm Hg and Pb: 750 – 1250 ppm Cr > 750 ppm Accurate Verification Test Cd, Pb: Hg: Cr(VI): • ED-XRF • CVAAS • UV-Vis • WD-XRF • CVAF • IC • AAS • ICP-OES • HG-ICP-OES Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za ELV Compliant
Summary: SOC testing Representative, homogeneous sample ED-XRF Screening > 125 ppm Cd < 75 ppm Cd > 1250 ppm Hg, Pb ELV Non -Compliant < 750 ppm Cr, Hg, Pb Cd: 75 – 125 ppm Hg and Pb: 750 – 1250 ppm Cr > 750 ppm Accurate Verification Test Cd, Pb: Hg: Cr(VI): • ED-XRF • CVAAS • UV-Vis • WD-XRF • CVAF • IC • AAS • ICP-OES • HG-ICP-OES Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za ELV Compliant
 Developing an In-house Analytical Method Ø Instrument selection: • Screening vs Accurate analysis • Detection limit of system vs. legislative limits (LOD vs. LOQ) Ø Sample preparation: • Special facilities • Additional equipment Ø Instrument calibration: • Fundamental Principals / Calibration standards • Working Range vs. Sample Concentration • Certified Reference Materials (calibration / verification) Ø Experienced Staff Ø ISO 17025 Accreditation Ø Cost Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Developing an In-house Analytical Method Ø Instrument selection: • Screening vs Accurate analysis • Detection limit of system vs. legislative limits (LOD vs. LOQ) Ø Sample preparation: • Special facilities • Additional equipment Ø Instrument calibration: • Fundamental Principals / Calibration standards • Working Range vs. Sample Concentration • Certified Reference Materials (calibration / verification) Ø Experienced Staff Ø ISO 17025 Accreditation Ø Cost Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 Outsourcing Analyses Ø Laboratory accredited to ISO 17025 (www. sanas. co. za) Accreditation Scope: • Cd, Cr(VI), Hg and Pb • Matrix (plastics, metals, etc. ) • Concentration levels • Analytical techniques Ø Quality assurance when laboratory is not accredited: • Submit Reference Standard (i. e. known concentration) • Submit sample in duplicate • Analysis by different techniques / laboratories NOTE: Homogeneity of sample is critical Ø Turn-around times Ø Cost Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Outsourcing Analyses Ø Laboratory accredited to ISO 17025 (www. sanas. co. za) Accreditation Scope: • Cd, Cr(VI), Hg and Pb • Matrix (plastics, metals, etc. ) • Concentration levels • Analytical techniques Ø Quality assurance when laboratory is not accredited: • Submit Reference Standard (i. e. known concentration) • Submit sample in duplicate • Analysis by different techniques / laboratories NOTE: Homogeneity of sample is critical Ø Turn-around times Ø Cost Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
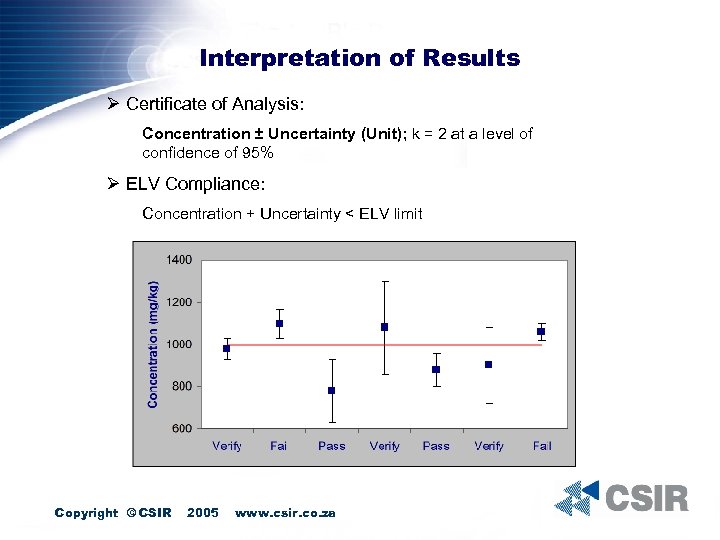 Interpretation of Results Ø Certificate of Analysis: Concentration ± Uncertainty (Unit); k = 2 at a level of confidence of 95% Ø ELV Compliance: Concentration + Uncertainty < ELV limit Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Interpretation of Results Ø Certificate of Analysis: Concentration ± Uncertainty (Unit); k = 2 at a level of confidence of 95% Ø ELV Compliance: Concentration + Uncertainty < ELV limit Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 NML Project : Meeting the SOC demands of the ELV Directive Ø NLA-Database: South African laboratories • Contact persons • Accreditation / Experience - Matrix (plastics, metals, etc. ) - Techniques available (XRF, ICP, etc. ) - Concentration levels (major, minor, trace) Ø Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) • Identify which materials are available • Calibration materials supplied by instrument manufacturers: SI traceability Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
NML Project : Meeting the SOC demands of the ELV Directive Ø NLA-Database: South African laboratories • Contact persons • Accreditation / Experience - Matrix (plastics, metals, etc. ) - Techniques available (XRF, ICP, etc. ) - Concentration levels (major, minor, trace) Ø Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) • Identify which materials are available • Calibration materials supplied by instrument manufacturers: SI traceability Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 NML Project : Meeting the SOC-demands of the ELV-Directive (2) Ø Consultation: • Assess current situation • Assisting with development of in-house analytical capabilities • Assisting with ISO 17025 accreditation Ø Evaluation of analytical techniques available at the NML: § GD-OES § UV-Vis § FT-IR § WD-XRF § ICP-OES § TGA-MS § LA-ICP-MS Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
NML Project : Meeting the SOC-demands of the ELV-Directive (2) Ø Consultation: • Assess current situation • Assisting with development of in-house analytical capabilities • Assisting with ISO 17025 accreditation Ø Evaluation of analytical techniques available at the NML: § GD-OES § UV-Vis § FT-IR § WD-XRF § ICP-OES § TGA-MS § LA-ICP-MS Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 To Conclude Ø Analytical Techniques • • Ø Screening vs. Quantitative Approach (e. g. EDXRF vs. ICP-OES) Sample preparation Calibration standards • • Matrix matched • Ø SI traceable Reputable manufacturer Laboratories • Experienced vs ISO 17025 -accreditation Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
To Conclude Ø Analytical Techniques • • Ø Screening vs. Quantitative Approach (e. g. EDXRF vs. ICP-OES) Sample preparation Calibration standards • • Matrix matched • Ø SI traceable Reputable manufacturer Laboratories • Experienced vs ISO 17025 -accreditation Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 NML Contacts Maré Linsky Tel: (012) 841 -3974 e-mail: mlinsky@csir. co. za Retha Rossouw Tel: (012) 841 -2607 e-mail: rrossouw@csir. co. za Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
NML Contacts Maré Linsky Tel: (012) 841 -3974 e-mail: mlinsky@csir. co. za Retha Rossouw Tel: (012) 841 -2607 e-mail: rrossouw@csir. co. za Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 Summary: Analytical Techniques Sample Prep Required? Screening Quantitative LOD (ppm) Skill of Operator Cost ED-XRF ~ ppm Medium $$ WD-XRF ~ ~ ppm Med-High $$$ AAS ppm Med-High $$ ICP-OES ppb High $$$ GF-AAS ppb High $$ CV-AAS ppb Med-High $$ HG-ICPOES ppb High $$$ GD-OES ~ ~ ~ ppm Med-High $$$ UV-Vis ppm Medium $$ IC ppm High $$ Technique Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Summary: Analytical Techniques Sample Prep Required? Screening Quantitative LOD (ppm) Skill of Operator Cost ED-XRF ~ ppm Medium $$ WD-XRF ~ ~ ppm Med-High $$$ AAS ppm Med-High $$ ICP-OES ppb High $$$ GF-AAS ppb High $$ CV-AAS ppb Med-High $$ HG-ICPOES ppb High $$$ GD-OES ~ ~ ~ ppm Med-High $$$ UV-Vis ppm Medium $$ IC ppm High $$ Technique Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
 Instrument Manufacturers • Bruker AXS • CETAC • Horiba Jobin Yvon (Wirsam Scientific) • Milestone (Apollo Scientific) • Oxford Instruments (SMM Instruments) • PANalytical • Spectro Analytical Instruments • Shimadzu (Lab. World) • Thermo Electron Corporation • Varian (SMM Instruments) Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za
Instrument Manufacturers • Bruker AXS • CETAC • Horiba Jobin Yvon (Wirsam Scientific) • Milestone (Apollo Scientific) • Oxford Instruments (SMM Instruments) • PANalytical • Spectro Analytical Instruments • Shimadzu (Lab. World) • Thermo Electron Corporation • Varian (SMM Instruments) Copyright © CSIR 2005 www. csir. co. za


