37f3a5b72dc7b2e0610ffdce54fb4dbc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Meeting Computing Needs Across Campus Mark Guzdial, School of Interactive Computing
Meeting Computing Needs Across Campus Mark Guzdial, School of Interactive Computing
 Story • Why we should teach computing to everyone • Making computing work for everyone at Georgia Tech. – Lesson Learned: Contextualized computing education. – What our courses are like • Side trip into second course – Results • Side trip: Applying the lesson to the BS in CS. • Finally, what does it buy us in CS? 2
Story • Why we should teach computing to everyone • Making computing work for everyone at Georgia Tech. – Lesson Learned: Contextualized computing education. – What our courses are like • Side trip into second course – Results • Side trip: Applying the lesson to the BS in CS. • Finally, what does it buy us in CS? 2
 Time Warp to Fall 1999 • Fall 1999: All students at Georgia Tech must take a course in computer science. – Considered part of General Education, like mathematics, social science, humanities… – Heroes: Peter Freeman, Rich Le. Blanc, Kurt Eiselt, Russ Shackelford • Why did Georgia Tech make that decision? – Computing was a College. – Making competitive distinctions for Liberal Arts – ABET might start requiring CS. 3
Time Warp to Fall 1999 • Fall 1999: All students at Georgia Tech must take a course in computer science. – Considered part of General Education, like mathematics, social science, humanities… – Heroes: Peter Freeman, Rich Le. Blanc, Kurt Eiselt, Russ Shackelford • Why did Georgia Tech make that decision? – Computing was a College. – Making competitive distinctions for Liberal Arts – ABET might start requiring CS. 3
 More reasons for computing across curriculum • Everyone needs to learn about process (Alan Perlis) • Algorithms control our lives: The tyranny of the computationally literate (C. P. Snow) • The tools of learning for computational scientists and engineers brought to the classrom. – Computers are cheaper than Super-Conducting Supercolliders 4
More reasons for computing across curriculum • Everyone needs to learn about process (Alan Perlis) • Algorithms control our lives: The tyranny of the computationally literate (C. P. Snow) • The tools of learning for computational scientists and engineers brought to the classrom. – Computers are cheaper than Super-Conducting Supercolliders 4
 1961 MIT Sloan School Symposium 5
1961 MIT Sloan School Symposium 5
 Computing for Everyone • In 1961, Alan Perlis argued that computer science should be part of a liberal education. – Explicitly, he argued that all students should learn to program. • Why? – Because Computer Science is the study of process. – Automated execution of process changes everything 6
Computing for Everyone • In 1961, Alan Perlis argued that computer science should be part of a liberal education. – Explicitly, he argued that all students should learn to program. • Why? – Because Computer Science is the study of process. – Automated execution of process changes everything 6
 The Power and Fear of Algorithms • The Economist (Sept. , 2007) spoke to the algorithms that control us, yet we don’t understand. – Credit Ratings, Adjustable Rate Mortgages, Google • C. P. Snow foresaw this in 1961. – Those who don’t understand algorithms, can’t understand how the decisions are made. “A handful of people, having no relation to the will of the society, having no communication with the rest of society will be taking decisions in secret which are going to affect our lives in the deepest sense. ” 7
The Power and Fear of Algorithms • The Economist (Sept. , 2007) spoke to the algorithms that control us, yet we don’t understand. – Credit Ratings, Adjustable Rate Mortgages, Google • C. P. Snow foresaw this in 1961. – Those who don’t understand algorithms, can’t understand how the decisions are made. “A handful of people, having no relation to the will of the society, having no communication with the rest of society will be taking decisions in secret which are going to affect our lives in the deepest sense. ” 7
 Adopting Computing—without us • At Georgia Tech and other Universities: – Biology teaches programming for mathematical and computational models. – Physics teaches VPython for labs where they solve three-body problems. • Computer science provides the tools and metaphors for understanding science. • Scientists and engineers use computing to model, simulate, and understand. – Why shouldn’t science and engineering students? – History repeating: Telescopes, microscopes. – Unlike other scientific instruments, computers are already cheap and plentiful. • Problem: They’re doing it without us. 8
Adopting Computing—without us • At Georgia Tech and other Universities: – Biology teaches programming for mathematical and computational models. – Physics teaches VPython for labs where they solve three-body problems. • Computer science provides the tools and metaphors for understanding science. • Scientists and engineers use computing to model, simulate, and understand. – Why shouldn’t science and engineering students? – History repeating: Telescopes, microscopes. – Unlike other scientific instruments, computers are already cheap and plentiful. • Problem: They’re doing it without us. 8
 Richard Dawkins on Fresh Aire GROSS: You close your book saying, "I am thrilled to be alive at a time when humanity is pushing against the limits of understanding. " How do you think that's happening in your field of evolutionary biology? Mr. DAWKINS: Well, it's the most exciting time to be a biologist…Since Watson and Crick in 1953, biology has become a sort of branch of computer science. I mean, genes are just long computer tapes, and they use a code which is just another kind of computer code. It's quaternary rather than binary, but it's read in a sequential way just like a computer tape. It's transcribed. It's copied and pasted. All the familiar metaphors from computer science fit. 9
Richard Dawkins on Fresh Aire GROSS: You close your book saying, "I am thrilled to be alive at a time when humanity is pushing against the limits of understanding. " How do you think that's happening in your field of evolutionary biology? Mr. DAWKINS: Well, it's the most exciting time to be a biologist…Since Watson and Crick in 1953, biology has become a sort of branch of computer science. I mean, genes are just long computer tapes, and they use a code which is just another kind of computer code. It's quaternary rather than binary, but it's read in a sequential way just like a computer tape. It's transcribed. It's copied and pasted. All the familiar metaphors from computer science fit. 9
 Back to Georgia Tech in 1999 • Key Point: Only one course met the requirement: CS 1321 Introduction to Computing – Shackelford’s pseudocode approach in 1999 – Later Scheme: How to Design Programs • Why only one? – Resource issues – “Service Ghetto” – The offer to help them do their own 10
Back to Georgia Tech in 1999 • Key Point: Only one course met the requirement: CS 1321 Introduction to Computing – Shackelford’s pseudocode approach in 1999 – Later Scheme: How to Design Programs • Why only one? – Resource issues – “Service Ghetto” – The offer to help them do their own 10
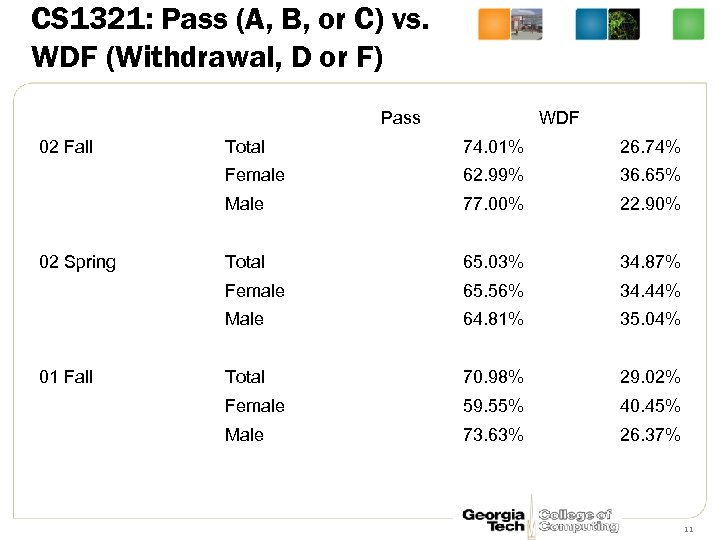 CS 1321: Pass (A, B, or C) vs. WDF (Withdrawal, D or F) Pass 02 Fall WDF 26. 74% 62. 99% 36. 65% Male 77. 00% 22. 90% Total 65. 03% 34. 87% Female 65. 56% 34. 44% Male 01 Fall 74. 01% Female 02 Spring Total 64. 81% 35. 04% Total 70. 98% 29. 02% Female 59. 55% 40. 45% Male 73. 63% 26. 37% 11
CS 1321: Pass (A, B, or C) vs. WDF (Withdrawal, D or F) Pass 02 Fall WDF 26. 74% 62. 99% 36. 65% Male 77. 00% 22. 90% Total 65. 03% 34. 87% Female 65. 56% 34. 44% Male 01 Fall 74. 01% Female 02 Spring Total 64. 81% 35. 04% Total 70. 98% 29. 02% Female 59. 55% 40. 45% Male 73. 63% 26. 37% 11
 Contextualized Computing Education • Since Spring 2003, we teach 3 introductory CS courses. – Responding to research results about CS being “irrelevant” – Based on Margolis and Fisher “alternative paths” • Each course introduces computing using a context (examples, homework assignments, lecture discussion) relevant to majors. • Make computing relevant by teaching it in terms of what computers are good for (from the students’ perspective). 12
Contextualized Computing Education • Since Spring 2003, we teach 3 introductory CS courses. – Responding to research results about CS being “irrelevant” – Based on Margolis and Fisher “alternative paths” • Each course introduces computing using a context (examples, homework assignments, lecture discussion) relevant to majors. • Make computing relevant by teaching it in terms of what computers are good for (from the students’ perspective). 12
 Our Three CS 1’s Today • CS 1301/1321 Introduction to Computing Traditional CS 1 for our CS majors and Science majors (math, physics, psychology, etc. ). • CS 1371 Computing for Engineers CS 1 for Engineers. Same topics as CS 1301, but using MATLAB with Engineering problems in homework and examples. • CS 1315 Introduction to Media Computation 13
Our Three CS 1’s Today • CS 1301/1321 Introduction to Computing Traditional CS 1 for our CS majors and Science majors (math, physics, psychology, etc. ). • CS 1371 Computing for Engineers CS 1 for Engineers. Same topics as CS 1301, but using MATLAB with Engineering problems in homework and examples. • CS 1315 Introduction to Media Computation 13
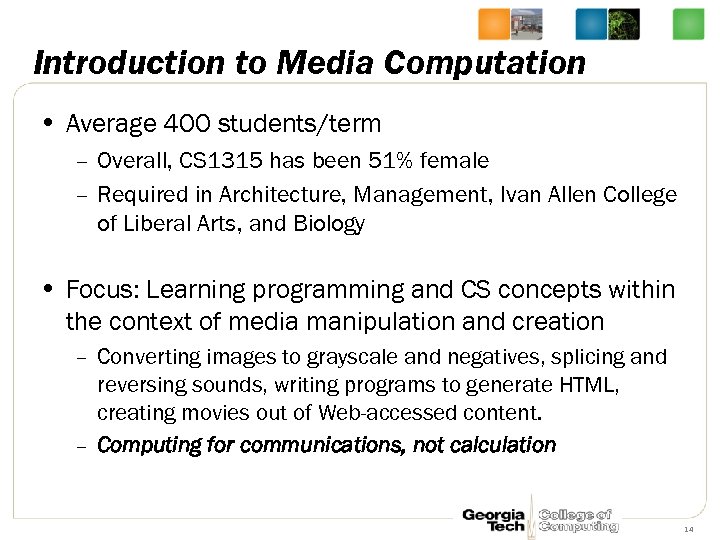 Introduction to Media Computation • Average 400 students/term – Overall, CS 1315 has been 51% female – Required in Architecture, Management, Ivan Allen College of Liberal Arts, and Biology • Focus: Learning programming and CS concepts within the context of media manipulation and creation – Converting images to grayscale and negatives, splicing and reversing sounds, writing programs to generate HTML, creating movies out of Web-accessed content. – Computing for communications, not calculation 14
Introduction to Media Computation • Average 400 students/term – Overall, CS 1315 has been 51% female – Required in Architecture, Management, Ivan Allen College of Liberal Arts, and Biology • Focus: Learning programming and CS concepts within the context of media manipulation and creation – Converting images to grayscale and negatives, splicing and reversing sounds, writing programs to generate HTML, creating movies out of Web-accessed content. – Computing for communications, not calculation 14
 Media Computation: Teaching in a Relevant Context • Presenting CS topics with media projects and examples – Iteration as creating negative and grayscale images – Indexing in a range as removing redeye – Algorithms for blending both images and sounds – Linked lists as song fragments woven to make music – Information encodings as sound visualizations 15
Media Computation: Teaching in a Relevant Context • Presenting CS topics with media projects and examples – Iteration as creating negative and grayscale images – Indexing in a range as removing redeye – Algorithms for blending both images and sounds – Linked lists as song fragments woven to make music – Information encodings as sound visualizations 15
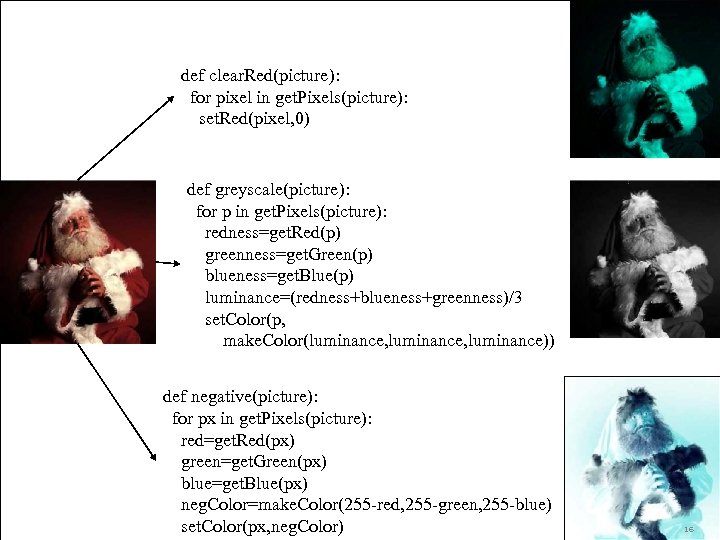 def clear. Red(picture): for pixel in get. Pixels(picture): set. Red(pixel, 0) def greyscale(picture): for p in get. Pixels(picture): redness=get. Red(p) greenness=get. Green(p) blueness=get. Blue(p) luminance=(redness+blueness+greenness)/3 set. Color(p, make. Color(luminance, luminance)) def negative(picture): for px in get. Pixels(picture): red=get. Red(px) green=get. Green(px) blue=get. Blue(px) neg. Color=make. Color(255 -red, 255 -green, 255 -blue) set. Color(px, neg. Color) 16
def clear. Red(picture): for pixel in get. Pixels(picture): set. Red(pixel, 0) def greyscale(picture): for p in get. Pixels(picture): redness=get. Red(p) greenness=get. Green(p) blueness=get. Blue(p) luminance=(redness+blueness+greenness)/3 set. Color(p, make. Color(luminance, luminance)) def negative(picture): for px in get. Pixels(picture): red=get. Red(px) green=get. Green(px) blue=get. Blue(px) neg. Color=make. Color(255 -red, 255 -green, 255 -blue) set. Color(px, neg. Color) 16
 Syllabus for Introductory Course • Getting started: Defining and executing functions • Pictures – Psychophysics, data structures, defining functions, loops, conditionals (redeye removal, posterizing) – Bitmap vs. vector notations • Sounds – Psychophysics, data structures, defining functions, loops, conditionals – Sampled sounds vs. synthesized, MP 3 vs. MIDI • Text – Converting between media, generating HTML, database, and networking – A little trees (directories) and hash tables (database) • Movies • Then, Computer Science topics (last 1/3 class) 17
Syllabus for Introductory Course • Getting started: Defining and executing functions • Pictures – Psychophysics, data structures, defining functions, loops, conditionals (redeye removal, posterizing) – Bitmap vs. vector notations • Sounds – Psychophysics, data structures, defining functions, loops, conditionals – Sampled sounds vs. synthesized, MP 3 vs. MIDI • Text – Converting between media, generating HTML, database, and networking – A little trees (directories) and hash tables (database) • Movies • Then, Computer Science topics (last 1/3 class) 17
 Computer Science Topics as solutions to their problems • “Why is Photo. Shop so much faster? ” – Compiling vs. interpreting – Machine language and how the computer works • “Writing programs is hard! Are there ways to make it easier? Or at least shorter? ” – Object-oriented programming – Functional programming and recursion • “Movie-manipulating programs take a long time to execute. Why? How fast/slow can programs be? ” – Algorithmic complexity 18
Computer Science Topics as solutions to their problems • “Why is Photo. Shop so much faster? ” – Compiling vs. interpreting – Machine language and how the computer works • “Writing programs is hard! Are there ways to make it easier? Or at least shorter? ” – Object-oriented programming – Functional programming and recursion • “Movie-manipulating programs take a long time to execute. Why? How fast/slow can programs be? ” – Algorithmic complexity 18
 Examples of Student Work Soup. Audio Collage Canon. Linked. List of (MIDI) Music 19
Examples of Student Work Soup. Audio Collage Canon. Linked. List of (MIDI) Music 19
 Student voices • Intro CS student (female): “I just wish I had more time to play around with that and make neat effects. But JES [IDE for class] will be on my computer forever, so… that’s the nice thing about this class is that you could go as deep into the homework as you wanted. So, I’d turn it in and then me and my roommate would do more after to see what we could do with it. ” • High School teacher: “This was the best (non-college credit) workshop I have ever taken. ” • Students in multimedia data structures: “Data structures is an important step. Use of media! It makes it fun. ” 20
Student voices • Intro CS student (female): “I just wish I had more time to play around with that and make neat effects. But JES [IDE for class] will be on my computer forever, so… that’s the nice thing about this class is that you could go as deep into the homework as you wanted. So, I’d turn it in and then me and my roommate would do more after to see what we could do with it. ” • High School teacher: “This was the best (non-college credit) workshop I have ever taken. ” • Students in multimedia data structures: “Data structures is an important step. Use of media! It makes it fun. ” 20
 A Media Computation Data Structures Course • Driving question: “How did the wildebeests stampede in The Lion King? ” 21
A Media Computation Data Structures Course • Driving question: “How did the wildebeests stampede in The Lion King? ” 21
 Connecting to the Wildebeests It’s all about data structures 22
Connecting to the Wildebeests It’s all about data structures 22
 Similar Assignments, but with Objects and Agents 23
Similar Assignments, but with Objects and Agents 23
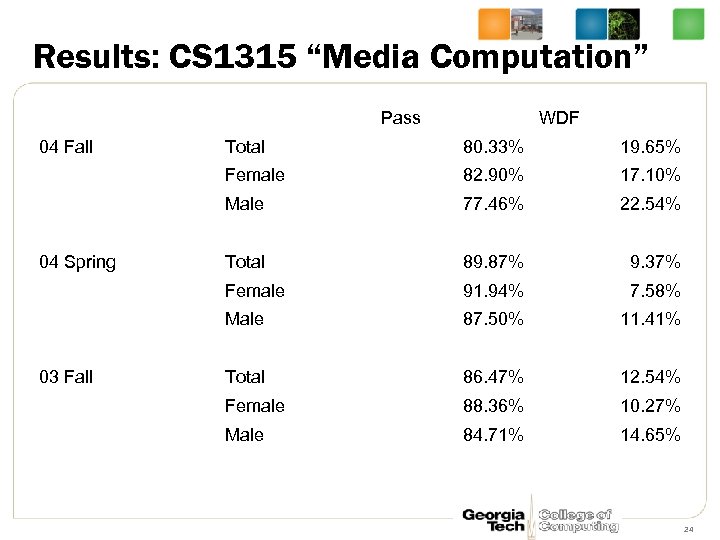 Results: CS 1315 “Media Computation” Pass 04 Fall WDF 19. 65% 82. 90% 17. 10% Male 77. 46% 22. 54% Total 89. 87% 9. 37% Female 91. 94% 7. 58% Male 03 Fall 80. 33% Female 04 Spring Total 87. 50% 11. 41% Total 86. 47% 12. 54% Female 88. 36% 10. 27% Male 84. 71% 14. 65% 24
Results: CS 1315 “Media Computation” Pass 04 Fall WDF 19. 65% 82. 90% 17. 10% Male 77. 46% 22. 54% Total 89. 87% 9. 37% Female 91. 94% 7. 58% Male 03 Fall 80. 33% Female 04 Spring Total 87. 50% 11. 41% Total 86. 47% 12. 54% Female 88. 36% 10. 27% Male 84. 71% 14. 65% 24
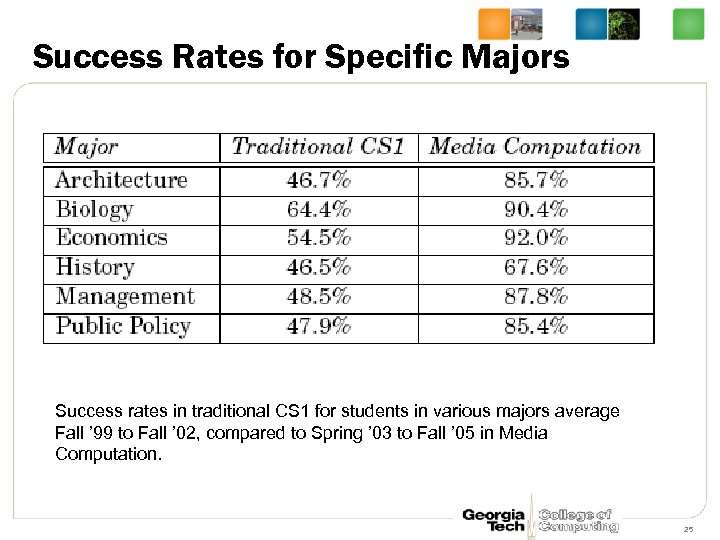 Success Rates for Specific Majors Success rates in traditional CS 1 for students in various majors average Fall ’ 99 to Fall ’ 02, compared to Spring ’ 03 to Fall ’ 05 in Media Computation. 25
Success Rates for Specific Majors Success rates in traditional CS 1 for students in various majors average Fall ’ 99 to Fall ’ 02, compared to Spring ’ 03 to Fall ’ 05 in Media Computation. 25
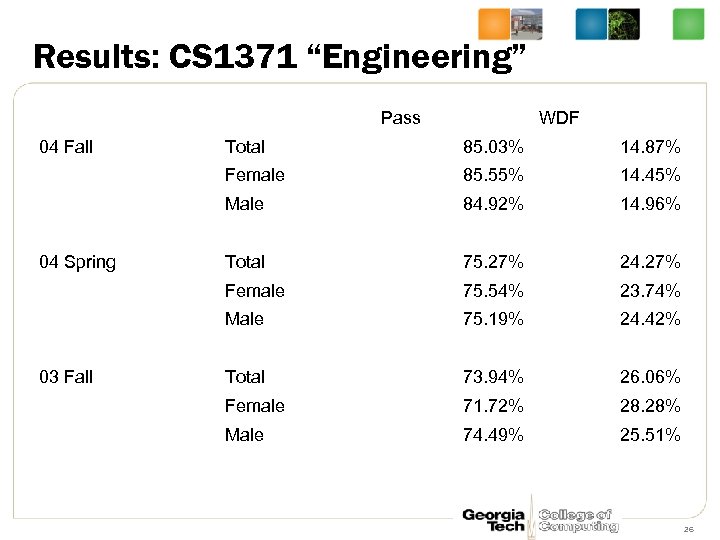 Results: CS 1371 “Engineering” Pass 04 Fall WDF 14. 87% 85. 55% 14. 45% Male 84. 92% 14. 96% Total 75. 27% 24. 27% Female 75. 54% 23. 74% Male 03 Fall 85. 03% Female 04 Spring Total 75. 19% 24. 42% Total 73. 94% 26. 06% Female 71. 72% 28. 28% Male 74. 49% 25. 51% 26
Results: CS 1371 “Engineering” Pass 04 Fall WDF 14. 87% 85. 55% 14. 45% Male 84. 92% 14. 96% Total 75. 27% 24. 27% Female 75. 54% 23. 74% Male 03 Fall 85. 03% Female 04 Spring Total 75. 19% 24. 42% Total 73. 94% 26. 06% Female 71. 72% 28. 28% Male 74. 49% 25. 51% 26
 Results of four years of evaluation • Media. Comp students are motivated and engaged (retention data, interviews), and find the course social, creative, and “relevant. ” – Replicated at several institutions now. • Students in the contextualized courses program outside of class. – Immediately (engineers) and even a year later (Media. Comp) • Students in Media. Comp classes (both, and new Architecture course) spend extra time on homework “because it’s cool. ” 27
Results of four years of evaluation • Media. Comp students are motivated and engaged (retention data, interviews), and find the course social, creative, and “relevant. ” – Replicated at several institutions now. • Students in the contextualized courses program outside of class. – Immediately (engineers) and even a year later (Media. Comp) • Students in Media. Comp classes (both, and new Architecture course) spend extra time on homework “because it’s cool. ” 27
 The Other Results • We don’t know if they learn the same. – The challenge of comparative studies when there is no common reality. • While engaging, majority of students do not find the Media. Comp courses relevant to their degrees or professions. – Many do find it relevant to their lives. • Students distinguish between “more Media. Comp classes” and “more CS classes” 28
The Other Results • We don’t know if they learn the same. – The challenge of comparative studies when there is no common reality. • While engaging, majority of students do not find the Media. Comp courses relevant to their degrees or professions. – Many do find it relevant to their lives. • Students distinguish between “more Media. Comp classes” and “more CS classes” 28
 Next steps… An alternative path and a minor • What happens when you have an intro to CS course for non-majors that students pass and even enjoy? • Define a CS minor – About 100 students today • Create new BS in Computational Media – Joint with School of Literature, Communications, and Culture – 58 majors in first year, 24% female Over 200 majors today, still about ¼ female 29
Next steps… An alternative path and a minor • What happens when you have an intro to CS course for non-majors that students pass and even enjoy? • Define a CS minor – About 100 students today • Create new BS in Computational Media – Joint with School of Literature, Communications, and Culture – 58 majors in first year, 24% female Over 200 majors today, still about ¼ female 29
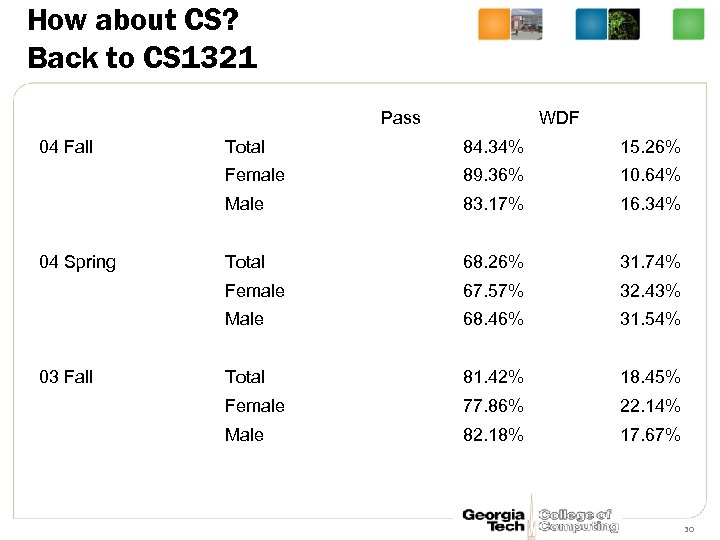 How about CS? Back to CS 1321 Pass 04 Fall WDF 15. 26% 89. 36% 10. 64% Male 83. 17% 16. 34% Total 68. 26% 31. 74% Female 67. 57% 32. 43% Male 03 Fall 84. 34% Female 04 Spring Total 68. 46% 31. 54% Total 81. 42% 18. 45% Female 77. 86% 22. 14% Male 82. 18% 17. 67% 30
How about CS? Back to CS 1321 Pass 04 Fall WDF 15. 26% 89. 36% 10. 64% Male 83. 17% 16. 34% Total 68. 26% 31. 74% Female 67. 57% 32. 43% Male 03 Fall 84. 34% Female 04 Spring Total 68. 46% 31. 54% Total 81. 42% 18. 45% Female 77. 86% 22. 14% Male 82. 18% 17. 67% 30
 A Context for CS 1 for CS majors: Robotics • Microsoft Research has funded the Institute for Personal Robotics in Education – Tucker Balch, Directing Joint between Bryn Mawr and Georgia Tech – http: //www. roboteducation. org • Goal is to develop a CS 1 (and CS 2) with robotics as the context. – Homework: • Recursively follow a light • Enter a pyramid and take a picture of it. • Hold a “Peacebot” demonstration. • Film a movie and use Media. Comp for special effects 31
A Context for CS 1 for CS majors: Robotics • Microsoft Research has funded the Institute for Personal Robotics in Education – Tucker Balch, Directing Joint between Bryn Mawr and Georgia Tech – http: //www. roboteducation. org • Goal is to develop a CS 1 (and CS 2) with robotics as the context. – Homework: • Recursively follow a light • Enter a pyramid and take a picture of it. • Hold a “Peacebot” demonstration. • Film a movie and use Media. Comp for special effects 31
 Using Context throughout the CS Curriculum • The future of computing is not in merely being a good programmer. – Those skills are now commodities that can be outsourced anywhere. • When “The World is Flat” (Friedman), we become competitive by bridging areas and differentiating. 32
Using Context throughout the CS Curriculum • The future of computing is not in merely being a good programmer. – Those skills are now commodities that can be outsourced anywhere. • When “The World is Flat” (Friedman), we become competitive by bridging areas and differentiating. 32
 Microsoft wants employees who know context for CS “The nature of these jobs is not closing the door and coding, ” (Bill) Gates said. “The great missing skill is somebody who’s good at understanding engineering and bridges that [understanding] to working with customers and marketing…We can promise these people most of what they’re doing won’t be coding. ” – Gates worried over decline in US computer scientists, Computer. World, July 18, 2005 (by Elizabeth Montalbano) 33
Microsoft wants employees who know context for CS “The nature of these jobs is not closing the door and coding, ” (Bill) Gates said. “The great missing skill is somebody who’s good at understanding engineering and bridges that [understanding] to working with customers and marketing…We can promise these people most of what they’re doing won’t be coding. ” – Gates worried over decline in US computer scientists, Computer. World, July 18, 2005 (by Elizabeth Montalbano) 33
 The Threads™ Curriculum • We have defined 8 Threads in Computing: – Computing and People – Computing and Information Internetworking – Computing and Media – Computing and Platforms – Computing and Intelligence – Computing and Foundations – Computing and Computational Modeling – Computing and Devices (was Embodiment) 34
The Threads™ Curriculum • We have defined 8 Threads in Computing: – Computing and People – Computing and Information Internetworking – Computing and Media – Computing and Platforms – Computing and Intelligence – Computing and Foundations – Computing and Computational Modeling – Computing and Devices (was Embodiment) 34
 The BS in Computer Science under Threads™ • Each Thread specifies the courses needed to know that area well. – From introductory computing, through advanced courses, to beyond Computer Science (Psychology, Physics, Computer Engineering). • A degree is the union of any two Threads. – Every Combination is a full Computer Science degree, but bridging disciplines and clearly different from “just programming. ” – No Thread choice is necessary in first year, Can always choose different Threads during degree. 35
The BS in Computer Science under Threads™ • Each Thread specifies the courses needed to know that area well. – From introductory computing, through advanced courses, to beyond Computer Science (Psychology, Physics, Computer Engineering). • A degree is the union of any two Threads. – Every Combination is a full Computer Science degree, but bridging disciplines and clearly different from “just programming. ” – No Thread choice is necessary in first year, Can always choose different Threads during degree. 35
 Back to Computing Across Campus • What do we get from teaching computing to the rest of campus? – Maybe make our students more competitive? • Maybe attract more students? – New problems to work on. • The difference between Computer Science and Computing. – Where the interesting stuff is. – A change in culture. • Pedagogical methods. – Critical design in Architecture • Research methods 36
Back to Computing Across Campus • What do we get from teaching computing to the rest of campus? – Maybe make our students more competitive? • Maybe attract more students? – New problems to work on. • The difference between Computer Science and Computing. – Where the interesting stuff is. – A change in culture. • Pedagogical methods. – Critical design in Architecture • Research methods 36
 Computer Scientists and Reading • Alan Perlis, Norbert Weiner, J. C. R. Licklider, C. P. Snow • Others included Vannevar Bush, Herbert A. Simon, Marvin L. Minsky, Jay W. Forrester, Grace M. Hopper, Claude E. Shannon, John G. Kemeny, Gene M. Amdahl 37
Computer Scientists and Reading • Alan Perlis, Norbert Weiner, J. C. R. Licklider, C. P. Snow • Others included Vannevar Bush, Herbert A. Simon, Marvin L. Minsky, Jay W. Forrester, Grace M. Hopper, Claude E. Shannon, John G. Kemeny, Gene M. Amdahl 37
 Summary • The rest of campus needs what we have to offer. • We have found that the way they need computing education is different than the way we offer it to our students. – Maybe we need to change what we offer to our own students. • We have found a contextualized computing approach works (for the measures we have now). • There may be benefits for our CS culture in making more connections to the rest of campus. 38
Summary • The rest of campus needs what we have to offer. • We have found that the way they need computing education is different than the way we offer it to our students. – Maybe we need to change what we offer to our own students. • We have found a contextualized computing approach works (for the measures we have now). • There may be benefits for our CS culture in making more connections to the rest of campus. 38
 Thank you! Mark Guzdial http: //www. cc. gatech. edu/~mark. guzdial http: //home. cc. gatech. edu/csl For more on Media. Comp approach (including papers, software, and slides): http: //coweb. cc. gatech. edu/media. Compplan Media Computation Teachers’ Site: http: //coweb. cc. gatech. edu/media. Compteach 39
Thank you! Mark Guzdial http: //www. cc. gatech. edu/~mark. guzdial http: //home. cc. gatech. edu/csl For more on Media. Comp approach (including papers, software, and slides): http: //coweb. cc. gatech. edu/media. Compplan Media Computation Teachers’ Site: http: //coweb. cc. gatech. edu/media. Compteach 39
 Next steps in Threads: Roles • Threads are about conceptual focus. • Within any Thread, might play different roles: – – – A Master Practitioner An Entrepreneur A Researcher A Communicator/Teacher A Public Policy Maker • We are defining recommendations for these roles in terms of experiences and elective classes in software engineering, management, and other areas. 40
Next steps in Threads: Roles • Threads are about conceptual focus. • Within any Thread, might play different roles: – – – A Master Practitioner An Entrepreneur A Researcher A Communicator/Teacher A Public Policy Maker • We are defining recommendations for these roles in terms of experiences and elective classes in software engineering, management, and other areas. 40
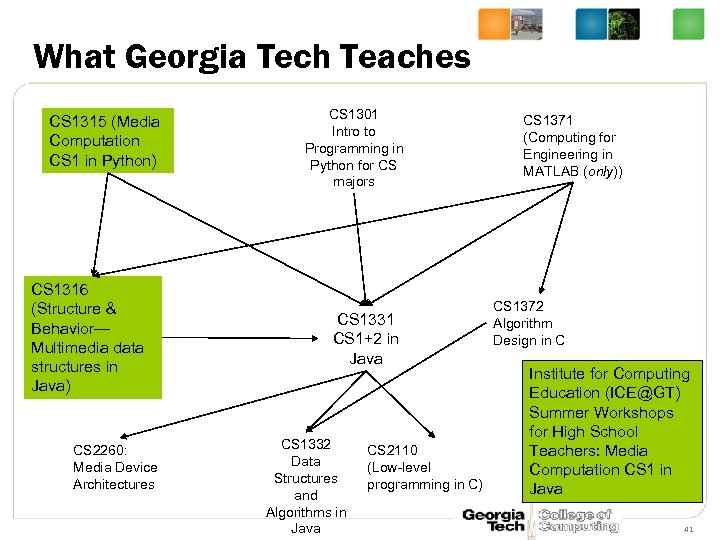 What Georgia Tech Teaches CS 1315 (Media Computation CS 1 in Python) CS 1316 (Structure & Behavior— Multimedia data structures in Java) CS 2260: Media Device Architectures CS 1301 Intro to Programming in Python for CS majors CS 1331 CS 1+2 in Java CS 1332 Data Structures and Algorithms in Java CS 2110 (Low-level programming in C) CS 1371 (Computing for Engineering in MATLAB (only)) CS 1372 Algorithm Design in C Institute for Computing Education (ICE@GT) Summer Workshops for High School Teachers: Media Computation CS 1 in Java 41
What Georgia Tech Teaches CS 1315 (Media Computation CS 1 in Python) CS 1316 (Structure & Behavior— Multimedia data structures in Java) CS 2260: Media Device Architectures CS 1301 Intro to Programming in Python for CS majors CS 1331 CS 1+2 in Java CS 1332 Data Structures and Algorithms in Java CS 2110 (Low-level programming in C) CS 1371 (Computing for Engineering in MATLAB (only)) CS 1372 Algorithm Design in C Institute for Computing Education (ICE@GT) Summer Workshops for High School Teachers: Media Computation CS 1 in Java 41
 Computing and Devices 42
Computing and Devices 42
 Computing and Information Internetworking 43
Computing and Information Internetworking 43
 Want a job in Information Security? • Information Internetworking + Foundations – Encoding and storing information securely for organizations • Information Internetworking + Platforms – Making information flow securely between large databases and small cell phones and PDAs. 44
Want a job in Information Security? • Information Internetworking + Foundations – Encoding and storing information securely for organizations • Information Internetworking + Platforms – Making information flow securely between large databases and small cell phones and PDAs. 44
 Preparing for Jobs to Come • The Future of Robotics: Devices + People 45
Preparing for Jobs to Come • The Future of Robotics: Devices + People 45
 Preparing for Jobs to Come • Platforms + Media • Platforms + People 46
Preparing for Jobs to Come • Platforms + Media • Platforms + People 46
 For More Information… http: //www. cc. gatech. edu/threads 47
For More Information… http: //www. cc. gatech. edu/threads 47


