1ca7f2315dda644be79185b86a787e49.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

Meet the People behind “We the People”

“Founding Fathers” Framers • George Washington …Chairman

“Father of the Constitution” James Madison

Preamble • “We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. ”

Preamble • List of Goals of the American Government • Explains the purpose of the Document • Short and to the Point

Constitutional Convention Key Compromises • Representation • Virginia Plan • New Jersey Plan • Great Compromise-- Bicameral Legislation…Two Houses

“Bundle of Compromises” • Slavery • 3/5 Compromise…Tax and representation purposes • 1808… Slave Trade Abolished

“Bundle of Compromises” • Tariffs. . . (Taxes on Imports) • Presidency… Created the Electoral College

Washington D. C.

Article ONE Legislative Branch Sections 1 -10 • What do we need to know for each Section? • What are the Clauses in some of these Sections? • What is Clause 18? •

House and Senate Requirements Section 2 -House Section 3 -Senate • Age: • Qualifications: • Term: • Presiding Officer: Special Powers: How Elected:

Section 4 • Elections and Meetings…The times, Places and Manner of holding elections for Senators and Representatives shall be prescribed in each state by the legislature thereof;

Section 5 • Rules of Order • Each House shall keep a Journal of all activities (Congressional Record)

Section 6 • Congressional Pay Congress: Rank-and-File Members' Salary The current salary (2008) for rank-and-file members of the House and Senate is $169, 300 per year. Senate Leadership Majority leader $188, 100 Minority Lead $ 188, 100 House Leadership Speaker of the House $217, 400 Majority and Minority Leaders $ 188, 100

Article ONE Section 7 Bills Become Laws • How does a bill becomes a law? • What are the steps to pass legislation in our Congress? • Need to Know this process.

Congressional Powers Section 8 • Delegated or Enumerated powers. Specific powers of Congress • Article I Sections 8 • Seventeen powers of the Congress

The Congress Article ONE-Section 8 Clause 1 -17 Lawmaking Naturalization Levying and collecting taxes declaring war regulating interstate commerce and foreign commerce • Coining money • • •

Continued: • Borrowing money • Federal Courts • establishing rules for Immigration • maintaining an Army and Navy • Create a Postal service

Implied Powers Clause 18 Section 8 • Elastic clause-gives the Congress the power to • “to make all laws necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers”

Powers Denied Powers Forbidden to Congress Section 9 • • • Writs of Habeas Corpus bills of Attainder Ex post facto Granting titles of Nobility Spending money without Appropriations

Powers denied the Federal government • Suspending the writs of habeas corpus (written court order informing an accused person of the charges) speedy arraignment Bills of attainder-legislative acts declaring people guilty without a trial Ex post facto- laws that declare an act a crime after it has been done.

Section 10 Powers Forbidden to States • • • No No No Treaties coining Money titles of Nobility import or export tax War Powers foreign relations

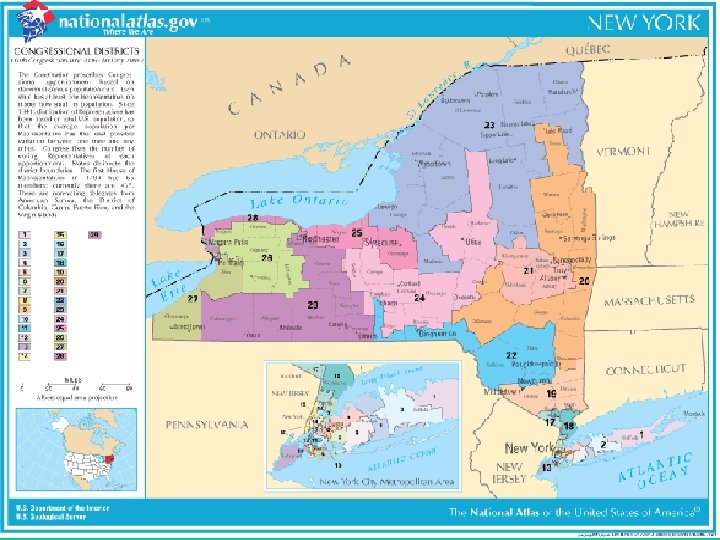
Christopher Lee 26 th Congressional District NY

th District 26 • • Erie County Genesee County Livingston County Monroe County Niagara County Orleans County Wyoming County

?

US Senators NEW YORK

Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi

Senate Majority leader President Pro-tempore • President Pro Tempore • Robert Byrd. • • • Duties The literal translation of President Pro Tempore is "president for a time. " The President Pro Tempore is a constitutionally appointed officer who presides over the Senate in the Vice President's absence. As the Chamber's presiding officer, the President Pro Tempore is authorized to perform certain duties, including ruling on points of order and enforcing decorum in the Senate Chamber and Galleries. The President Pro Tempore also signs Legislation passed by the Senate before it is sent to the President for his signature. Since 1947, the President Pro Tempore has been third in the line of presidential succession, behind the Vice President and the Speaker of the House. The President Pro Tempore also serves as a member of the majority party's leadership team.

Senator Robert Byrd is serving as the current President Pro Tempore

Article II • • • President Requirements Age ? ? Vice-President

Article II Executive Branch • Sections 1 -4 • Section I- about the Presidency • Term / Age requirement /Natural born citizen / 14 year resident • Section II – about Presidential powers

Presidential Powers Section II continued • • • Chief Executive Chief of State Chief Legislator Judicial Enforcer Political Chief Commander-in-Chief

Section III • State of the Union • Budget • Economic reports • Special messages

Section IV- about Impeachment • House – charges the President • Senate … has the sole power to try all impeachment cases

Article III Judicial Branch • Supreme Court • • How many Justices? How long is their term of office? How do you get on the Court? What is their job?

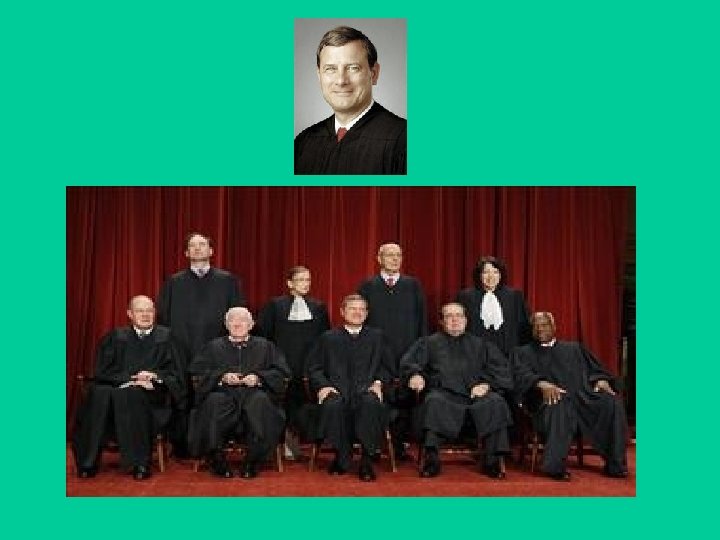
Supreme Court • Current U. S. Supreme Court Justices • Chief Justice: • John Roberts • Associate Justices: • • Samuel Alito Stephan Breyer Ruth Bader Ginsburg Anthony Kennedy Antonin Scalia Sonia Sotomayor John Paul Stevens Clarence Thomas
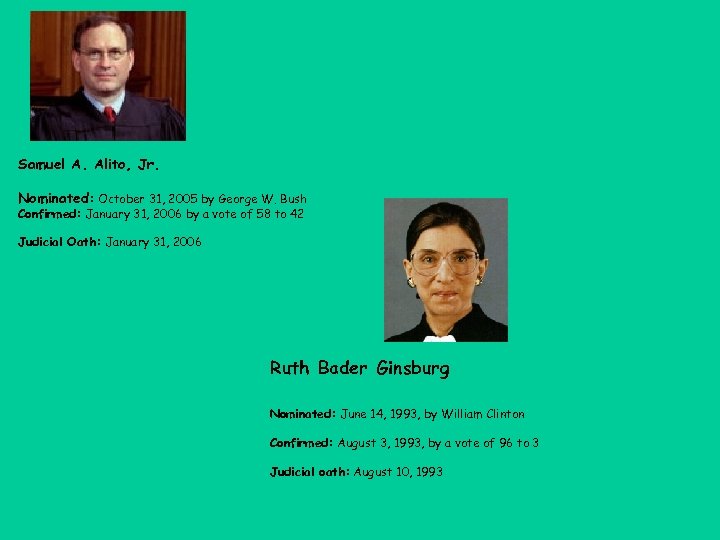
Samuel A. Alito, Jr. Nominated: October 31, 2005 by George W. Bush Confirmed: January 31, 2006 by a vote of 58 to 42 Judicial Oath: January 31, 2006 Ruth Bader Ginsburg Nominated: June 14, 1993, by William Clinton Confirmed: August 3, 1993, by a vote of 96 to 3 Judicial oath: August 10, 1993

Anthony Kennedy Nominated: November 30, 1987, by Ronald Reagan Confirmed: February 3, 1988, by a vote of 97 to 0 Judicial oath: February 18, 1988 John Stevens Nominated: December 1, 1975, by Gerald Ford Confirmed: December 17, 1975, by a vote of 98 to 0 Judicial oath: December 19, 1975

Antonin Scalia Clarence Thomas Nominated: June 24, 1986, by Ronald Reagan Nominated: July 1, 1991, by George H. W. Bush Confirmed: September 17, 1986, by a vote of 98 to 0 Confirmed: October 15, 1991, by a vote of 52 to 48 Judicial oath: September 26, 1986 Judicial oath: October 23, 1991

Stephan Breyer Sonia Sotomayor Nominated: May 13, 1994, by William Clinton Nominated: May 26, 2009, by Barack Obama Confirmed: July 29, 1994, by a vote of 87 to 9 Confirmed: August 6, 2009, by a vote of 68 to 31 Judicial oath: August 3, 1994 Judicial oath: August 8, 2009


Article IV Sections 1 - 4 • (Concerning the States) • Rights and Duties of states/ Section 1 • Rights Liabilities of citizens/ Section 2 • New States / Section 3 • Guarantee to states / Section 4

Article V • Amending the Constitution • How is this different than a bill becoming a law?

Article VI • Supreme Law of the Land • All public officials must take an oath to support the Constitution

Article VII • Ratification • Who signed? • Who did not • Why did some refuse?
1ca7f2315dda644be79185b86a787e49.ppt