709fa8af7ac5594a5f2e616c5feef2ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Medium term plans for Agriculture and Growth By Hon Anastase MUREKEZI Minister of Agriculture and Animal Resources 1
Importance of Agriculture for Growth and poverty reduction in Rwanda n Background of the Sector q n n For 90%: employment, incomes, food supply and multiplier effects Growth strong but below PRSP target: 2002 -2005: 4. 2% PSTA under implementation with institutional reforms underway 2

EDPRS Outcomes n n Vision 2020 and LTIF Objectives and Targets align with EDPRS Medium Term and EDPRS outcomes q q Agricultural growth of 6% annually Annual growth rate of agricultural export revenues is 7% Average per capita real income in agriculture increases by 5% from baseline Halve the proportion of population below minimum food requirements 3

Overview n n n Challenges and Opportunities PSTA & Institutional FW Seven Sector Priorities for 2007 and beyond Cross cutting issues Conclusion 4
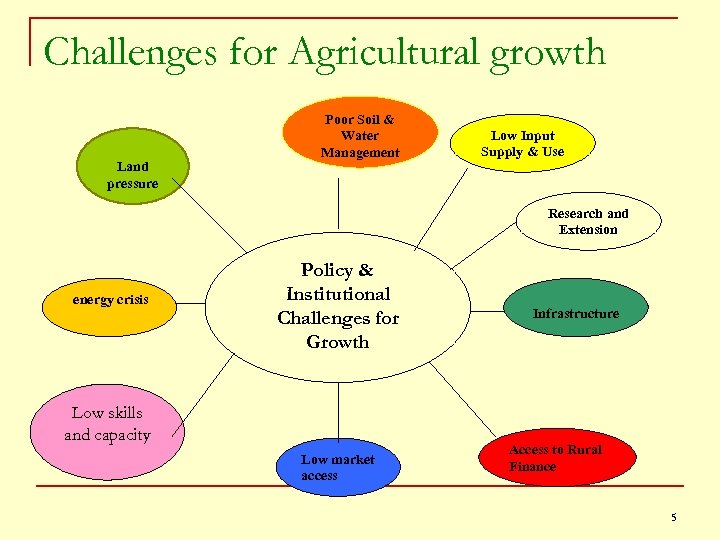
Challenges for Agricultural growth Land pressure Poor Soil & Water Management Low Input Supply & Use Research and Extension energy crisis Policy & Institutional Challenges for Growth Low skills and capacity Low market access Infrastructure Access to Rural Finance 5

Opportunities Institutional Opportunities n There is political will and commitment in the sector n Existence of decentralised structures n Land reform n EDPRS provides the opportunity to guide and review the targets Agro Climatic Opportunities n Availability of organic manure and travertine n Rwanda rich volcanic soils in north and acidic soils for quality tea. n Two agricultural seasons and an mostly a third one in the marshlands n Abundance of water resources n 165 000 Ha marshlands n Diversity of agroclimatic zones 6

PSTA 2005 -2008 PROGRAMS National Agricultural Policy (NAP/PNA) Strategic Plan for Agricultural Transformation (SPAT/PSTA) PROGRAMME 1: Intensification and development of sustainable production systems PROGRAMME 2: Support to the professionalization of farmers PROGRAMME 3: Promotion of commodity chains and development of agribusiness PROGRAMME 4: Institutional development 7
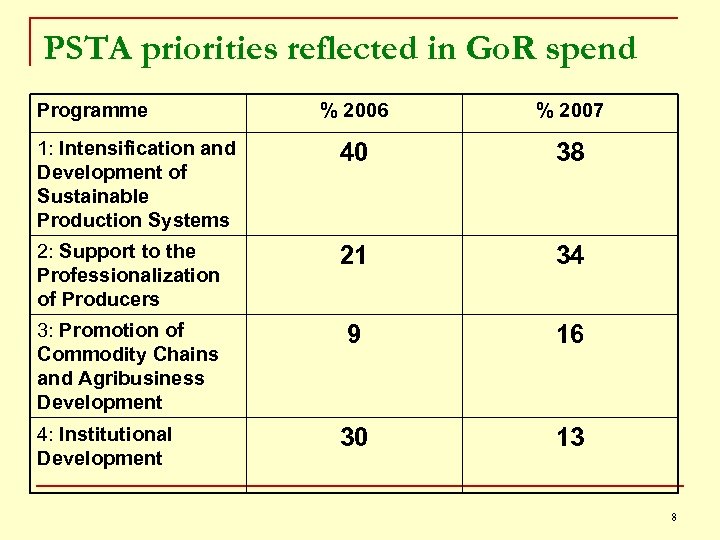
PSTA priorities reflected in Go. R spend Programme % 2006 % 2007 1: Intensification and Development of Sustainable Production Systems 40 38 2: Support to the Professionalization of Producers 21 34 3: Promotion of Commodity Chains and Agribusiness Development 9 16 30 13 4: Institutional Development 8

Actors in Agriculture Who is implementing our Priorities? n Decentralized implementation q n n The private sector, Cooperatives and NGOs MINAGRI Agencies q q n n Next year 40% of recurrent Ministry budget to districts for implementation RADA RARDA ISAR RHODA Other government Agencies and Ministries, i. e. OCIR-The and OCIR-Café; and Rwanda Bureau of Standards (RBS); MINITERE, REMA etc. Donors 9

Priorities 1. Soil Conservation of soil is the foundation of sustainable agricultural growth Ø EDPRS target: 30, 000 Ha Radical Terraces n Constructing radical and progressive terraces q q 13, 000 Ha completed Dec. 2006 Decentralized implementation 10

Priorities 2. Development of the Marshlands Increasing the land under cultivation relieves land pressure and increases productivity Ø EDPRS target: 26, 000 Ha by 2012 n Master Plan for the Marshlands q q q n 66, 000 Ha by 2016 2006 (11, 105 Ha) reclaimed as rice fields Environmental Impact Assessment Cash crops for Marshlands q q q Rice and Maize fields Private sector pilot rice project in Muvumba (2000 Ha) Increased mechanization 11

Priorities 3. Upland Irrigation Development Ø n Reducing the dependence on rainfall and increasing stability of yields EDPRS target: 10, 000 Ha upland irrigation by 2012 Irrigation master plan to be developed in 2007 q By 2006 approximately 200 Ha completed Upland: gravity, sprinklers and drip irrigation Community based initiatives q Rain water catchment q n 500 microdams, 8 small dams, 10 large dams Cost of irrigation in Rwanda 12

Priorities 4. Enhancing Animal Resources Livestock offers opportunities for rapid increase in income and economic growth. Ø EDPRS target outcomes q Improving quality of stock q Increased production of meat and dairy through cattle and small animals q Increase diversification of animal resource produce (e. g. fish, honey) q Disease control improved q Improved feed mainly through zero grazing 13

Support for Animal Resources Professionalisation, Veterinary services, Animal Health and Feeding n n Professionalisation q Agribusinesses, zero grazing, increasing competitiveness Veterinary Services q Client score card pilot q Training inseminators in cooperation with private sector Ø n Animal Health q Disease control Ø n EDPRS: Three trained inseminator in each sector by 2012 EDPRS: 80% of national herd immunised annually against major epidemic diseases. Improved Animal Feeding q Natural and industrial fodder Ø EDPRS- 2 Tns of improved forage seed disseminated every year 14

One Cow per poor Family ‘Girinka’ programme n n Goal: Poverty reduction and enhancing productivity q Economic benefits: dairy, meat and manure q Improving the social status of the poor Criteria for selection q < 0. 75 Ha of land (communal grazing possible) q No cows at present q Erosion control and fodder (20 Ares) q Community approval and appraisal n n n Ø Exemplary behaviour: ‘inyangamugayo’ Participation in community work: umuganda and gacaca Stakeholders: Farmers, districts, ADB, IFAD and other partners join please EDPRS target: 100% of 668. 763 households under the programme one cow one family by 2016 15

Priorities 5. Increasing use of Inputs Increase in utilization of inputs to increase production quantity and quality and improve food security Ø EDPRS target: Increase from average of 4 kg per Ha to 20 Kg per Ha by 2012 n Guidelines for national fertilizer strategy in use n Encouraging improved inputs q Ø n EDPRS Increase use of improved seeds from 10% to 30% by 2012. Extension Services: under development q q n Seed strategy with ISAR, RADA and private sector Building farmers organisations Increased decentralised funding Private sector involvement in distribution of inputs q Revolving fund with BNR 16

Priorities 6. Ensuring Food Security Ensuring food security in communities is a necessary condition for human development and any economic growth Ø EDPRS: At least halve the proportion of population below minimum food requirements Production, Access and Nutritional aspects n Calories: 2100 Kcal per day Ø q q n Proteins: 59 g per day, in which 10% should be from animals q q n Rwanda average intake is 83% for 2006 A Sources: banana, tubers, cereals Rwanda average intake is 72% for 2006 A Sources: leguminous, milk, meat, eggs, fish Lipids : 40 g per day q q Rwanda average intake is 30% for 2006 A Sources: plant oil, animal products 17

Priorities 7. Promotion of Exports Foreign earnings have positive macroeconomic impact as well as direct income impact on rural population. Ø Ø n EDPRS: (by 2012) 80% of exported tea is good leaf tea (By 2012) 80% fully washed coffee from 5% of total production in 2006 Traditional crops q q q n New export crops q q n In 2005 (28 Mln US$ from tea), 30. 000 employed In 2005 (38 Mln US$ from coffee), 400. 000 farmers 4. 7 mln US$ from hides and skins 2005 Horticulture (vegetables, fruits, flowers) Alternatives: Macadamia, Moringa, essential oils, sericulture Transformation into agri-businesses Ø EDPRS target: raise membership of farmers cooperatives by 50% 18

Supporting Priority Programmes n n n Capacity Building q To further increase absorptive capacity of the sector q Build capacity in Districts for planning, budgeting, delivery & M&E q Promoting Professionalisation and Transformation from subsistence towards commodity chain approach and agri-business Building extension services and research for development q Improved access to and quality of extension services q Increased range of stakeholders and partnerships for delivery q Client oriented research Capital investments and increasing access to credit q Rural infrastructure q Agricultural and Rural credit q Microfinance 19

Cross cutting issues n Environmental sustainability q q n Social Inclusion q n Youth and vulnerable groups targeted in extension Gender q n EIA guidelines Sustainable Agricultural Practices Skills, services and knowledge for women in Agriculture HIV/AIDS q Special programs to ensure food security and support health 20
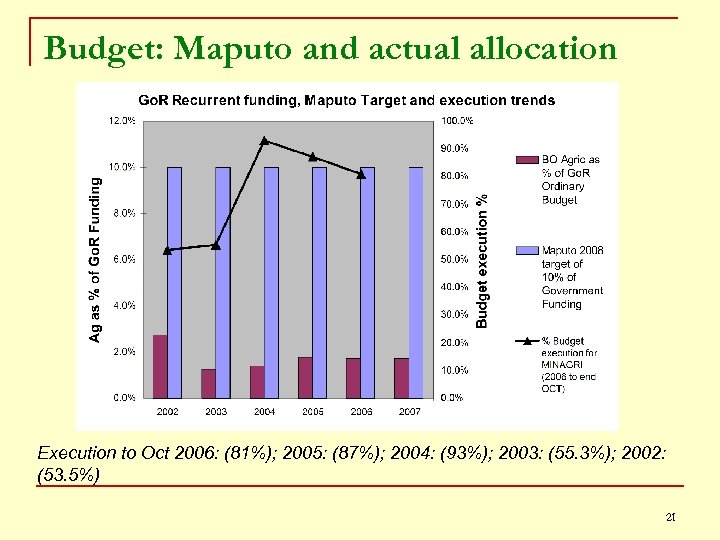
Budget: Maputo and actual allocation Execution to Oct 2006: (81%); 2005: (87%); 2004: (93%); 2003: (55. 3%); 2002: (53. 5%) 21

Outputs Vision 2020 and Long term Strategy q q q Agricultural sector grows 6% annually Population living on agriculture decreases from 90% to 50% Ha of Modern farms increases from 3% to 50% Agricultural production kcal/pers/day from 1612 kcal to international standard (2100 kcal) Availability of proteins g/pers/day increases from 35 to international standard 22

n Reaching our Growth Targets Conclusion Sector priorities EDPRS investments planned in LTIF to achieve Vision 2020 n Agriculture provides the foundation for sustained economic growth and poverty reduction in the medium term for Rwanda Murakoze Cyane 23
709fa8af7ac5594a5f2e616c5feef2ba.ppt