Lecture 4. Medieval philosophy.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 Medieval philosophy
Medieval philosophy
 The Middle Ages are a time period in history, which started around the year 476 CE when the Western Roman Empire ended, and continued until around the time Christopher Columbus discovered the New World in 1492.
The Middle Ages are a time period in history, which started around the year 476 CE when the Western Roman Empire ended, and continued until around the time Christopher Columbus discovered the New World in 1492.
 The “Middle Ages” are called this because it is the time between the fall of Imperial Rome and the beginning of the Early modern Europe.
The “Middle Ages” are called this because it is the time between the fall of Imperial Rome and the beginning of the Early modern Europe.
 This period of time in Europe is also known as the Medieval Age, the Dark Ages, or the Age of Faith (because of the rise of Christianity).
This period of time in Europe is also known as the Medieval Age, the Dark Ages, or the Age of Faith (because of the rise of Christianity).
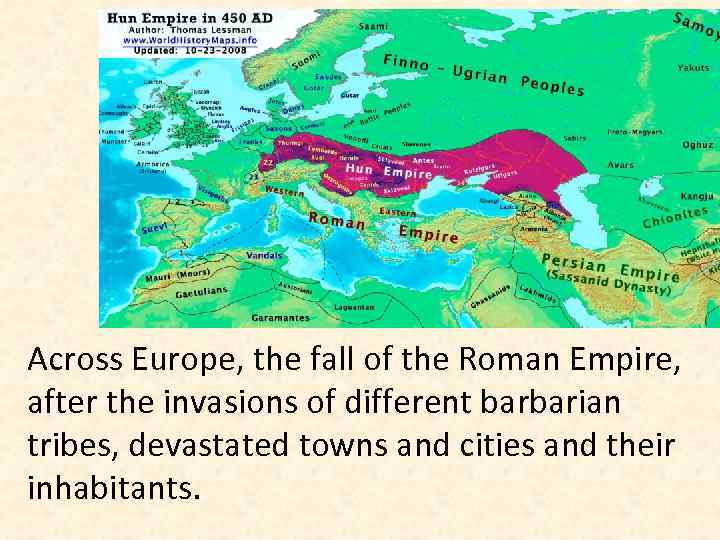 Across Europe, the fall of the Roman Empire, after the invasions of different barbarian tribes, devastated towns and cities and their inhabitants.
Across Europe, the fall of the Roman Empire, after the invasions of different barbarian tribes, devastated towns and cities and their inhabitants.
 Much of the knowledge that the Romans used (science, technology, medicine, and literature) was lost. The Dark Ages period was marked by mass migrations, wars and plagues (чума, эпидемии).
Much of the knowledge that the Romans used (science, technology, medicine, and literature) was lost. The Dark Ages period was marked by mass migrations, wars and plagues (чума, эпидемии).
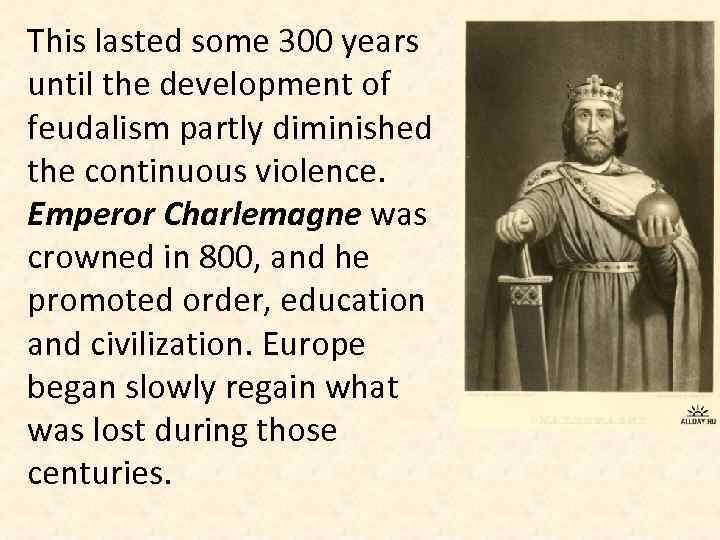 This lasted some 300 years until the development of feudalism partly diminished the continuous violence. Emperor Charlemagne was crowned in 800, and he promoted order, education and civilization. Europe began slowly regain what was lost during those centuries.
This lasted some 300 years until the development of feudalism partly diminished the continuous violence. Emperor Charlemagne was crowned in 800, and he promoted order, education and civilization. Europe began slowly regain what was lost during those centuries.
 Chronological framework of European medieval philosophy: • Beginning of the Middle Ages refer to the III centuries AD due to appearance of Christianity. • Completion of the Middle Ages is to the XIIXIII centuries AD. However, beginning of the Middle Ages is still controversial for historians of philosophy.
Chronological framework of European medieval philosophy: • Beginning of the Middle Ages refer to the III centuries AD due to appearance of Christianity. • Completion of the Middle Ages is to the XIIXIII centuries AD. However, beginning of the Middle Ages is still controversial for historians of philosophy.
 Philosophy of this period had two main sources of its formation. The first is the ancient Greek philosophy, especially in its Platonic and Aristotelian traditions.
Philosophy of this period had two main sources of its formation. The first is the ancient Greek philosophy, especially in its Platonic and Aristotelian traditions.
 The second source is the Holy Bible, turning this philosophy into the mainstream of Christianity (from the Greek word Christos – “Anointed One”, “Messiah”) originated as one of the sects within Judaism in I cent. A. D. in Palestine.
The second source is the Holy Bible, turning this philosophy into the mainstream of Christianity (from the Greek word Christos – “Anointed One”, “Messiah”) originated as one of the sects within Judaism in I cent. A. D. in Palestine.
 However, in a strict religious dictatorship, supported by state power, philosophy was declared as ancilla theologiae (“servant of theology”)
However, in a strict religious dictatorship, supported by state power, philosophy was declared as ancilla theologiae (“servant of theology”)
 Medieval European philosophy has developed five core principles: Ø theocentrism, Ø creationism, Ø providentialism, Ø personalism, Ø revelationizm.
Medieval European philosophy has developed five core principles: Ø theocentrism, Ø creationism, Ø providentialism, Ø personalism, Ø revelationizm.
 1. Theocentrism (Greek theos - God) – in the center of the universe is God. 2. Creationism is the idea that the world and mankind created by God.
1. Theocentrism (Greek theos - God) – in the center of the universe is God. 2. Creationism is the idea that the world and mankind created by God.
 3. Providentialism is the idea that destinies of the world and people are determined by God. 4. Revelationizm is a principle that there are two ways of revelation: Holy Bible and sacred tradition.
3. Providentialism is the idea that destinies of the world and people are determined by God. 4. Revelationizm is a principle that there are two ways of revelation: Holy Bible and sacred tradition.
 5. Personalism is the principle according to which human is created in image and similarity of God, but because of the Fall human has lost his likeness, retaining only the image of God.
5. Personalism is the principle according to which human is created in image and similarity of God, but because of the Fall human has lost his likeness, retaining only the image of God.
 The Medieval European philosophy is divided into three periods: 1. Apologetic period (II-III cc. ) 2. Patristic period (III-VII cc. ) 3. Scholasticism (VIII-XV cc. )
The Medieval European philosophy is divided into three periods: 1. Apologetic period (II-III cc. ) 2. Patristic period (III-VII cc. ) 3. Scholasticism (VIII-XV cc. )
 The first stage of the medieval Christian philosophy is apologetic (II-III cc. ).
The first stage of the medieval Christian philosophy is apologetic (II-III cc. ).
 Apologetic period, coming after the apostles, gives us a number of well-known Christian writers and thinkers (Justin the Philosopher, Tatian, Tertullian, and others).
Apologetic period, coming after the apostles, gives us a number of well-known Christian writers and thinkers (Justin the Philosopher, Tatian, Tertullian, and others).
 Justin Martyr (100 -165 AD) is known for his writings defending Christianity. He first gave Christianity the concepts of Greek philosophy and laid the foundation of theological interpretation of history.
Justin Martyr (100 -165 AD) is known for his writings defending Christianity. He first gave Christianity the concepts of Greek philosophy and laid the foundation of theological interpretation of history.
 “The First Apology”, Justin’s most well known text, passionately defends the morality of the Christian life. Further, he also makes theologicallyinnovative suggestion that the “seeds of Christianity” (manifestations of the Logos acting in history) actually predated Christ’s incarnation. This notion allows him to claim many historical Greek philosophers (including Socrates and Plato), in whose works he was well studied, as unknowing Christians.
“The First Apology”, Justin’s most well known text, passionately defends the morality of the Christian life. Further, he also makes theologicallyinnovative suggestion that the “seeds of Christianity” (manifestations of the Logos acting in history) actually predated Christ’s incarnation. This notion allows him to claim many historical Greek philosophers (including Socrates and Plato), in whose works he was well studied, as unknowing Christians.
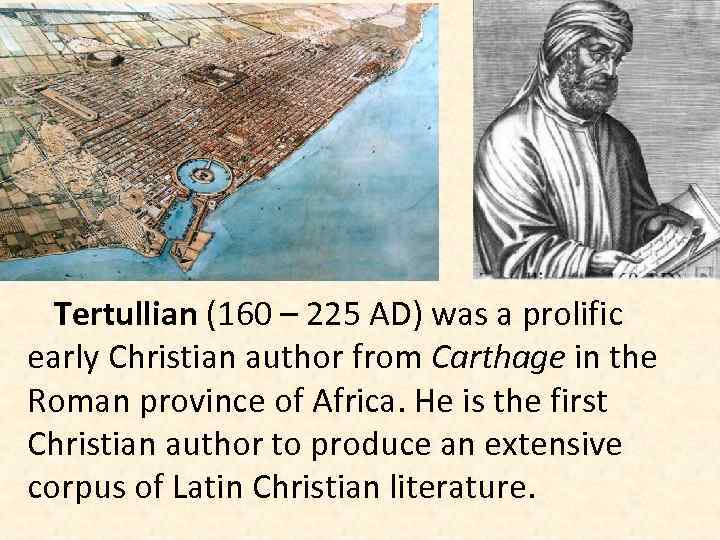 Tertullian (160 – 225 AD) was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He is the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of Latin Christian literature.
Tertullian (160 – 225 AD) was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He is the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of Latin Christian literature.
 Tertullian also was a notable early Christian apologist and a polemicist against heresy. Tertullian has been called “the father of Latin Christianity” and “the founder of Western theology”. He first expressed the concept of the Trinity. “I believe, because it is absurd” (Credo quia absurdum).
Tertullian also was a notable early Christian apologist and a polemicist against heresy. Tertullian has been called “the father of Latin Christianity” and “the founder of Western theology”. He first expressed the concept of the Trinity. “I believe, because it is absurd” (Credo quia absurdum).
 Patristics. At the heart of this theology was Alexandrian School (Clement of Alexandria, Origen etc).
Patristics. At the heart of this theology was Alexandrian School (Clement of Alexandria, Origen etc).
 Titus Flavius Clemens (150 – 215), known as Clement of Alexandria, was a Christian theologian who taught in Alexandria. He was an educated man who was familiar with classical Greek philosophy and literature. Clement was influenced by Hellenistic philosophy, in particular by Plato and the Stoics.
Titus Flavius Clemens (150 – 215), known as Clement of Alexandria, was a Christian theologian who taught in Alexandria. He was an educated man who was familiar with classical Greek philosophy and literature. Clement was influenced by Hellenistic philosophy, in particular by Plato and the Stoics.
 Three of Clement’s major works have survived in full, and they are collectively referred to as the trilogy: the Protrepticus (Exhortation) – проповедь к эллинам the Paedagogus (Tutor) – учитель the Stromata (Miscellanies) – сборник
Three of Clement’s major works have survived in full, and they are collectively referred to as the trilogy: the Protrepticus (Exhortation) – проповедь к эллинам the Paedagogus (Tutor) – учитель the Stromata (Miscellanies) – сборник
 Origenes Adamantius (184/185 – 253/254) was an early Christian theologian who was born and spent the first half of his career in Alexandria. He was a writer in multiple branches of theology, including textual criticism, hermeneutics, philosophical theology, preaching, and spirituality.
Origenes Adamantius (184/185 – 253/254) was an early Christian theologian who was born and spent the first half of his career in Alexandria. He was a writer in multiple branches of theology, including textual criticism, hermeneutics, philosophical theology, preaching, and spirituality.
 Origenes Adamantius was a founder of biblical philology. Created the term “God-man”. God is Providence in action. In his doctrine, apocatastasis means reconstitution (воспроизведение) to the primordial (к изначальному) condition (universal salvationспасение)
Origenes Adamantius was a founder of biblical philology. Created the term “God-man”. God is Providence in action. In his doctrine, apocatastasis means reconstitution (воспроизведение) to the primordial (к изначальному) condition (universal salvationспасение)
 Aurelius Augustinus – Saint Austin (354 -430). Writing during the Patristic Era, he is viewed as one of the most important Church Fathers. Among his most important works are City of God and Confessions, which continue to be read widely today. The ancestor of the Christian philosophy of history.
Aurelius Augustinus – Saint Austin (354 -430). Writing during the Patristic Era, he is viewed as one of the most important Church Fathers. Among his most important works are City of God and Confessions, which continue to be read widely today. The ancestor of the Christian philosophy of history.
 “the City of God” can be divided into two parts. Part I (books 1 -10) is devoted to a critique of Roman cultures and of pagan philosophy. Interpreters often take these first ten books to correspond with the Earthly City, in contrast to the City of God. Part II (books 11 -22) is where Augustine shifts from criticism to positing the relationship between the City of God an Earthly City subordinated to it.
“the City of God” can be divided into two parts. Part I (books 1 -10) is devoted to a critique of Roman cultures and of pagan philosophy. Interpreters often take these first ten books to correspond with the Earthly City, in contrast to the City of God. Part II (books 11 -22) is where Augustine shifts from criticism to positing the relationship between the City of God an Earthly City subordinated to it.
 “The Confessions” of St. Augustine outlines Augustine's sinful youth and his conversion to Christianity. It is widely seen as the first Western autobiography ever written. God created matter and endowed (наделить) it with different shapes. Evil is the deficiency (недостаток) of good.
“The Confessions” of St. Augustine outlines Augustine's sinful youth and his conversion to Christianity. It is widely seen as the first Western autobiography ever written. God created matter and endowed (наделить) it with different shapes. Evil is the deficiency (недостаток) of good.
 Scholasticism is a systematic medieval philosophy, centered around universities and is a synthesis of Catholic theology and Aristotelian logic.
Scholasticism is a systematic medieval philosophy, centered around universities and is a synthesis of Catholic theology and Aristotelian logic.
 The third period Scholasticism is characterized by two trends: the realists and nominalists. According to realism only general concepts, or universals, have true reality (Guillaume de Champeaux). According to nominalism, common concepts are only the names (Johannes Roscelin, Anselm of Canterbury, William of Ockham etc. )
The third period Scholasticism is characterized by two trends: the realists and nominalists. According to realism only general concepts, or universals, have true reality (Guillaume de Champeaux). According to nominalism, common concepts are only the names (Johannes Roscelin, Anselm of Canterbury, William of Ockham etc. )
 Thomas Aquinas (12251274) Doctor Angelicus, Doctor Universalis was an Italian Dominican priest and the most influential philosopher and theologian in the tradition of scholasticism.
Thomas Aquinas (12251274) Doctor Angelicus, Doctor Universalis was an Italian Dominican priest and the most influential philosopher and theologian in the tradition of scholasticism.
 Thomas Aquinas linked Christian faith with the philosophy of Aristotle. Unlike many currents in the Church of the time, Thomas attempted to combine Aristotelian philosophy with the principles of Christianity. The works for which he is best known are the ”Summa Theologica” and the ”Summa contra Gentiles”. His commentaries on Aristotle are an important part of his work.
Thomas Aquinas linked Christian faith with the philosophy of Aristotle. Unlike many currents in the Church of the time, Thomas attempted to combine Aristotelian philosophy with the principles of Christianity. The works for which he is best known are the ”Summa Theologica” and the ”Summa contra Gentiles”. His commentaries on Aristotle are an important part of his work.
 Thomas Aquinas considered that Nature ends in grace, intelligence ends in faith, philosophical knowledge and natural theology end in a supernatural revelation.
Thomas Aquinas considered that Nature ends in grace, intelligence ends in faith, philosophical knowledge and natural theology end in a supernatural revelation.
 Five proofs of God’s existence: • Proof through motion • Proof through producing cause • Proof through necessity • Proof through degrees of being and perfection • Proof through a target cause.
Five proofs of God’s existence: • Proof through motion • Proof through producing cause • Proof through necessity • Proof through degrees of being and perfection • Proof through a target cause.
 Arab-Muslim philosophy
Arab-Muslim philosophy
 http: //simple. wikipedia. org/wiki/Middle_Ages#Islam_and_its _Golden_Age, http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Early_Muslim_philosophy The main question during the development of Islamic dogma, was the question of monotheism (tawhid). The idea of monism, the unity of existence and uniqueness of the universe has become a central theme of philosophy.
http: //simple. wikipedia. org/wiki/Middle_Ages#Islam_and_its _Golden_Age, http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Early_Muslim_philosophy The main question during the development of Islamic dogma, was the question of monotheism (tawhid). The idea of monism, the unity of existence and uniqueness of the universe has become a central theme of philosophy.
 As a philosophical problem unity of being was discussed in two plans: the mystical vision and rationalistic justification.
As a philosophical problem unity of being was discussed in two plans: the mystical vision and rationalistic justification.
 Rationalism of Islamic philosophy was expressed in the development of special teaching – Kalam. Adherents of kalam were Mutakallims.
Rationalism of Islamic philosophy was expressed in the development of special teaching – Kalam. Adherents of kalam were Mutakallims.
 Among them there were two basic directions: Ascharites (followers Ashari’s theology) and Mu'tazila. First group developed conceptions of unity being proposed by Mutasillits (isolated): religious rationalists-philosophers.
Among them there were two basic directions: Ascharites (followers Ashari’s theology) and Mu'tazila. First group developed conceptions of unity being proposed by Mutasillits (isolated): religious rationalists-philosophers.
 Mutasillits shared attributes of God to “attributes of the self” (Ift az-zat) and “attributes of action” (Ift al-fi’l)
Mutasillits shared attributes of God to “attributes of the self” (Ift az-zat) and “attributes of action” (Ift al-fi’l)
 Asharizm, which became the main school of Kalam in X cent. , is solution “theological” questions as “middle ground” between the position of Mu'tazila and the doctrine of the traditionalists (the Salafittes), proponents of free will and predestination (предопределения) supporters.
Asharizm, which became the main school of Kalam in X cent. , is solution “theological” questions as “middle ground” between the position of Mu'tazila and the doctrine of the traditionalists (the Salafittes), proponents of free will and predestination (предопределения) supporters.
 Falsafa (Eastern peripatetism) is a direction of secular philosophy in classical Islam, which develops the ancient model of philosophizing, mainly of Aristotle.
Falsafa (Eastern peripatetism) is a direction of secular philosophy in classical Islam, which develops the ancient model of philosophizing, mainly of Aristotle.
 Al-Kindi (801 -873), (philosopher of Arabs) has formulated the main questions: § the rational-allegorical interpretation of the “sacred texts” § identification of God with the primordial cause
Al-Kindi (801 -873), (philosopher of Arabs) has formulated the main questions: § the rational-allegorical interpretation of the “sacred texts” § identification of God with the primordial cause
 § the interpretation of creation as granting the existence of things with a kind of causal relationships § a process of emanation (the origin of the Universe through emergence beyond first principles);
§ the interpretation of creation as granting the existence of things with a kind of causal relationships § a process of emanation (the origin of the Universe through emergence beyond first principles);
 Abu Nasr al-Farabi (873 -950) Philosophy and religion arise after people mastered the “practical arts” and seek to understand the causes of surrounding things.
Abu Nasr al-Farabi (873 -950) Philosophy and religion arise after people mastered the “practical arts” and seek to understand the causes of surrounding things.
 People are attached to the truths by two ways: by using apodictic judgments and through the dialectical, rhetorical or poetic expressions.
People are attached to the truths by two ways: by using apodictic judgments and through the dialectical, rhetorical or poetic expressions.
 The need for religion related to the needs in Political Science and Law. Ideally, people should managed by philosophers, who give the truth to “the public” through “true religion” in images and allegorical discourses. (“Treatise on the views of the virtuous city residents”)
The need for religion related to the needs in Political Science and Law. Ideally, people should managed by philosophers, who give the truth to “the public” through “true religion” in images and allegorical discourses. (“Treatise on the views of the virtuous city residents”)
 Ibn Sina (Avicenna) (980 -1037) - Central Asian philosopher and physician, a representative of the eastern Aristotelianism.
Ibn Sina (Avicenna) (980 -1037) - Central Asian philosopher and physician, a representative of the eastern Aristotelianism.
 Ibn Sina proved co-eternity of the world with the Creator. Creation in eternity Ibn Sina explained by Neoplatonic concept of emanation, thus justifying the logical progression from the initial substance to the plurality of the created world.
Ibn Sina proved co-eternity of the world with the Creator. Creation in eternity Ibn Sina explained by Neoplatonic concept of emanation, thus justifying the logical progression from the initial substance to the plurality of the created world.
 According to him, absolute truth can be comprehended by intuitive vision which presents the culmination of the thinking process. Works: § The Canon of Medicine § About predestination etc.
According to him, absolute truth can be comprehended by intuitive vision which presents the culmination of the thinking process. Works: § The Canon of Medicine § About predestination etc.
 Ibn Bājjah (Avempace) (10701138) is the first major representative of the eastern peripatetism in Muslim Spain. • In his “Farewell (прощальный) message” Ibn Bājjah considers the questions of first ‘engi[i]ne, a human goal, connection of person with an active mind.
Ibn Bājjah (Avempace) (10701138) is the first major representative of the eastern peripatetism in Muslim Spain. • In his “Farewell (прощальный) message” Ibn Bājjah considers the questions of first ‘engi[i]ne, a human goal, connection of person with an active mind.
 Ibn Rushd (Averroes) (1126 -1198) – Western-Arab philosopher.
Ibn Rushd (Averroes) (1126 -1198) – Western-Arab philosopher.
 • Developed the doctrine of dual truth. • The first substance is identical to world order • Genesis of things based on their unity, relationships.
• Developed the doctrine of dual truth. • The first substance is identical to world order • Genesis of things based on their unity, relationships.
 Ibn Khaldun (1332 -1406). He almost did not interested in classical problems of cosmology and philosophy. His areas of interest was history.
Ibn Khaldun (1332 -1406). He almost did not interested in classical problems of cosmology and philosophy. His areas of interest was history.
 He has created a theory of social development from the lowest level (barbarism) to the highest (civilization), through the development of productive activities of people, explaining the development of social life through the development of production.
He has created a theory of social development from the lowest level (barbarism) to the highest (civilization), through the development of productive activities of people, explaining the development of social life through the development of production.
 A mystical form of Islam expressed in such a direction as Sufism. Fundamentals of Sufism incorporated in the 9 th century by Egyptian al-Misri and a resident of Baghdad al-Muhasibi.
A mystical form of Islam expressed in such a direction as Sufism. Fundamentals of Sufism incorporated in the 9 th century by Egyptian al-Misri and a resident of Baghdad al-Muhasibi.
 • However, Sufism has been developed in the esoteric concepts of al-Hallaj (I am truth) and al-Ghazali (Sufism is the essence of Islam. )
• However, Sufism has been developed in the esoteric concepts of al-Hallaj (I am truth) and al-Ghazali (Sufism is the essence of Islam. )


