fe75a1f37784af6e43cc0fd022b5b7dc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84

Medication Data from Nationally Representative Provider- and Population-Based Surveys Lisa L. Dwyer, MPH Saeid Raofi, MS Pharmacy Karen A. Lees, MPH Ryne Paulose, Ph. D National Center for Health Statistics 2006 Data Users Conference (Session #50) Washington, D. C. July 12, 2006

Background § NCHS is the Nation’s principal health statistics agency • compile statistical information to guide actions and policies to improve the health of our people • provide public use files of survey data to the public û Congress û researchers û health planners 2

Background § Our health statistics allow us to: • document the health status of the population • monitor trends in health status and health care delivery • support biomedical and health services research • provide information to guide and evaluate health policy decisions and programs 3

4

5

Background § NCHS surveys that have collected medication data: • National Health Care Survey (NHCS) û û National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NHAMCS) û National Nursing Home Survey (NNHS) û • National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS) National Hospital Discharge Survey (NHDS) National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 6

Background § National Health Care Survey • • § family of mostly provider-based surveys collects information about health care facilities, their services, and their patients National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey • population-based survey • consists of a household interview, medical/dental examinations, and lab tests 7

Objectives § To describe how the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) collects medication data across its surveys § To describe how our data can be used to generate national estimates § To discuss the future direction of NCHS surveys 8

Prescription Medications § Drugs and their associated costs are at the forefront of national health care debates. § According to figures reported by CMS, prescription drug expenditures increased at a much faster rate than the total health care expenditure for most of 19952004. § Access to and affordability of drugs for the elderly were major drivers behind the Medicare Part D Drug Benefit implementation. 9
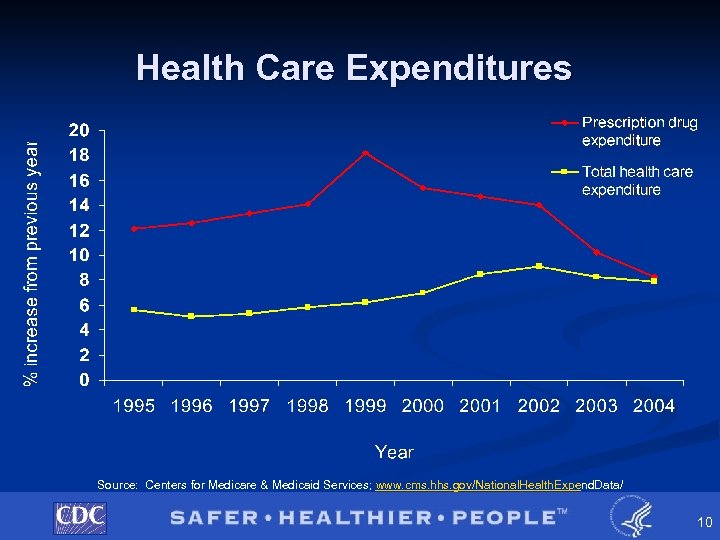
Health Care Expenditures Source: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services; www. cms. hhs. gov/National. Health. Expend. Data/ 10

Drug Utilization § This increase in cost is driven, in part, by an increase in utilization. § The national ambulatory health care surveys show that the number of drugs mentioned per visit increased between the 10 -year period, 1993/1994 and 2003/2004. § Previous study reports that medication use is highest among the institutionalized elderly. This population continues to increase. 11
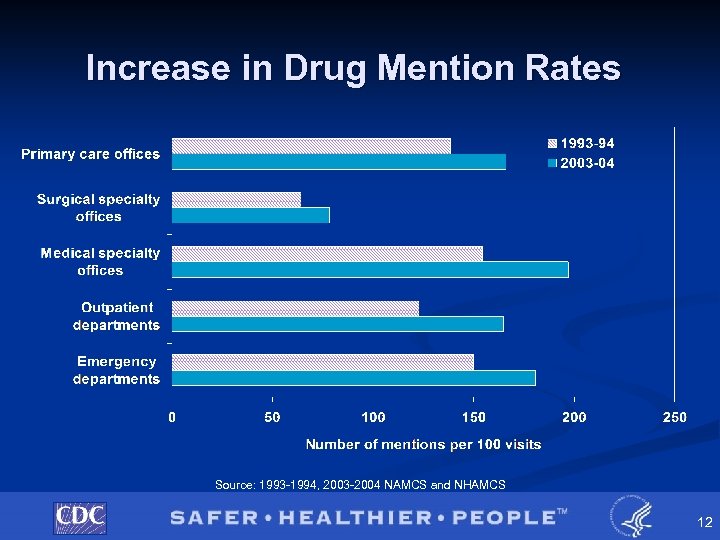
Increase in Drug Mention Rates Source: 1993 -1994, 2003 -2004 NAMCS and NHAMCS 12

Collection and Processing of Drug Information in National Ambulatory Medical Care and National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Surveys

Drug Data Collection in National Health Care Surveys § I will focus on the National Ambulatory Health Care surveys, NAMCS and NHAMCS, which have collected drug data the longest. § The system developed for the processing and coding of the collected drug data for NAMCS and NHAMCS will be used for processing of the data in other surveys as well. § I will also give a detailed description of this processing and coding system. 14
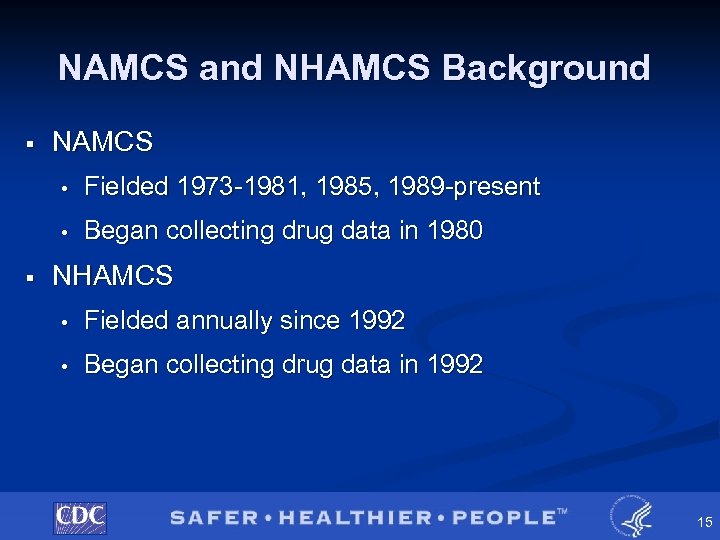
NAMCS and NHAMCS Background § NAMCS • • § Fielded 1973 -1981, 1985, 1989 -present Began collecting drug data in 1980 NHAMCS • Fielded annually since 1992 • Began collecting drug data in 1992 15

Items Collected § Patient characteristics • § Visit characteristics • § Age, sex, race, ethnicity Source of payment, continuity of care, reason for visit, diagnosis, treatment, medications ordered or provided Provider characteristics • Physician specialty, hospital ownership 16

NCHS Common Methodology § National probability sample surveys § Complex sample designs § Common definitions, data items, sampling frames § Medical diagnoses coded to ICD-9 -CM § High response rates § Data processed by private contractor 17
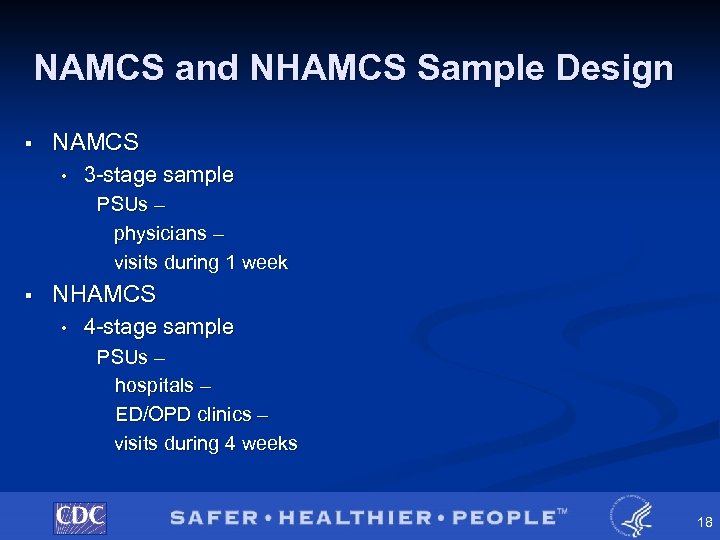
NAMCS and NHAMCS Sample Design § NAMCS • 3 -stage sample PSUs – physicians – visits during 1 week § NHAMCS • 4 -stage sample PSUs – hospitals – ED/OPD clinics – visits during 4 weeks 18

Generating National Estimates from Samples § Statistics from the NAMCS and NHAMCS are derived by a multistage estimation procedures that produce essentially unbiased national estimates. § The basic components of estimation are: • Inflation by reciprocals of the sampling selection probabilities • Adjustment for nonresponse • Weight smoothing • A calibration ratio adjustment 19

Sample Weight § The estimation procedure produces a single weight, called Patient Visit weight, for each NAMCS, OPD, and ED record. § This weight is used for both visits and drug mentions. § Weight must be applied or estimates of totals, percents and effects will be incorrect. 20

Definition of Drug Mentions A drug mention is the provider’s entry of drugs (prescription or over the counter), immunizations, allergy shots, anesthetics, chemotherapy, and dietary supplements that were ordered, supplied administered or continued during the visit. 21

Drug Data Processing § Since 2003, the provider can list up to eight drug mentions on the survey form. From 1995 to 2002 the provider could enter up to six drug mentions and before then up to five mentions. § Each drug mention will be associated with a drug code at data entry stage. § Drugs not in the database will be assigned a new unique code. 22

Adding Drug Characteristics § Upon completion of visit files, the following drug characteristics are added to visit files for each drug mention • Generic name • Therapeutic class • Ingredients • Composition • Control status • Rx or OTC 23
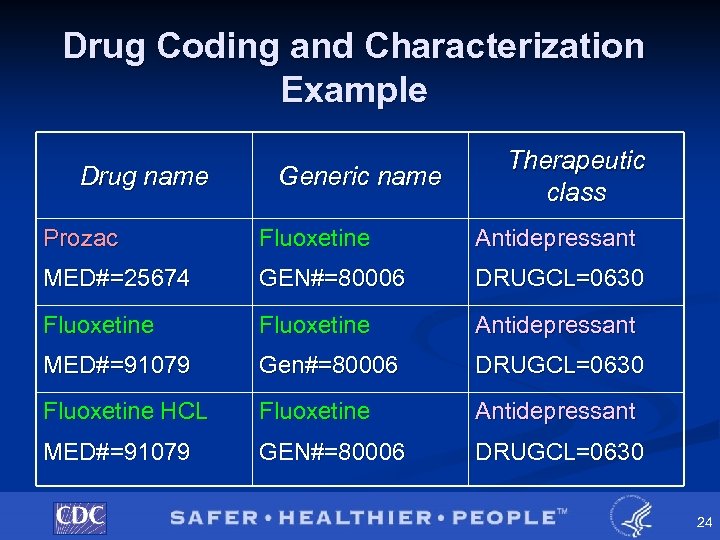
Drug Coding and Characterization Example Drug name Generic name Therapeutic class Prozac Fluoxetine Antidepressant MED#=25674 GEN#=80006 DRUGCL=0630 Fluoxetine Antidepressant MED#=91079 Gen#=80006 DRUGCL=0630 Fluoxetine HCL Fluoxetine Antidepressant MED#=91079 GEN#=80006 DRUGCL=0630 24

Utility of Drug Characteristics § Drug characteristics can be used to create summary reports based on therapeutic class, active ingredients, etc. § They can be used in combination with patient and visit characteristics to study pharmacotherapy in specific disease areas. § They can be used in combination with physician characteristics in studies looking at prescribing behavior. 25
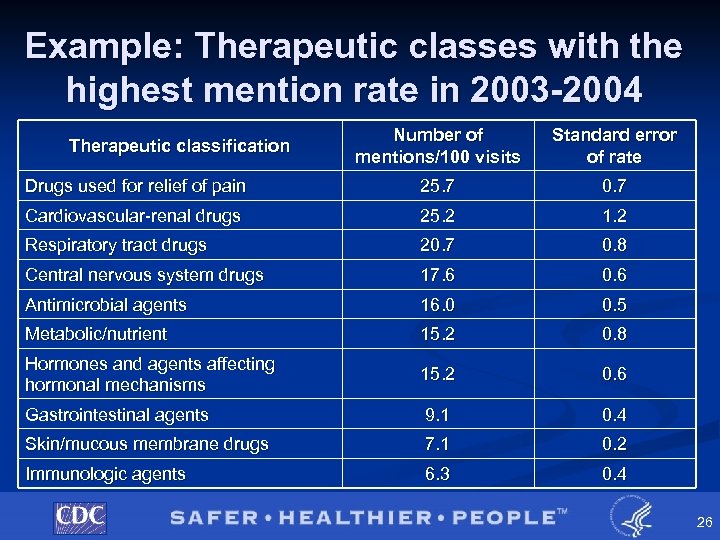
Example: Therapeutic classes with the highest mention rate in 2003 -2004 Number of mentions/100 visits Standard error of rate Drugs used for relief of pain 25. 7 0. 7 Cardiovascular-renal drugs 25. 2 1. 2 Respiratory tract drugs 20. 7 0. 8 Central nervous system drugs 17. 6 0. 6 Antimicrobial agents 16. 0 0. 5 Metabolic/nutrient 15. 2 0. 8 Hormones and agents affecting hormonal mechanisms 15. 2 0. 6 Gastrointestinal agents 9. 1 0. 4 Skin/mucous membrane drugs 7. 1 0. 2 Immunologic agents 6. 3 0. 4 Therapeutic classification 26
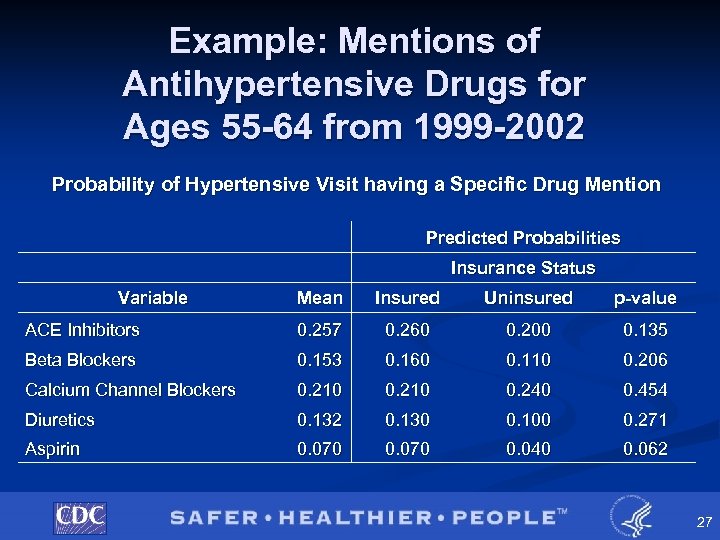
Example: Mentions of Antihypertensive Drugs for Ages 55 -64 from 1999 -2002 Probability of Hypertensive Visit having a Specific Drug Mention Predicted Probabilities Insurance Status Variable Mean Insured Uninsured p-value ACE Inhibitors 0. 257 0. 260 0. 200 0. 135 Beta Blockers 0. 153 0. 160 0. 110 0. 206 Calcium Channel Blockers 0. 210 0. 240 0. 454 Diuretics 0. 132 0. 130 0. 100 0. 271 Aspirin 0. 070 0. 040 0. 062 27

Therapeutic Classification System Through 2004 § Since 1985, the FDA’s NDC therapeutic classification has been used § Limitations of this system: • Only has one level of sub-classification • FDA has discontinued this product 28

Adoption of Multum Lexicon as the Therapeutic Classification System § Starting with 2005 data, Multum therapeutic classification system will be used for classifying NAMCS and NHAMCS drug data. § This system has two level of sub-classification. § It is regularly updated. 29

Example: Classification of Paroxetine by the two classification systems § NDC system • 0600 central nervous system û § 0630 antidepressants Multum Lexicon system • 242 psychotherapeutic agents û 249 antidepressants û 208 SSRI antidepressants 30

Using NAMCS/NHAMCS public use files for analyzing drug data
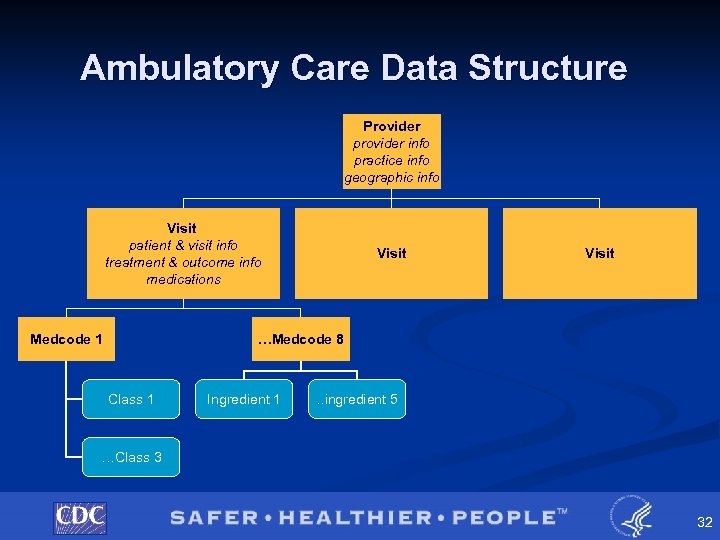
Ambulatory Care Data Structure Provider provider info practice info geographic info Visit patient & visit info treatment & outcome info medications Medcode 1 Visit …Medcode 8 Class 1 Ingredient 1 . . ingredient 5 …Class 3 32

File Structure § Flat ASCII files for each setting and year § Use file layout to read the data § Input and format code available for: • • STATA • § SAS SPSS Can use SETS (but no sampling variance estimates) 33
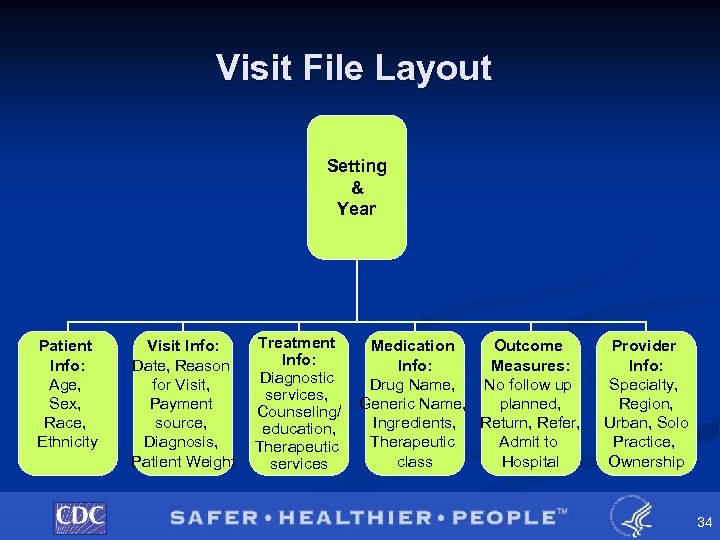
Visit File Layout Setting & Year Patient Info: Age, Sex, Race, Ethnicity Visit Info: Date, Reason for Visit, Payment source, Diagnosis, Patient Weight Treatment Info: Diagnostic services, Counseling/ education, Therapeutic services Medication Outcome Info: Measures: Drug Name, No follow up Generic Name, planned, Ingredients, Return, Refer, Therapeutic Admit to class Hospital Provider Info: Specialty, Region, Urban, Solo Practice, Ownership 34

Ambulatory Health Care Data http: //www. cdc. gov/nchs/about/major/ahcd 1. htm 35
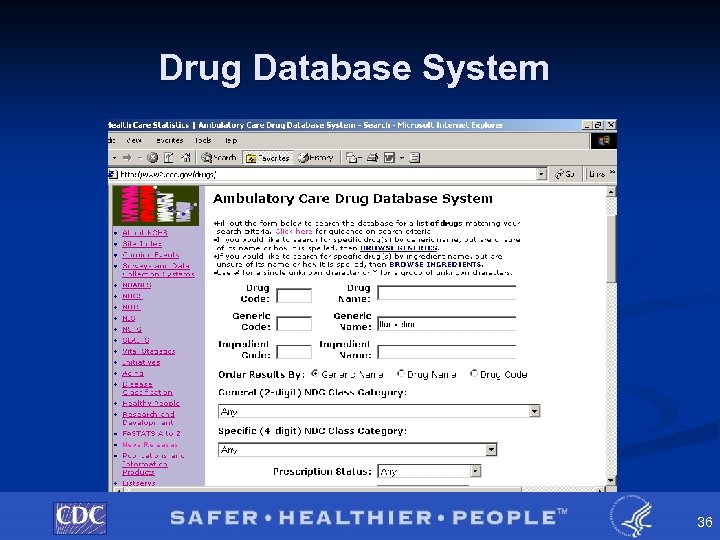
Drug Database System 36

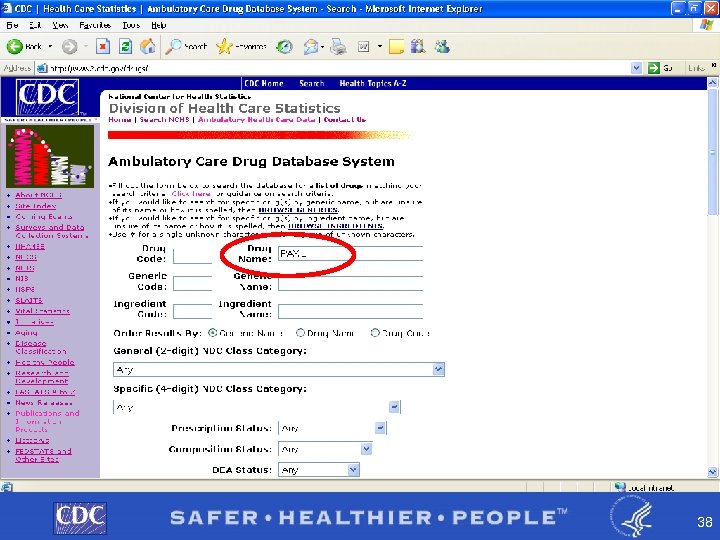
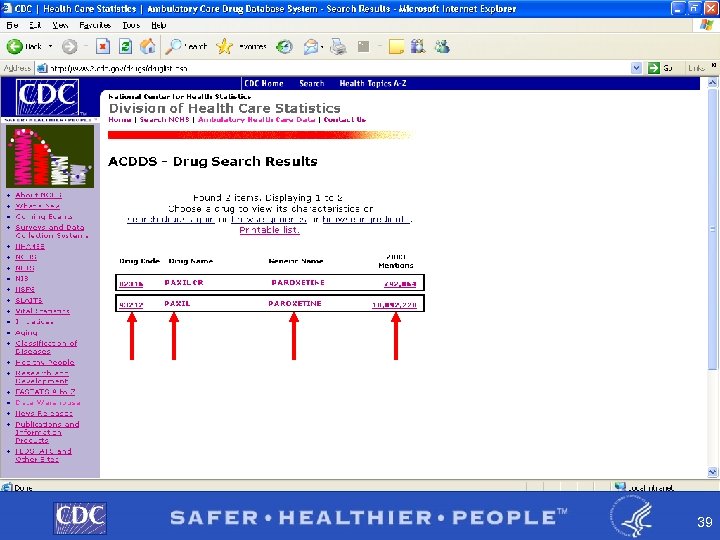
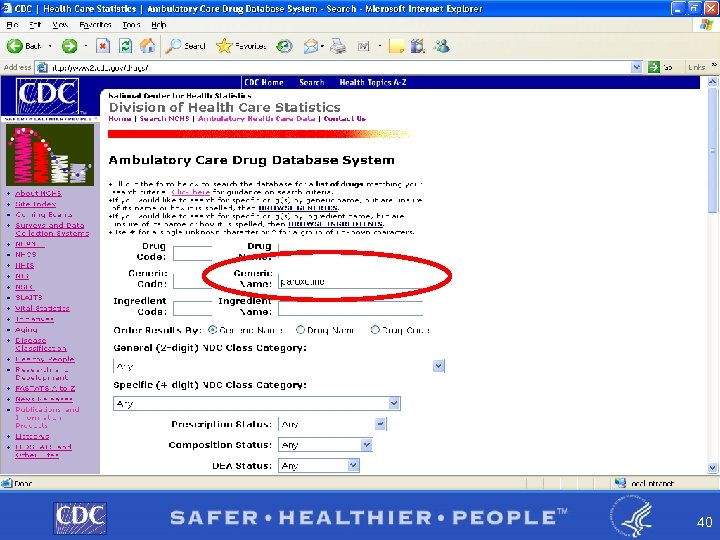
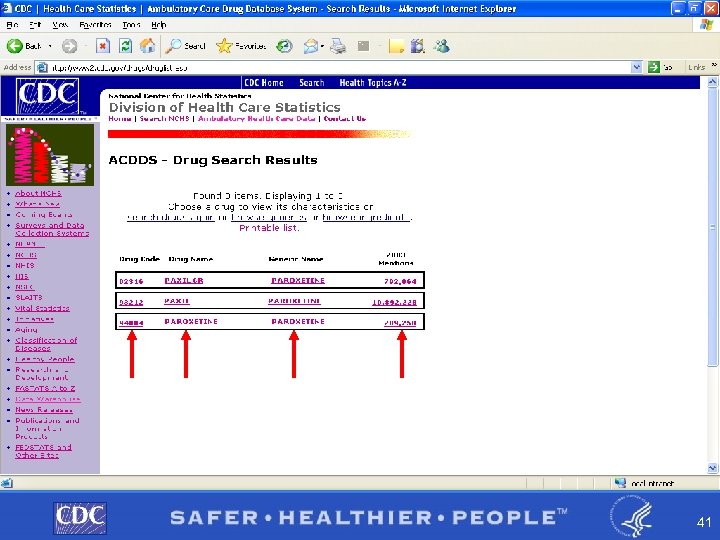
Example of Drug Lookup Function § By brand name PAXIL § BY GENERIC NAME PAROXETINE http: //www 2. cdc. gov/drugs/ 37
38
39
40
41

For more information on the NAMCS and NHAMCS, please visit http: //www. cdc. gov/nchs/about/major/ahcd 1. htm 42

Medication Data Collected in the 2004 National Nursing Home Survey

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Nationally representative sample survey of U. S. nursing homes û û staff û § services/programs residents Conducted periodically since 1973 -74 û 1977, 1985, 1997, 1999, 2004 44

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Taken out of the field after the 1999 survey for a major redesign. § Put back into the field in 2004 • computerized data collection • many new content items, including collection of medication data • supplemental survey on nursing assistants, NNAS 45

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Two-stage probability survey design • nursing home facility • residents (up to 12 current residents) 46

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Sampling frame • Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Provider of Services file of U. S. nursing homes • state licensing lists compiled by private organization • total of 16, 628 nursing homes in frame 47

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Eligibility criteria • licensed by State as a nursing facility • certified and non-certified facilities • three or more beds 48

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Survey items • medications taken 24 hrs before facility interview û standing û up • to 25 medications taken regularly but not 24 hrs before facility interview û up • or routine medications, or PRNs to 25 medications reason medications were prescribed 49

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Medication data • found in medication administration records û did not collect dosage, frequency, route • collected during in-person interview at facility • entered into CAPI system by interviewer • processed like NAMCS/NHAMCS data 50

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Medication data collected • prescription and nonprescription medications • generics • supplements û vitamin/mineral, herbal, nutritional 51

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Drug characteristics appended • generic name • ingredients • therapeutic classes • composition status • prescription status • DEA status 52

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Data collected in 2004 NNHS are organized into three independent files: • Facility • Resident • Prescribed medication 53

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § Resident File • age • sex • race • • marital status admission diagnosis current primary and secondary diagnoses services/treatments received § Facility File • bed size • ownership • services • per diem rates • special programs • staffing activities of daily living (ADLs) vaccination status expected source(s) of payment 54

2004 National Nursing Home Survey § The Prescribed Medications (PM) file includes: • medication codes • ICD-9 codes • drug characteristics 55

2004 National Nursing Home Survey Link data files using a randomly assigned ID # PM Data File (164, 000 KB) + Resident Data File = Analytic File (13, 000 KB) Warning: Great analytic potential but very large file with over 13, 000 records and over 1000 variables per record. 56
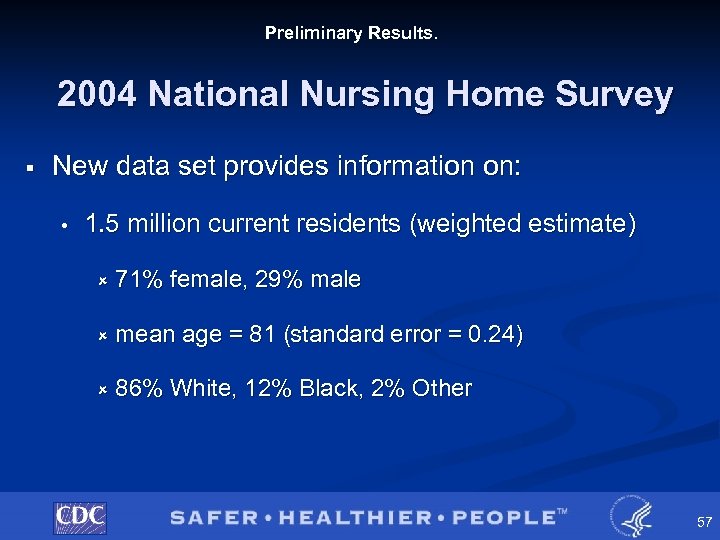
Preliminary Results. 2004 National Nursing Home Survey § New data set provides information on: • 1. 5 million current residents (weighted estimate) û 71% female, 29% male û mean age = 81 (standard error = 0. 24) û 86% White, 12% Black, 2% Other 57

2004 National Nursing Home Survey Resources available to data users: § Tab delimited ASCII file of PM data § Long-term Care Drug Database § Data dictionary document § User’s manual § SAS, SPSS, and STATA input statements 58

2004 National Nursing Home Survey Things to consider when analyzing NNHS data: • complex sample survey design û • multiple stages of selection sampling weights are required û û • point estimate standard error statistical software that takes the sample design into account 59

2004 National Nursing Home Survey Guidelines for Reporting Estimates § Check sample size and standard error. § Calculate the relative standard error (RSE). If sample size < 30, then the value of the estimate should not be reported. If sample size is 30 59, or greater than 59 and the RSE 30%, then the estimate can be reported but should not be considered reliable. If sample size 60 and the RSE < 30, then the estimate is considered reliable. 60

Preliminary Results. 2004 National Nursing Home Survey Example: Mean number of medications per resident Total population: Mean = 8. 73, SE Mean = 0. 07 Male population: Mean = 8. 52, SE Mean = 0. 11 Female population: Mean = 8. 81, SE Mean = 0. 07 61

Preliminary Results. 2004 National Nursing Home Survey RSE = (S. E. of point estimate/point estimate) * 100 RSE for Total population = (0. 07/8. 73) * 100 = 0. 80 RSE for Male population = (0. 11/8. 52) * 100 = 1. 29 RSE for Female population = (0. 07/8. 81) * 100 = 0. 79 62

2004 National Nursing Home Survey Other examples of how data can be used: § to analyze how medications are used and if used for offlabel indications § to examine the differences in medication use among subpopulations § to explore which medications were taken by residents receiving hospice/palliative/end-of-life care § to determine the top therapeutic classes taken by nursing home residents 63
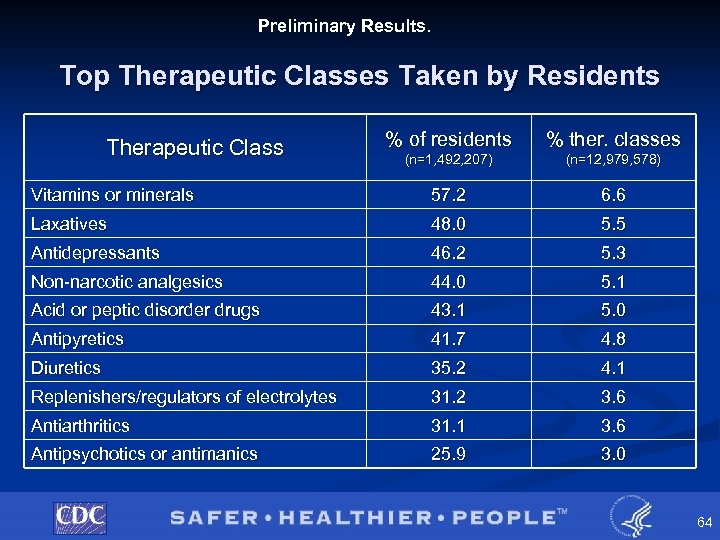
Preliminary Results. Top Therapeutic Classes Taken by Residents % of residents % ther. classes (n=1, 492, 207) (n=12, 979, 578) Vitamins or minerals 57. 2 6. 6 Laxatives 48. 0 5. 5 Antidepressants 46. 2 5. 3 Non-narcotic analgesics 44. 0 5. 1 Acid or peptic disorder drugs 43. 1 5. 0 Antipyretics 41. 7 4. 8 Diuretics 35. 2 4. 1 Replenishers/regulators of electrolytes 31. 2 3. 6 Antiarthritics 31. 1 3. 6 Antipsychotics or antimanics 25. 9 3. 0 Therapeutic Class 64

For more information on the NNHS, please visit http: //www. cdc. gov/nchs/nnhs. htm 65

Collecting Medication Data in the National Hospital Discharge Survey: Results from a Pilot Study

National Hospital Discharge Survey § Conducted annually since 1965 § Produces nationally representative data on characteristics of patients discharged from Non. Federal, short-stay hospitals 67

National Hospital Discharge Survey § National probability sample: • § Short-stay, non-Federal hospitals Three stage design: • Geographic units (PSUs) • Hospitals • Discharges 68

National Hospital Discharge Survey § Hospitals included: • • Children’s general hospitals • § General hospitals Hospitals with an average length of stay of less than 30 days Hospitals excluded: • Federal hospitals • Military and VA hospitals • Hospitals in institutions (such as prisons) • Hospitals with fewer than 6 beds 69

National Hospital Discharge Survey § Sample Size • • § Approximately 500 hospitals sampled per year Over 300, 000 discharges sampled per year Data Collection • 55% manual • 45% automated û States, commercial firms, individual hospitals 70
National Hospital Discharge Survey § Data are abstracted from the patient’s medical record § Data are edited and weighted to produce national estimates 71

National Hospital Discharge Survey § Patient Data § Hospital Data • Age • Bed size • Sex • Ownership • Race • Geographic region • Expected source of payment • Admission source and type • Discharge status 72

National Hospital Discharge Survey § Medical Data • • § Diagnoses – principal and up to six secondary Surgical, diagnostic, or therapeutic procedures – up to four Coded according to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9 -CM) 73

National Hospital Discharge Survey § Weight: • Inverse of the probability of selection • Adjustments for non-response • Population weighting ratio adjustment 74

National Hospital Discharge Survey and Uniform Bill-92 (UB-92) § Objective of UB-92 • To standardize and increase the submission of electronic claims § UB-92 limits the information available for the NHDS to that which is necessary for billing § Unable to modify the variables collected in the NHDS 75

NHDS Pilot Study § To examine whether pharmaceutical data can be added to the manual or primary data collection part of NHDS § Two-phase study conducted in 34 hospitals in three areas of the country • 791 discharges from 2003 • Registered Health Information Technicians (RHIT) collected data • Collected the names of all medications listed as administered in the medical record for that discharge 76

NHDS Pilot Study § Medications • Total of 10, 839 medications collected û 74 were illegible or indeterminate (<1%) • Range: 0 to 63 • Mean: 13. 61, • 3% had no medications listed Median: 13. 00 77
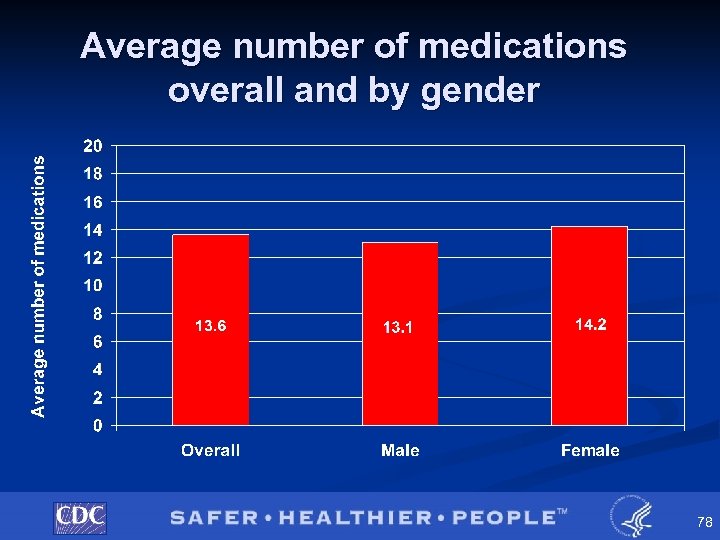
Average number of medications overall and by gender 78
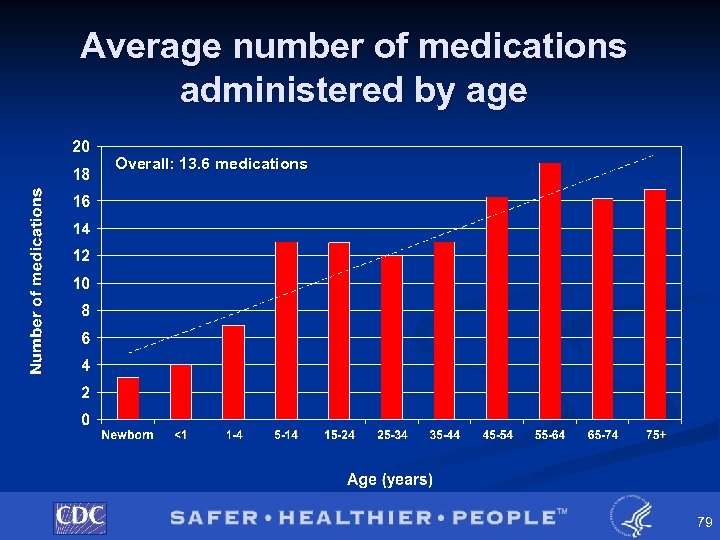
Average number of medications administered by age Overall: 13. 6 medications 79
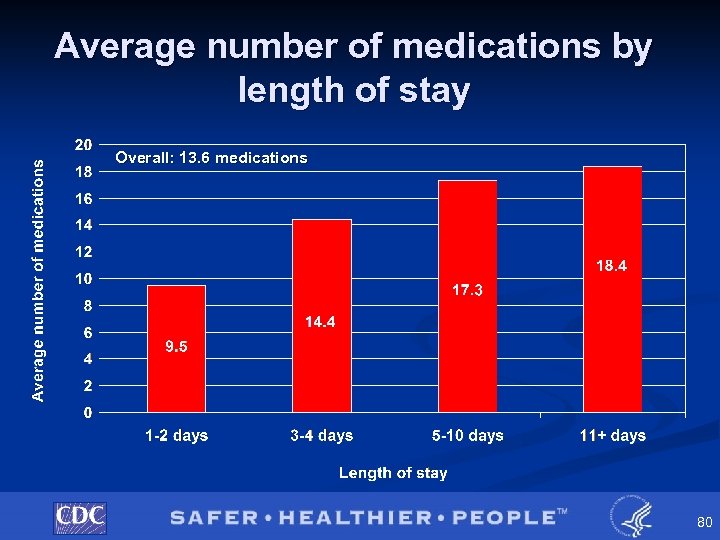
Average number of medications by length of stay Overall: 13. 6 medications 80
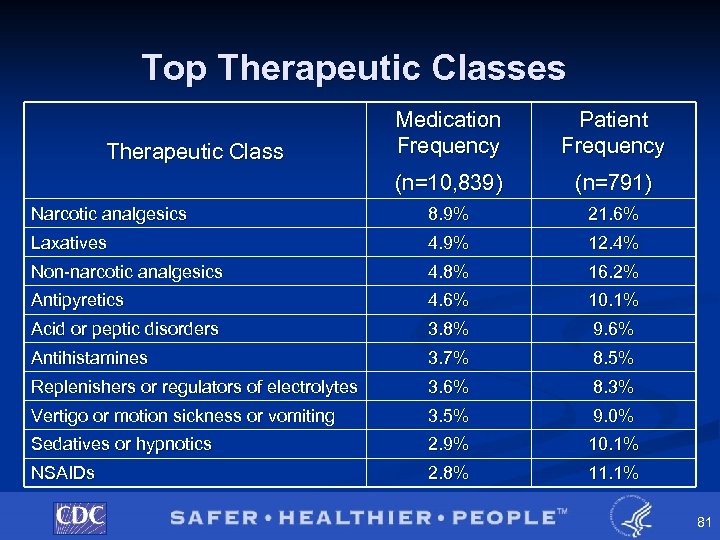
Top Therapeutic Classes Medication Frequency Patient Frequency (n=10, 839) (n=791) Narcotic analgesics 8. 9% 21. 6% Laxatives 4. 9% 12. 4% Non-narcotic analgesics 4. 8% 16. 2% Antipyretics 4. 6% 10. 1% Acid or peptic disorders 3. 8% 9. 6% Antihistamines 3. 7% 8. 5% Replenishers or regulators of electrolytes 3. 6% 8. 3% Vertigo or motion sickness or vomiting 3. 5% 9. 0% Sedatives or hypnotics 2. 9% 10. 1% NSAIDs 2. 8% 11. 1% Therapeutic Class 81
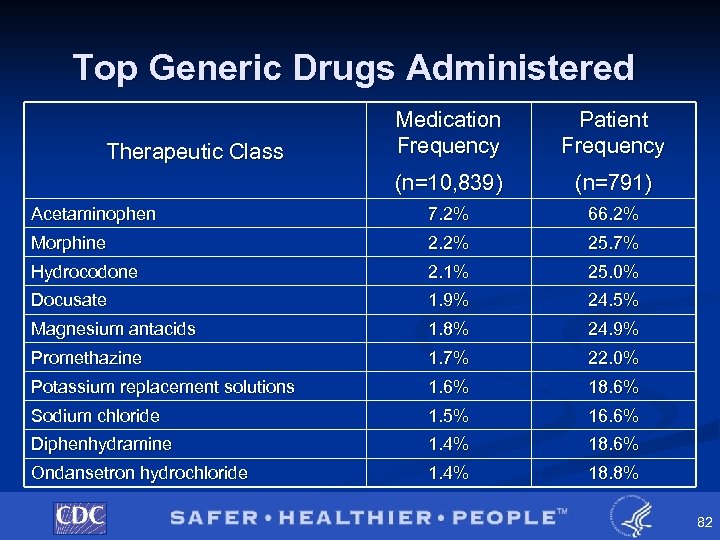
Top Generic Drugs Administered Medication Frequency Patient Frequency (n=10, 839) (n=791) Acetaminophen 7. 2% 66. 2% Morphine 2. 2% 25. 7% Hydrocodone 2. 1% 25. 0% Docusate 1. 9% 24. 5% Magnesium antacids 1. 8% 24. 9% Promethazine 1. 7% 22. 0% Potassium replacement solutions 1. 6% 18. 6% Sodium chloride 1. 5% 16. 6% Diphenhydramine 1. 4% 18. 6% Ondansetron hydrochloride 1. 4% 18. 8% Therapeutic Class 82

For more information on the NHDS, please visit our webpage: http: //www. cdc. gov/nchs/nhds. htm For more information on the pilot study or the NHDS redesign, please contact me at: Karen Lees, MPH Email: KLees@cdc. gov Phone: (301) 458 -4518 83

NHCS Future Steps § Adoption of Multum therapeutic classification system beginning with 2005 data § 2007 National Home and Hospice Care Survey § 2008 National Survey of Residential Care Facilities § 2006 National Survey of Ambulatory Surgery § NHDS Redesign • Contract currently let with RAND • Options being evaluated currently • Anticipate new NHDS collecting data in 2010 84
fe75a1f37784af6e43cc0fd022b5b7dc.ppt