de3ce9b6de9a0fcaf046e7665465bb03.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 85
 Medical Terminology A Living Language Chapter 12 Nervous System Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Medical Terminology A Living Language Chapter 12 Nervous System Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous System at a Glance l Functions of Nervous System l l Coordinates and controls body function Receives sensory input Makes decisions Orders body responses Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System at a Glance l Functions of Nervous System l l Coordinates and controls body function Receives sensory input Makes decisions Orders body responses Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous System at a Glance l Organs of Nervous System l l l Brain Spinal cord Nerves Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System at a Glance l Organs of Nervous System l l l Brain Spinal cord Nerves Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
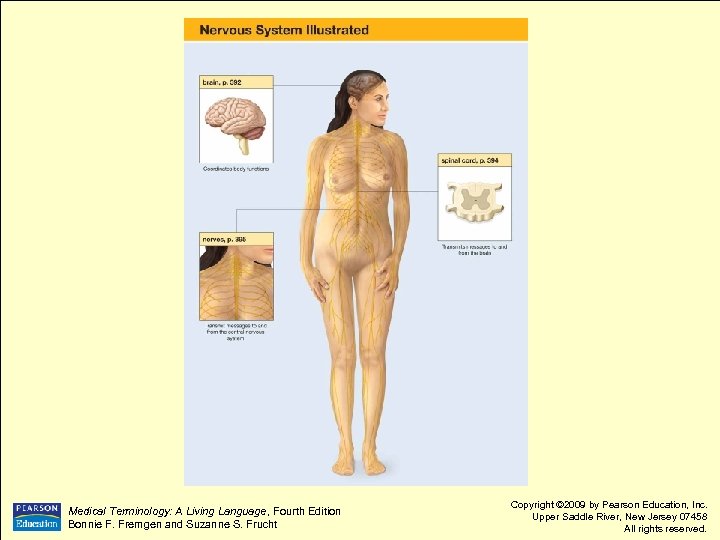 Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous System Combining Forms l l l cephal/o cerebell/o cerebr/o encephal/o gli/o medull/o head cerebellum cerebrum brain glue medulla Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Combining Forms l l l cephal/o cerebell/o cerebr/o encephal/o gli/o medull/o head cerebellum cerebrum brain glue medulla Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous System Combining Forms l l l mening/o meningi/o myel/o neur/o phas/o poli/o meninges spinal cord nerve speech gray matter Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Combining Forms l l l mening/o meningi/o myel/o neur/o phas/o poli/o meninges spinal cord nerve speech gray matter Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous System Combining Forms l l l pont/o radicul/o thalam/o thec/o ventricul/o pons nerve root thalamus sheath (meninges) ventricle Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Combining Forms l l l pont/o radicul/o thalam/o thec/o ventricul/o pons nerve root thalamus sheath (meninges) ventricle Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous System Suffixes l l l –algesia –esthesia –paresis –phasia –plegia –taxia pain, sensitivity feeling, sensation weakness speech paralysis muscle coordination Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Suffixes l l l –algesia –esthesia –paresis –phasia –plegia –taxia pain, sensitivity feeling, sensation weakness speech paralysis muscle coordination Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Anatomy and Physiology l Coordinates all activity of body l l l Receives information from both external and internal sensory receptors Uses that information to adjust activity of muscles and glands to match needs of body Nervous system is divided into: l l Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Anatomy and Physiology l Coordinates all activity of body l l l Receives information from both external and internal sensory receptors Uses that information to adjust activity of muscles and glands to match needs of body Nervous system is divided into: l l Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Anatomy and Physiology l Central nervous system consists of: l l l Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system consists of: l l Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Anatomy and Physiology l Central nervous system consists of: l l l Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system consists of: l l Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous Tissue l Nervous system composed of two types of cells l l l Neurons Neuroglial cells Neurons l l Individual nerve cells Capable of conducting electrical impulses Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous Tissue l Nervous system composed of two types of cells l l l Neurons Neuroglial cells Neurons l l Individual nerve cells Capable of conducting electrical impulses Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous Tissue l Neurons have three basic parts: l l l Dendrites – highly branched projections that receive impulses Nerve cell body – contains nucleus & organelles Axon – conducts electrical impulse to destination Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous Tissue l Neurons have three basic parts: l l l Dendrites – highly branched projections that receive impulses Nerve cell body – contains nucleus & organelles Axon – conducts electrical impulse to destination Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
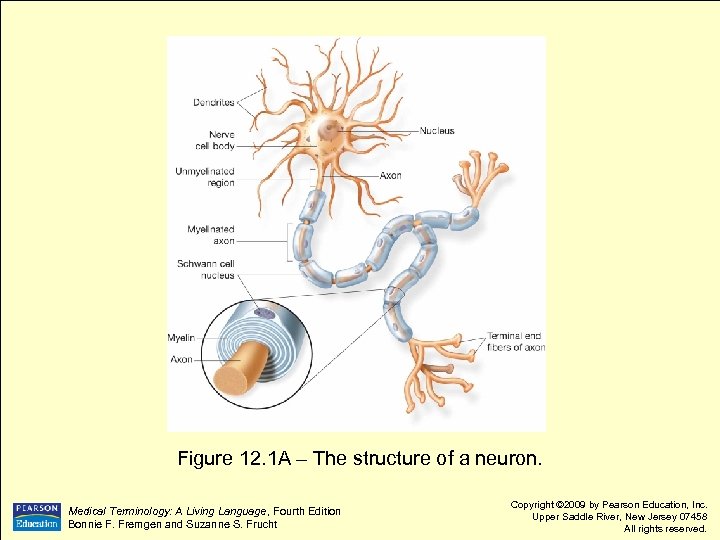 Figure 12. 1 A – The structure of a neuron. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 1 A – The structure of a neuron. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
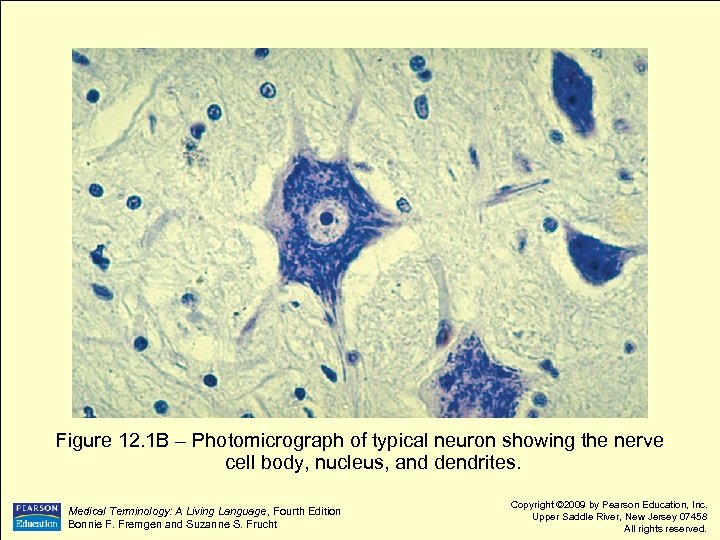 Figure 12. 1 B – Photomicrograph of typical neuron showing the nerve cell body, nucleus, and dendrites. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 1 B – Photomicrograph of typical neuron showing the nerve cell body, nucleus, and dendrites. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous Tissue l Synapse l l Synaptic cleft l l l Point where axon of one neuron meets dendrite of second neuron Gap between two neurons in a synapse Electrical impulse cannot cross Neurotransmitter l l Chemical released by axon Crosses gap to stimulate dendrite of second neuron Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous Tissue l Synapse l l Synaptic cleft l l l Point where axon of one neuron meets dendrite of second neuron Gap between two neurons in a synapse Electrical impulse cannot cross Neurotransmitter l l Chemical released by axon Crosses gap to stimulate dendrite of second neuron Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nervous Tissue l Neuroglial cells l l Variety of cells found in nervous tissue Each has different support function for neurons Some neuroglial cells produce myelin, a fatty substance that acts as insulation for many axons Neuroglial cells do not conduct electrical impulses Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous Tissue l Neuroglial cells l l Variety of cells found in nervous tissue Each has different support function for neurons Some neuroglial cells produce myelin, a fatty substance that acts as insulation for many axons Neuroglial cells do not conduct electrical impulses Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Central Nervous System Combination of the brain and spinal cord l Function l l l Receives impulses from all over body Processes this information Responds with action Bundles of nerve fibers interconnecting different parts of CNS are called tracts Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Central Nervous System Combination of the brain and spinal cord l Function l l l Receives impulses from all over body Processes this information Responds with action Bundles of nerve fibers interconnecting different parts of CNS are called tracts Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Central Nervous System Consists of both gray and white matter l Gray matter l l l Comprised of unsheathed or uncovered cell bodies and dendrites White matter l Myelinated nerve fibers Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Central Nervous System Consists of both gray and white matter l Gray matter l l l Comprised of unsheathed or uncovered cell bodies and dendrites White matter l Myelinated nerve fibers Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 The Brain One of the largest organs in body l Coordinates most body activities l It is center for: l l l Thoughts Memory Judgment Emotion Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
The Brain One of the largest organs in body l Coordinates most body activities l It is center for: l l l Thoughts Memory Judgment Emotion Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
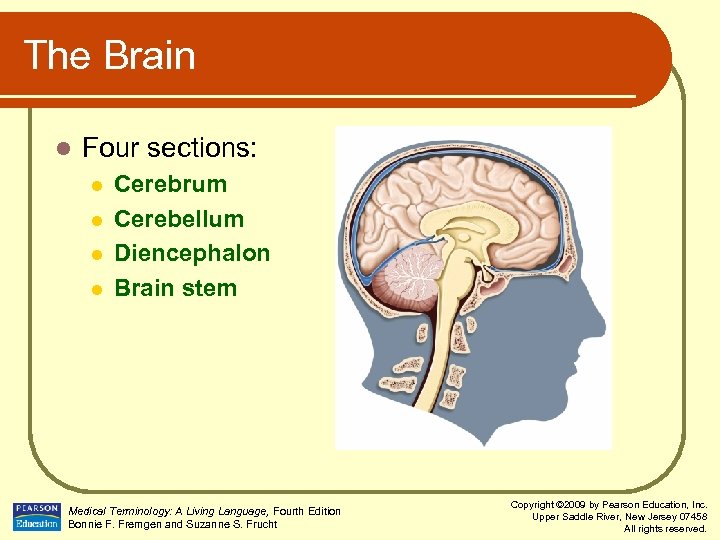 The Brain l Four sections: l l Cerebrum Cerebellum Diencephalon Brain stem Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
The Brain l Four sections: l l Cerebrum Cerebellum Diencephalon Brain stem Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
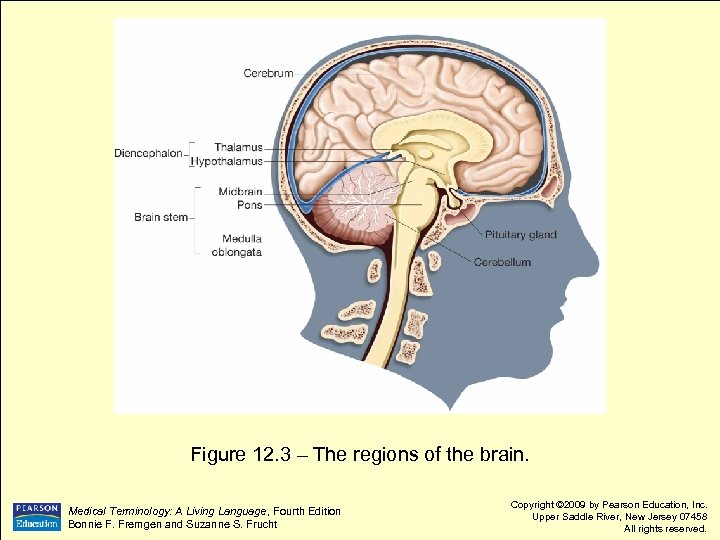 Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
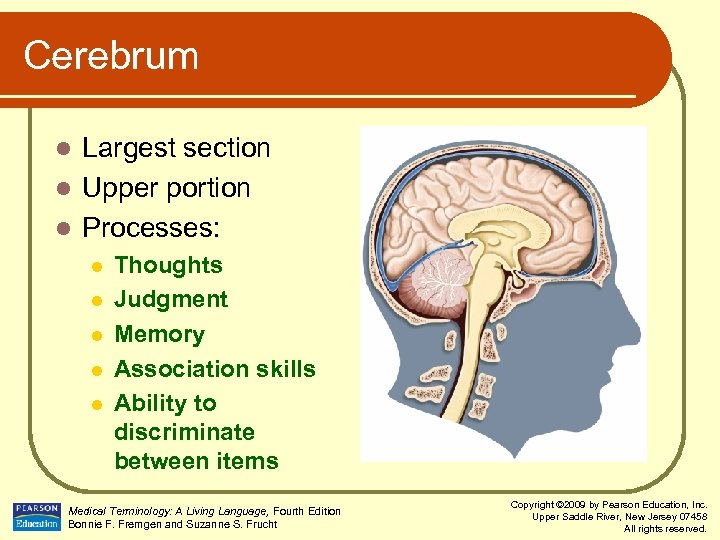 Cerebrum Largest section l Upper portion l Processes: l l l Thoughts Judgment Memory Association skills Ability to discriminate between items Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Cerebrum Largest section l Upper portion l Processes: l l l Thoughts Judgment Memory Association skills Ability to discriminate between items Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
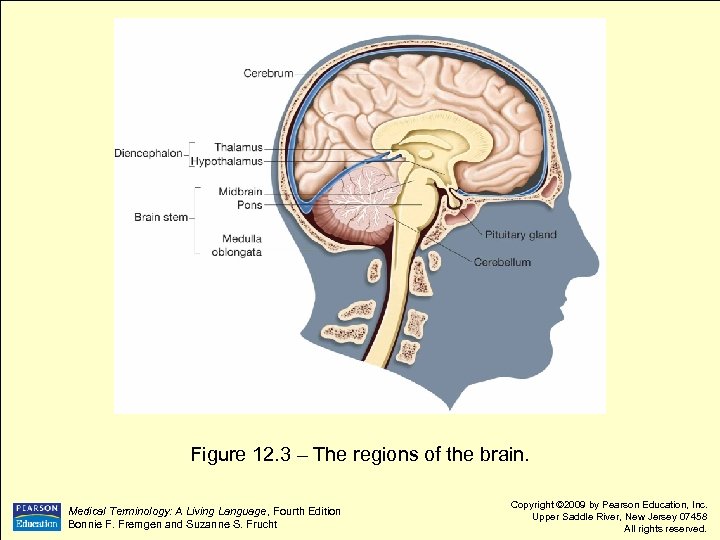 Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
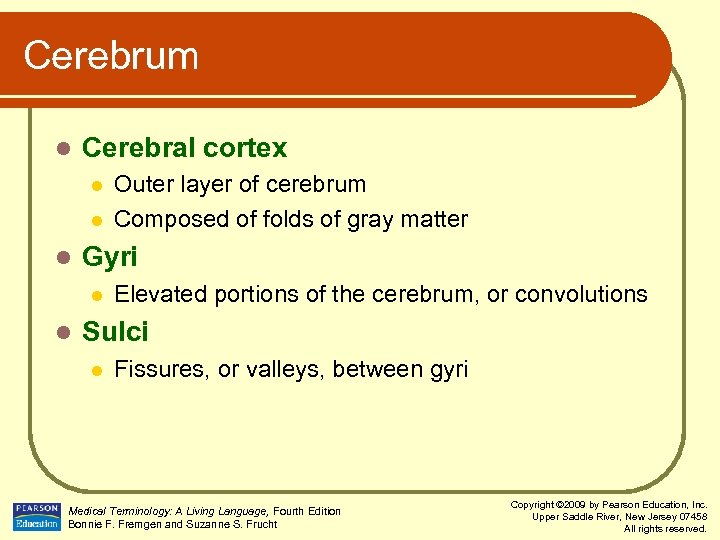 Cerebrum l Cerebral cortex l l l Gyri l l Outer layer of cerebrum Composed of folds of gray matter Elevated portions of the cerebrum, or convolutions Sulci l Fissures, or valleys, between gyri Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Cerebrum l Cerebral cortex l l l Gyri l l Outer layer of cerebrum Composed of folds of gray matter Elevated portions of the cerebrum, or convolutions Sulci l Fissures, or valleys, between gyri Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Lobes of Cerebrum Subdivided into left and right halves called cerebral hemispheres l Each hemisphere has four lobes: l l l Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Lobes of Cerebrum Subdivided into left and right halves called cerebral hemispheres l Each hemisphere has four lobes: l l l Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
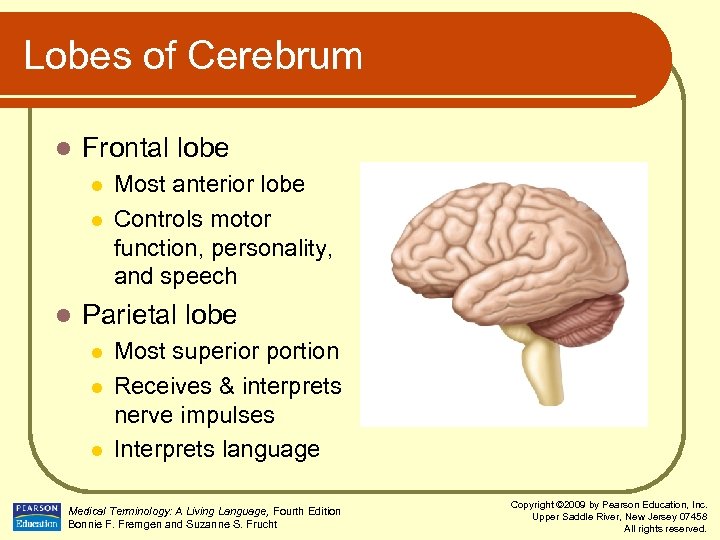 Lobes of Cerebrum l Frontal lobe l l l Most anterior lobe Controls motor function, personality, and speech Parietal lobe l l l Most superior portion Receives & interprets nerve impulses Interprets language Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Lobes of Cerebrum l Frontal lobe l l l Most anterior lobe Controls motor function, personality, and speech Parietal lobe l l l Most superior portion Receives & interprets nerve impulses Interprets language Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
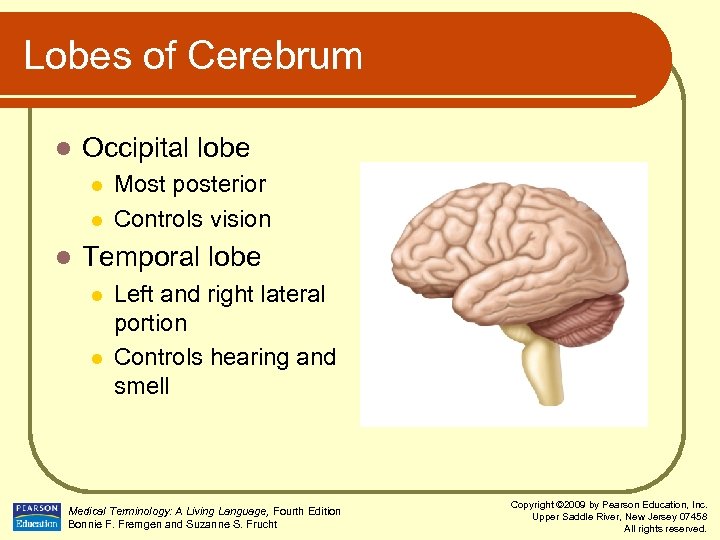 Lobes of Cerebrum l Occipital lobe l l l Most posterior Controls vision Temporal lobe l l Left and right lateral portion Controls hearing and smell Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Lobes of Cerebrum l Occipital lobe l l l Most posterior Controls vision Temporal lobe l l Left and right lateral portion Controls hearing and smell Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
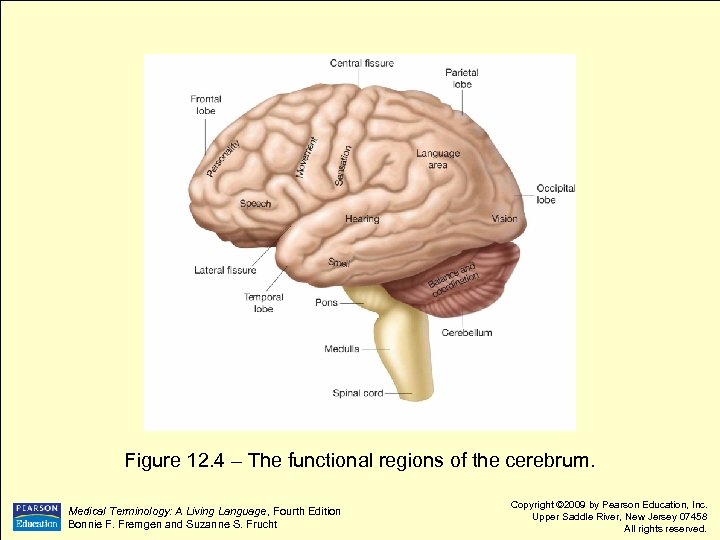 Figure 12. 4 – The functional regions of the cerebrum. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 4 – The functional regions of the cerebrum. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
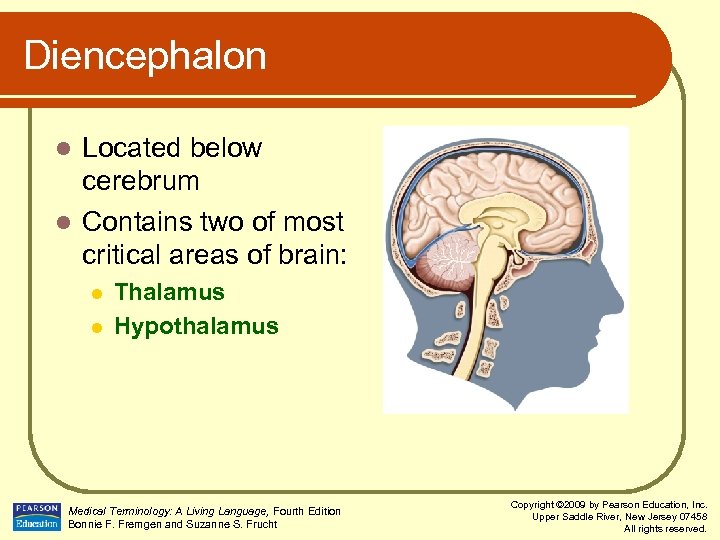 Diencephalon Located below cerebrum l Contains two of most critical areas of brain: l l l Thalamus Hypothalamus Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Diencephalon Located below cerebrum l Contains two of most critical areas of brain: l l l Thalamus Hypothalamus Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
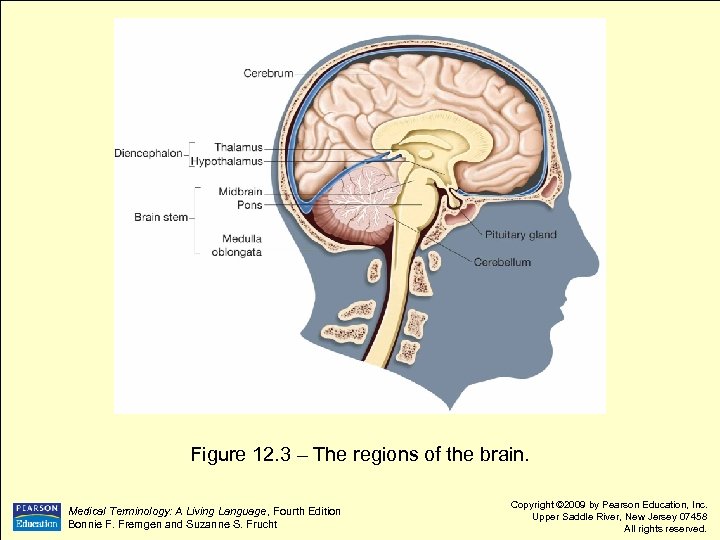 Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
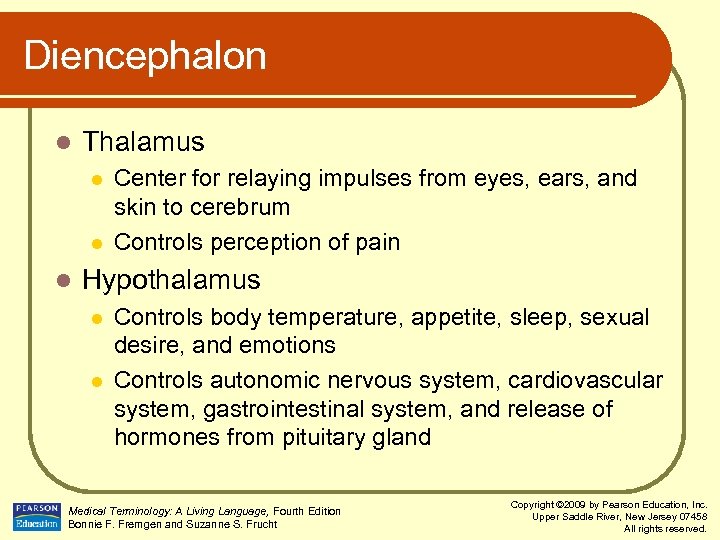 Diencephalon l Thalamus l l l Center for relaying impulses from eyes, ears, and skin to cerebrum Controls perception of pain Hypothalamus l l Controls body temperature, appetite, sleep, sexual desire, and emotions Controls autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal system, and release of hormones from pituitary gland Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Diencephalon l Thalamus l l l Center for relaying impulses from eyes, ears, and skin to cerebrum Controls perception of pain Hypothalamus l l Controls body temperature, appetite, sleep, sexual desire, and emotions Controls autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal system, and release of hormones from pituitary gland Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
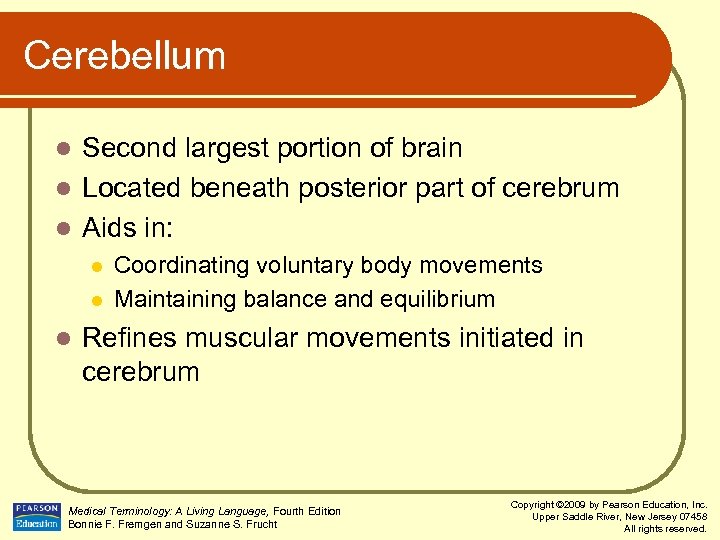 Cerebellum Second largest portion of brain l Located beneath posterior part of cerebrum l Aids in: l l Coordinating voluntary body movements Maintaining balance and equilibrium Refines muscular movements initiated in cerebrum Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Cerebellum Second largest portion of brain l Located beneath posterior part of cerebrum l Aids in: l l Coordinating voluntary body movements Maintaining balance and equilibrium Refines muscular movements initiated in cerebrum Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
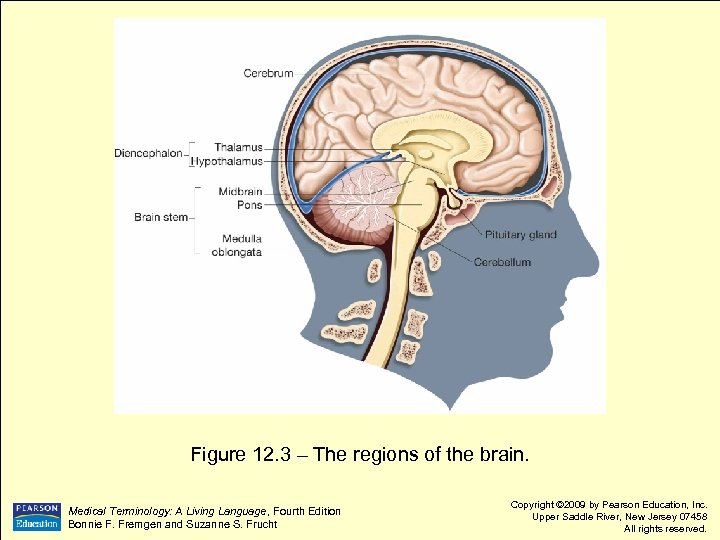 Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
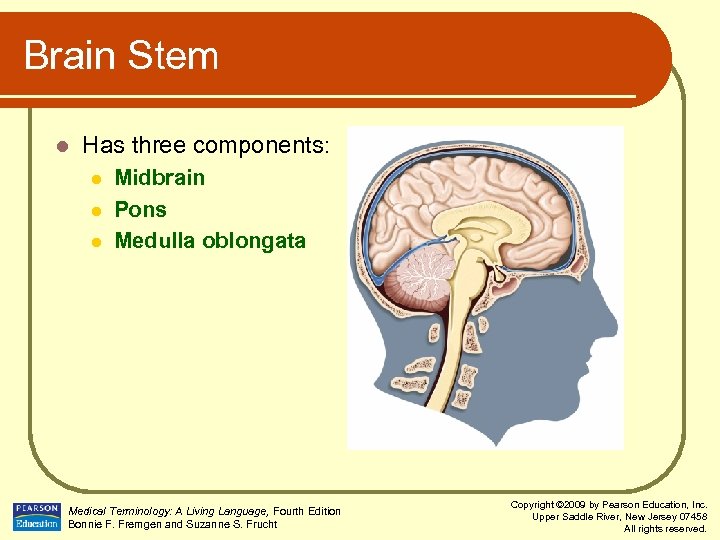 Brain Stem l Has three components: l l l Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Brain Stem l Has three components: l l l Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
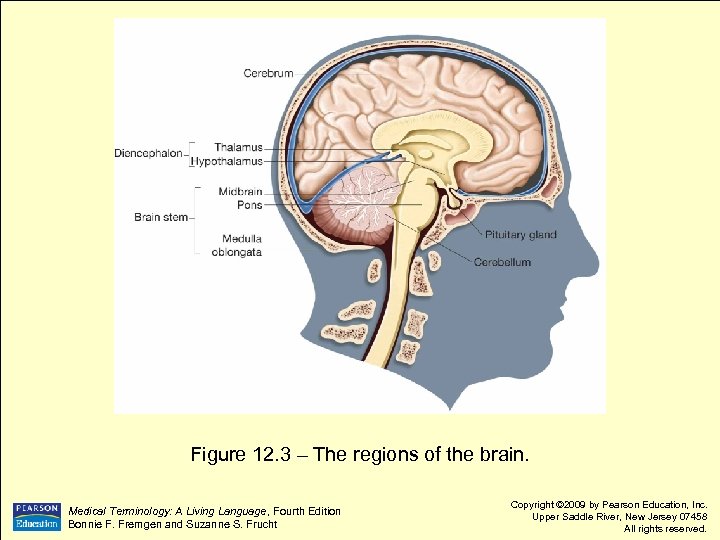 Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 3 – The regions of the brain. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
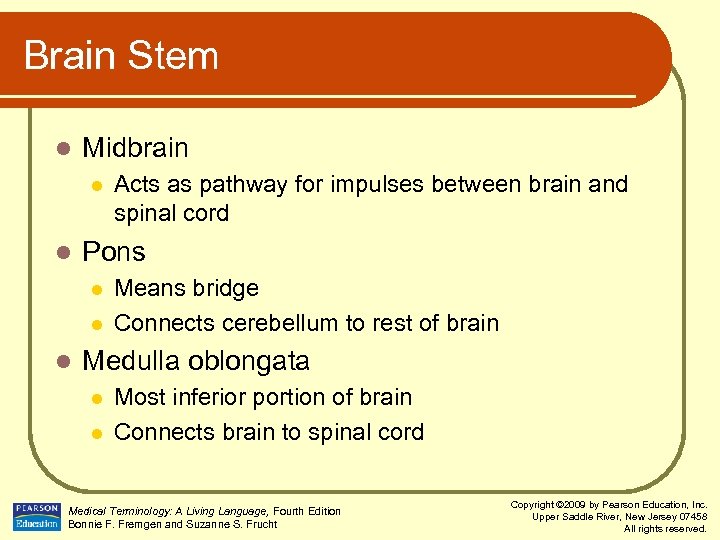 Brain Stem l Midbrain l l Pons l l l Acts as pathway for impulses between brain and spinal cord Means bridge Connects cerebellum to rest of brain Medulla oblongata l l Most inferior portion of brain Connects brain to spinal cord Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Brain Stem l Midbrain l l Pons l l l Acts as pathway for impulses between brain and spinal cord Means bridge Connects cerebellum to rest of brain Medulla oblongata l l Most inferior portion of brain Connects brain to spinal cord Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
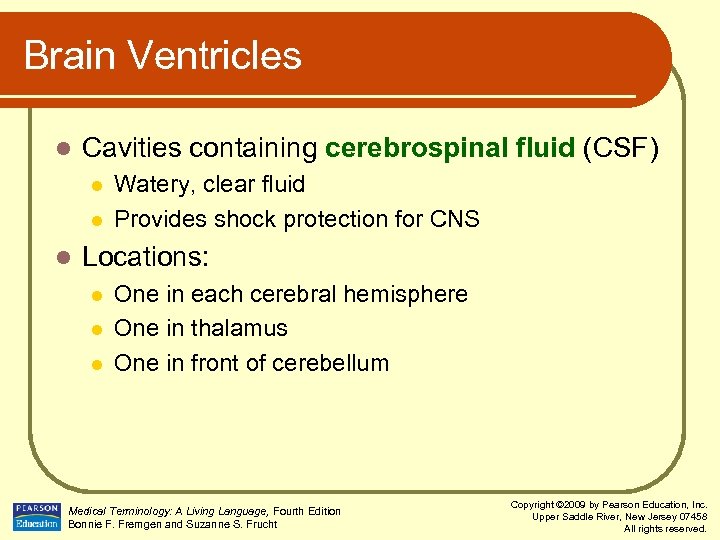 Brain Ventricles l Cavities containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) l l l Watery, clear fluid Provides shock protection for CNS Locations: l l l One in each cerebral hemisphere One in thalamus One in front of cerebellum Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Brain Ventricles l Cavities containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) l l l Watery, clear fluid Provides shock protection for CNS Locations: l l l One in each cerebral hemisphere One in thalamus One in front of cerebellum Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
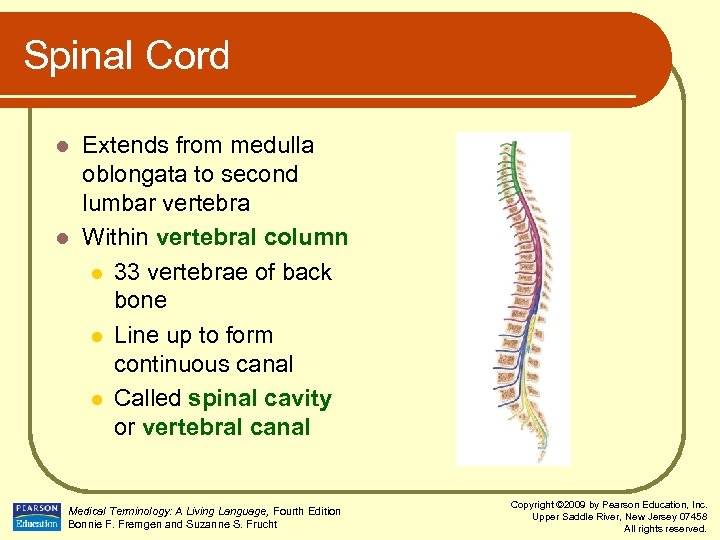 Spinal Cord Extends from medulla oblongata to second lumbar vertebra l Within vertebral column l 33 vertebrae of back bone l Line up to form continuous canal l Called spinal cavity or vertebral canal l Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Spinal Cord Extends from medulla oblongata to second lumbar vertebra l Within vertebral column l 33 vertebrae of back bone l Line up to form continuous canal l Called spinal cavity or vertebral canal l Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
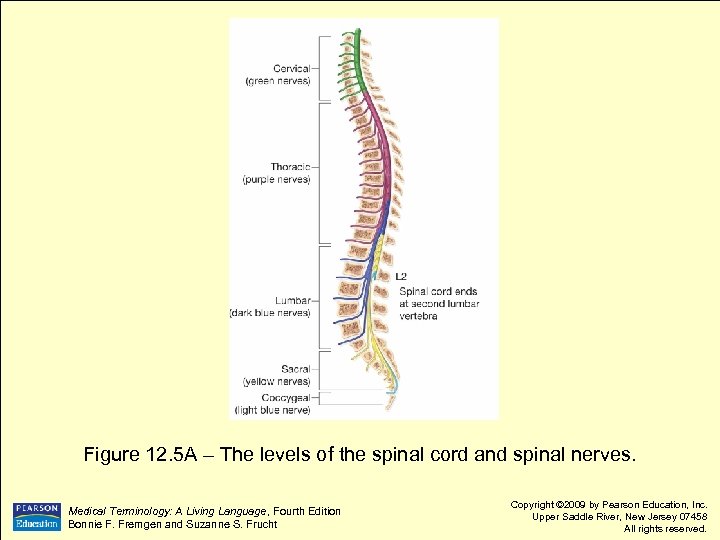 Figure 12. 5 A – The levels of the spinal cord and spinal nerves. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 5 A – The levels of the spinal cord and spinal nerves. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
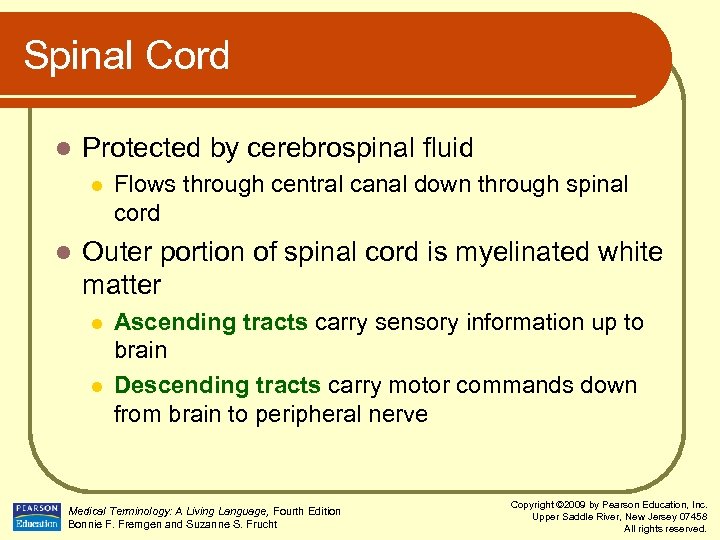 Spinal Cord l Protected by cerebrospinal fluid l l Flows through central canal down through spinal cord Outer portion of spinal cord is myelinated white matter l l Ascending tracts carry sensory information up to brain Descending tracts carry motor commands down from brain to peripheral nerve Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Spinal Cord l Protected by cerebrospinal fluid l l Flows through central canal down through spinal cord Outer portion of spinal cord is myelinated white matter l l Ascending tracts carry sensory information up to brain Descending tracts carry motor commands down from brain to peripheral nerve Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
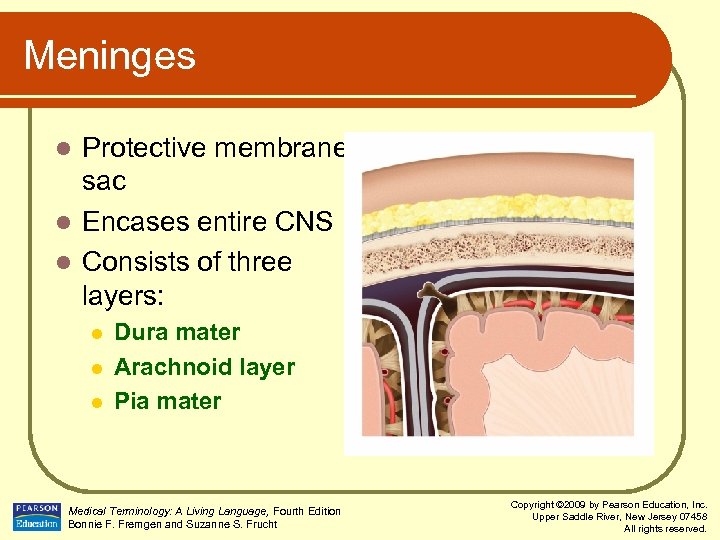 Meninges Protective membrane sac l Encases entire CNS l Consists of three layers: l l Dura mater Arachnoid layer Pia mater Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Meninges Protective membrane sac l Encases entire CNS l Consists of three layers: l l Dura mater Arachnoid layer Pia mater Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
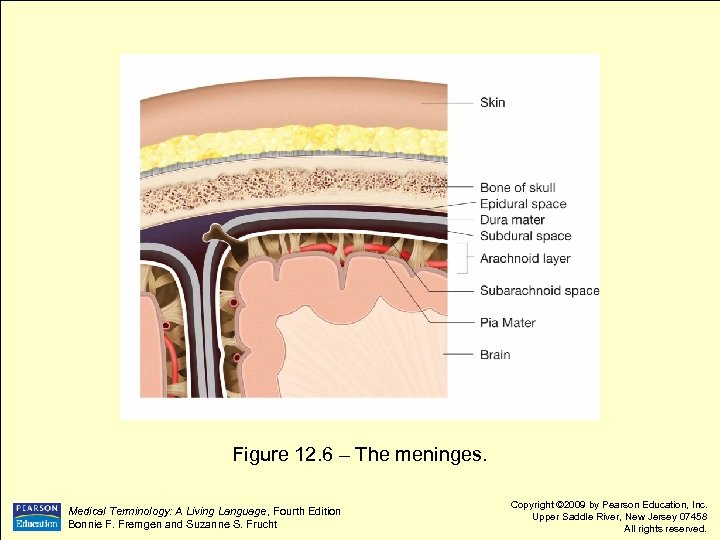 Figure 12. 6 – The meninges. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 6 – The meninges. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
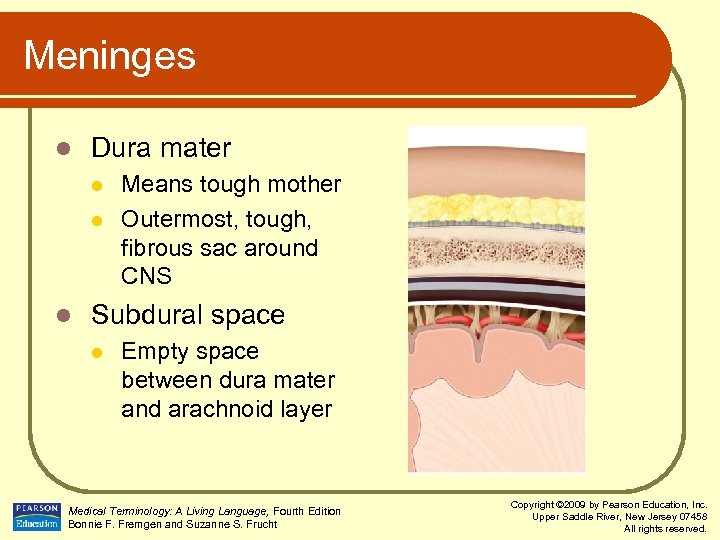 Meninges l Dura mater l l l Means tough mother Outermost, tough, fibrous sac around CNS Subdural space l Empty space between dura mater and arachnoid layer Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Meninges l Dura mater l l l Means tough mother Outermost, tough, fibrous sac around CNS Subdural space l Empty space between dura mater and arachnoid layer Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
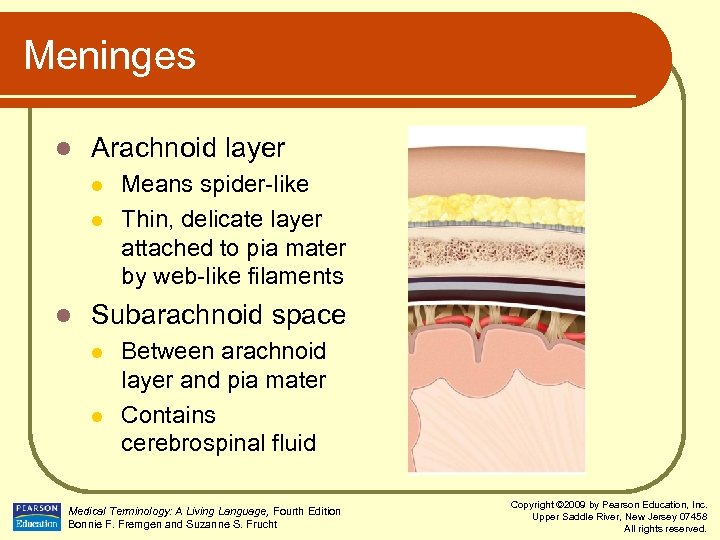 Meninges l Arachnoid layer l l l Means spider-like Thin, delicate layer attached to pia mater by web-like filaments Subarachnoid space l l Between arachnoid layer and pia mater Contains cerebrospinal fluid Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Meninges l Arachnoid layer l l l Means spider-like Thin, delicate layer attached to pia mater by web-like filaments Subarachnoid space l l Between arachnoid layer and pia mater Contains cerebrospinal fluid Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
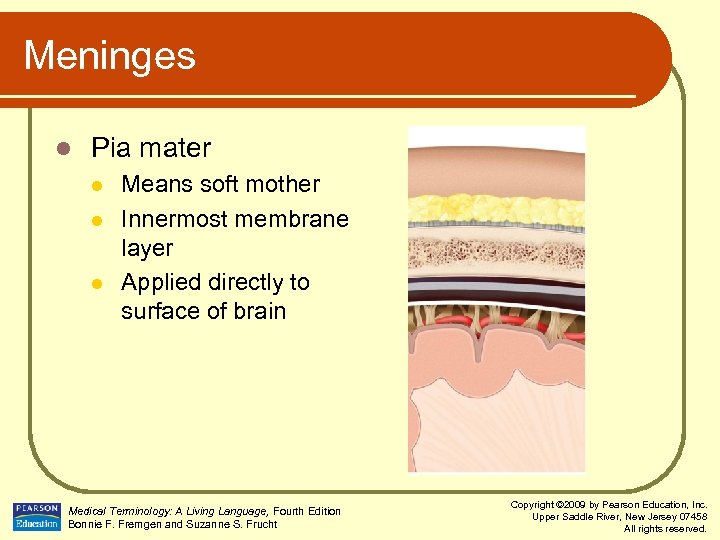 Meninges l Pia mater l l l Means soft mother Innermost membrane layer Applied directly to surface of brain Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Meninges l Pia mater l l l Means soft mother Innermost membrane layer Applied directly to surface of brain Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) l Consists of: l l l Cranial nerves l l 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves Arise from brain Spinal nerves l l Split off from spinal cord One pair (left and right) exit between each pair of vertebrae Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) l Consists of: l l l Cranial nerves l l 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves Arise from brain Spinal nerves l l Split off from spinal cord One pair (left and right) exit between each pair of vertebrae Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nerves l A nerve: l l l Nerve root l l Is a bundle of axon fibers located outside CNS Carries messages between CNS and various parts of body Point where nerve is attached to CNS Names of most nerves reflect: l l Organ the nerve serves Portion of body the nerve is traveling through Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nerves l A nerve: l l l Nerve root l l Is a bundle of axon fibers located outside CNS Carries messages between CNS and various parts of body Point where nerve is attached to CNS Names of most nerves reflect: l l Organ the nerve serves Portion of body the nerve is traveling through Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
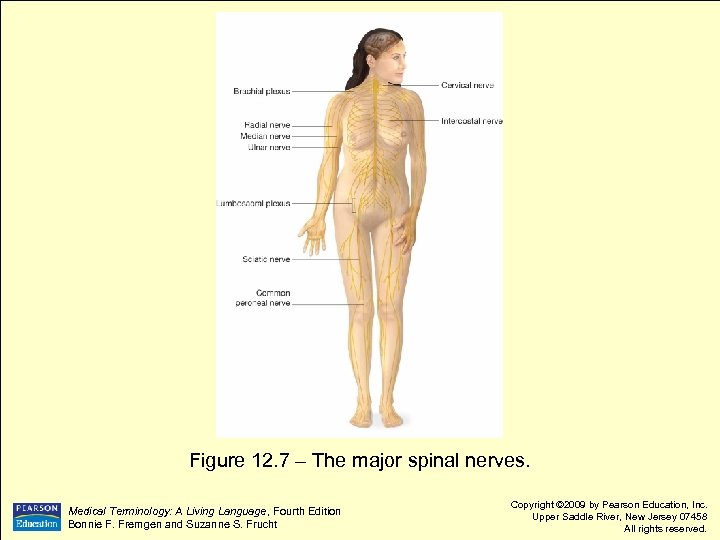 Figure 12. 7 – The major spinal nerves. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 7 – The major spinal nerves. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
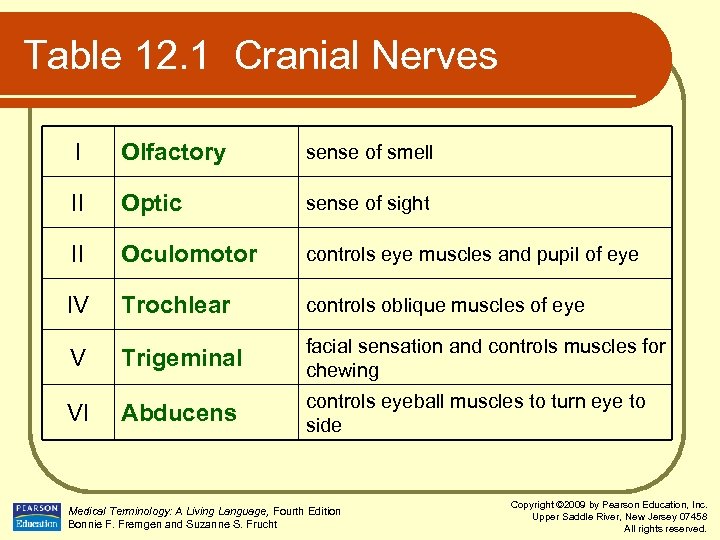 Table 12. 1 Cranial Nerves I Olfactory sense of smell II Optic sense of sight II Oculomotor controls eye muscles and pupil of eye IV Trochlear controls oblique muscles of eye V Trigeminal facial sensation and controls muscles for chewing Abducens controls eyeball muscles to turn eye to side VI Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Table 12. 1 Cranial Nerves I Olfactory sense of smell II Optic sense of sight II Oculomotor controls eye muscles and pupil of eye IV Trochlear controls oblique muscles of eye V Trigeminal facial sensation and controls muscles for chewing Abducens controls eyeball muscles to turn eye to side VI Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Table 12. 1 Cranial Nerves VII Facial controls facial muscles for expression, salivation, and taste on two-thirds of tongue (anterior) VIII Vestibulocochlear sense of equilibrium and hearing Glossopharyngeal sensation from pharynx and taste on one-third of tongue X Vagus supplies most organs in abdominal and thoracic cavities XI Accessory controls neck and shoulder muscles XII Hypoglossal controls tongue muscles IX Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Table 12. 1 Cranial Nerves VII Facial controls facial muscles for expression, salivation, and taste on two-thirds of tongue (anterior) VIII Vestibulocochlear sense of equilibrium and hearing Glossopharyngeal sensation from pharynx and taste on one-third of tongue X Vagus supplies most organs in abdominal and thoracic cavities XI Accessory controls neck and shoulder muscles XII Hypoglossal controls tongue muscles IX Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Neurons Each nerve can carry information both to and from CNS l But any individual neuron carry information in only one direction l Either an: l l l Afferent neuron Efferent neuron Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Neurons Each nerve can carry information both to and from CNS l But any individual neuron carry information in only one direction l Either an: l l l Afferent neuron Efferent neuron Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
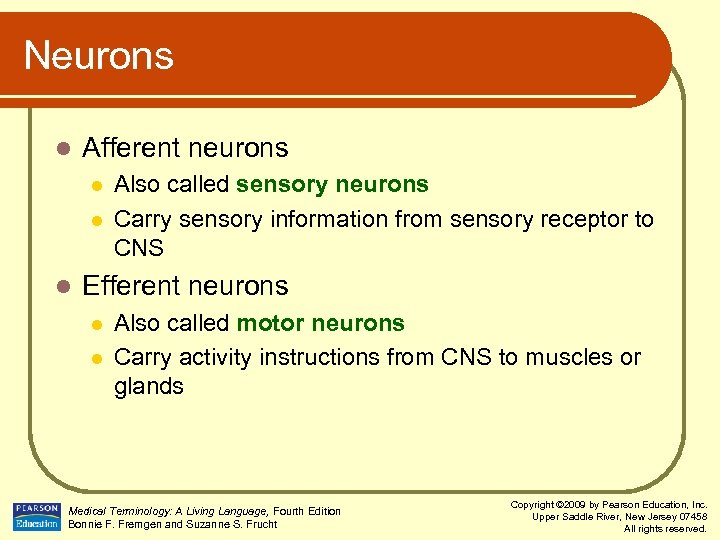 Neurons l Afferent neurons l l l Also called sensory neurons Carry sensory information from sensory receptor to CNS Efferent neurons l l Also called motor neurons Carry activity instructions from CNS to muscles or glands Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Neurons l Afferent neurons l l l Also called sensory neurons Carry sensory information from sensory receptor to CNS Efferent neurons l l Also called motor neurons Carry activity instructions from CNS to muscles or glands Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Divisions of PNS l Nerves of PNS are subdivided into two divisions l l l Autonomic nervous system (ANS) Somatic nerves Each division serves different area of body Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Divisions of PNS l Nerves of PNS are subdivided into two divisions l l l Autonomic nervous system (ANS) Somatic nerves Each division serves different area of body Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
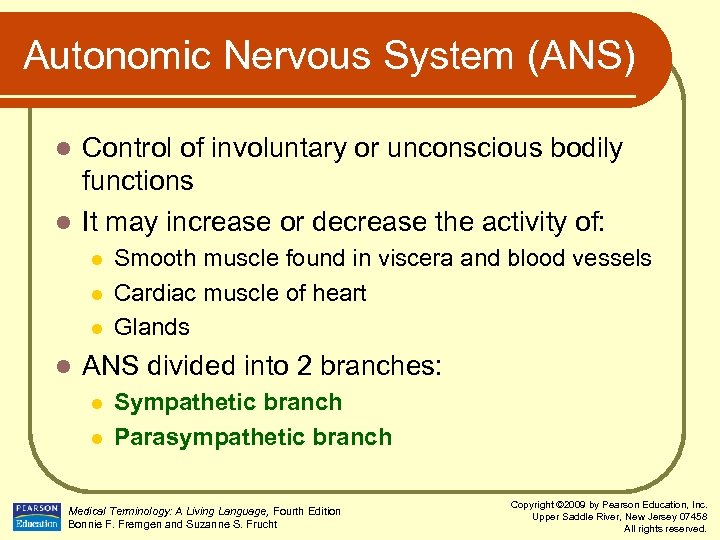 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Control of involuntary or unconscious bodily functions l It may increase or decrease the activity of: l l l Smooth muscle found in viscera and blood vessels Cardiac muscle of heart Glands ANS divided into 2 branches: l l Sympathetic branch Parasympathetic branch Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Control of involuntary or unconscious bodily functions l It may increase or decrease the activity of: l l l Smooth muscle found in viscera and blood vessels Cardiac muscle of heart Glands ANS divided into 2 branches: l l Sympathetic branch Parasympathetic branch Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) l Sympathetic branch l l l Stimulates body in times of stress and crisis Increases heart rate, dilates airways, increases blood pressure, inhibits digestion, and stimulates production of adrenaline Parasympathetic branch l l Serves as counterbalance for sympathetic nerves Causes heart rate to slow down, lowers blood pressure, and stimulates digestion Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) l Sympathetic branch l l l Stimulates body in times of stress and crisis Increases heart rate, dilates airways, increases blood pressure, inhibits digestion, and stimulates production of adrenaline Parasympathetic branch l l Serves as counterbalance for sympathetic nerves Causes heart rate to slow down, lowers blood pressure, and stimulates digestion Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Somatic Nerves Mainly involved with conscious and voluntary activities of body l Serve skin and skeletal muscles l l Carry information from sensory receptors of skin l l Such as touch, temperature, pressure, and pain Carry motor commands to skeletal muscles Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Somatic Nerves Mainly involved with conscious and voluntary activities of body l Serve skin and skeletal muscles l l Carry information from sensory receptors of skin l l Such as touch, temperature, pressure, and pain Carry motor commands to skeletal muscles Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
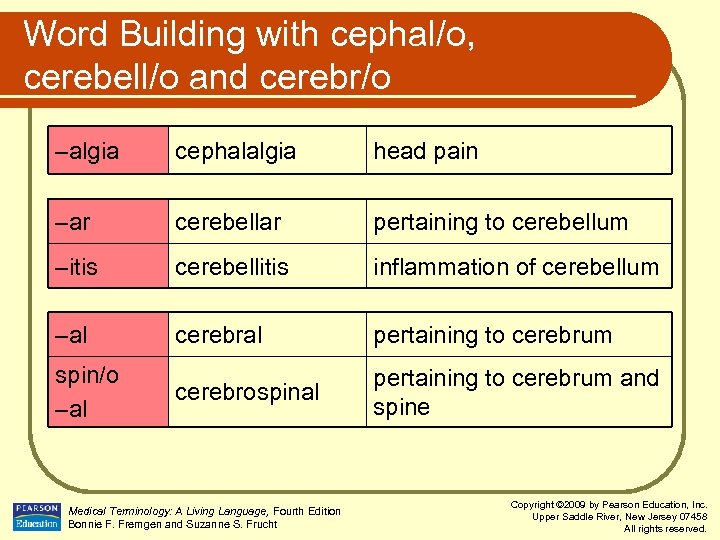 Word Building with cephal/o, cerebell/o and cerebr/o –algia cephalalgia head pain –ar cerebellar pertaining to cerebellum –itis cerebellitis inflammation of cerebellum –al cerebral pertaining to cerebrum cerebrospinal pertaining to cerebrum and spine spin/o –al Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Word Building with cephal/o, cerebell/o and cerebr/o –algia cephalalgia head pain –ar cerebellar pertaining to cerebellum –itis cerebellitis inflammation of cerebellum –al cerebral pertaining to cerebrum cerebrospinal pertaining to cerebrum and spine spin/o –al Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
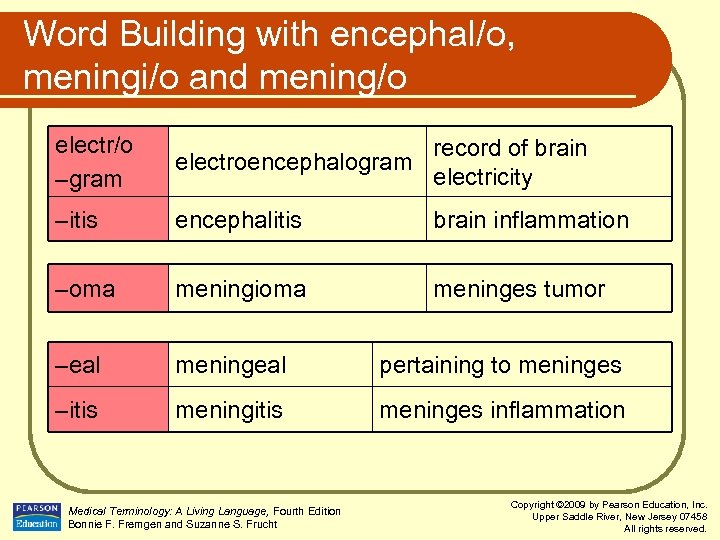 Word Building with encephal/o, meningi/o and mening/o electr/o –gram record of brain electroencephalogram electricity –itis encephalitis brain inflammation –oma meningioma meninges tumor –eal meningeal pertaining to meninges –itis meninges inflammation Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Word Building with encephal/o, meningi/o and mening/o electr/o –gram record of brain electroencephalogram electricity –itis encephalitis brain inflammation –oma meningioma meninges tumor –eal meningeal pertaining to meninges –itis meninges inflammation Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
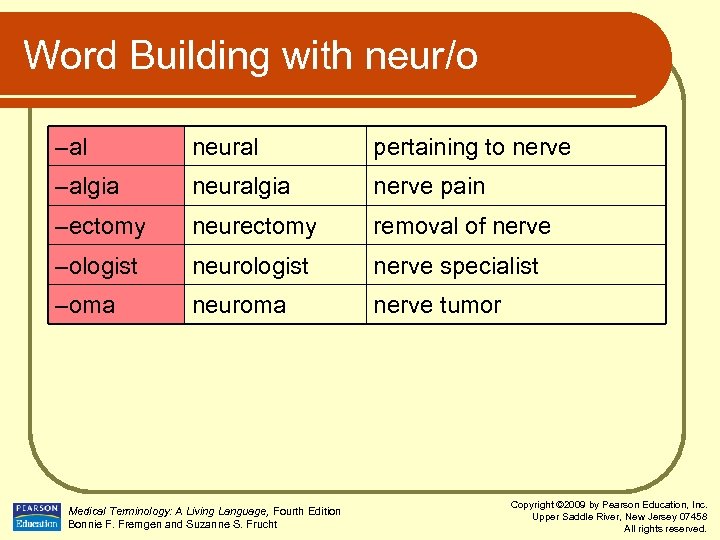 Word Building with neur/o –al neural pertaining to nerve –algia neuralgia nerve pain –ectomy neurectomy removal of nerve –ologist neurologist nerve specialist –oma neuroma nerve tumor Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Word Building with neur/o –al neural pertaining to nerve –algia neuralgia nerve pain –ectomy neurectomy removal of nerve –ologist neurologist nerve specialist –oma neuroma nerve tumor Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
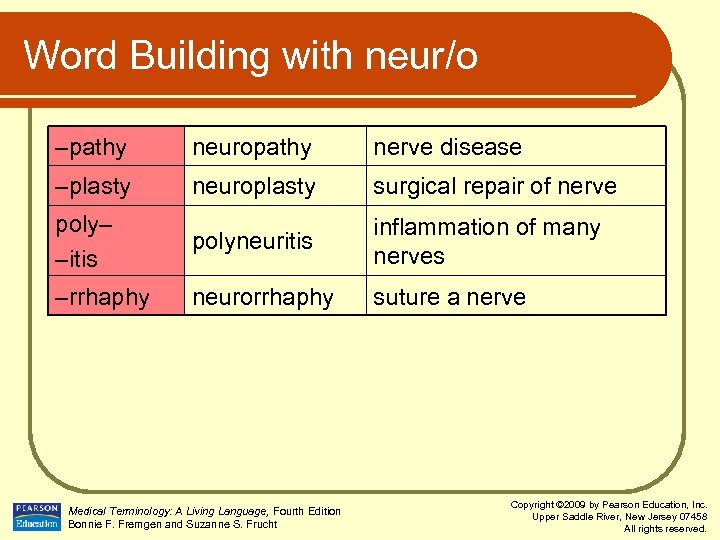 Word Building with neur/o –pathy neuropathy nerve disease –plasty neuroplasty surgical repair of nerve poly– –itis polyneuritis inflammation of many nerves –rrhaphy neurorrhaphy suture a nerve Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Word Building with neur/o –pathy neuropathy nerve disease –plasty neuroplasty surgical repair of nerve poly– –itis polyneuritis inflammation of many nerves –rrhaphy neurorrhaphy suture a nerve Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
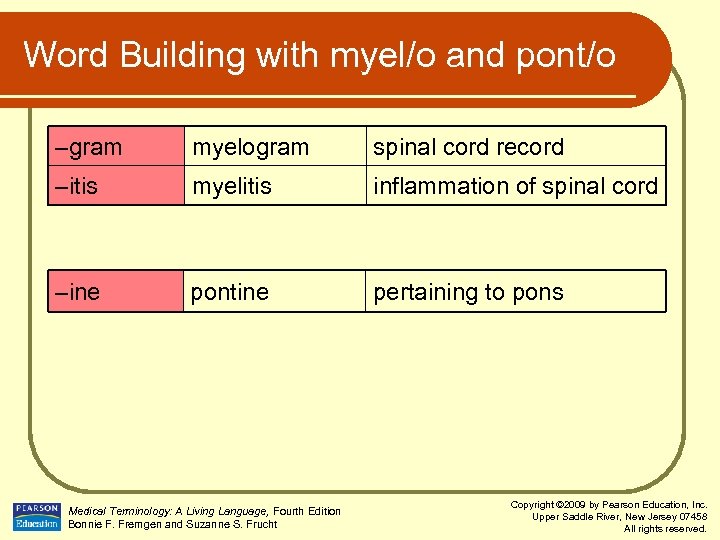 Word Building with myel/o and pont/o –gram myelogram spinal cord record –itis myelitis inflammation of spinal cord –ine pontine pertaining to pons Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Word Building with myel/o and pont/o –gram myelogram spinal cord record –itis myelitis inflammation of spinal cord –ine pontine pertaining to pons Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
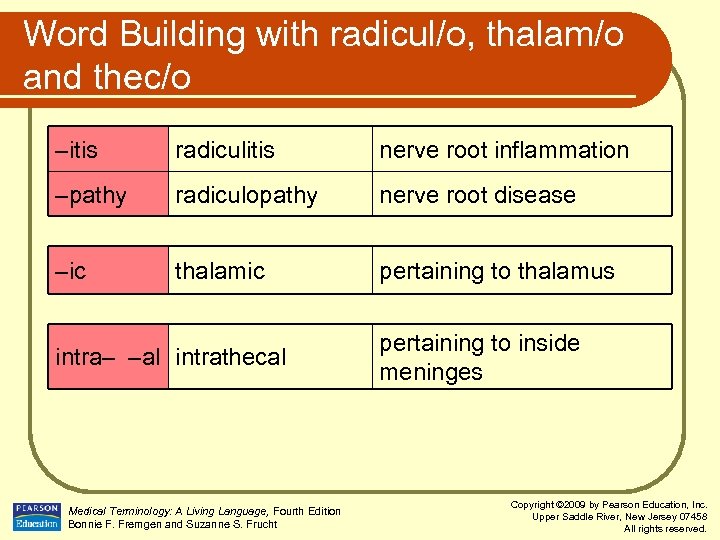 Word Building with radicul/o, thalam/o and thec/o –itis radiculitis nerve root inflammation –pathy radiculopathy nerve root disease –ic thalamic pertaining to thalamus intra– –al intrathecal Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht pertaining to inside meninges Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Word Building with radicul/o, thalam/o and thec/o –itis radiculitis nerve root inflammation –pathy radiculopathy nerve root disease –ic thalamic pertaining to thalamus intra– –al intrathecal Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht pertaining to inside meninges Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
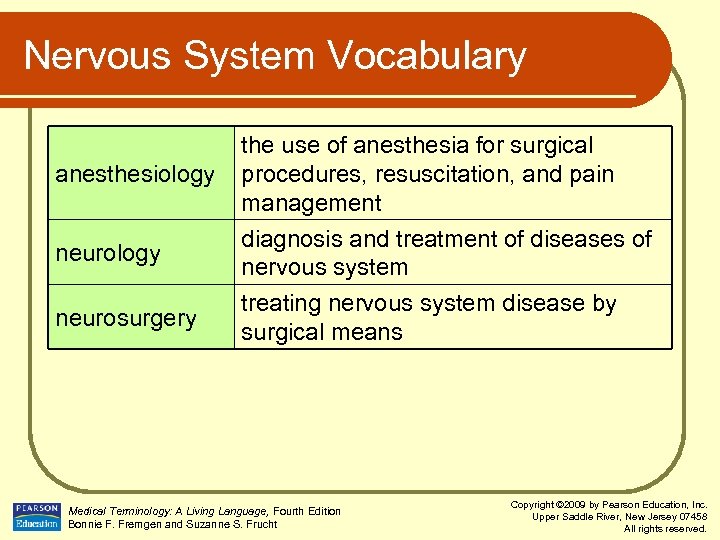 Nervous System Vocabulary anesthesiology neurosurgery the use of anesthesia for surgical procedures, resuscitation, and pain management diagnosis and treatment of diseases of nervous system treating nervous system disease by surgical means Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Vocabulary anesthesiology neurosurgery the use of anesthesia for surgical procedures, resuscitation, and pain management diagnosis and treatment of diseases of nervous system treating nervous system disease by surgical means Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
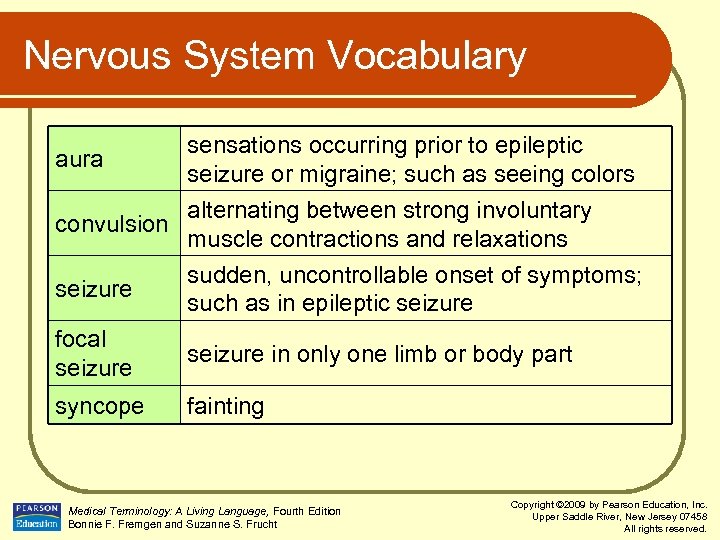 Nervous System Vocabulary aura sensations occurring prior to epileptic seizure or migraine; such as seeing colors alternating between strong involuntary convulsion muscle contractions and relaxations seizure sudden, uncontrollable onset of symptoms; such as in epileptic seizure focal seizure in only one limb or body part syncope fainting Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Vocabulary aura sensations occurring prior to epileptic seizure or migraine; such as seeing colors alternating between strong involuntary convulsion muscle contractions and relaxations seizure sudden, uncontrollable onset of symptoms; such as in epileptic seizure focal seizure in only one limb or body part syncope fainting Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
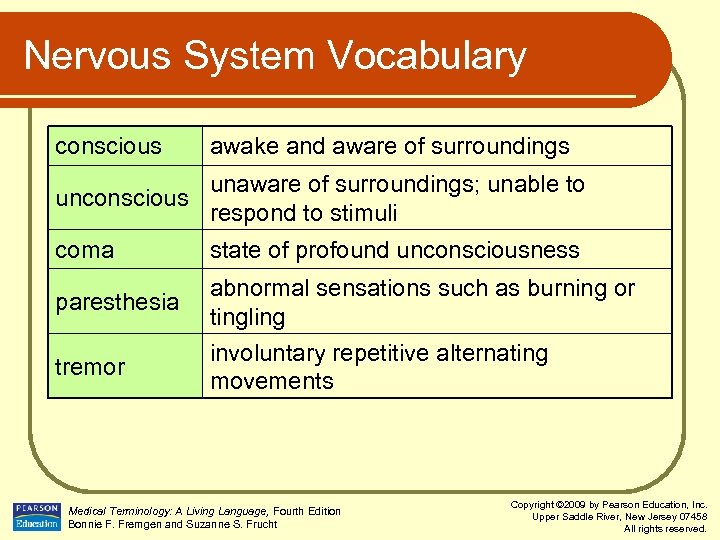 Nervous System Vocabulary conscious awake and aware of surroundings unaware of surroundings; unable to unconscious respond to stimuli coma paresthesia tremor state of profound unconsciousness abnormal sensations such as burning or tingling involuntary repetitive alternating movements Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Vocabulary conscious awake and aware of surroundings unaware of surroundings; unable to unconscious respond to stimuli coma paresthesia tremor state of profound unconsciousness abnormal sensations such as burning or tingling involuntary repetitive alternating movements Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
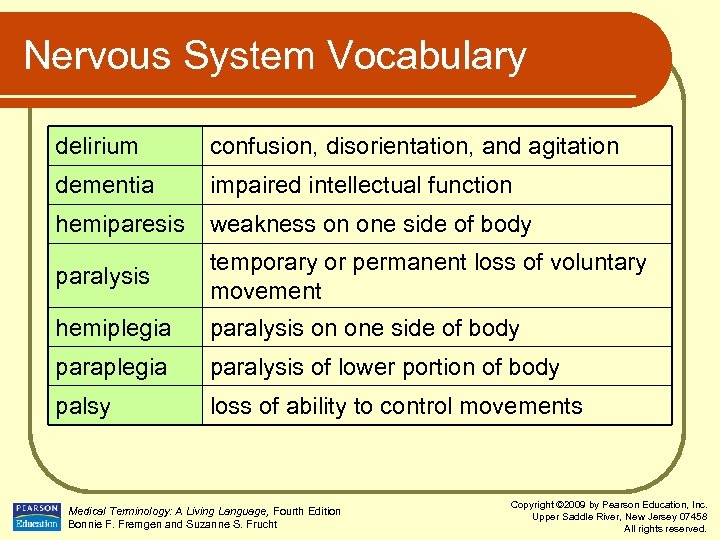 Nervous System Vocabulary delirium confusion, disorientation, and agitation dementia impaired intellectual function hemiparesis weakness on one side of body paralysis temporary or permanent loss of voluntary movement hemiplegia paralysis on one side of body paraplegia paralysis of lower portion of body palsy loss of ability to control movements Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Vocabulary delirium confusion, disorientation, and agitation dementia impaired intellectual function hemiparesis weakness on one side of body paralysis temporary or permanent loss of voluntary movement hemiplegia paralysis on one side of body paraplegia paralysis of lower portion of body palsy loss of ability to control movements Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
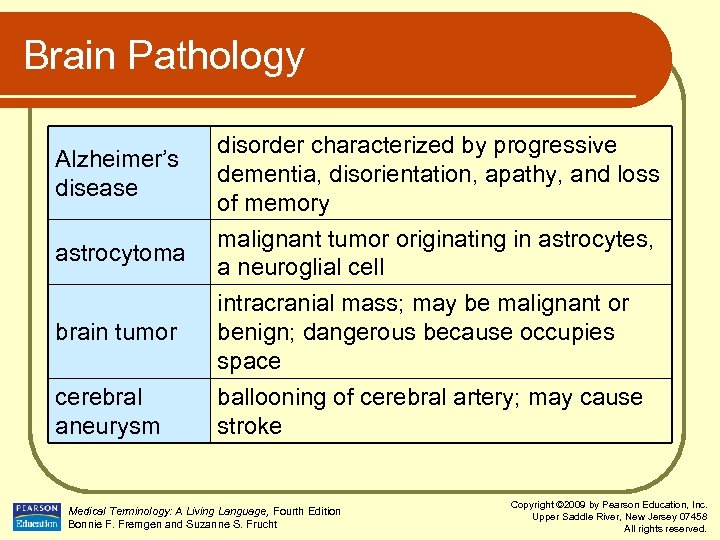 Brain Pathology Alzheimer’s disease astrocytoma brain tumor cerebral aneurysm disorder characterized by progressive dementia, disorientation, apathy, and loss of memory malignant tumor originating in astrocytes, a neuroglial cell intracranial mass; may be malignant or benign; dangerous because occupies space ballooning of cerebral artery; may cause stroke Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Brain Pathology Alzheimer’s disease astrocytoma brain tumor cerebral aneurysm disorder characterized by progressive dementia, disorientation, apathy, and loss of memory malignant tumor originating in astrocytes, a neuroglial cell intracranial mass; may be malignant or benign; dangerous because occupies space ballooning of cerebral artery; may cause stroke Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
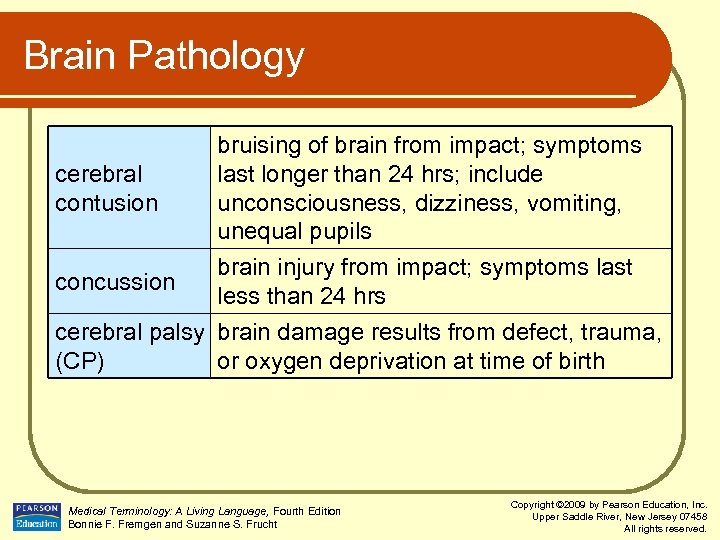 Brain Pathology cerebral contusion concussion bruising of brain from impact; symptoms last longer than 24 hrs; include unconsciousness, dizziness, vomiting, unequal pupils brain injury from impact; symptoms last less than 24 hrs cerebral palsy brain damage results from defect, trauma, (CP) or oxygen deprivation at time of birth Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Brain Pathology cerebral contusion concussion bruising of brain from impact; symptoms last longer than 24 hrs; include unconsciousness, dizziness, vomiting, unequal pupils brain injury from impact; symptoms last less than 24 hrs cerebral palsy brain damage results from defect, trauma, (CP) or oxygen deprivation at time of birth Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
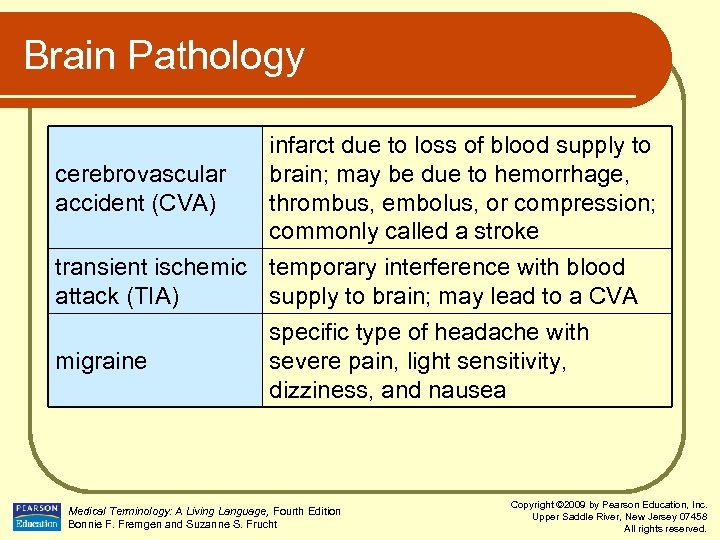 Brain Pathology infarct due to loss of blood supply to cerebrovascular brain; may be due to hemorrhage, accident (CVA) thrombus, embolus, or compression; commonly called a stroke transient ischemic temporary interference with blood attack (TIA) supply to brain; may lead to a CVA migraine specific type of headache with severe pain, light sensitivity, dizziness, and nausea Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Brain Pathology infarct due to loss of blood supply to cerebrovascular brain; may be due to hemorrhage, accident (CVA) thrombus, embolus, or compression; commonly called a stroke transient ischemic temporary interference with blood attack (TIA) supply to brain; may lead to a CVA migraine specific type of headache with severe pain, light sensitivity, dizziness, and nausea Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
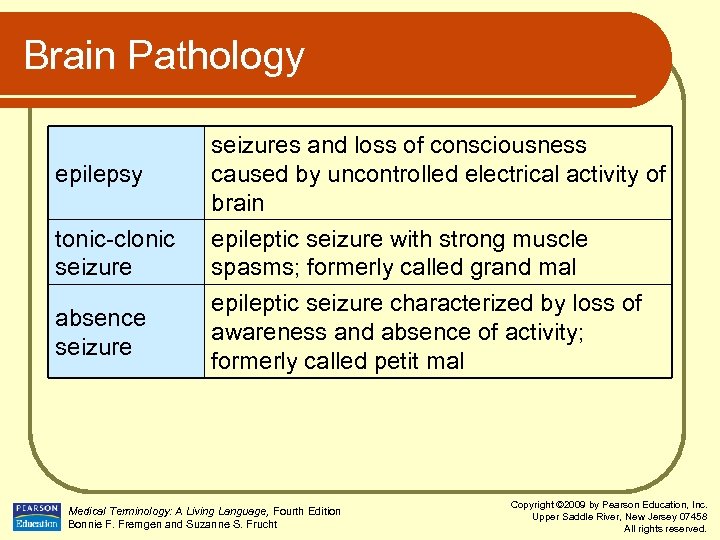 Brain Pathology epilepsy tonic-clonic seizure absence seizures and loss of consciousness caused by uncontrolled electrical activity of brain epileptic seizure with strong muscle spasms; formerly called grand mal epileptic seizure characterized by loss of awareness and absence of activity; formerly called petit mal Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Brain Pathology epilepsy tonic-clonic seizure absence seizures and loss of consciousness caused by uncontrolled electrical activity of brain epileptic seizure with strong muscle spasms; formerly called grand mal epileptic seizure characterized by loss of awareness and absence of activity; formerly called petit mal Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
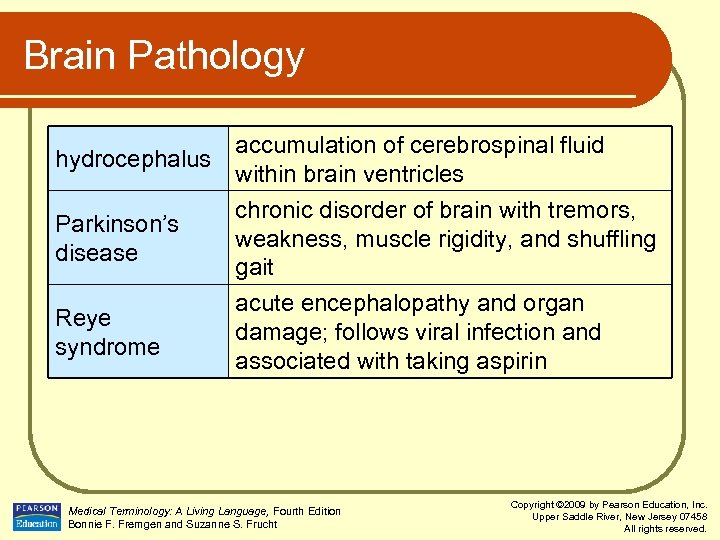 Brain Pathology hydrocephalus Parkinson’s disease Reye syndrome accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within brain ventricles chronic disorder of brain with tremors, weakness, muscle rigidity, and shuffling gait acute encephalopathy and organ damage; follows viral infection and associated with taking aspirin Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Brain Pathology hydrocephalus Parkinson’s disease Reye syndrome accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within brain ventricles chronic disorder of brain with tremors, weakness, muscle rigidity, and shuffling gait acute encephalopathy and organ damage; follows viral infection and associated with taking aspirin Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Spinal Cord Pathology amyotrophic degeneration of motor neurons of spinal lateral sclerosis cord; also called Lou Gehrig’s disease (ALS) viral infection affecting spinal cord; poliomyelitis paralysis may be mild and temporary or severe and permanent spinal cord injury (SCI) damage to spinal cord due to trauma; may be bruised and recover or severed and permanent Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Spinal Cord Pathology amyotrophic degeneration of motor neurons of spinal lateral sclerosis cord; also called Lou Gehrig’s disease (ALS) viral infection affecting spinal cord; poliomyelitis paralysis may be mild and temporary or severe and permanent spinal cord injury (SCI) damage to spinal cord due to trauma; may be bruised and recover or severed and permanent Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Spinal Cord Pathology spina bifida meningocele congenital defect where lamina of vertebra do not meet or close to form spinal canal protrusion of meninges sac through opening left by spina bifida defect protrusion of meninges and spinal myelomeningocele cord through opening left by spina bifida defect Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Spinal Cord Pathology spina bifida meningocele congenital defect where lamina of vertebra do not meet or close to form spinal canal protrusion of meninges sac through opening left by spina bifida defect protrusion of meninges and spinal myelomeningocele cord through opening left by spina bifida defect Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
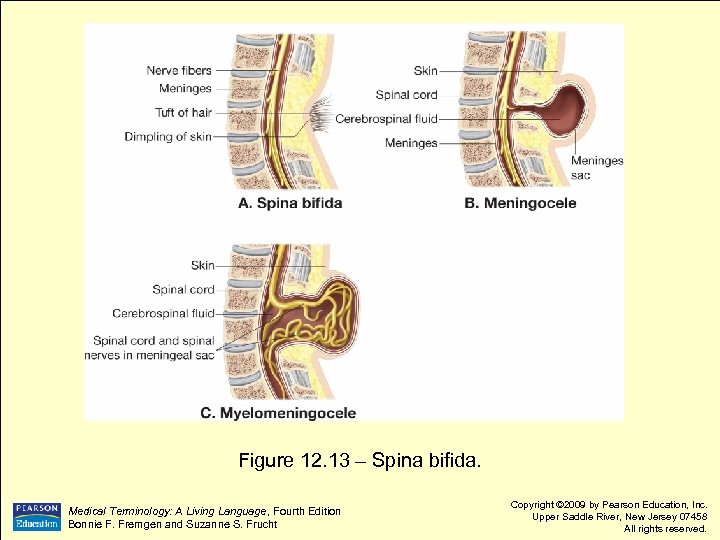 Figure 12. 13 – Spina bifida. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 13 – Spina bifida. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nerve Pathology one-sided facial paralysis due to Bell’s palsy inflammation of facial nerve caused by virus temporary loss of myelin sheath; may be Guillain-Barré autoimmune; starts in legs and syndrome progresses up nervous system multiple loss of myelin sheath; results in sclerosis (MS) weakness and numbness Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nerve Pathology one-sided facial paralysis due to Bell’s palsy inflammation of facial nerve caused by virus temporary loss of myelin sheath; may be Guillain-Barré autoimmune; starts in legs and syndrome progresses up nervous system multiple loss of myelin sheath; results in sclerosis (MS) weakness and numbness Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Nerve Pathology muscular weakness and fatigue due myasthenia gravis to insufficient neurotransmitter at synapses eruption of painful blisters on body shingles along a nerve path; caused by Herpes zoster virus Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nerve Pathology muscular weakness and fatigue due myasthenia gravis to insufficient neurotransmitter at synapses eruption of painful blisters on body shingles along a nerve path; caused by Herpes zoster virus Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Meninges Pathology epidural hematoma mass of blood in space outside dura mater subdural hematoma mass of blood forming inside subdural space; due to torn meningeal blood vessel; space occupying lesion Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Meninges Pathology epidural hematoma mass of blood in space outside dura mater subdural hematoma mass of blood forming inside subdural space; due to torn meningeal blood vessel; space occupying lesion Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
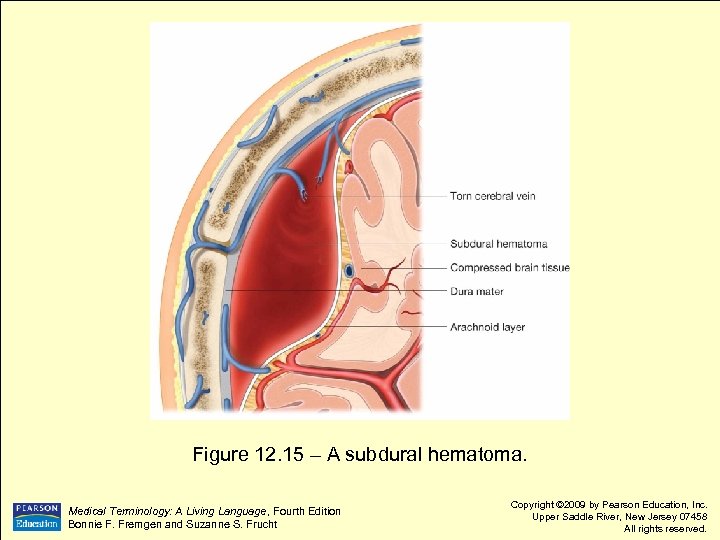 Figure 12. 15 – A subdural hematoma. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Figure 12. 15 – A subdural hematoma. Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
 Clinical Laboratory Tests cerebrospinal examination of CSF; may detect fluid analysis infections and blood in the fluid Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Clinical Laboratory Tests cerebrospinal examination of CSF; may detect fluid analysis infections and blood in the fluid Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
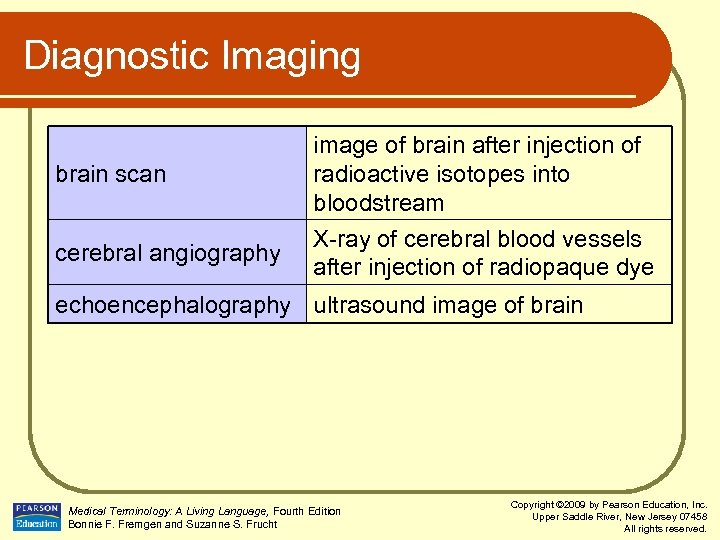 Diagnostic Imaging brain scan cerebral angiography image of brain after injection of radioactive isotopes into bloodstream X-ray of cerebral blood vessels after injection of radiopaque dye echoencephalography ultrasound image of brain Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Diagnostic Imaging brain scan cerebral angiography image of brain after injection of radioactive isotopes into bloodstream X-ray of cerebral blood vessels after injection of radiopaque dye echoencephalography ultrasound image of brain Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
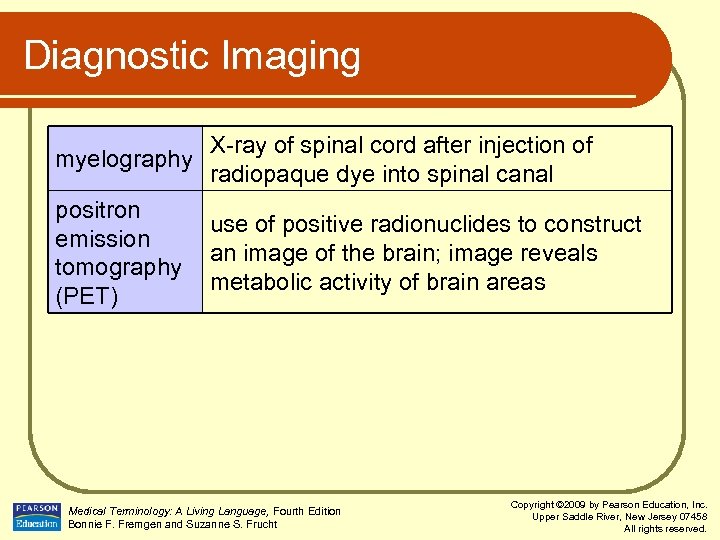 Diagnostic Imaging myelography X-ray of spinal cord after injection of radiopaque dye into spinal canal positron use of positive radionuclides to construct emission an image of the brain; image reveals tomography metabolic activity of brain areas (PET) Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Diagnostic Imaging myelography X-ray of spinal cord after injection of radiopaque dye into spinal canal positron use of positive radionuclides to construct emission an image of the brain; image reveals tomography metabolic activity of brain areas (PET) Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
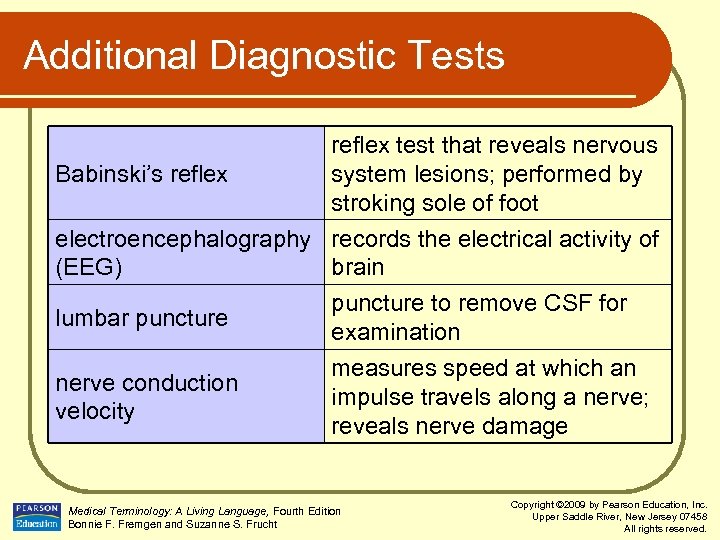 Additional Diagnostic Tests reflex test that reveals nervous Babinski’s reflex system lesions; performed by stroking sole of foot electroencephalography records the electrical activity of (EEG) brain lumbar puncture nerve conduction velocity puncture to remove CSF for examination measures speed at which an impulse travels along a nerve; reveals nerve damage Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Additional Diagnostic Tests reflex test that reveals nervous Babinski’s reflex system lesions; performed by stroking sole of foot electroencephalography records the electrical activity of (EEG) brain lumbar puncture nerve conduction velocity puncture to remove CSF for examination measures speed at which an impulse travels along a nerve; reveals nerve damage Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
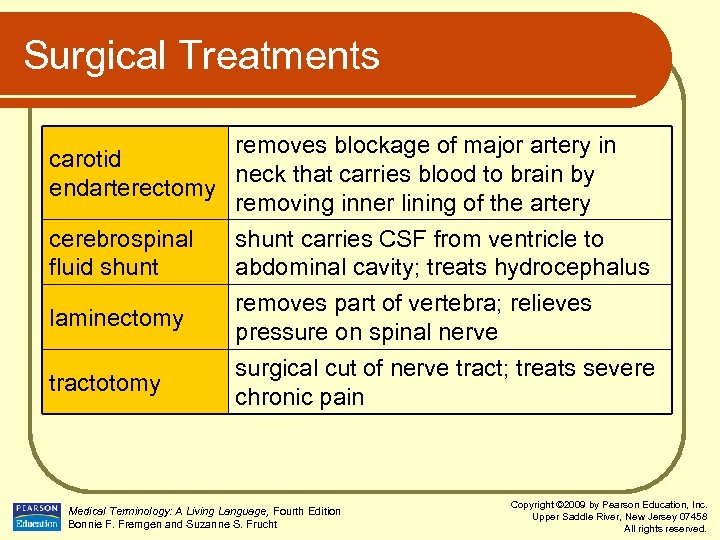 Surgical Treatments removes blockage of major artery in carotid neck that carries blood to brain by endarterectomy removing inner lining of the artery cerebrospinal shunt carries CSF from ventricle to fluid shunt abdominal cavity; treats hydrocephalus laminectomy tractotomy removes part of vertebra; relieves pressure on spinal nerve surgical cut of nerve tract; treats severe chronic pain Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Surgical Treatments removes blockage of major artery in carotid neck that carries blood to brain by endarterectomy removing inner lining of the artery cerebrospinal shunt carries CSF from ventricle to fluid shunt abdominal cavity; treats hydrocephalus laminectomy tractotomy removes part of vertebra; relieves pressure on spinal nerve surgical cut of nerve tract; treats severe chronic pain Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
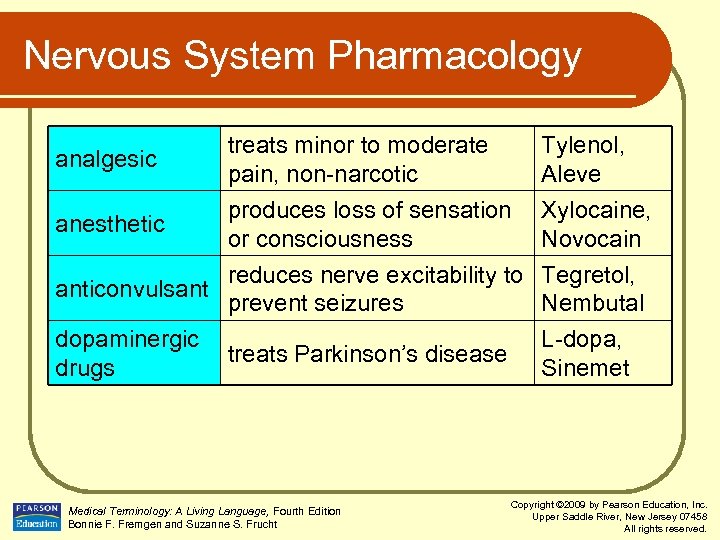 Nervous System Pharmacology analgesic treats minor to moderate pain, non-narcotic Tylenol, Aleve produces loss of sensation anesthetic or consciousness reduces nerve excitability to anticonvulsant prevent seizures Xylocaine, Novocain Tegretol, Nembutal dopaminergic treats Parkinson’s disease drugs L-dopa, Sinemet Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Pharmacology analgesic treats minor to moderate pain, non-narcotic Tylenol, Aleve produces loss of sensation anesthetic or consciousness reduces nerve excitability to anticonvulsant prevent seizures Xylocaine, Novocain Tegretol, Nembutal dopaminergic treats Parkinson’s disease drugs L-dopa, Sinemet Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
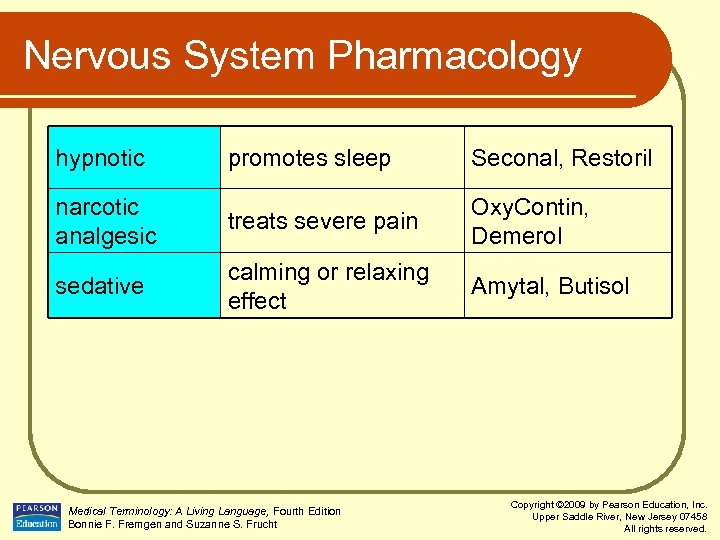 Nervous System Pharmacology hypnotic promotes sleep Seconal, Restoril narcotic analgesic treats severe pain Oxy. Contin, Demerol sedative calming or relaxing effect Amytal, Butisol Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Nervous System Pharmacology hypnotic promotes sleep Seconal, Restoril narcotic analgesic treats severe pain Oxy. Contin, Demerol sedative calming or relaxing effect Amytal, Butisol Medical Terminology: A Living Language, Fourth Edition Bonnie F. Fremgen and Suzanne S. Frucht Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.


