MEDIA TRENDS2015-2020.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 MEDIA TRENDS 20152020
MEDIA TRENDS 20152020
 Competitions You under attack !
Competitions You under attack !
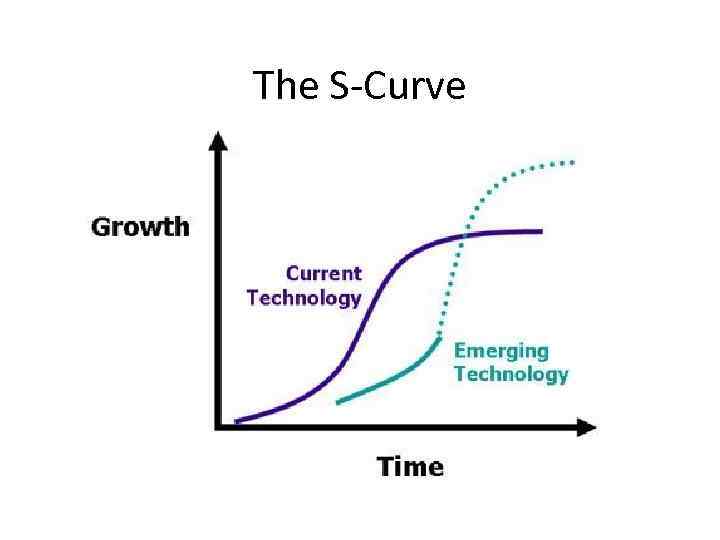 The S-Curve
The S-Curve
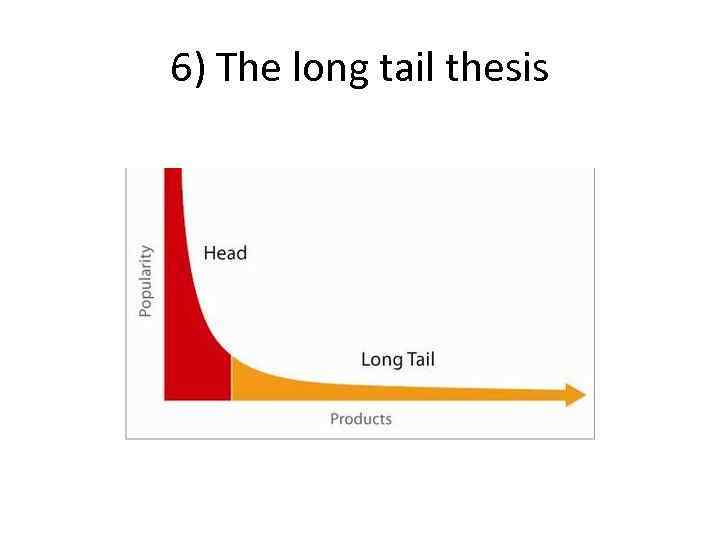 6) The long tail thesis
6) The long tail thesis
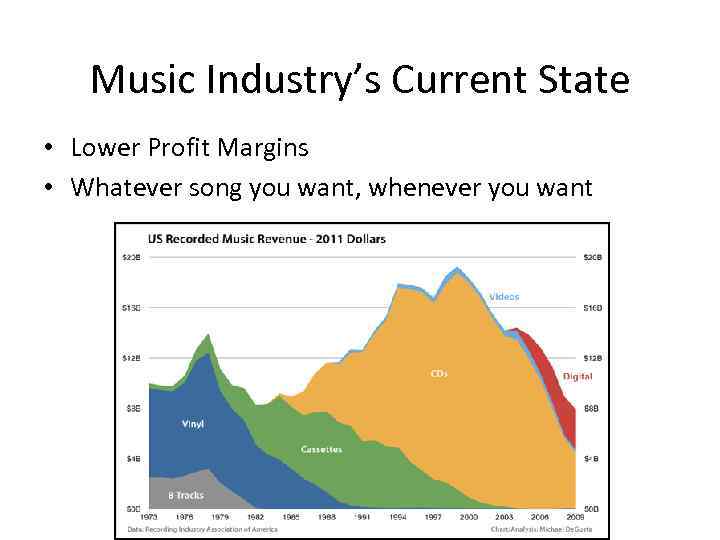 Music Industry’s Current State • Lower Profit Margins • Whatever song you want, whenever you want
Music Industry’s Current State • Lower Profit Margins • Whatever song you want, whenever you want
![Some trends • Forecasts for 2011 [IDC White Paper, March 2008 ] – (Mostly) Some trends • Forecasts for 2011 [IDC White Paper, March 2008 ] – (Mostly)](https://present5.com/presentation/-76548429_330198691/image-6.jpg) Some trends • Forecasts for 2011 [IDC White Paper, March 2008 ] – (Mostly) ‘Visual’ digital universe • Growth in size from 281 exabytes in 2007 to 1800 exabytes in 2011 – (exa = 1018; still less than Avogadro’s 1023). Towards a 2020 vision – Physical information overload • 2011 Information created (X) ~ 1800 Exabytes • 2011 Available storage (Y) ~ 800 Exabytes • X – Y = ~ 1000 Exab – (Higher) Storage consumption • growth of storage consumption underestimated by 10% for the period 2007 -2010 due to growing consumer needs – … Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 6 6
Some trends • Forecasts for 2011 [IDC White Paper, March 2008 ] – (Mostly) ‘Visual’ digital universe • Growth in size from 281 exabytes in 2007 to 1800 exabytes in 2011 – (exa = 1018; still less than Avogadro’s 1023). Towards a 2020 vision – Physical information overload • 2011 Information created (X) ~ 1800 Exabytes • 2011 Available storage (Y) ~ 800 Exabytes • X – Y = ~ 1000 Exab – (Higher) Storage consumption • growth of storage consumption underestimated by 10% for the period 2007 -2010 due to growing consumer needs – … Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 6 6
![Some trends • Forecasts for 2011 [IDC White Paper, March 2008 ] – Diversity Some trends • Forecasts for 2011 [IDC White Paper, March 2008 ] – Diversity](https://present5.com/presentation/-76548429_330198691/image-7.jpg) Some trends • Forecasts for 2011 [IDC White Paper, March 2008 ] – Diversity (production & content) Towards a 2020 vision • More than 70% of the digital universe is created, captured or replicated by individuals, but – enterprises are responsible and liable for 85% of this volume with regard to security, privacy protection, copyright protection, screening, fraud detection, etc. – Industry (responsible & liable for) distribution • the financial services industry accounts for 6% of the worldwide gross economic output with a share of 6% of the digital universe • the broadcast, media and entertainment industries account for 4% of the worldwide gross economic output with a share of 50% of the digital universe • the 100 million daily video streams of You. Tube account for almost as much as all of medical imaging Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 7 7
Some trends • Forecasts for 2011 [IDC White Paper, March 2008 ] – Diversity (production & content) Towards a 2020 vision • More than 70% of the digital universe is created, captured or replicated by individuals, but – enterprises are responsible and liable for 85% of this volume with regard to security, privacy protection, copyright protection, screening, fraud detection, etc. – Industry (responsible & liable for) distribution • the financial services industry accounts for 6% of the worldwide gross economic output with a share of 6% of the digital universe • the broadcast, media and entertainment industries account for 4% of the worldwide gross economic output with a share of 50% of the digital universe • the 100 million daily video streams of You. Tube account for almost as much as all of medical imaging Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 7 7
 The vision for 2015 • The NEM Initiative hopes that by 2015 electronic media will appear as a ubiquitous service, easily and simply available to all users for professional and recreational purposes. • The distinction between today’s basic routing technologies – such as unicast, multicast and broadcast – must become invisible, not only to the user but also the media application itself; • Media must become networkable, an integral part of any kind of network rather than just something to be transmitted from A to B; • Media must become ubiquitous; content will come from any user, with highly sophisticated and user-friendly indexing engines to generate the accompanying metadata; • The infrastructure must become context-aware, recognising users to know their needs, and adapting itself to the environment; • Intuitive and multi-modal interfaces must offer a more natural way to interact with and within media environments; Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 8
The vision for 2015 • The NEM Initiative hopes that by 2015 electronic media will appear as a ubiquitous service, easily and simply available to all users for professional and recreational purposes. • The distinction between today’s basic routing technologies – such as unicast, multicast and broadcast – must become invisible, not only to the user but also the media application itself; • Media must become networkable, an integral part of any kind of network rather than just something to be transmitted from A to B; • Media must become ubiquitous; content will come from any user, with highly sophisticated and user-friendly indexing engines to generate the accompanying metadata; • The infrastructure must become context-aware, recognising users to know their needs, and adapting itself to the environment; • Intuitive and multi-modal interfaces must offer a more natural way to interact with and within media environments; Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 8
 The vision for 2015 • To make networked media communication inclusively available to all, using or consuming any kind of media should be known by its content and not by the technology used (‘FM’, ‘MP 3’, ‘DVB’ etc. ). • Media retrieval must become affective, using genre-based playlists representing moods and degrees of user involvement; • Networked media should allow new groups to form, for social or business purposes, defined by their media interests; • Video must be represented in a much more human way, by realistically modelling entire media environments on an object-byobject basis, offering exciting new creative possibilities; • There must be seamless and intuitive service handover between devices and environments, allowing users to access services wherever they are, whatever terminal they are using; • ‘Federated’ services – complex services built up from multiple elements from different originators – must be enabled, offering valuable commercial opportunities for service differentiation; Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 9
The vision for 2015 • To make networked media communication inclusively available to all, using or consuming any kind of media should be known by its content and not by the technology used (‘FM’, ‘MP 3’, ‘DVB’ etc. ). • Media retrieval must become affective, using genre-based playlists representing moods and degrees of user involvement; • Networked media should allow new groups to form, for social or business purposes, defined by their media interests; • Video must be represented in a much more human way, by realistically modelling entire media environments on an object-byobject basis, offering exciting new creative possibilities; • There must be seamless and intuitive service handover between devices and environments, allowing users to access services wherever they are, whatever terminal they are using; • ‘Federated’ services – complex services built up from multiple elements from different originators – must be enabled, offering valuable commercial opportunities for service differentiation; Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 9
 Strategic Research Agenda • Most important research topics Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 10
Strategic Research Agenda • Most important research topics Waterloo, 23 -24 March 2011 Canada-EU Future Internet Workshop 10
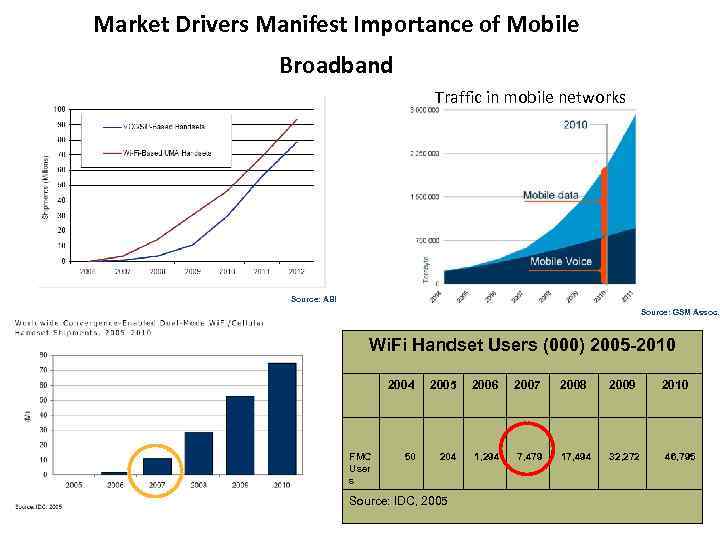 Market Drivers Manifest Importance of Mobile Broadband Traffic in mobile networks Source: ABI Source: GSM Assoc. Wi. Fi Handset Users (000) 2005 -2010 2004 FMC User s 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 50 204 1, 294 7, 479 17, 494 32, 272 Source: IDC, 2005 2010 46, 795
Market Drivers Manifest Importance of Mobile Broadband Traffic in mobile networks Source: ABI Source: GSM Assoc. Wi. Fi Handset Users (000) 2005 -2010 2004 FMC User s 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 50 204 1, 294 7, 479 17, 494 32, 272 Source: IDC, 2005 2010 46, 795
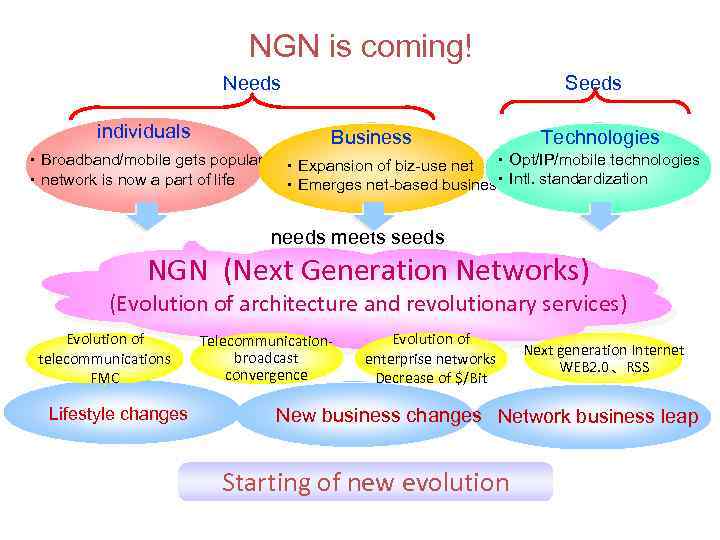 NGN is coming! Needs individuals Seeds Business ・Broadband/mobile gets popular ・network is now a part of life Technologies ・Expansion of biz-use net ・Opt/IP/mobile technologies ・Intl. standardization ・Emerges net-based business needs meets seeds NGN (Next Generation Networks) (Evolution of architecture and revolutionary services) Evolution of telecommunications FMC Lifestyle changes Telecommunicationbroadcast convergence Evolution of enterprise networks Decrease of $/Bit Next generation Internet WEB 2. 0、RSS New business changes Network business leap Starting of new evolution
NGN is coming! Needs individuals Seeds Business ・Broadband/mobile gets popular ・network is now a part of life Technologies ・Expansion of biz-use net ・Opt/IP/mobile technologies ・Intl. standardization ・Emerges net-based business needs meets seeds NGN (Next Generation Networks) (Evolution of architecture and revolutionary services) Evolution of telecommunications FMC Lifestyle changes Telecommunicationbroadcast convergence Evolution of enterprise networks Decrease of $/Bit Next generation Internet WEB 2. 0、RSS New business changes Network business leap Starting of new evolution
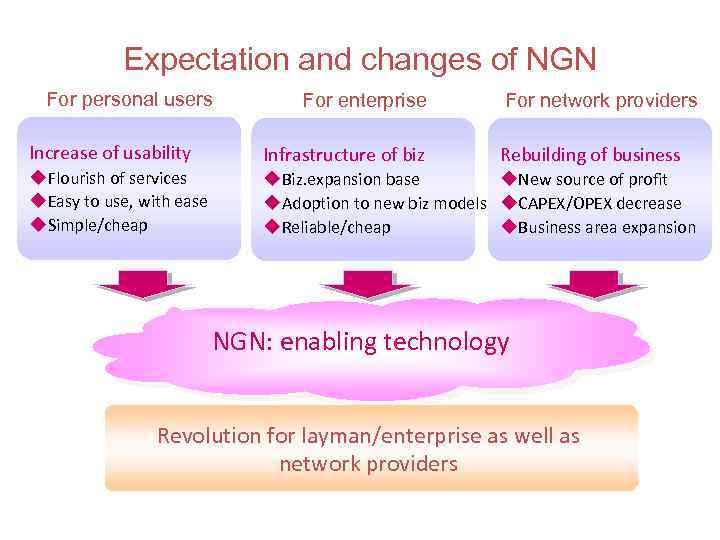 Expectation and changes of NGN For personal users For enterprise For network providers Increase of usability Infrastructure of biz u. Flourish of services u. Easy to use, with ease u. Simple/cheap u. Biz. expansion base u. New source of profit u. Adoption to new biz models u. CAPEX/OPEX decrease u. Reliable/cheap u. Business area expansion Rebuilding of business NGN: enabling technology Revolution for layman/enterprise as well as network providers
Expectation and changes of NGN For personal users For enterprise For network providers Increase of usability Infrastructure of biz u. Flourish of services u. Easy to use, with ease u. Simple/cheap u. Biz. expansion base u. New source of profit u. Adoption to new biz models u. CAPEX/OPEX decrease u. Reliable/cheap u. Business area expansion Rebuilding of business NGN: enabling technology Revolution for layman/enterprise as well as network providers
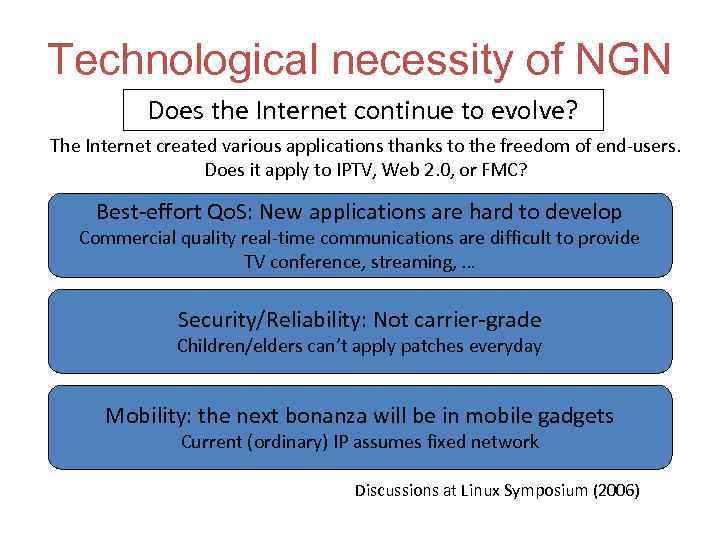 Technological necessity of NGN Does the Internet continue to evolve? The Internet created various applications thanks to the freedom of end-users. Does it apply to IPTV, Web 2. 0, or FMC? Best-effort Qo. S: New applications are hard to develop Commercial quality real-time communications are difficult to provide TV conference, streaming, … Security/Reliability: Not carrier-grade Children/elders can’t apply patches everyday Mobility: the next bonanza will be in mobile gadgets Current (ordinary) IP assumes fixed network Discussions at Linux Symposium (2006)
Technological necessity of NGN Does the Internet continue to evolve? The Internet created various applications thanks to the freedom of end-users. Does it apply to IPTV, Web 2. 0, or FMC? Best-effort Qo. S: New applications are hard to develop Commercial quality real-time communications are difficult to provide TV conference, streaming, … Security/Reliability: Not carrier-grade Children/elders can’t apply patches everyday Mobility: the next bonanza will be in mobile gadgets Current (ordinary) IP assumes fixed network Discussions at Linux Symposium (2006)
 Future of print • Future of print is closely related to the future of advertising • Advertising is a big demand driver for print – Newspaper and magazine publishers would not exist without advertising • Between 50%-60% of newspaper revenues comes from advertising* – Direct Mail – Other promotional applications * - Info. Trends estimates; 53% of revenues from German Newspapers stem from advertising in 2007, German Newspaper Publishing Association (BDZV)
Future of print • Future of print is closely related to the future of advertising • Advertising is a big demand driver for print – Newspaper and magazine publishers would not exist without advertising • Between 50%-60% of newspaper revenues comes from advertising* – Direct Mail – Other promotional applications * - Info. Trends estimates; 53% of revenues from German Newspapers stem from advertising in 2007, German Newspaper Publishing Association (BDZV)
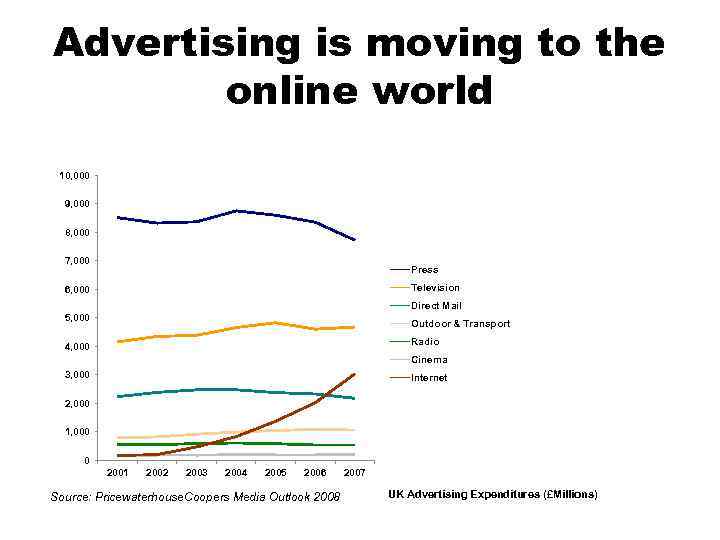 Advertising is moving to the online world 10, 000 9, 000 8, 000 7, 000 Press Television 6, 000 Direct Mail 5, 000 Outdoor & Transport Radio 4, 000 Cinema 3, 000 Internet 2, 000 1, 000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Source: Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Media Outlook 2008 2007 UK Advertising Expenditures (£Millions)
Advertising is moving to the online world 10, 000 9, 000 8, 000 7, 000 Press Television 6, 000 Direct Mail 5, 000 Outdoor & Transport Radio 4, 000 Cinema 3, 000 Internet 2, 000 1, 000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Source: Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Media Outlook 2008 2007 UK Advertising Expenditures (£Millions)
 Local Publishing / Micro-zone Publishing • Local / Micro-Zone Publishing Local “journalists” use an online portal to submit stories, photos, and community events for the neighbourhood’s community Web site and print product • Triblocal Example of a Micro-Zone website where people can upload local stories and pictures which will be printed in a local newspaper (Chicago Tribune)
Local Publishing / Micro-zone Publishing • Local / Micro-Zone Publishing Local “journalists” use an online portal to submit stories, photos, and community events for the neighbourhood’s community Web site and print product • Triblocal Example of a Micro-Zone website where people can upload local stories and pictures which will be printed in a local newspaper (Chicago Tribune)
 Reverse Publishing • • • Reverse Publishing Inverts the publication process. Takes existing online (user generated) content and makes them available in printed form Example: www. Shared. Book. com Technology to gather content from blogs or websites and print them in a book. Allows for annotations and even some customisation. Example: www. Hot. Print. com UK company that develops software to create photo books from Face. Book
Reverse Publishing • • • Reverse Publishing Inverts the publication process. Takes existing online (user generated) content and makes them available in printed form Example: www. Shared. Book. com Technology to gather content from blogs or websites and print them in a book. Allows for annotations and even some customisation. Example: www. Hot. Print. com UK company that develops software to create photo books from Face. Book
 Self Publishing • • Self Publishing of books and other media by the authors of those works, rather than by established, third-party publishers Example: Mag. Cloud Website where writers can publish their own magazine. Mag. Cloud takes care of printing and fulfillment. Mag. Cloud is an initiative that allows for self-publishing of magazines
Self Publishing • • Self Publishing of books and other media by the authors of those works, rather than by established, third-party publishers Example: Mag. Cloud Website where writers can publish their own magazine. Mag. Cloud takes care of printing and fulfillment. Mag. Cloud is an initiative that allows for self-publishing of magazines
 Tailored Publishing • • Tailored Publishing of magazines or other media where users can pick and choose the content Example: Mine from Time. CMG is a website where users can indicate their interests and preferences by choosing content from up to 5 different magazines Mine from Time. CMG is a website where users can pick content from up to 5 different magazines
Tailored Publishing • • Tailored Publishing of magazines or other media where users can pick and choose the content Example: Mine from Time. CMG is a website where users can indicate their interests and preferences by choosing content from up to 5 different magazines Mine from Time. CMG is a website where users can pick content from up to 5 different magazines
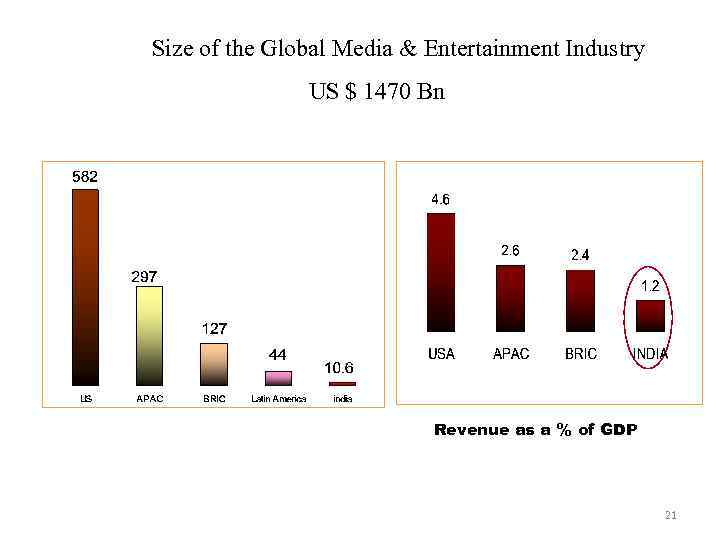 Global M & E Industry: Overview Size of the Global Media & Entertainment Industry US $ 1470 Bn Revenue as a % of GDP 21
Global M & E Industry: Overview Size of the Global Media & Entertainment Industry US $ 1470 Bn Revenue as a % of GDP 21
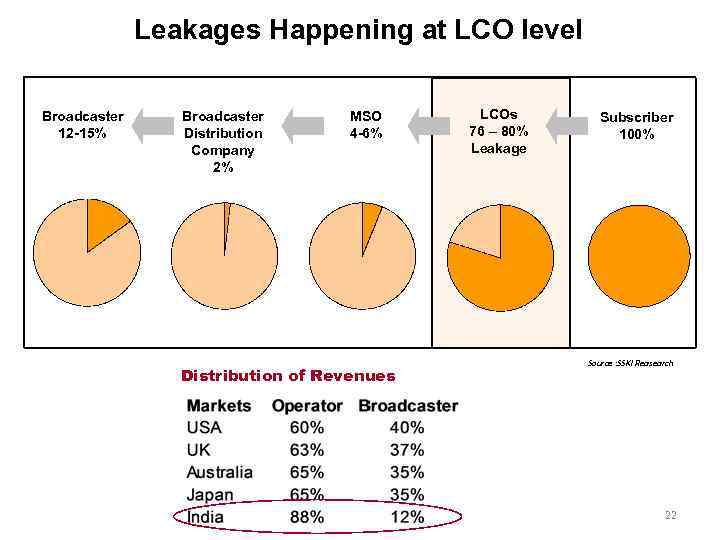 Leakages Happening at LCO level Broadcaster 12 -15% Broadcaster Distribution Company 2% MSO 4 -6% Distribution of Revenues LCOs 76 – 80% Leakage Subscriber 100% Source : SSKI Reasearch 22
Leakages Happening at LCO level Broadcaster 12 -15% Broadcaster Distribution Company 2% MSO 4 -6% Distribution of Revenues LCOs 76 – 80% Leakage Subscriber 100% Source : SSKI Reasearch 22
 The Romanticized History
The Romanticized History


