984e01c2f183aa6d2e38924ba4e8b683.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

MEDIA LAB ASIA CRAFT REVIVAL PROJECT INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KANPUR 1

Objective: Objective In Lucknow Chickan Embroidery, the present practice of using wooden blocks to convert designs is time consuming and expensive, with limited variations in design. The project intends in concentrating on Lucknow Chickan embroidery. The present project would like to investigate and develop the following areas. Understanding the contemporary design style and the past the heritage. 2

Using Computer Aided Design(CAD), developing new motifs and composition of past Indian and original Persian design motifs. The project would also develop hand-held computer printer, in place of block for easy transferring design directly from the computer to the fabric surface. 3

Project Goals: Goals Developing a design tool : Using Computer Aided Design(CAD), developing an in house software tool for making Chikan Embroidery. Developing a printer : Developing a hand-held computer printer for easy transferring designs directly from the computer on to the fabric surface Conclusion: Conclusion Using this software it is possible to make many deigns with lots of variations and takes less time than Traditional Chikan Embroidery. 4

Description: Chic is a 2 D graphics and diagram editor for Windows system and it is user friendly. In order for Chic to run you need to have JDK installed on your system. Chic should run on all Java compatible platforms like Windows 9 x/NT/2000. 5
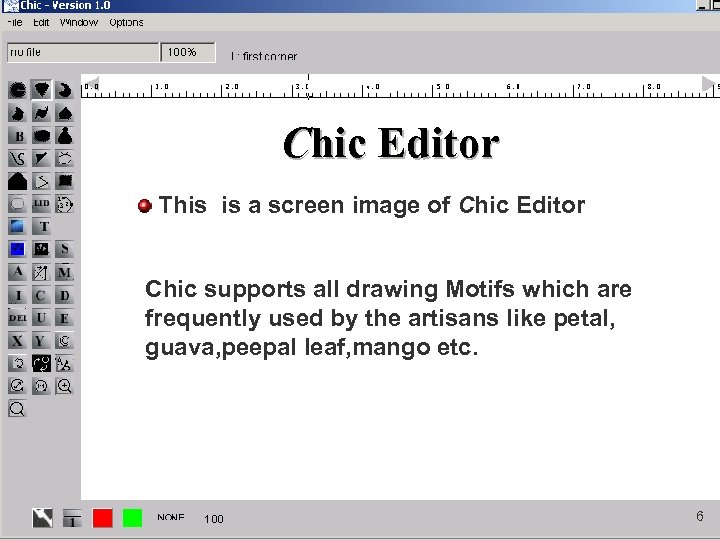
Chic Editor This is a screen image of Chic Editor Chic supports all drawing Motifs which are frequently used by the artisans like petal, guava, peepal leaf, mango etc. 6

Motifs These are the basic Motifs used for drawing. 7
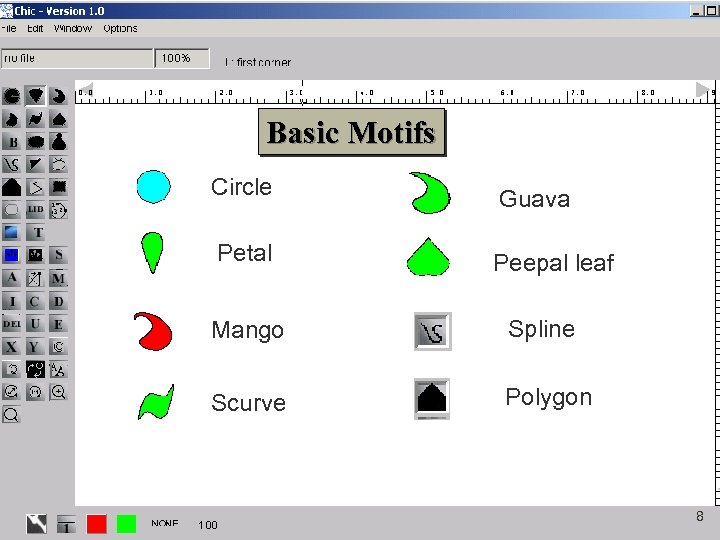
Basic Motifs Circle Guava Petal Peepal leaf Mango Spline Scurve Polygon 8
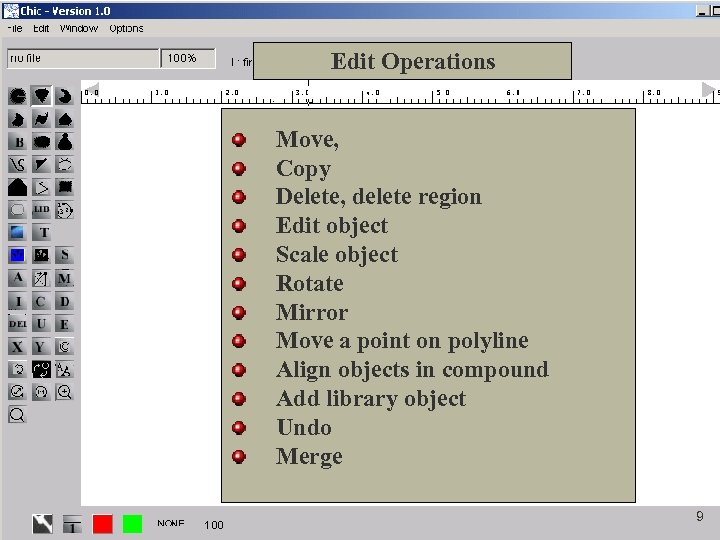
Edit Operations Move, Copy Delete, delete region Edit object Scale object Rotate Mirror Move a point on polyline Align objects in compound Add library object Undo Merge 9

These buttons are for Edit Operations Copy Motif: Using this function we can make a replica of the original object Move Motif: This function is used to move an object from one point on the screen to another. Delete Motif: This function is used to remove an object from the screen. 10

These buttons are for Edit Operations Group (compound) : This function is used to make a Single compound Motif from individual Motifs. Library : The library objects are built in designs which contain different Motifs for Chikan designing. 11

These buttons are for Edit Operations Copy Motif: Using this function we can make a replica of the original object Original Duplicate 12
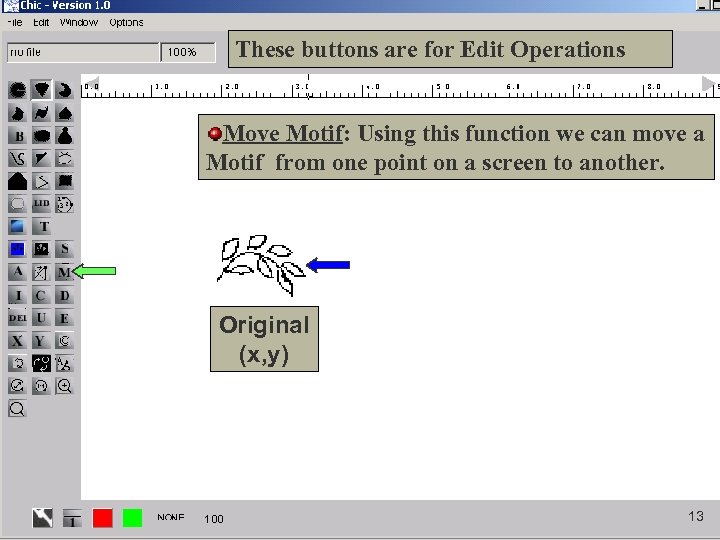
These buttons are for Edit Operations Move Motif: Using this function we can move a Motif from one point on a screen to another. Original (x, y) 13
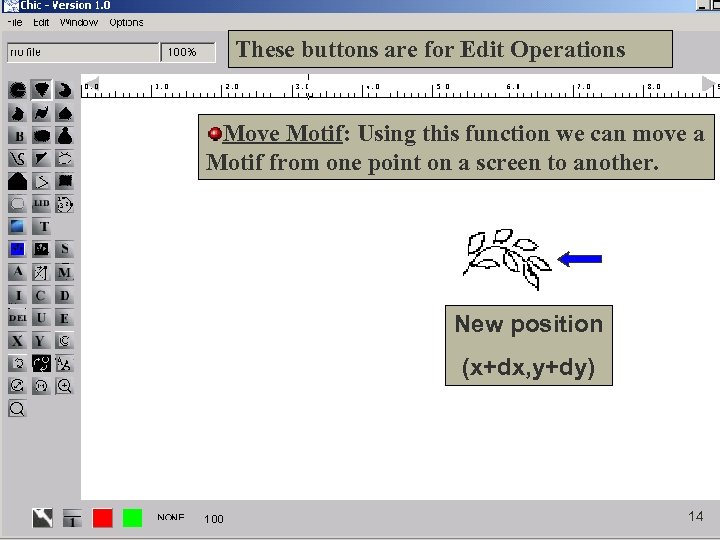
These buttons are for Edit Operations Move Motif: Using this function we can move a Motif from one point on a screen to another. New position (x+dx, y+dy) 14
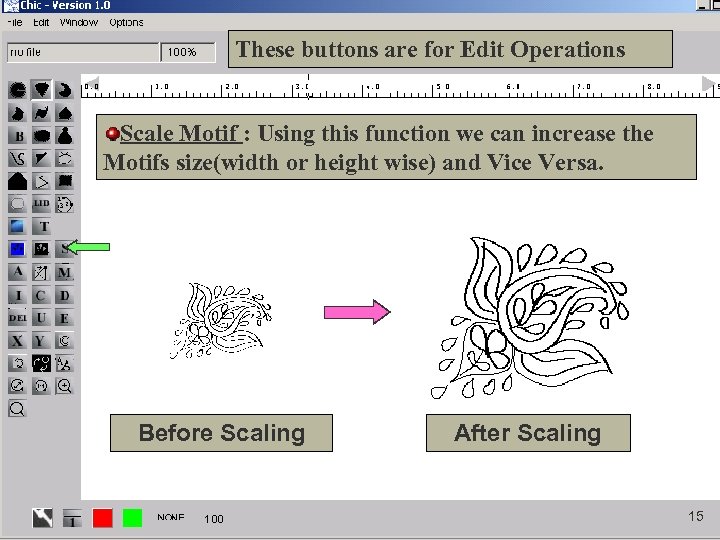
These buttons are for Edit Operations Scale Motif : Using this function we can increase the Motifs size(width or height wise) and Vice Versa. Before Scaling After Scaling 15

Library Motifs 16
Library Motifs Simple Motifs 17
Complex Motifs 18

Complex Motifs 19
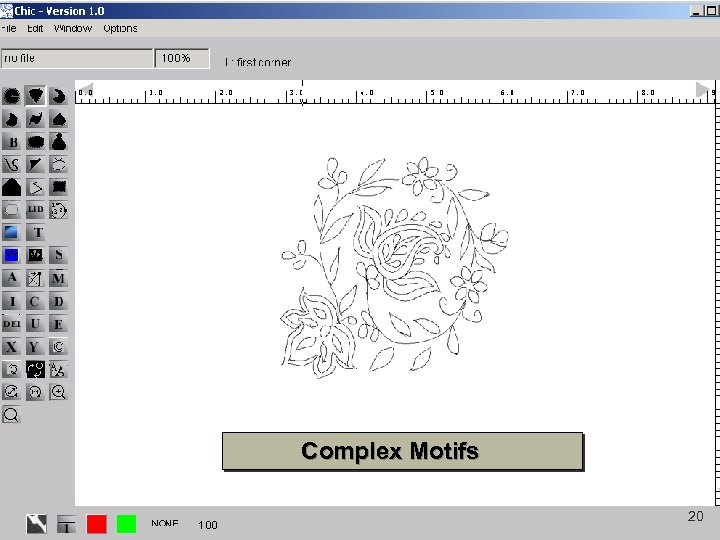
Complex Motifs 20

Various Designs The above Composition is a combination of complex motifs 21
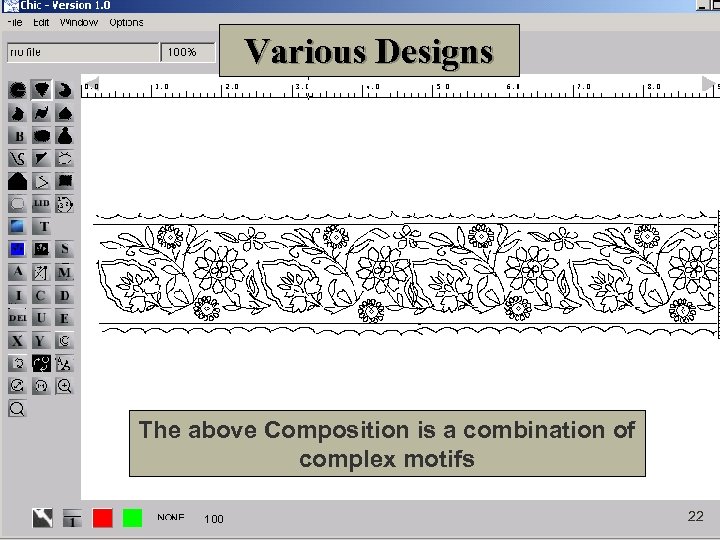
Various Designs The above Composition is a combination of complex motifs 22

Cultural Aspects Of Motifs: Traditional Chikan design: Traditional Persian design: The earliest mention of word Chikan goes back to Persia. Its literal translation is Embroidery. It is believed that the history of Chikan Embroidery goes back to the 3 rd century B. C 23

Indian Tradition : The overall embroidery of Chikan work is divided into thirty-two stitches. The popular types are Taipchi , Bakia or Shadow Work , Phanda, Khatau, Murri, Jali, Hatkati, Penchi, Ghas Patti, Channa Patti, Chikana Phanda, Bijali. Malmal and organdie were the common fabrics used for Chikan Embroidery. Presently it is being done on voil, lenin, rubia , chiffon , Terri cotton and georgette, silk. It used to be done on white fabric with white thread therefore, called as white embroidery. 24

Persian Tradition Persian Art reached its peak during Timural time (1405) in Bagdad , Hirut, Summerkhand. It was brought to India by Mughal Emperors. Earlier work is known as Irani Kam. Persian decorative designs were popular on floors, walls roofs, carpets, etc. They past on to India and synthesized in different forms. Lucknowi Chikan design is a synthesis of Persian design on Indian soil. 25

END 26
984e01c2f183aa6d2e38924ba4e8b683.ppt