f8f14097ef492805ef5d67327481137d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75

Media Distribution Management Platform and IPTV over Internet 2 Tereza Cristina Melo de Brito Carvalho carvalho@larc. usp. br Regina Melo Silveira regina@larc. usp. br Christiane Marie Schweitzer chrism@larc. usp. br LARC- Laboratory of Computer Network Architecture EPUSP – Escola Politecnica Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member University of São Paulo - Brazil 4 -7 December, 2006 Meeting

IPTV over Internet 2 Tereza Cristina Melo de Brito Carvalho carvalho@larc. usp. br Regina Melo Silveira regina@larc. usp. br LARC – PCS/EP – University of São Paulo Ericsson Research Sweden Kyatera Project – TIDIA Program - FAPESP Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member 4 -7 December, 2006 Meeting

Team Ayodele Damola ayodele. damola@ericsson. com Marcio Augusto Lima e Silva msilva@larc. usp. br Christiane Marie Schweitzer christiane. schweitzer@ufabc. edu. br Regina Melo Silveira regina@larc. usp. br Daniel Pires dpires@larc. usp. br Diego Sanchez Gallo dsgallo@larc. usp. br Flávio Urschei furschei@larc. usp. br 4 -7 December, 2006 Tereza Cristina Melo de Brito Carvalho carvalho@larc. usp. br Wilson Vicente Ruggiero wilson@larc. usp. br Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 3

Agenda Introduction ¡ Scenario ¡ Requirements ¡ IPTV Architecture ¡ IPTV over Internet 2 ¡ Final Considerations ¡ Acknowledgments ¡ 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 4
Introduction ¡ What is IPTV? l l ¡ TV Channels over the Internet ? Video streams encapsulated in IP packets over a “service provider” network ? Will Internet support a High Definition IPTV Service? “Internet no ready for its future roles” (Bill St. Arnaud) 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 5

Scenario ¡ High Definition Streamings (HDTV) l ¡ Typically, 25 Mbps per TV Channel for MPEG 2 encoding. Multiple channels sent simultaneously to multiple receivers at a same location. l 4 -7 December, 2006 A home with three TV sets would require at least 3 x 25 Mbps. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 6
Scenario ¡ IPTV requires high levels of: l l Quality of Service (Qo. S) Quality of Experience (Qo. E) … at least on par with analog or digital TV broadcast system. ¡ Access networks technologies like x. DSL do not support high definition IPTV services: l 4 -7 December, 2006 VDSL has bandwidth and distance limitations. It achieves 50 Mbps at 300 m. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 7
Scenario ¡ Currently, FTTH (Fiber-To-The-Home) services seems to be the only one alternative for the fulfillment of IPTV (HDTV) needs ¡ PON (Passive Optical Network) presents itself as the most viable FTTH technology, both from economical and operational standpoint l 4 -7 December, 2006 WDM-PON can provide 100 Mbps fiber connection far beyond 300 m – around tens of kilometers) Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 8

Requirements ¡ Security l Content protection: protection of the intellectual property of the content owner, while allowing fair use for the final user. l Service protection: authentication, confidentiality and access control. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 9
Requirements ¡ Quality of Experience (simple and convenient handling): l l ¡ Multi-channel. Zapping. Infrastructure: l l l 4 -7 December, 2006 Availability (at least on par with analog or digital TV broadcast system). Accessibility (diversity of devices – e. g. PCs, Set-Top-Boxes). Network/Application scalability. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 10
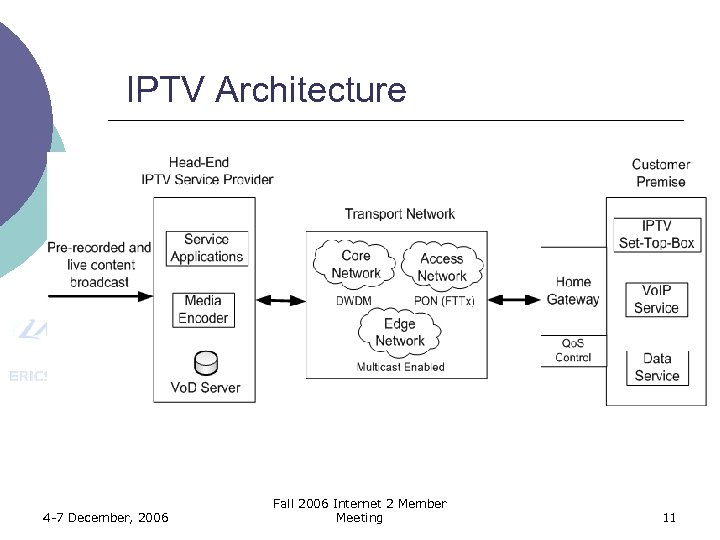
IPTV Architecture 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 11
Architecture Entities ¡ ¡ ¡ Head-End: provides IPTV services (Broadcast TV and Vo. D). Transport Network: delivers video streams to the customers. Customer Premises: broadband network termination. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 12
IPTV Architecture: Head-End ¡ Broadcast TV Head-End system: l l l 4 -7 December, 2006 Receives an analog or digital signal via satellite or other mean, typically with multiple transport streams. Converts it to a series of single program streams. Encodes or transcodes the signals (e. g. to MPEG-4 format). Encapsulates streams in IP packets for transmission. Sends streams to a specific IP multicast group Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 13
IPTV Architecture: Head-End ¡ Vo. D (Video-On-Demand) Head. End System: l l 4 -7 December, 2006 Encapsulates video streams in IP packets. Sends streams to the users. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 14
IPTV Architecture: Transport Network ¡ Core Network: l ¡ Edge Network: l ¡ High capacity optical network with technologies such as IP over DWDM and MPLS/GMPLS. Multicast enabled network that connects the core network to the access network. Access Network: l 4 -7 December, 2006 It is a FTTH-PON (Fiber-To-The-Home Passive Optical Network). Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 15
IPTV Architecture: Customer Premise ¡ Provides broadband network termination functionalities. ¡ It is the IPTV service client. ¡ The heterogeneous technologies existing in a home network devices lead to the need for a robust Home Gateway to connect it, providing the necessary services. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 16
Multicast X Overlay ¡ Overlay tries to provide multicast functionalities at the application layer: l ¡ ¡ It is still a immature solution to provide a reliable and Qo. E enabled service for Highdefinition content with scalability. Multicast is proven to be a more efficient distribution scheme with scalability. This work proposes an auto-contained, controlled private network: l 4 -7 December, 2006 Internet does (still) not provide the required levels of availability, scalability, Qo. E and Qo. S. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 17
IPTV over Internet 2 Demonstration ¡ ¡ Creation of an infrastructure for High Definition Streamings (HDTV) support Specification and performance evaluation of high definition video distribution experiments 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 18
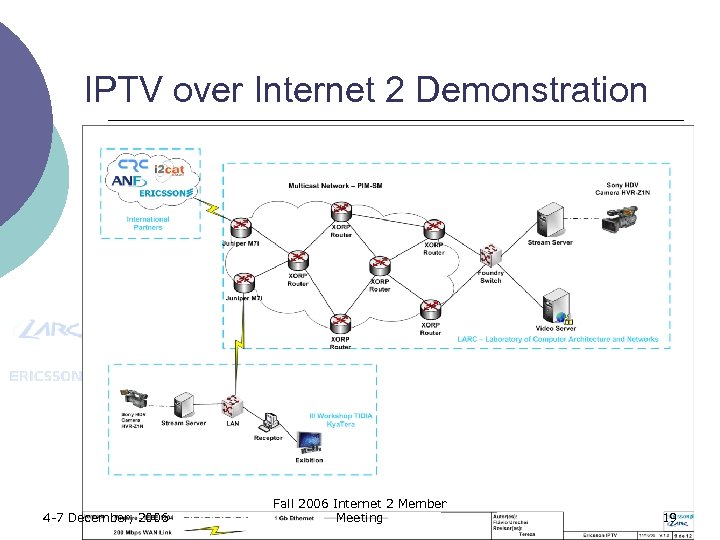
IPTV over Internet 2 Demonstration 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 19
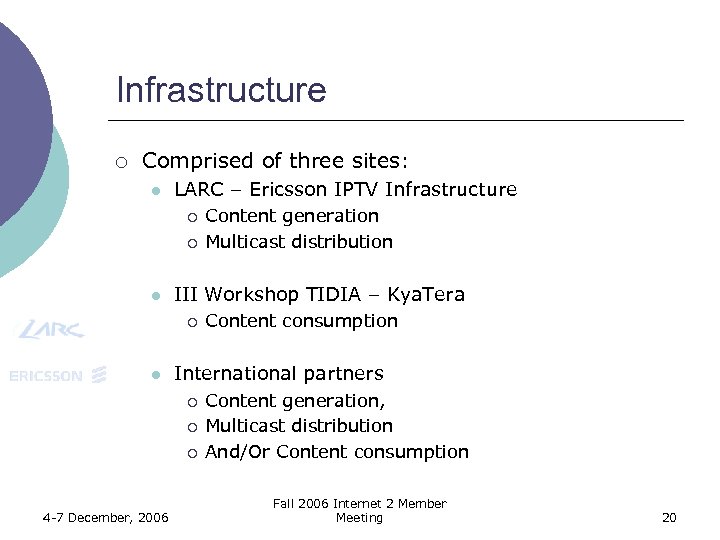
Infrastructure ¡ Comprised of three sites: l LARC – Ericsson IPTV Infrastructure ¡ ¡ l III Workshop TIDIA – Kya. Tera ¡ l Content consumption International partners ¡ ¡ ¡ 4 -7 December, 2006 Content generation Multicast distribution Content generation, Multicast distribution And/Or Content consumption Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 20
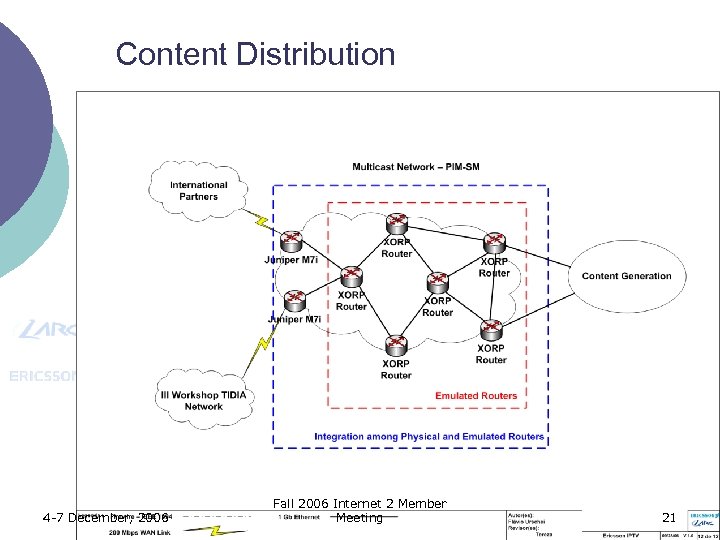
Content Distribution 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 21
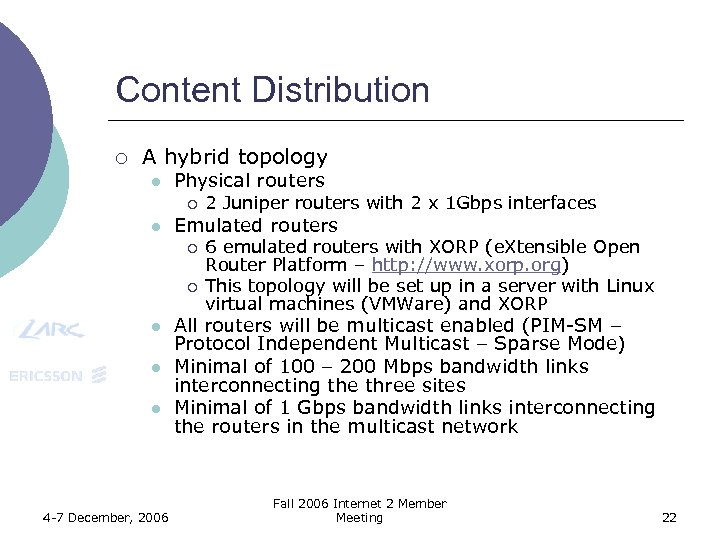
Content Distribution ¡ A hybrid topology l Physical routers ¡ l Emulated routers ¡ ¡ l l l 4 -7 December, 2006 2 Juniper routers with 2 x 1 Gbps interfaces 6 emulated routers with XORP (e. Xtensible Open Router Platform – http: //www. xorp. org) This topology will be set up in a server with Linux virtual machines (VMWare) and XORP All routers will be multicast enabled (PIM-SM – Protocol Independent Multicast – Sparse Mode) Minimal of 100 – 200 Mbps bandwidth links interconnecting the three sites Minimal of 1 Gbps bandwidth links interconnecting the routers in the multicast network Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 22
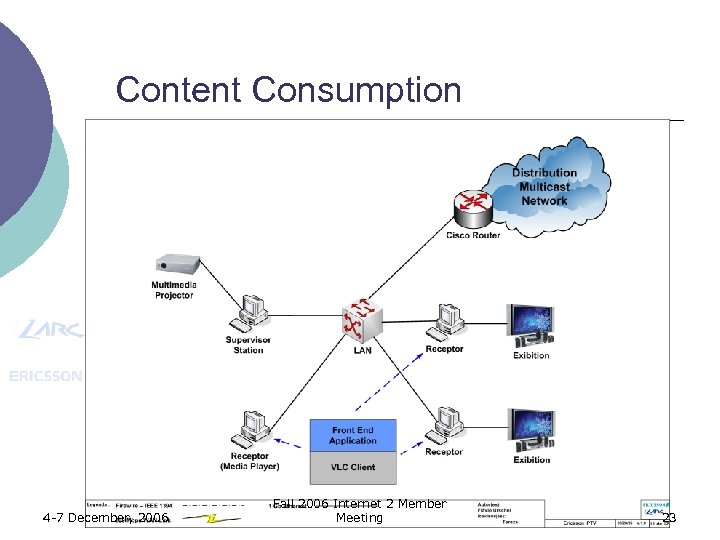
Content Consumption 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 23
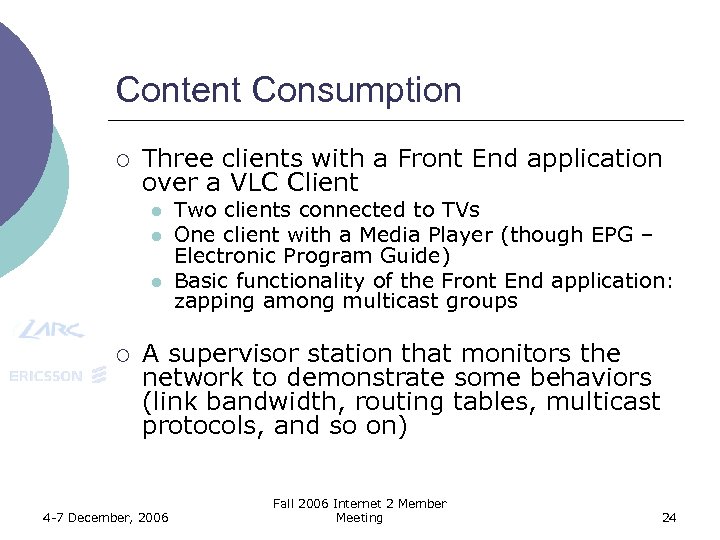
Content Consumption ¡ Three clients with a Front End application over a VLC Client l l l ¡ Two clients connected to TVs One client with a Media Player (though EPG – Electronic Program Guide) Basic functionality of the Front End application: zapping among multicast groups A supervisor station that monitors the network to demonstrate some behaviors (link bandwidth, routing tables, multicast protocols, and so on) 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 24
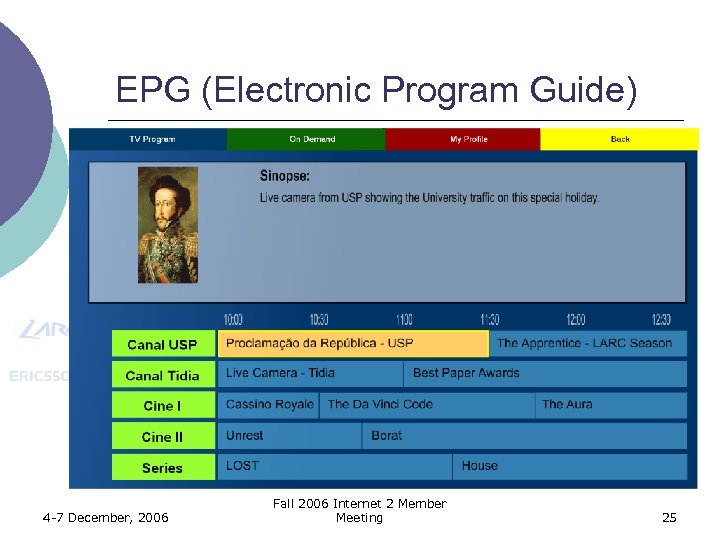
EPG (Electronic Program Guide) 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 25

IPTV over Internet 2 Demonstration: EPG (Electronic Program Guide) 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 26
Final Considerations ¡ IPTV over Internet 2 l HDTV over Internet with stringent Qo. S and Qo. E requirements it is not possible in the current infrastructure. l Due to Qo. E requirements (e. g. zapping), a bandwidth of hundreds of Mbps per service user (per subscriber) is required. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 27

A Platform for Media Distribution Management Regina Melo Silveira regina@larc. usp. br LARC- Laboratory of Computer Network Architecture EPUSP – Escola Politecnica University of Sao Paulo - Brazil 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting

Agenda ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Introduction Our Challenge Related Work Proposal l Conceptual Model l Physical Model Main Functionalities General View Work in Progress Final Considerations 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 29

Introduction ¡ ¡ Huge number of multimedia applications (documentation, advertisement, entertainment …); New multimedia services (broadcast, telecommunications, CATV); Convergence - services integration with access network independence; Progressive demand of storage, distribution and consume management allowing largely media utilization and re-use. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 30
Introduction ¡ Multimedia services management includes: (i) multimedia content storage, retrieval and search; (ii) users and groups of users access control and authentication; (iii) system distribution, adaptation, configuration and monitoring (server and clients) to multimedia content delivery and consumption; (iv) network elements management. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 31
Our Challenge ¡ To develop a Platform for Media Distribution Management respecting the following requirements: l l l ¡ Use open standards (ISMA, MPEG-7, MPEG-21); Define integrated interfaces for different multimedia services already implanted at RNP network; Prototype development and tests at RNP network. At the prototype uses two multimedia distribution services developed by LAVID/UFPB: l l dvod - video on demand dlive – live video 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 32

Related Work ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ MUFFINS - MUltimedia Framework For INteroperability in Secure – IST PERSEO - Personalised Multichannel Services for Advanced Multimedia Stream Management – IST CODAC - Modeling and Querying Content Description and Quality Adaptation Capabilities of Audio-Visual Data Klagenfurt University – Austria ADMITS - Adaptation in Distributed Multimedia IT Systems Klagenfurt University – Austria DANAE - Dynamic and distributed Adaptation of scalable multimedia co. Ntent in a context Aware Environment – IST i. TVP - Interactive TV Services over IP Networks - PSNC – PIONNER Rich Content Infrastructure and Middleware for Media - IBM 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 33
Proposal ¡ 4 (four) users types l l ¡ 4 (four) sub-systems l l ¡ Client, Content Provider, Administrator, Manager. Portal; Access control, storage and retrieval, Manager (Coordinator and Monitor), Transmitter (Multimedia delivery service). 3 (three) management levels l l l 4 -7 December, 2006 Service, Server, Network. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 34
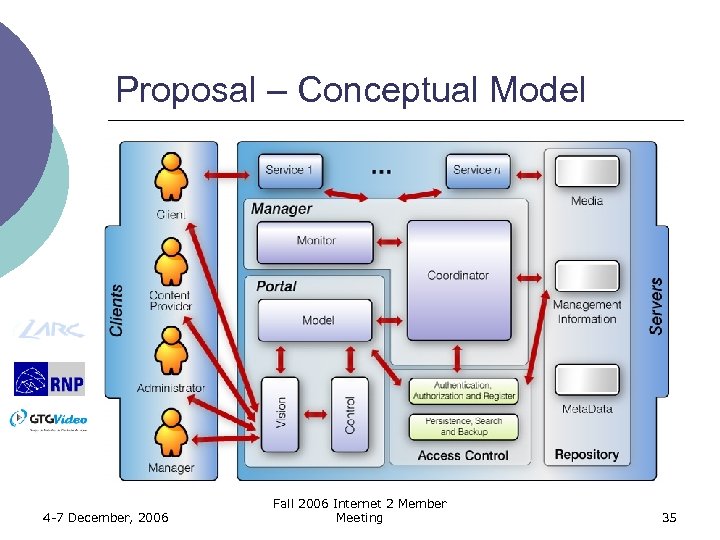
Proposal – Conceptual Model 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 35
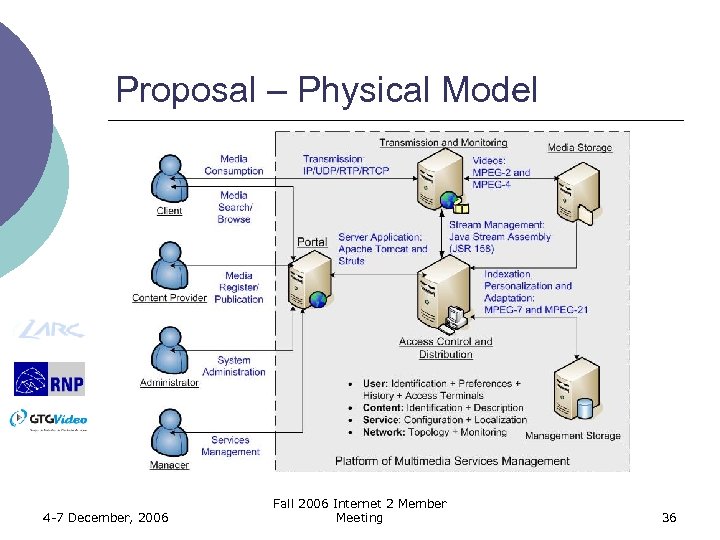
Proposal – Physical Model 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 36
Main Functionalities ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Video Upload and Indexation Live events Transmission registration Media search Media catalogue (Personalized) Media Visualization (Personalized) Users, groups and projects management Applications/services (sections) management Servers management Network elements management 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 37
4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 38
Ne tw or k La ye r Se rv er La y er Se rv ice s La ye r General View – Overlay Network 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 39
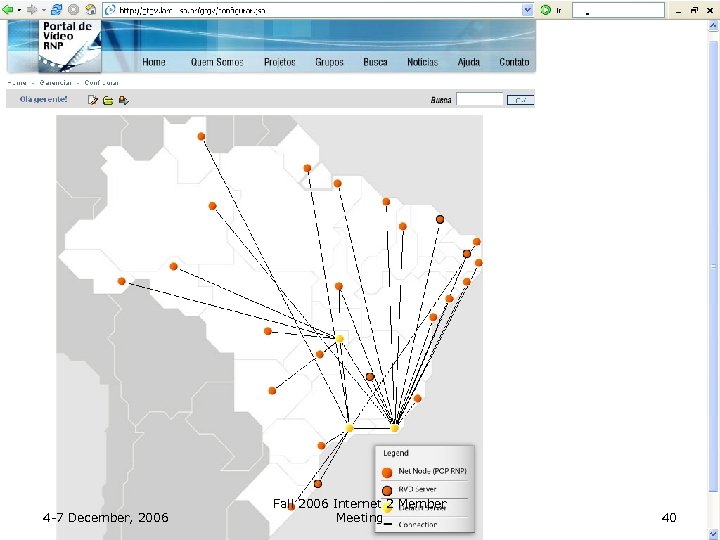
4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 40
4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 41
Work in Progress ¡ ¡ Testing prototype New functionalities and optimization l l l ¡ Video replication Access control and distributed metadata Multicast Overlay proposal adoption (for example, Overlay Multicast Control Protocol from IETF); Adoption of management data models based on XML from Global Grid Fórum Use of components model for Manager dynamic configuration update Integration with measurement infrastructure and new services. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 42
Final Considerations ¡ Our project proposed/implemented: l l l ¡ Common infrastructure for multimedia services; Architecture based on open standards allow uniform interfaces for all the applications; Web-based Management system; Resources Optimization; Flexibility and scalability. Service will be personalized for different context: l schools, hospitals e community and educational TVs. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 43
Acknowledgements ¡ Financial Support l RNP (National Education and Research Network) ¡ Collaboration l Prof. Guido Lemos de Souza Filho – LAVID/DI/UFPB l Prof. José Augusto Suruagy Monteiro – UNIFACS 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 44

Applying Security in IPTV Environment Tereza Cristina Melo de Brito Carvalho carvalho@larc. usp. br LARC – PCS/EP – University of São Paulo Ericsson Research Sweden 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting

Team Ayodele Damola ayodele. damola@ericsson. com Marcio Augusto Lima e Silva msilva@larc. usp. br Christiane Marie Schweitzer christiane. schweitzer@ufabc. edu. br Regina Melo Silveira regina@larc. usp. br Daniel Pires dpires@larc. usp. br Tereza Cristina Melo de Brito Carvalho carvalho@larc. usp. br Diego Sanchez Gallo dsgallo@larc. usp. br Wilson Vicente Ruggiero wilson@larc. usp. br Flávio Urschei furschei@larc. usp. br 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 46

Agenda Security Context (Application Layer and Network Layer) ¡ Threats (Service and Content) ¡ IPTV Security ¡ Countermeasures ¡ IPTV Policies ¡ Final Considerations ¡ 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 47
Security Context ¡ Application Level Security l On STB (Set-Top Box) video client, video services and content store. l Referred as Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems, enclosing conditional access, copy protection, encryption and watermarking. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 48
Security Context ¡ Network Level Security l On the content delivery architecture confidentiality, integrity and availability of the data flows Prevention, ¡ Detection, and ¡ Reaction. ¡ 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 49
![Security Threats in Multimedia Communications [ITU-T 2003] 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet Security Threats in Multimedia Communications [ITU-T 2003] 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet](https://present5.com/presentation/f8f14097ef492805ef5d67327481137d/image-50.jpg)
Security Threats in Multimedia Communications [ITU-T 2003] 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 50

Threats ¡ Service l Illegal service usage. l Disruption of service. ¡ Content l l l 4 -7 December, 2006 An insider stealing content from the service core. A subscriber stealing content from the STB. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 51

Threats: Illegal service usage ¡ ¡ Rogue subscription: An attacker gains access to broadband video services without a subscription. Escalation of subscription: An attacker gains access to video services that are beyond the parameters of his/her subscription. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 52

Threats : Disruption of service ¡ Attack against other subscribers l ¡ Attack against the access and transport infrastructure l ¡ The attacker attempts to disrupt the service for a specific subscriber or group of subscribers by directly acting on equipment that resides on the victim’s home network. The attacker attempts to disrupt the service by degrading the performance of one or several components of the architecture (access node, Broadband Service Aggregators, Broadband Service Routers, etc). Attack against the video service core l 4 -7 December, 2006 The attacker directly targets the components that render the video services, such as the Vo. D servers. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 53

Threats: Content ¡ An insider stealing content from the service core l ¡ A subscriber stealing content from the service core l ¡ The thief is an insider, i. e. , a service provider’s employee, who has easy access to the stored content. Weaknesses in the broadband TV architecture allow the attacker (from his/her home network) to compromise the servers that host the content. A subscriber stealing content from the STB l 4 -7 December, 2006 The attacker is a subscriber who wants to use the content acquired beyond his/her fair right of usage. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 54
IPTV Security Privacy ¡ Confidentiality ¡ Integrity ¡ Availability ¡ Interoperability ¡ 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 55
IPTV Security: Privacy ¡ The Service Provider must handle customer information, without any personal identifiable information. ¡ The Service Provider must manage CPEs (Customer Premise Equipments) and it must not know if it belong to a customer, or how many equipments this customer has at home. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 56

IPTV Security: Confidentiality ¡ Video Content l l The video must be transported encrypted. The content must be recorded protected. ¡ 4 -7 December, 2006 Authentication and authorization guarantees. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 57
IPTV Security: Integrity ¡ The content cannot be modified: l l ¡ Multicast and unicast security. Content source security. Billing system integrity: l 4 -7 December, 2006 Just authorized person should have access to billing system. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 58
IPTV Security: Availability ¡ Can someone disrupt your IPTV service? To what scale? l l l ¡ Any of the IPTV device could be vulnerable to Denial-of-Service attack. Buffer overflow. Weak TCP/IP or protocol stack implementation. If other service is down (Voice and Data) would it take down IPTV too? l 4 -7 December, 2006 System dependencies. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 59
IPTV Security: Interoperability ¡ There is currently no common standard on IPTV l l l ¡ Other than the use of multicast/unicast. This may help security as a ‘diversity factor’. One vulnerability for one service provider may not work for another. Standards on the work: l l l 4 -7 December, 2006 ITU (ISO) ISMA. tv Others Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 60
![Security Architecture [ITU-T/IPTV] 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 61 Security Architecture [ITU-T/IPTV] 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 61](https://present5.com/presentation/f8f14097ef492805ef5d67327481137d/image-61.jpg)
Security Architecture [ITU-T/IPTV] 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 61

Countermeasures Protection of content. ¡ Transport infrastructure protection. ¡ Home network protection. ¡ Secure operation of the infrastructure. ¡ 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 62
Countermeasures: Protection of Content ¡ DRM state-of-the-art mechanisms l l ¡ To protect the content delivered to the subscriber. To apply appropriate content/service usage policies enforcement mechanisms in the STB. Content stored on the service delivery must be encrypted. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 63

Transport Infrastructure Protection ¡ ¡ ¡ To restrict traffic dependency on the user’s subscription. IGMP proxies on the access node must have some awareness of the user subscription and refuse to forward any channel outside of the user’s subscription. Subscriber traffic should be segregated to disable residential bridging. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 64

Transport Infrastructure Protection ¡ ¡ ¡ Efficient traffic filtering mechanisms need to be provided to keep the communication flow between home network and service delivery platform to a strict minimum. The infrastructure must provide a way to enforce Qo. S parameters on a per subscriber basis in order to mitigate the effect on the infrastructure of abusive usage of bandwidth by a specific subscriber. The access node must provide a number of protection mechanisms against MAC and IGMPbased attacks. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 65
Home Network Protection ¡ ¡ Secure storage for security sensitive information on the STB is required to avoid cloning and disclosure of this information. Secure provisioning mechanisms of the STB are needed for the service provider to be able to support these systems. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 66
Secure Operation of the Infrastructure ¡ Appropriate patch and vulnerability management on the service delivery platform. ¡ Adding IDS or IPS mechanisms in order to detect and prevent attempts by the subscriber or any other attacker to compromise the content delivery infrastructure. ¡ Efficient revocation mechanisms are needed for authentication information and key material used in the STB to access services. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 67
IPTV Policies ¡ Security policies l ¡ DRM Specific ones and infrastructure. Qo. S policies l 4 -7 December, 2006 Adaptability and performance both provided media and services. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 68

IPTV Security Policies ¡ Content owners are extremely reluctant to provide content to a distributor that doesn’t have an effective DRM system because a perfect digital, copy of the content could be used to create copies for illegal resale. ¡ This control needs to prevent copying not only at the distributor facility, but also on any device that a user may use to play back the content, such as a set-top-box or a PC. 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 69
IPTV Security Policies - example ¡ DRM Specific Policies l 4 -7 December, 2006 Can be intended as content usage policies, regarding the content owner media rights. ¡ The content can not be modified by Service Provider. ¡ Samples from the content can not be performed by Service Provider. ¡ The content can/cannot be replicated. ¡ The content can/cannot be saved. ¡ The content can be displayed five times. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 70
IPTV Security Policies - example ¡ Infrastructure Policies l Can be intended as service policies, regarding the security or Qo. S issues on the content delivery/transport architecture: All content MUST BE encrypted. ¡ All content MUST BE watermarked. ¡ All content users MUST BE identified. ¡ 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 71
IPTV Qo. S Policies - example ¡ Interaction Policy l l l 4 -7 December, 2006 The service must provide a specified Qo. E level. The service must adapt itself to the user device capabilities. The service must adapt the provided content to the device resolution (e. g. HDTV 1920 x 1080 to low resolutions). Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 72
IPTV Qo. S Policies - examples ¡ Infrastructure Policy l l 4 -7 December, 2006 The network guarantees. The network must have bandwidth must have delay must have jitter must have loss guarantees. Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 73

Final Considerations IPTV Security = Content + Service + Transport Security ¡ DRM System is not enough, but it is a good start. ¡ Encryption and Authentication must be priority. ¡ 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 74

Acknowledgments 4 -7 December, 2006 Fall 2006 Internet 2 Member Meeting 75
f8f14097ef492805ef5d67327481137d.ppt