cd35981ef507497e49a016a6e730d9c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62

Media Communications Richard Trombly Contact : Email : richard@trombly. com Wechat and phone: +86 13818837641

Introduction The media is the message As soon as we had manufacturers trying to sell radios in mass production, there was a need for programs for them to listen to. So the manufacture of radio necessitated a new industry. News and entertainment on the radio.

Radio While early radio focused on long distance, like Marconi making the first intercontinental transmission of radio telegraphs the reception was low quality and hard to tune into, relying on a crystal and “cat's whiskers” fine wires to manually tune into the correct frequency.

Radio Low frequencies have a long wave and low energy. They travel for long distances following earth curvature. They are easily interfered with by weather conditions or ground obstacles and the data (voice and sound in the case of radio) is low quality.

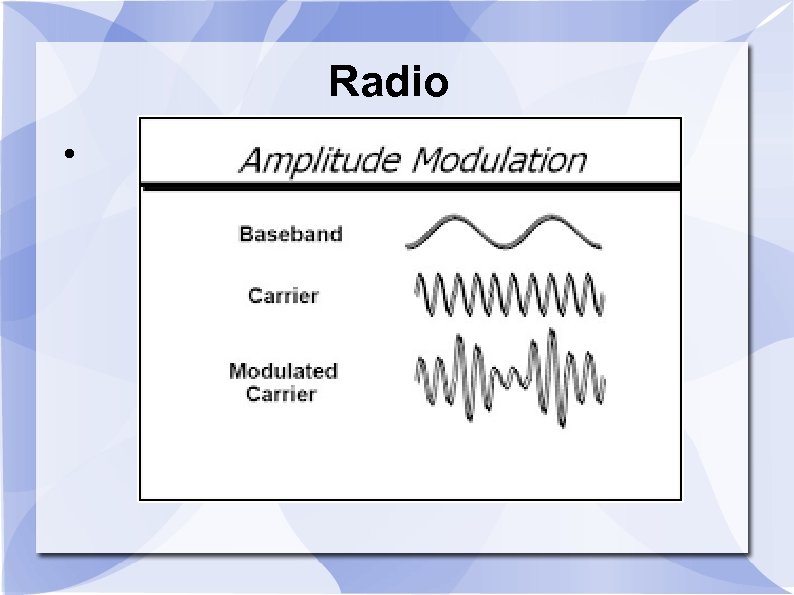
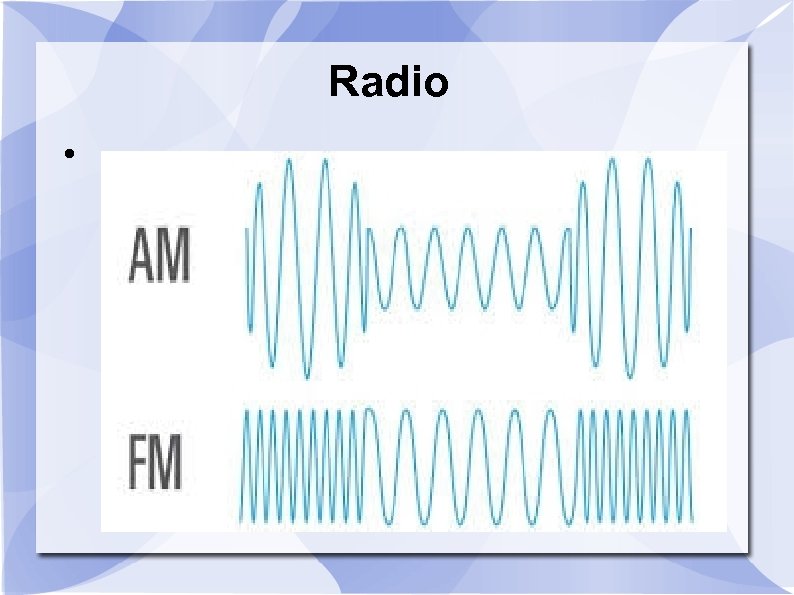
Radio This was the basis of A. M. Band radio amplitude modulation. The data is encoded in the power of the transmission , the amplitude of the signal. This also limits the quality of the data and the frequency response

Radio It turns out that the long distance characteristic was not that wanted. There is a limited number of frequencies. If broadcasts are too close togethere is “spill over” which also causes interference.

Radio The higher frequency waves travel in line of sight and therefore are limited by the curvature of the earth (unless they bounce off something, in which case after bouncing they will again continue line of sight)

Radio This is the basis of FM Band radio. Frequency Modulation. It changes the frequency slightly to encode the data. This leads to greater fidelity in sound and higher frequency response. FM broadcasts are much less prone to interference
Radio

Radio
Radio
Radio FM frequencies. VHF – Very-high Frequency - radio UHF – Ultra-high Frequency more data bandwidth ( can carry more data per second) was needed to transmit television images.

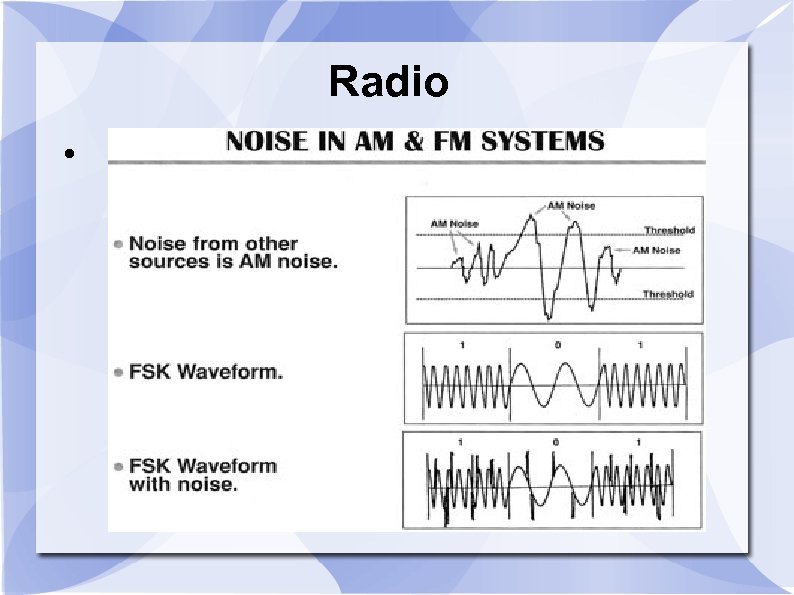
Radio FSK Frequency Shift Key - is using FM with digital data. In AM , noise becomes part of the received data , corrupts it. In FM noise does not affect the carrier signal therefore noise can be filtered out This is CRITICAL for digital data.
Radio

Radio Since early broadcasts went a long way, but were hard to listen to, it meant that in practical terms, many people could not receive signal worth listening to. The higher frequency , shorter distance waves meant that the same frequency could be re-used outside that limited range
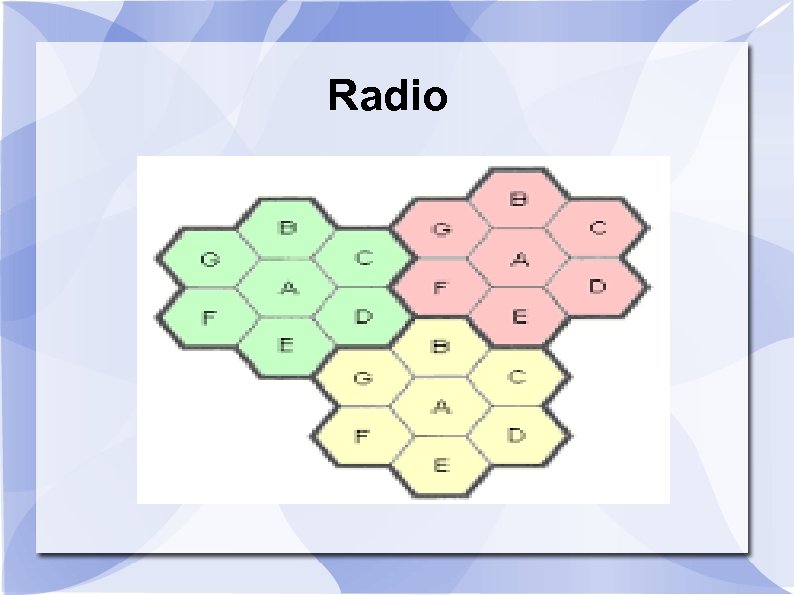
Radio

Radio By the end of the 1920 s radio has become a household item. They were constructed as furniture and not viewed as a portable item Critics still doubted AM radio's value due to poor quality and the doubting transmitted media itself

Radio In the early 40 s, VHF was developed and even TV became possible. WWII delayed the development of the TV broadcasting infrastructure and industry.

Radio In this golden age of radio it was recognized as a social institution and seen as offering great power in cultural exchange and promoting peace through shared international communication. It also developed its own role in the news industry and came into conflict with the print news industry.

Radio It was used as a propaganda tool both nationalistic and as an offensive weapon during and after WWII. Socialists saw it as a way for the common man to get a voice and low cost – local transmitters were possible to set up to communicate community-based broadcasts Alternative voices

Radio Radio in the future Radio has become digital broadcast, high fidelity. Broadcast music , entertainment and news will still have some market even in the internet and mp 3 era. We can download and buy our music, but we are limited to our own choice and music or information knowledge. A broadcast is like walking into a library.

Television Radio was arguably ahead of its time. People were slow to develop the entertainment and to fully exploit its possibilities, In TV the opposite was true. WWII delayed its implementation and the radio industry lessons were quickly applied to TV.

Television Early tv , Like cinema, a progression of still frames , that the eye sees with movement due to “Persistence of vision” Stare at a light and then look suddenly at a black wall. You will see the light there for a while. Partly a cognitive thing too. Your brain actively tries to make sense of the images.

Television Later tv turned to scanning technology spin a disc with spiral succession on holes targeting the screen.

Television Since it was data, it could be recorded. First recordings were on “record albums” and could hold nearly 3 minutes of data.

Television Continental USA has three time zones and networks wanted to play certain shows in prime time. Across the country. They wanted certain shows played at the best time. It needed recording. They pointed a film camera at the screen of a tv and made a copy and sent that image out for the local stations to use

Television That broadcast taping was expensive and time consuming to develop film. This lead to experimenting with magnetic tape.

Television Standards USA Nation Television Standards Committe NTSC is still a USA standard PAL Phase Alternating Line is used in most other countries 50 hz power in most country USA has 60 hz the

Television The scan on the TV screen involves 2 different fields sending the information. A positive and a negative field. So there are 60 fields per second. Or 30 frames in NTSC 50 field scans or 25 frames in PAL

Television The camera and tv screen really are no different than the telegraph switch and the magnetic coil or the mike and the speaker. One end encodes , the other decodes.

Television The HDTV now offers 1080 lines in the scan It requires digital broadcasting for the data stream rate.

Television It is interesting to note that tv sound is critical to the watching experience but the industry only recently capitalized on that with low quality sound in TV sets for most of the period of TV history.

Television VCR – recording of the video image when not shooting on film the price to record broadcasts or shows was reduced and there was no developing costs. Variations in the magnetic field on a magnetized tape are encoded and read much in the way broadcast signals are.

Television This lead to Cheap Syndication of rerun shows more choice in viewing by buying or renting tapes A chance for classic movies to have a valuable shelf life past theatrical screenings.

Television Teletext It lead to the idea of hypertext links in the internet. Teletext except for subtitles never caught on in USA but was common in some E. U. Countries.

Television Tv technology has progressed but audience watching and tv show format remain similar today based off experiments in radio Web broadcast and mobile programs remain similar to the tv format. Likely other new tech will still retain similar attributes.

Television Tv broadcast began on terrestrial airwave broadcast Higher frequency, limited range was a benefit to allow clear signal near the broadcast antenna. Limited to number of broadcast airwave frequencies but requires only the broadcast tower infrastructure.

Television Cable allowed the broadcaster to control the information flow better. Charge for premium, some two-way flow of information But it requires an infrastructure of point to point wires COST so started in urban area Uninterrupted signal ,

Television Satellite communications Envisioned by Sci Fi writer Arthur C Clark. At a specified altitude a satellite would orbit the earth at the exact rate as the earth turns and so therefore appear to be no moving to a ground-based observer geo-stationary

Television Tv and radio were viewed largely as a utility like power and water and gas They were therefore regulated New ideology is freemarket controls and deregulation / profit based

Television “Thievery” of satellite signals used by broadcasters led to them encrypting the signal It also lead to a home satellite market

Television The telephone network was established by the government in USA and then private utilities were allowed to run them for profit Later technologies were rolled out by privatized industry. Competition fires innovation but means multiple infrastructure Private networks for TV via cable took premium viewership from broadcast, lowering budgets and reducing quality

Television This lead to cable subscription in virtually every home in USA (80% by 2009) Britain's BBC and China's CCTV offered more support to non-premium film and tv production providing national culture broadcasts USA developed the reality-type and game shows for cheap production attributes.

Television Teletex (tv broadcast channels) and fax (facsimilie) via telephone channels Two-way tv communication offered an idea that TV might be the basis for information The internet , due to the rise of the personal computer , was the actual development

Television Digital broadcasting In USA the public gave away its airwaves as it went digital and in doing so gave each existing company the extra frequencies allowed by the digital transfer. Deregulation and consolidation of media firms Freemarket dominates the tv and radio broadcasts in USA.

ethnomethodology Ethno

ethnomethodology Ethno indicating race, people, or culture: ethnology. via French from Greek ethnos race. TRIBE in the past and in our new “global village” we have been retribalized

ethnomethodology Ethnomethodology is the study of methods people use for understanding and producing the social order in which they live. It generally seeks to provide an alternative to mainstream sociological approaches to research and theorising.

ethnomethodology Ethnomethodology Focuses on everyday commonsense interactions Like the study of common language This is the study of common behavior and how a society understands its own daily behavior ie RATIONALIZES it

ethnomethodology Ethnometodology avoids the lab In research, People recognize they are being studied so the results are not truly representative of real social forces

ethnomethodology Advertisers use this to “reach” market segments and to understand what will have results in groups of people. The assumption is groups of people have common understandings , even if they do not articulate them.

ethnomethodology Sociologists might investigate some common social situation as its starting point They do not look at how the society and its order is even possible in the first place. – that is ethnomethodology's realm

ethnomethodology Sociologists might investigate some common social situation as its starting point They do not look at how the society and its order is even possible in the first place. – that is ethnomethodology's realm

ethnomethodology GOALS To define the commonsense of everyday life To show the relevance of everyday activities in a sociological theory To [re]discover the significance of the commonsense world of people

ethnomethodology The goal is NOT to interpret the meanings or significance But rather to find the rules and codes that govern these interactions To uncover how common people interpret their world and interactions

ethnomethodology Like Dian Fossey and her apes Like in the movie gorillas in the mist View people like an outside researcher Like you were viewing a gorilla tribe Also to use the manners you would use among strangers at home “stupefied” family.

ethnomethodology Combines psychology and semiotics Much of our thinking is unconscious So a mix of signs and psychological forces drive much of our everyday behavior So does our politeness and etiquette

ethnomethodology Turning love into a game Follows rules , winner / loser in each interaction, outcome unclear, cheating is a violation , games often end

ethnomethodology Codes Love follows codes Comics – they creatively break codes That violation is what we find funny if they do it right … it exposes our codes as it violates them

ethnomethodology Ethnomethodology can be applied to conversation as well as song lyrics or any other part of culture It can be used for comparative analysis of subgroups in a population. It can help define and explore unique interests and behaviors of market segments

ethnomethodology Conclusion Going from the specific to general Enthomethodologists take the codes of the everyday in small groups and apply it to make broader observations and understanding in mass media and popular culture. It is deeply exploited by marketing firms

Career in media Will you educate or market?
cd35981ef507497e49a016a6e730d9c2.ppt