a8947a1ba944a60018902db2c5bb8238.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Med. LEE, a Natural Language Processing Service, on the Public Health Research Grid Albert Lai, Ph. D. Carol Friedman, Ph. D. Department of Biomedical Informatics, Columbia University © Columbia University
Med. LEE, a Natural Language Processing Service, on the Public Health Research Grid Albert Lai, Ph. D. Carol Friedman, Ph. D. Department of Biomedical Informatics, Columbia University © Columbia University
 Goals Better understand grid technology n Provide NLP service to members of the Public Health Research Grid n © Columbia University
Goals Better understand grid technology n Provide NLP service to members of the Public Health Research Grid n © Columbia University
 Motivation Coded information is urgently needed for clinical applications that improve care and lower costs n Coded data other than laboratory data and pharmacy data - very scarce and difficult to obtain n © Columbia University
Motivation Coded information is urgently needed for clinical applications that improve care and lower costs n Coded data other than laboratory data and pharmacy data - very scarce and difficult to obtain n © Columbia University
 Why NLP? NLP technology offers high throughput method for automatic encoding of clinical information in narrative patient reports n Applicable to a broad range of clinical domains n Appropriate for diverse applications n © Columbia University
Why NLP? NLP technology offers high throughput method for automatic encoding of clinical information in narrative patient reports n Applicable to a broad range of clinical domains n Appropriate for diverse applications n © Columbia University
 Outline Med. LEE Overview n Getting on the Grid n Service Generalization Issues n © Columbia University
Outline Med. LEE Overview n Getting on the Grid n Service Generalization Issues n © Columbia University
 Med. LEE Overview n Medical Language Extraction and Encoding ¨ Extracts, structures, and encodes clinical information in narrative patient reports ¨ Comprehensive coverage ¨ Can be used for diverse clinical applications ¨ Development started in 1991 ¨ Used at Columbia University Medical Center since 1995 ¨ Numerous independent evaluations © Columbia University
Med. LEE Overview n Medical Language Extraction and Encoding ¨ Extracts, structures, and encodes clinical information in narrative patient reports ¨ Comprehensive coverage ¨ Can be used for diverse clinical applications ¨ Development started in 1991 ¨ Used at Columbia University Medical Center since 1995 ¨ Numerous independent evaluations © Columbia University
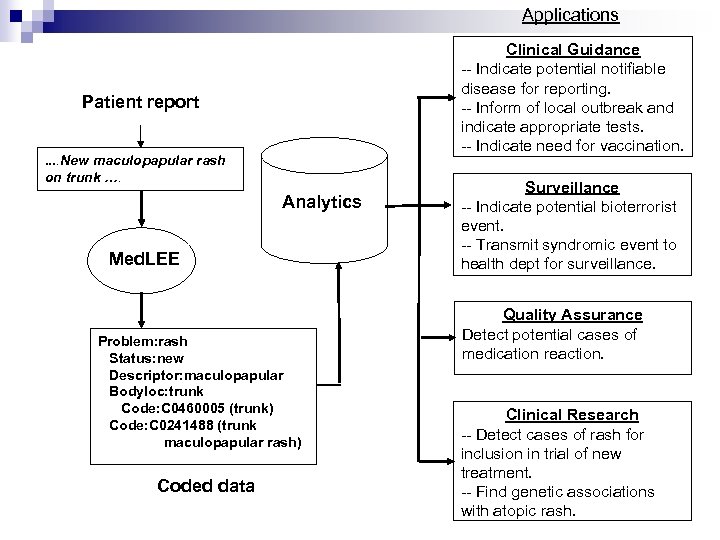 Applications Clinical Guidance -- Indicate potential notifiable disease for reporting. -- Inform of local outbreak and indicate appropriate tests. -- Indicate need for vaccination. Patient report. . New maculopapular rash on trunk …. Analytics Med. LEE Problem: rash Status: new Descriptor: maculopapular Bodyloc: trunk Code: C 0460005 (trunk) Code: C 0241488 (trunk maculopapular rash) Coded data Surveillance -- Indicate potential bioterrorist event. -- Transmit syndromic event to health dept for surveillance. Quality Assurance Detect potential cases of medication reaction. Clinical Research -- Detect cases of rash for inclusion in trial of new treatment. -- Find genetic associations with atopic rash.
Applications Clinical Guidance -- Indicate potential notifiable disease for reporting. -- Inform of local outbreak and indicate appropriate tests. -- Indicate need for vaccination. Patient report. . New maculopapular rash on trunk …. Analytics Med. LEE Problem: rash Status: new Descriptor: maculopapular Bodyloc: trunk Code: C 0460005 (trunk) Code: C 0241488 (trunk maculopapular rash) Coded data Surveillance -- Indicate potential bioterrorist event. -- Transmit syndromic event to health dept for surveillance. Quality Assurance Detect potential cases of medication reaction. Clinical Research -- Detect cases of rash for inclusion in trial of new treatment. -- Find genetic associations with atopic rash.
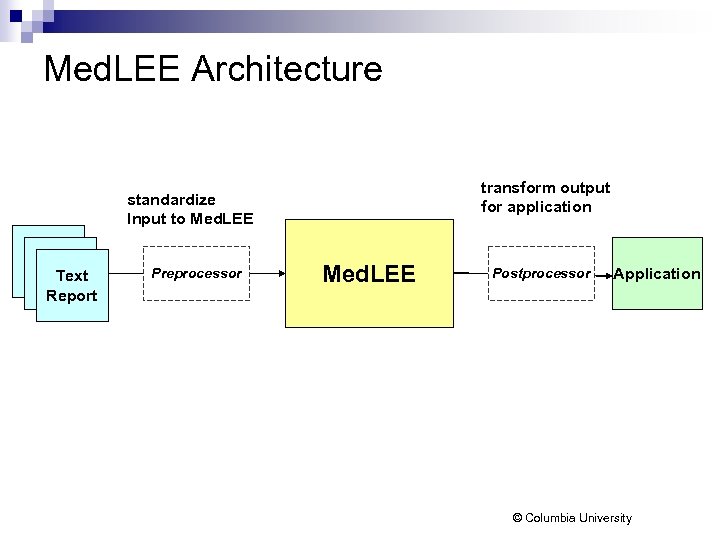 Med. LEE Architecture transform output for application standardize Input to Med. LEE Text Report Preprocessor Med. LEE Postprocessor Application © Columbia University
Med. LEE Architecture transform output for application standardize Input to Med. LEE Text Report Preprocessor Med. LEE Postprocessor Application © Columbia University
 Text Reports Processed n n n n Radiology Reports Cardiology Reports Pathology Reports Admission notes Discharge Summaries Resident Sign out notes Office Visits Telephone encounters © Columbia University
Text Reports Processed n n n n Radiology Reports Cardiology Reports Pathology Reports Admission notes Discharge Summaries Resident Sign out notes Office Visits Telephone encounters © Columbia University
 Applications using Med. LEE n n n Biosurveillance Syndromic surveillance Adverse Drug Event detection Decision Support Clinical Research Clinical Trials Quality Assurance Automated Encoding Patient Management Data mining – finding trends and associations Linking patient record to the literature Summarization © Columbia University
Applications using Med. LEE n n n Biosurveillance Syndromic surveillance Adverse Drug Event detection Decision Support Clinical Research Clinical Trials Quality Assurance Automated Encoding Patient Management Data mining – finding trends and associations Linking patient record to the literature Summarization © Columbia University
 Adverse Event Detection n n Use NLP system to detect events defined in the New York Patient Occurrence Reporting and Tracking System (NYPORTS) System: Med. LEE + ¨ Queries consisiting of criteria mapping output to NYPORTS event n Results: system outperformed traditional and previous automated methods NLP effective method for automated adverse event detection Melton GB, Hripcsak G. Automated detection of adverse events using natural language processing of discharge summaries. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2005 Jul-Aug; 12(4): 448 -57. © Columbia University
Adverse Event Detection n n Use NLP system to detect events defined in the New York Patient Occurrence Reporting and Tracking System (NYPORTS) System: Med. LEE + ¨ Queries consisiting of criteria mapping output to NYPORTS event n Results: system outperformed traditional and previous automated methods NLP effective method for automated adverse event detection Melton GB, Hripcsak G. Automated detection of adverse events using natural language processing of discharge summaries. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2005 Jul-Aug; 12(4): 448 -57. © Columbia University
 Syndromic Surveillance n EHR from Institute of Family Health (IFH) ¨ 13 n community health centers System: Med. LEE+queries detecting flu-like illness ¨ Processed all types of notes: n nursing and physician notes n several types of encounters n Results: ¨ System correlated well with a proven syndromic surveillance system based on chief complaints © Columbia University
Syndromic Surveillance n EHR from Institute of Family Health (IFH) ¨ 13 n community health centers System: Med. LEE+queries detecting flu-like illness ¨ Processed all types of notes: n nursing and physician notes n several types of encounters n Results: ¨ System correlated well with a proven syndromic surveillance system based on chief complaints © Columbia University
 Challenges for Grid-enabling Med. LEE Setting up a grid node n Firewalls n Security / PHI concerns n Wrapping Med. LEE into a grid service n © Columbia University
Challenges for Grid-enabling Med. LEE Setting up a grid node n Firewalls n Security / PHI concerns n Wrapping Med. LEE into a grid service n © Columbia University
 Getting on the Grid n CUMC on hospital network ¨ Setting up Globus node required numerous port openings No DMZ available n Solution: install main campus w/ no firewall n © Columbia University
Getting on the Grid n CUMC on hospital network ¨ Setting up Globus node required numerous port openings No DMZ available n Solution: install main campus w/ no firewall n © Columbia University
 Security Concerns No firewall n Medical data being sent to node n Medical data remains on node for some period of time n Currently, we do not send data containing PHI to the Grid service, only in demonstration mode n © Columbia University
Security Concerns No firewall n Medical data being sent to node n Medical data remains on node for some period of time n Currently, we do not send data containing PHI to the Grid service, only in demonstration mode n © Columbia University
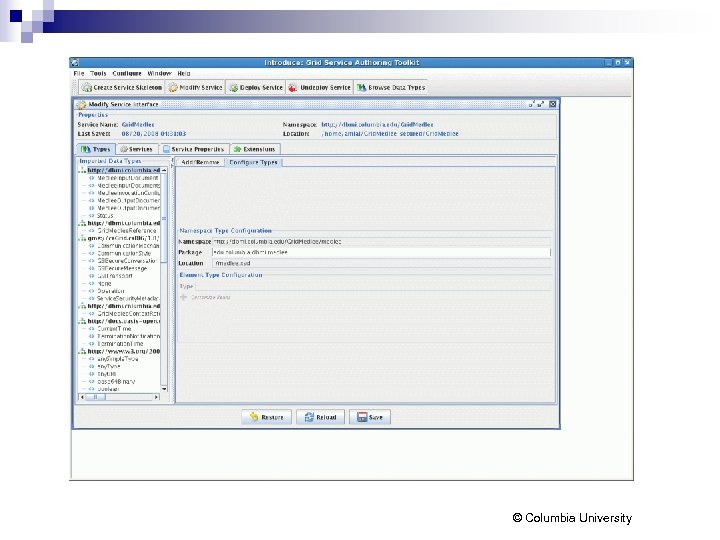
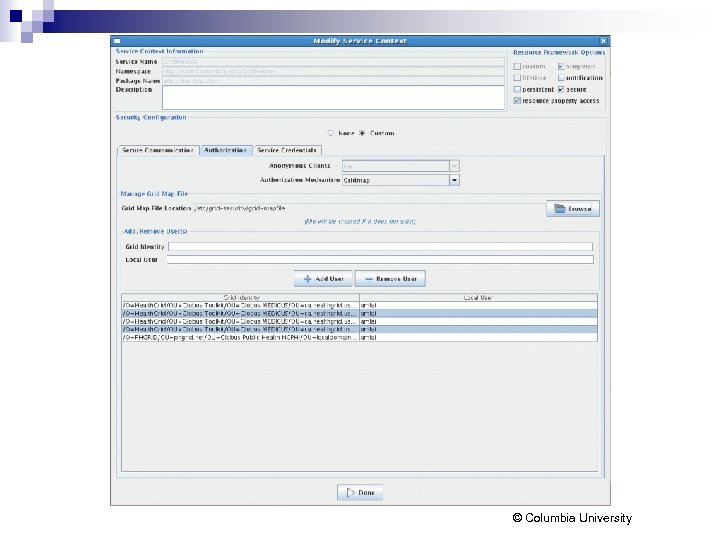
 Wrapping Med. LEE Introduce framework from ca. Grid / OSU n Using schema for web service, automatically generates custom beans n Automatically generates method stubs for service operations n Can configure security parameters for service n © Columbia University
Wrapping Med. LEE Introduce framework from ca. Grid / OSU n Using schema for web service, automatically generates custom beans n Automatically generates method stubs for service operations n Can configure security parameters for service n © Columbia University
 © Columbia University
© Columbia University
 © Columbia University
© Columbia University
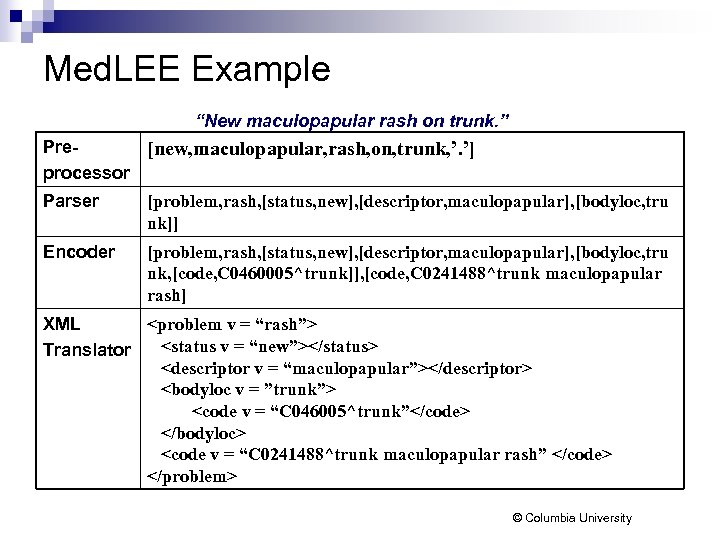 Med. LEE Example “New maculopapular rash on trunk. ” Pre[new, maculopapular, rash, on, trunk, ’. ’] processor Parser [problem, rash, [status, new], [descriptor, maculopapular], [bodyloc, tru nk]] Encoder [problem, rash, [status, new], [descriptor, maculopapular], [bodyloc, tru nk, [code, C 0460005^trunk]], [code, C 0241488^trunk maculopapular rash]
Med. LEE Example “New maculopapular rash on trunk. ” Pre[new, maculopapular, rash, on, trunk, ’. ’] processor Parser [problem, rash, [status, new], [descriptor, maculopapular], [bodyloc, tru nk]] Encoder [problem, rash, [status, new], [descriptor, maculopapular], [bodyloc, tru nk, [code, C 0460005^trunk]], [code, C 0241488^trunk maculopapular rash]
 Service Generalization Issues n Preprocessing needed to standardize narrative prior to Med. LEE n Allow user-specified customization © Columbia University
Service Generalization Issues n Preprocessing needed to standardize narrative prior to Med. LEE n Allow user-specified customization © Columbia University
 Preprocessor – Standardize Report for Med. LEE n Handle problematic text (formatted data in narrative) Her 2/Neu-2+ n n n Her 2/Neu measured 2+. Add punctuations (e. g. , ‘. ’) for run on sentences Add ignore tags to indicate text that should be ignored This neoplasm is strongly estrogen positive
Preprocessor – Standardize Report for Med. LEE n Handle problematic text (formatted data in narrative) Her 2/Neu-2+ n n n Her 2/Neu measured 2+. Add punctuations (e. g. , ‘. ’) for run on sentences Add ignore tags to indicate text that should be ignored This neoplasm is strongly estrogen positive
 Postprocessor – Transform output n Modify and transform output for different views/applications ¨ Map into tabular form for spreadsheet/database ¨ Problem-oriented/summarization/highlighting ¨ Execute queries to interpret output according to needs of application © Columbia University
Postprocessor – Transform output n Modify and transform output for different views/applications ¨ Map into tabular form for spreadsheet/database ¨ Problem-oriented/summarization/highlighting ¨ Execute queries to interpret output according to needs of application © Columbia University
 User-Specified Knowledge n Section headings ¨ New n n PMH|Past Medical History New abbreviations containing ‘. ’ (O. D. ) n n sections/abbreviated section headers: Avoids breaking up sentence at abbreviation Add/replace lexical definitions n OD|bodyloc|right eye © Columbia University
User-Specified Knowledge n Section headings ¨ New n n PMH|Past Medical History New abbreviations containing ‘. ’ (O. D. ) n n sections/abbreviated section headers: Avoids breaking up sentence at abbreviation Add/replace lexical definitions n OD|bodyloc|right eye © Columbia University
 Example of Need for Custom Lexicon “ 27 yo male no sig PMH presented to ED on 4/23 w/ fevers, backache, headache, pharyngitis, no rhinorrhea, no cough, lasting 1 day; Now sxs improved. ” n Add/replace lexical definitions n ed|service|emergency department n sxs|cfinding|symptom n © Columbia University
Example of Need for Custom Lexicon “ 27 yo male no sig PMH presented to ED on 4/23 w/ fevers, backache, headache, pharyngitis, no rhinorrhea, no cough, lasting 1 day; Now sxs improved. ” n Add/replace lexical definitions n ed|service|emergency department n sxs|cfinding|symptom n © Columbia University
![finding: demo age>> [27, [idref, 2], year, [idref, 4]] parsemode>> mode 2 sectname>> report finding: demo age>> [27, [idref, 2], year, [idref, 4]] parsemode>> mode 2 sectname>> report](https://present5.com/presentation/a8947a1ba944a60018902db2c5bb8238/image-25.jpg) finding: demo age>> [27, [idref, 2], year, [idref, 4]] parsemode>> mode 2 sectname>> report clinical information item sex>> male idref>> 6 sid>> 1 status: past medical history certainty>> no idref>> 8 idref>> 12 timeper>> presentation idref>> 14 sectname>> report clinical information item parsemode>> mode 4 sid>> 1. . . finding: demo age>> [27, [idref, 2], year, [idref, 4]] parsemode>> mode 2 sectname>> report clinical information item sex>> male idref>> 6 sid>> 1 status: past medical history certainty>> no idref>> 8 idref>> 12 timeper>> presentation idref>> 14 service>> emergency department idref>> 18 location>> to idref>> 16 date>> 00000423 idref>> 22 sectname>> report clinical information item parsemode>> mode 4 sid>> 1 …. . finding: better idref>> 63 parsemode>> mode 4 sectname>> report clinical information item sid>> 2 timeper>> now idref>> 59 problem: symptom change>> better idref>> 63 idref>> 61 parsemode>> mode 1 sectname>> report clinical information item sid>> 2 timeper>> now idref>> 59
finding: demo age>> [27, [idref, 2], year, [idref, 4]] parsemode>> mode 2 sectname>> report clinical information item sex>> male idref>> 6 sid>> 1 status: past medical history certainty>> no idref>> 8 idref>> 12 timeper>> presentation idref>> 14 sectname>> report clinical information item parsemode>> mode 4 sid>> 1. . . finding: demo age>> [27, [idref, 2], year, [idref, 4]] parsemode>> mode 2 sectname>> report clinical information item sex>> male idref>> 6 sid>> 1 status: past medical history certainty>> no idref>> 8 idref>> 12 timeper>> presentation idref>> 14 service>> emergency department idref>> 18 location>> to idref>> 16 date>> 00000423 idref>> 22 sectname>> report clinical information item parsemode>> mode 4 sid>> 1 …. . finding: better idref>> 63 parsemode>> mode 4 sectname>> report clinical information item sid>> 2 timeper>> now idref>> 59 problem: symptom change>> better idref>> 63 idref>> 61 parsemode>> mode 1 sectname>> report clinical information item sid>> 2 timeper>> now idref>> 59
 Where are we at now? Basic Med. LEE node n Encrypted data transport using TLS n Authentication using gridmap file n © Columbia University
Where are we at now? Basic Med. LEE node n Encrypted data transport using TLS n Authentication using gridmap file n © Columbia University
 Next Steps n Addition of customization features to Grid. Med. LEE for greater generalization ¨ User-defined / domain-specific lexicons, terminology, section headings, etc. ¨ Additional output formats Investigate other security mechanisms n Investigate real usage on grid in research applications n © Columbia University
Next Steps n Addition of customization features to Grid. Med. LEE for greater generalization ¨ User-defined / domain-specific lexicons, terminology, section headings, etc. ¨ Additional output formats Investigate other security mechanisms n Investigate real usage on grid in research applications n © Columbia University
 Acknowledgments Ken Hall n Dan Washington n Brian Lee n Shannon Hastings n Philip Payne n This work was supported by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention grant P 01 HK 000029 © Columbia University
Acknowledgments Ken Hall n Dan Washington n Brian Lee n Shannon Hastings n Philip Payne n This work was supported by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention grant P 01 HK 000029 © Columbia University


