bf5e1df34e3528fa294e0b73ec07bdca.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Mechanical Biological Treatment of Residual Waste - Lessons from Europe Jeremy O’Brien, PE, BCEE Director of Applied Research, SWANA NC SWANA Fall Conference – Oct. 31 – Nov 2, 2017

SWANA Applied Research Foundation • Founded in 2001 • 46 Local Government and Corporate Subscribers • Conducts applied research on topics submitted by and voted on by Subscribers • Four Research Groups – Collection, Recycling, WTE, and Disposal.

SWANA 2018 ARF Subscribers From North Carolina Mecklenburg County, NC North Carolina SWANA Chapter Jeff Smithberger Solid Waste Director Vice President - HDR Joe Readling, PE Engineering, Inc. Senior Project Smith Gardner Inc. Mike Brinchek, PE Manager Solid Waste Winston-Salem , NC Jan Mc. Hargue, PE Administrator

Mechanical Biological Treatment of Residual Waste – Lessons from Europe 1. Capital costs and tipping fees can be high 2. Material recovery rates are low 3. Compost quality is poor 4. Diversion rates are 20% without energy recovery 4

Mechanical Biological Treatment of Residual Waste – Lessons from Europe • Developed to meet landfill treatment and stabilization requirements • 570 active MBT facilities in 2017 • 55 million tons per year • Another 120 facilities by 2025. 5
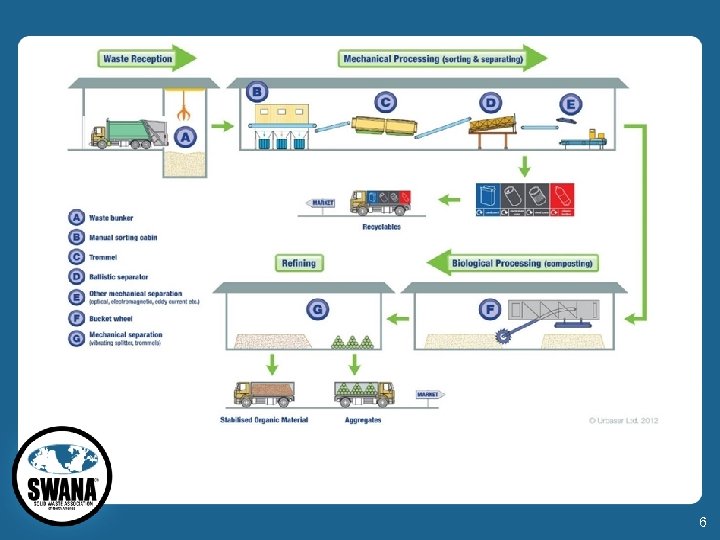
6

Parameter Mechanical. Biological Treatment Facility (MBT) Mixed Waste Processing Facility (MWPF) Type of waste processed Residual waste MSW Supplement to source-separation recycling Alternative to sourceseparation recycling Purpose Waste Yes No stabilization? Solid Yes In some cases recovered fuel? Status Over 550 facilities Very few facilities Europe 7

Residual Waste Composition in Austria in 2004 Fraction Mass (%) Organic / biogenic waste 37% Paper, cardboard and cartons 11% Hygiene products 11% Plastics 10% Composite materials 8% Textiles 6% Glass 5% Inert materials 4% Metals 3% Hazardous household wastes 2% Fine / coarse fractions 2% Wood – leather – rubber 1% Total 100% 8

Company Arrow. Bio Bedminster Biodegma BTA Civic Eco. Deco GRL Grontmij Haase Herhof Hese Horstmann Iska Where Process was Company Process was Developed Israel Linde Austria Sweden/USA Nehlsen Germany New Earth UK Germany OWS Dranco Belgium UK Ros. Roca Spain/Germany Italy Rumen Finland Australia SBI-Friesland Nether. /Finland SRS (Wright) Canada Germany Sutco Germany Valorga France Germany VKW Austria Germany Wastec UK Switzerland/Ge 9 Wherle
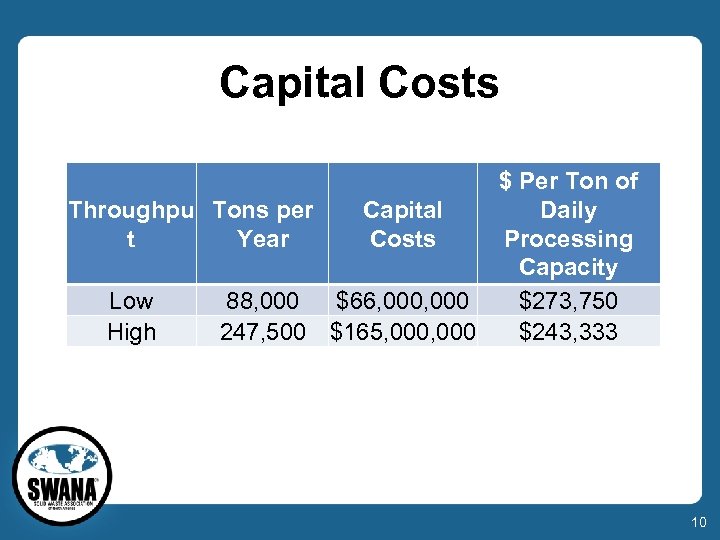
Capital Costs $ Per Ton of Capital Daily Throughpu Tons per Costs Processing t Year Capacity Low 88, 000 $66, 000 $273, 750 High 247, 500 $165, 000 $243, 333 10
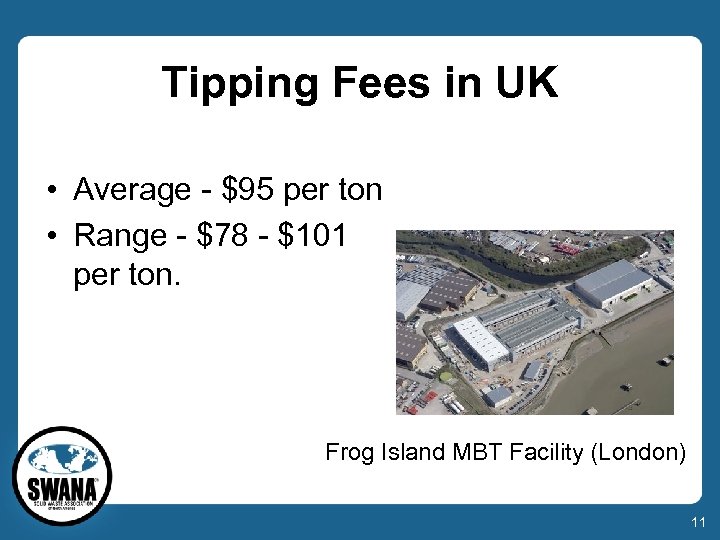
Tipping Fees in UK • Average - $95 per ton • Range - $78 - $101 per ton. Frog Island MBT Facility (London) 11
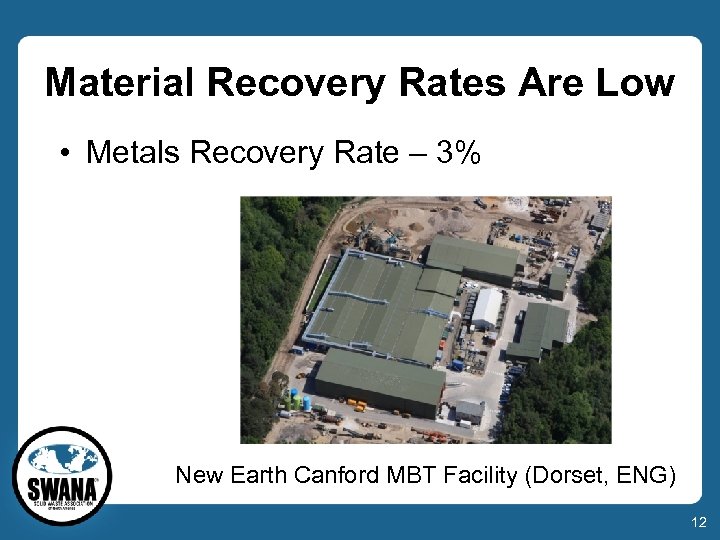
Material Recovery Rates Are Low • Metals Recovery Rate – 3% New Earth Canford MBT Facility (Dorset, ENG) 12

Compost Quality is Poor 13

Diversion Rates 14
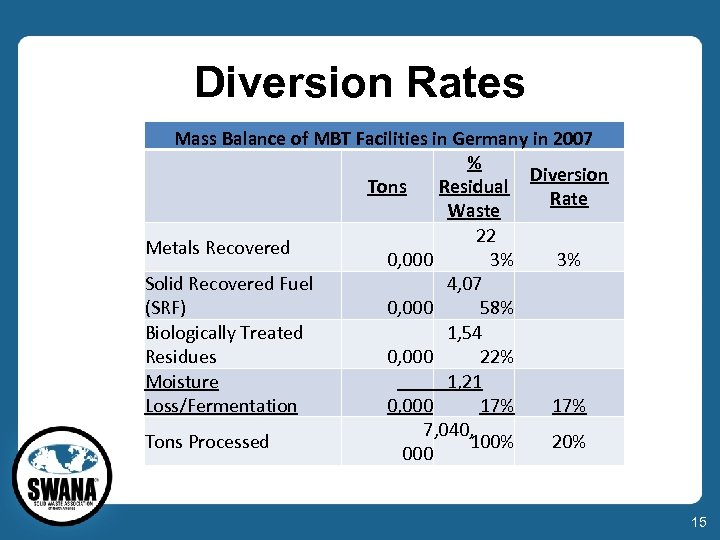
Diversion Rates Mass Balance of MBT Facilities in Germany in 2007 % Diversion Tons Residual Rate Waste 22 Metals Recovered 0, 000 3% 3% Solid Recovered Fuel 4, 07 (SRF) 0, 000 58% Biologically Treated 1, 54 Residues 0, 000 22% Moisture 1, 21 Loss/Fermentation 0, 000 17% 7, 040, Tons Processed 100% 20% 000 15

Reality Check • Residue Stream = 30% of MSW • MBT Diversion Rate = 20% of RS = 20% x 30% = 6%. 16

Mechanical Biological Treatment of Residual Waste – Lessons from Europe 1. Capital costs and tipping fees can be high 2. Material recovery rates are low 3. Compost quality is poor 4. Diversion rates are 20% without energy recovery 17

Thank You! • Questions? • Thoughts? • Comments? 18
bf5e1df34e3528fa294e0b73ec07bdca.ppt