dde487fcf7ba0a41e9ef426db36f94f4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 81
 Measuring Your Department’s Progress in the Advancement of Pharmacy Practice and Patient Safety CSHP Professional Practice Conference - Jan 2006 Patricia Macgregor, Nancy Roberts Editorial Board members
Measuring Your Department’s Progress in the Advancement of Pharmacy Practice and Patient Safety CSHP Professional Practice Conference - Jan 2006 Patricia Macgregor, Nancy Roberts Editorial Board members
 Outline l Overview of the sections of the 2003/04 Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Report (HPCR) – l l l Specialty Focus of the 2003/04 Report HPCR 2003/04 Indicators and trends Conducting a Self-Operational Review – l l Using ave. results for all hospital types Using specific results by hospital size & type Aligning Your Organizations Priorities Testimonials
Outline l Overview of the sections of the 2003/04 Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Report (HPCR) – l l l Specialty Focus of the 2003/04 Report HPCR 2003/04 Indicators and trends Conducting a Self-Operational Review – l l Using ave. results for all hospital types Using specific results by hospital size & type Aligning Your Organizations Priorities Testimonials
 Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Report (HPCR) l l l Measuring hospital pharmacy progress Data collection every two years Also known as “Lilly” report l www. lillyhospitalsurvey. ca
Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Report (HPCR) l l l Measuring hospital pharmacy progress Data collection every two years Also known as “Lilly” report l www. lillyhospitalsurvey. ca
 HPCR Sections l l l l Demographics Clinical Pharmacy Services Drug Information and Drug Use Evaluation Drug Distribution Drug Purchasing and Inventory Control Human Resources Medication Safety
HPCR Sections l l l l Demographics Clinical Pharmacy Services Drug Information and Drug Use Evaluation Drug Distribution Drug Purchasing and Inventory Control Human Resources Medication Safety
 HPCR Sections continued l l Technology Education and Research Pharmacy Staffing and Drug Costs for Clinical Programs - Acute Care Hospitals - Pediatric Hospitals Benchmarking
HPCR Sections continued l l Technology Education and Research Pharmacy Staffing and Drug Costs for Clinical Programs - Acute Care Hospitals - Pediatric Hospitals Benchmarking
 2003/04 HPCR Report Focus l l l l Medication safety and role of pharmacy leaders Clinical practice, direct patient care, pharmacist prescribing Incident reporting and reduction strategies Distribution delivery systems Escalating drug costs - utilization issues Human resources – impacts of shortages Technology applications
2003/04 HPCR Report Focus l l l l Medication safety and role of pharmacy leaders Clinical practice, direct patient care, pharmacist prescribing Incident reporting and reduction strategies Distribution delivery systems Escalating drug costs - utilization issues Human resources – impacts of shortages Technology applications
 Demographics l 144 hospitals responded Nationally – l l Inclusion criteria – 100 beds total, 50 acute beds 77% response rate overall 59% of respondents were multi-site facilities, similar to previous survey (higher in BC, Prairies and Atlantic)
Demographics l 144 hospitals responded Nationally – l l Inclusion criteria – 100 beds total, 50 acute beds 77% response rate overall 59% of respondents were multi-site facilities, similar to previous survey (higher in BC, Prairies and Atlantic)
 Clinical Data Captured l l l l Staffing allocations per specialty program Clinical pharmacy activity by type with occurrence rate Specific clinical activity priority and service level Methods and types of practice evaluation Prescribing privileges by profession Pharmacist prescribing authority by activity Clinical practice models and seamless care
Clinical Data Captured l l l l Staffing allocations per specialty program Clinical pharmacy activity by type with occurrence rate Specific clinical activity priority and service level Methods and types of practice evaluation Prescribing privileges by profession Pharmacist prescribing authority by activity Clinical practice models and seamless care
 Clinical Practice Trends l Decentralizing pharmacists may decrease medication errors by 45%. * l Centralized pharmacist -errors/bed 3. 15 Centralized with occasional unit visits -errors/bed 1. 93 Decentralized pharmacist -errors/bed 1. 74 l l l % clinical time unchanged, at 38%, from previous surveys *(Bond et al. Pharmacotherapy 2002 22 (2): 134 -47)
Clinical Practice Trends l Decentralizing pharmacists may decrease medication errors by 45%. * l Centralized pharmacist -errors/bed 3. 15 Centralized with occasional unit visits -errors/bed 1. 93 Decentralized pharmacist -errors/bed 1. 74 l l l % clinical time unchanged, at 38%, from previous surveys *(Bond et al. Pharmacotherapy 2002 22 (2): 134 -47)
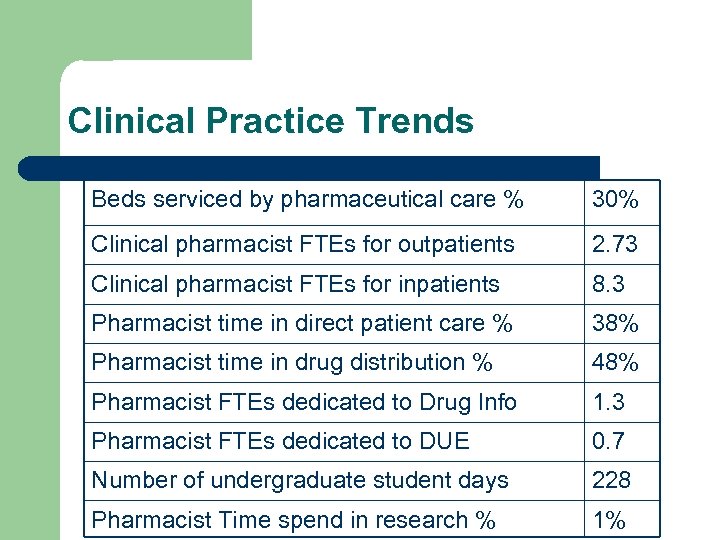 Clinical Practice Trends Beds serviced by pharmaceutical care % 30% Clinical pharmacist FTEs for outpatients 2. 73 Clinical pharmacist FTEs for inpatients 8. 3 Pharmacist time in direct patient care % 38% Pharmacist time in drug distribution % 48% Pharmacist FTEs dedicated to Drug Info 1. 3 Pharmacist FTEs dedicated to DUE 0. 7 Number of undergraduate student days 228 Pharmacist Time spend in research % 1%
Clinical Practice Trends Beds serviced by pharmaceutical care % 30% Clinical pharmacist FTEs for outpatients 2. 73 Clinical pharmacist FTEs for inpatients 8. 3 Pharmacist time in direct patient care % 38% Pharmacist time in drug distribution % 48% Pharmacist FTEs dedicated to Drug Info 1. 3 Pharmacist FTEs dedicated to DUE 0. 7 Number of undergraduate student days 228 Pharmacist Time spend in research % 1%
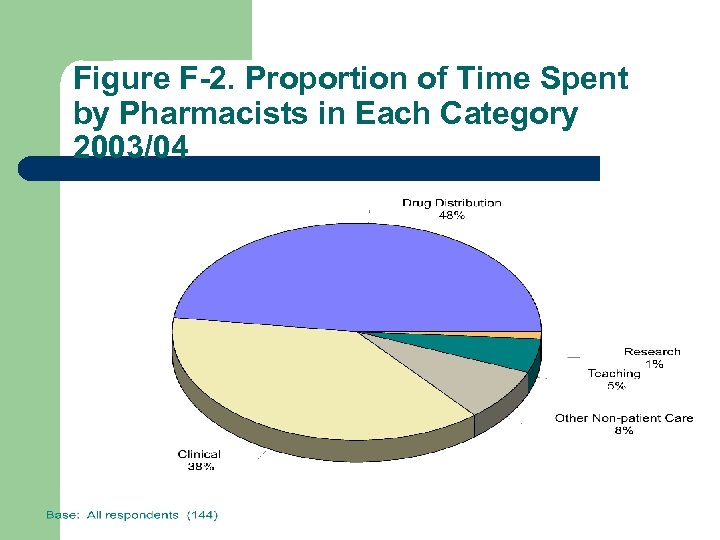 Figure F-2. Proportion of Time Spent by Pharmacists in Each Category 2003/04
Figure F-2. Proportion of Time Spent by Pharmacists in Each Category 2003/04
 Outpatient Pharmacist FTE Ratios Average 0. 14 FTE pharmacist/10, 000 visits l DVT/anticoagulation 2. 02 FTE/10, 000 visit l Infectious disease 2. 00 FTE l Cardiovascular/lipid 1. 67 FTE l Diabetes 1. 16 FTE l Hematology/oncology 1. 06 FTE l Emerg 0. 02 FTE
Outpatient Pharmacist FTE Ratios Average 0. 14 FTE pharmacist/10, 000 visits l DVT/anticoagulation 2. 02 FTE/10, 000 visit l Infectious disease 2. 00 FTE l Cardiovascular/lipid 1. 67 FTE l Diabetes 1. 16 FTE l Hematology/oncology 1. 06 FTE l Emerg 0. 02 FTE
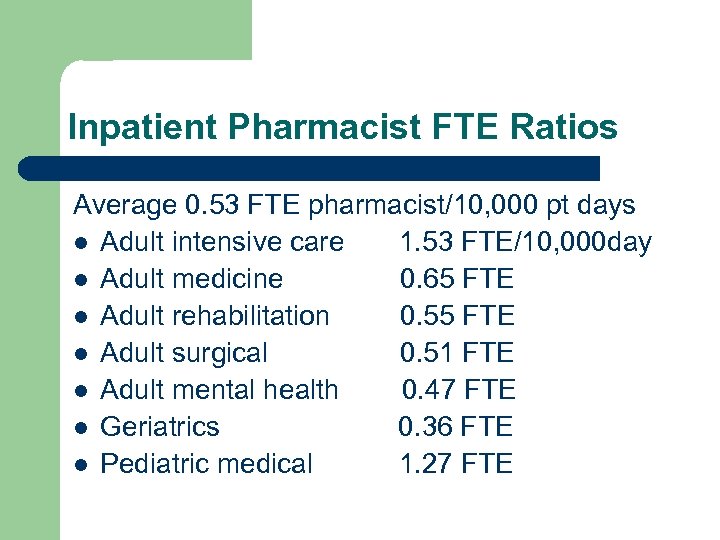 Inpatient Pharmacist FTE Ratios Average 0. 53 FTE pharmacist/10, 000 pt days l Adult intensive care 1. 53 FTE/10, 000 day l Adult medicine 0. 65 FTE l Adult rehabilitation 0. 55 FTE l Adult surgical 0. 51 FTE l Adult mental health 0. 47 FTE l Geriatrics 0. 36 FTE l Pediatric medical 1. 27 FTE
Inpatient Pharmacist FTE Ratios Average 0. 53 FTE pharmacist/10, 000 pt days l Adult intensive care 1. 53 FTE/10, 000 day l Adult medicine 0. 65 FTE l Adult rehabilitation 0. 55 FTE l Adult surgical 0. 51 FTE l Adult mental health 0. 47 FTE l Geriatrics 0. 36 FTE l Pediatric medical 1. 27 FTE
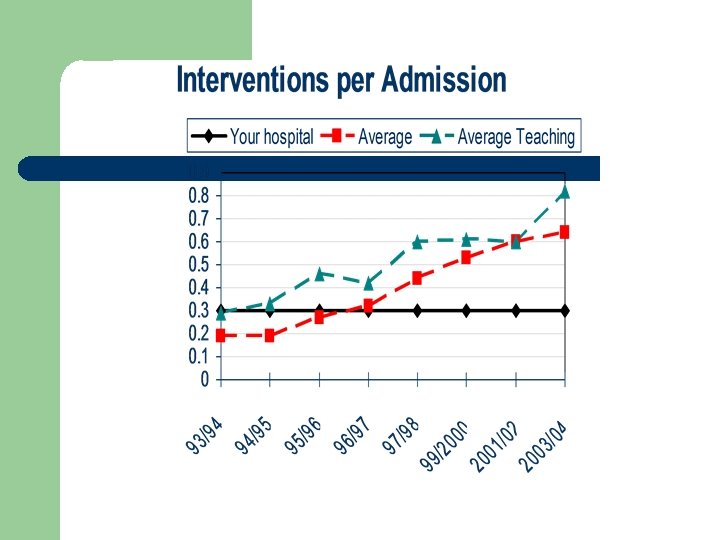
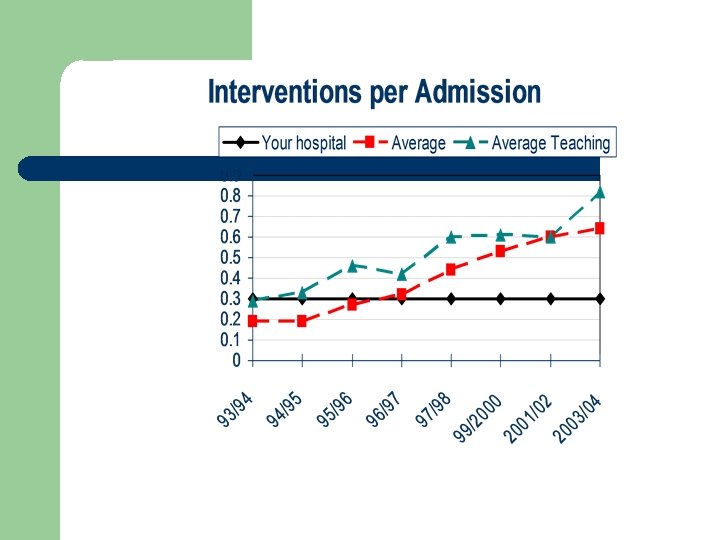
 Clinical Activities Documentation l # interventions per admission – 0. 64 – Increase from 0. 6 in 2001/02 and 0. 53 in 1999/00 Annual interventions per pharm FTE – 645 l Still 20% respondents who do document do not do it in the patient chart l Pharmacokinetic documentations on the increase l
Clinical Activities Documentation l # interventions per admission – 0. 64 – Increase from 0. 6 in 2001/02 and 0. 53 in 1999/00 Annual interventions per pharm FTE – 645 l Still 20% respondents who do document do not do it in the patient chart l Pharmacokinetic documentations on the increase l
 Priority Ranking vs Actual Activity l Bond et al – 6 clinical services associated with lower total cost of care – l l DUE, drug information, ADE monitoring, Drug protocol management, medical rounds participation, admission drug histories Yet none was reported by more than 70% of respondents as being among the top 10 priorities Participants rated clinical services by priority and by extent offered – striking discrepancy
Priority Ranking vs Actual Activity l Bond et al – 6 clinical services associated with lower total cost of care – l l DUE, drug information, ADE monitoring, Drug protocol management, medical rounds participation, admission drug histories Yet none was reported by more than 70% of respondents as being among the top 10 priorities Participants rated clinical services by priority and by extent offered – striking discrepancy
 Clinical Practice Models and Evaluation l 81% reported clinical practice services NOT offered to some inpatients – l l Equals 33% of inpatient beds Pharmaceutical care – 70% reported using average 30 beds serviced Only 17% evaluate clinical practice
Clinical Practice Models and Evaluation l 81% reported clinical practice services NOT offered to some inpatients – l l Equals 33% of inpatient beds Pharmaceutical care – 70% reported using average 30 beds serviced Only 17% evaluate clinical practice
 Prescribing Privileges l l Pharmacists Midwives Nurse practitioners Other professionals 66% 45% 47% 20%
Prescribing Privileges l l Pharmacists Midwives Nurse practitioners Other professionals 66% 45% 47% 20%
 Pharmacists Prescribing l l l Lab tests – 21% Independent dosage adjustments – 23% New therapy – 5% Dependent, dosage adjustment – 46% Dependent, new therapy -13%
Pharmacists Prescribing l l l Lab tests – 21% Independent dosage adjustments – 23% New therapy – 5% Dependent, dosage adjustment – 46% Dependent, new therapy -13%
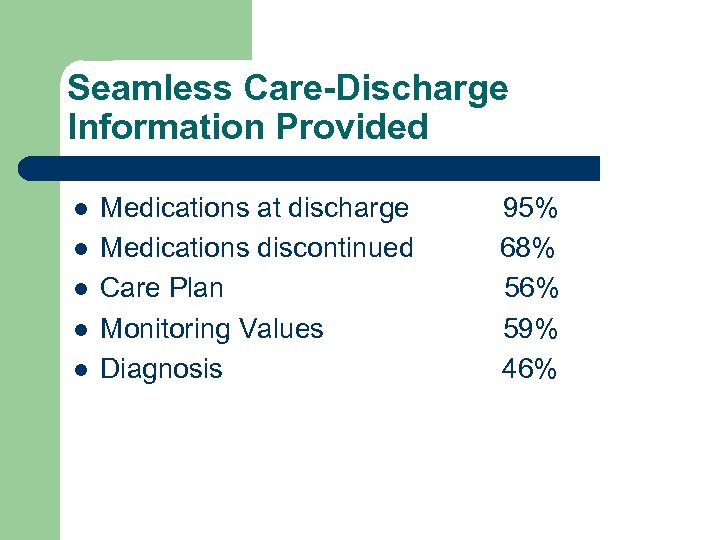 Seamless Care-Discharge Information Provided l l l Medications at discharge Medications discontinued Care Plan Monitoring Values Diagnosis 95% 68% 56% 59% 46%
Seamless Care-Discharge Information Provided l l l Medications at discharge Medications discontinued Care Plan Monitoring Values Diagnosis 95% 68% 56% 59% 46%
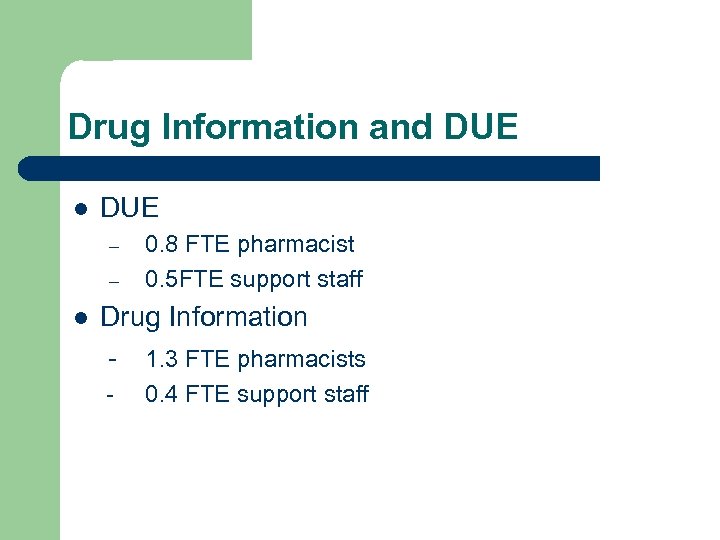 Drug Information and DUE l DUE – – l 0. 8 FTE pharmacist 0. 5 FTE support staff Drug Information - 1. 3 FTE pharmacists - 0. 4 FTE support staff
Drug Information and DUE l DUE – – l 0. 8 FTE pharmacist 0. 5 FTE support staff Drug Information - 1. 3 FTE pharmacists - 0. 4 FTE support staff
 Drug Distribution and Delivery l l l l Systems used Order entry Order verification MARs, medication profiles etc Technician check technician IV admixture Oncology Ambulatory services
Drug Distribution and Delivery l l l l Systems used Order entry Order verification MARs, medication profiles etc Technician check technician IV admixture Oncology Ambulatory services
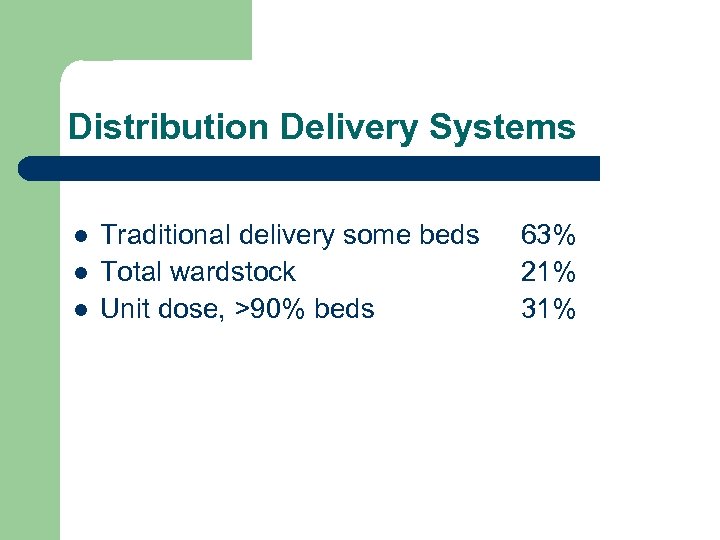 Distribution Delivery Systems l l l Traditional delivery some beds Total wardstock Unit dose, >90% beds 63% 21% 31%
Distribution Delivery Systems l l l Traditional delivery some beds Total wardstock Unit dose, >90% beds 63% 21% 31%
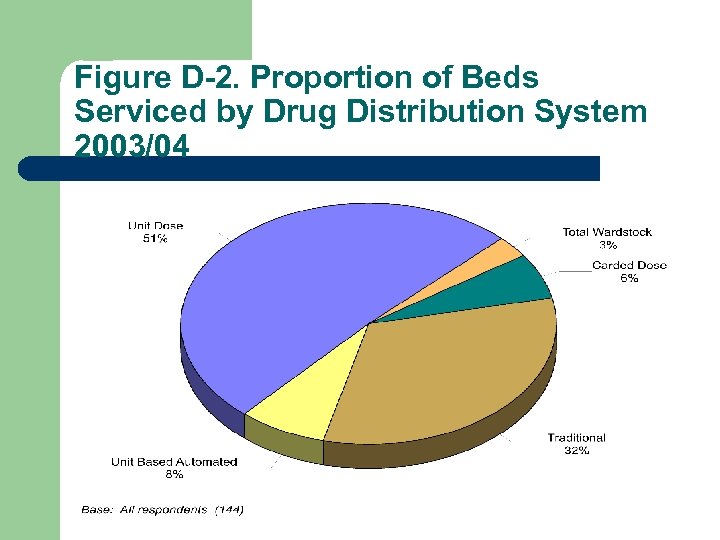 Figure D-2. Proportion of Beds Serviced by Drug Distribution System 2003/04
Figure D-2. Proportion of Beds Serviced by Drug Distribution System 2003/04
 Order Entry l Pharmacists Technicians Nurses Physicians l Pharmacist verify pharmacist OE l l l 79% 78% 5% 3% *Significant increase from 01/02 report -41% - 27%
Order Entry l Pharmacists Technicians Nurses Physicians l Pharmacist verify pharmacist OE l l l 79% 78% 5% 3% *Significant increase from 01/02 report -41% - 27%
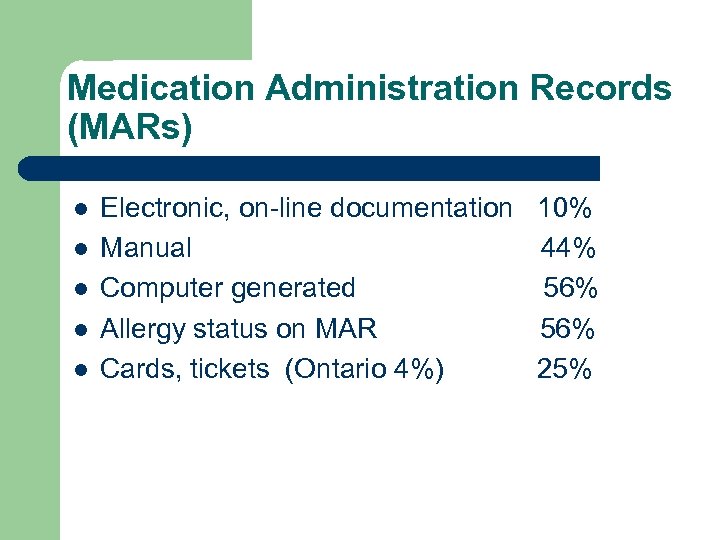 Medication Administration Records (MARs) l l l Electronic, on-line documentation Manual Computer generated Allergy status on MAR Cards, tickets (Ontario 4%) 10% 44% 56% 25%
Medication Administration Records (MARs) l l l Electronic, on-line documentation Manual Computer generated Allergy status on MAR Cards, tickets (Ontario 4%) 10% 44% 56% 25%
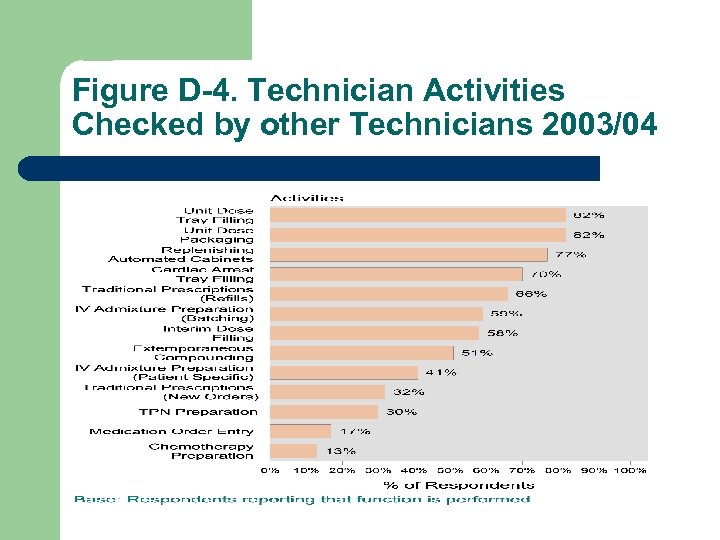 Figure D-4. Technician Activities Checked by other Technicians 2003/04
Figure D-4. Technician Activities Checked by other Technicians 2003/04
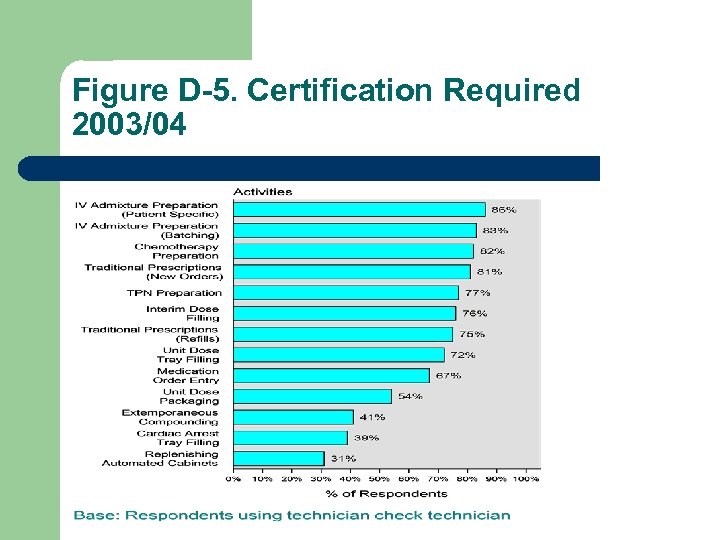 Figure D-5. Certification Required 2003/04
Figure D-5. Certification Required 2003/04
 Drug Purchasing and Inventory Control l l PMRB reported sales from drugs increased 14. 5% in 2003 Since 2001/02 report: – – – l Acute care inpatient drug cost/pt day only increased 26 cents. (Ave $31. 25) Emerg costs/patient day increased 24% Ave inventory increased by 10. 6% CIHI - Drugs = 16. 2% of total healthcare costs
Drug Purchasing and Inventory Control l l PMRB reported sales from drugs increased 14. 5% in 2003 Since 2001/02 report: – – – l Acute care inpatient drug cost/pt day only increased 26 cents. (Ave $31. 25) Emerg costs/patient day increased 24% Ave inventory increased by 10. 6% CIHI - Drugs = 16. 2% of total healthcare costs
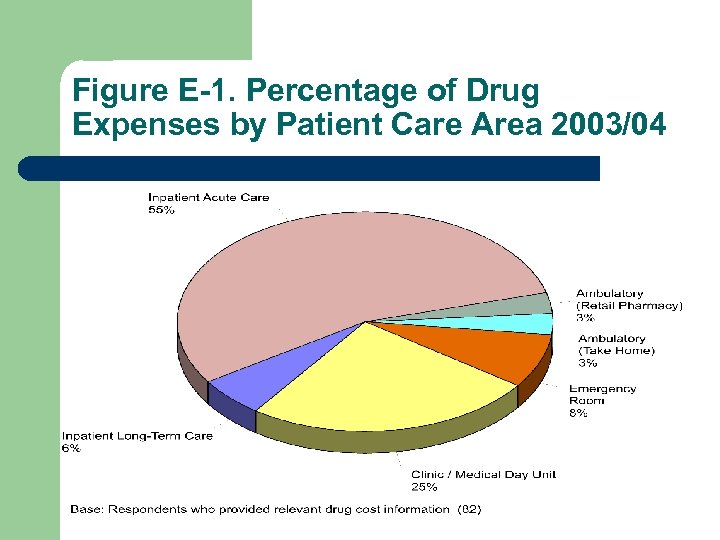 Figure E-1. Percentage of Drug Expenses by Patient Care Area 2003/04
Figure E-1. Percentage of Drug Expenses by Patient Care Area 2003/04
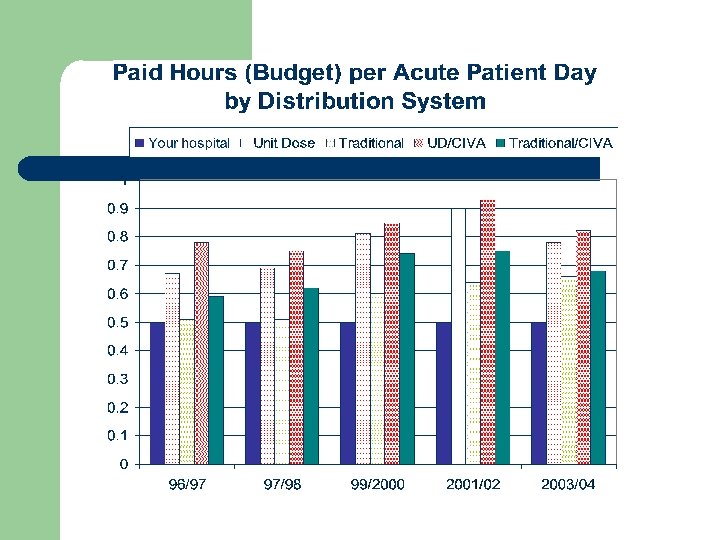
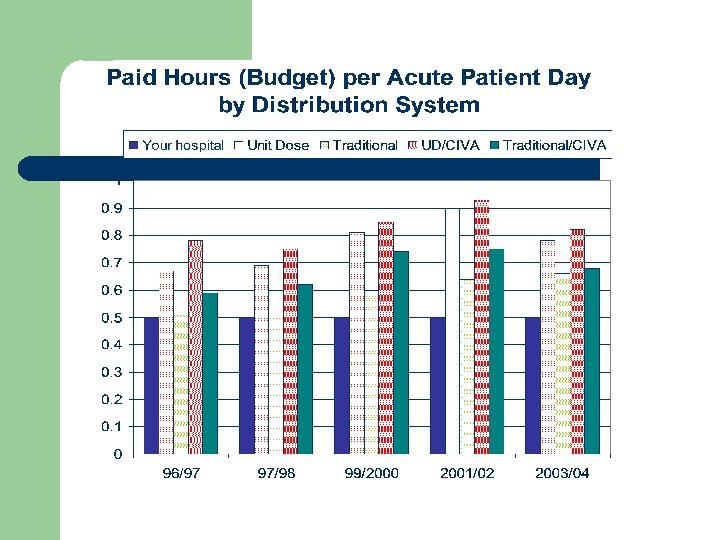
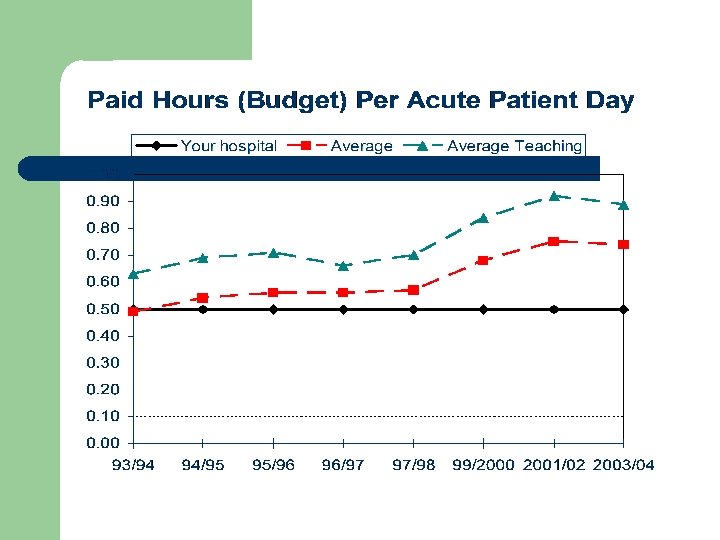
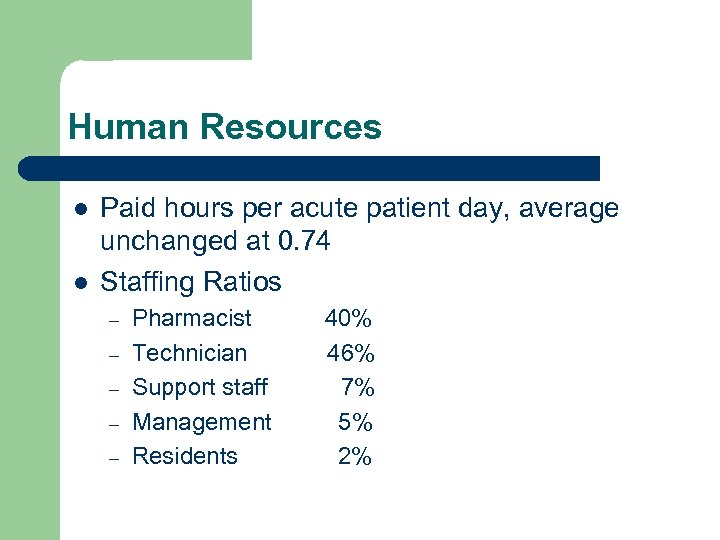 Human Resources l l Paid hours per acute patient day, average unchanged at 0. 74 Staffing Ratios – – – Pharmacist Technician Support staff Management Residents 40% 46% 7% 5% 2%
Human Resources l l Paid hours per acute patient day, average unchanged at 0. 74 Staffing Ratios – – – Pharmacist Technician Support staff Management Residents 40% 46% 7% 5% 2%
 Human Resource Shortages l 63% of respondents reported vacancies as follows: – – Pharmacist vacancies Management Technicians Residency vacancies 12. 9% 6. 9% 0. 9% 13. 8% *Concern expressed re reduced student applications
Human Resource Shortages l 63% of respondents reported vacancies as follows: – – Pharmacist vacancies Management Technicians Residency vacancies 12. 9% 6. 9% 0. 9% 13. 8% *Concern expressed re reduced student applications
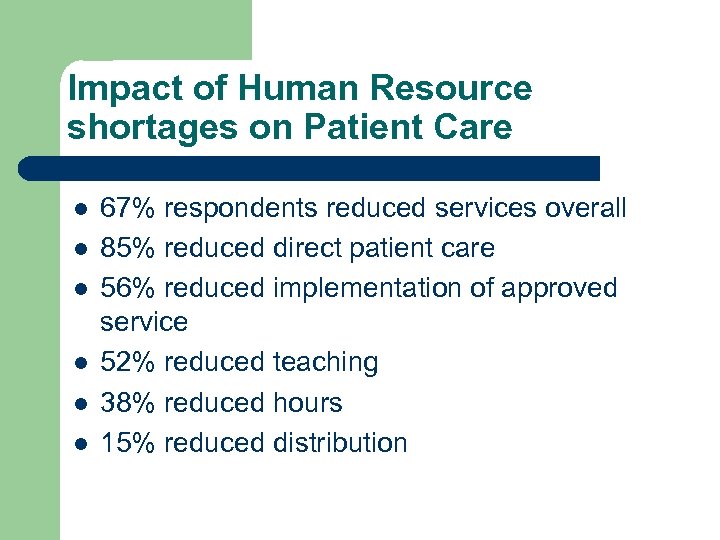 Impact of Human Resource shortages on Patient Care l l l 67% respondents reduced services overall 85% reduced direct patient care 56% reduced implementation of approved service 52% reduced teaching 38% reduced hours 15% reduced distribution
Impact of Human Resource shortages on Patient Care l l l 67% respondents reduced services overall 85% reduced direct patient care 56% reduced implementation of approved service 52% reduced teaching 38% reduced hours 15% reduced distribution
 Medication Incident Reporting and Reduction Strategies l l l 100% use med incident reporting tool 67% implemented strategies to increase reporting 63% disclosure policy 80% have committee to review med safety DTC, risk, quality, MAC, Pharm/nursing 51% completed self assessment tool 95% of assessment tools used were ISMP
Medication Incident Reporting and Reduction Strategies l l l 100% use med incident reporting tool 67% implemented strategies to increase reporting 63% disclosure policy 80% have committee to review med safety DTC, risk, quality, MAC, Pharm/nursing 51% completed self assessment tool 95% of assessment tools used were ISMP
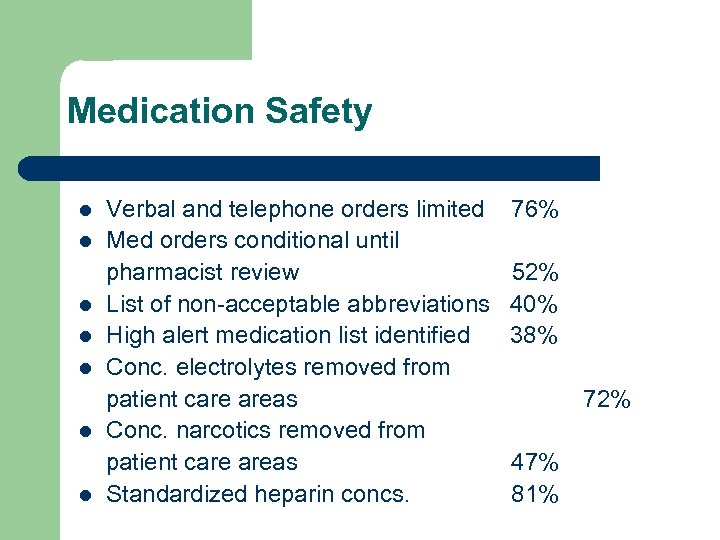 Medication Safety l l l l Verbal and telephone orders limited Med orders conditional until pharmacist review List of non-acceptable abbreviations High alert medication list identified Conc. electrolytes removed from patient care areas Conc. narcotics removed from patient care areas Standardized heparin concs. 76% 52% 40% 38% 72% 47% 81%
Medication Safety l l l l Verbal and telephone orders limited Med orders conditional until pharmacist review List of non-acceptable abbreviations High alert medication list identified Conc. electrolytes removed from patient care areas Conc. narcotics removed from patient care areas Standardized heparin concs. 76% 52% 40% 38% 72% 47% 81%
 Issues for Patient Safety l Medication safety is related to the extent of pharmacist involvement in direct patient care, yet why is: – – Time spent in clinical activity unchanged since 1999 (38%) Clinical services still NOT provided to some inpatients (33% inpatient beds) Specific safety initiatives only partially implemented ? Related to pharmacist shortage
Issues for Patient Safety l Medication safety is related to the extent of pharmacist involvement in direct patient care, yet why is: – – Time spent in clinical activity unchanged since 1999 (38%) Clinical services still NOT provided to some inpatients (33% inpatient beds) Specific safety initiatives only partially implemented ? Related to pharmacist shortage
 Technology Pharmacy systems with clinical decision support l Automated max. dosage alerts l Fully interfaced lab results l CPOE l Handheld devices l Wireless network with handheld l 40% 28% 25% 5% 49% 8%
Technology Pharmacy systems with clinical decision support l Automated max. dosage alerts l Fully interfaced lab results l CPOE l Handheld devices l Wireless network with handheld l 40% 28% 25% 5% 49% 8%
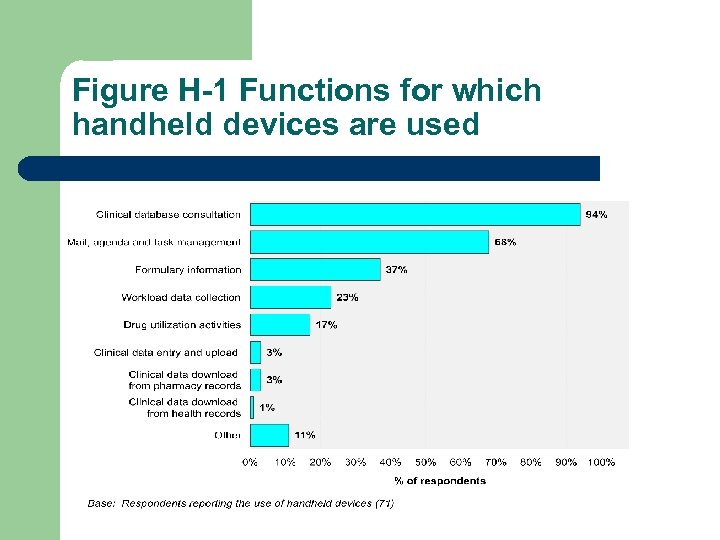 Figure H-1 Functions for which handheld devices are used
Figure H-1 Functions for which handheld devices are used
 Bar Code Technology l l FDA - USA mandate bar codes at bedside – by May 2006 22% respondents use bar code technology – Up from 11% in 2002
Bar Code Technology l l FDA - USA mandate bar codes at bedside – by May 2006 22% respondents use bar code technology – Up from 11% in 2002
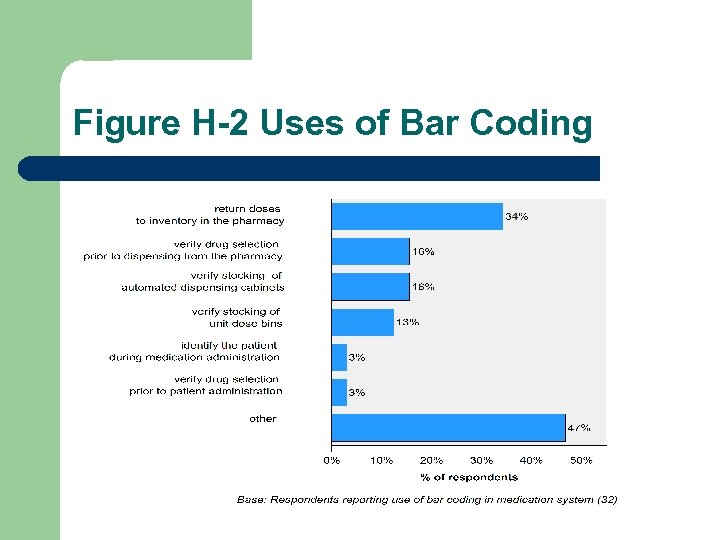 Figure H-2 Uses of Bar Coding
Figure H-2 Uses of Bar Coding
 Education and Research l Education - Student training remained a high priority with: – – l 83% reporting training for under-graduate pharmacy students 26% reporting training for pharmacy residents Research – Sites conducting research decreased to 35% from 43% in 1999/2000 ( may be related to the 13. 8% residency position vacancy rate)
Education and Research l Education - Student training remained a high priority with: – – l 83% reporting training for under-graduate pharmacy students 26% reporting training for pharmacy residents Research – Sites conducting research decreased to 35% from 43% in 1999/2000 ( may be related to the 13. 8% residency position vacancy rate)
 Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Annual Report Analysis of Indicators
Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Annual Report Analysis of Indicators
 Lilly Report User Customizable Benchmarking Report l l l l Paid hours per acute patient day by distribution system Drug costs per acute patient day Drug costs per acute admission Inventory turns IV production per acute patient day Interventions per admission
Lilly Report User Customizable Benchmarking Report l l l l Paid hours per acute patient day by distribution system Drug costs per acute patient day Drug costs per acute admission Inventory turns IV production per acute patient day Interventions per admission
 Additional benchmarking tables in the Report l l l Ave drug costs per day by clinical program Ave paid hours per admixture – CIVA, oncology, per investigational drug study Ave paid hours for inventory/procurement and for DUE per $1 m drug purchases Ave paid hours per patient day for high acuity programs e. g bone marrow transplant, neonatal or pediatric ICU Changes in drug expense by patient care area Total drug costs by patient care area
Additional benchmarking tables in the Report l l l Ave drug costs per day by clinical program Ave paid hours per admixture – CIVA, oncology, per investigational drug study Ave paid hours for inventory/procurement and for DUE per $1 m drug purchases Ave paid hours per patient day for high acuity programs e. g bone marrow transplant, neonatal or pediatric ICU Changes in drug expense by patient care area Total drug costs by patient care area
 What’s Next? How does your Organization shape up in comparison to your peers?
What’s Next? How does your Organization shape up in comparison to your peers?
 Conducting a Self-Operational Review
Conducting a Self-Operational Review
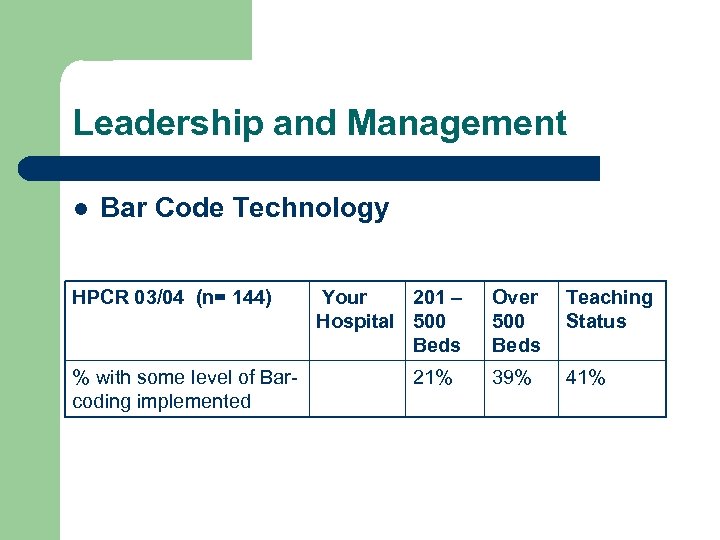 Leadership and Management l Bar Code Technology HPCR 03/04 (n= 144) % with some level of Barcoding implemented Your 201 – Hospital 500 Beds 21% Over 500 Beds Teaching Status 39% 41%
Leadership and Management l Bar Code Technology HPCR 03/04 (n= 144) % with some level of Barcoding implemented Your 201 – Hospital 500 Beds 21% Over 500 Beds Teaching Status 39% 41%
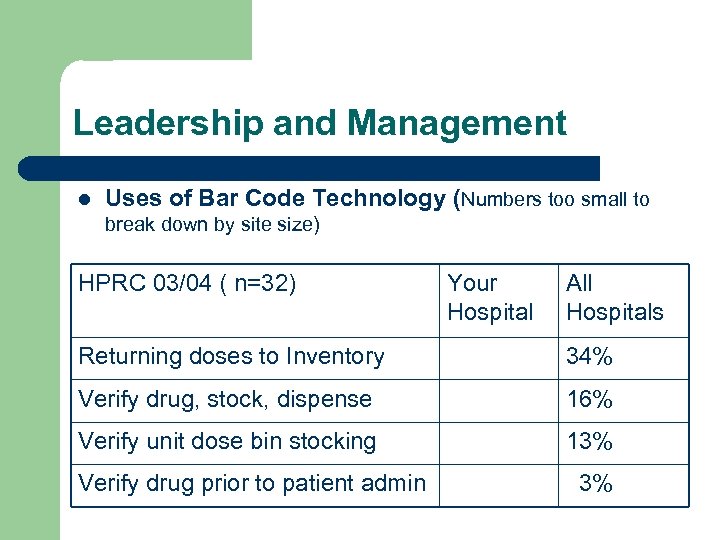 Leadership and Management l Uses of Bar Code Technology (Numbers too small to break down by site size) HPRC 03/04 ( n=32) Your Hospital All Hospitals Returning doses to Inventory 34% Verify drug, stock, dispense 16% Verify unit dose bin stocking 13% Verify drug prior to patient admin 3%
Leadership and Management l Uses of Bar Code Technology (Numbers too small to break down by site size) HPRC 03/04 ( n=32) Your Hospital All Hospitals Returning doses to Inventory 34% Verify drug, stock, dispense 16% Verify unit dose bin stocking 13% Verify drug prior to patient admin 3%
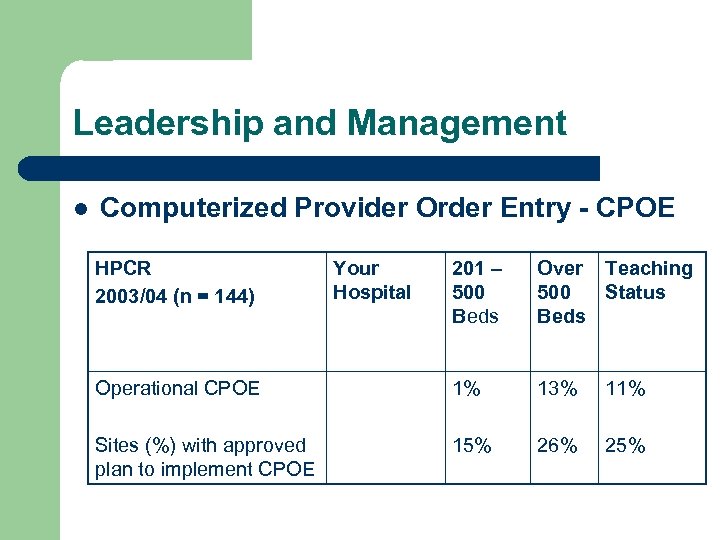 Leadership and Management l Computerized Provider Order Entry - CPOE HPCR 2003/04 (n = 144) Your Hospital 201 – 500 Beds Over Teaching 500 Status Beds Operational CPOE 1% 13% 11% Sites (%) with approved plan to implement CPOE 15% 26% 25%
Leadership and Management l Computerized Provider Order Entry - CPOE HPCR 2003/04 (n = 144) Your Hospital 201 – 500 Beds Over Teaching 500 Status Beds Operational CPOE 1% 13% 11% Sites (%) with approved plan to implement CPOE 15% 26% 25%
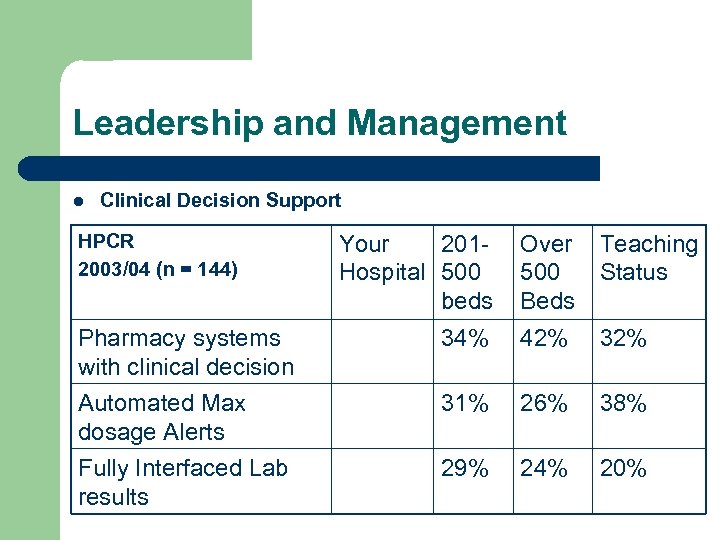 Leadership and Management l Clinical Decision Support HPCR 2003/04 (n = 144) Your 201 Hospital 500 beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status Pharmacy systems with clinical decision 34% 42% 32% Automated Max dosage Alerts Fully Interfaced Lab results 31% 26% 38% 29% 24% 20%
Leadership and Management l Clinical Decision Support HPCR 2003/04 (n = 144) Your 201 Hospital 500 beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status Pharmacy systems with clinical decision 34% 42% 32% Automated Max dosage Alerts Fully Interfaced Lab results 31% 26% 38% 29% 24% 20%
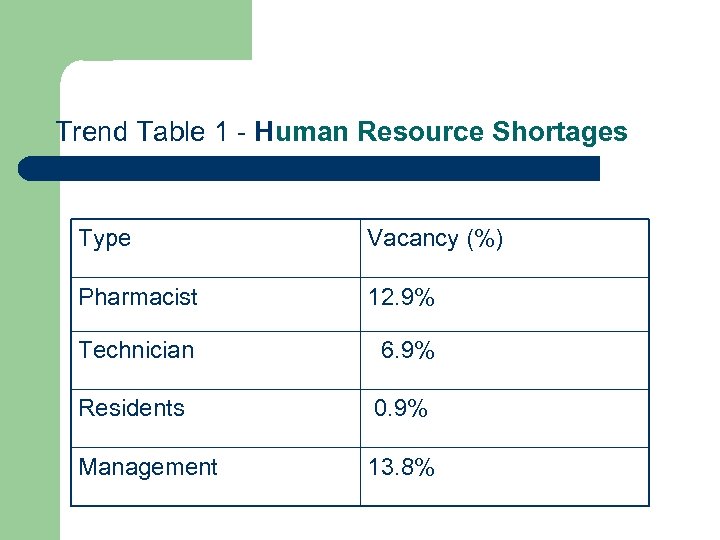 Trend Table 1 - Human Resource Shortages Type Vacancy (%) Pharmacist 12. 9% Technician 6. 9% Residents 0. 9% Management 13. 8%
Trend Table 1 - Human Resource Shortages Type Vacancy (%) Pharmacist 12. 9% Technician 6. 9% Residents 0. 9% Management 13. 8%
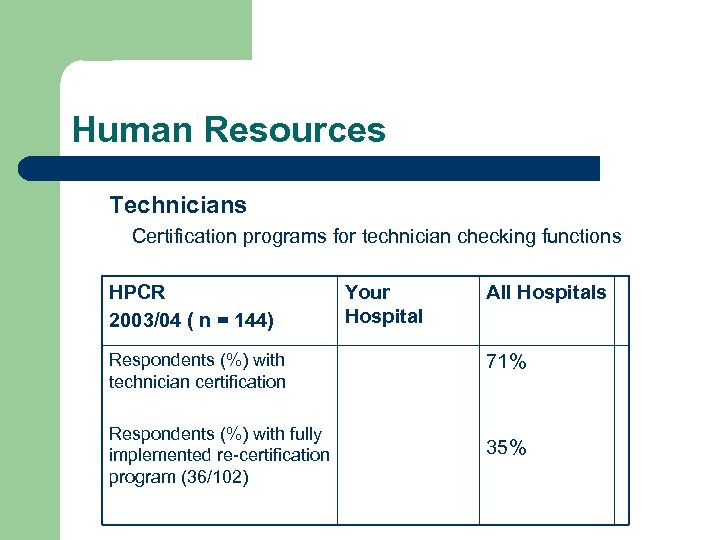 Human Resources Technicians Certification programs for technician checking functions HPCR 2003/04 ( n = 144) Respondents (%) with technician certification Respondents (%) with fully implemented re-certification program (36/102) Your Hospital All Hospitals 71% 35%
Human Resources Technicians Certification programs for technician checking functions HPCR 2003/04 ( n = 144) Respondents (%) with technician certification Respondents (%) with fully implemented re-certification program (36/102) Your Hospital All Hospitals 71% 35%
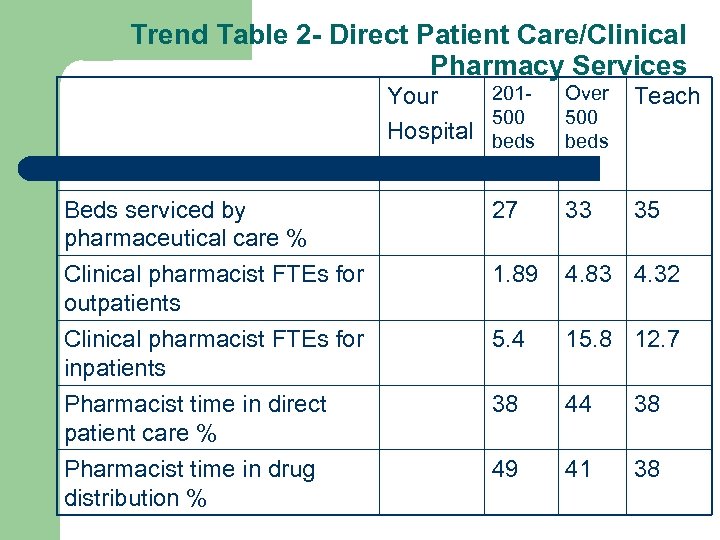 Trend Table 2 - Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services 201 Your 500 Hospital beds Over 500 beds Teach 35 Beds serviced by pharmaceutical care % 27 33 Clinical pharmacist FTEs for outpatients Clinical pharmacist FTEs for inpatients 1. 89 4. 83 4. 32 5. 4 15. 8 12. 7 Pharmacist time in direct patient care % Pharmacist time in drug distribution % 38 44 38 49 41 38
Trend Table 2 - Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services 201 Your 500 Hospital beds Over 500 beds Teach 35 Beds serviced by pharmaceutical care % 27 33 Clinical pharmacist FTEs for outpatients Clinical pharmacist FTEs for inpatients 1. 89 4. 83 4. 32 5. 4 15. 8 12. 7 Pharmacist time in direct patient care % Pharmacist time in drug distribution % 38 44 38 49 41 38
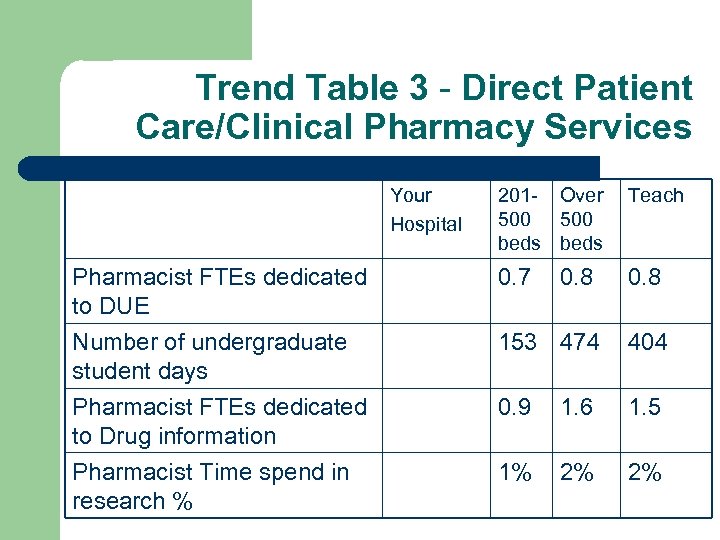 Trend Table 3 - Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services Your Hospital 201 - Over 500 beds Teach Pharmacist FTEs dedicated to DUE 0. 7 0. 8 Number of undergraduate student days 153 474 404 Pharmacist FTEs dedicated to Drug information Pharmacist Time spend in research % 0. 9 1. 6 1. 5 1% 2% 2%
Trend Table 3 - Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services Your Hospital 201 - Over 500 beds Teach Pharmacist FTEs dedicated to DUE 0. 7 0. 8 Number of undergraduate student days 153 474 404 Pharmacist FTEs dedicated to Drug information Pharmacist Time spend in research % 0. 9 1. 6 1. 5 1% 2% 2%
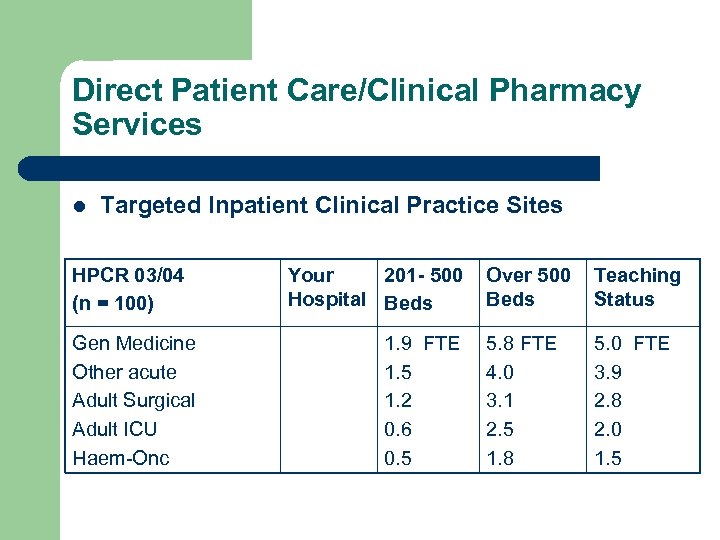 Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services l Targeted Inpatient Clinical Practice Sites HPCR 03/04 (n = 100) Gen Medicine Other acute Adult Surgical Adult ICU Haem-Onc Your 201 - 500 Hospital Beds 1. 9 FTE 1. 5 1. 2 0. 6 0. 5 Over 500 Beds Teaching Status 5. 8 FTE 4. 0 3. 1 2. 5 1. 8 5. 0 FTE 3. 9 2. 8 2. 0 1. 5
Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services l Targeted Inpatient Clinical Practice Sites HPCR 03/04 (n = 100) Gen Medicine Other acute Adult Surgical Adult ICU Haem-Onc Your 201 - 500 Hospital Beds 1. 9 FTE 1. 5 1. 2 0. 6 0. 5 Over 500 Beds Teaching Status 5. 8 FTE 4. 0 3. 1 2. 5 1. 8 5. 0 FTE 3. 9 2. 8 2. 0 1. 5
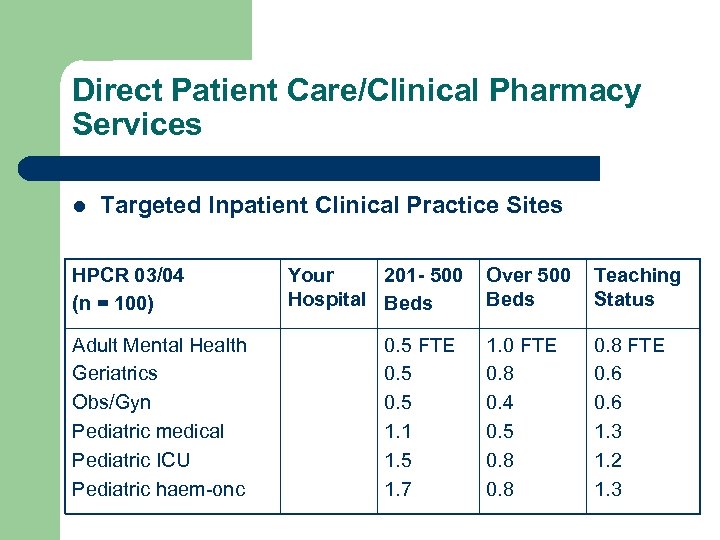 Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services l Targeted Inpatient Clinical Practice Sites HPCR 03/04 (n = 100) Adult Mental Health Geriatrics Obs/Gyn Pediatric medical Pediatric ICU Pediatric haem-onc Your 201 - 500 Hospital Beds 0. 5 FTE 0. 5 1. 1 1. 5 1. 7 Over 500 Beds Teaching Status 1. 0 FTE 0. 8 0. 4 0. 5 0. 8 FTE 0. 6 1. 3 1. 2 1. 3
Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services l Targeted Inpatient Clinical Practice Sites HPCR 03/04 (n = 100) Adult Mental Health Geriatrics Obs/Gyn Pediatric medical Pediatric ICU Pediatric haem-onc Your 201 - 500 Hospital Beds 0. 5 FTE 0. 5 1. 1 1. 5 1. 7 Over 500 Beds Teaching Status 1. 0 FTE 0. 8 0. 4 0. 5 0. 8 FTE 0. 6 1. 3 1. 2 1. 3
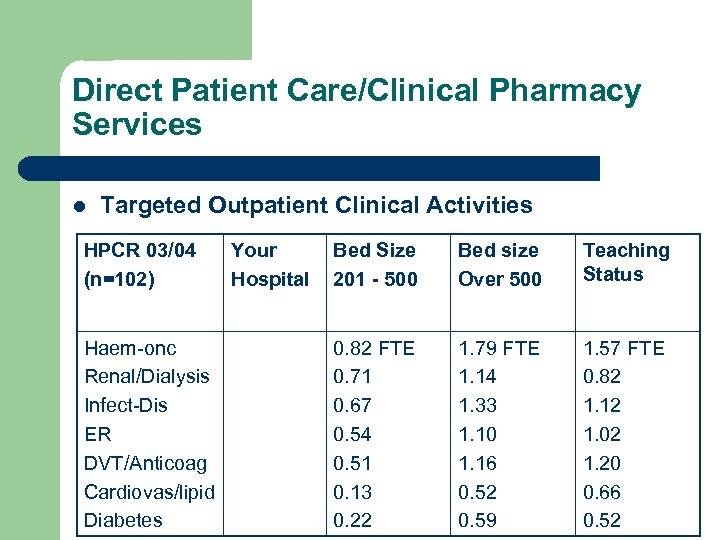 Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services l Targeted Outpatient Clinical Activities HPCR 03/04 (n=102) Haem-onc Renal/Dialysis Infect-Dis ER DVT/Anticoag Cardiovas/lipid Diabetes Your Hospital Bed Size 201 - 500 Bed size Over 500 Teaching Status 0. 82 FTE 0. 71 0. 67 0. 54 0. 51 0. 13 0. 22 1. 79 FTE 1. 14 1. 33 1. 10 1. 16 0. 52 0. 59 1. 57 FTE 0. 82 1. 12 1. 02 1. 20 0. 66 0. 52
Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services l Targeted Outpatient Clinical Activities HPCR 03/04 (n=102) Haem-onc Renal/Dialysis Infect-Dis ER DVT/Anticoag Cardiovas/lipid Diabetes Your Hospital Bed Size 201 - 500 Bed size Over 500 Teaching Status 0. 82 FTE 0. 71 0. 67 0. 54 0. 51 0. 13 0. 22 1. 79 FTE 1. 14 1. 33 1. 10 1. 16 0. 52 0. 59 1. 57 FTE 0. 82 1. 12 1. 02 1. 20 0. 66 0. 52
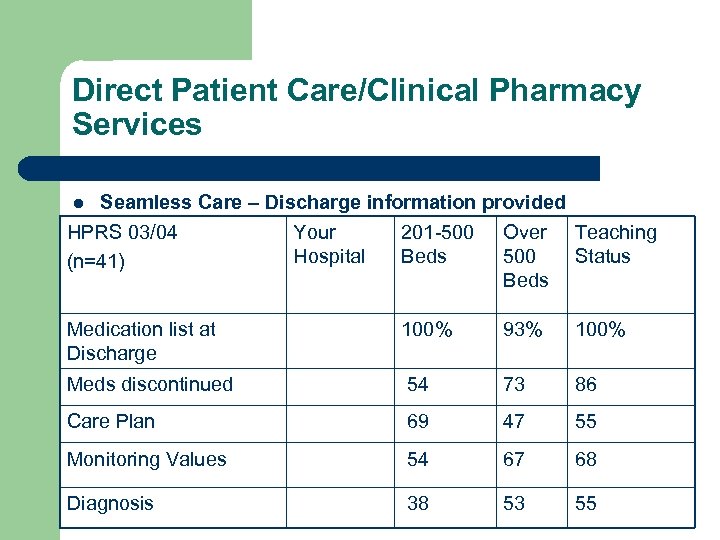 Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services Seamless Care – Discharge information provided HPRS 03/04 Your 201 -500 Over Teaching Hospital Beds 500 Status (n=41) Beds l Medication list at Discharge 100% 93% 100% Meds discontinued 54 73 86 Care Plan 69 47 55 Monitoring Values 54 67 68 Diagnosis 38 53 55
Direct Patient Care/Clinical Pharmacy Services Seamless Care – Discharge information provided HPRS 03/04 Your 201 -500 Over Teaching Hospital Beds 500 Status (n=41) Beds l Medication list at Discharge 100% 93% 100% Meds discontinued 54 73 86 Care Plan 69 47 55 Monitoring Values 54 67 68 Diagnosis 38 53 55
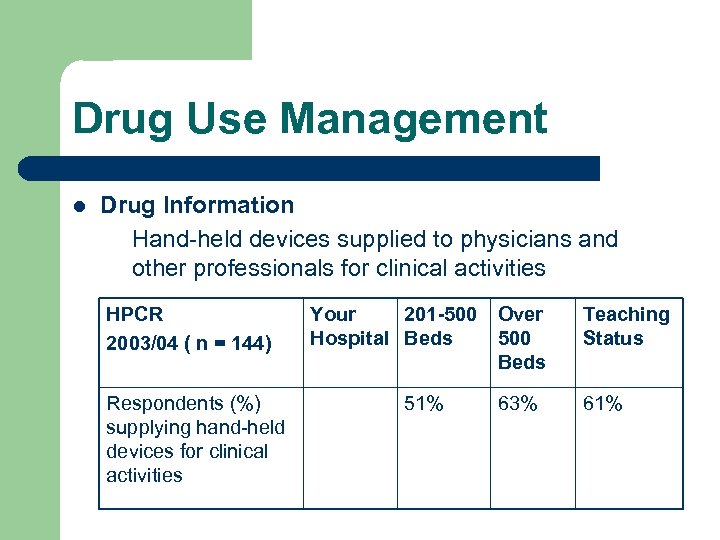 Drug Use Management l Drug Information Hand-held devices supplied to physicians and other professionals for clinical activities HPCR 2003/04 ( n = 144) Respondents (%) supplying hand-held devices for clinical activities Your 201 -500 Over Hospital Beds 500 Beds 51% 63% Teaching Status 61%
Drug Use Management l Drug Information Hand-held devices supplied to physicians and other professionals for clinical activities HPCR 2003/04 ( n = 144) Respondents (%) supplying hand-held devices for clinical activities Your 201 -500 Over Hospital Beds 500 Beds 51% 63% Teaching Status 61%
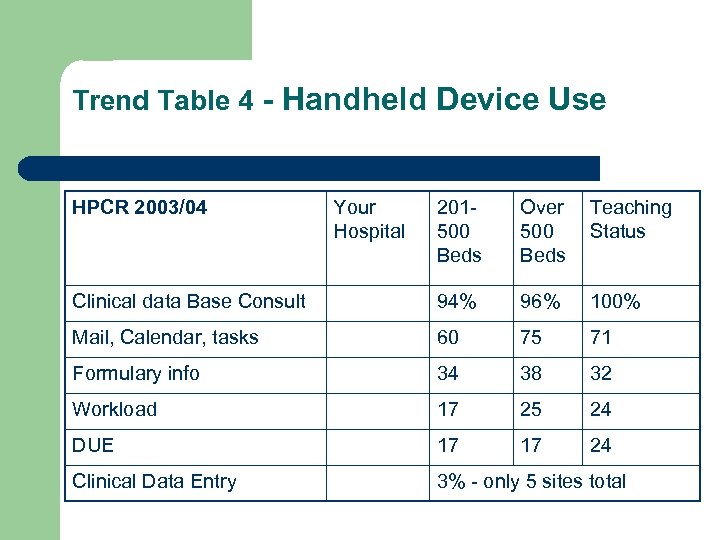 Trend Table 4 - Handheld Device Use HPCR 2003/04 Your Hospital 201500 Beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status Clinical data Base Consult 94% 96% 100% Mail, Calendar, tasks 60 75 71 Formulary info 34 38 32 Workload 17 25 24 DUE 17 17 24 Clinical Data Entry 3% - only 5 sites total
Trend Table 4 - Handheld Device Use HPCR 2003/04 Your Hospital 201500 Beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status Clinical data Base Consult 94% 96% 100% Mail, Calendar, tasks 60 75 71 Formulary info 34 38 32 Workload 17 25 24 DUE 17 17 24 Clinical Data Entry 3% - only 5 sites total
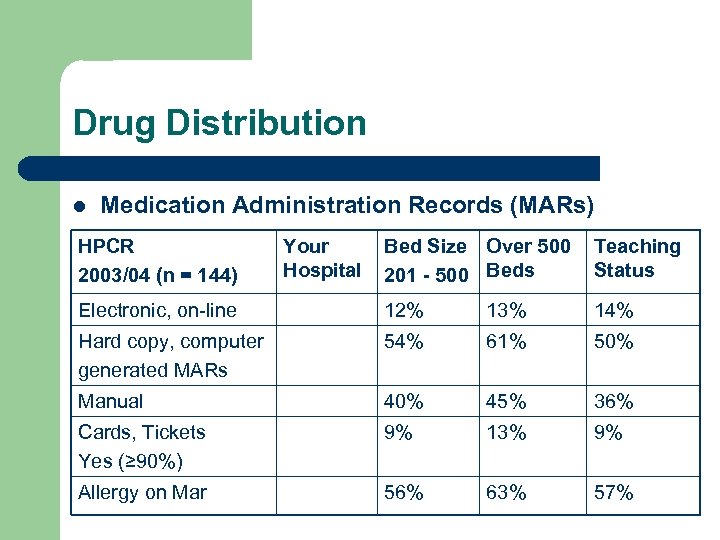 Drug Distribution l Medication Administration Records (MARs) HPCR 2003/04 (n = 144) Your Hospital Bed Size Over 500 201 - 500 Beds Teaching Status Electronic, on-line 12% 13% 14% Hard copy, computer generated MARs 54% 61% 50% Manual 40% 45% 36% Cards, Tickets Yes (≥ 90%) 9% 13% 9% Allergy on Mar 56% 63% 57%
Drug Distribution l Medication Administration Records (MARs) HPCR 2003/04 (n = 144) Your Hospital Bed Size Over 500 201 - 500 Beds Teaching Status Electronic, on-line 12% 13% 14% Hard copy, computer generated MARs 54% 61% 50% Manual 40% 45% 36% Cards, Tickets Yes (≥ 90%) 9% 13% 9% Allergy on Mar 56% 63% 57%
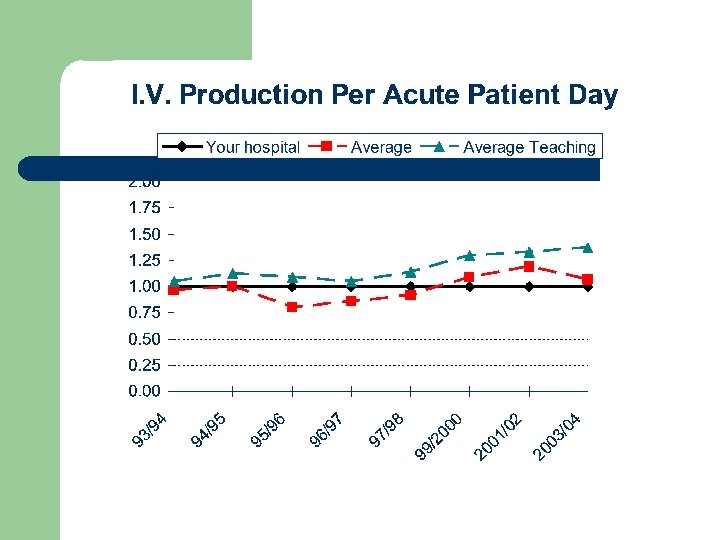
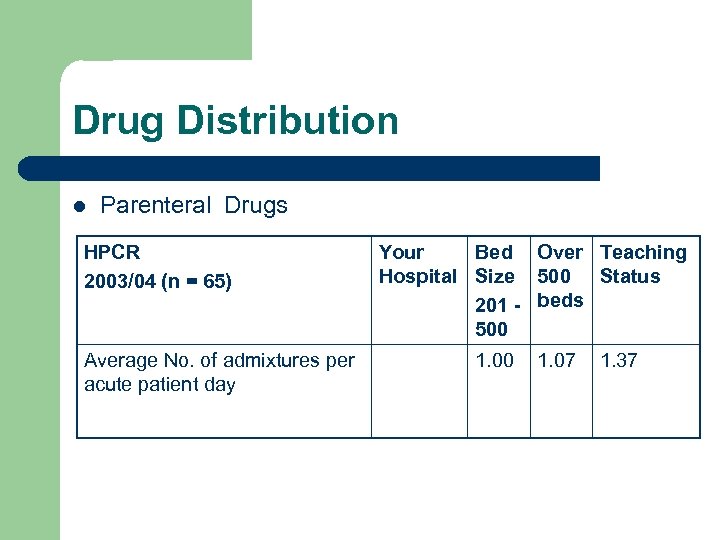 Drug Distribution l Parenteral Drugs HPCR 2003/04 (n = 65) Average No. of admixtures per acute patient day Your Bed Over Teaching Hospital Size 500 Status 201 - beds 500 1. 07 1. 37
Drug Distribution l Parenteral Drugs HPCR 2003/04 (n = 65) Average No. of admixtures per acute patient day Your Bed Over Teaching Hospital Size 500 Status 201 - beds 500 1. 07 1. 37
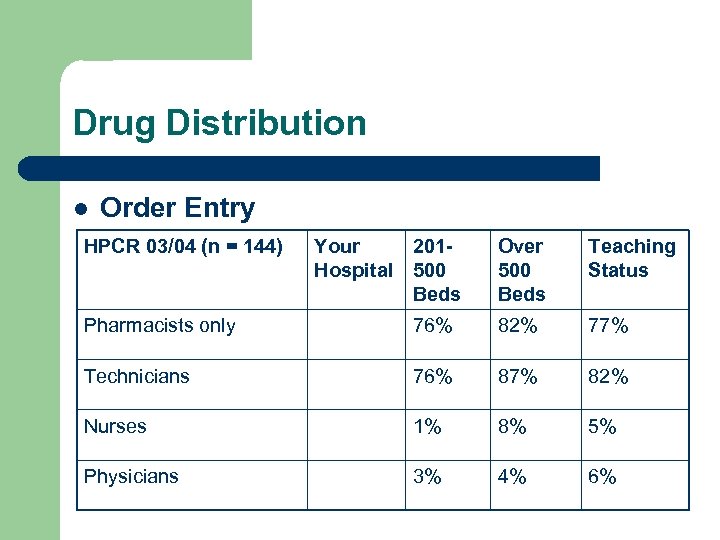 Drug Distribution l Order Entry HPCR 03/04 (n = 144) Your 201 Hospital 500 Beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status Pharmacists only 76% 82% 77% Technicians 76% 87% 82% Nurses 1% 8% 5% Physicians 3% 4% 6%
Drug Distribution l Order Entry HPCR 03/04 (n = 144) Your 201 Hospital 500 Beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status Pharmacists only 76% 82% 77% Technicians 76% 87% 82% Nurses 1% 8% 5% Physicians 3% 4% 6%
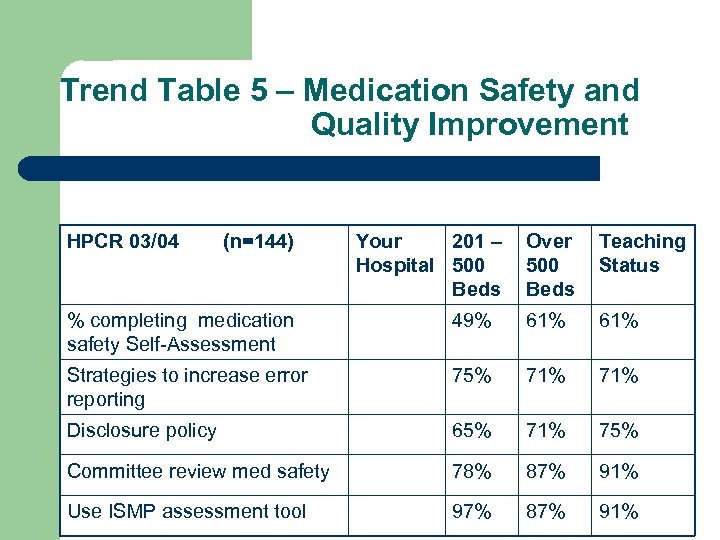 Trend Table 5 – Medication Safety and Quality Improvement HPCR 03/04 (n=144) Your 201 – Hospital 500 Beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status % completing medication safety Self-Assessment 49% 61% Strategies to increase error reporting 75% 71% Disclosure policy 65% 71% 75% Committee review med safety 78% 87% 91% Use ISMP assessment tool 97% 87% 91%
Trend Table 5 – Medication Safety and Quality Improvement HPCR 03/04 (n=144) Your 201 – Hospital 500 Beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status % completing medication safety Self-Assessment 49% 61% Strategies to increase error reporting 75% 71% Disclosure policy 65% 71% 75% Committee review med safety 78% 87% 91% Use ISMP assessment tool 97% 87% 91%
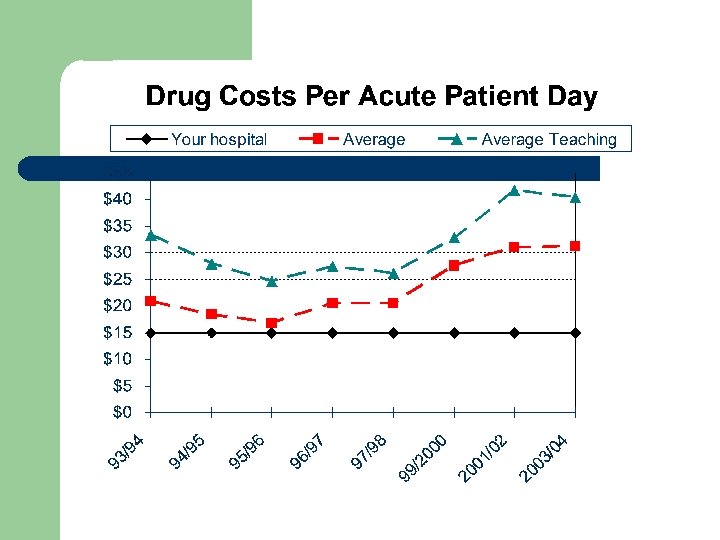
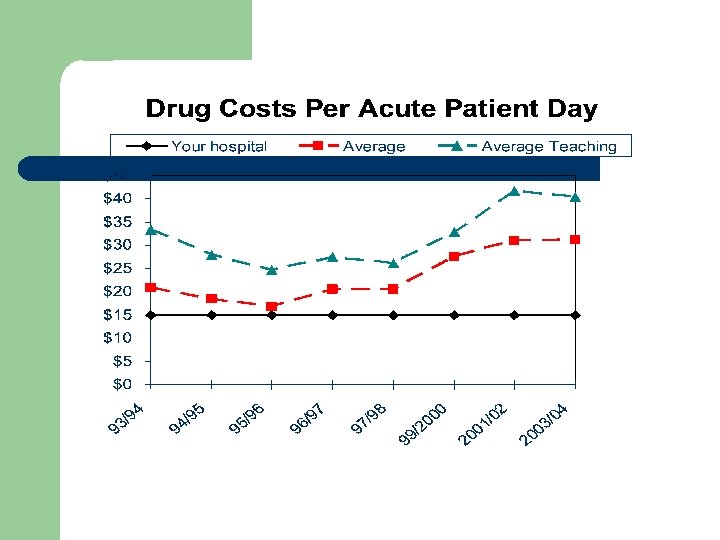
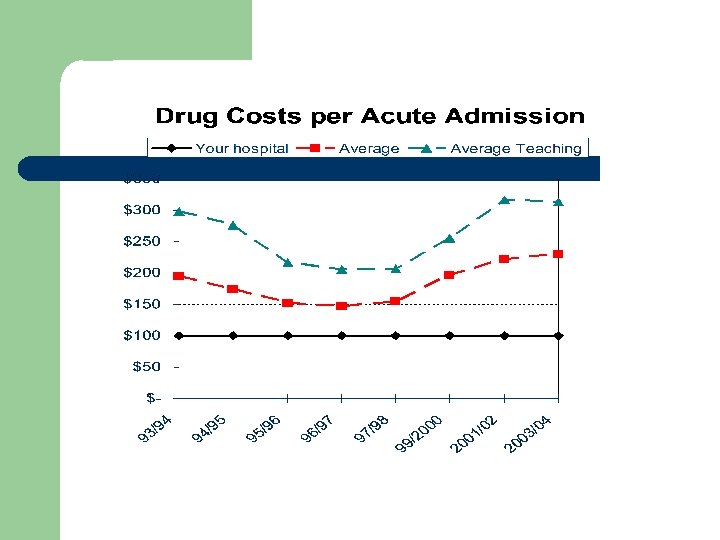
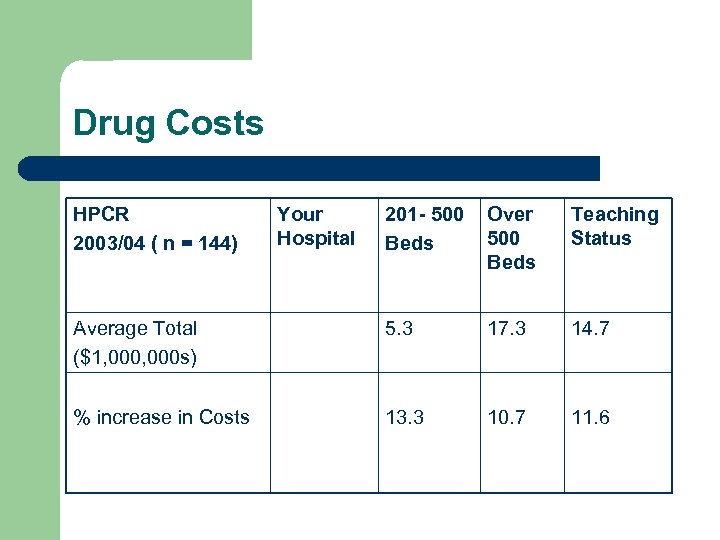 Drug Costs HPCR 2003/04 ( n = 144) Your Hospital 201 - 500 Beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status Average Total ($1, 000 s) 5. 3 17. 3 14. 7 % increase in Costs 13. 3 10. 7 11. 6
Drug Costs HPCR 2003/04 ( n = 144) Your Hospital 201 - 500 Beds Over 500 Beds Teaching Status Average Total ($1, 000 s) 5. 3 17. 3 14. 7 % increase in Costs 13. 3 10. 7 11. 6
 Aligning Your Organizations Priorities
Aligning Your Organizations Priorities
 Supporting your Priorities l l l Canadian Society of Hospital Pharmacists (CSHP) Standards, Statements and Guidelines - www. cshp. ca Canadian Council on Health Services Accreditation (CCHSA) – New Patient Safety Standards effective 2006 – www. cchsa. ca Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) – Canada - www. ismp-canada. org
Supporting your Priorities l l l Canadian Society of Hospital Pharmacists (CSHP) Standards, Statements and Guidelines - www. cshp. ca Canadian Council on Health Services Accreditation (CCHSA) – New Patient Safety Standards effective 2006 – www. cchsa. ca Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) – Canada - www. ismp-canada. org
 Supporting your Priorities Cont’d… l l l Canadian Patient Safety Institute www. patientsafetyinstitute. ca Safer Healthcare Now Initiatives www. saferhealthcarenow. ca American Society of Health System Pharmacists – www. ashp. org Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) www. ihi. org Institute of Medicine (IOM) - www. iom. edu
Supporting your Priorities Cont’d… l l l Canadian Patient Safety Institute www. patientsafetyinstitute. ca Safer Healthcare Now Initiatives www. saferhealthcarenow. ca American Society of Health System Pharmacists – www. ashp. org Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) www. ihi. org Institute of Medicine (IOM) - www. iom. edu
 Supporting your Priorities Cont’d… Last but not least…… l Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Report – www. lillyhospitalsurvey. ca – extensive inventory of references at the end of each section of the document.
Supporting your Priorities Cont’d… Last but not least…… l Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Report – www. lillyhospitalsurvey. ca – extensive inventory of references at the end of each section of the document.
 Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Annual Report Analysis of Indicators
Hospital Pharmacy in Canada Annual Report Analysis of Indicators

 Using the Data - Testimonials “…it takes 17 years for a new piece of science/evidence to be propagated through the system. ” (IOM Report)
Using the Data - Testimonials “…it takes 17 years for a new piece of science/evidence to be propagated through the system. ” (IOM Report)
 Contact Information l l Patricia Macgregor - pmacgregor@tsh. to Nancy Roberts – narobert 2@serha. ca THANK-YOU - MERCI
Contact Information l l Patricia Macgregor - pmacgregor@tsh. to Nancy Roberts – narobert 2@serha. ca THANK-YOU - MERCI


