7dc5ce6718dad695fc8dec0b6a570847.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Measuring true profits using embedded value Peter Luk Plan-B Consulting Ltd. August 2004
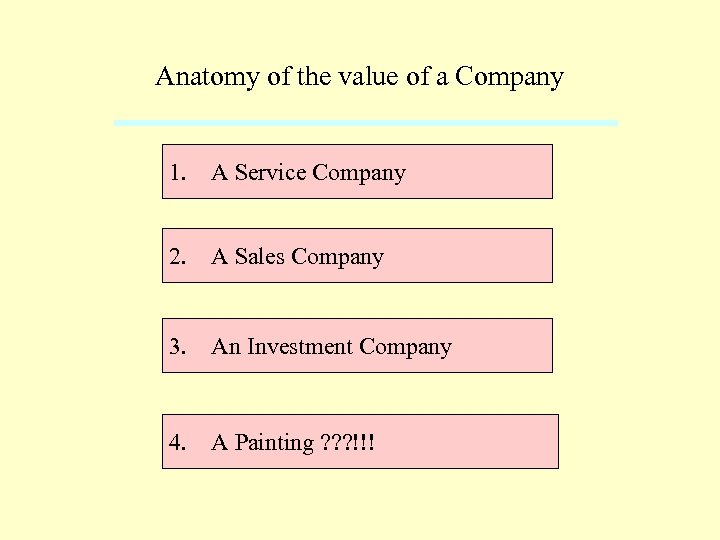
Anatomy of the value of a Company 1. A Service Company 2. A Sales Company 3. An Investment Company 4. A Painting ? ? ? !!!
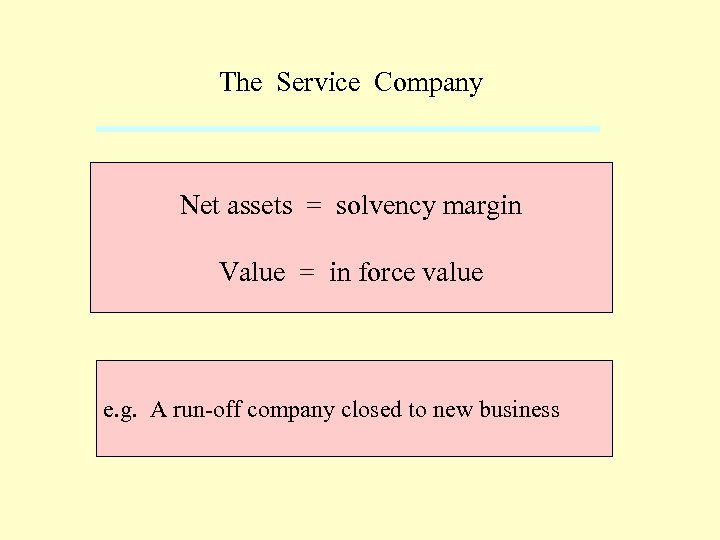
The Service Company Net assets = solvency margin Value = in force value e. g. A run-off company closed to new business
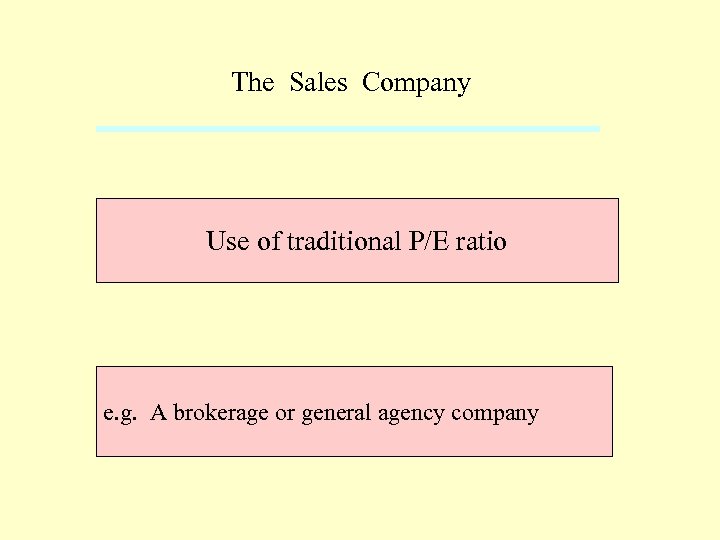
The Sales Company Use of traditional P/E ratio e. g. A brokerage or general agency company

The Investment Company Use free surplus to earn investment income e. g. Microsoft’s billion dollars of cash

The Painting value ? ? ? !!! Investors’ psychology e. g. Picasso’s “Boy with a pipe” – US$104 M
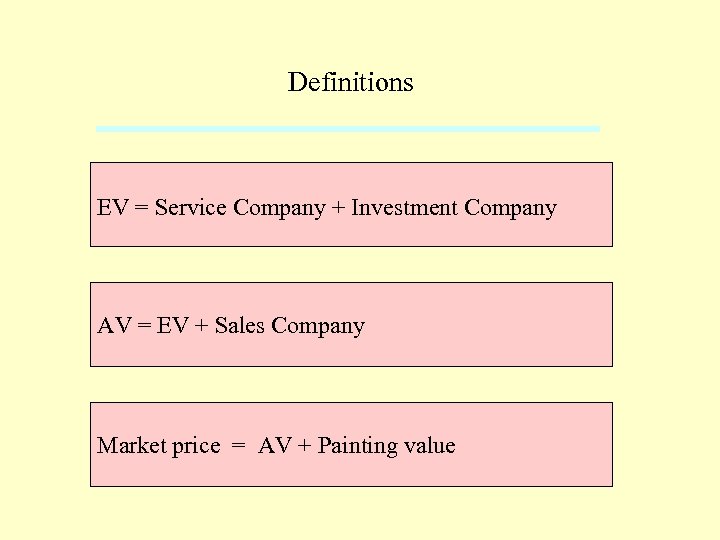
Definitions EV = Service Company + Investment Company AV = EV + Sales Company Market price = AV + Painting value
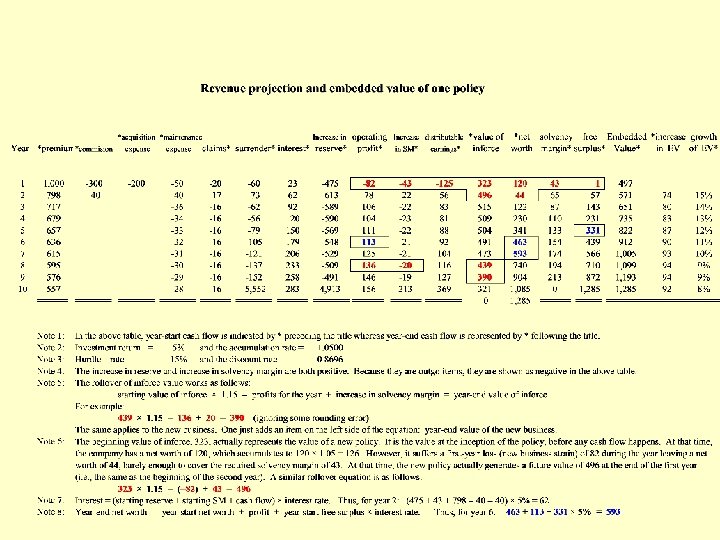
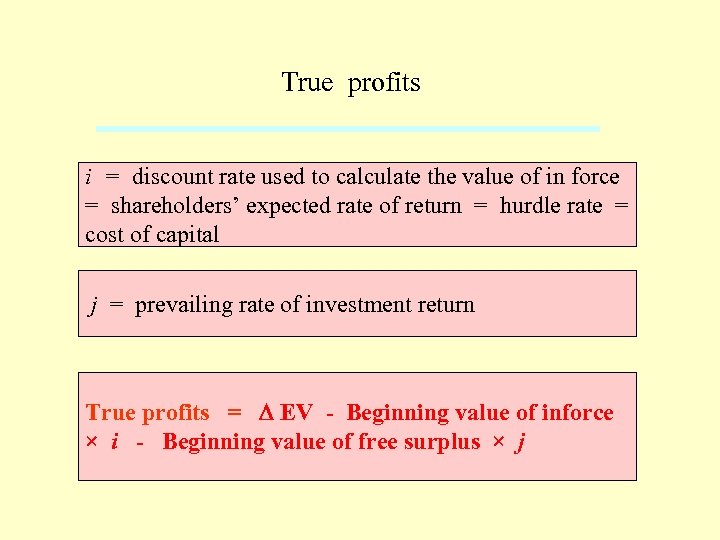
True profits i = discount rate used to calculate the value of in force = shareholders’ expected rate of return = hurdle rate = cost of capital j = prevailing rate of investment return True profits = D EV - Beginning value of inforce × i - Beginning value of free surplus × j
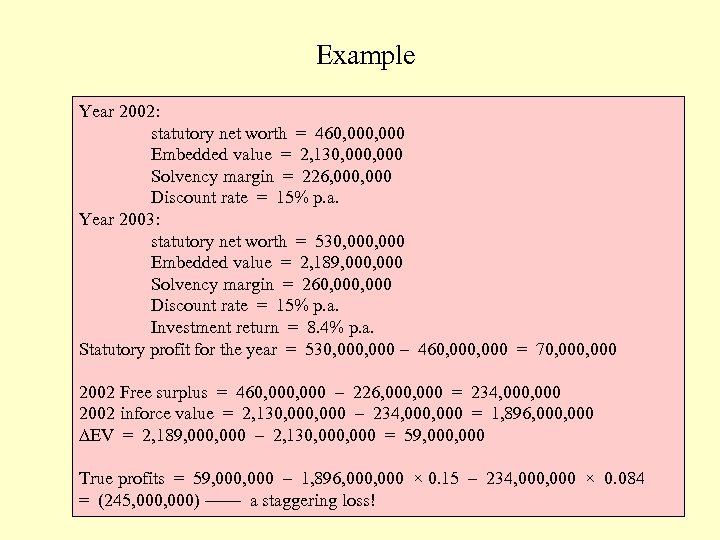
Example Year 2002: statutory net worth = 460, 000 Embedded value = 2, 130, 000 Solvency margin = 226, 000 Discount rate = 15% p. a. Year 2003: statutory net worth = 530, 000 Embedded value = 2, 189, 000 Solvency margin = 260, 000 Discount rate = 15% p. a. Investment return = 8. 4% p. a. Statutory profit for the year = 530, 000 – 460, 000 = 70, 000 2002 Free surplus = 460, 000 – 226, 000 = 234, 000 2002 inforce value = 2, 130, 000 – 234, 000 = 1, 896, 000 DEV = 2, 189, 000 – 2, 130, 000 = 59, 000 True profits = 59, 000 – 1, 896, 000 × 0. 15 – 234, 000 × 0. 084 = (245, 000) –––– a staggering loss!

Debate ?

Determination of i 1. For the buyer? 2. For the seller? 3. For IPO? 4. CAPM 5. Perceived risks? 6. Exchange risk premium

Determination of j 1. What is the prevailing rate of return? 2. Use risk-free rate? 3. Use a model portfolio? 4. A fantastically high return for the company?

P/E method ? Pros: 1. People are familiar with it. 2. Easy to use. Cons: 1. Assume a constant rate of growth of earnings. 2. Ignore free surplus, if it is large. 3. What earnings? ?

AV or EV ? For AV: 1. Theoretically correct. 2. Wide use internationally. For EV: 1. Multiples in AV can be very subjective and volatile. 2. Widely used in Europe (particularly UK).

What assumptions ? 1. The biggest black box in actuarial practice. 2. If a company’s reported profits are very good but the true profits calculated by this method is not very good, this is a good indication that the assumptions used may not be correct. 3. Disclosure, disclosure.

What is goodwill ? 1. Goodwill is not painting value. 2. It is rationally determined. 3. It is subject to amortization. 4. It may be considered as part of inforce value.
7dc5ce6718dad695fc8dec0b6a570847.ppt