bfb1b76e0bde329d65e4b37cc6bf9bb3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 123

Measuring Liquid Volume Temperature Density Observation Inference Quantitative Qualitative

Review: 1. 2. 3. 4. Matter Everything is made of _________ is described as anything Matter that has volume and mass. Volume is ______________. The amount of space an object takes up Volume can be measured in two ways Direct measurement w/ ruler (cm 1. ___________________ 3) Water displacement (m. L) 2. ___________________

Review: 5. 6. Length You need the _________, ____ width Height of a solid regular object to find volume. 1 1 m. L equals ______ cm 3.

Look at the Sheet with the 3 lines n n n Using the cm or mm side of the ruler measure each line to the nearest mm. Put the first line of the cm side at the end of the line on the paper. Measure how long the line is The line is 7. 7 cm long If you can convert your cm to mm like this 7. 7 cm = 77 mm

What is the length of each line? Measure in cm and mm 154 15. 4 1. ______cm ______mm 6. 1 61 2. ______cm ______mm 19. 2 192 3. ______cm ______mm
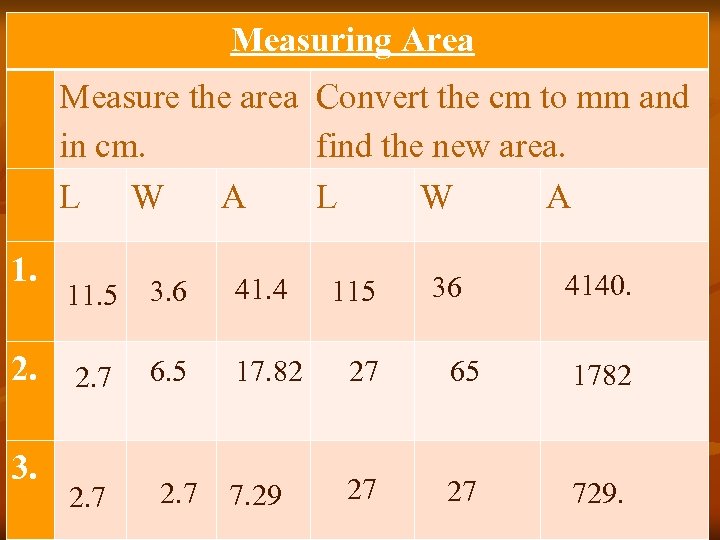
Measuring Area Measure the area Convert the cm to mm and in cm. find the new area. L W A 1. 36 4140. 2. 2. 7 6. 5 17. 82 27 65 1782 3. 11. 5 2. 7 3. 6 2. 7 41. 4 7. 29 115 27 27 729.

Practice converting these Lengths 174 1. 17. 4 cm or ______ mm 1. 4 2. ______ cm or 14 mm 95 3. 9. 5 cm or ______ mm 5. 1 4. ______ cm or 51 mm 127 5. 12. 7 cm or ______ mm
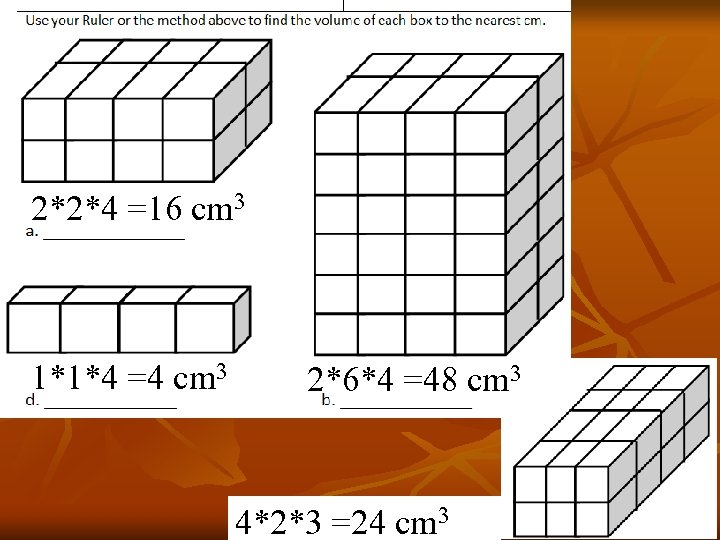
2*2*4 =16 cm 3 1*1*4 =4 cm 3 2*6*4 =48 cm 3 4*2*3 =24 cm 3
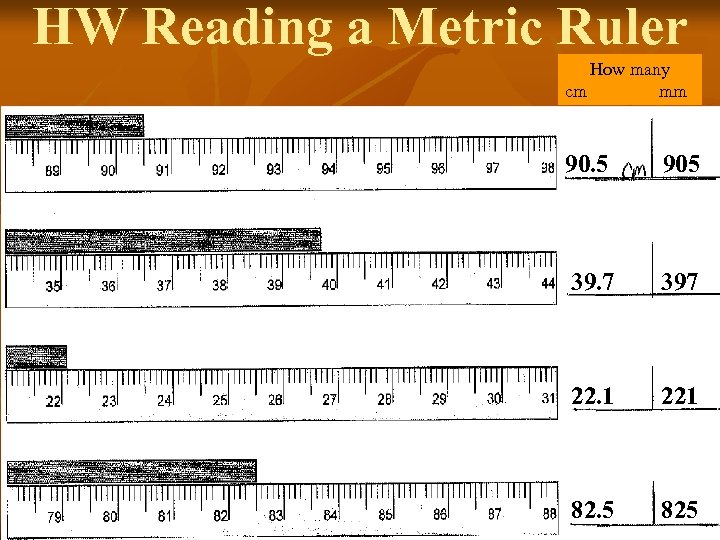
HW Reading a Metric Ruler How many cm mm 90. 5 905 39. 7 397 22. 1 221 82. 5 825

HW Reading a Metric Ruler How many cm mm 67. 9 679 87. 1 871 32. 3 323 44. 1 441

Liquid Volume & Volume of Irregular objects

1 m. L 2 m. L . 2 m. L . 5 m. L
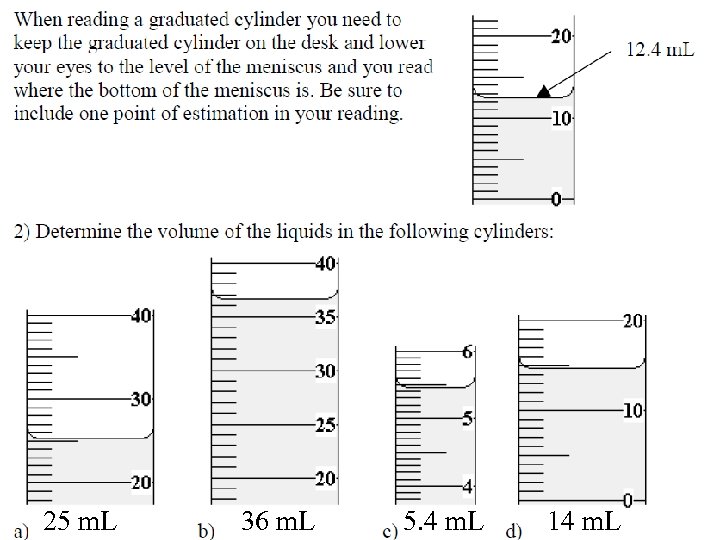
25 m. L 36 m. L 5. 4 m. L 14 m. L
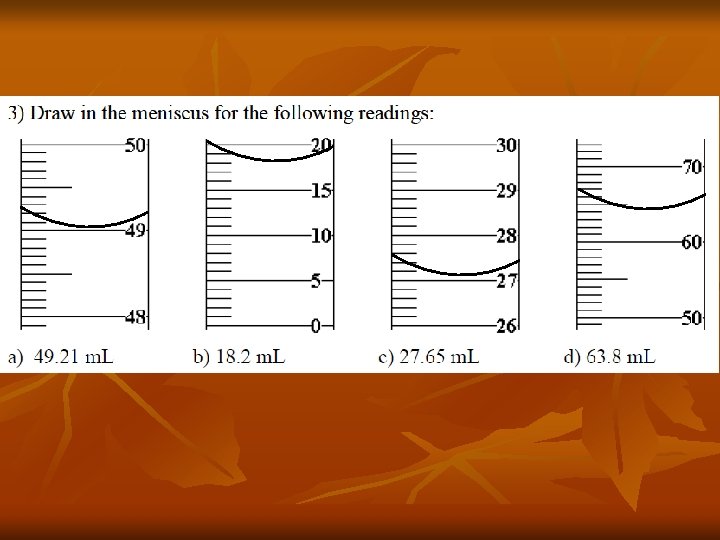

Read the Glassware Lab
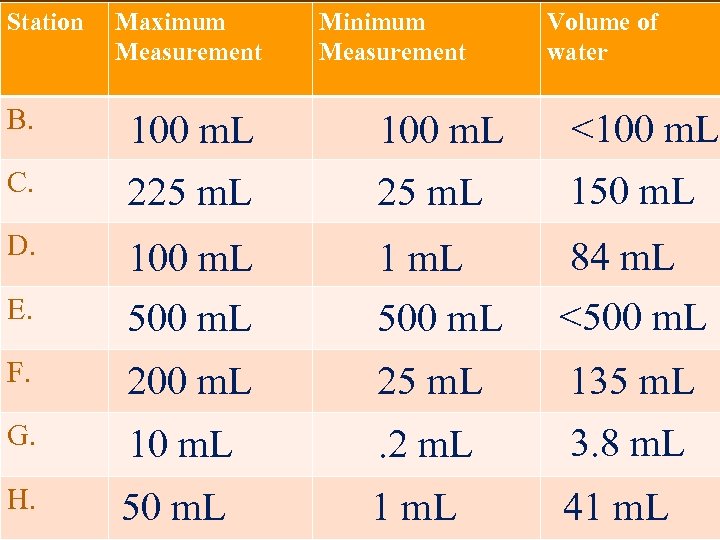
Station Maximum Measurement Minimum Measurement Volume of water B. 100 m. L <100 m. L C. 225 m. L 150 m. L D. E. 100 m. L 500 m. L 1 m. L 500 m. L 84 m. L <500 m. L F. 200 m. L 25 m. L 135 m. L G. 10 m. L . 2 m. L 3. 8 m. L H. 50 m. L 1 m. L 41 m. L
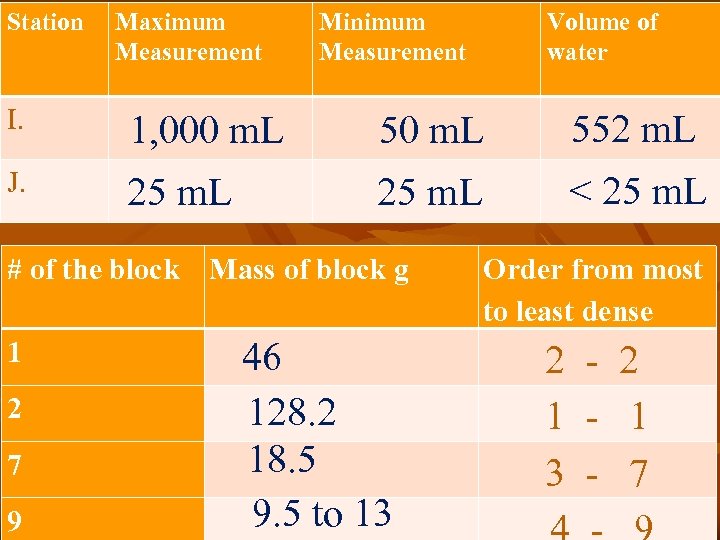
Station Maximum Measurement Minimum Measurement Volume of water I. 1, 000 m. L 552 m. L J. 25 m. L < 25 m. L # of the block Mass of block g 1 2 7 9 46 128. 2 18. 5 9. 5 to 13 Order from most to least dense 2 - 2 1 - 1 3 - 7

Explain why you were able to order the blocks by density even though you only knew the mass. n n n You can use mass to organize the blocks because the volume is the same for all blocks. See an example… Blocks 1, 2, 7, 9 all have a volume of 17. 6 g/cm 3 so block two’s density is 128 / 17. 6 = 7. 28 and block nine’s density is 9. 5 / 17. 6 =. 5 Only the mass changes so you can organise the density by looking at only mass.

K H Da Base D 25. 6 1. 256 m = _______ dam 2. 97. 25 cm = _______ mm 972. 5 3. 952 dag = _______ g 9, 520. 4. . 574 m = _______ mm 574. 5. 287 d. L = _______ da. L . 05287 C M

K H Da Base D 785, 300. 6. 785. 3 km = _______ m 7. 84. 363 L = ______ d. L 843. 63 8. 872 hm = _______ mm 87, 200, 000 9. 95, 824 dam = ______ dm 9, 582, 400 10. 8. 26 k. L = _______ d. L 82, 600 C M

6 m. L 12 m. L 1. 6 m. L 3. 4 m. L 4. 5 m. L 60 m. L 30 m. L . 4 m. L 2. 66 m. L 8 m. L 3. 2 m. L 4 m. L 1. 5 m. L 5. 2 m. L

Practice with Liquid Volume

3 m. L 18 m. L 30 m. L 15 m. L . 6 m. L 3. 8 m. L 1. 6 m. L 2 m. L 12 m. L

Finding Solid Volume Through Water Displacement

7 m. L 38 m. L 33 m. L 20 m. L 40 – 20 = 20 m. L water and 20 m. L rock Place a known quantity of water in the GC. Add object calculate change in water level. Change in the mass of the object.
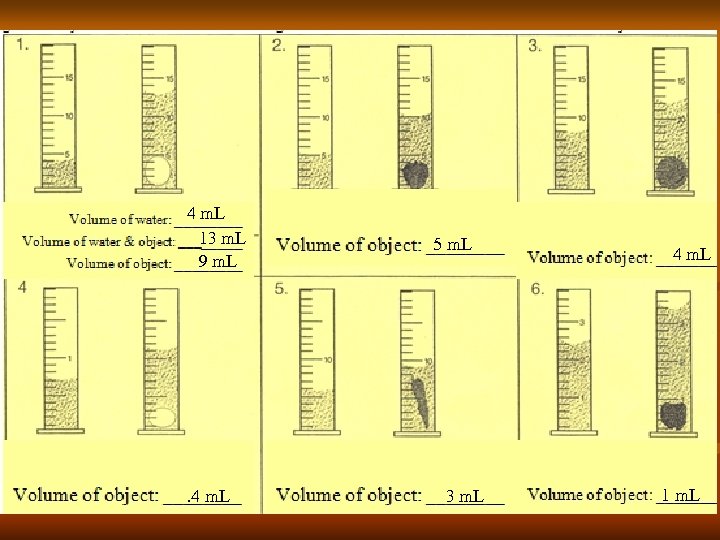
4 m. L 13 m. L 9 m. L . 4 m. L 5 m. L 3 m. L 4 m. L 1 m. L

1. 8 m. L 4 m. L 16 m. L 3 m. L 9 m. L

Temperature n Measure of the average Kinetic Energy of the particles in a sample of matter n What is Kinetic Energy? n The energy of motion.

The units of Temperature n n n n What Units are used in the US? Fahrenheit Fo Creator: Daniel Creator: Fahrenheit What units are used in most of Europe? Celsius Co Creator: Anders Celsius What is the Celsius scale based on? What units are used by scientists? Kelvin K Why is Kelvin not in degrees?

Kelvin n Developed by Lord Kelvin in the mid 1800’s n What happens at absolute zero? n Absolute Zero is the lowest temperature. It is the place where all atomic motion stops.

What Countries still use Fahrenheit? n n n USA Burma Liberia Jamaica Belize

Fill in the table. Conversion Formulas C to F O F = ( 9/5 X C ) + 32 F to C O C = 5/9 X ( F - 32 ) C to K K = OC + 273 K to C O C = K - 273 Hint: 9/5 = 1. 8 & 5/9=. 556
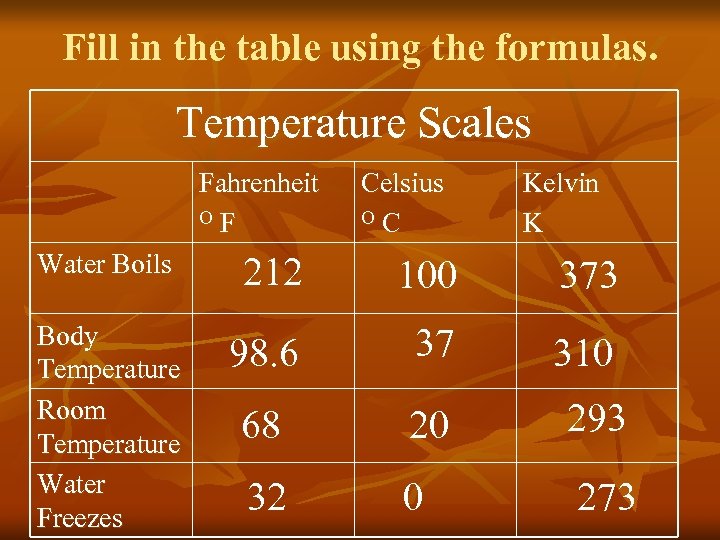
Fill in the table using the formulas. Temperature Scales Fahrenheit O F Water Boils Body Temperature Room Temperature Water Freezes Celsius O C Kelvin K 212 100 373 98. 6 37 310 68 20 293 32 0 273

Comparing the Scales 1. “The weather forecaster predicts that today’s high will be 70 o. ” Fahrenheit Which scale is being used? ______ 21. 1 o. C On the Celsius scale? ______ 294. 1 K On the Kelvin scale? ______

Comparing the Scales 2. “It was so cold yesterday that the temperature only reached 275!” Kelvin Which scale is being used? ______ 2 o. C On the Celsius scale? ______ 35. 6 o F On the Fahrenheit scale? ______

Comparing the Scales 3. “Today’s temperature of 42 o in Chicago set a record high for the month of August. Celsius Which scale is being used? ______ 315 K On the Kelvin scale? ______ 107. 6 o F On the Fahrenheit scale? ______
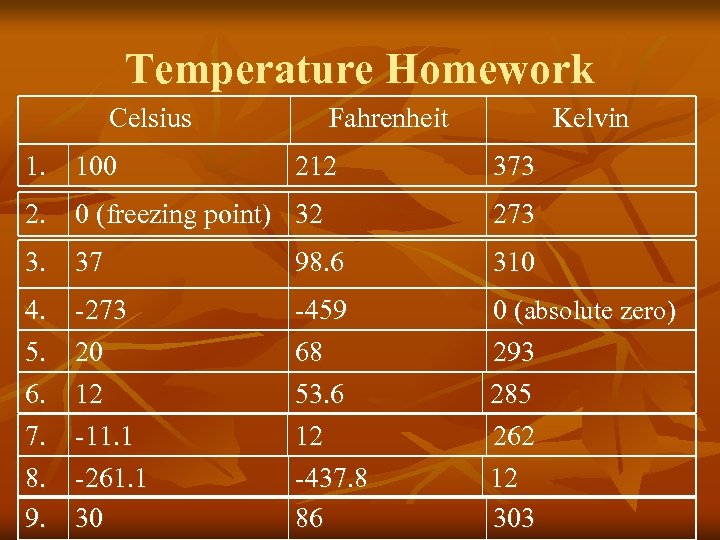
Temperature Homework Celsius 1. 100 Fahrenheit 212 Kelvin 373 2. 0 (freezing point) 32 273 3. 37 98. 6 310 4. -273 5. 20 6. 12 7. -11. 1 8. -261. 1 9. 30 -459 68 53. 6 0 (absolute zero) 293 285 12 -437. 8 86 262 12 303
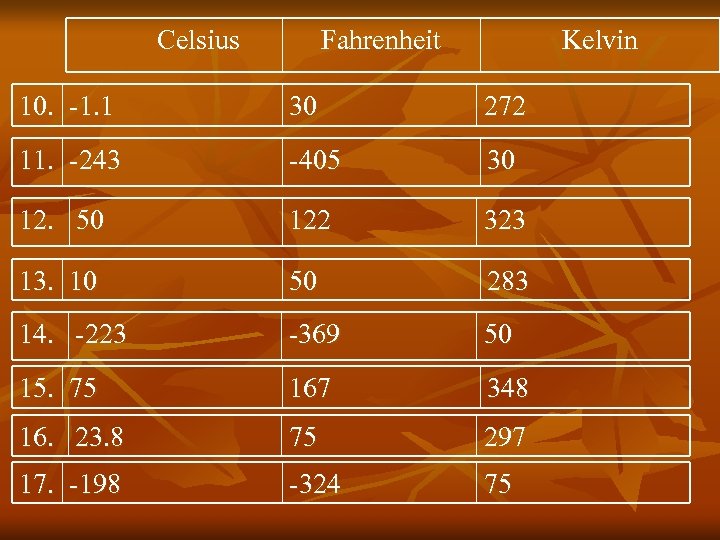
Celsius Fahrenheit Kelvin 10. -1. 1 30 272 11. -243 -405 30 12. 50 122 323 13. 10 50 283 14. -223 -369 50 15. 75 167 348 16. 23. 8 75 297 17. -198 -324 75
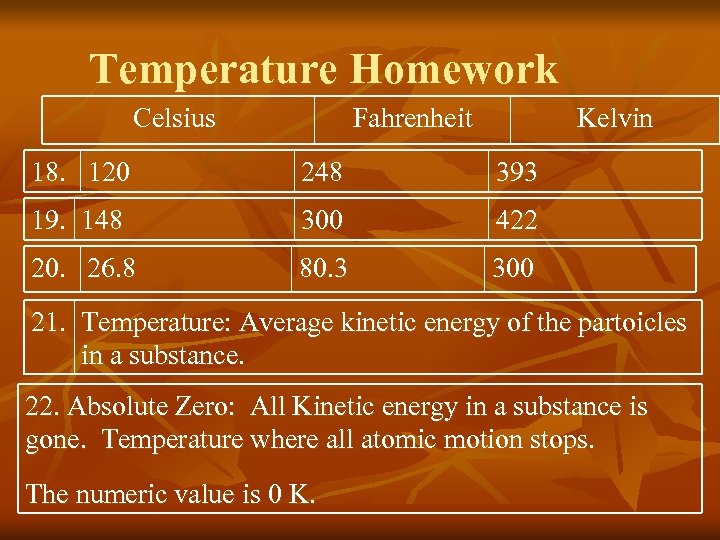
Temperature Homework Celsius Fahrenheit Kelvin 18. 120 248 393 19. 148 300 422 20. 26. 8 80. 3 300 21. Temperature: Average kinetic energy of the partoicles in a substance. 22. Absolute Zero: All Kinetic energy in a substance is gone. Temperature where all atomic motion stops. The numeric value is 0 K.

Metric Conversions

illi enti eca ecto ilo n Base units K H Da B D C M Base units are Meters, Liters, Grams, Watts, Newtons, and any other units we learn this year.

K H Da B D C M Kyle Hates Dates Because Dates Cost Money

K H Da B D C M n n n n n Let’s look at a metric ruler… How many meters are in a meter? 1 How many decimeters are in a meter? 10 How many centimeters are in a meter? 100 How many millimeters are in a meter? 1000

K H Da B D C M n n n n Let’s look at a metric ruler in the other direction… How many meters are needed to make a decameter? 10 How many meters are needed to make a hectometer? 100 How many meters are needed to make a kilometer? 1000

K H Da B D C M n n 47424. 6 m. L= _______h. L. 474246 Put your finger on the units that you are given which are m. L. Move your finger left to h. L, and count the number of moves. Five to the left. Move the decimal the name number of places in the same direction.

K H Da B D C M n n 5. 0342 k. L= _______L 5034. 2 Put your finger on the units that you are given which are k. L. Move your finger left to L, and count the number of moves. Three to the right. Move the decimal the name number of places in the same direction.
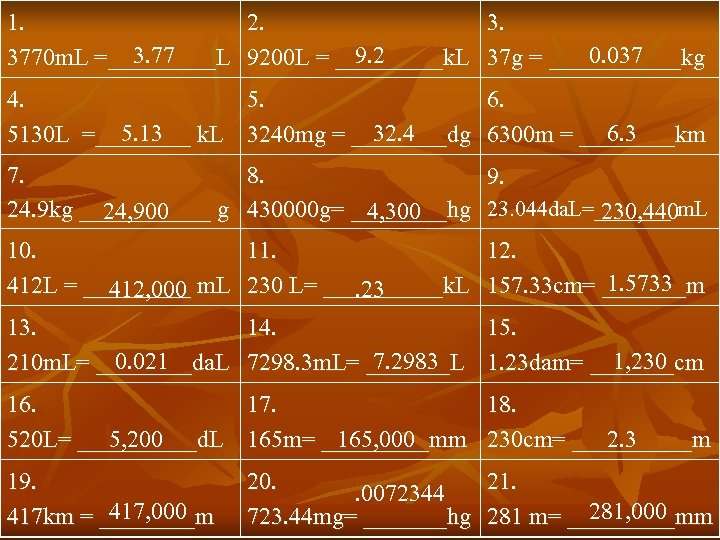
1. 2. 3. 77 9. 2 0. 037 3770 m. L =_____L 9200 L = _____k. L 37 g = ______kg 4. 5. 6. 5. 13 32. 4 6. 3 5130 L =____ k. L 3240 mg = ____dg 6300 m = ____km 7. 8. 9. 24. 9 kg ______ g 430000 g= ____hg 23. 044 da. L=_______ m. L 24, 900 4, 300 230, 440 10. 11. 12. 1. 5733 412 L = _____ m. L 230 L= _____k. L 157. 33 cm= _______m 412, 000. 23 13. 14. 15. 0. 021 7. 2983 1, 230 210 m. L= ____da. L 7298. 3 m. L= _______L 1. 23 dam= _______cm 16. 17. 18. 5, 200 165, 000 2. 3 520 L= _____d. L 165 m= _____mm 230 cm= _____m 19. 417, 000 417 km = ____m 20. 21. . 0072344 281, 000 723. 44 mg= _______hg 281 m= _____mm
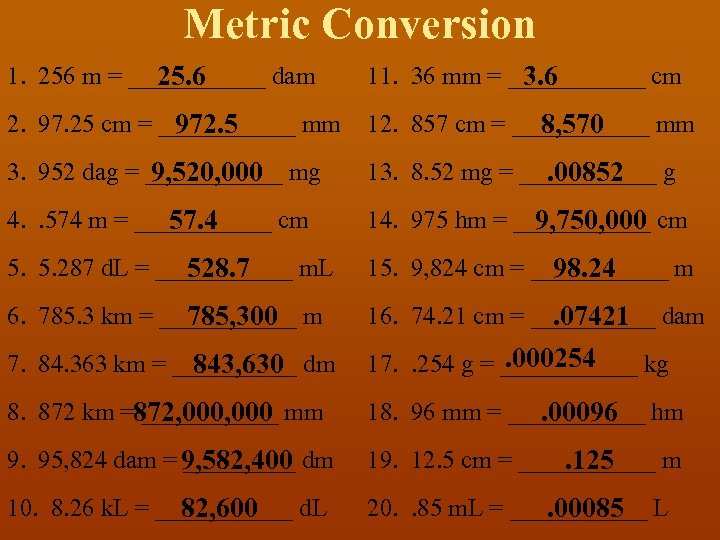
Metric Conversion 1. 256 m = ______ dam 25. 6 11. 36 mm = ______ cm 3. 6 2. 97. 25 cm = ______ mm 12. 857 cm = ______ mm 972. 5 8, 570 3. 952 dag = ______ mg 9, 520, 000 13. 8. 52 mg = ______ g . 00852 4. . 574 m = ______ cm 57. 4 14. 975 hm = ______ cm 9, 750, 000 5. 287 d. L = ______ m. L 528. 7 15. 9, 824 cm = ______ m 98. 24 6. 785. 3 km = ______ m 785, 300 16. 74. 21 cm = _____ dam . 07421 7. 84. 363 km = _____ dm 843, 630 . 000254 17. . 254 g = ______ kg 8. 872 km = ______ mm 872, 000 18. 96 mm = ______ hm . 00096 9. 95, 824 dam = _____ dm 9, 582, 400 19. 12. 5 cm = ______ m . 125 10. 8. 26 k. L = ______ d. L 82, 600 20. . 85 m. L = ______ L. 00085
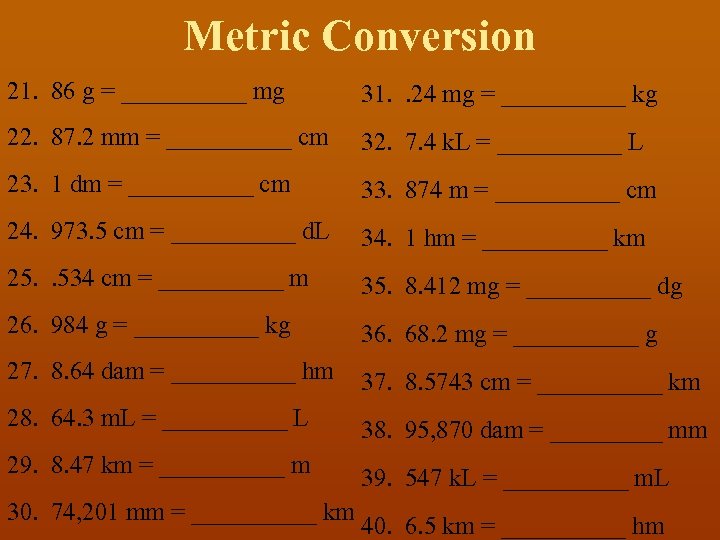
Metric Conversion 21. 86 g = _____ mg 31. . 24 mg = _____ kg 22. 87. 2 mm = _____ cm 32. 7. 4 k. L = _____ L 23. 1 dm = _____ cm 33. 874 m = _____ cm 24. 973. 5 cm = _____ d. L 34. 1 hm = _____ km 25. . 534 cm = _____ m 35. 8. 412 mg = _____ dg 26. 984 g = _____ kg 36. 68. 2 mg = _____ g 27. 8. 64 dam = _____ hm 37. 8. 5743 cm = _____ km 28. 64. 3 m. L = _____ L 38. 95, 870 dam = _____ mm 29. 8. 47 km = _____ m 30. 74, 201 mm = _____ km 39. 547 k. L = _____ m. L 40. 6. 5 km = _____ hm

Finding Density
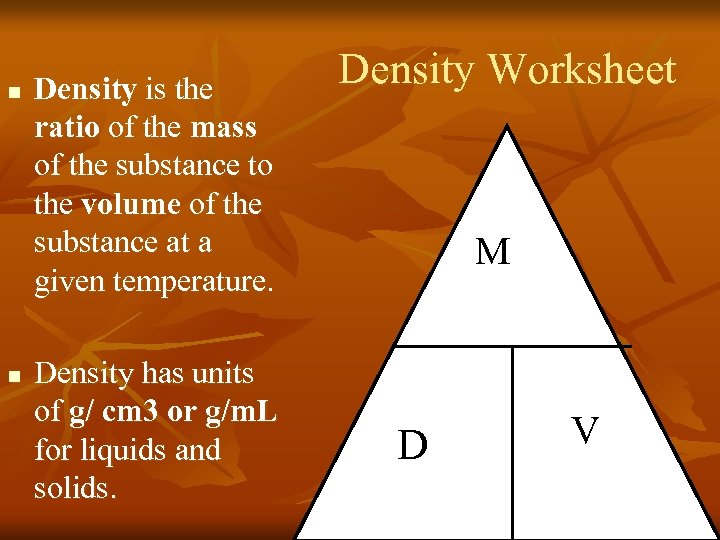
n Density is the ratio of the mass of the substance to the volume of the substance at a given temperature. Density Worksheet M n Density has units of g/ cm 3 or g/m. L for liquids and solids. D V

Density Calculations Worksheet I

1. Find the unknown quantity A) D= 3 g/m. L V=100 m. L M= ? B) D= ? V= 950 m. L M= 95 g C) D= 0. 5 g/cm 3 V= ? M= 20 g M= D * V D= M/V V= M/D 3 * 100= 95 / 950= 300 g =. 1 g/m. L 20 / 0. 5 = = 40 cm 3

2. Find the unknown quantity . (CONVERT FIRST to g or m. L) A) D= 24 g/m. L V=1. 2 L= ______ 1, 200 m. L M= ? B) D= ? V= 100 m. L M= 1. 5 kg ______ g 1, 500 D= M/V M= D * V 3 * 100= 300 g C) D= ? V= 0. 52 L _____m. L 520 M= 500 mg ______g. 5 1, 500 / 100= D = M /V. 5 / 520 = = 15 g/m. L =. 00096 g/cm 3

WORD PROBLEMS

2. Mercury metal is poured into a graduated cylinder that holds exactly 22. 5 m. L. The mercury used to fill the cylinder weighs 306. 0 g. From this information, calculate the density of mercury. D = M = 306 g = 13. 6 g/m. L V 22. 5 m. L

1. A block of aluminum occupies a volume of 15. 0 m. L and weighs 40. 5 g. What is its density? D = M = 40. 5 g = 2. 7 g/cm 3 V 15 m. L 15 cm 3

3. What is the weight of the ethanol that exactly fills a 200. 0 m. L container? The density of ethanol is 0. 789 g/m. L. M = Dx. V = 0. 789 g/m. L x 200 m. L = 157. 8 g

4. A rectangular block of copper metal weighs 1896 g. The dimensions of the block are 8. 4 cm by 5. 5 cm by 4. 6 cm. From this data, what is the density of copper? (hint: find the volume of a block first) V = L x W x H = 8. 4 cm x 5. 5 cm x 4. 6 cm = 212. 52 cm 3 THEN D = M = 1896 g = 8. 92 g/m. L V 212. 52 cm 3

5. What volume of silver metal will weigh exactly 2500. 0 g. The density of silver is 10. 5 g/cm 3. V = M = 2500 g = 238. 1 cm 3 D 10. 5 g/cm 3

6. Find the mass of 250. 0 m. L of benzene. The density of benzene is 0. 8765 g/m. L. M = Dx. V = 0. 8765 g/m. L x 250 m. L = 219. 13 g

7. A block of lead has dimensions of 4. 50 cm by 5. 20 cm by 6. 00 cm. The block weighs 1587 g. From this information, calculate the density of lead. V = L x W x H = 4. 5 cm x 5. 2 cm x 6 cm = 140. 4 cm 3 D = M = 1587 g = 11. 3 g/cm 3 V 140. 4 cm 3

8. 28. 5 g of iron shot is added to a graduated cylinder containing 45. 50 m. L of water (V 1). The water level rises to the 49. 10 m. L (V 2) mark. From this information, calculate the density of iron. V = V 2 – V 1 = 49. 1 – 45. 5 = 3. 6 m. L = 3. 6 cm 3 D = M = 28. 5 g = 7. 92 g/cm 3 V 3. 6 cm 3

1. A Silver-colored coin has a mass of 18. 9 grams and a volume of 1. 12 m. L. Is the coin pure silver? (Hint: The density of silver is 10. 5 g/m. L. ) Work Answer D = M 18. 9 V 1. 12 16. 9 g/m. L No 2. What volume would a 0. 871 gram sample of air occupy if the density of air is 1. 29 g/L? Work Answer V = M . 871 D 1. 29 . 68 L

3. Pumice is volcanic rock that contains many trapped air bubbles. A 225 gram sample occupied 236. 6 m. L. 1. What is the density of pumice? 2. Will pumice float on water? The density of water is 1. 0 g/m. L. ) Work Answer D = M 225 V 236. 6 1. . 95 g/m. L 2. yes 4. A cup of sugar has a volume of 237 m. L. What is the mass of the cup of sugar if the density is 1. 59 g/m. L? Work Answer M= D * V 237 * 1. 59 376. 8 g

5. Which has the greater mass, 1 liter of water or l liter of gasoline? The density of water is 1. 00 g/m. L and that of gasoline is approximately 0. 68 g/m. L. Work Answer M= D * V 1 * 1 = 1 g/m. L 1 *. 68 =. 68 g/m. L Water has more density 6. A crumpet recipe calls for 175 grams of flour. According to Julia Child's data, the density of flour is 0. 620 g/m. L. How many m. L of flour are needed for this recipe? Work Answer V = M 175 D . 620 282. 25 L

7. A sample of lead is found to have a mass of 32. 6 g. A graduated cylinder contains 2. 8 m. L of water. After the lead sample is added to the cylinder the water level reads 5. 7 m. L. Calculate the density of the lead sample. Work Answer D = M 32. 6 V 2. 9 11. 2 g/cm 3 8. From their density values, decide whether each of the following substances will sink or float when placed in sea water, which has a density of 1. 025 g/m. L. Place an S on the line if it sinks and an F on the line if it floats. Float Sink A. Gasoline 0. 66 g/m. L ____ B. Asphalt l. 2 g/cm 3 _____ Float Sink C. Mercury 13. 6 g/m. L _____D. Cork 0. 26 g/ cm 3 _____ Float E. Distilled water 1 g/m. L ______ F. Plastic Bag. 88 g/ cm 3 ____

Observation Inference

Observations vs. Inferences Observations: Something that you experience with your 5 senses Inferences: a statement, conclusion or reflection Quantitative: an observation that is expressed using numbers Qualitative: An observation that is described in terms of the qualities of the object (made using 5 senses)

REMEMBER! n Observations must be specific and accurate, not relative, so that it means the same to everyone. n Example: n n n Qualitative observations – n n Incorrect - the burning bag smelled nasty Correct - the burning bag smelled similar to rotten eggs Example: Mr. Jones has blue eyes Quantitative observations Example: Mr. Jones has two eyes Inference – n Example: you leave the movie theater and see the ground is wet so you infer that it rained.



Obs. Inf.

The ice cream in the freezer was melted

The lights in the house go out during a thunderstorm.

Water is splashing down the window.

Using what you just learned! On the next slide there is a photo. Use the photo to make. . . inferences observations qualitative observations quantitative observations

What do you think?

Review For the Intro to Science Quiz
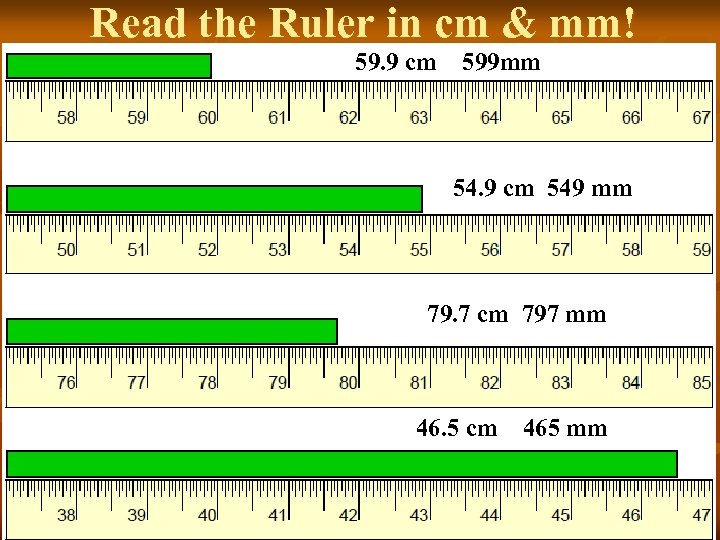
Read the Ruler in cm & mm! 59. 9 cm 599 mm 54. 9 cm 549 mm 79. 7 cm 797 mm 46. 5 cm 465 mm

Fill in the Formulas for a rectangle n Side + Side Perimeter= __________ n Length * Width Area =____________ n Length * Width * Height Volume: ___________
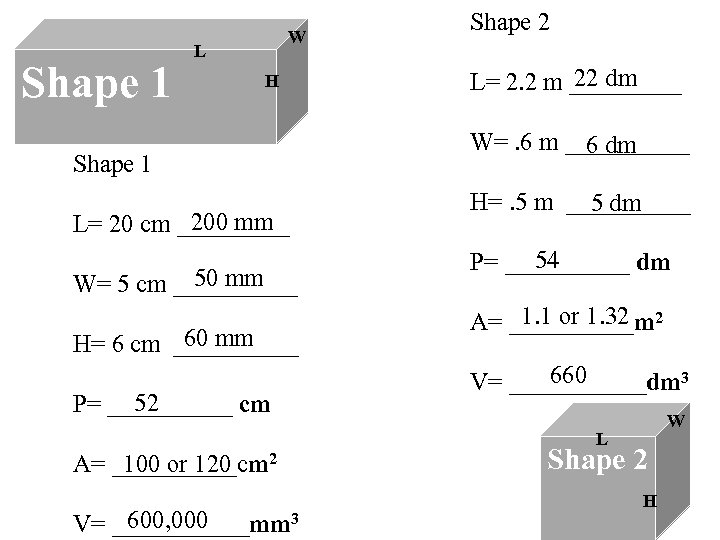
Shape 1 W L H Shape 1 200 mm L= 20 cm _____ 50 mm W= 5 cm _____ 60 mm H= 6 cm _____ 52 P= _____ cm Shape 2 22 dm L= 2. 2 m _____ W=. 6 m _____ 6 dm H=. 5 m _____ 5 dm 54 P= _____ dm 1. 1 or 1. 32 A= _____m 2 660 V= ______dm 3 W L A= _____cm 2 100 or 120 600, 000 V= ______mm 3 Shape 2 H
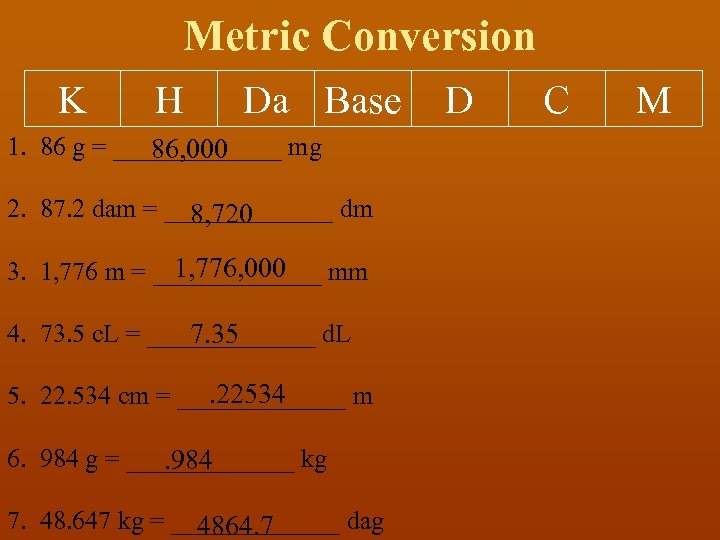
Metric Conversion K H Da Base 1. 86 g = _______ mg 86, 000 2. 87. 2 dam = _______ dm 8, 720 1, 776, 000 3. 1, 776 m = _______ mm 4. 73. 5 c. L = _______ d. L 7. 35 . 22534 5. 22. 534 cm = _______ m 6. 984 g = _______ kg . 984 7. 48. 647 kg = _______ dag 4864. 7 D C M
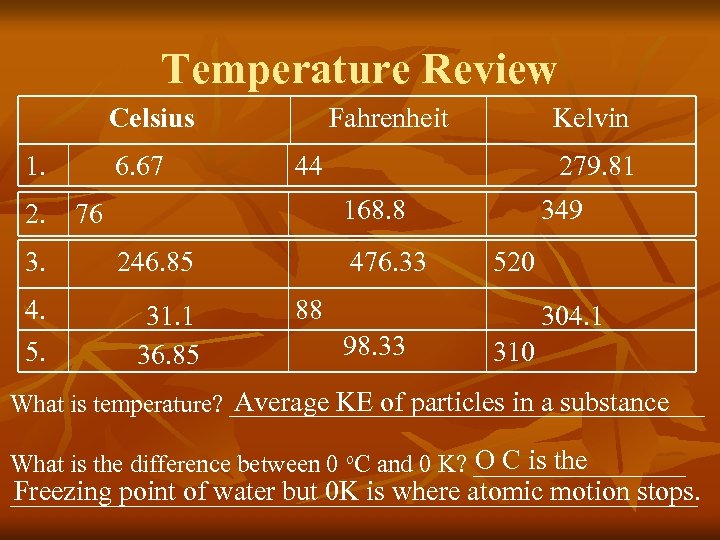
Temperature Review Celsius 1. 6. 67 Fahrenheit Kelvin 44 279. 81 168. 8 2. 76 3. 246. 85 4. 5. 31. 1 36. 85 476. 33 349 520 88 98. 33 304. 1 310 Average KE of particles in a substance What is temperature? ___________________ O C is the What is the difference between 0 o. C and 0 K? _________ Freezing point of water but 0 K is where atomic motion stops. ____________________________

Review Liquid Volume Always read meniscus down. 1 1 m. L = _____cm 3 The density of water is 1 _______g/cm 3 58 m. L 33 m. L 14. 5 m. L

Explain how you would find the volume of the rock. n Place water in the n n n 6 m. L 7 m. L Rock’s volume = 1 m. L Graduated cylinder Measure the water Place object in the water Measure level of water and object Subtract water from total The difference is the volume of the object
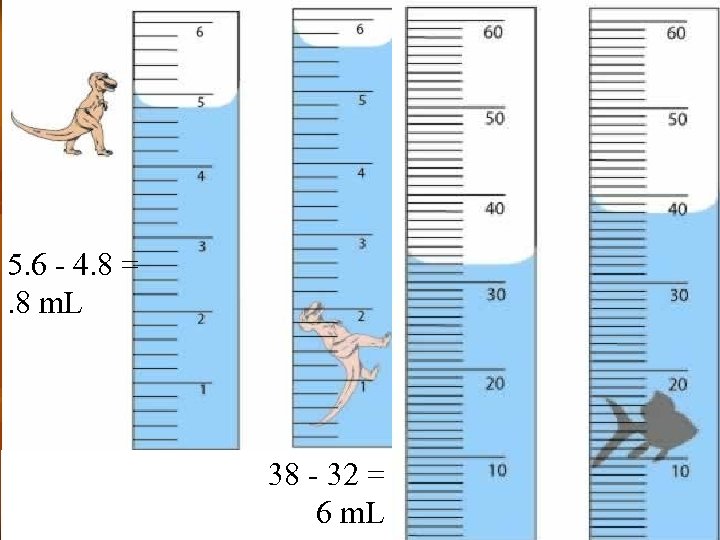
5. 6 - 4. 8 = . 8 m. L 38 - 32 = 6 m. L
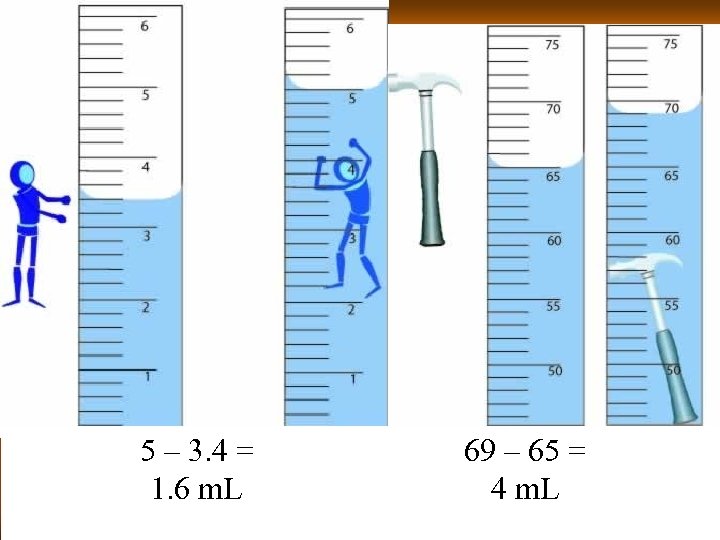
5 – 3. 4 = 1. 6 m. L 69 – 65 = 4 m. L
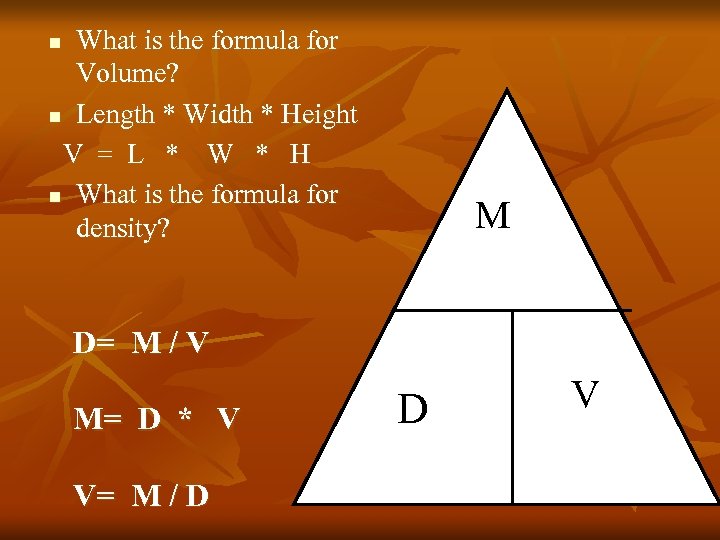
What is the formula for Volume? n Length * Width * Height V = L * W * H n What is the formula for density? n M D= M / V M= D * V V= M / D D V
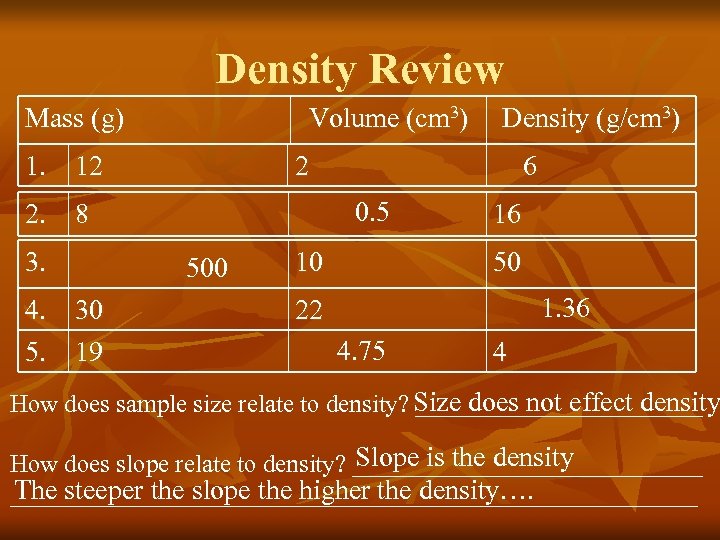
Density Review Mass (g) Volume (cm 3) 1. 12 2 4. 30 5. 19 6 0. 5 2. 8 3. Density (g/cm 3) 500 10 16 50 1. 36 22 4. 75 4 Size does not effect density How does sample size relate to density? ____________ Slope is the density How does slope relate to density? ______________ The steeper the slope the higher the density…. ____________________________

Observations vs. Inferences Observations: Something that you experience with your 5 senses Inferences: a statement, conclusion or reflection Quantitative: an observation that is expresses using numbers Qualitative: An observation that is described in terms of the qualities of the object (made using 5 senses)

Make observations & inferences about this photo. Are they Quantitative or Qualitative?
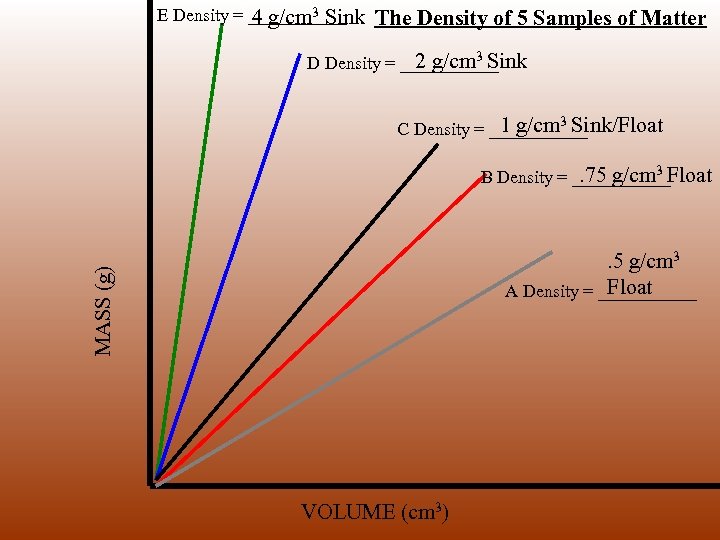
E Density = ______ 4 g/cm 3 Sink The Density of 5 Samples of Matter 2 g/cm 3 Sink D Density = ______ 1 g/cm Sink/Float C Density = ______ 3 . 75 g/cm 3 Float B Density = ______ MASS (g) . 5 g/cm 3 Float A Density = ______ VOLUME (cm 3)
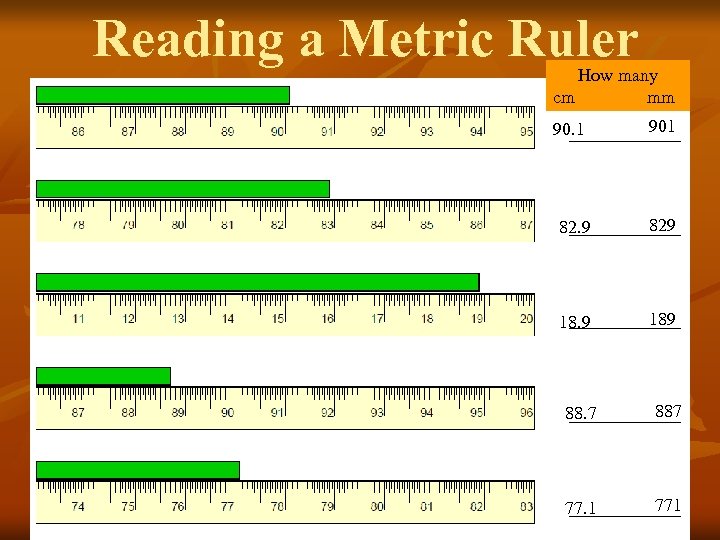
Reading a Metric Ruler How many cm mm 90. 1 901 82. 9 829 189 88. 7 887 77. 1 771

Quiz Friday n n n n n Using / reading a metric ruler Perimeter, Area, Volume of rectangles Temperature conversions Temperature scales- Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin Define: Temperature & Absolute Zero Metric Conversions: Know what the Meter, Liter and Gram measure. Density Reading a Graduated Cylinder Using a graduated cylinder to measure the volume of irregular solids Quantitative & Qualitative Observations & Inferences

Lab Skills Review Lab

1. Which pieces of lab equipment would be useful for pouring liquids? Beaker or Graduated Cylindar 2. Which pieces of equipment are measuring devices? Give examples… 3. What are some uses of the other items that are nonmeasuring devises? Microscope, Scissors, Goggles, Hand Lens, maybe Graph Paper 4. Which piece of equipment will protect your eyes from splashes of liquid, shattered glass and flying chips of rock? Goggles
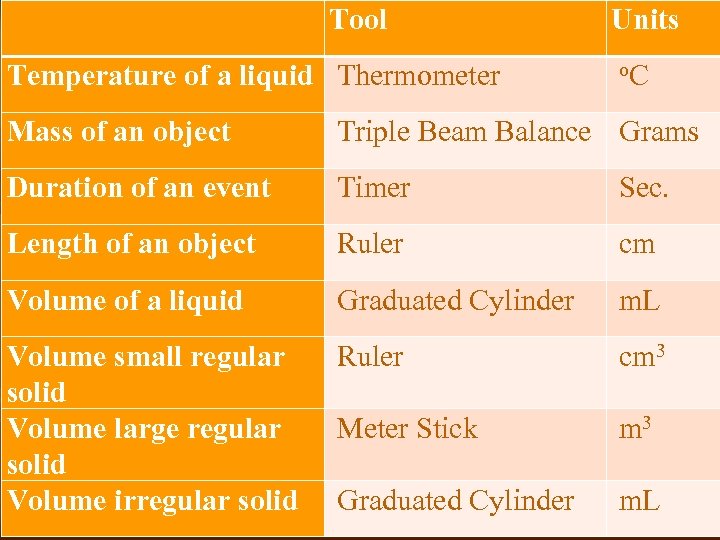
Tool Temperature of a liquid Thermometer Units o. C Mass of an object Triple Beam Balance Grams Duration of an event Timer Sec. Length of an object Ruler cm Volume of a liquid Graduated Cylinder m. L Volume small regular solid Volume large regular solid Volume irregular solid Ruler cm 3 Meter Stick m 3 Graduated Cylinder m. L

Density: is the ratio of the mass of an Density: object to its volume 8. A kilogram of rocks and a kilogram of feather (finch) have the same mass, but the rocks take up less space. The rocks are said to be denser than the feathers. What instruments would be needed to determine the density of a small pebble? Balance and ruler or Graduated cylinder. Describe the procedure you would use to find the density. Mass item, measure volume, divide. What is the formula for density? D = M / V
What Should we learn?
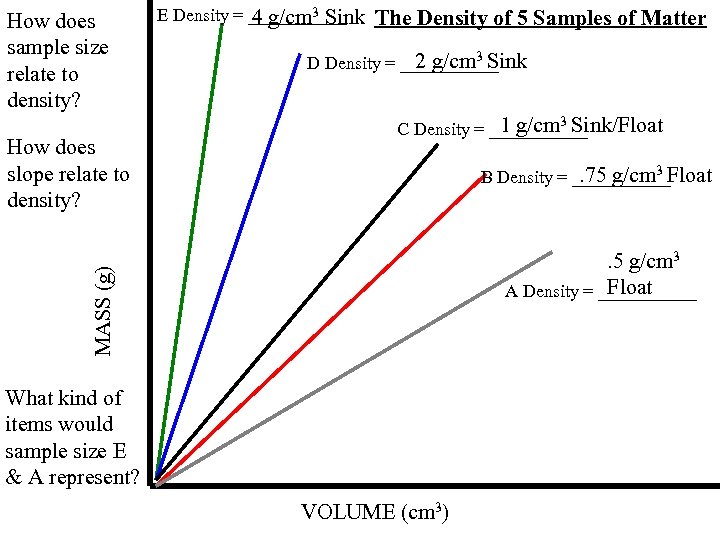
How does sample size relate to density? E Density = ______ 4 g/cm 3 Sink The Density of 5 Samples of Matter 2 g/cm 3 Sink D Density = ______ 1 g/cm Sink/Float C Density = ______ 3 . 75 g/cm 3 Float B Density = ______ . 5 g/cm 3 Float A Density = ______ MASS (g) How does slope relate to density? What kind of items would sample size E & A represent? VOLUME (cm 3)

Density of objects lab
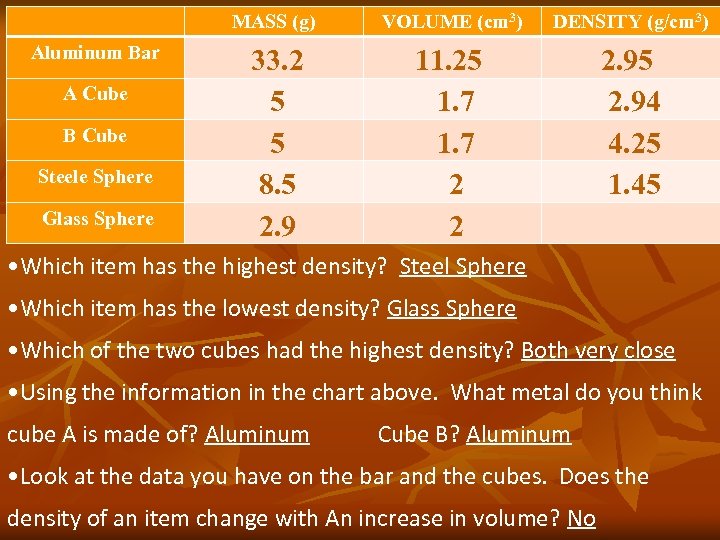
MASS (g) VOLUME (cm 3) DENSITY (g/cm 3) Aluminum Bar 33. 2 5 5 8. 5 2. 9 11. 25 1. 7 2 2 2. 95 2. 94 4. 25 1. 45 A Cube B Cube Steele Sphere Glass Sphere • Which item has the highest density? Steel Sphere • Which item has the lowest density? Glass Sphere • Which of the two cubes had the highest density? Both very close • Using the information in the chart above. What metal do you think cube A is made of? Aluminum Cube B? Aluminum • Look at the data you have on the bar and the cubes. Does the density of an item change with An increase in volume? No
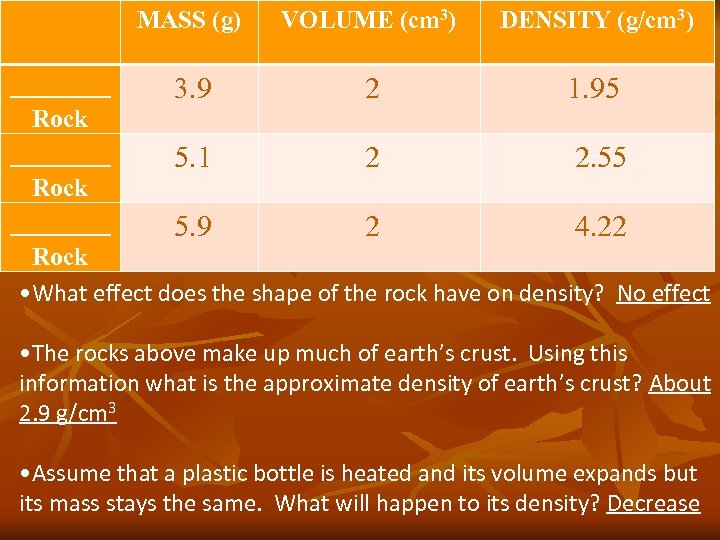
MASS (g) VOLUME (cm 3) DENSITY (g/cm 3) ____ 3. 9 2 1. 95 Rock ____ 5. 1 2 2. 55 Rock ____ 5. 9 2 4. 22 Rock • What effect does the shape of the rock have on density? No effect • The rocks above make up much of earth’s crust. Using this information what is the approximate density of earth’s crust? About 2. 9 g/cm 3 • Assume that a plastic bottle is heated and its volume expands but its mass stays the same. What will happen to its density? Decrease

Density of Water 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Mass the cylinder Place 50 m. L of water into the cylinder Mass the water and cylinder (Cylinder + water) - cylinder = water So v = 50 cm 3 And m = 49. 1 g 49. 1 / 50 =. 98 g/ cm 3 Very close to the true density of 1 g/cm 3
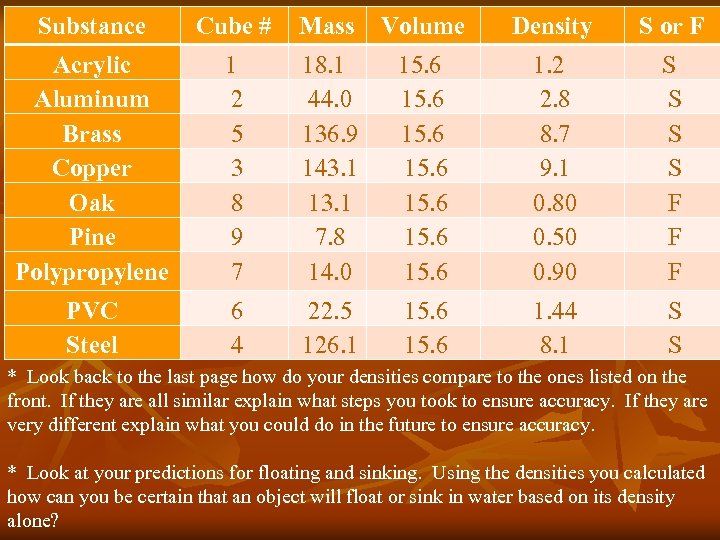
Substance Cube # Mass Volume Density S or F Acrylic Aluminum Brass Copper Oak Pine Polypropylene 1 2 5 3 8 9 7 18. 1 44. 0 136. 9 143. 1 13. 1 7. 8 14. 0 15. 6 15. 6 1. 2 2. 8 8. 7 9. 1 0. 80 0. 50 0. 90 S S S S F F F PVC Steel 6 4 22. 5 126. 1 15. 6 1. 44 8. 1 S S * Look back to the last page how do your densities compare to the ones listed on the front. If they are all similar explain what steps you took to ensure accuracy. If they are very different explain what you could do in the future to ensure accuracy. * Look at your predictions for floating and sinking. Using the densities you calculated how can you be certain that an object will float or sink in water based on its density alone?
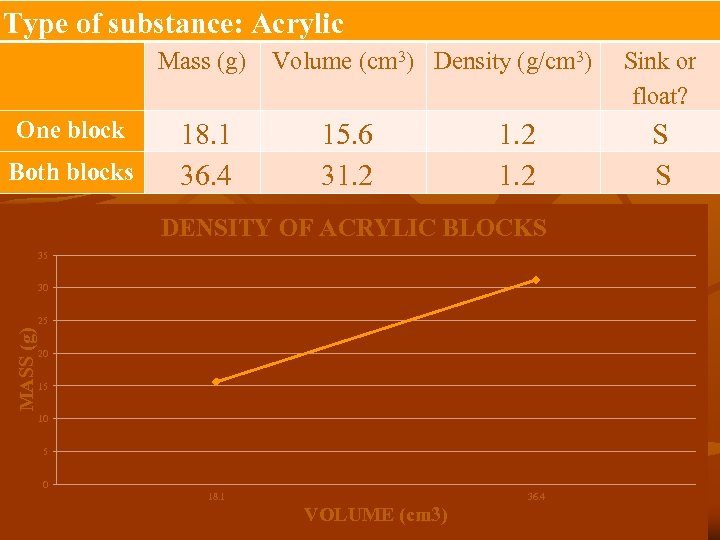
Type of substance: Acrylic Mass (g) One block Both blocks 18. 1 36. 4 Volume (cm 3) Density (g/cm 3) 15. 6 31. 2 DENSITY OF ACRYLIC BLOCKS 35 30 MASS (g) 25 20 15 10 5 0 18. 1 36. 4 VOLUME (cm 3) Sink or float? S S

n As volume increases mass ________. n As volume decreases mass _________. n n n As the mass and volume of a substance increase, the density of that substance __________. Look at the slope of the line. What does the slope represent? _____________ What do you predict would happen to density if there were three blocks? ___________

Measuring Liquid Volume Quiz Help

Step 1 n Work out what it counts by…
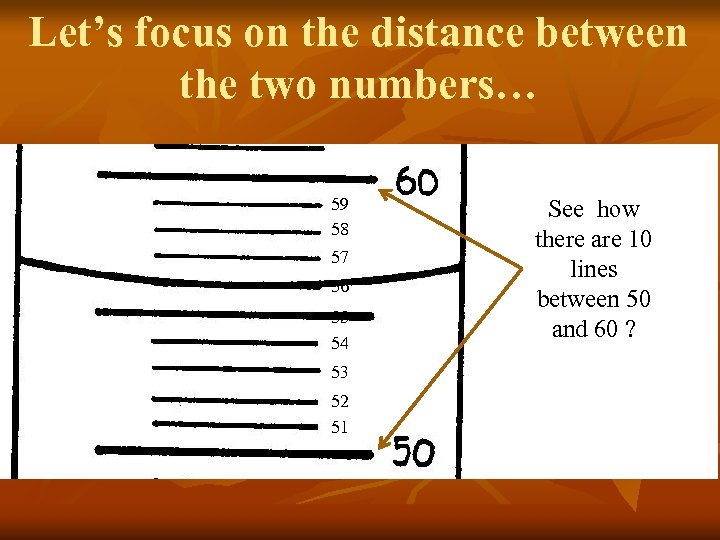
Let’s focus on the distance between the two numbers… 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 See how there are 10 lines between 50 and 60 ?
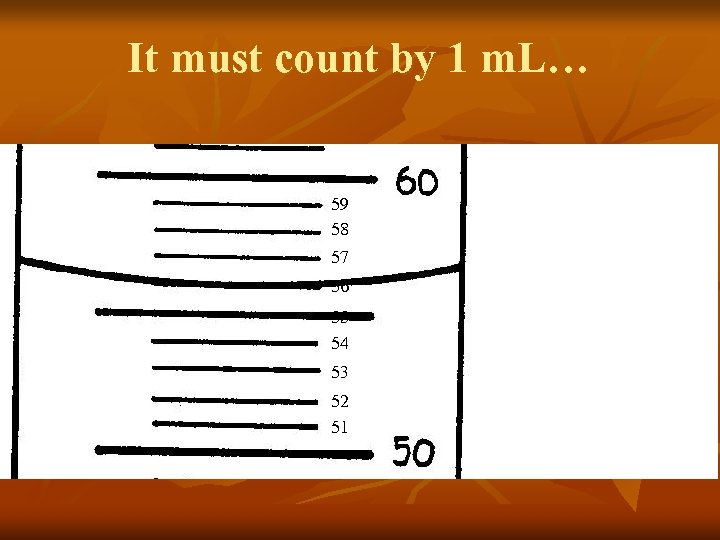
It must count by 1 m. L… 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51

Step 2 n Now we read the water level. Because it counts by 1 m. L and we don’t guess the answer must be a whole number.
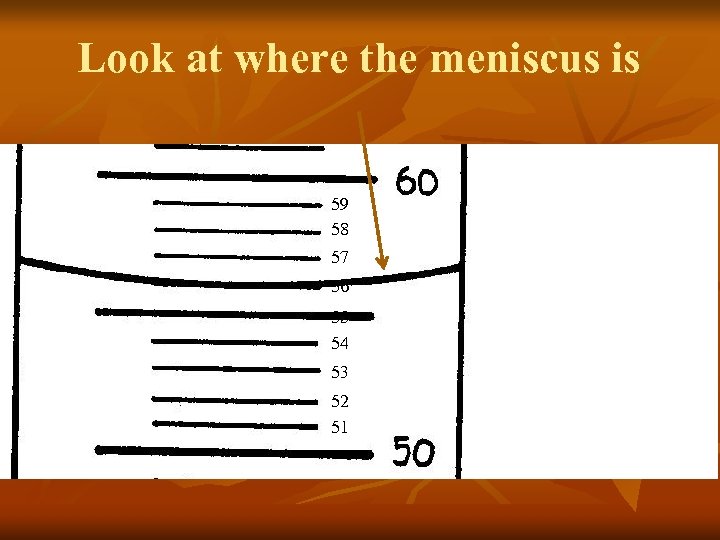
Look at where the meniscus is 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51
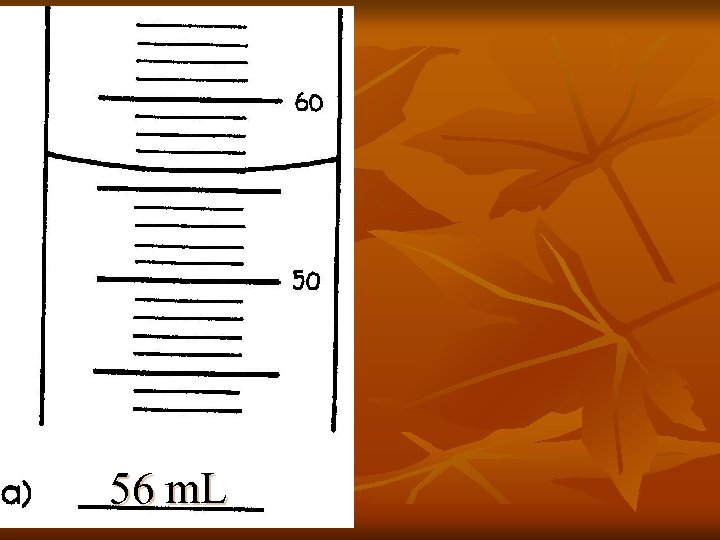
56 m. L

Step 1 again. n Work out what it counts by…

Let’s focus on the distance between the two numbers… 3. 9 3. 8 3. 7 3. 6 3. 5 3. 4 3. 3 3. 2 3. 1 See how there also 10 lines here between 3 and 4?

It must count by. 1 m. L… 3. 9 3. 8 3. 7 3. 6 3. 5 3. 4 3. 3 3. 2 3. 1
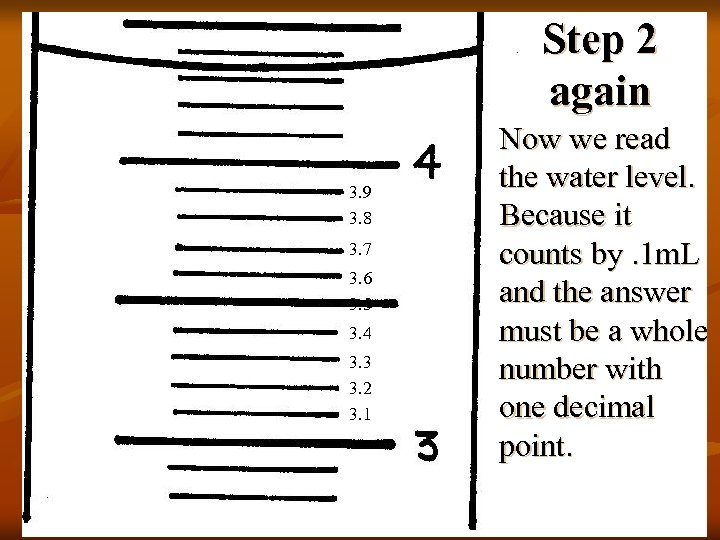
Step 2 again 3. 9 3. 8 3. 7 3. 6 3. 5 3. 4 3. 3 3. 2 3. 1 Now we read the water level. Because it counts by. 1 m. L and the answer must be a whole number with one decimal point.
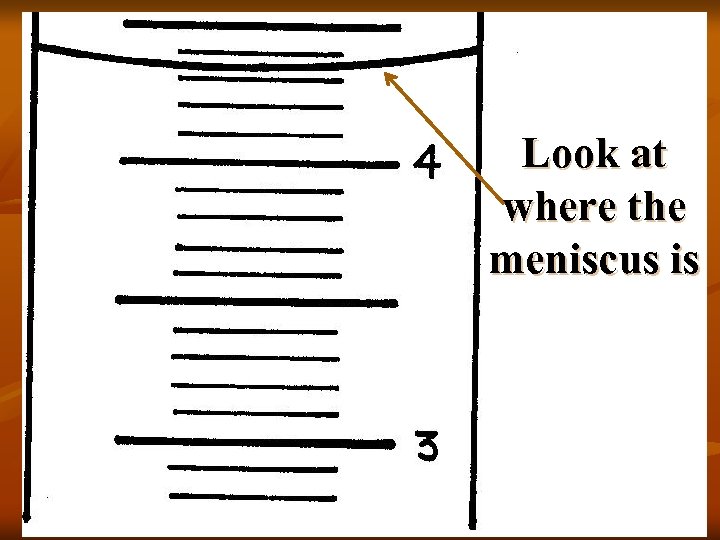
Look at where the meniscus is
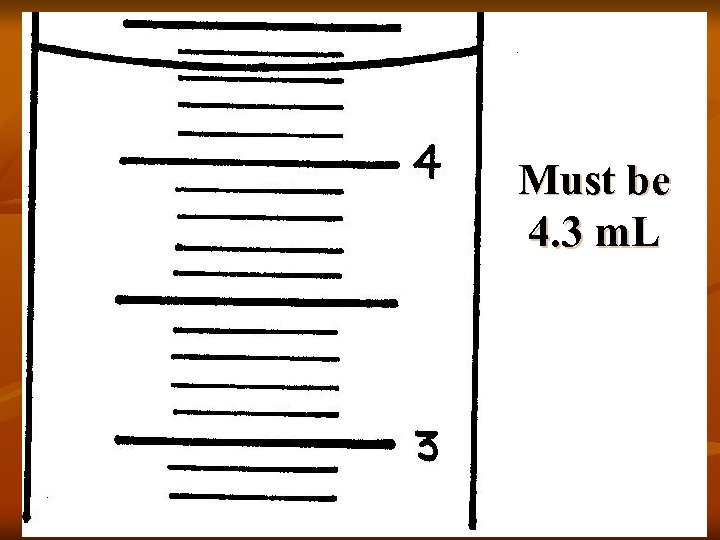
Must be 4. 3 m. L

bfb1b76e0bde329d65e4b37cc6bf9bb3.ppt