263f3dd76c1edb3b922e1b14c92c382e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Measuring and Reporting Basic Skills Success; You Need a Valid Instrument - CB 21 Coding 1 CAROLE BOGUE-FEINOUR, RETIRED VICE CHANCELLOR OF ACADEMIC AFFAIRS, CCCCO MYRNA HUFFMAN, DIRECTOR MIS, CCCCO JANET FULKS, ASCCC CURRICULUM CHAIR JULY 2009 CURRICULUM INSTITUTE

Background 2 BSI directed attention to the ARCC data Some measures did not make sense Investigating the coding revealed inaccuracies Particularly the Basic Skills Progress Outcome ESL Progress Outcome Progress for courses prior to transfer Needed to define the Supplemental Basic Skills Report for accountability on the BSI funding and noncredit enhanced funding

“CB 21 -Course Prior to Transfer Course Level” 3 CB 21 is code for the course “level”, in terms of number of levels below the transferrable level How many levels below transfer level is this course? It is used primarily for basic skills but can be used for non-basic skills, degree-applicable courses It is used only for English, writing, ESL, reading, or mathematics (TOP codes) We are reporting credit courses; noncredit in progress

MIS Data Element CB 21 4 Is used for a lot of accountability reporting Which in turn is used to justify investments and expenditures in basic skills ARCC Technical Advisory Group: defines metrics for mandated reports Is necessary to show student progress through basic skills curriculum 4… 3… 2… 1…transferrable
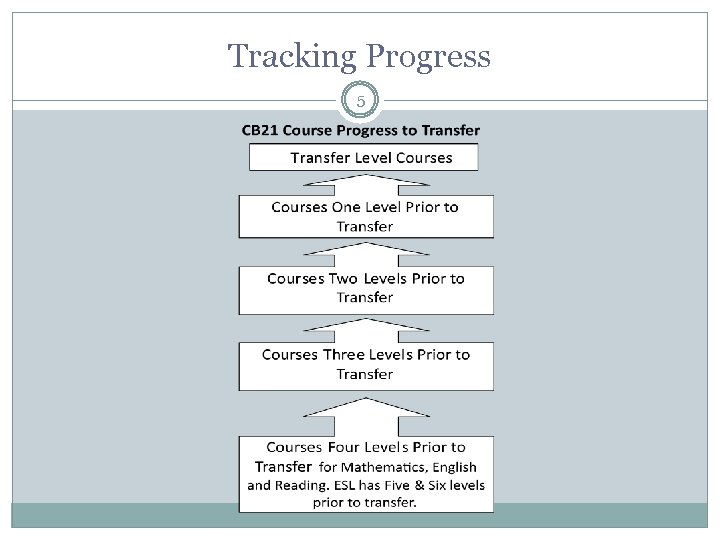
Tracking Progress 5
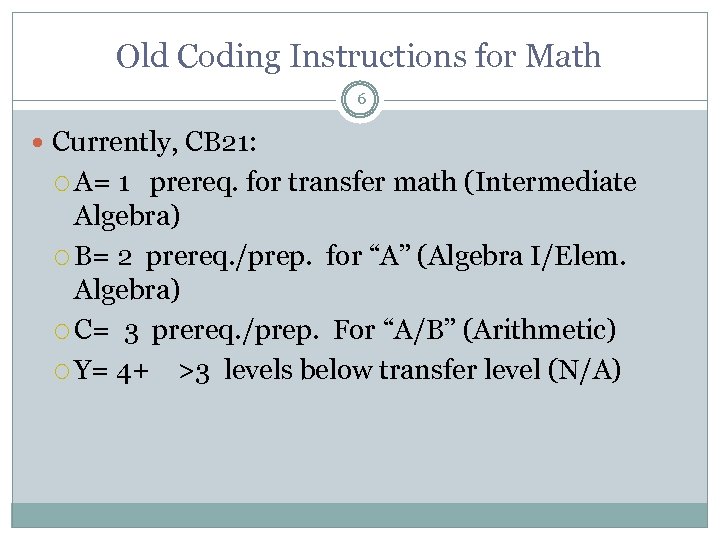
Old Coding Instructions for Math 6 Currently, CB 21: A= 1 prereq. for transfer math (Intermediate Algebra) B= 2 prereq. /prep. for “A” (Algebra I/Elem. Algebra) C= 3 prereq. /prep. For “A/B” (Arithmetic) Y= 4+ >3 levels below transfer level (N/A)

Old Coding Instructions for English 7 Currently, CB 21: A= 1 prereq. for transfer Eng. Comp. (Subject A) B= 2 prereq. /prep. for “A” (Not available) C= 3 prereq. /prep. For “A/B” (Not available) Y= 4+ >3 levels below transfer level (Not available)

Old Coding Instructions for Reading and ESL 8 Not addressed at all

Coding problems 9 No colleges had a common beginning; college level was different for every college – even colleges within a district Some college coding had no progress – all courses one level Some courses were in the wrong order of progression Some courses were incorrectly identified as transfer
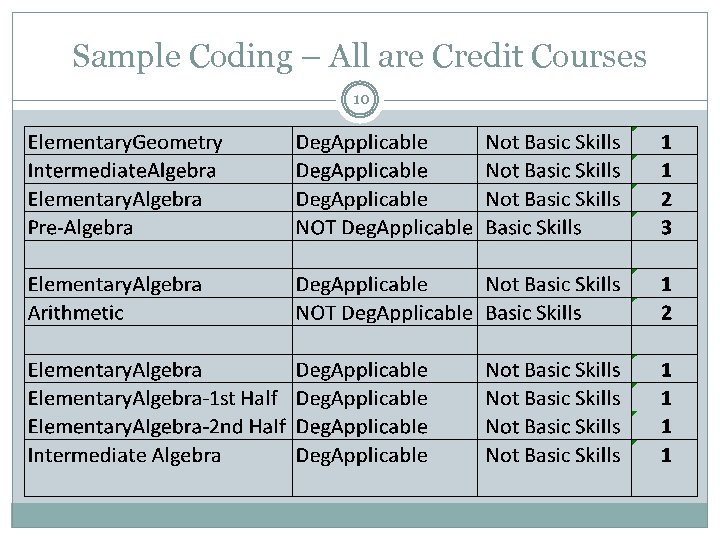
Sample Coding – All are Credit Courses 10
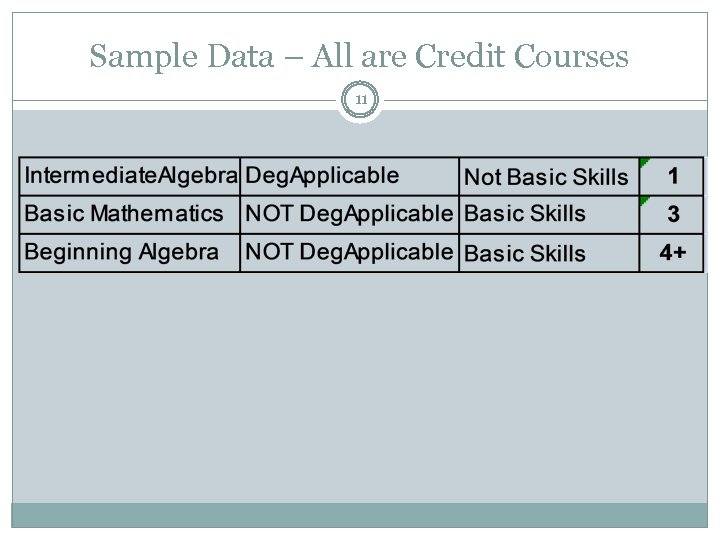
Sample Data – All are Credit Courses 11
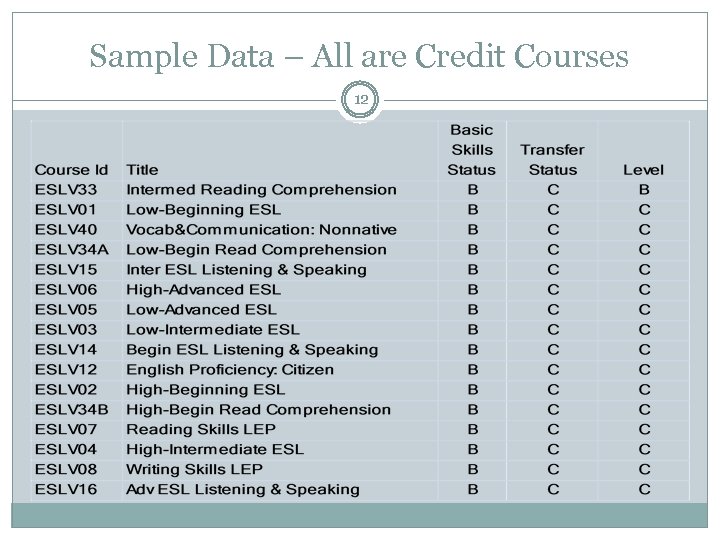
Sample Data – All are Credit Courses 12
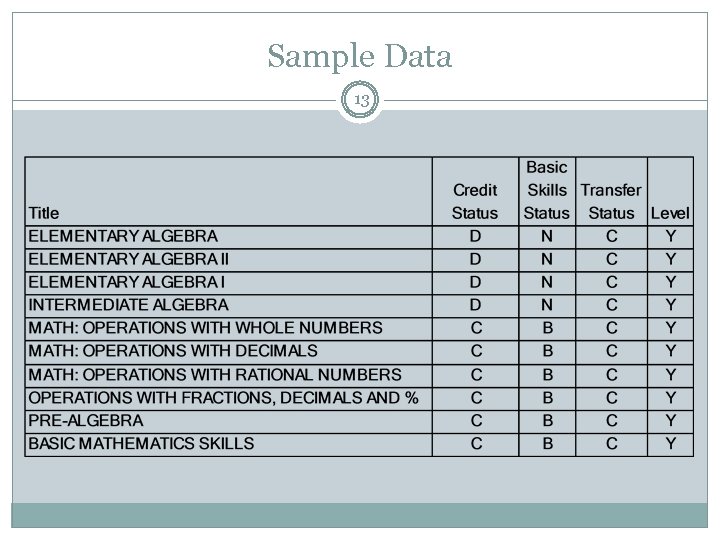
Sample Data 13
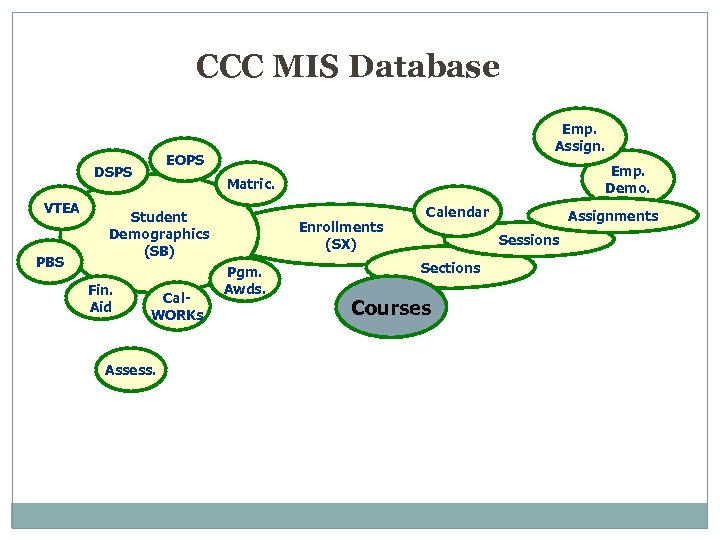
CCC MIS Database EOPS DSPS VTEA PBS Emp. Assign. Matric. Student Demographics (SB) Fin. Aid Emp. Demo. Cal. WORKs Assess. Enrollments (SX) Pgm. Awds. Calendar Assignments Sessions Sections Courses

Why do we code courses? What are the data uses? 15
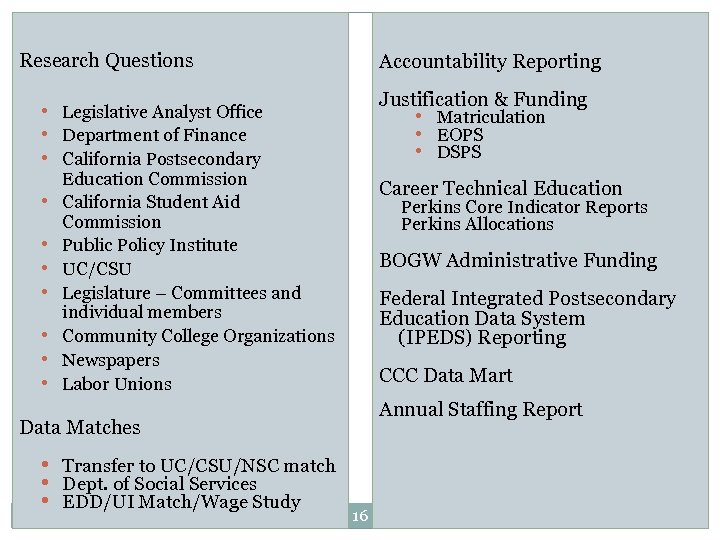
Research Questions Accountability Reporting Justification & Funding • Legislative Analyst Office • Department of Finance • California Postsecondary • • Matriculation • EOPS • DSPS Education Commission California Student Aid Commission Public Policy Institute UC/CSU Legislature – Committees and individual members Community College Organizations Newspapers Labor Unions Career Technical Education Perkins Core Indicator Reports Perkins Allocations BOGW Administrative Funding Federal Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS) Reporting CCC Data Mart Annual Staffing Report Data Matches • Transfer to UC/CSU/NSC match • Dept. of Social Services • EDD/UI Match/Wage Study 16
MIS Data Element CB 21 17 Chancellor’s Office MIS system collects all course information each term Courses are coded for identification purposes TOP code, credit status, transfer status, units, basic skills status, SAM/voc code, etc. CB 21=Course Prior to College Level (Current)

MIS Data Element CB 21 18 Last changed in 1994 Defined number of “codeable” levels at 5 (xfer + 4 below) Is used across math/English/reading/writing/ESL Has little curricular definition of levels
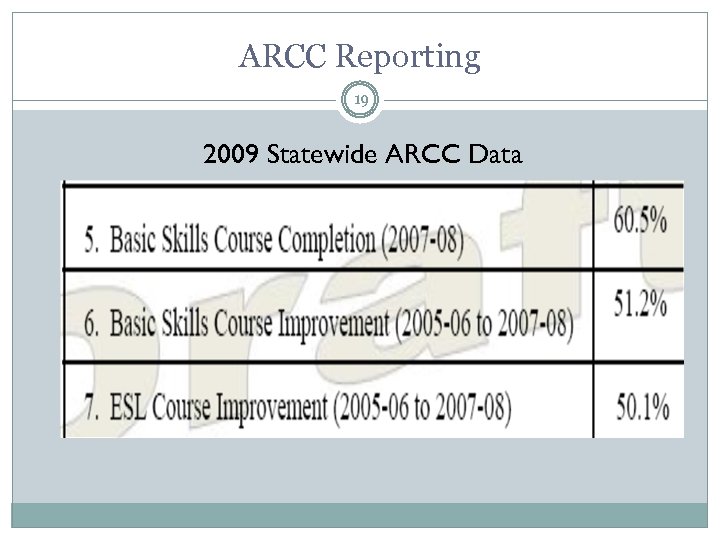
ARCC Reporting 19 2009 Statewide ARCC Data
What CB 21 is used for 20 Basic Skills Improvement Rate (ARCC) ◦ ◦ ◦ Credit courses only Completed (A, B, C, CR, P) any math/Eng basic skills course at 2 or more levels below Within 3 years, successfully completed a higher level basic skills course of same discipline Anywhere in the system where SSN’s are reported Current data range: 24%-62%, ◦ avg 49%. ◦
What CB 21 is used for 21 ESL Improvement Rate (ARCC) Credit ESL courses only Completed (A, B, C, CR, P) any ESL course at 2 or more levels below Within 3 years, successfully completed a higher level ESL course Anywhere in the system where SSN’s are reported Current 81%, avg. 42% data range: 0% to

The Strategy - Establishing a Rubric 22 Is not standardization Does not drive curricular changes Is not common course numbering or articulation IS a mapping exercise designed to maximize our ability to show student progress AND your good work

Newly Designed CB 21 – Attached to Rubrics 23 Each college retains their own curriculum Does not affect degree applicability Allows for uniformity throughout state Will enhance collection of accurate and comparable data Can be used to collect assessment and placement data

The Process 24 140 Faculty Research for standards, outcomes and exit skills Divided by Discipline Developed rubrics based on need and curriculum Universally acceptable, not comprehensive

The results 25 Rubrics created using 4 levels below transfer ◦ ◦ ◦ Reading Writing Math, ESL created 3 rubrics and needed 6 levels below transfer ◦ ◦ ESL Writing ESL Reading ESL Listening and Speaking **ESL Integrated
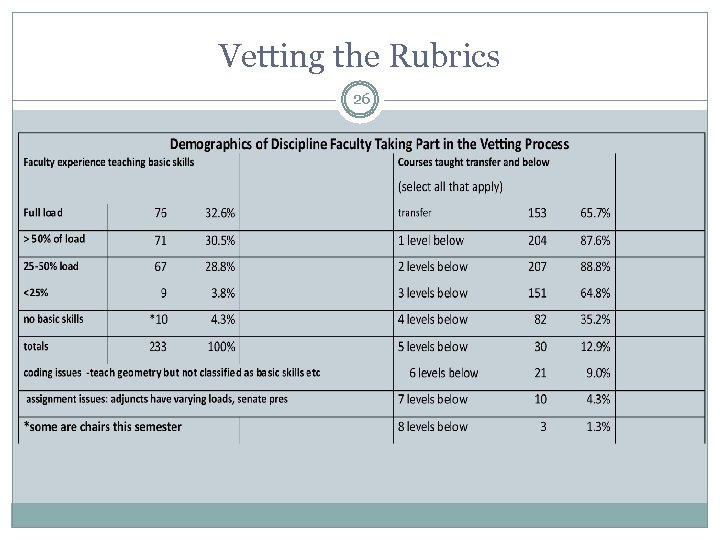
Vetting the Rubrics 26
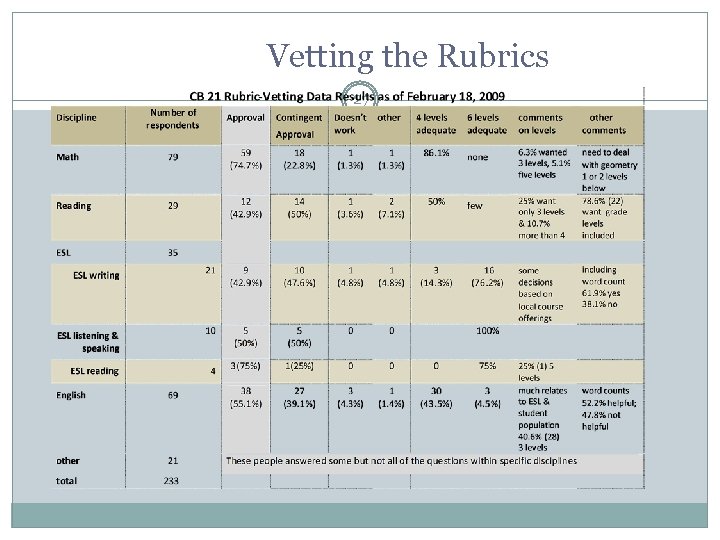
Vetting the Rubrics 27

Moving on to noncredit 28 ABE/ASE Math English ESL integrated

Next Steps 29 What will this mean? How will it change ARCC reporting? Will the data suddenly show a big difference due to recoding? How will you proceed?

Next Steps & Timeline 30 Coding instructions CIOs and Researchers meetings and listservs Possible web training Contact people for questions All recoding must be done by November 30

Questions 31
263f3dd76c1edb3b922e1b14c92c382e.ppt