64c4e1417b179a602704f42e55827f31.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 MEASURING A NATION’S INCOME ETP Economics 102 Lecturer: Jack Wu
MEASURING A NATION’S INCOME ETP Economics 102 Lecturer: Jack Wu
 MAJOR MACROECONOMIC CONCERNS National Income: Low Economic Growth Rate Employment Opportunity: High Unemployment Rate Cost of Living: High Inflation Rate Direct Investment: Low FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) Income Distribution: High Gini Coefficient
MAJOR MACROECONOMIC CONCERNS National Income: Low Economic Growth Rate Employment Opportunity: High Unemployment Rate Cost of Living: High Inflation Rate Direct Investment: Low FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) Income Distribution: High Gini Coefficient
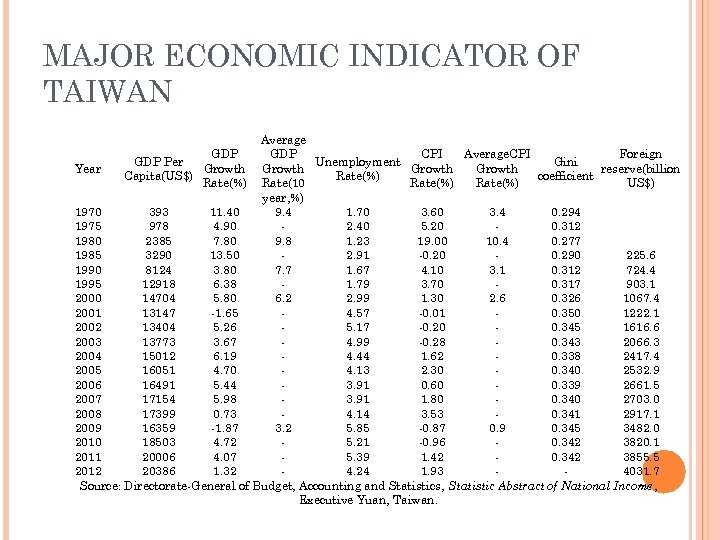 MAJOR ECONOMIC INDICATOR OF TAIWAN Average GDP CPI Average. CPI Foreign GDP Per Unemployment Gini Year Growth reserve(billion Capita(US$) Rate(%) coefficient Rate(%) Rate(10 Rate(%) US$) year, %) 1970 393 11. 40 9. 4 1. 70 3. 60 3. 4 0. 294 1975 978 4. 90 2. 40 5. 20 0. 312 1980 2385 7. 80 9. 8 1. 23 19. 00 10. 4 0. 277 1985 3290 13. 50 2. 91 -0. 20 0. 290 225. 6 1990 8124 3. 80 7. 7 1. 67 4. 10 3. 1 0. 312 724. 4 1995 12918 6. 38 1. 79 3. 70 0. 317 903. 1 2000 14704 5. 80 6. 2 2. 99 1. 30 2. 6 0. 326 1067. 4 2001 13147 -1. 65 4. 57 -0. 01 0. 350 1222. 1 2002 13404 5. 26 5. 17 -0. 20 0. 345 1616. 6 2003 13773 3. 67 4. 99 -0. 28 0. 343 2066. 3 2004 15012 6. 19 4. 44 1. 62 0. 338 2417. 4 2005 16051 4. 70 4. 13 2. 30 0. 340 2532. 9 2006 16491 5. 44 3. 91 0. 60 0. 339 2661. 5 2007 17154 5. 98 3. 91 1. 80 0. 340 2703. 0 2008 17399 0. 73 4. 14 3. 53 0. 341 2917. 1 2009 16359 -1. 87 3. 2 5. 85 -0. 87 0. 9 0. 345 3482. 0 2010 18503 4. 72 5. 21 -0. 96 0. 342 3820. 1 2011 20006 4. 07 5. 39 1. 42 0. 342 3855. 5 2012 20386 1. 32 4. 24 1. 93 4031. 7 Source: Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics, Statistic Abstract of National Income, Executive Yuan, Taiwan.
MAJOR ECONOMIC INDICATOR OF TAIWAN Average GDP CPI Average. CPI Foreign GDP Per Unemployment Gini Year Growth reserve(billion Capita(US$) Rate(%) coefficient Rate(%) Rate(10 Rate(%) US$) year, %) 1970 393 11. 40 9. 4 1. 70 3. 60 3. 4 0. 294 1975 978 4. 90 2. 40 5. 20 0. 312 1980 2385 7. 80 9. 8 1. 23 19. 00 10. 4 0. 277 1985 3290 13. 50 2. 91 -0. 20 0. 290 225. 6 1990 8124 3. 80 7. 7 1. 67 4. 10 3. 1 0. 312 724. 4 1995 12918 6. 38 1. 79 3. 70 0. 317 903. 1 2000 14704 5. 80 6. 2 2. 99 1. 30 2. 6 0. 326 1067. 4 2001 13147 -1. 65 4. 57 -0. 01 0. 350 1222. 1 2002 13404 5. 26 5. 17 -0. 20 0. 345 1616. 6 2003 13773 3. 67 4. 99 -0. 28 0. 343 2066. 3 2004 15012 6. 19 4. 44 1. 62 0. 338 2417. 4 2005 16051 4. 70 4. 13 2. 30 0. 340 2532. 9 2006 16491 5. 44 3. 91 0. 60 0. 339 2661. 5 2007 17154 5. 98 3. 91 1. 80 0. 340 2703. 0 2008 17399 0. 73 4. 14 3. 53 0. 341 2917. 1 2009 16359 -1. 87 3. 2 5. 85 -0. 87 0. 9 0. 345 3482. 0 2010 18503 4. 72 5. 21 -0. 96 0. 342 3820. 1 2011 20006 4. 07 5. 39 1. 42 0. 342 3855. 5 2012 20386 1. 32 4. 24 1. 93 4031. 7 Source: Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics, Statistic Abstract of National Income, Executive Yuan, Taiwan.
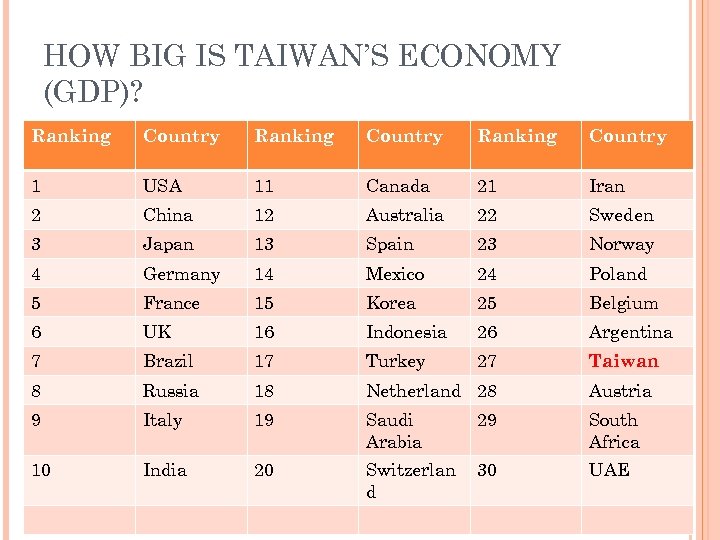 HOW BIG IS TAIWAN’S ECONOMY (GDP)? Ranking Country 1 USA 11 Canada 21 Iran 2 China 12 Australia 22 Sweden 3 Japan 13 Spain 23 Norway 4 Germany 14 Mexico 24 Poland 5 France 15 Korea 25 Belgium 6 UK 16 Indonesia 26 Argentina 7 Brazil 17 Turkey 27 Taiwan 8 Russia 18 Netherland 28 Austria 9 Italy 19 Saudi Arabia 29 South Africa 10 India 20 Switzerlan d 30 UAE
HOW BIG IS TAIWAN’S ECONOMY (GDP)? Ranking Country 1 USA 11 Canada 21 Iran 2 China 12 Australia 22 Sweden 3 Japan 13 Spain 23 Norway 4 Germany 14 Mexico 24 Poland 5 France 15 Korea 25 Belgium 6 UK 16 Indonesia 26 Argentina 7 Brazil 17 Turkey 27 Taiwan 8 Russia 18 Netherland 28 Austria 9 Italy 19 Saudi Arabia 29 South Africa 10 India 20 Switzerlan d 30 UAE
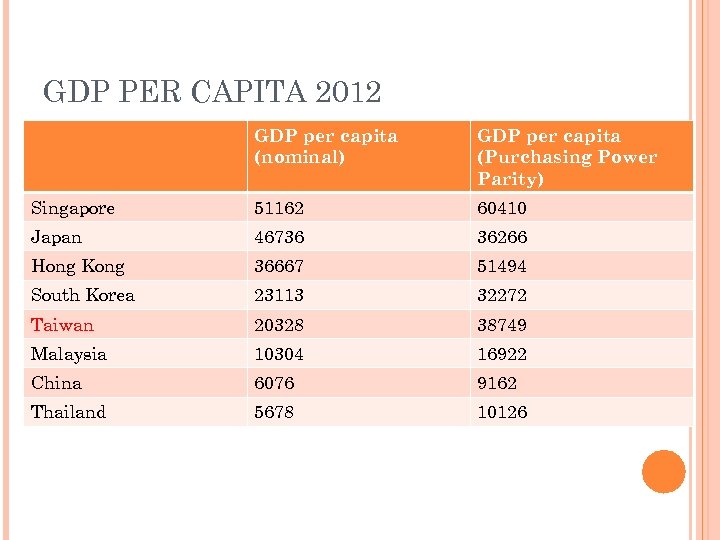 GDP PER CAPITA 2012 GDP per capita (nominal) GDP per capita (Purchasing Power Parity) Singapore 51162 60410 Japan 46736 36266 Hong Kong 36667 51494 South Korea 23113 32272 Taiwan 20328 38749 Malaysia 10304 16922 China 6076 9162 Thailand 5678 10126
GDP PER CAPITA 2012 GDP per capita (nominal) GDP per capita (Purchasing Power Parity) Singapore 51162 60410 Japan 46736 36266 Hong Kong 36667 51494 South Korea 23113 32272 Taiwan 20328 38749 Malaysia 10304 16922 China 6076 9162 Thailand 5678 10126
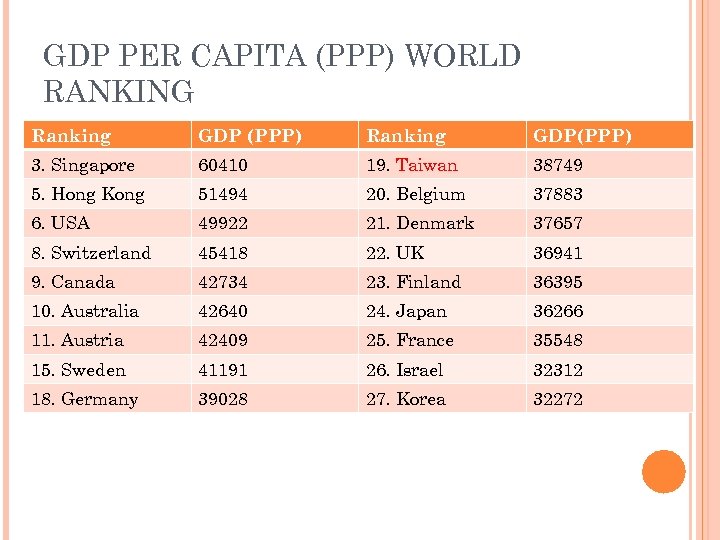 GDP PER CAPITA (PPP) WORLD RANKING Ranking GDP (PPP) Ranking GDP(PPP) 3. Singapore 60410 19. Taiwan 38749 5. Hong Kong 51494 20. Belgium 37883 6. USA 49922 21. Denmark 37657 8. Switzerland 45418 22. UK 36941 9. Canada 42734 23. Finland 36395 10. Australia 42640 24. Japan 36266 11. Austria 42409 25. France 35548 15. Sweden 41191 26. Israel 32312 18. Germany 39028 27. Korea 32272
GDP PER CAPITA (PPP) WORLD RANKING Ranking GDP (PPP) Ranking GDP(PPP) 3. Singapore 60410 19. Taiwan 38749 5. Hong Kong 51494 20. Belgium 37883 6. USA 49922 21. Denmark 37657 8. Switzerland 45418 22. UK 36941 9. Canada 42734 23. Finland 36395 10. Australia 42640 24. Japan 36266 11. Austria 42409 25. France 35548 15. Sweden 41191 26. Israel 32312 18. Germany 39028 27. Korea 32272
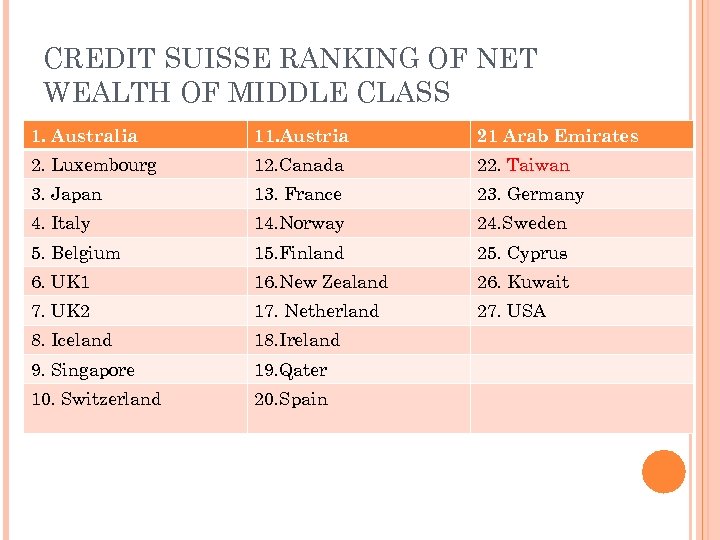 CREDIT SUISSE RANKING OF NET WEALTH OF MIDDLE CLASS 1. Australia 11. Austria 21 Arab Emirates 2. Luxembourg 12. Canada 22. Taiwan 3. Japan 13. France 23. Germany 4. Italy 14. Norway 24. Sweden 5. Belgium 15. Finland 25. Cyprus 6. UK 1 16. New Zealand 26. Kuwait 7. UK 2 17. Netherland 27. USA 8. Iceland 18. Ireland 9. Singapore 19. Qater 10. Switzerland 20. Spain
CREDIT SUISSE RANKING OF NET WEALTH OF MIDDLE CLASS 1. Australia 11. Austria 21 Arab Emirates 2. Luxembourg 12. Canada 22. Taiwan 3. Japan 13. France 23. Germany 4. Italy 14. Norway 24. Sweden 5. Belgium 15. Finland 25. Cyprus 6. UK 1 16. New Zealand 26. Kuwait 7. UK 2 17. Netherland 27. USA 8. Iceland 18. Ireland 9. Singapore 19. Qater 10. Switzerland 20. Spain
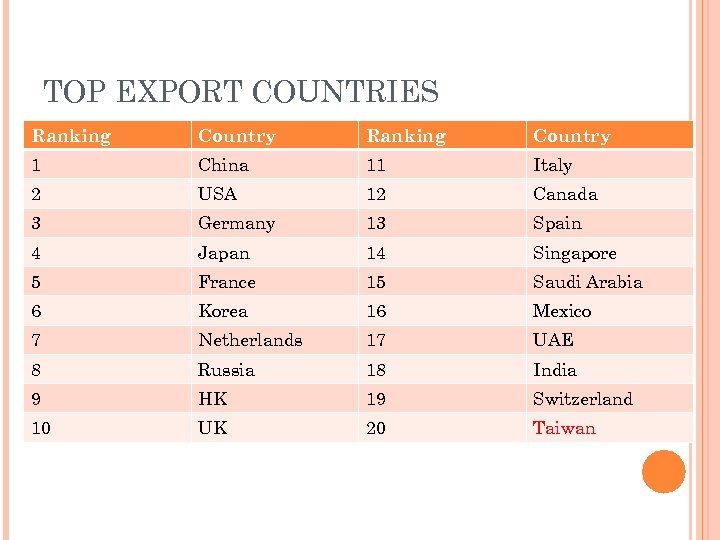 TOP EXPORT COUNTRIES Ranking Country 1 China 11 Italy 2 USA 12 Canada 3 Germany 13 Spain 4 Japan 14 Singapore 5 France 15 Saudi Arabia 6 Korea 16 Mexico 7 Netherlands 17 UAE 8 Russia 18 India 9 HK 19 Switzerland 10 UK 20 Taiwan
TOP EXPORT COUNTRIES Ranking Country 1 China 11 Italy 2 USA 12 Canada 3 Germany 13 Spain 4 Japan 14 Singapore 5 France 15 Saudi Arabia 6 Korea 16 Mexico 7 Netherlands 17 UAE 8 Russia 18 India 9 HK 19 Switzerland 10 UK 20 Taiwan
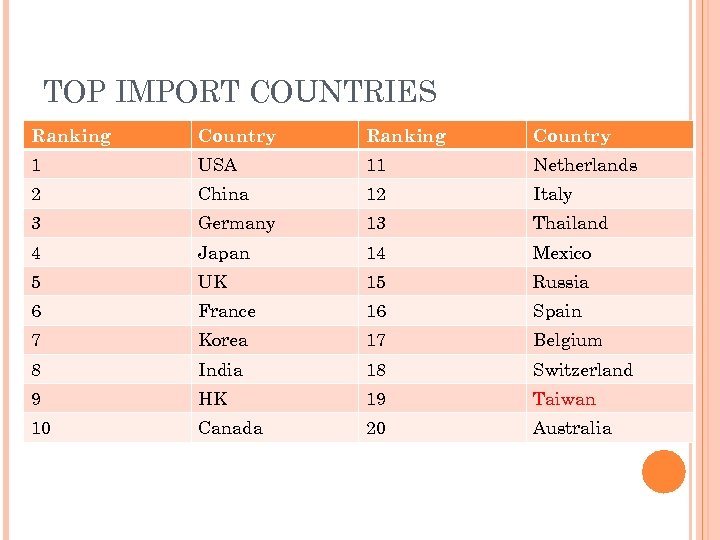 TOP IMPORT COUNTRIES Ranking Country 1 USA 11 Netherlands 2 China 12 Italy 3 Germany 13 Thailand 4 Japan 14 Mexico 5 UK 15 Russia 6 France 16 Spain 7 Korea 17 Belgium 8 India 18 Switzerland 9 HK 19 Taiwan 10 Canada 20 Australia
TOP IMPORT COUNTRIES Ranking Country 1 USA 11 Netherlands 2 China 12 Italy 3 Germany 13 Thailand 4 Japan 14 Mexico 5 UK 15 Russia 6 France 16 Spain 7 Korea 17 Belgium 8 India 18 Switzerland 9 HK 19 Taiwan 10 Canada 20 Australia
 EXAMPLES OF MACROECONOMIC QUESTIONS Macroeconomics answers questions like the following: Why is average income high in some countries and low in others? Why do prices rise rapidly in some time periods while they are more stable in others? Why do production and employment expand in some years and contract in others?
EXAMPLES OF MACROECONOMIC QUESTIONS Macroeconomics answers questions like the following: Why is average income high in some countries and low in others? Why do prices rise rapidly in some time periods while they are more stable in others? Why do production and employment expand in some years and contract in others?
 ECONOMY’S INCOME AND EXPENDITURE When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy is earning. For an economy as a whole, income must equal expenditure because: Every transaction has a buyer and a seller. Every dollar of spending by some buyer is a dollar of income for some seller.
ECONOMY’S INCOME AND EXPENDITURE When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy is earning. For an economy as a whole, income must equal expenditure because: Every transaction has a buyer and a seller. Every dollar of spending by some buyer is a dollar of income for some seller.
 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross domestic product (GDP) is a measure of the income and expenditures of an economy. It is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. The equality of income and expenditure can be illustrated with the circular-flow diagram.
GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross domestic product (GDP) is a measure of the income and expenditures of an economy. It is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. The equality of income and expenditure can be illustrated with the circular-flow diagram.
 DEFINITION OF GDP “GDP “. is the Market Value. . . ” Output is valued at market prices. . . Of All Final. . . ” It records only the value of final goods, not intermediate goods (the value is counted only once). . . Goods and Services. . . “ It includes both tangible goods (food, clothing, cars) and intangible services (haircuts, housecleaning, doctor visits).
DEFINITION OF GDP “GDP “. is the Market Value. . . ” Output is valued at market prices. . . Of All Final. . . ” It records only the value of final goods, not intermediate goods (the value is counted only once). . . Goods and Services. . . “ It includes both tangible goods (food, clothing, cars) and intangible services (haircuts, housecleaning, doctor visits).
 DEFINITION OF GDP “. . . Produced. . . ” “. . . Within a Country. . . ” It includes goods and services currently produced, not transactions involving goods produced in the past. It measures the value of production within the geographic confines of a country. “. . . In a Given Period of Time. ” It measures the value of production that takes place within a specific interval of time, usually a year or a quarter (three months).
DEFINITION OF GDP “. . . Produced. . . ” “. . . Within a Country. . . ” It includes goods and services currently produced, not transactions involving goods produced in the past. It measures the value of production within the geographic confines of a country. “. . . In a Given Period of Time. ” It measures the value of production that takes place within a specific interval of time, usually a year or a quarter (three months).
 COMPONENTS OF GDP includes all items produced in the economy and sold legally in markets. What Is Not Counted in GDP? GDP excludes most items that are produced and consumed at home and that never enter the marketplace. It excludes items produced and sold illicitly, such as illegal drugs.
COMPONENTS OF GDP includes all items produced in the economy and sold legally in markets. What Is Not Counted in GDP? GDP excludes most items that are produced and consumed at home and that never enter the marketplace. It excludes items produced and sold illicitly, such as illegal drugs.
 FORMULA OF GDP (Y) is the sum of the following: Consumption (C) Investment (I) Government Purchases (G) Net Exports (NX) Y = C + I + G + NX
FORMULA OF GDP (Y) is the sum of the following: Consumption (C) Investment (I) Government Purchases (G) Net Exports (NX) Y = C + I + G + NX
 COMPONENTS: C AND I Consumption (C): The spending by households on goods and services, with the exception of purchases of new housing. Investment (I): The spending on capital equipment, inventories, and structures, including new housing.
COMPONENTS: C AND I Consumption (C): The spending by households on goods and services, with the exception of purchases of new housing. Investment (I): The spending on capital equipment, inventories, and structures, including new housing.
 COMPONENTS: G AND NX Government Purchases (G): The spending on goods and services by local, state, and federal governments. Does not include transfer payments because they are not made in exchange for currently produced goods or services. Net Exports (NX): Exports minus imports.
COMPONENTS: G AND NX Government Purchases (G): The spending on goods and services by local, state, and federal governments. Does not include transfer payments because they are not made in exchange for currently produced goods or services. Net Exports (NX): Exports minus imports.
 TAIWAN’S GDP (2012) Consumption 8465030 (Million) Investment 2795080 (Million) Government Purchase 1746482 (Million) Export 10325648 (Million) Import 9254141 (Million) GDP 14077099 (Million) Net Income from Abroad 454191 (Million) GNP 14531290 (Million)
TAIWAN’S GDP (2012) Consumption 8465030 (Million) Investment 2795080 (Million) Government Purchase 1746482 (Million) Export 10325648 (Million) Import 9254141 (Million) GDP 14077099 (Million) Net Income from Abroad 454191 (Million) GNP 14531290 (Million)
 NOMINAL VERSUS REAL GDP Nominal GDP values the production of goods and services at current prices. Real GDP values the production of goods and services at constant prices.
NOMINAL VERSUS REAL GDP Nominal GDP values the production of goods and services at current prices. Real GDP values the production of goods and services at constant prices.
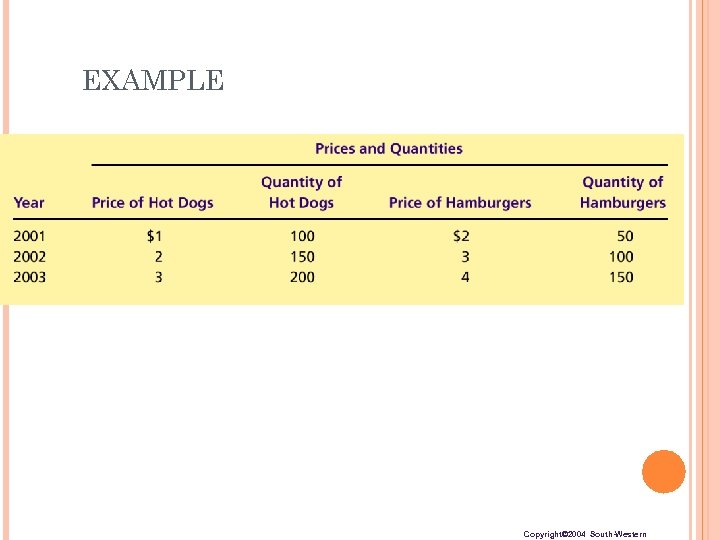 EXAMPLE Copyright© 2004 South-Western
EXAMPLE Copyright© 2004 South-Western
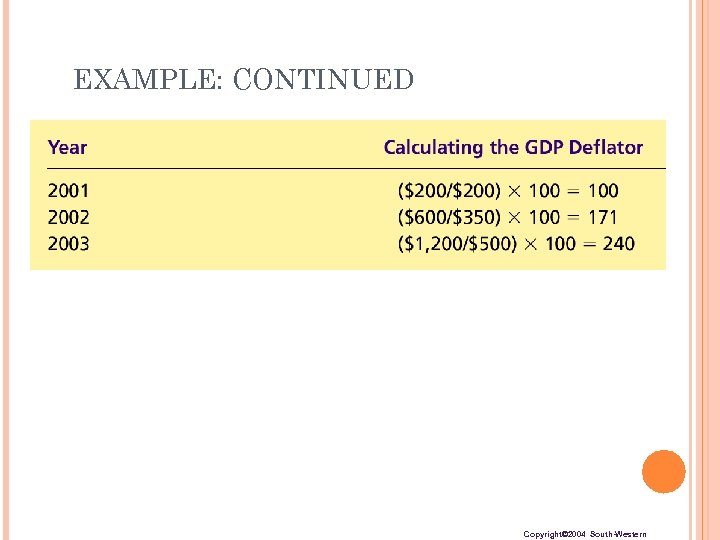
 EXAMPLE: CONTINUED Copyright© 2004 South-Western
EXAMPLE: CONTINUED Copyright© 2004 South-Western
 EXAMPLE: CONTINUED Copyright© 2004 South-Western
EXAMPLE: CONTINUED Copyright© 2004 South-Western
 GDP DEFLATOR An accurate view of the economy requires adjusting nominal to real GDP by using the GDP deflator. The GDP deflator is a measure of the price level calculated as the ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP times 100. It tells us the rise in nominal GDP that is attributable to a rise in prices rather than a rise in the quantities produced.
GDP DEFLATOR An accurate view of the economy requires adjusting nominal to real GDP by using the GDP deflator. The GDP deflator is a measure of the price level calculated as the ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP times 100. It tells us the rise in nominal GDP that is attributable to a rise in prices rather than a rise in the quantities produced.
 THE GDP DEFLATOR The GDP deflator is calculated as follows:
THE GDP DEFLATOR The GDP deflator is calculated as follows:
 EXAMPLE: CONTINUED Copyright© 2004 South-Western
EXAMPLE: CONTINUED Copyright© 2004 South-Western
 THE GDP DEFLATOR Converting Nominal GDP to Real GDP Nominal GDP is converted to real GDP as follows:
THE GDP DEFLATOR Converting Nominal GDP to Real GDP Nominal GDP is converted to real GDP as follows:
 GDP AND ECONOMIC WELL-BEING GDP is the best single measure of the economic well-being of a society. GDP person tells us the income and expenditure of the average person in the economy. Higher GDP person indicates a higher standard of living. GDP is not a perfect measure of the happiness or quality of life, however.
GDP AND ECONOMIC WELL-BEING GDP is the best single measure of the economic well-being of a society. GDP person tells us the income and expenditure of the average person in the economy. Higher GDP person indicates a higher standard of living. GDP is not a perfect measure of the happiness or quality of life, however.
 GDP AND ECONOMIC WELL-BEING Some things that contribute to well-being are not included in GDP. The value of leisure. The value of a clean environment. The value of almost all activity that takes place outside of markets, such as the value of the time parents spend with their children and the value of volunteer work.
GDP AND ECONOMIC WELL-BEING Some things that contribute to well-being are not included in GDP. The value of leisure. The value of a clean environment. The value of almost all activity that takes place outside of markets, such as the value of the time parents spend with their children and the value of volunteer work.
 OTHER MEASURES OF INCOME Gross National Product (GNP) Net National Product (NNP) National Income (NI) Personal Income (PI) Disposable Personal Income (DPI)
OTHER MEASURES OF INCOME Gross National Product (GNP) Net National Product (NNP) National Income (NI) Personal Income (PI) Disposable Personal Income (DPI)
 GROSS NATIONAL PRODUCT GNP is the total income earned by a nation’s permanent residents. It differs from GDP by including income that citizens earn abroad and excluding income that foreigners earn here.
GROSS NATIONAL PRODUCT GNP is the total income earned by a nation’s permanent residents. It differs from GDP by including income that citizens earn abroad and excluding income that foreigners earn here.
 NET NATIONAL PRODUCT NNP is the total income of a nation’s residents (GNP) minus losses from depreciation (“consumption of fixed capital).
NET NATIONAL PRODUCT NNP is the total income of a nation’s residents (GNP) minus losses from depreciation (“consumption of fixed capital).
 NATIONAL INCOME NI is the total income earned by a nation’s residents in the production of goods and services. It differs from NNP by excluding indirect business taxes (such as sales taxes) and including business subsidy.
NATIONAL INCOME NI is the total income earned by a nation’s residents in the production of goods and services. It differs from NNP by excluding indirect business taxes (such as sales taxes) and including business subsidy.
 PERSONAL INCOME PI is the income that households and noncorporate businesses receive. Unlike NI, it excludes retained earnings and subtracts corporate income taxes and contributions for social insurance. It also includes interest incomes from holding government bonds and government transfer payments.
PERSONAL INCOME PI is the income that households and noncorporate businesses receive. Unlike NI, it excludes retained earnings and subtracts corporate income taxes and contributions for social insurance. It also includes interest incomes from holding government bonds and government transfer payments.
 DISPOSABLE PERSONAL INCOME DPI is the income that households and noncorporate businesses have left after satisfying all their obligations to the government (such as personal taxes).
DISPOSABLE PERSONAL INCOME DPI is the income that households and noncorporate businesses have left after satisfying all their obligations to the government (such as personal taxes).
 GREEN GDP Green GDP is an index of economic growth with the environmental consequences of that growth factored in. Green GDP=Traditional GDPenvironmental/ecological costs
GREEN GDP Green GDP is an index of economic growth with the environmental consequences of that growth factored in. Green GDP=Traditional GDPenvironmental/ecological costs
 GDP(PPP) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
GDP(PPP) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
 GDP PER CAPITA 2012 GDP per capita (nominal) GDP per capita (Purchasing Power Parity) Singapore 51162 60410 Japan 46736 36266 Hong Kong 36667 51494 South Korea 23113 32272 Taiwan 20328 38749 Malaysia 10304 16922 China 6076 9162 Thailand 5678 10126
GDP PER CAPITA 2012 GDP per capita (nominal) GDP per capita (Purchasing Power Parity) Singapore 51162 60410 Japan 46736 36266 Hong Kong 36667 51494 South Korea 23113 32272 Taiwan 20328 38749 Malaysia 10304 16922 China 6076 9162 Thailand 5678 10126
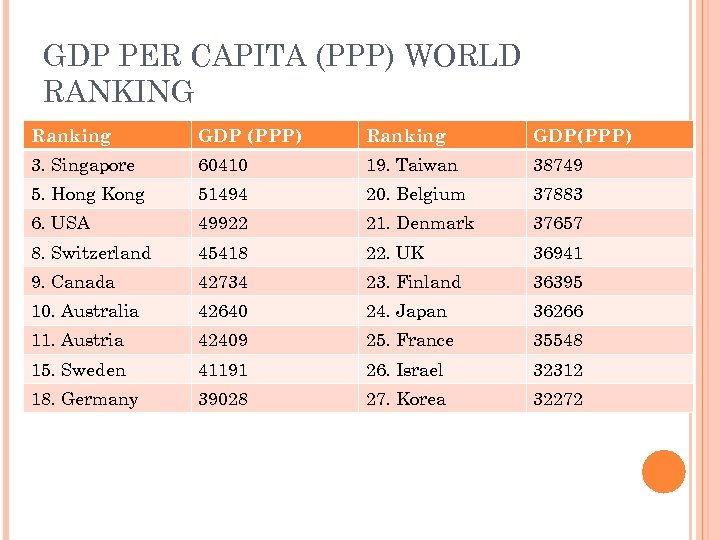 GDP PER CAPITA (PPP) WORLD RANKING Ranking GDP (PPP) Ranking GDP(PPP) 3. Singapore 60410 19. Taiwan 38749 5. Hong Kong 51494 20. Belgium 37883 6. USA 49922 21. Denmark 37657 8. Switzerland 45418 22. UK 36941 9. Canada 42734 23. Finland 36395 10. Australia 42640 24. Japan 36266 11. Austria 42409 25. France 35548 15. Sweden 41191 26. Israel 32312 18. Germany 39028 27. Korea 32272
GDP PER CAPITA (PPP) WORLD RANKING Ranking GDP (PPP) Ranking GDP(PPP) 3. Singapore 60410 19. Taiwan 38749 5. Hong Kong 51494 20. Belgium 37883 6. USA 49922 21. Denmark 37657 8. Switzerland 45418 22. UK 36941 9. Canada 42734 23. Finland 36395 10. Australia 42640 24. Japan 36266 11. Austria 42409 25. France 35548 15. Sweden 41191 26. Israel 32312 18. Germany 39028 27. Korea 32272
 DISCUSSION QUESTIONS Identify the immediate effect of each of the following circumstances on U. S. GDP and its components. a. James receives a unemployment compensation check. b. John buys an Italian sports car. c. Henry buys domestically produced tools for his construction company.
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS Identify the immediate effect of each of the following circumstances on U. S. GDP and its components. a. James receives a unemployment compensation check. b. John buys an Italian sports car. c. Henry buys domestically produced tools for his construction company.


