b6608a0533a7b6a43f58747a5fdbb74d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Measures of Participation in Global Value Chains and Global Business Cycles Zhi Wang University of International Business and Economics & George Mason University Shang-Jin Wei Asian Development Bank & Columbia University Xinding Yu and Kunfu Zhu University of International Business and Economics AEA ANNUAL MEETING Philadelphia, January 5 -7, 2018

Motivations To better understand what type production and trade are GVC activities, what are not, thus lay out the economic accounting foundation for GVC measurement; Constructing various GVC indexes based on consistent decomposition and accounting exercises, will allow follow-up econometric studies of determinants and consequences of cross country production sharing that are guided by economic theory.
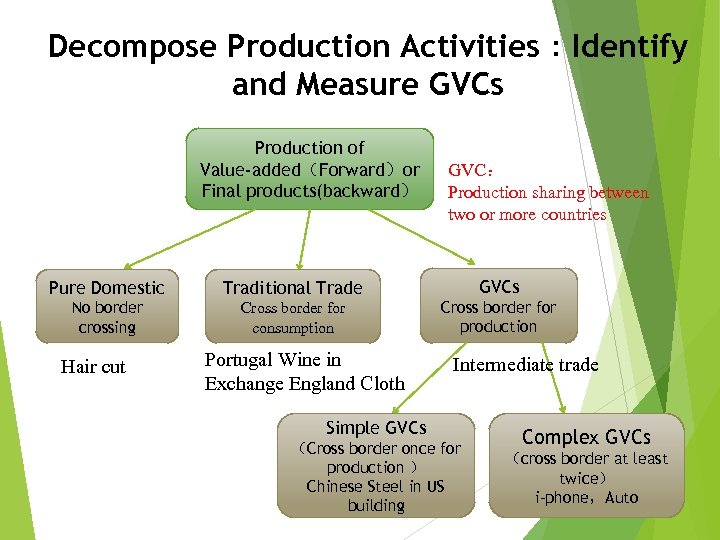
Decompose Production Activities:Identify and Measure GVCs Production of Value-added(Forward)or Final products(backward) Pure Domestic Traditional Trade No border crossing Cross border for consumption Hair cut Portugal Wine in Exchange England Cloth GVC: Production sharing between two or more countries GVCs Cross border for production Intermediate trade Simple GVCs (Cross border once for production ) Chinese Steel in US building Complex GVCs (cross border at least twice) 3 i-phone,Auto
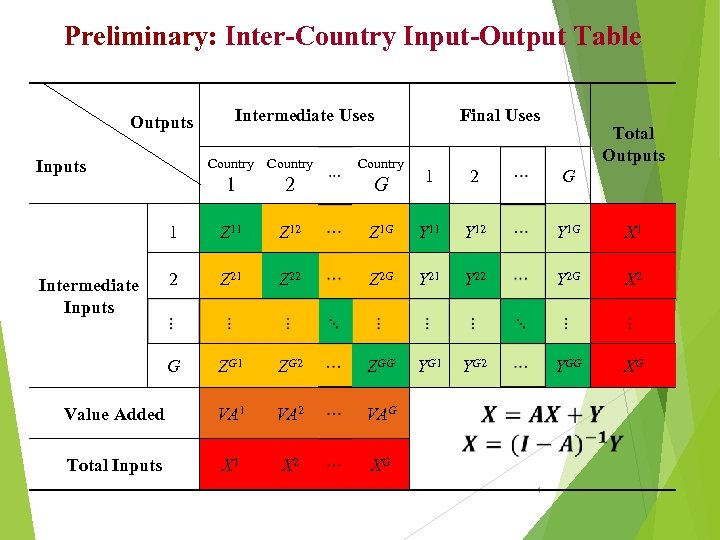
Preliminary: Inter-Country Input-Output Table Outputs Intermediate Uses Country Final Uses Total Outputs 1 2 G 1 Z 12 Z 1 G Y 11 Y 12 Y 1 G X 1 2 Z 21 Z 22 Z 2 G Y 21 Y 22 Y 2 G X 2 G ZG 1 ZG 2 ZGG YG 1 YG 2 YGG XG Value Added VA 1 VA 2 VAG Total Inputs X 1 X 2 XG Intermediate Inputs 4
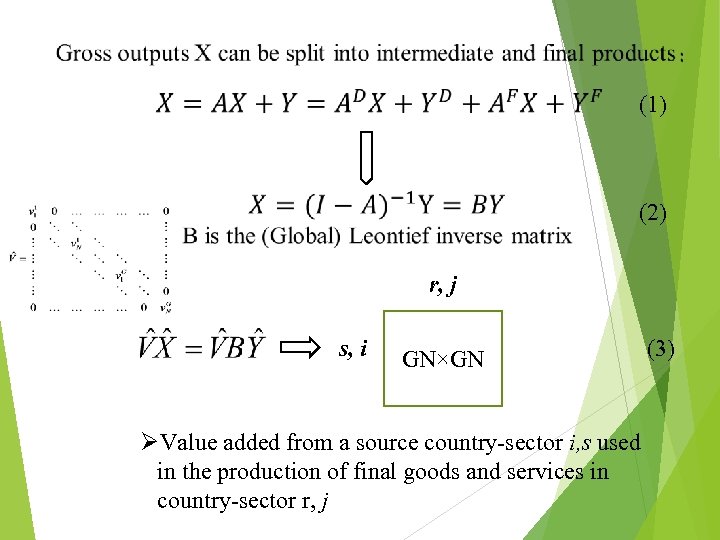
(1) (2) r, j s, i GN×GN ØValue added from a source country-sector i, s used in the production of final goods and services in country-sector r, j (3)
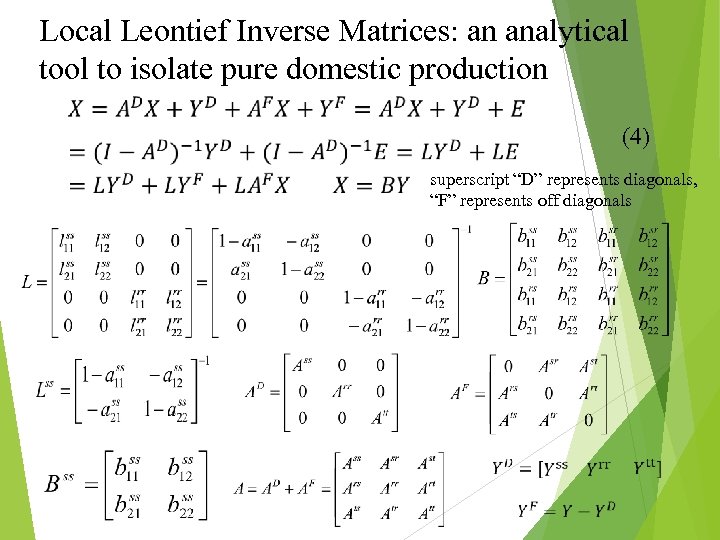
Local Leontief Inverse Matrices: an analytical tool to isolate pure domestic production (4) superscript “D” represents diagonals, “F” represents off diagonals
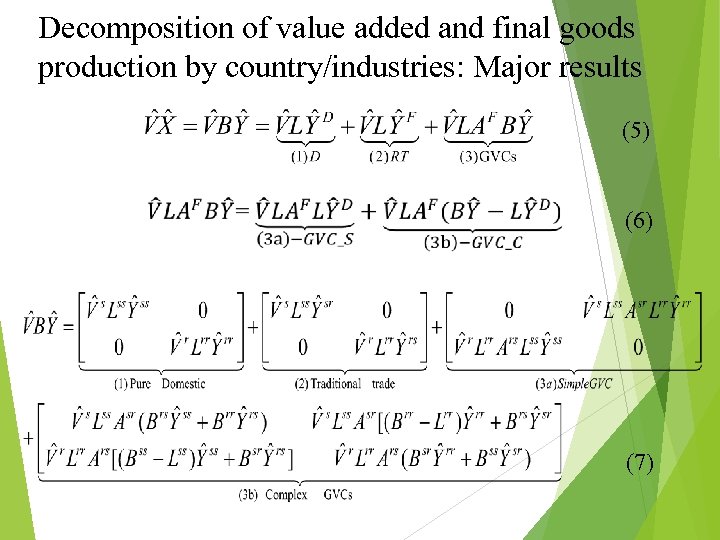
Decomposition of value added and final goods production by country/industries: Major results (5) (6) (7)
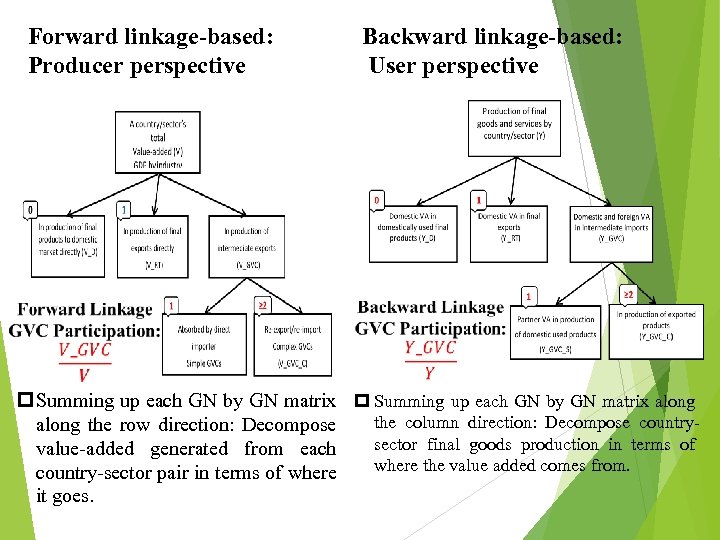
Forward linkage-based: Producer perspective Backward linkage-based: User perspective p Summing up each GN by GN matrix along the column direction: Decompose countryalong the row direction: Decompose sector final goods production in terms of value-added generated from each where the value added comes from. country-sector pair in terms of where it goes.
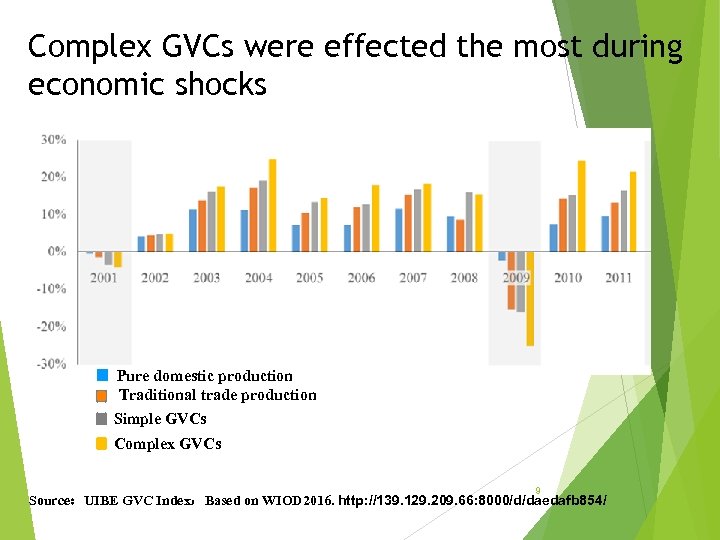
Complex GVCs were effected the most during economic shocks Pure domestic production Traditional trade production Simple GVCs Complex GVCs 9 Source:UIBE GVC Index,Based on WIOD 2016. http: //139. 129. 209. 66: 8000/d/daedafb 854/
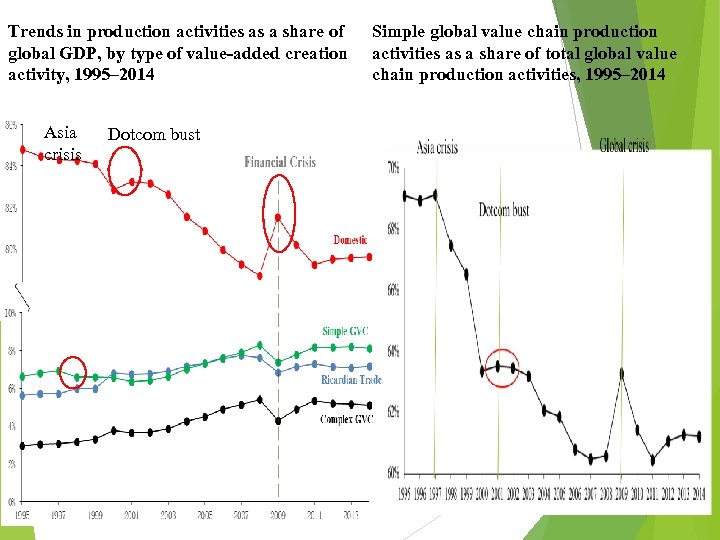
Trends in production activities as a share of global GDP, by type of value-added creation activity, 1995– 2014 Asia crisis Simple global value chain production activities as a share of total global value chain production activities, 1995– 2014 Dotcom bust 10
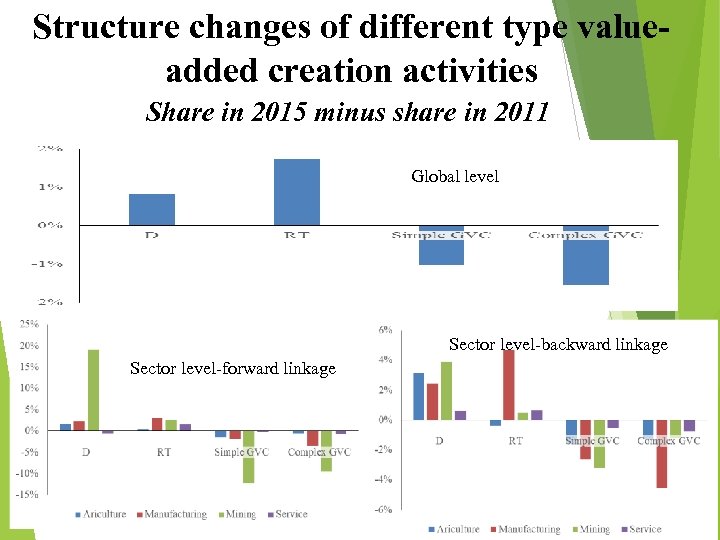
Structure changes of different type valueadded creation activities Share in 2015 minus share in 2011 Global level Sector level-backward linkage Sector level-forward linkage 11

New pattern of global production structure in recent slow economic recovery since 2012 Contradict to the rapid production globalization driven by the growth of complex GVC activities in previous periods, current economic recovery presents de-production globalization character with the shrinking complex GVC cross country production sharing activities; The economic recovery is mainly driven by production of traditional trade foreign demand, also contradicting with the pattern of production structure changes in previous period of economic growth; Participation in simple GVC was mixed, increased in some developed economies, but decline in emerging Asian economies. 12
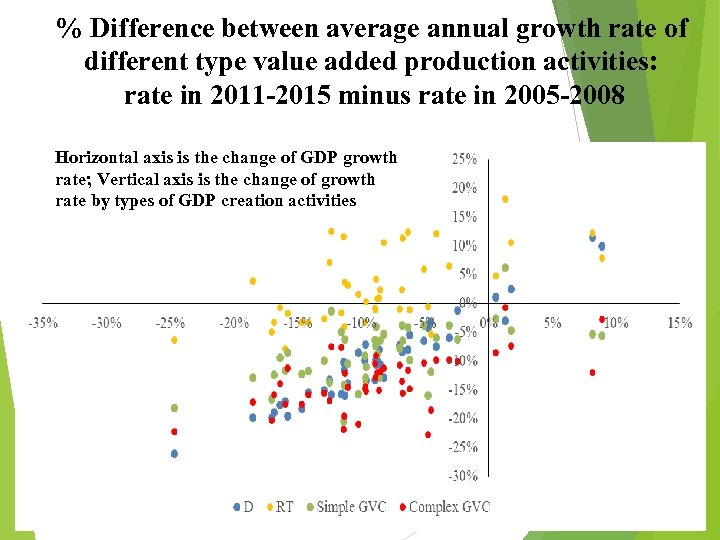
% Difference between average annual growth rate of different type value added production activities: rate in 2011 -2015 minus rate in 2005 -2008 Horizontal axis is the change of GDP growth rate; Vertical axis is the change of growth rate by types of GDP creation activities 13

What we learned from the data The new GDP decomposition method can help us understand the role of cross country production sharing activities in global macro-economic cycle. GVC activities, especially complex GVCs are one of the major driving forces during the 3 economic growth periods during last 20 years; The global production presents a different trend of structure change in recent slow economic recovery since 2012. Comparing to previous 3 economic growth periods, GVC activities, especially complex GVCs significantly slow down. It remains to be seen whether this will become a permeant trend in the future. It largely depend on whether the global community has the ability to solve the core distribution issues have brought by the rapid development of production globalization and GVCs during last 20 years. 14

Limitations Our production decomposition method may underestimate GVC production activities: Current residence-based national account rules treat all firms within national borders as domestic firms, thus the value-added creation of foreign affiliates are treated as part of domestic GDP production. While it may also be a type of GVC activity, especially in services Since the supply of services through commercial presence abroad is an important way of conducting international transactions in services (mode 3 – commercial presence), the distinction between foreign and domestic owned firms is particularly relevant for services. No inter-country input–output (ICIO) table currently exists to separate production activities between domestic firms and foreign affiliates. but initiatives in this direction are being taken in the international statistical community
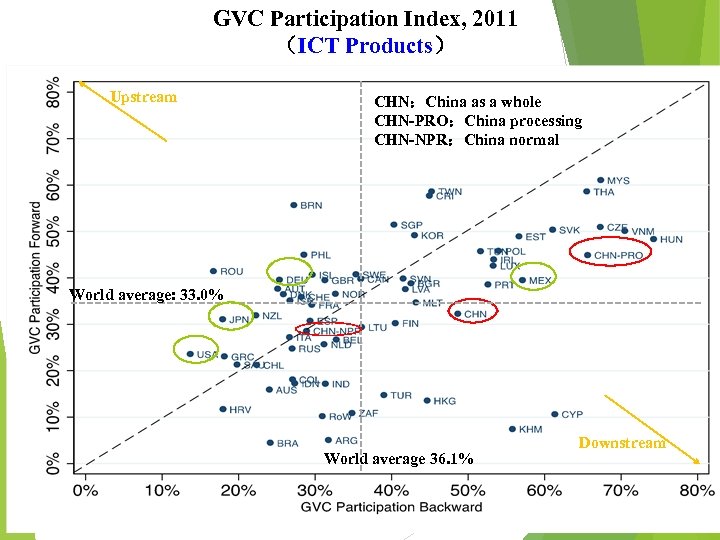
GVC Participation Index, 2011 (ICT Products) Upstream CHN:China as a whole CHN-PRO:China processing CHN-NPR:China normal World average: 33. 0% Downstream World average 36. 1% 16
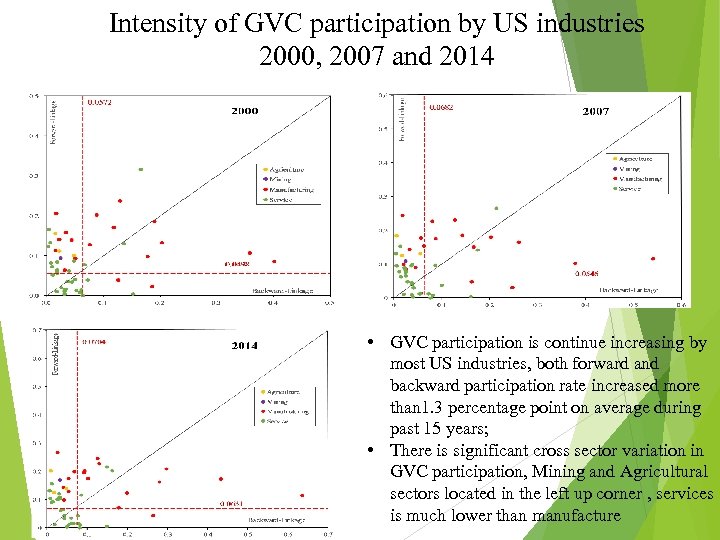
Intensity of GVC participation by US industries 2000, 2007 and 2014 • GVC participation is continue increasing by most US industries, both forward and backward participation rate increased more than 1. 3 percentage point on average during past 15 years; • There is significant cross sector variation in GVC participation, Mining and Agricultural sectors located in the left up corner , services is much lower than manufacture
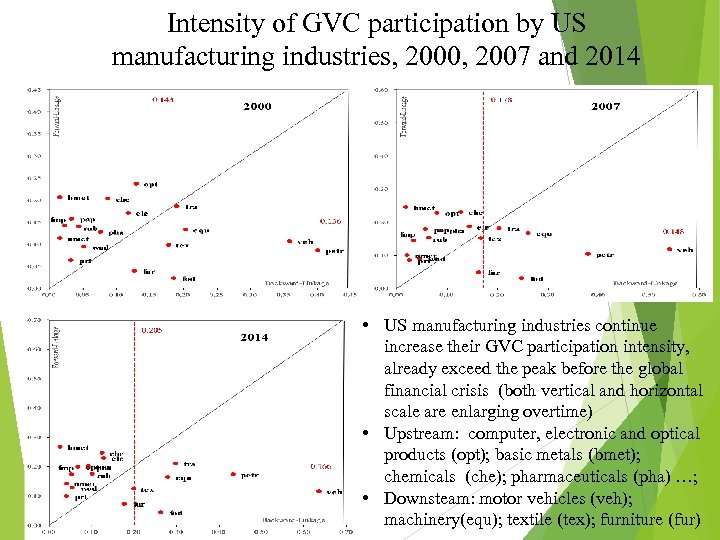
Intensity of GVC participation by US manufacturing industries, 2000, 2007 and 2014 • US manufacturing industries continue increase their GVC participation intensity, already exceed the peak before the global financial crisis (both vertical and horizontal scale are enlarging overtime) • Upstream: computer, electronic and optical products (opt); basic metals (bmet); chemicals (che); pharmaceuticals (pha) …; • Downsteam: motor vehicles (veh); machinery(equ); textile (tex); furniture (fur)
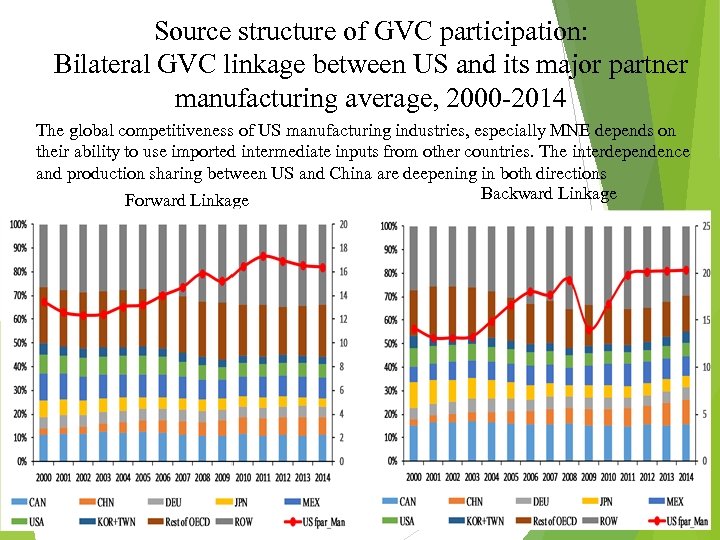
Source structure of GVC participation: Bilateral GVC linkage between US and its major partner manufacturing average, 2000 -2014 The global competitiveness of US manufacturing industries, especially MNE depends on their ability to use imported intermediate inputs from other countries. The interdependence and production sharing between US and China are deepening in both directions Backward Linkage Forward Linkage
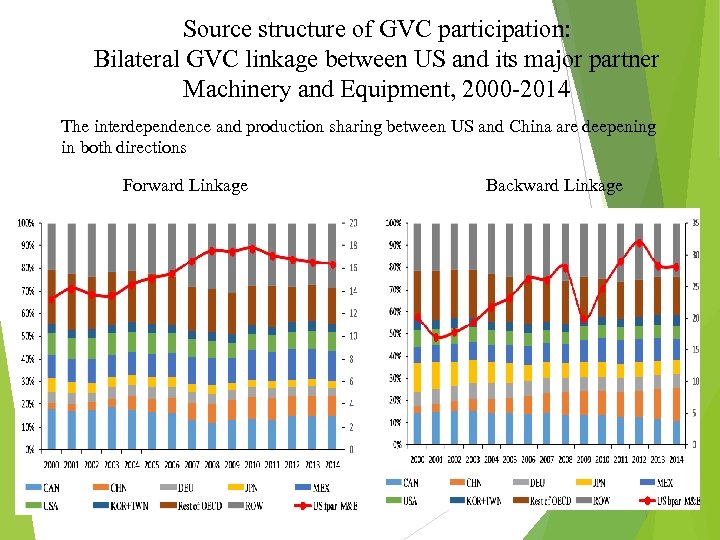
Source structure of GVC participation: Bilateral GVC linkage between US and its major partner Machinery and Equipment, 2000 -2014 The interdependence and production sharing between US and China are deepening in both directions Forward Linkage Backward Linkage
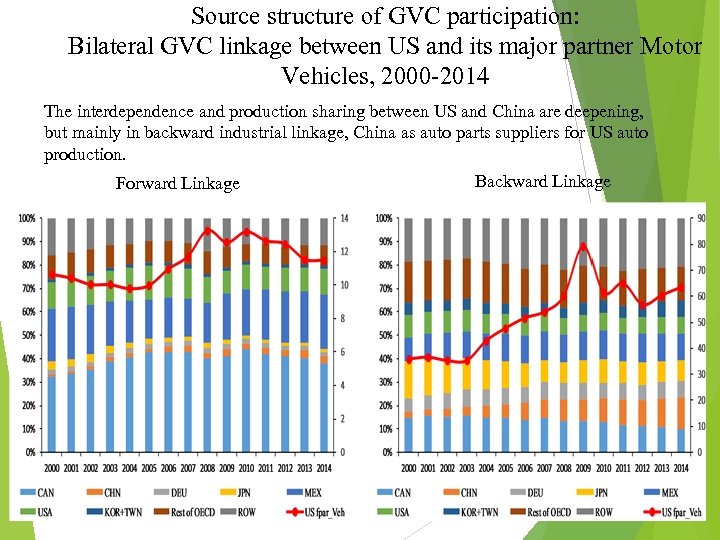
Source structure of GVC participation: Bilateral GVC linkage between US and its major partner Motor Vehicles, 2000 -2014 The interdependence and production sharing between US and China are deepening, but mainly in backward industrial linkage, China as auto parts suppliers for US auto production. Backward Linkage Forward Linkage
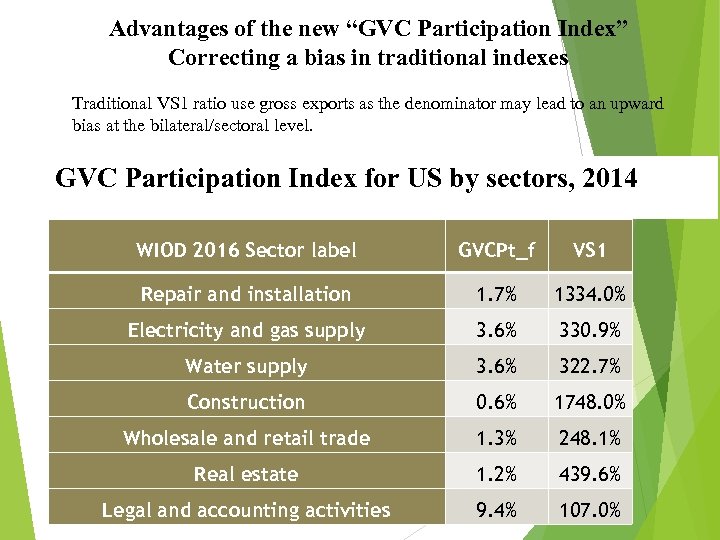
Advantages of the new “GVC Participation Index” Correcting a bias in traditional indexes Traditional VS 1 ratio use gross exports as the denominator may lead to an upward bias at the bilateral/sectoral level. GVC Participation Index for US by sectors, 2014 WIOD 2016 Sector label GVCPt_f VS 1 Repair and installation 1. 7% 1334. 0% Electricity and gas supply 3. 6% 330. 9% Water supply 3. 6% 322. 7% Construction 0. 6% 1748. 0% Wholesale and retail trade 1. 3% 248. 1% Real estate 1. 2% 439. 6% Legal and accounting activities 9. 4% 107. 0%
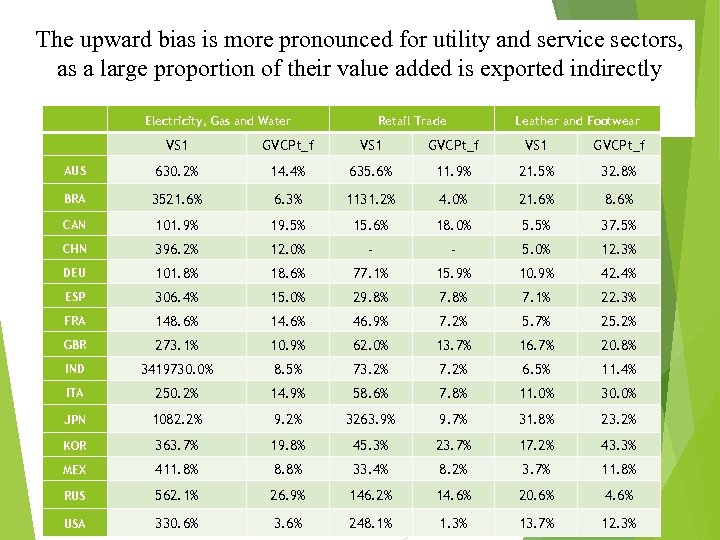
The upward bias is more pronounced for utility and service sectors, as a large proportion of their value added is exported indirectly Electricity, Gas and Water Retail Trade Leather and Footwear VS 1 GVCPt_f AUS 630. 2% 14. 4% 635. 6% 11. 9% 21. 5% 32. 8% BRA 3521. 6% 6. 3% 1131. 2% 4. 0% 21. 6% 8. 6% CAN 101. 9% 19. 5% 15. 6% 18. 0% 5. 5% 37. 5% CHN 396. 2% 12. 0% - - 5. 0% 12. 3% DEU 101. 8% 18. 6% 77. 1% 15. 9% 10. 9% 42. 4% ESP 306. 4% 15. 0% 29. 8% 7. 1% 22. 3% FRA 148. 6% 14. 6% 46. 9% 7. 2% 5. 7% 25. 2% GBR 273. 1% 10. 9% 62. 0% 13. 7% 16. 7% 20. 8% IND 3419730. 0% 8. 5% 73. 2% 7. 2% 6. 5% 11. 4% ITA 250. 2% 14. 9% 58. 6% 7. 8% 11. 0% 30. 0% JPN 1082. 2% 9. 2% 3263. 9% 9. 7% 31. 8% 23. 2% KOR 363. 7% 19. 8% 45. 3% 23. 7% 17. 2% 43. 3% MEX 411. 8% 8. 8% 33. 4% 8. 2% 3. 7% 11. 8% RUS 562. 1% 26. 9% 146. 2% 14. 6% 20. 6% 4. 6% USA 330. 6% 3. 6% 248. 1% 1. 3% 13. 7% 12. 3%
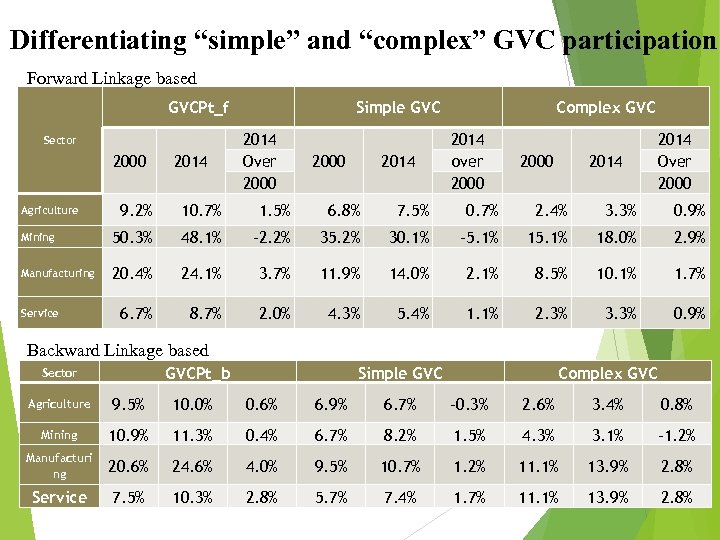
Differentiating “simple” and “complex” GVC participation Forward Linkage based GVCPt_f Sector 2000 2014 Simple GVC 2014 Over 2000 2014 Complex GVC 2014 over 2000 2014 Over 2000 9. 2% 10. 7% 1. 5% 6. 8% 7. 5% 0. 7% 2. 4% 3. 3% 0. 9% Mining 50. 3% 48. 1% -2. 2% 35. 2% 30. 1% -5. 1% 18. 0% 2. 9% Manufacturing 20. 4% 24. 1% 3. 7% 11. 9% 14. 0% 2. 1% 8. 5% 10. 1% 1. 7% 6. 7% 8. 7% 2. 0% 4. 3% 5. 4% 1. 1% 2. 3% 3. 3% 0. 9% Agriculture Service Backward Linkage based GVCPt_b Sector Simple GVC Complex GVC Agriculture 9. 5% 10. 0% 0. 6% 6. 9% 6. 7% -0. 3% 2. 6% 3. 4% 0. 8% Mining 10. 9% 11. 3% 0. 4% 6. 7% 8. 2% 1. 5% 4. 3% 3. 1% -1. 2% Manufacturi ng 20. 6% 24. 6% 4. 0% 9. 5% 10. 7% 1. 2% 11. 1% 13. 9% 2. 8% Service 7. 5% 10. 3% 2. 8% 5. 7% 7. 4% 1. 7% 11. 1% 13. 9% 2. 8%

ΔVAict = β 0 + β 1×V-Shareict + β 2×Wct + β 3× Zit + γt + δc + uict pΔVAict: The annual percentage change of sectoral GDP in industry i of Country c; p. V-Shareict: The share of different types of value added creation activities (D, RT, Simple GVC and Complex GVC) in sectoral GDP; p. Wct and Zit: Country and sectoral level control variables; pγt and δc: Year and country fixed effects.
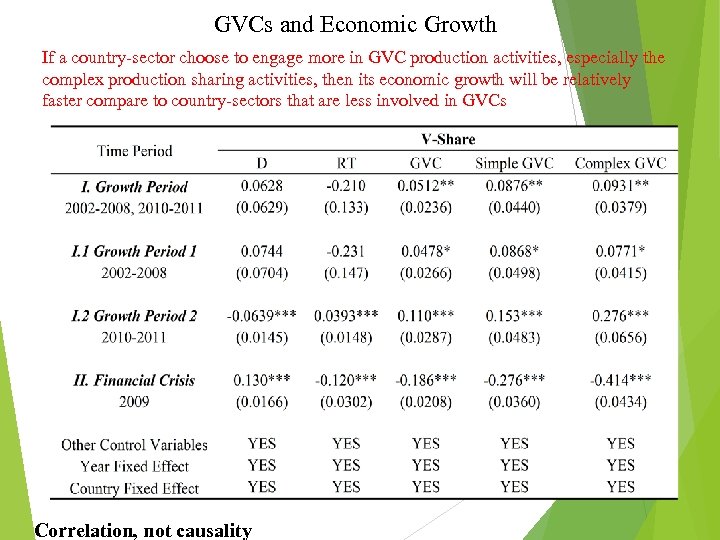
GVCs and Economic Growth If a country-sector choose to engage more in GVC production activities, especially the complex production sharing activities, then its economic growth will be relatively faster compare to country-sectors that are less involved in GVCs 26 Correlation, not causality
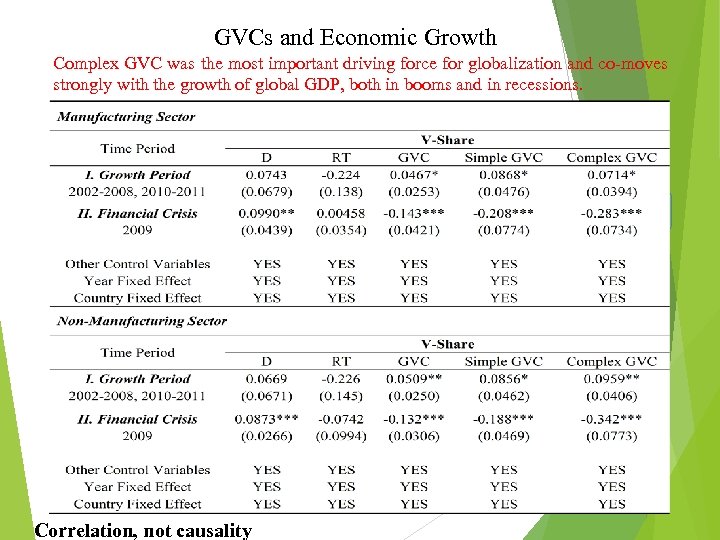
GVCs and Economic Growth Complex GVC was the most important driving force for globalization and co-moves strongly with the growth of global GDP, both in booms and in recessions. 27 Correlation, not causality
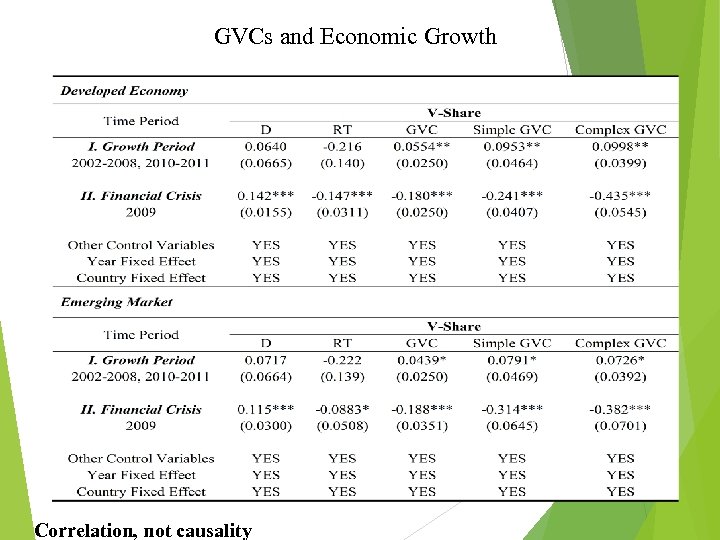
GVCs and Economic Growth 28 Correlation, not causality
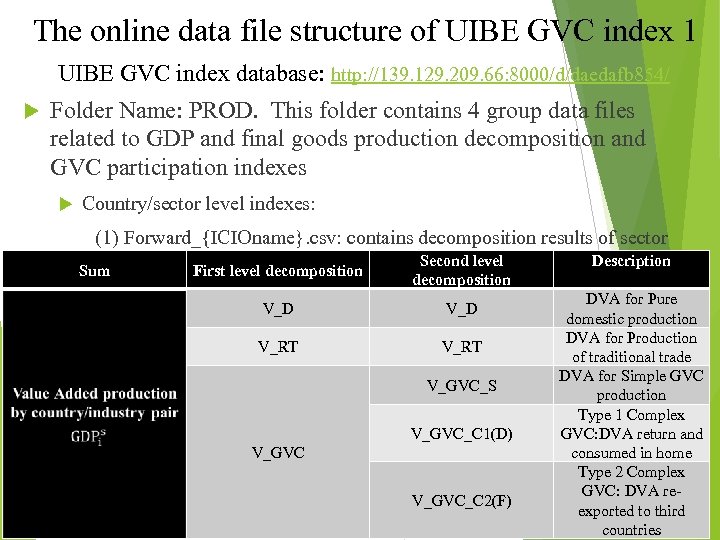
The online data file structure of UIBE GVC index 1 UIBE GVC index database: http: //139. 129. 209. 66: 8000/d/daedafb 854/ Folder Name: PROD. This folder contains 4 group data files related to GDP and final goods production decomposition and GVC participation indexes Country/sector level indexes: (1) Forward_{ICIOname}. csv: contains decomposition results of sector Description Second level GDP based on forward industrial linkage, including 15 indexes; Sum First level decomposition V_D V_RT V_GVC_S V_GVC_C 1(D) V_GVC_C 2(F) DVA for Pure domestic production DVA for Production of traditional trade DVA for Simple GVC production Type 1 Complex GVC: DVA return and consumed in home Type 2 Complex GVC: DVA reexported to third countries
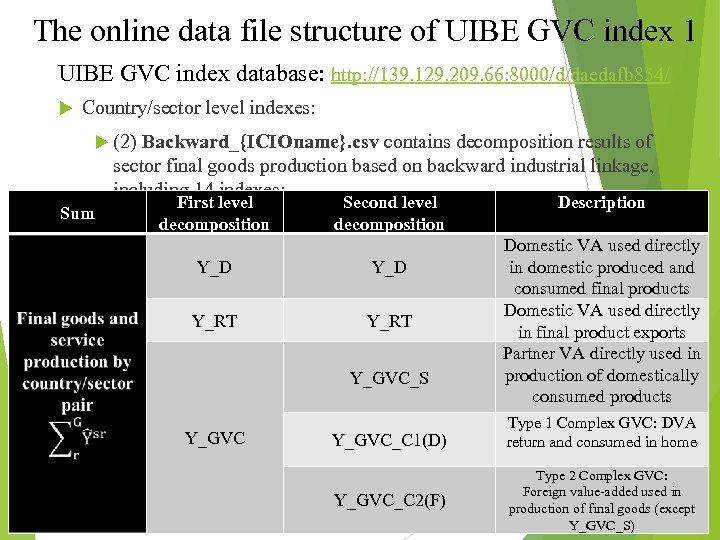
The online data file structure of UIBE GVC index 1 UIBE GVC index database: http: //139. 129. 209. 66: 8000/d/daedafb 854/ Country/sector level indexes: (2) Backward_{ICIOname}. csv contains decomposition results of sector final goods production based on backward industrial linkage, including 14 indexes: Sum First level decomposition Second level decomposition Y_D Y_RT Y_GVC_S Y_GVC_C 1(D) Y_GVC_C 2(F) Description Domestic VA used directly in domestic produced and consumed final products Domestic VA used directly in final product exports Partner VA directly used in production of domestically consumed products Type 1 Complex GVC: DVA return and consumed in home Type 2 Complex GVC: Foreign value-added used in production of final goods (except Y_GVC_S)
The online data file structure of UIBE GVC index 1 UIBE GVC index database: http: //139. 129. 209. 66: 8000/d/daedafb 854/ (3) Decompose production activities with source structures: There are 6 GN by GN data files each year (corresponding to the five components of production plus GVC total) can be used to compute the GVC participation by country and sector sources, the row sum decompose GDP, the column sum decompose final goods production. For the country at interest, only need its row forward linkage based decomposition, while its column for backward linkage based decomposition. All files are in the same structure: Column label givers the place of production, row label gives the year and source of value-added. i. e value added from a source country-sector (s, i) (row label) used in the production of final goods and services in country-sector (r, j) (column label). (4) Decompose final goods production into domestic and foreign value-added: 2 GN by GN data files each year Domestic value-added in final products; Foreign value-added in final products.

Conclusion Remarks p In this paper we propose a production activity accounting framework based on whether factor content crosses national borders for production or not. p We show that a set of GVC participation indexes built on such framework have more desirable properties than the existing ones in the literature. p Complex GVC was the most important driving force for globalization and co-moves strongly with the growth of global GDP, both in booms and in recessions. p By estimating these indexes according to real world data, we produce a large set of indicators and put them on our website for public access. We hope these indexes could be widely used by both theoretical and empirical economists in advancing studies for economics of global supply chains.

Major Reference Leontief, W. (1936). Quantitative input and output relations in the economic system of the United States. The Review of Economic and Statistics, 18, 105 -25. Wang Z, Wei S J, Yu X, Zhu K (2017 a). Measures of Participation in Global Value Chain and Global Business Cycles, National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper 23222. Wang Z, Wei S J, Yu X, Zhu K (2017 b). Characterizing Global Value Chains: Production Length and Upstreamness, National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper 23261. Timmer, M. P. , Erumban, A. A. , Los, B. , Stehrer, R. , De Vries, G. J. 2014. Slicing Up Global Value Chains. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 28(2): 99 -118.

Thank you for your attention! Zhi Wang, Professor and Dean, Research Institute of Global Value Chain, University of International Business Economics Research Professor and Senior Policy Research Fellow, Schar School of Policy and Government, George Mason University Email: zwang 36@gmu. edu Website: https: //schar. gmu. edu/about/faculty-directory/zhi-wang UIBE GVC indictor database: http: //139. 129. 209. 66: 8000/d/daedafb 854/ When use this database, please make a Reference to: UIBE GVC Index Team, “Data files structure of the UIBE GVC index system” http: //139. 129. 209. 66: 8000/d/daedafb 854/ Any questions and suggestions about UIBE GVC Index, please contact GVC index team at UIBE. Contact: team leader, Professor Fei Wang; E-mail: 01535@uibe. edu. cn The 2017 GVC development report: https: //www. wto. org/english/res_e/publications_e/gvcd_report_17_e. htm http: //www. worldbank. org/en/topic/trade/publication/global-value-chain-development-report-measuringand-analyzing-the-impact-of-gvcs-on-economic-development The discussion of the 2017 GVC development report at Brookings https: //www. brookings. edu/events/the-impact-of-global-value-chains-on-rich-and-poor-countries/
b6608a0533a7b6a43f58747a5fdbb74d.ppt