7e475d1611680040707db9d27ee577a5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Measurements of Multicast Service Discovery in a Campus Wireless Network Se Gi Hong, Suman Srinivasan, and Henning Schulzrinne Columbia University
Measurements of Multicast Service Discovery in a Campus Wireless Network Se Gi Hong, Suman Srinivasan, and Henning Schulzrinne Columbia University
 Multicast service discovery • Problem – Applications using multicast service discovery are widely deployed • DNS-based service discovery (DNS-SD/m. DNS) • i. Tunes, Printer setup by browsing – Multicast service discovery generates network traffic overhead • Princeton University filters DNS-SD/m. DNS discovery traffic • DNS-SD/m. DNS degrades campus network service – Wireless network • same channel interference, channel 1, 6, 11 – No formal measurement and analysis of the overhead of multicast service discovery traffic • Measurements – Columbia University’s wireless network (IEEE 802. 11 b/g) • single subnet
Multicast service discovery • Problem – Applications using multicast service discovery are widely deployed • DNS-based service discovery (DNS-SD/m. DNS) • i. Tunes, Printer setup by browsing – Multicast service discovery generates network traffic overhead • Princeton University filters DNS-SD/m. DNS discovery traffic • DNS-SD/m. DNS degrades campus network service – Wireless network • same channel interference, channel 1, 6, 11 – No formal measurement and analysis of the overhead of multicast service discovery traffic • Measurements – Columbia University’s wireless network (IEEE 802. 11 b/g) • single subnet
 Multicast service discovery • Host naming on a local network without a central DNS server – Multicast DNS (m. DNS) • Windows, Linux, Mac OS X – Link-local multicast name resolution (LLMNR) • Windows Vista, Windows CE • DNS-based service discovery (DNS-SD) – – – Used with m. DNS (DNS-SD/m. DNS) i. Tunes, Printer setup by browsing Record types: PTR, SRV and TXT records PTR lookup: Discover service instances,
Multicast service discovery • Host naming on a local network without a central DNS server – Multicast DNS (m. DNS) • Windows, Linux, Mac OS X – Link-local multicast name resolution (LLMNR) • Windows Vista, Windows CE • DNS-based service discovery (DNS-SD) – – – Used with m. DNS (DNS-SD/m. DNS) i. Tunes, Printer setup by browsing Record types: PTR, SRV and TXT records PTR lookup: Discover service instances,
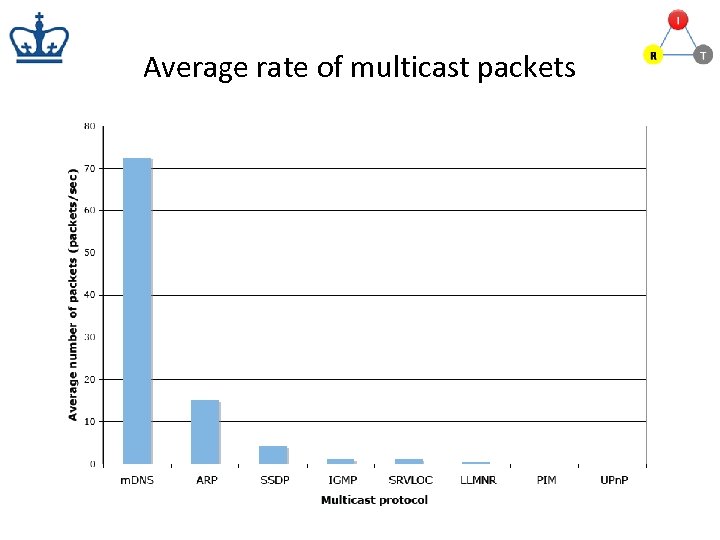 Average rate of multicast packets
Average rate of multicast packets
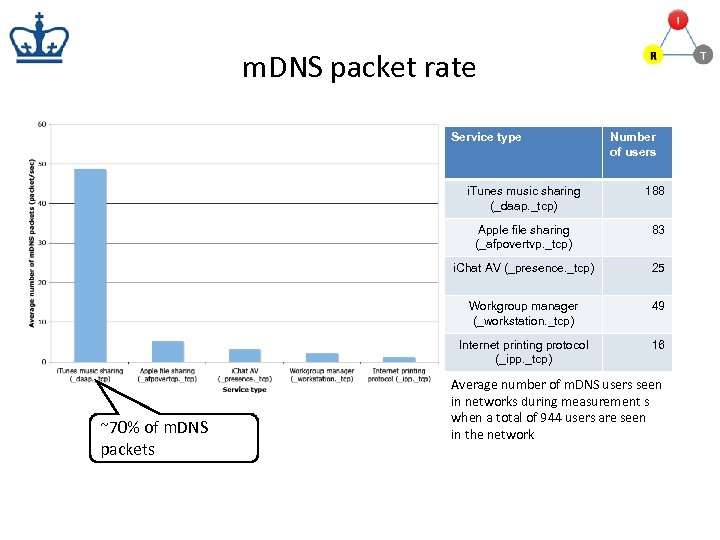 m. DNS packet rate Service type Number of users i. Tunes music sharing (_daap. _tcp) Apple file sharing (_afpovertvp. _tcp) 83 i. Chat AV (_presence. _tcp) 25 Workgroup manager (_workstation. _tcp) 49 Internet printing protocol (_ipp. _tcp) ~70% of m. DNS packets 188 16 Average number of m. DNS users seen in networks during measurement s when a total of 944 users are seen in the network
m. DNS packet rate Service type Number of users i. Tunes music sharing (_daap. _tcp) Apple file sharing (_afpovertvp. _tcp) 83 i. Chat AV (_presence. _tcp) 25 Workgroup manager (_workstation. _tcp) 49 Internet printing protocol (_ipp. _tcp) ~70% of m. DNS packets 188 16 Average number of m. DNS users seen in networks during measurement s when a total of 944 users are seen in the network
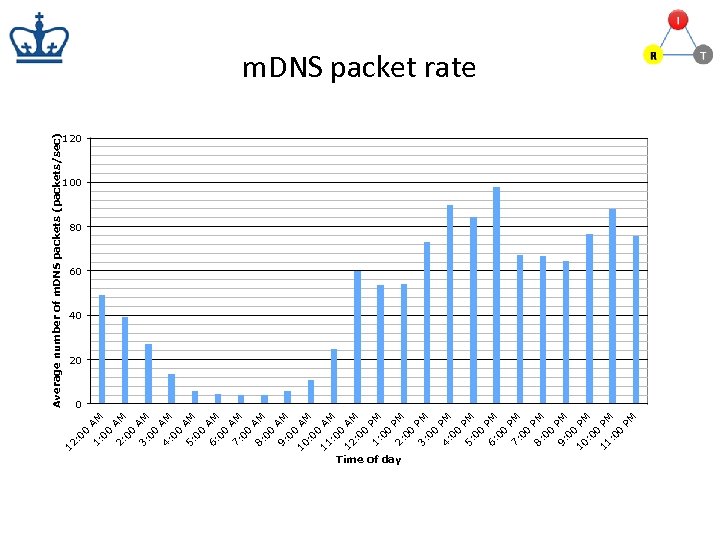 12 : 0 0 1: AM 00 2: AM 00 3: AM 00 4: AM 00 5: AM 00 6: AM 00 7: AM 00 8: AM 00 9: AM 00 10 A : 0 M 0 11 A : 0 M 0 12 AM : 0 0 1: PM 00 2: PM 00 3: PM 00 4: PM 00 5: PM 00 6: PM 00 7: PM 00 8: PM 00 9: PM 00 10 PM : 0 0 11 PM : 0 0 PM Average number of m. DNS packets (packets/sec) m. DNS packet rate 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Time of day
12 : 0 0 1: AM 00 2: AM 00 3: AM 00 4: AM 00 5: AM 00 6: AM 00 7: AM 00 8: AM 00 9: AM 00 10 A : 0 M 0 11 A : 0 M 0 12 AM : 0 0 1: PM 00 2: PM 00 3: PM 00 4: PM 00 5: PM 00 6: PM 00 7: PM 00 8: PM 00 9: PM 00 10 PM : 0 0 11 PM : 0 0 PM Average number of m. DNS packets (packets/sec) m. DNS packet rate 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Time of day
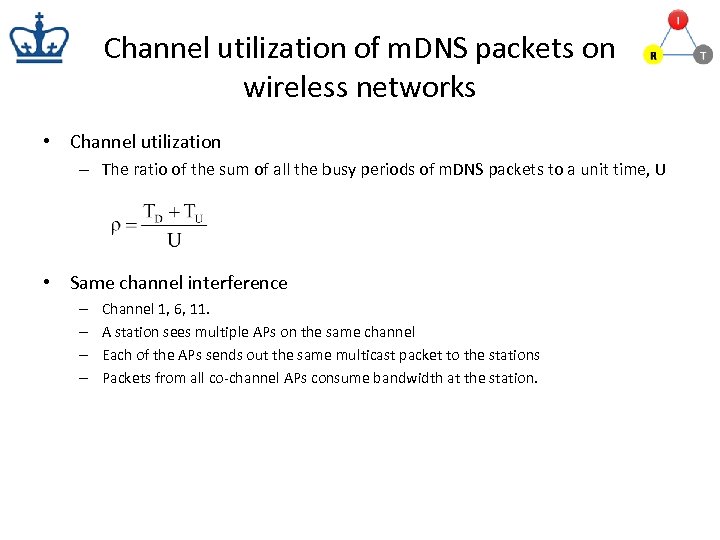 Channel utilization of m. DNS packets on wireless networks • Channel utilization – The ratio of the sum of all the busy periods of m. DNS packets to a unit time, U • Same channel interference – – Channel 1, 6, 11. A station sees multiple APs on the same channel Each of the APs sends out the same multicast packet to the stations Packets from all co-channel APs consume bandwidth at the station.
Channel utilization of m. DNS packets on wireless networks • Channel utilization – The ratio of the sum of all the busy periods of m. DNS packets to a unit time, U • Same channel interference – – Channel 1, 6, 11. A station sees multiple APs on the same channel Each of the APs sends out the same multicast packet to the stations Packets from all co-channel APs consume bandwidth at the station.
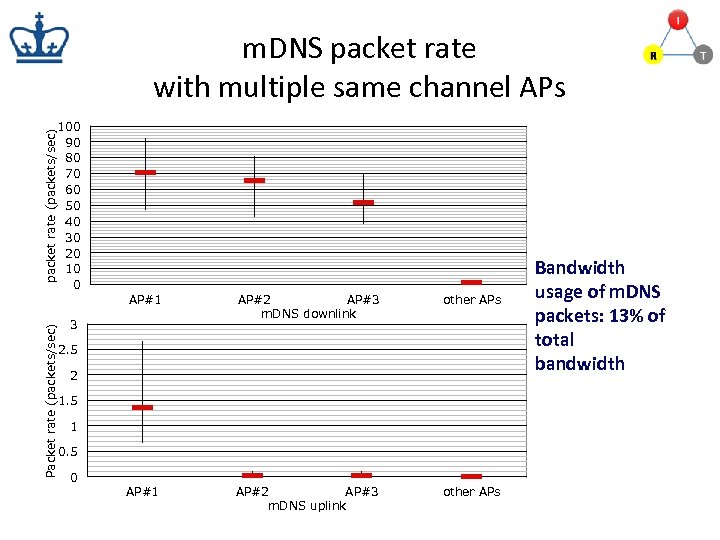 packet rate (packets/sec) m. DNS packet rate with multiple same channel APs 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Packet rate (packets/sec) AP#1 AP#2 AP#3 m. DNS downlink other APs AP#1 AP#2 AP#3 m. DNS uplink other APs 3 2. 5 2 1. 5 1 0. 5 0 Bandwidth usage of m. DNS packets: 13% of total bandwidth
packet rate (packets/sec) m. DNS packet rate with multiple same channel APs 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Packet rate (packets/sec) AP#1 AP#2 AP#3 m. DNS downlink other APs AP#1 AP#2 AP#3 m. DNS uplink other APs 3 2. 5 2 1. 5 1 0. 5 0 Bandwidth usage of m. DNS packets: 13% of total bandwidth
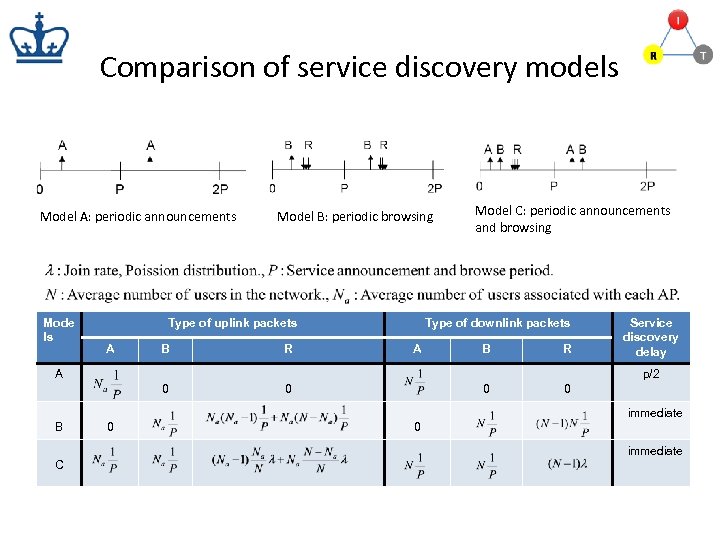 Comparison of service discovery models Model A: periodic announcements Mode ls Model B: periodic browsing Type of uplink packets A B R Model C: periodic announcements and browsing Type of downlink packets A B R A Service discovery delay p/2 0 0 immediate B 0 0 immediate C
Comparison of service discovery models Model A: periodic announcements Mode ls Model B: periodic browsing Type of uplink packets A B R Model C: periodic announcements and browsing Type of downlink packets A B R A Service discovery delay p/2 0 0 immediate B 0 0 immediate C
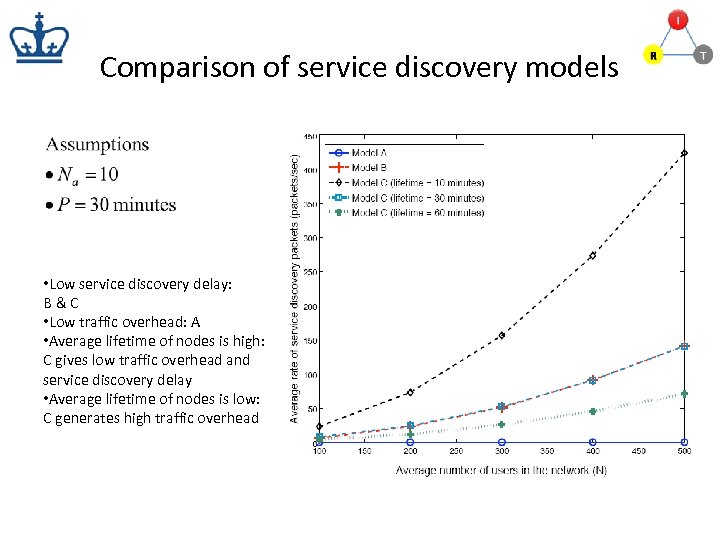 Comparison of service discovery models • Low service discovery delay: B&C • Low traffic overhead: A • Average lifetime of nodes is high: C gives low traffic overhead and service discovery delay • Average lifetime of nodes is low: C generates high traffic overhead
Comparison of service discovery models • Low service discovery delay: B&C • Low traffic overhead: A • Average lifetime of nodes is high: C gives low traffic overhead and service discovery delay • Average lifetime of nodes is low: C generates high traffic overhead
 Conclusion • Multicast service discovery – “Popular” • i. Tunes (~70% of m. DNS) – “Chatty” • Need to evaluate network traffic overhead • 13% bandwidth usage – Define and analyze service discovery models • Provide insights for making design choice with different trade-offs • Traffic overhead, service discovery delay, network size, lifetime – Distributed system • Comparison between distributed system and client-server system • Network size, churn rate, lifetime, overhead
Conclusion • Multicast service discovery – “Popular” • i. Tunes (~70% of m. DNS) – “Chatty” • Need to evaluate network traffic overhead • 13% bandwidth usage – Define and analyze service discovery models • Provide insights for making design choice with different trade-offs • Traffic overhead, service discovery delay, network size, lifetime – Distributed system • Comparison between distributed system and client-server system • Network size, churn rate, lifetime, overhead
 backup
backup
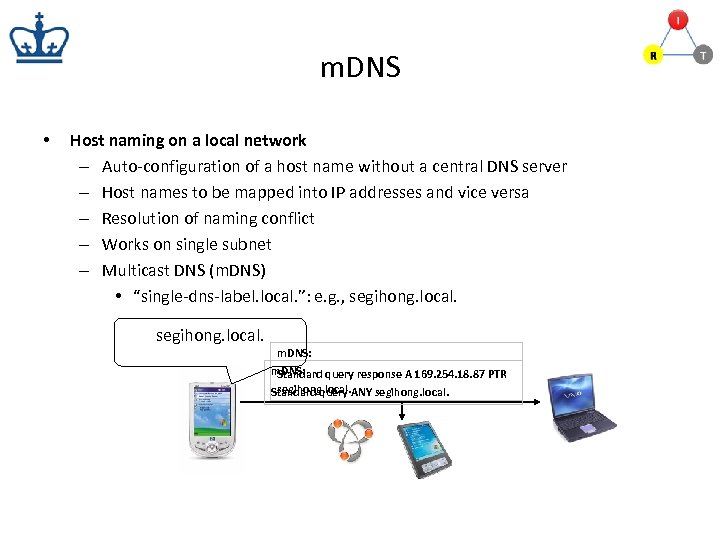 m. DNS • Host naming on a local network – Auto-configuration of a host name without a central DNS server – Host names to be mapped into IP addresses and vice versa – Resolution of naming conflict – Works on single subnet – Multicast DNS (m. DNS) • “single-dns-label. local. ”: e. g. , segihong. local. m. DNS: Standard query response A 169. 254. 18. 87 PTR segihong. local. Standard query ANY segihong. local.
m. DNS • Host naming on a local network – Auto-configuration of a host name without a central DNS server – Host names to be mapped into IP addresses and vice versa – Resolution of naming conflict – Works on single subnet – Multicast DNS (m. DNS) • “single-dns-label. local. ”: e. g. , segihong. local. m. DNS: Standard query response A 169. 254. 18. 87 PTR segihong. local. Standard query ANY segihong. local.
 DNS-Based service discovery • Service discovery on a local network – Users can discover services and choose the services without knowing the location of the service provider in advance to communicate with the provider – DNS-Based service discovery (DNS-SD) • • • Used with m. DNS (DNS-SD/m. DNS) Record types: PTR, SRV and TXT records PTR lookup: Discover service instances,
DNS-Based service discovery • Service discovery on a local network – Users can discover services and choose the services without knowing the location of the service provider in advance to communicate with the provider – DNS-Based service discovery (DNS-SD) • • • Used with m. DNS (DNS-SD/m. DNS) Record types: PTR, SRV and TXT records PTR lookup: Discover service instances,
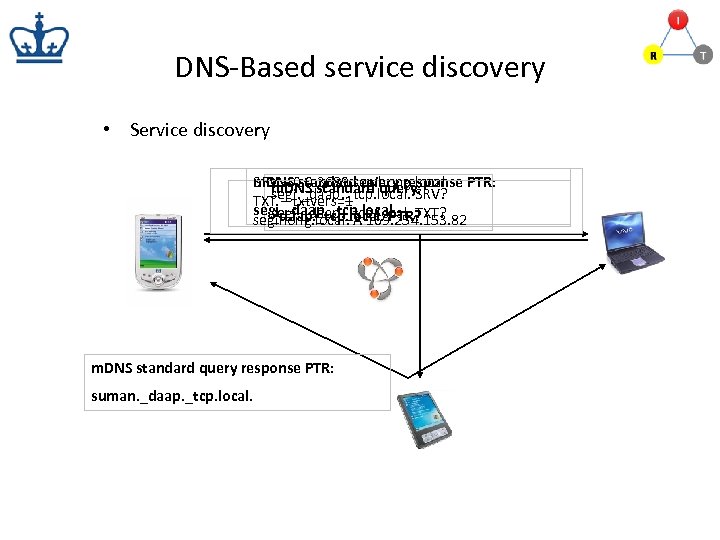 DNS-Based service discovery • Service discovery SRV – standard query response PTR: m. DNS 0 0 standard query: m. DNS 3689 segihong. local. segi. _daap. _tcp. local. SRV? TXT – txtvers=1 segi. _daap. _tcp. local. TXT? segi. _daap. _tcp. local. PTR? segihong. local. A 169. 254. 153. 82 m. DNS standard query response PTR: suman. _daap. _tcp. local.
DNS-Based service discovery • Service discovery SRV – standard query response PTR: m. DNS 0 0 standard query: m. DNS 3689 segihong. local. segi. _daap. _tcp. local. SRV? TXT – txtvers=1 segi. _daap. _tcp. local. TXT? segi. _daap. _tcp. local. PTR? segihong. local. A 169. 254. 153. 82 m. DNS standard query response PTR: suman. _daap. _tcp. local.
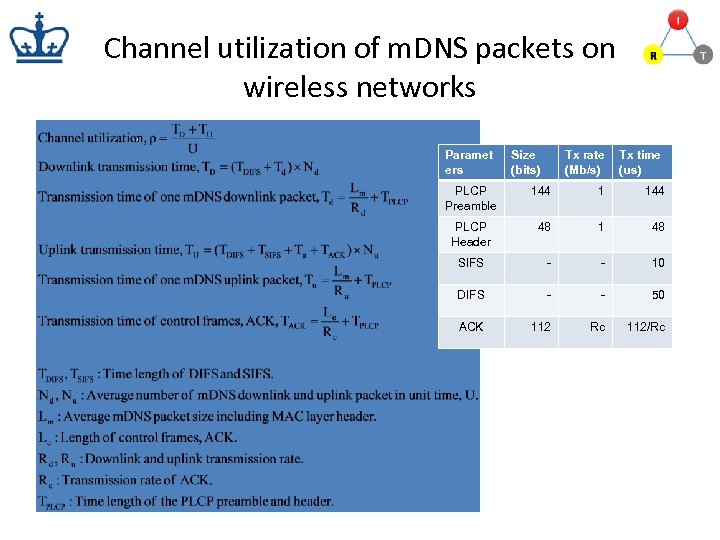 Channel utilization of m. DNS packets on wireless networks Paramet ers Size (bits) Tx rate (Mb/s) Tx time (us) PLCP Preamble 144 1 144 PLCP Header 48 1 48 SIFS - - 10 DIFS - - 50 ACK 112 Rc 112/Rc
Channel utilization of m. DNS packets on wireless networks Paramet ers Size (bits) Tx rate (Mb/s) Tx time (us) PLCP Preamble 144 1 144 PLCP Header 48 1 48 SIFS - - 10 DIFS - - 50 ACK 112 Rc 112/Rc
 What is Zeroconf? • IETF Zero Configuration Networking (Zeroconf) WG • 4 requirements – IP interface configuration – Translation between host name and IP address – IP multicast address allocation – Service discovery • Implementation – Bonjour • Apple’s implementation of zero-configuration networking • i. Tunes, i. Chat – Avahi • Open source for Linux
What is Zeroconf? • IETF Zero Configuration Networking (Zeroconf) WG • 4 requirements – IP interface configuration – Translation between host name and IP address – IP multicast address allocation – Service discovery • Implementation – Bonjour • Apple’s implementation of zero-configuration networking • i. Tunes, i. Chat – Avahi • Open source for Linux
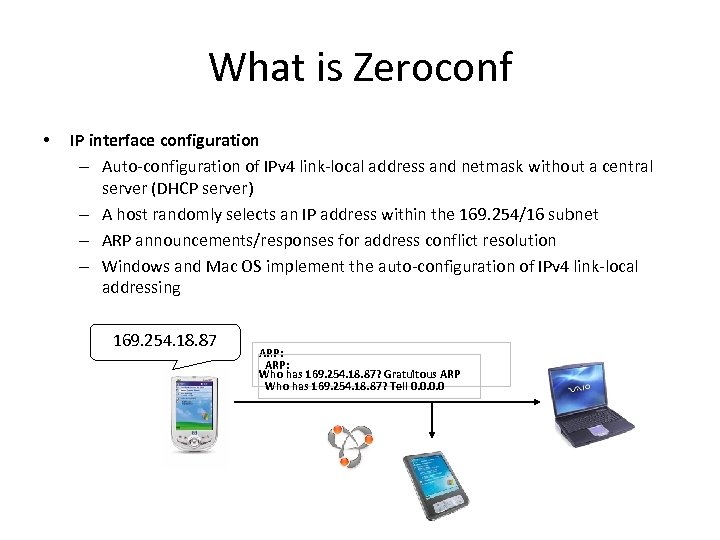 What is Zeroconf • IP interface configuration – Auto-configuration of IPv 4 link-local address and netmask without a central server (DHCP server) – A host randomly selects an IP address within the 169. 254/16 subnet – ARP announcements/responses for address conflict resolution – Windows and Mac OS implement the auto-configuration of IPv 4 link-local addressing 169. 254. 18. 87 ARP: Who has 169. 254. 18. 87? Gratuitous ARP Who has 169. 254. 18. 87? Tell 0. 0
What is Zeroconf • IP interface configuration – Auto-configuration of IPv 4 link-local address and netmask without a central server (DHCP server) – A host randomly selects an IP address within the 169. 254/16 subnet – ARP announcements/responses for address conflict resolution – Windows and Mac OS implement the auto-configuration of IPv 4 link-local addressing 169. 254. 18. 87 ARP: Who has 169. 254. 18. 87? Gratuitous ARP Who has 169. 254. 18. 87? Tell 0. 0
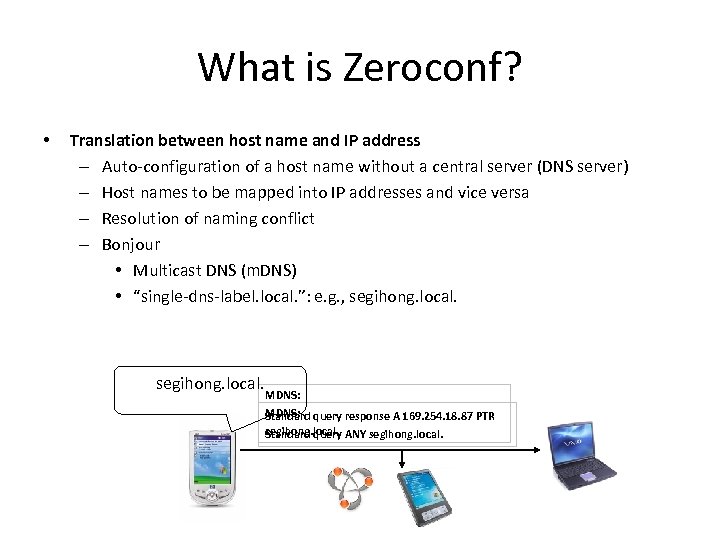 What is Zeroconf? • Translation between host name and IP address – Auto-configuration of a host name without a central server (DNS server) – Host names to be mapped into IP addresses and vice versa – Resolution of naming conflict – Bonjour • Multicast DNS (m. DNS) • “single-dns-label. local. ”: e. g. , segihong. local. MDNS: query response A 169. 254. 18. 87 PTR Standard segihong. local. ANY segihong. local. Standard query
What is Zeroconf? • Translation between host name and IP address – Auto-configuration of a host name without a central server (DNS server) – Host names to be mapped into IP addresses and vice versa – Resolution of naming conflict – Bonjour • Multicast DNS (m. DNS) • “single-dns-label. local. ”: e. g. , segihong. local. MDNS: query response A 169. 254. 18. 87 PTR Standard segihong. local. ANY segihong. local. Standard query
 What is Zeroconf? • IP multicast address allocation – Range of IP multicast: 224. 0. 0. 0 to 239. 255 – Bonjour • m. DNS multicast address • 224. 0. 0. 251
What is Zeroconf? • IP multicast address allocation – Range of IP multicast: 224. 0. 0. 0 to 239. 255 – Bonjour • m. DNS multicast address • 224. 0. 0. 251
 What is Zeroconf? • Service discovery – Users can discover services and choose the services without knowing the location of the service provider in advance to communicate with the provider – Bonjour • Multicast DNS-Based service discovery (m. DNS-SD) • PTR, SRV and TXT records • PTR lookup:
What is Zeroconf? • Service discovery – Users can discover services and choose the services without knowing the location of the service provider in advance to communicate with the provider – Bonjour • Multicast DNS-Based service discovery (m. DNS-SD) • PTR, SRV and TXT records • PTR lookup:
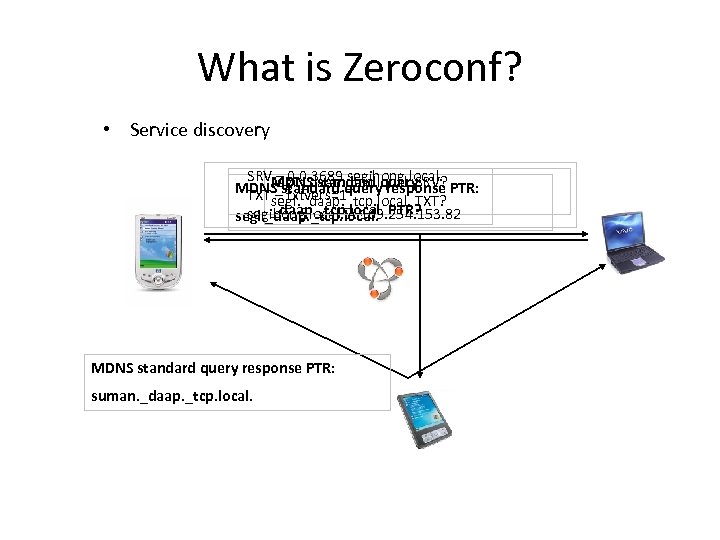 What is Zeroconf? • Service discovery SRVsegi. _daap. _tcp. local. SRV? – 0 0 standard MDNS 3689 segihong. local. PTR: MDNS–standard query: response TXTsegi. _daap. _tcp. local. TXT? txtvers=1 _daap. _tcp. local. segihong. local. A 169. 254. 153. 82 segi. _daap. _tcp. local. PTR? MDNS standard query response PTR: suman. _daap. _tcp. local.
What is Zeroconf? • Service discovery SRVsegi. _daap. _tcp. local. SRV? – 0 0 standard MDNS 3689 segihong. local. PTR: MDNS–standard query: response TXTsegi. _daap. _tcp. local. TXT? txtvers=1 _daap. _tcp. local. segihong. local. A 169. 254. 153. 82 segi. _daap. _tcp. local. PTR? MDNS standard query response PTR: suman. _daap. _tcp. local.
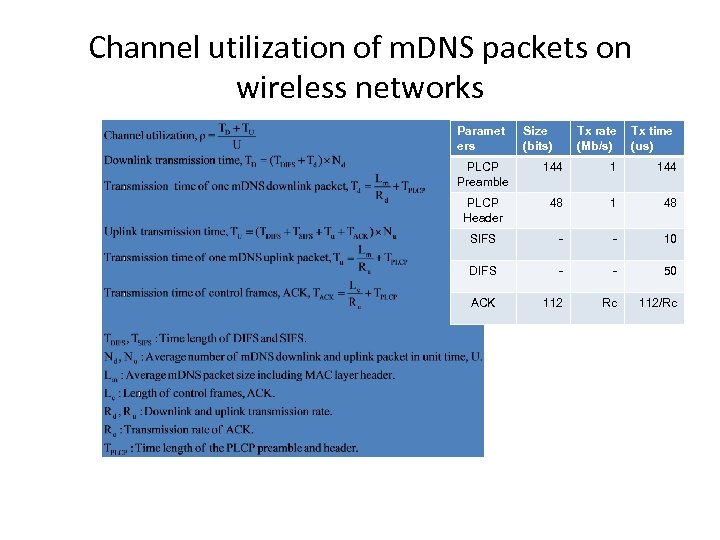 Channel utilization of m. DNS packets on wireless networks Paramet ers Size (bits) Tx rate (Mb/s) Tx time (us) PLCP Preamble 144 1 144 PLCP Header 48 1 48 SIFS - - 10 DIFS - - 50 ACK 112 Rc 112/Rc
Channel utilization of m. DNS packets on wireless networks Paramet ers Size (bits) Tx rate (Mb/s) Tx time (us) PLCP Preamble 144 1 144 PLCP Header 48 1 48 SIFS - - 10 DIFS - - 50 ACK 112 Rc 112/Rc


