824f61e37d82c1f405efd4d5bab5ebe0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 91

Measurement Instruments &Tools Accurate Measurement

Objectives What is an ‘accurate’ measurement n Review different types of measuring instruments and their application n Learn how to calibrate instruments n Care and maintenance of instruments n Advanced diagnostic session n

Why are these measuring devices called ‘instruments’

Definition of Accurate (from dictionary) n free from error especially as the result of care n able to give an accurate result What happens if you do not measure accurately?

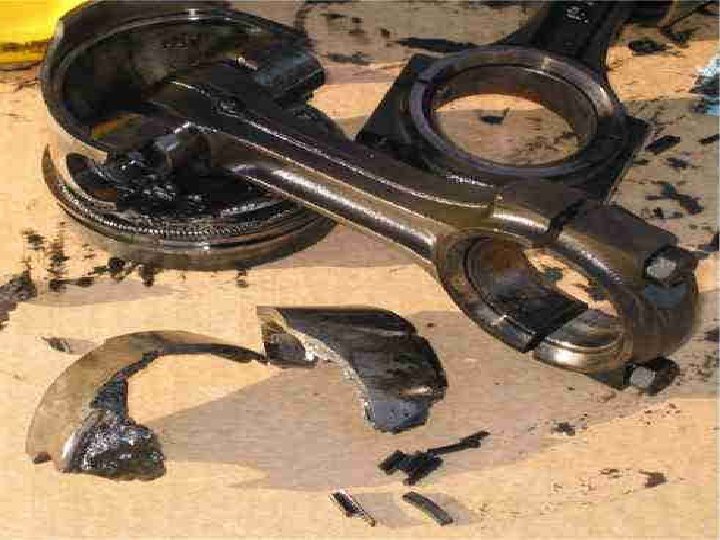
Examples of Failed Measurements
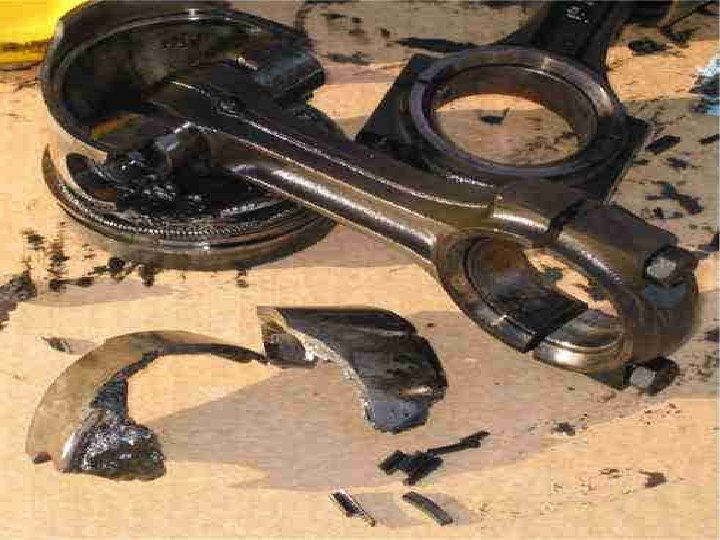
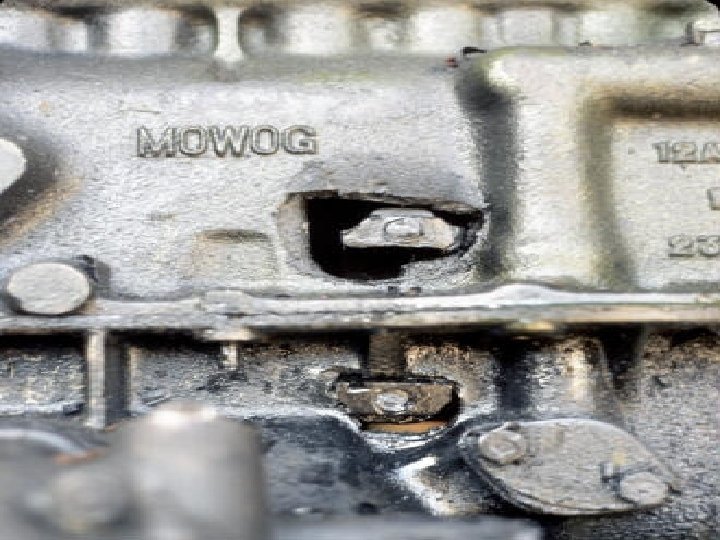
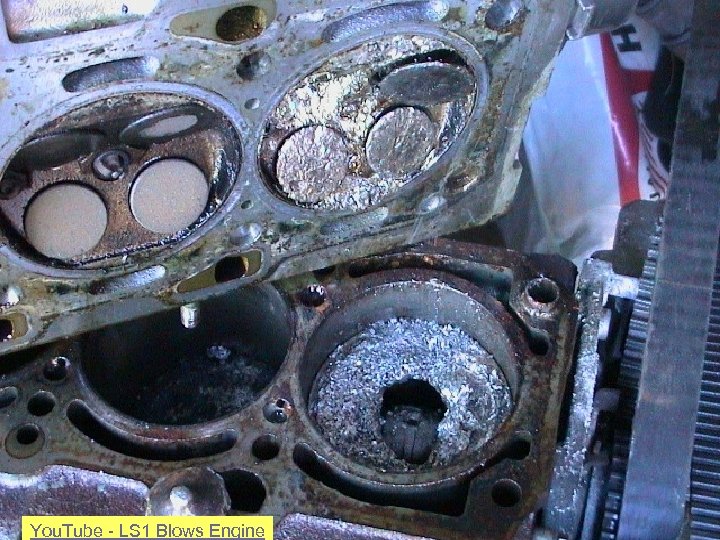




You. Tube - LS 1 Blows Engine

Name here

Measuring Instruments Micrometers n Vernier Calipers n Dial Indicators n Telescopic Gauges n Small Hole Gauges n Thickness Gauges n Straight Edge n

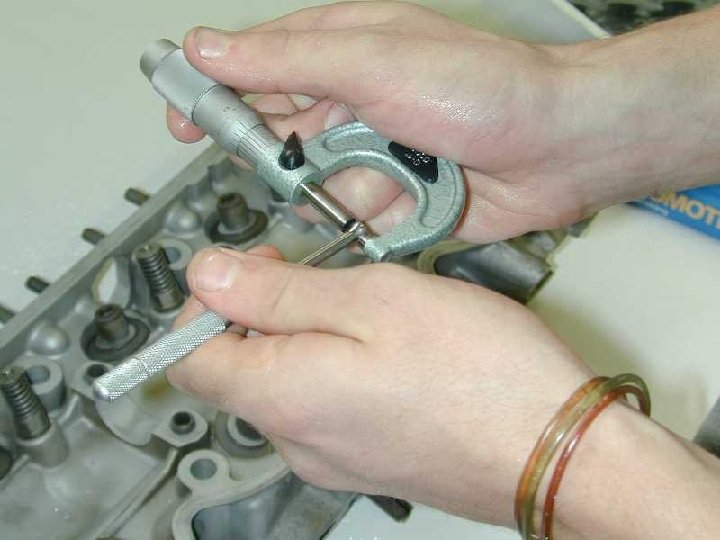
Outside Micrometer Instrument for making precise linear measurements of dimensions such as diameters, thicknesses, and lengths of solid bodies. It consists of a C-shaped frame with a movable jaw operated by a screw. The accuracy of the measurements depends on the accuracy of the screw -nut combination.
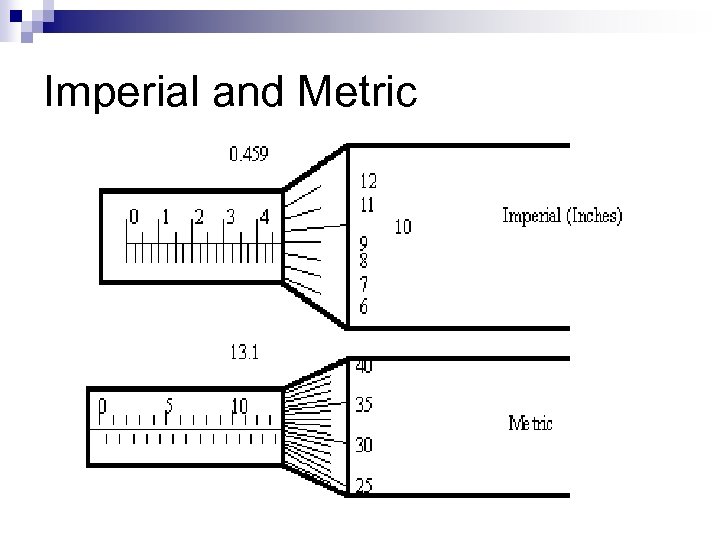
Imperial and Metric

Inside Micrometer
Depth Micrometer
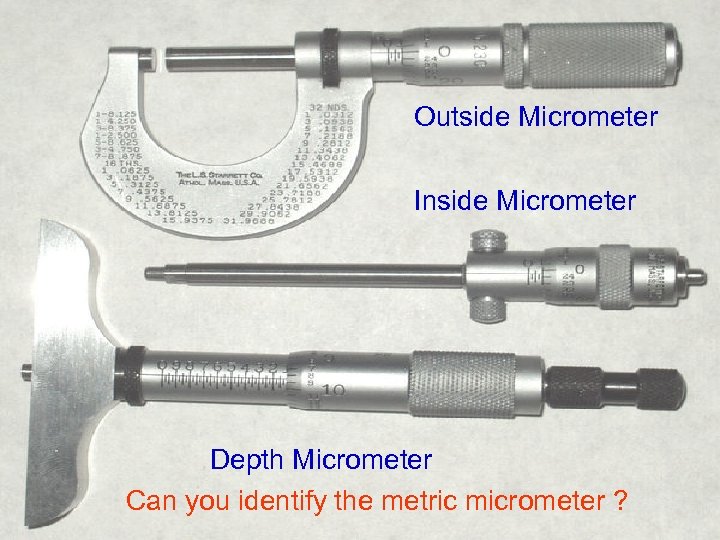
Outside Micrometer Inside Micrometer Depth Micrometer Can you identify the metric micrometer ?

Digital Micrometers

Combination Digital Metric or Imperial at the push of a button
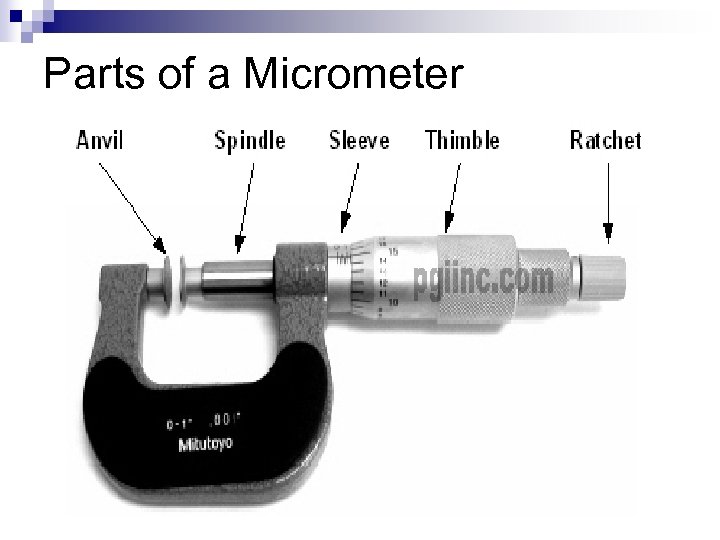
Parts of a Micrometer
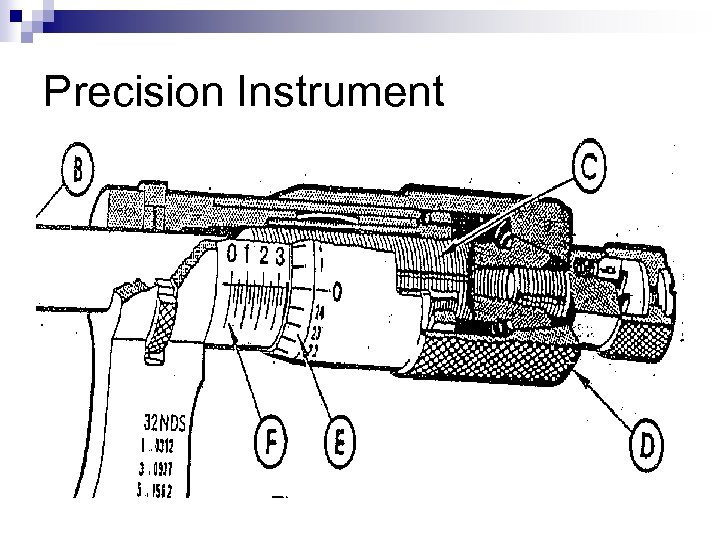
Precision Instrument

Micrometer Don’ts Do not drop n Do not run over n Do not over tighten (it is not a vice) n Do not drop in chemicals n Do not leave it covered in grease n Do not let anyone borrow it n Do not leave lying around n

Micrometer Do’s Keep clean n Keep calibrated n Keep in storage box n Keep locked up n Keep away from everyone n Keep in practice reading it ! n
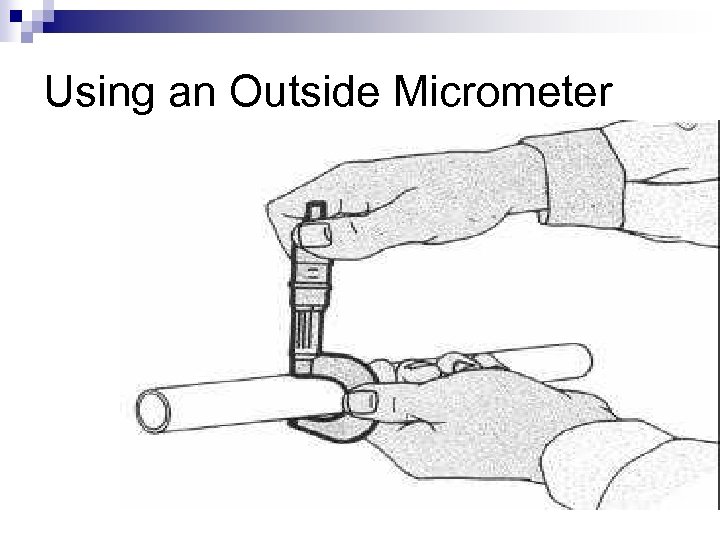
Using an Outside Micrometer

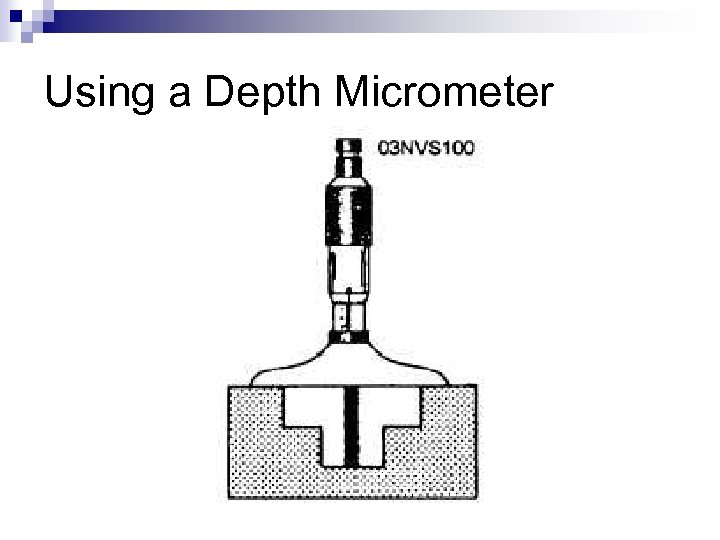
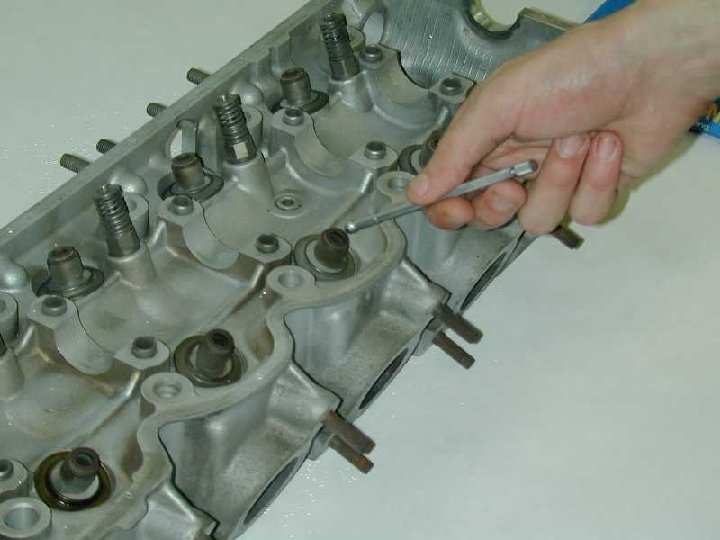
Using a Depth Micrometer

Using Inside Micrometer

Brake Drum Micrometer Essentially it is a heavy duty Inside Micrometer
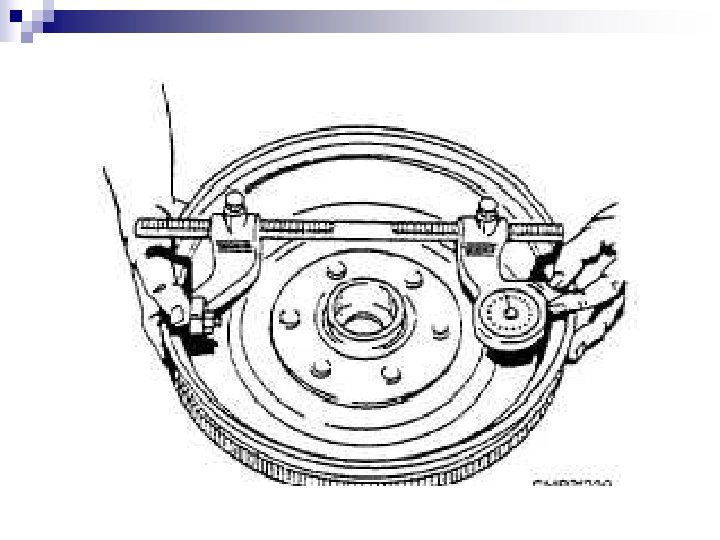
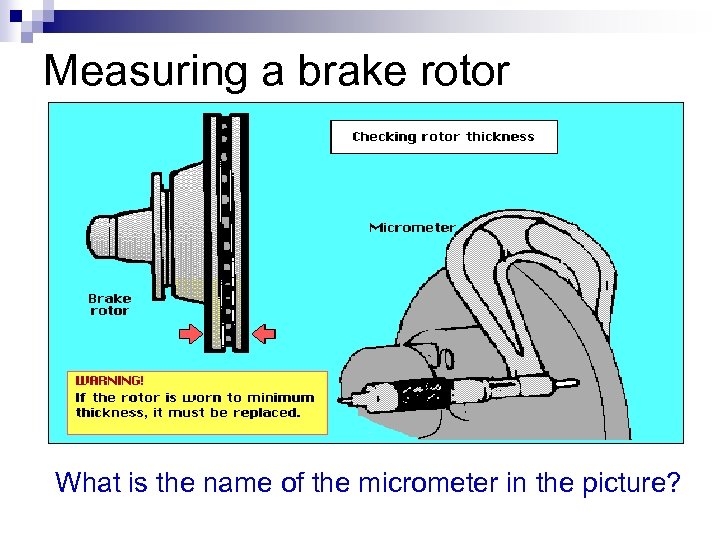
Measuring a brake rotor What is the name of the micrometer in the picture?

Steps to reading a micrometer n n n Calibrate unit Identify scale (metric or imperial) Identify range of micrometer (size) Read Sleeve first number you see Read Sleeve for second number (graduation) Read Thimble Note-if it is a 4 digit mic, read last number on Sleeve (will discuss later)

Step # 1 Calibrate Micrometer Before using any measuring instrument you must check to ensure it is calibrated (accurate) TGB Computing & Publishing You. Tube - measuring the thickness of a block using a micrometer www. tgbcomputing. com
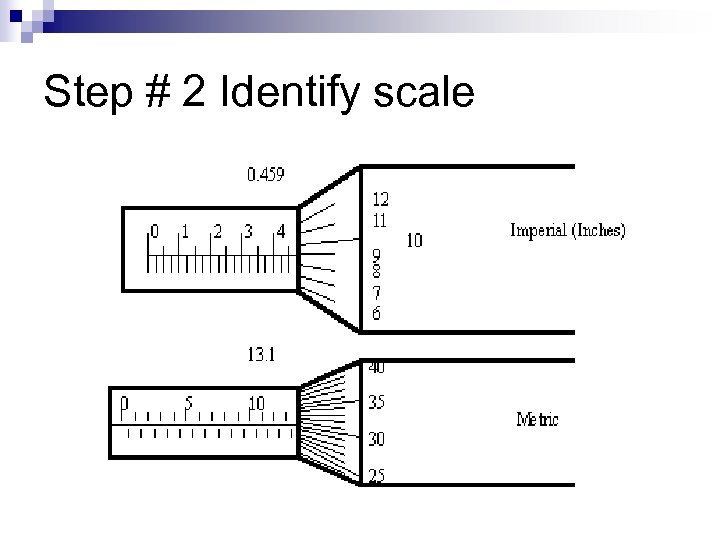
Step # 2 Identify scale

Step # 3 Identify Range (size)

Where to find range Imperial equivalent would be a 0 -1”
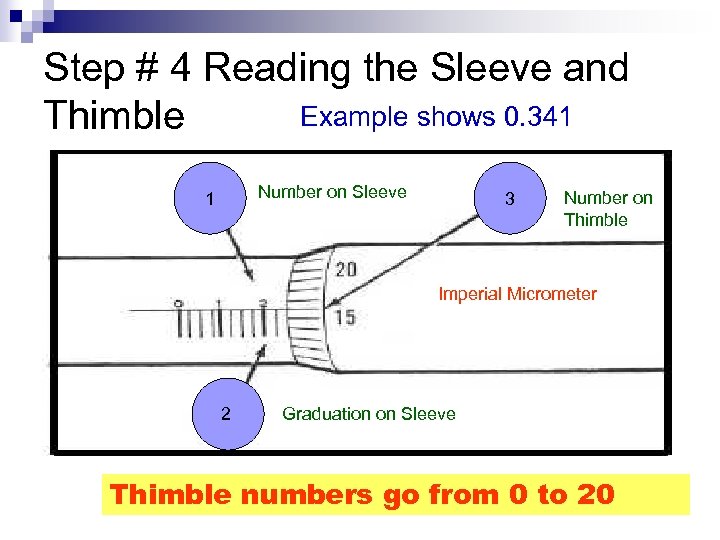
Step # 4 Reading the Sleeve and Example shows 0. 341 Thimble Number on Sleeve 1 3 Number on Thimble Imperial Micrometer 2 Graduation on Sleeve Thimble numbers go from 0 to 20
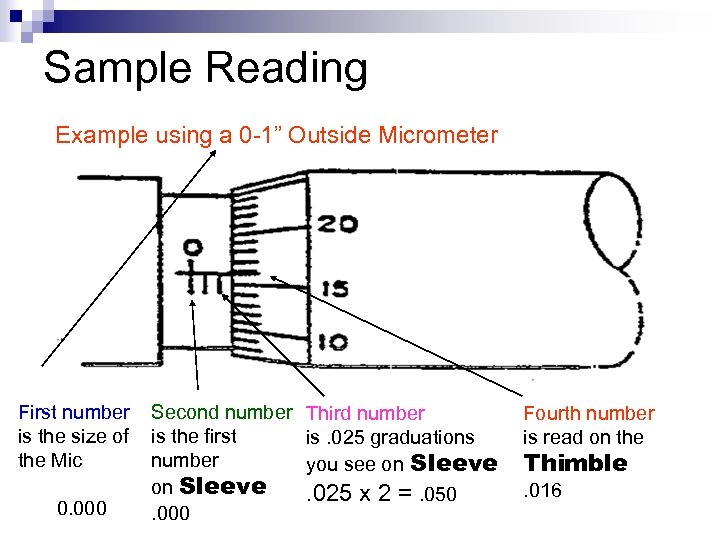
Sample Reading Example using a 0 -1” Outside Micrometer First number is the size of the Mic 0. 000 Second number Third number is the first is. 025 graduations number you see on Sleeve. 025 x 2 =. 050. 000 Fourth number is read on the Thimble. 016
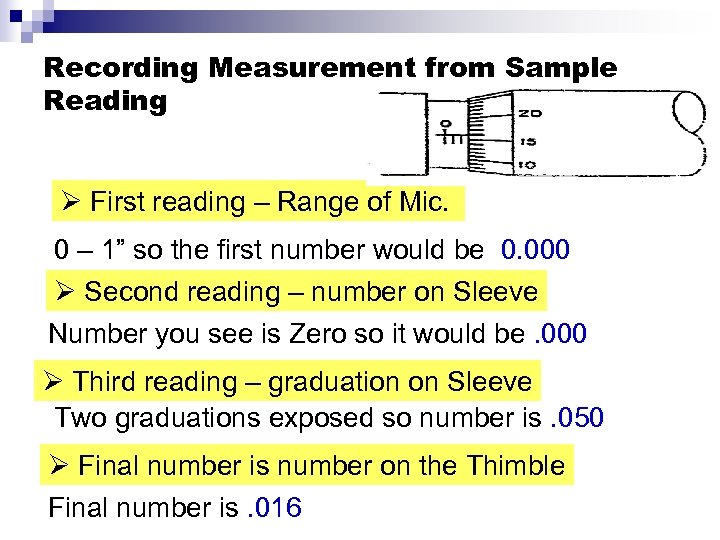
Recording Measurement from Sample Reading Ø First reading – Range of Mic. 0 – 1” so the first number would be 0. 000 Ø Second reading – number on Sleeve Number you see is Zero so it would be. 000 Ø Third reading – graduation on Sleeve Two graduations exposed so number is. 050 Ø Final number is number on the Thimble Final number is. 016
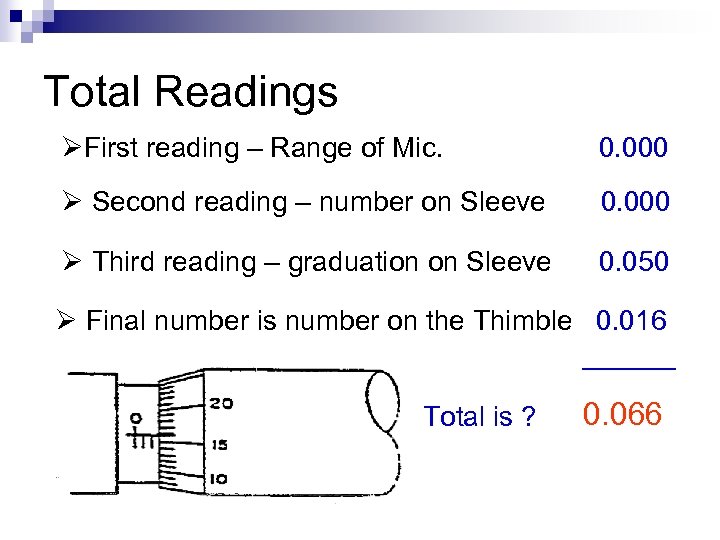
Total Readings ØFirst reading – Range of Mic. 0. 000 Ø Second reading – number on Sleeve 0. 000 Ø Third reading – graduation on Sleeve 0. 050 Ø Final number is number on the Thimble 0. 016 ______ Total is ? 0. 066

Reading an Imperial Micrometer
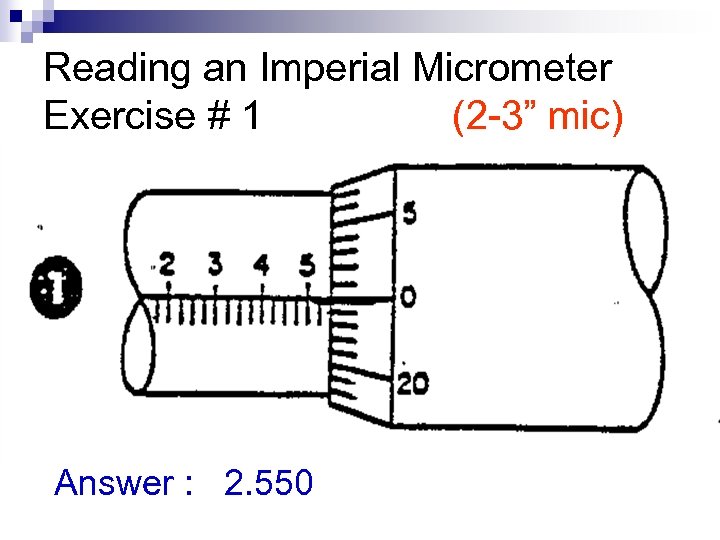
Reading an Imperial Micrometer Exercise # 1 (2 -3” mic) Answer : 2. 550
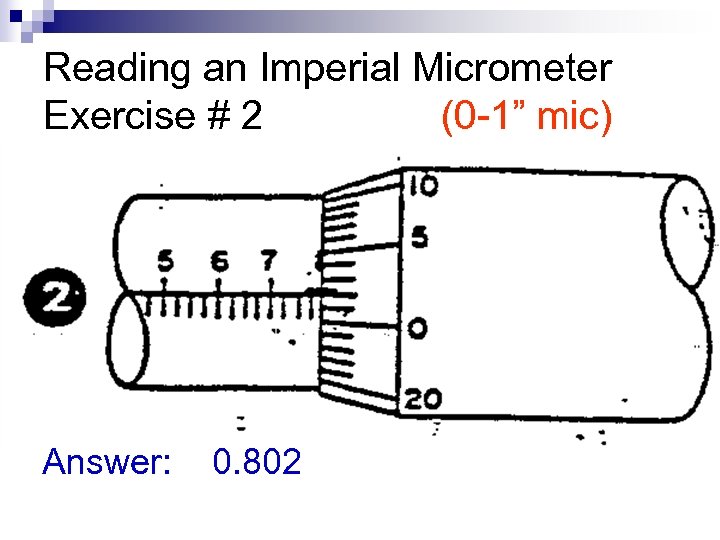
Reading an Imperial Micrometer Exercise # 2 (0 -1” mic) Answer: 0. 802
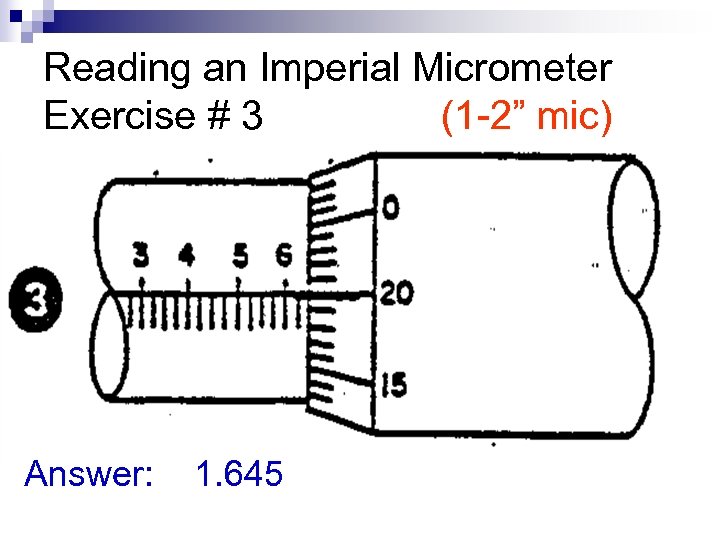
Reading an Imperial Micrometer Exercise # 3 (1 -2” mic) Answer: 1. 645

Reading a Metric Micrometer
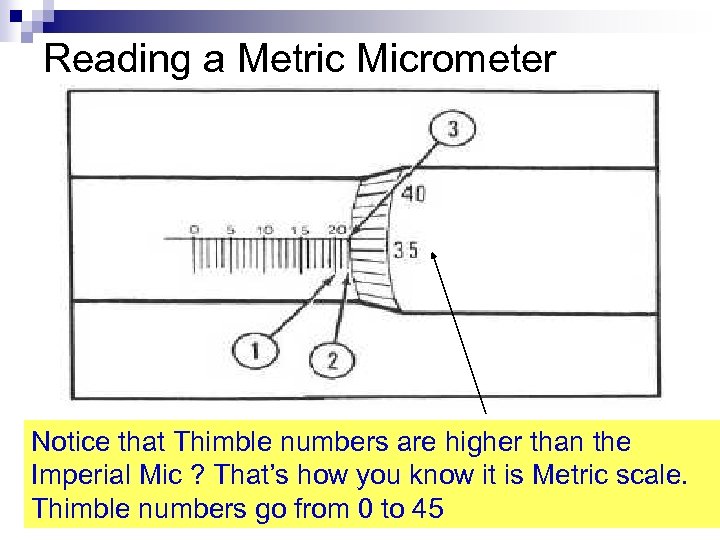
Reading a Metric Micrometer Notice that Thimble numbers are higher than the Imperial Mic ? That’s how you know it is Metric scale. Thimble numbers go from 0 to 45

Example of 4 digit Metric Micrometer 0. 0000

Reading a Metric Micrometer Exercise # 1 (0 -25 mm Range) Answer : 12. 69

Reading a Metric Micrometer Exercise # 2 (0 -25 mm Range) Answer : 23. 99

Telescopic Gauges ØSpring loaded ØMeasure large inside dia.
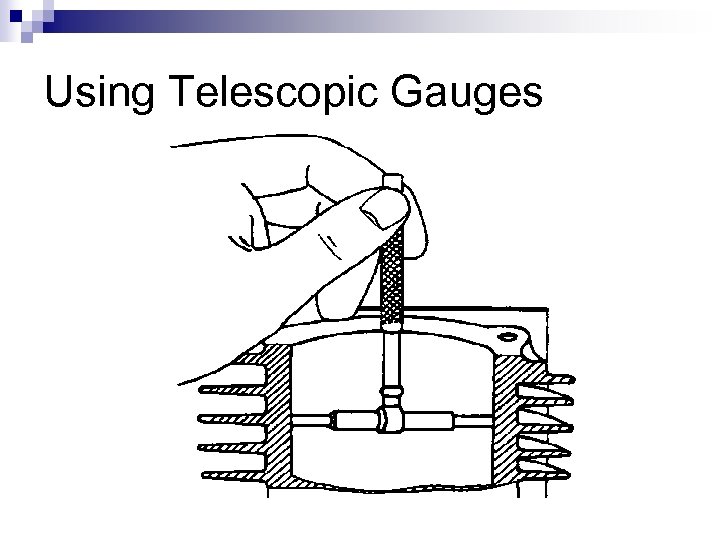
Using Telescopic Gauges

Small Holes Gauges Measure small Inside Diameters



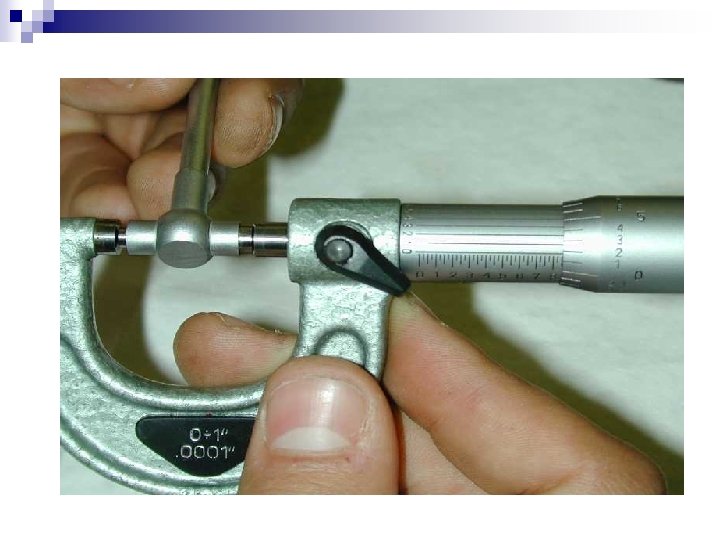
Dividers or Caliper Instrument that consists of two adjustable legs or jaws for measuring the dimensions of material parts. Outside calipers measure thicknesses and outside diameters of objects; inside calipers measure hole diameters and distances between surfaces.
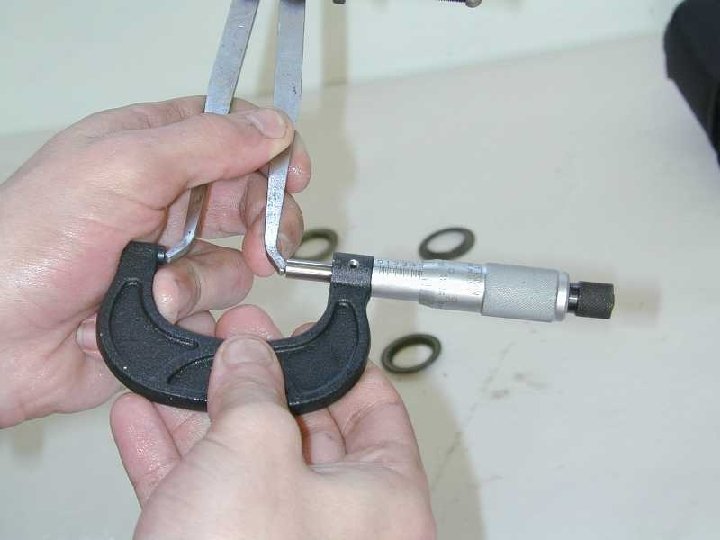

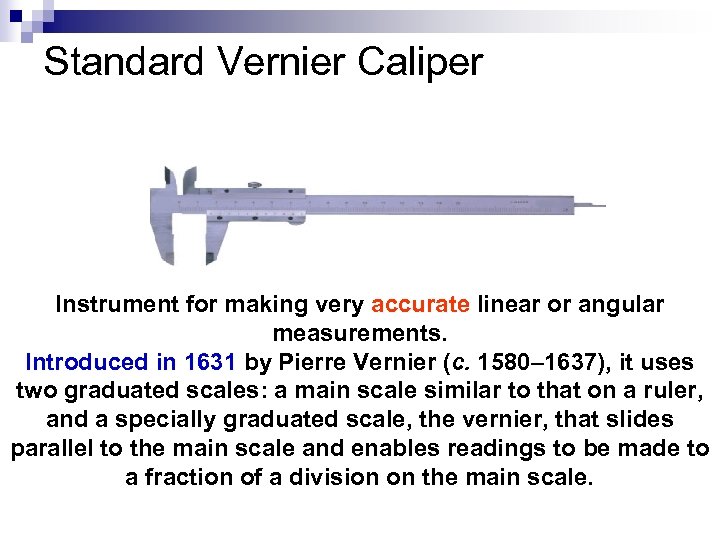
Standard Vernier Caliper Instrument for making very accurate linear or angular measurements. Introduced in 1631 by Pierre Vernier (c. 1580– 1637), it uses two graduated scales: a main scale similar to that on a ruler, and a specially graduated scale, the vernier, that slides parallel to the main scale and enables readings to be made to a fraction of a division on the main scale.

Why buy a Vernier Caliper? Ø Durable Ø Accurate measuring instrument Ø Multiple reading use Ø Easy to store and maintain Readings that can be taken Ø Outside Diameter Ø Inside Diameter Ø Thickness Ø Depth Can this instrument not take place of a mic?

Dividers or Caliper

Small Holes Gauges

Telescopic Gauges
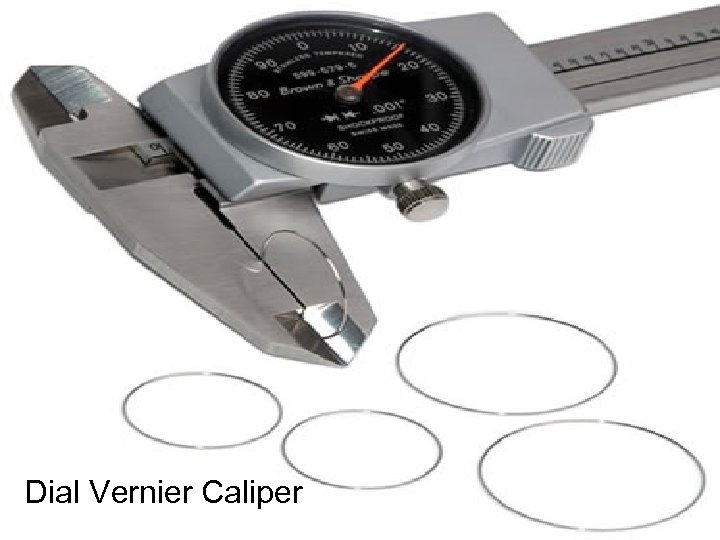

Dial Vernier Caliper

Digital Vernier Caliper You. Tube - Digital Caliper Bug


Using a Vernier Caliper How to use and read a Vernier Caliper You. Tube - all about verniers Checking calibration of Vernier Caliper and allowing for error You. Tube - measuring a weight using a vernier caliper
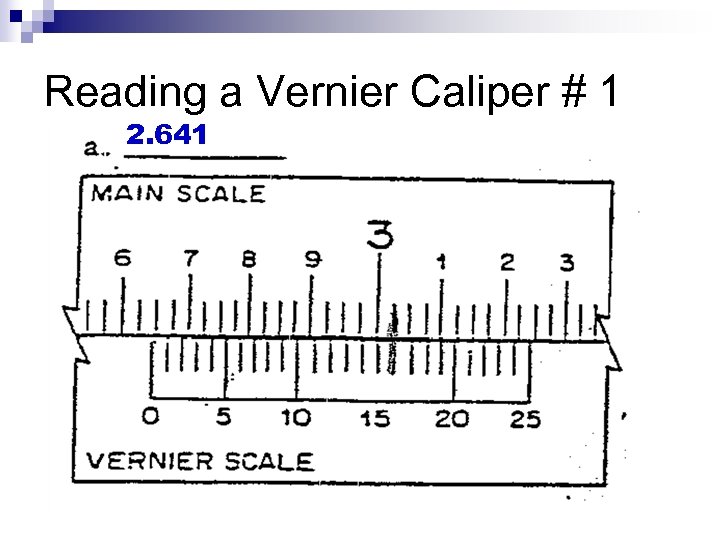
Reading a Vernier Caliper # 1 2. 641
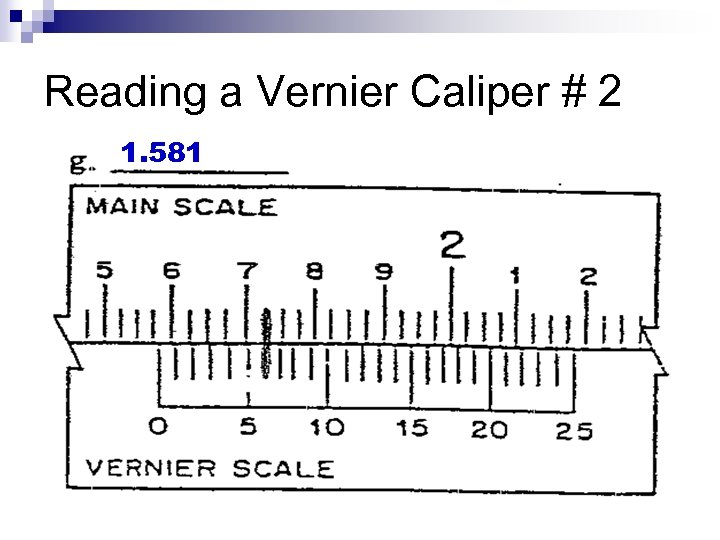
Reading a Vernier Caliper # 2 1. 581
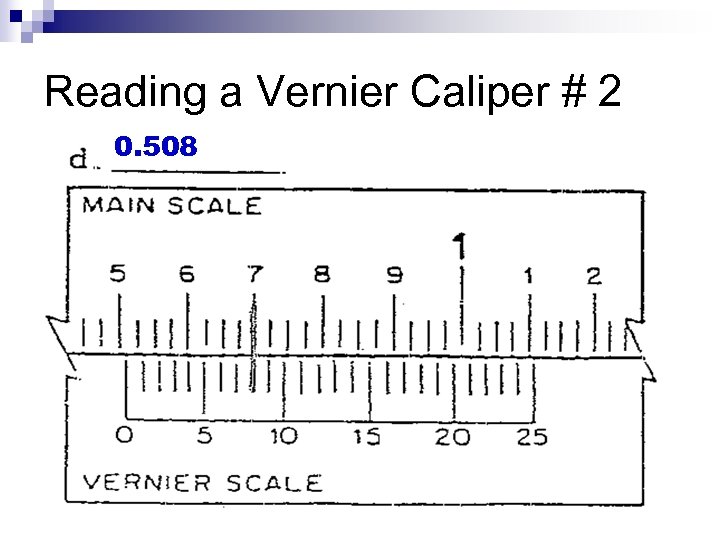
Reading a Vernier Caliper # 2 0. 508

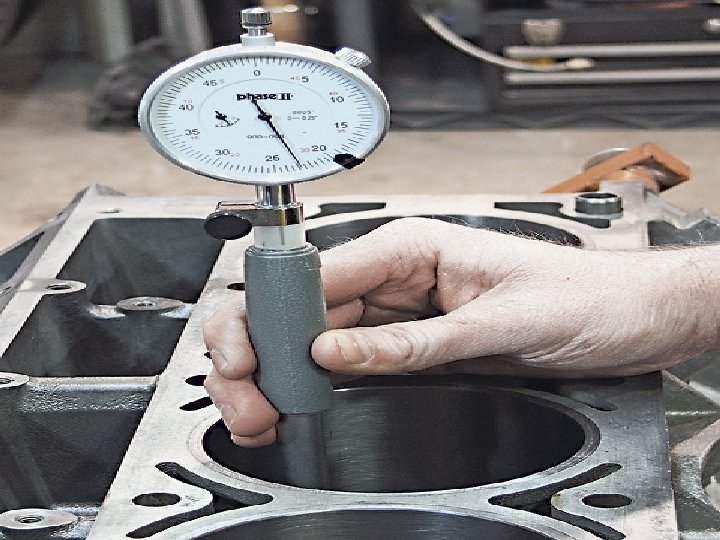
Dial Indicators Any of a number of deviationtype gauges that indicate the amount by which an object being gauged deviates from the standard. This deviation is shown in units of measurement, in which movement of a gauging spindle deflects a pointer on a graduated dial

Calibration of Dial Indicator Turn dial until pointer aligns with the Zero TGB Computing & Publishing

Note-example of Metric Dial Indicator Calibration button
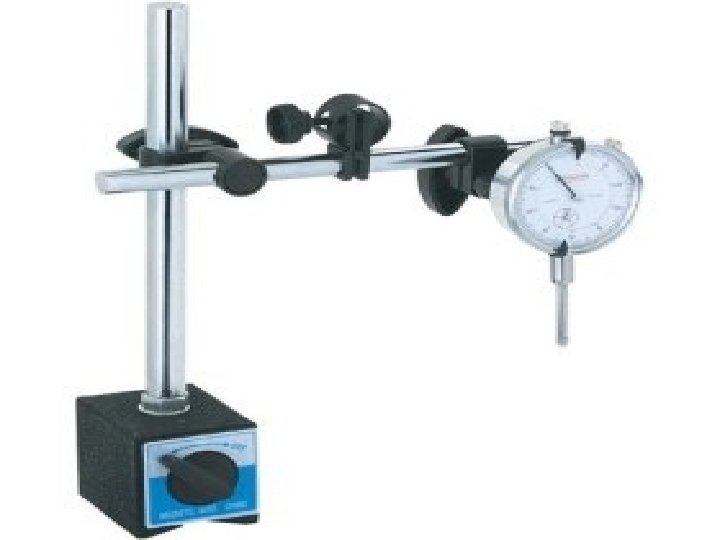

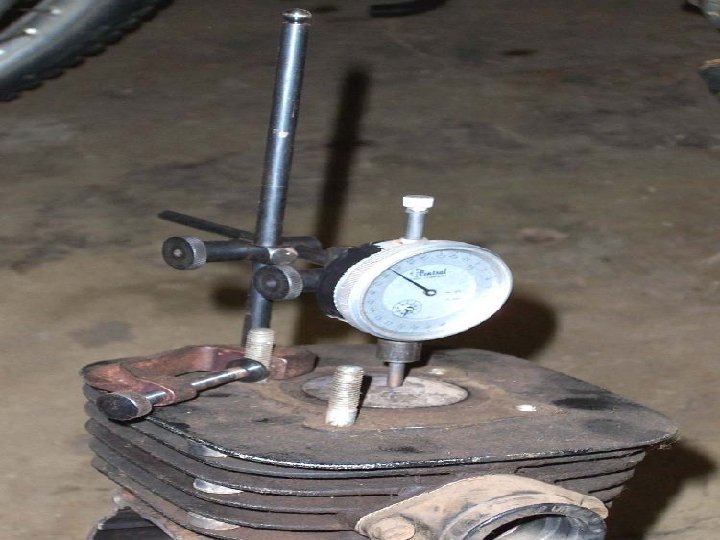
Dial Indicator with Stand
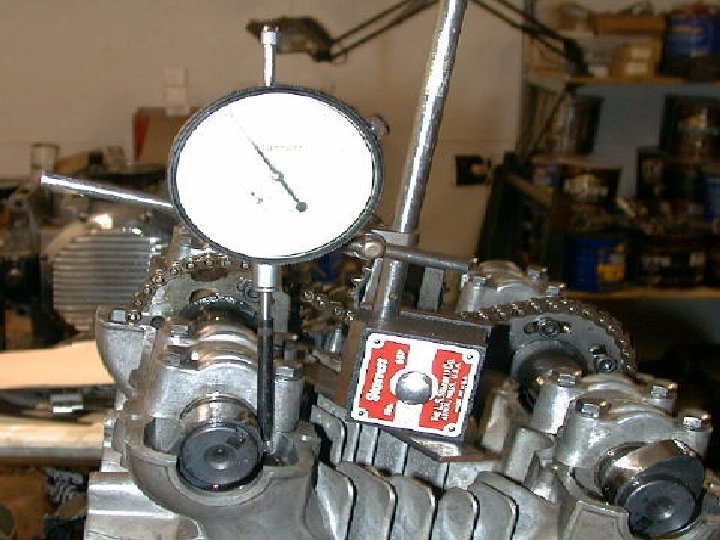
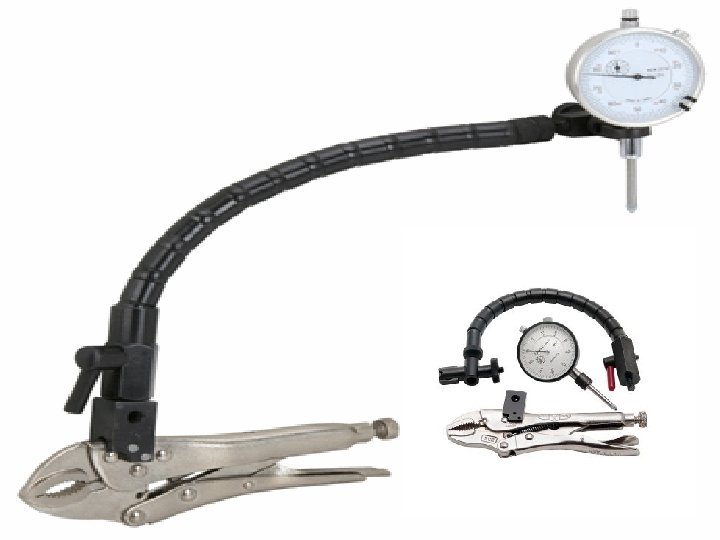



Very useful instrument for checking Steering and Suspension components



Simpler Measuring Devices Thickness Gauges Flat Blade Feeler Gauges n Wire Gauges n Taper Gauge n

Metric Feeler Gauges
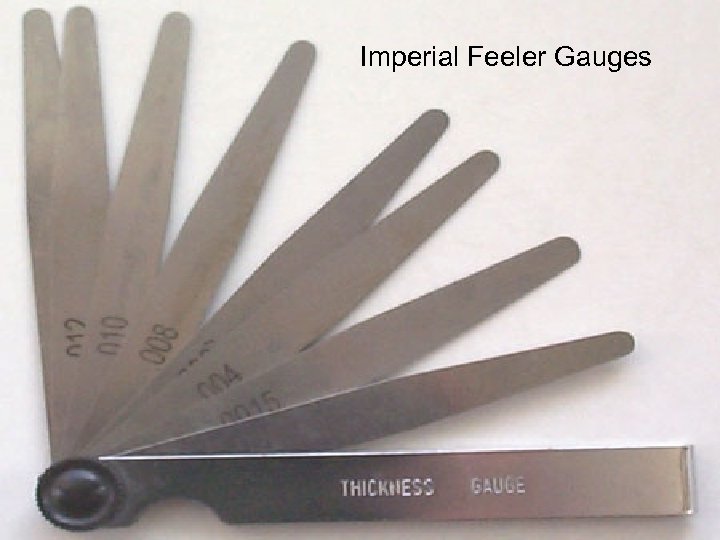

Imperial Feeler Gauges
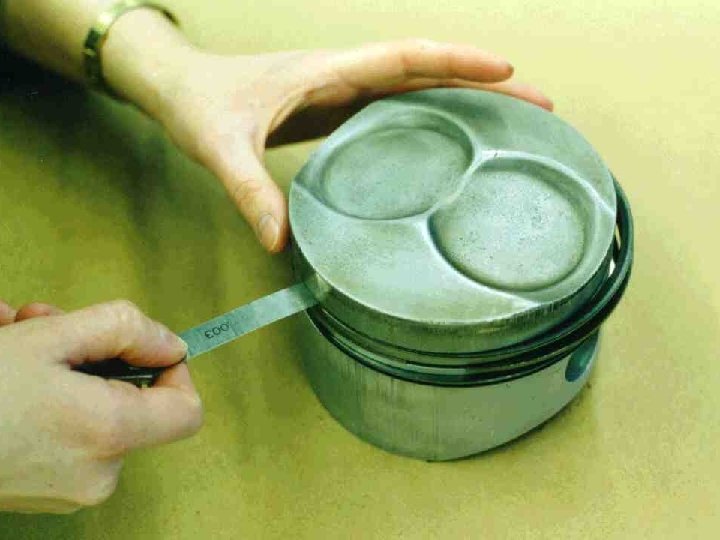






Straight Edge Accurately machined surface
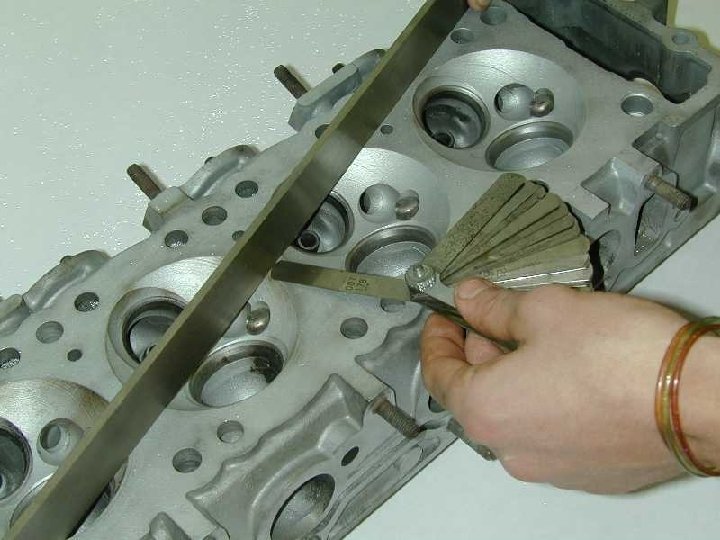




References - Links Ø You. Tube - all about verniers Ø You. Tube - measuring a weight using a vernier caliper Ø You. Tube - measuring the thickness of a block using a micrometer Ø www. tgbcomputing. com Ø TGB Computing & Publishing
824f61e37d82c1f405efd4d5bab5ebe0.ppt