c14363910be044f1143114fb37fad7e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat By Steven Gianvecchio, Mengjun Xie, Zhenyu Wu, and Haining Wang College of William and Mary

Outline § § § Background Measurement Classification System Experimental Evaluation Conclusion USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 2
Outline § § § Background Measurement Classification System Experimental Evaluation Conclusion USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 3

Bots § Bots - programs that automate human tasks § web bots automate browsing the web § chat bots automate online chat § can be harmful and/or helpful USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 4
Chat Bots vs. Bot. Nets § Bot. Nets – networks of compromised machines § some use chat systems (IRC) for C&C, others use P 2 P, HTTP, etc. § abuse various systems § Chat Bots – automated chat programs § some are helpful, e. g. , chat loggers § can abuse chat systems and their users USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 5
The Chat Bot Problem § The Problem – chat bots abuse chat services (e. g. , AOL, Yahoo!, MSN) MSN § send spam § spread malicious software § mount phishing attacks § Our focus is on the Yahoo! chat system USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 6
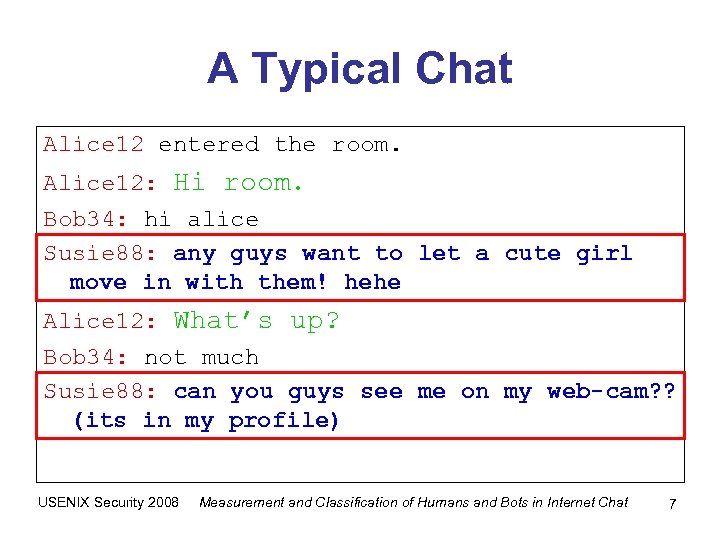
A Typical Chat Alice 12 entered the room. Alice 12: Hi room. Bob 34: hi alice Susie 88: any guys want to let a cute girl move in with them! hehe Alice 12: What’s up? Bob 34: not much Susie 88: can you guys see me on my web-cam? ? (its in my profile) USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 7
Yahoo! Chat § Yahoo! chat is a large commercial chat service § over 3, 000 chat rooms AUTH, CHAT, IM, … USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 8
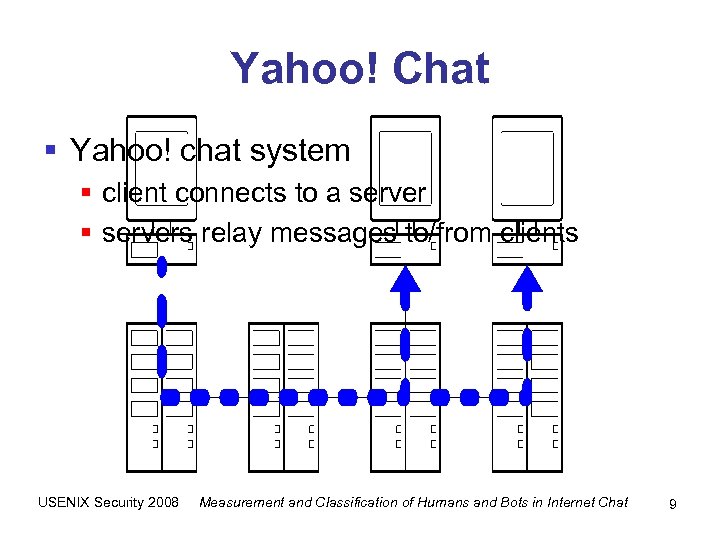
Yahoo! Chat § Yahoo! chat system § client connects to a server § servers relay messages to/from clients USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 9
Outline § § § Background Measurement Classification System Experimental Evaluation Conclusion USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 10
Measurement § August-November 2007 – we collect data § August 2007 – Yahoo! adds CAPTCHA § must pass to join a chat room § protocol update, prevents some 3 rd party clients from accessing chat § October 2007 – bots are back § some bots return before 3 rd party clients USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 11
Measurement § September and October 2007 § very few chat bots § August and November 2007 § § many chat bots 1, 440 hours of chat logs 147 chat logs 21 chat rooms USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 12
Measurement § To create our dataset, we read and label the chat users as § human, bot, or ambiguous § In total, we recognized 14 different types of chat bots § different triggering mechanisms § different text generation techniques USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 13
Triggering Mechanisms § Timer-Based § periodic timers, e. g. , 40 seconds § random timers, e. g. , 45 -125 seconds § Response-Based § responds to other users Sam 77: Bob 12, you’re just full of questions, aren’t you? Sam 77: Bob 12, lots of evidence for evolution can be found here http: // USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 14

Text Generation § Character Padding Fiona 88: anyone boredjn wanna chat? uklcss § Synonym Phrases Marjorie 99: Hi Babes! Marjorie Here! Inspect My Site Marjorie 99: Mmmm Folks! Im Marjorie! View My Webpage § Odd Line or Word Spacing § Message Replay USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 15
Types of Chat Bots § Periodic Bots – sends messages based on periodic timers § Random Bots – sends messages based on random timers § Responder Bots – responds to messages of other users § Replay Bots – replays messages of other users USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 16
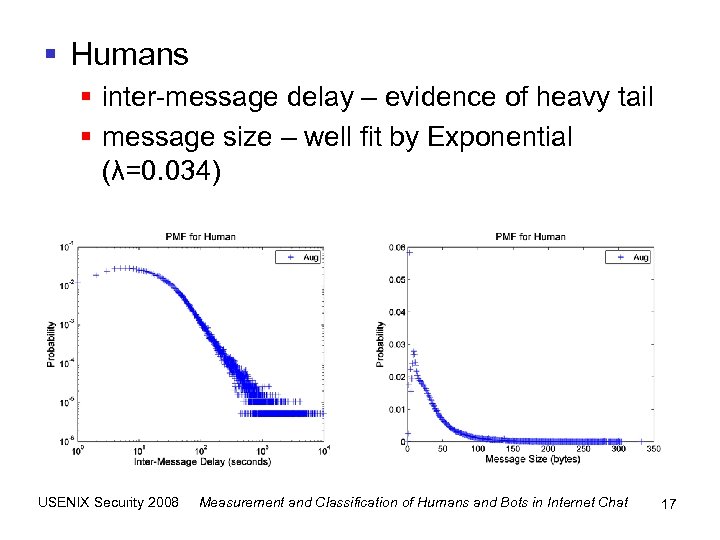
§ Humans § inter-message delay – evidence of heavy tail § message size – well fit by Exponential (λ=0. 034) USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 17
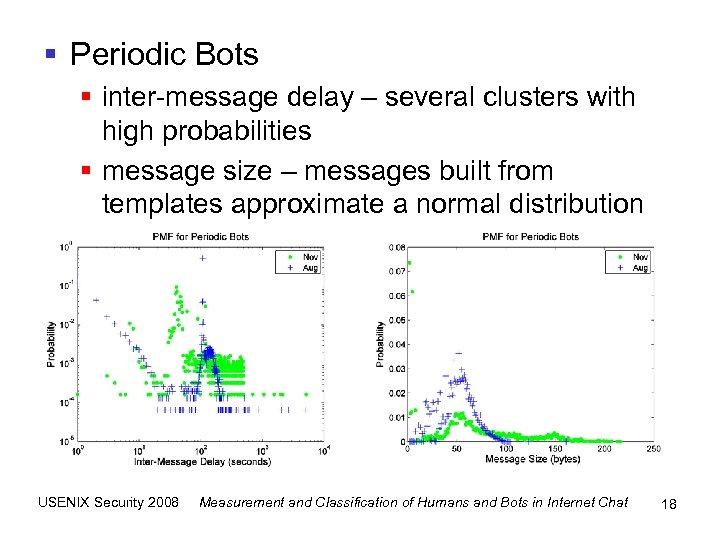
§ Periodic Bots § inter-message delay – several clusters with high probabilities § message size – messages built from templates approximate a normal distribution USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 18
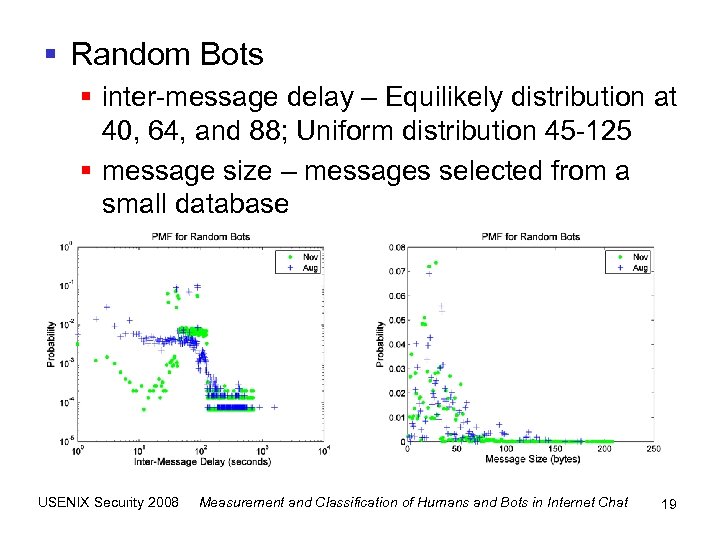
§ Random Bots § inter-message delay – Equilikely distribution at 40, 64, and 88; Uniform distribution 45 -125 § message size – messages selected from a small database USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 19
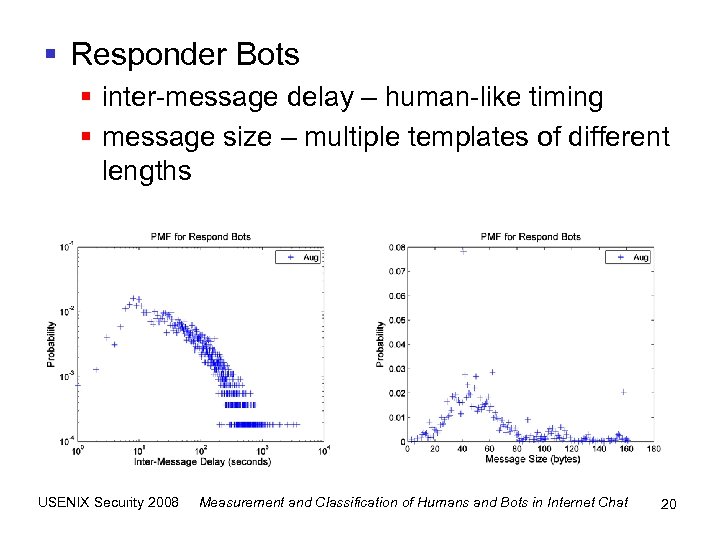
§ Responder Bots § inter-message delay – human-like timing § message size – multiple templates of different lengths USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 20
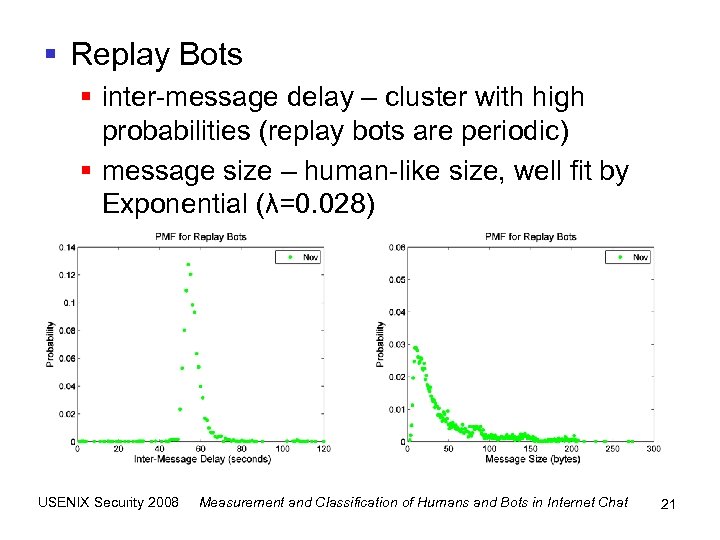
§ Replay Bots § inter-message delay – cluster with high probabilities (replay bots are periodic) § message size – human-like size, well fit by Exponential (λ=0. 028) USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 21
Outline § § § Background Measurement Classification System Experimental Evaluation Conclusion USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 22
Classification System § Entropy Classifier § detects abnormal behavior § based on message sizes and inter-message delays § accurate but slow § Machine Learning Classifier § detects “learned” patterns § based on message content § fast but must be trained USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 23
Entropy Classifier § Observation – chat bots are less complex than humans, and thus, lower in entropy § exploits the low entropy of chat bots § Corrected Conditional Entropy Test (CCE) § estimates higher-order entropy § Entropy Test (EN) § estimates first-order entropy USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 24
Machine Learning Classifier § Observation - chat spam like email spam is a text classification problem § exploits message content of chat bots § CRM 114 § a powerful text classification system § several built-in classifiers: HMM, KNN/Hyperspace, OSB, SVM, Winnow, etc. § we use OSB USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 25
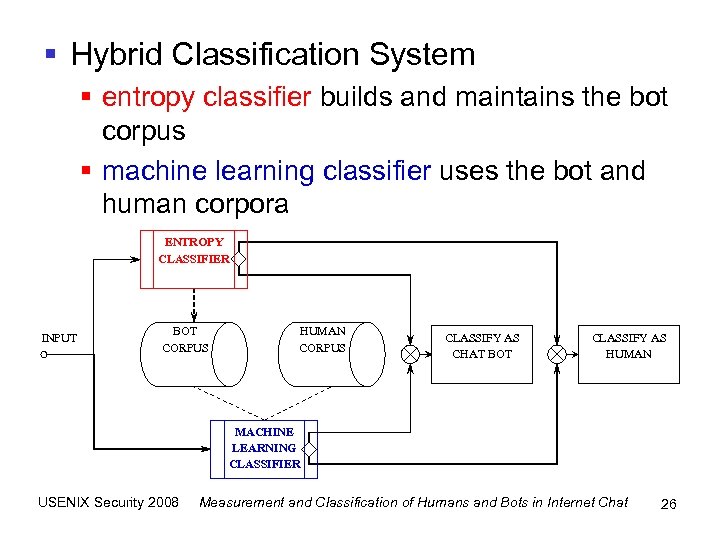
§ Hybrid Classification System § entropy classifier builds and maintains the bot corpus § machine learning classifier uses the bot and human corpora ENTROPY CLASSIFIER INPUT BOT CORPUS HUMAN CORPUS CLASSIFY AS CHAT BOT CLASSIFY AS HUMAN MACHINE LEARNING CLASSIFIER USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 26

Outline § § § Background Measurement Classification System Experimental Evaluation Conclusion USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 27
Experimental Evaluation § Types of Chat Bots § § Periodic Bots Random Bots Responder Bots Replay Bots § Classifiers § entropy classifier – 100 messages § machine learning classifier – 25 messages USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 28
Experimental Evaluation § Classification Tests § Ent – entropy classifier § Sup. ML – fully-supervised ML classifier, trained on AUG BOTS § Sup. MLre – fully-supervised ML classifier, retrained on NOV BOTS § Ent. ML – entropy-trained ML USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 29
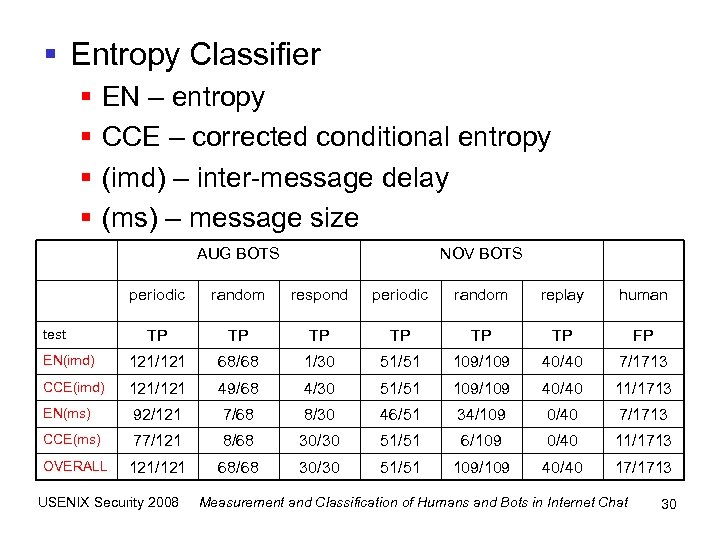
§ Entropy Classifier § § EN – entropy CCE – corrected conditional entropy (imd) – inter-message delay (ms) – message size AUG BOTS NOV BOTS periodic random respond periodic random replay human TP TP TP FP EN(imd) 121/121 68/68 1/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 7/1713 CCE(imd) 121/121 49/68 4/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 11/1713 EN(ms) 92/121 7/68 8/30 46/51 34/109 0/40 7/1713 CCE(ms) 77/121 8/68 30/30 51/51 6/109 0/40 11/1713 OVERALL 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 17/1713 test USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 30
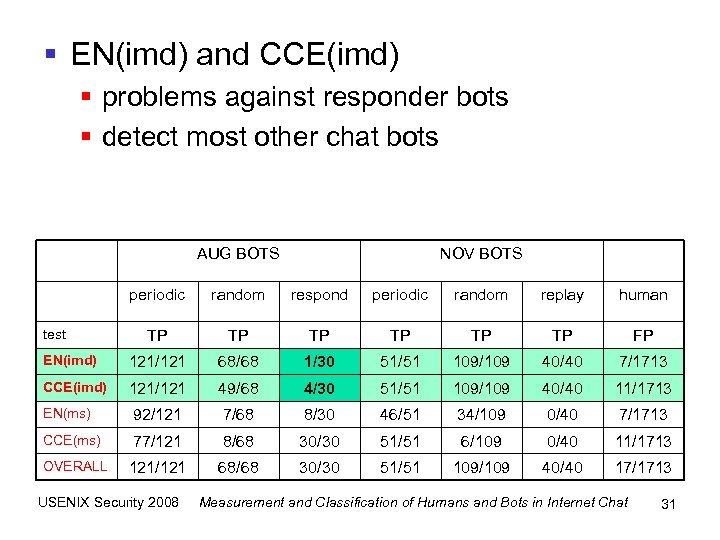
§ EN(imd) and CCE(imd) § problems against responder bots § detect most other chat bots AUG BOTS NOV BOTS periodic random respond periodic random replay human TP TP TP FP EN(imd) 121/121 68/68 1/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 7/1713 CCE(imd) 121/121 49/68 4/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 11/1713 EN(ms) 92/121 7/68 8/30 46/51 34/109 0/40 7/1713 CCE(ms) 77/121 8/68 30/30 51/51 6/109 0/40 11/1713 OVERALL 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 17/1713 test USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 31
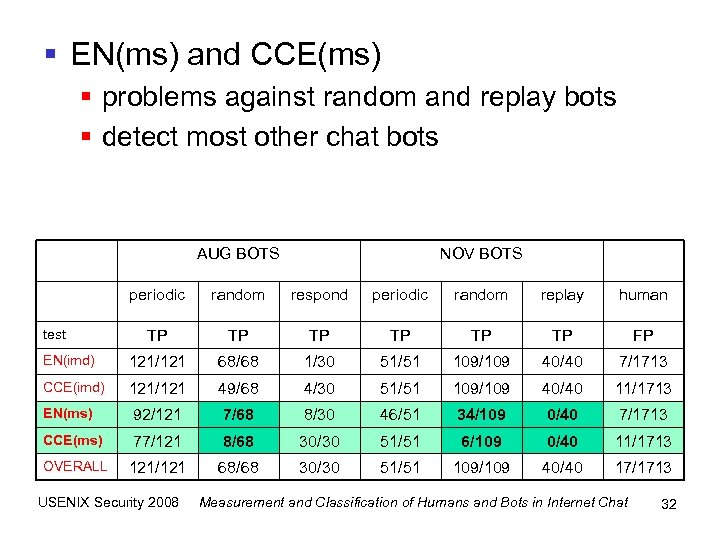
§ EN(ms) and CCE(ms) § problems against random and replay bots § detect most other chat bots AUG BOTS NOV BOTS periodic random respond periodic random replay human TP TP TP FP EN(imd) 121/121 68/68 1/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 7/1713 CCE(imd) 121/121 49/68 4/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 11/1713 EN(ms) 92/121 7/68 8/30 46/51 34/109 0/40 7/1713 CCE(ms) 77/121 8/68 30/30 51/51 6/109 0/40 11/1713 OVERALL 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 17/1713 test USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 32
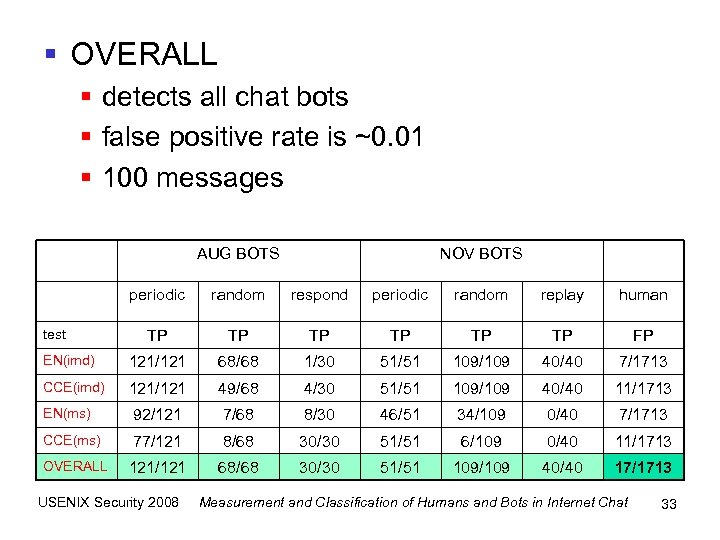
§ OVERALL § detects all chat bots § false positive rate is ~0. 01 § 100 messages AUG BOTS NOV BOTS periodic random respond periodic random replay human TP TP TP FP EN(imd) 121/121 68/68 1/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 7/1713 CCE(imd) 121/121 49/68 4/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 11/1713 EN(ms) 92/121 7/68 8/30 46/51 34/109 0/40 7/1713 CCE(ms) 77/121 8/68 30/30 51/51 6/109 0/40 11/1713 OVERALL 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 17/1713 test USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 33
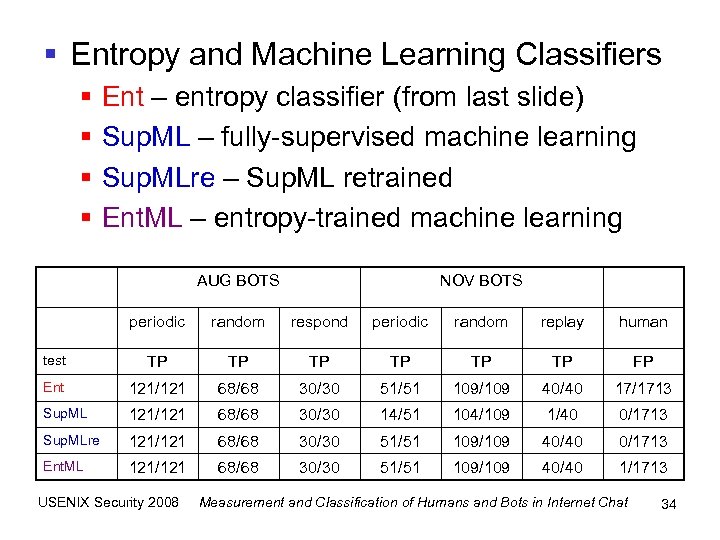
§ Entropy and Machine Learning Classifiers § § Ent – entropy classifier (from last slide) Sup. ML – fully-supervised machine learning Sup. MLre – Sup. ML retrained Ent. ML – entropy-trained machine learning AUG BOTS NOV BOTS periodic random respond periodic random replay human test TP TP TP FP Ent 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 17/1713 Sup. ML 121/121 68/68 30/30 14/51 104/109 1/40 0/1713 Sup. MLre 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 0/1713 Ent. ML 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 1/1713 USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 34
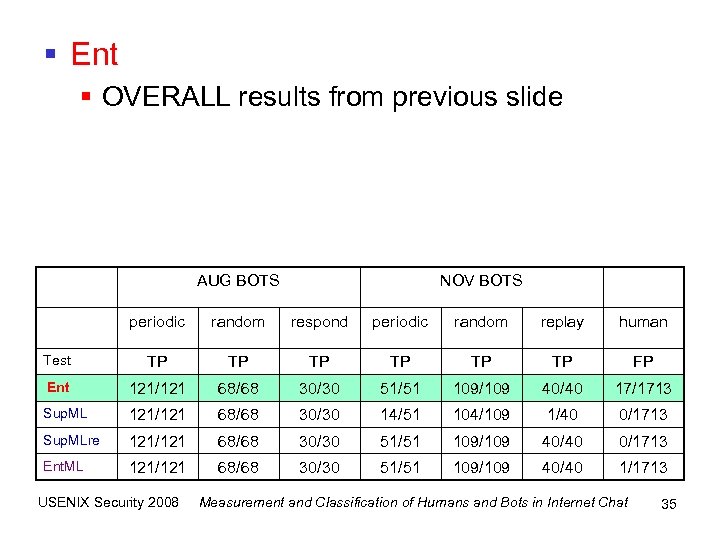
§ Ent § OVERALL results from previous slide AUG BOTS NOV BOTS periodic random respond periodic random replay human Test TP TP TP FP Ent 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 17/1713 Sup. ML 121/121 68/68 30/30 14/51 104/109 1/40 0/1713 Sup. MLre 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 0/1713 Ent. ML 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 1/1713 USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 35
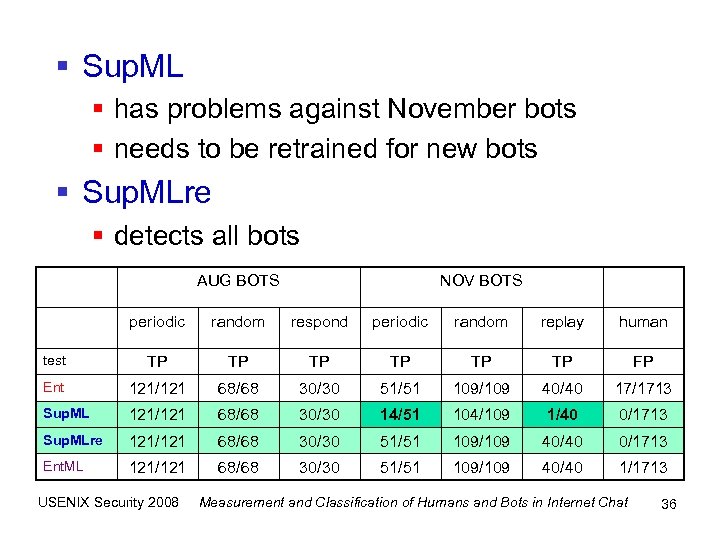
§ Sup. ML § has problems against November bots § needs to be retrained for new bots § Sup. MLre § detects all bots AUG BOTS NOV BOTS periodic random respond periodic random replay human test TP TP TP FP Ent 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 17/1713 Sup. ML 121/121 68/68 30/30 14/51 104/109 1/40 0/1713 Sup. MLre 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 0/1713 Ent. ML 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 1/1713 USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 36
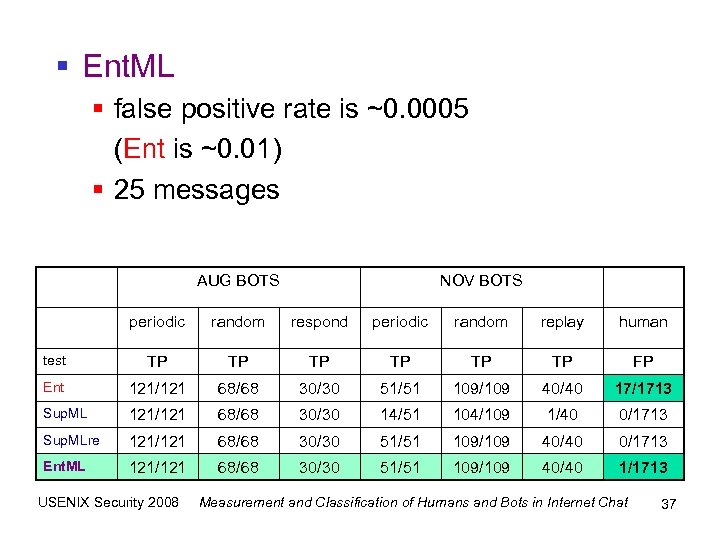
§ Ent. ML § false positive rate is ~0. 0005 (Ent is ~0. 01) § 25 messages AUG BOTS NOV BOTS periodic random respond periodic random replay human test TP TP TP FP Ent 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 17/1713 Sup. ML 121/121 68/68 30/30 14/51 104/109 1/40 0/1713 Sup. MLre 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 0/1713 Ent. ML 121/121 68/68 30/30 51/51 109/109 40/40 1/1713 USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 37

Outline § § § Background Measurement Classification System Experimental Evaluation Conclusion USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 38
Conclusion § Measurements § overall, chat bots are less complex than humans § some chat bots more human-like § Classification System § exploits benefits of both classifiers § quickly classifies known chat bots § accurately classifies unknown chat bots USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 39
Conclusion (cont. ) § Future Work § investigate more advanced chat bots § explore applications of entropy on other forms of bots (e. g. , web bots) § explore other applications of entropy (e. g. , detecting covert timing channels) USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 40

Questions? Thank You! USENIX Security 2008 Measurement and Classification of Humans and Bots in Internet Chat 41
c14363910be044f1143114fb37fad7e8.ppt