Means, causing drug dependence.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 23

MEANS, CAUSING DRUG DEPENDENCE Made by: Kalambekov Merey Group: General Medicine 13 -045

DEFINITIONS • Drug Use -Taking a psychoactive substance for non-medical purposes, out of curiosity • Drug Abuse -Drug use that leads to problems (e. g. loss of effectiveness in society; behavioral psychopathology, criminal acts) • Drug Dependence -A maladaptive pattern of drug use leading to clinically-significant impairment or distress, associated with difficulty in controlling drug-taking behavior, withdrawal, and tolerance -The state of needing a drug to function within ‘normal limits’
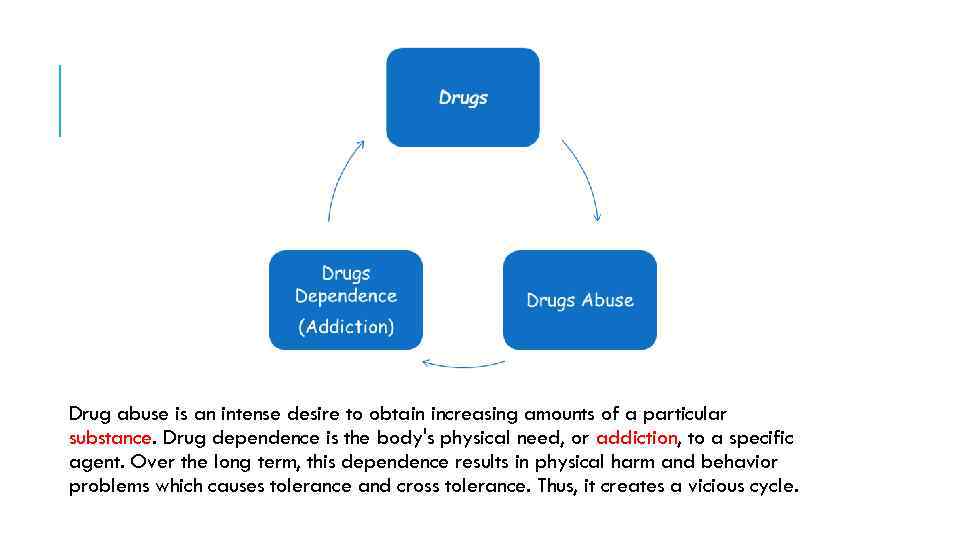
Drug abuse is an intense desire to obtain increasing amounts of a particular substance. Drug dependence is the body's physical need, or addiction, to a specific agent. Over the long term, this dependence results in physical harm and behavior problems which causes tolerance and cross tolerance. Thus, it creates a vicious cycle.

CRITERIAS FOR SUBSTANCE DEPENDENCE • Tolerance • Withdrawal • Substance taken in larger amounts or over a longer period than intended • Persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control substance use • Great deal of time spent in activities necessary to obtain substance, use substance (e. g. , chain smoking), or recover from effects • Important social, occupational, or recreational activities given up or reduced because of substance use • Substance use continued despite knowledge of persistent or recurrent physical or psychological problem likely to have been caused or exacerbated by substance

PHYSICAL VS. PSYCHOLOGICAL DEPENDENCE Physical Dependence Withdrawal symptoms in the absence of the drug Tolerance to its effects with repeated use Psychological Dependence “a relatively extreme, pathological state in which obtaining, taking, and recovering from a drug represents a loss of behavioral control over drug taking which occurs at the expense of most other activities and despite adverse consequences” (Altman et al) “a situation where drug procurement and administration appear to govern the organism’s behavior, and where the drug seems to dominate the organism’s motivational hierarchy” (Bozarth)
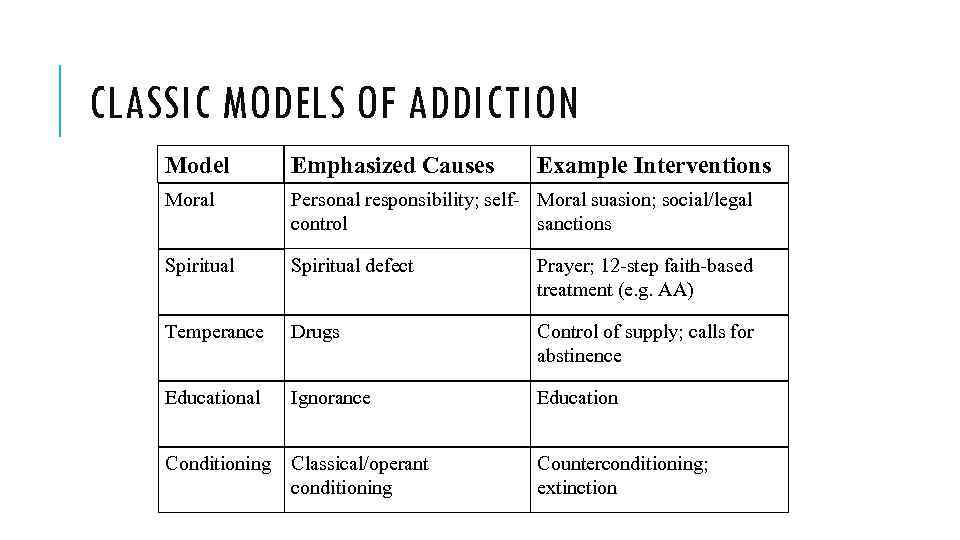
CLASSIC MODELS OF ADDICTION Model Emphasized Causes Example Interventions Moral Personal responsibility; self- Moral suasion; social/legal control sanctions Spiritual defect Prayer; 12 -step faith-based treatment (e. g. AA) Temperance Drugs Control of supply; calls for abstinence Educational Ignorance Education Conditioning Classical/operant conditioning Counterconditioning; extinction
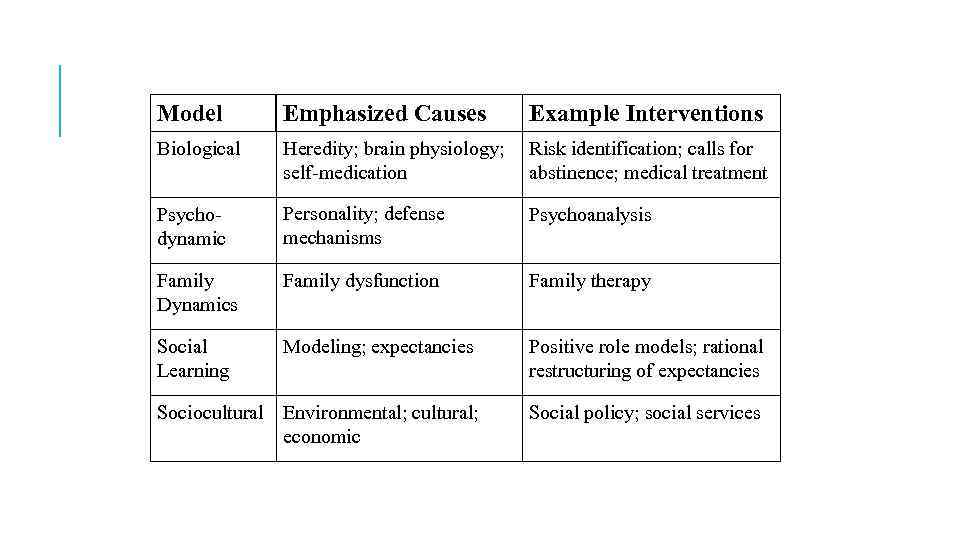
Model Emphasized Causes Example Interventions Biological Heredity; brain physiology; self-medication Risk identification; calls for abstinence; medical treatment Psychodynamic Personality; defense mechanisms Psychoanalysis Family Dynamics Family dysfunction Family therapy Social Learning Modeling; expectancies Positive role models; rational restructuring of expectancies Sociocultural Environmental; cultural; economic Social policy; social services

PHYSICAL DEPENDENCE • Some drugs produce physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation of drug-taking. – Withdrawal symptoms are produced by the body in order to compensate for the unusual effects of the drug. – Withdrawal symptoms are generally the opposite of the effect produced by the drug. • Addicts continue to use drugs in order to avoid withdrawal. • Over time, drugs no longer have the same rewarding effects - they merely allow the person to feel “normal. ”

INADEQUACIES OF PHYSICAL DEPENDENCE ØNot all abused drugs generate withdrawal symptoms (cocaine, amphetamine). ØDifferent drugs produce different withdrawal symptoms with different neural bases. ØOnce dependent you should continue taking drug, but people spontaneously stop. ØOnce drug-abstinent, users should not relapse since motivation has disappeared, but they do. ØNo explanation as to why people take drugs in the first place.
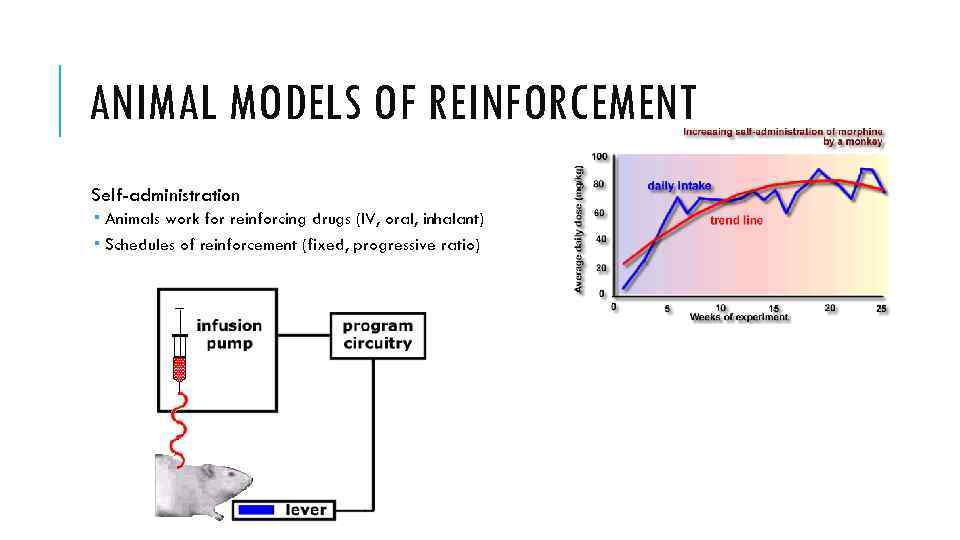
ANIMAL MODELS OF REINFORCEMENT Self-administration Animals work for reinforcing drugs (IV, oral, inhalant) Schedules of reinforcement (fixed, progressive ratio)

DRUGS THAT ARE AND ARE NOT SELF ADMINISTERED BY ANIMALS ØAlcohol ØAmphetamine ØBarbiturates ØCaffeine ØCocaine ØNicotine ØOpiates ØProcaine (n. a. by humans) ØPCP ØTHC Ø Ø Imipramine Mescaline (abused by humans) Phenothiazines Scopolamine
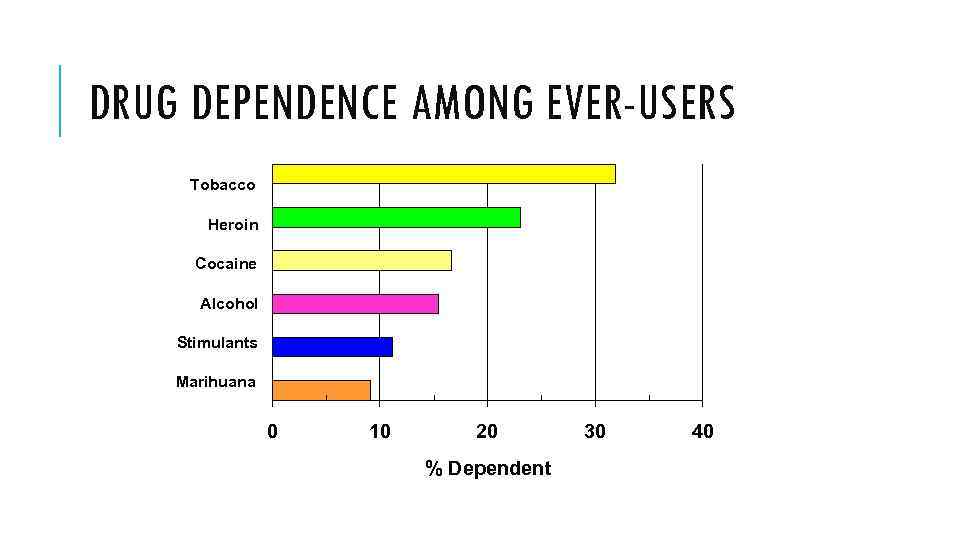
DRUG DEPENDENCE AMONG EVER-USERS Tobacco Heroin Cocaine Alcohol Stimulants Marihuana 0 10 20 % Dependent 30 40
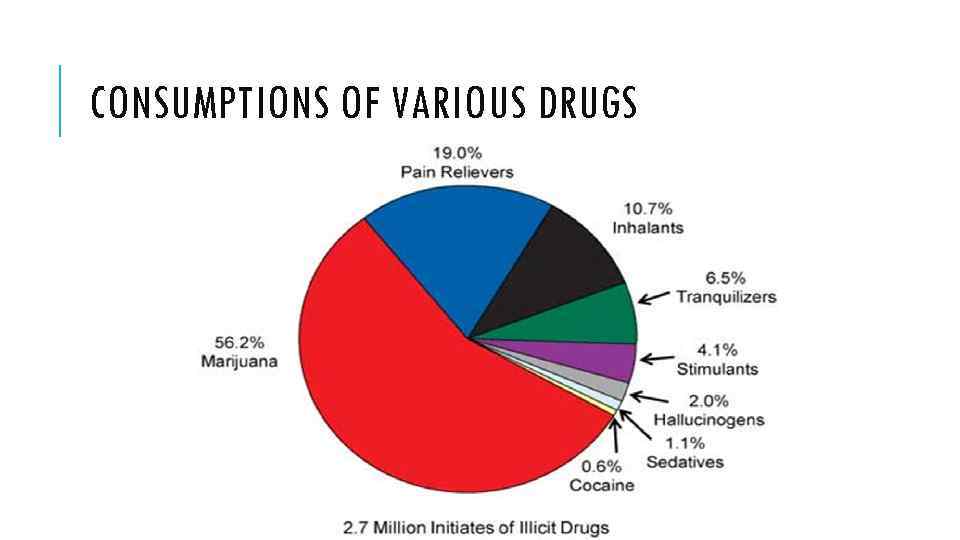
CONSUMPTIONS OF VARIOUS DRUGS
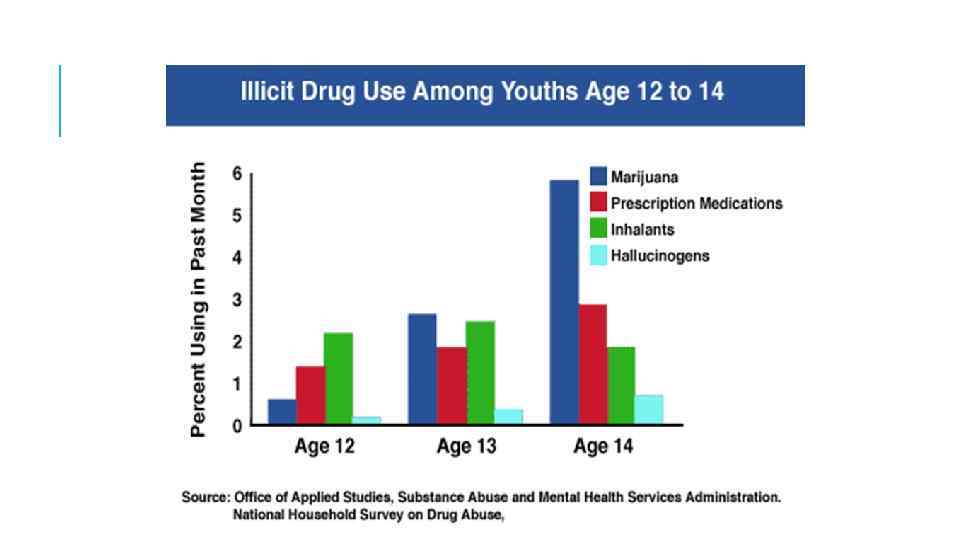

WHY DO SO MANY TEENAGERS START DOWN THIS POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS PATH ?
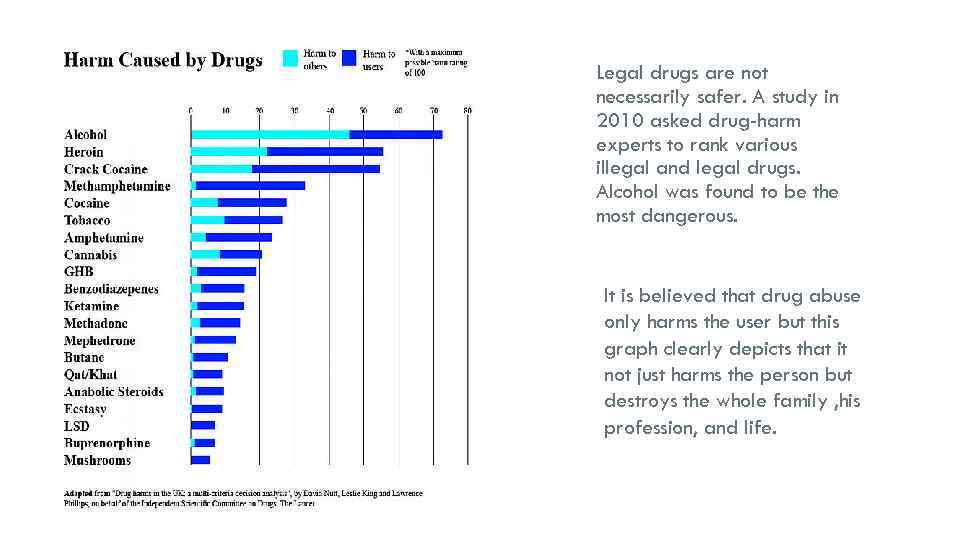
Legal drugs are not necessarily safer. A study in 2010 asked drug-harm experts to rank various illegal and legal drugs. Alcohol was found to be the most dangerous. It is believed that drug abuse only harms the user but this graph clearly depicts that it not just harms the person but destroys the whole family , his profession, and life.

STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF DRUG DEPENDENCE ØStage 1 - the first experience ØStage 2 - beginning to like ØStage 3 - there is a problem ØStage 4 - the use becomes the target

FIRST EXPERIENCE This stage is characterized by: §Natural curiosity, a desire to "just try it"; §Active search for new types of buzz; §Inability to say "NO"; §Difficulty understanding their own borders; §Falling under the influence of various myths about chemicals; §Fear of being branded as "black sheep" or "mama's boy"; §Unconscious desire to escape from the complexities of life (or conscious); §Care attitude to himself, to his life, "apathy" as a worldview; §The desire to make your life interesting and filled; §Not knowing how to actually act on the psyche of the surfactant and the human body.

STARTING TO LIKE This stage is characterized by: Conscious desire to get "high" using drugs; Planning consumption; Search reasonable excuses use; Search for "suitable" companies; Drugs become a necessary attribute of fun and relaxation; Starting to use drugs as - Remedy against "complexes"; - A cure for stress; - Mode of communication; - Companion of sexual relations; "Growth" the dose required to obtain the desired sensations; Formed a special "get-together" - a drug, its music, fashion, humor.

THERE IS A PROBLEM This stage is characterized by: ØHealth Problems (hangover, smashing, discomfort after consuming drugs, infectious diseases); ØLoss of control over behavior (trauma, violence, crime); ØPromiscuous sex (sexually transmitted diseases, unwanted pregnancy, relationship problems); ØScandals in the family; ØProblems with studies, trouble in schools (school, college, university); ØFinancial difficulties (debts, selling things from the house, the constant search for money, theft); ØConflicts with friends;

USE BECOMES THE TARGET This stage is characterized by: ØUsing for use; ØThe constant need for drugs; ØUsing extreme means and methods of searching dose; ØThe destruction of moral values; ØApathy and unwillingness to live, the loss of the meaning of existence; ØSuicide attempts; ØSerious health problems, the occurrence of chronic diseases; ØBreak with the family, friends and society; ØIsolation, «сlosed in itself"; ØTHE DEATH.

REFERENCES ØNeverovič N. E. , N. V. Shkarina, Yatsnitskaya A. V. I choose life. Correspondence conversation about teen life and drugs - St. Petersburg, 2003 - 40. ØPerezhogin L. O. , Kryukov S. V. Drug prevention in children and adolescents - M. , 2005 - 10. ØTerentyeva A. V. Lagutin O. V. , Molev E. I. Whose choice? - M. Foundation, National Academy of Sciences, 2008 - 18. ØPharmocology D. A. Kharkeevich 2005, 76.

DO NOT USE DRUGS!!! YOU CAN DIE!!!
Means, causing drug dependence.pptx