 Meanings
Meanings
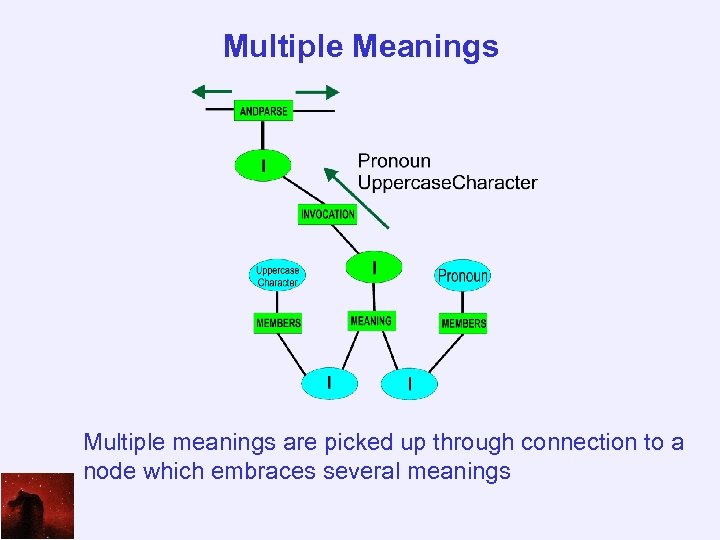 Multiple Meanings Multiple meanings are picked up through connection to a node which embraces several meanings
Multiple Meanings Multiple meanings are picked up through connection to a node which embraces several meanings
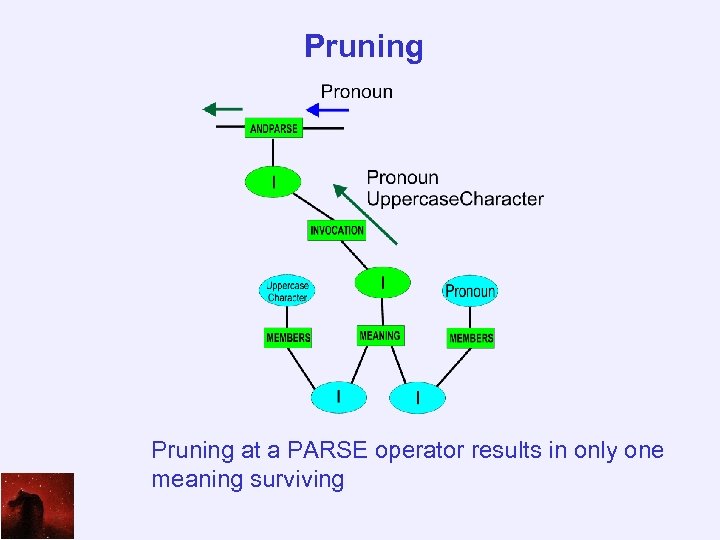 Pruning at a PARSE operator results in only one meaning surviving
Pruning at a PARSE operator results in only one meaning surviving
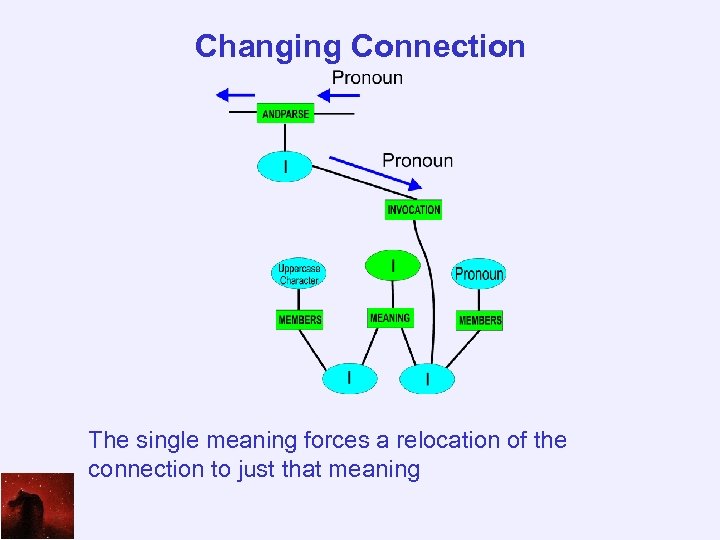 Changing Connection The single meaning forces a relocation of the connection to just that meaning
Changing Connection The single meaning forces a relocation of the connection to just that meaning
 Why Change? Changing the point of connection allows collocations and other properties that apply only to that meaning to become active
Why Change? Changing the point of connection allows collocations and other properties that apply only to that meaning to become active
 Dynamic Structure Some meaning structure needs to be dynamically created - we don’t have points of connection for every verb for Base Form Present Tense Third Person Singular Present Tense Third Person Plural Past Tense Present Participle Past Participle Adjectival Participle - only special cases like “to be” The points are created on demand when there are multiple meanings - noun or verb
Dynamic Structure Some meaning structure needs to be dynamically created - we don’t have points of connection for every verb for Base Form Present Tense Third Person Singular Present Tense Third Person Plural Past Tense Present Participle Past Participle Adjectival Participle - only special cases like “to be” The points are created on demand when there are multiple meanings - noun or verb
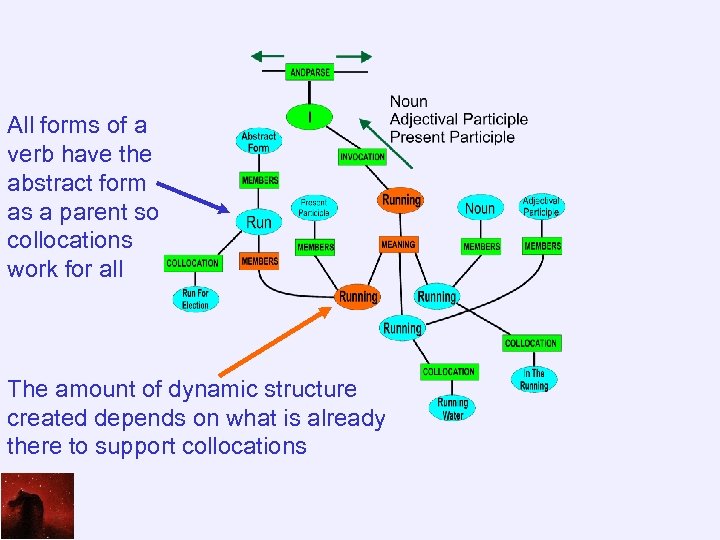 All forms of a verb have the abstract form as a parent so collocations work for all The amount of dynamic structure created depends on what is already there to support collocations
All forms of a verb have the abstract form as a parent so collocations work for all The amount of dynamic structure created depends on what is already there to support collocations
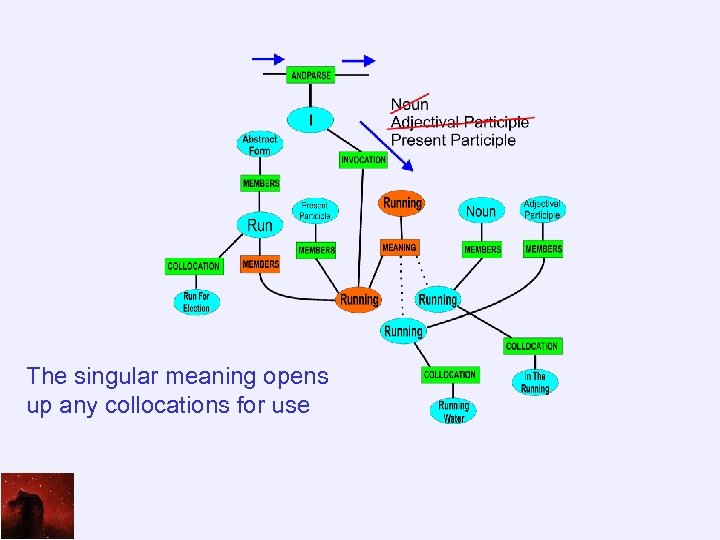 The singular meaning opens up any collocations for use
The singular meaning opens up any collocations for use
 Multiple Meanings
Multiple Meanings
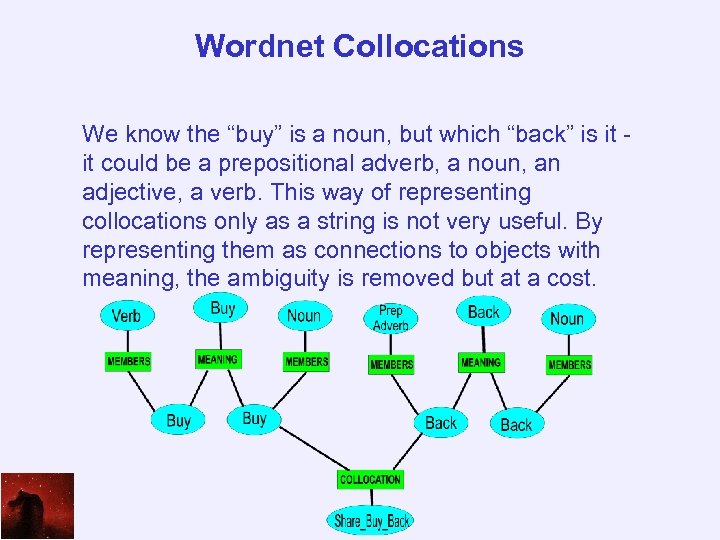 Wordnet Collocations We know the “buy” is a noun, but which “back” is it it could be a prepositional adverb, a noun, an adjective, a verb. This way of representing collocations only as a string is not very useful. By representing them as connections to objects with meaning, the ambiguity is removed but at a cost.
Wordnet Collocations We know the “buy” is a noun, but which “back” is it it could be a prepositional adverb, a noun, an adjective, a verb. This way of representing collocations only as a string is not very useful. By representing them as connections to objects with meaning, the ambiguity is removed but at a cost.
 Efficiency
Efficiency