 Meaning of Psychology, Sociology, Educational Psychology, and Sociology of Education
Meaning of Psychology, Sociology, Educational Psychology, and Sociology of Education
 Education • Education has been derive from the Latin word “EDUCARE” which means to rear, to nourish, to bring up, to train”
Education • Education has been derive from the Latin word “EDUCARE” which means to rear, to nourish, to bring up, to train”
 Education • Education consists of building up in the individual an organization of knowledge and skills, habit and attitudes of values and ideals which will aid in fulfilling life’s purposes. • It must develop • Is an active process
Education • Education consists of building up in the individual an organization of knowledge and skills, habit and attitudes of values and ideals which will aid in fulfilling life’s purposes. • It must develop • Is an active process
 Education • The fundamental aim of education is to help each individual to make of himself all that it is possible for him to become.
Education • The fundamental aim of education is to help each individual to make of himself all that it is possible for him to become.
 PSYCHOLOGY • Come from the Greek word psukhe and behaviour “soul” and logos “study of”. • Study of mental function and behaviour. • Study of the human personality
PSYCHOLOGY • Come from the Greek word psukhe and behaviour “soul” and logos “study of”. • Study of mental function and behaviour. • Study of the human personality
 Psychologist • A social, behavioural or cognitive scientist. • Attempt to understand the role of mental functions in individual and social behaviour.
Psychologist • A social, behavioural or cognitive scientist. • Attempt to understand the role of mental functions in individual and social behaviour.
 Educational psychology • The application of the scientific knowledge concerning human personality to the process of teaching, that is, to the motivation, direction, control, and evaluation of learning.
Educational psychology • The application of the scientific knowledge concerning human personality to the process of teaching, that is, to the motivation, direction, control, and evaluation of learning.
 SOCIOLOGY • Sociology came from the Latin word SOCIUS “companion”, OLOGY “the study of”, LOGOS “word, knowledge”. • The study of the nature, origin and development of human society. • It was first coin in 1780 by the French essayist EMMANUEL JOSEPH SEIYES (1748 -1836)
SOCIOLOGY • Sociology came from the Latin word SOCIUS “companion”, OLOGY “the study of”, LOGOS “word, knowledge”. • The study of the nature, origin and development of human society. • It was first coin in 1780 by the French essayist EMMANUEL JOSEPH SEIYES (1748 -1836)
 Educational Sociology • Is the study of how public institutions and individual experiences affect education and its outcomes
Educational Sociology • Is the study of how public institutions and individual experiences affect education and its outcomes
 Nature and Fundamental equipment of the learner.
Nature and Fundamental equipment of the learner.
 Sensation • Sensation is defined as the conscious processes which are the immediate results of the stimulation of the sense organs, by which means of which man becomes aware of existence and properties of particular objects which stimulate senses to actions.
Sensation • Sensation is defined as the conscious processes which are the immediate results of the stimulation of the sense organs, by which means of which man becomes aware of existence and properties of particular objects which stimulate senses to actions.
 • Sensation is the first source of all knowledge, without sensation there would be nothing to converted into knowledge.
• Sensation is the first source of all knowledge, without sensation there would be nothing to converted into knowledge.
 Necessary conditions of sensation are: Physical Physiological Psychological
Necessary conditions of sensation are: Physical Physiological Psychological
 Three attributes of sensation are: • Intensity • Quality • Duration
Three attributes of sensation are: • Intensity • Quality • Duration
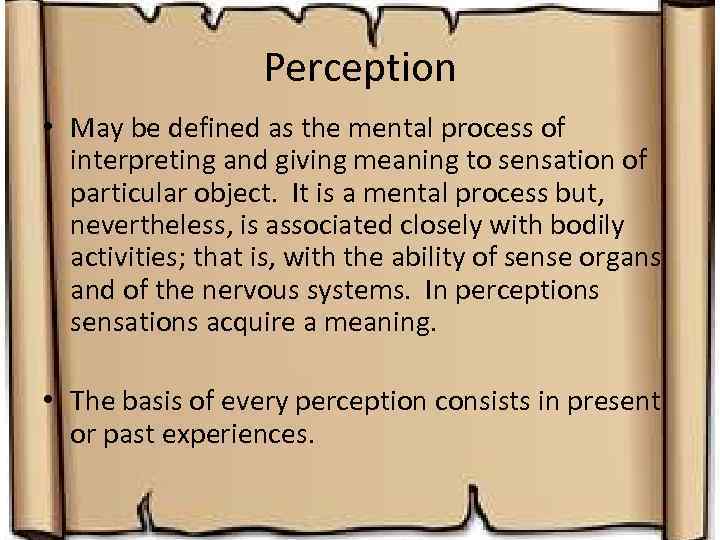 Perception • May be defined as the mental process of interpreting and giving meaning to sensation of particular object. It is a mental process but, nevertheless, is associated closely with bodily activities; that is, with the ability of sense organs and of the nervous systems. In perceptions sensations acquire a meaning. • The basis of every perception consists in present or past experiences.
Perception • May be defined as the mental process of interpreting and giving meaning to sensation of particular object. It is a mental process but, nevertheless, is associated closely with bodily activities; that is, with the ability of sense organs and of the nervous systems. In perceptions sensations acquire a meaning. • The basis of every perception consists in present or past experiences.
 Imagination • The mental power of forming representations of material objects which are not actually present to the senses.
Imagination • The mental power of forming representations of material objects which are not actually present to the senses.
 • The training, direction, and guidance of the child’s imagination is one of the teachers most important task.
• The training, direction, and guidance of the child’s imagination is one of the teachers most important task.
 • Two function of Imagination – Reproductive – Constructive Hyperphantasy- over extravagant activity of the Imagination
• Two function of Imagination – Reproductive – Constructive Hyperphantasy- over extravagant activity of the Imagination
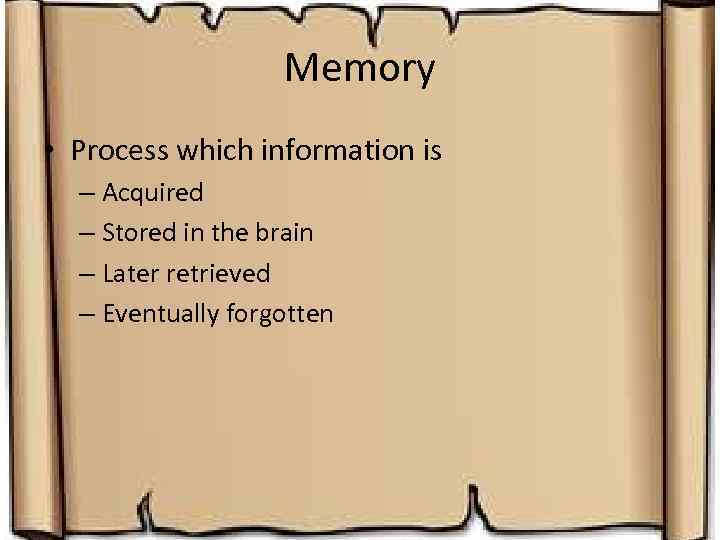 Memory • Process which information is – Acquired – Stored in the brain – Later retrieved – Eventually forgotten
Memory • Process which information is – Acquired – Stored in the brain – Later retrieved – Eventually forgotten
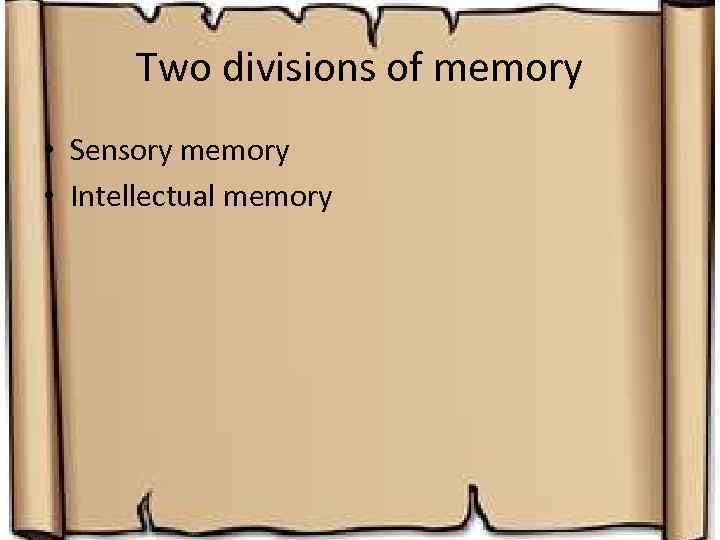 Two divisions of memory • Sensory memory • Intellectual memory
Two divisions of memory • Sensory memory • Intellectual memory
 Basic Factors to the Learner Growth and Development • Maturation • Environment
Basic Factors to the Learner Growth and Development • Maturation • Environment