3b9ed19cdec9ff0c06cbf3e50e22c57d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Me, VANGOGH, and Game Development
Me, VANGOGH, and Game Development
 Me • Started at UMBC in 2002 (CMSC 104) • Undergraduate Research in DIADIC lab (data mining) • Received BS in CMSC, 2006 (Minors in Math and Philosophy) • Started MS program in 2006 in VANGOGH lab • Multiple TA/RA – TA for Computer Security (CMSC 426/626), Cryptography (CMSC 443), Computer Graphics (CMSC 435) – RA for high-quality, fast volume rendering (NSF grant) – RA on LINES project • 2 published graphics papers (3 more in the works) • 2 nd year in game development (Firaxis)
Me • Started at UMBC in 2002 (CMSC 104) • Undergraduate Research in DIADIC lab (data mining) • Received BS in CMSC, 2006 (Minors in Math and Philosophy) • Started MS program in 2006 in VANGOGH lab • Multiple TA/RA – TA for Computer Security (CMSC 426/626), Cryptography (CMSC 443), Computer Graphics (CMSC 435) – RA for high-quality, fast volume rendering (NSF grant) – RA on LINES project • 2 published graphics papers (3 more in the works) • 2 nd year in game development (Firaxis)
 VANGOGH • Graphics lab at UMBC – ITE 352 • 2 faculty members – Dr. Rheingans – visualization – Dr. Olano – real-time graphics • I joined in 2005 – and loving it! • Join us at our lab meetings: – Wednesday, 10: 30 am, ITE 352
VANGOGH • Graphics lab at UMBC – ITE 352 • 2 faculty members – Dr. Rheingans – visualization – Dr. Olano – real-time graphics • I joined in 2005 – and loving it! • Join us at our lab meetings: – Wednesday, 10: 30 am, ITE 352
 RESEARCH • Undergraduate Thesis “Pre-computed Radiance Transfer Fur over Arbitrary Surfaces” • John Kloetzli, Brian Strege, Jonathan Decker, and Marc Olano - “Leveraging Graphics Hardware to Accelerate Dynamic Programming” to be published in EGPGV ’ 08, EUROGRAPHICS assc. • John Kloetzli, Marc Olano, Penny Rheingans – “Interactive Volume Isosurface Rendering Using BT Volumes” i 3 D 2008, ACM SIGGRAPH
RESEARCH • Undergraduate Thesis “Pre-computed Radiance Transfer Fur over Arbitrary Surfaces” • John Kloetzli, Brian Strege, Jonathan Decker, and Marc Olano - “Leveraging Graphics Hardware to Accelerate Dynamic Programming” to be published in EGPGV ’ 08, EUROGRAPHICS assc. • John Kloetzli, Marc Olano, Penny Rheingans – “Interactive Volume Isosurface Rendering Using BT Volumes” i 3 D 2008, ACM SIGGRAPH
 MRI Data
MRI Data
 MRI Data
MRI Data
 Image: Segami Corporation
Image: Segami Corporation
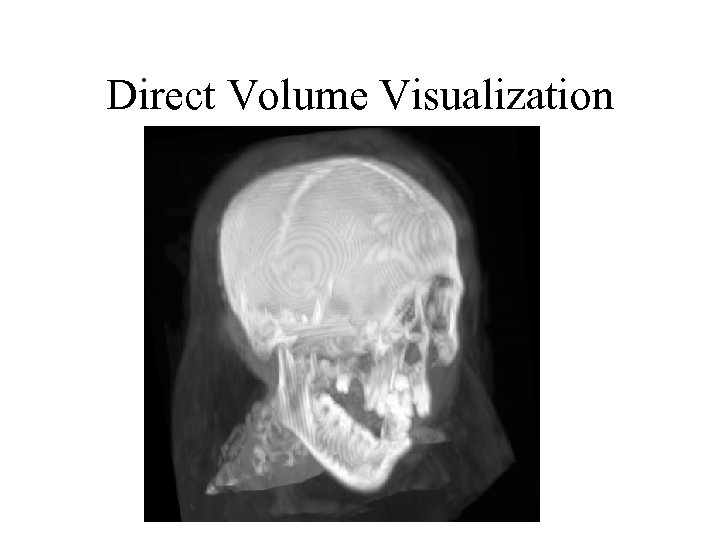 Direct Volume Visualization
Direct Volume Visualization
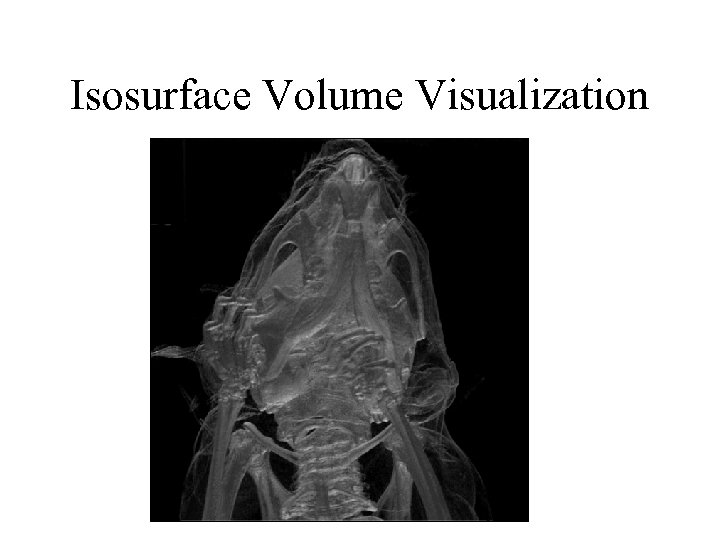 Isosurface Volume Visualization
Isosurface Volume Visualization
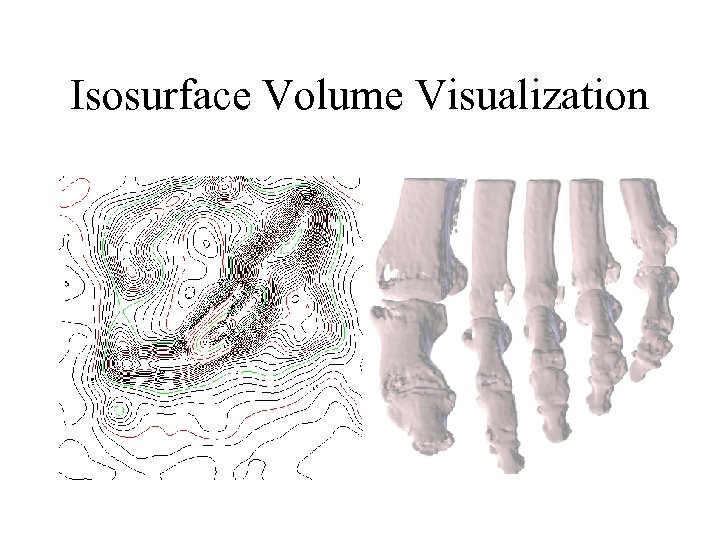 Isosurface Volume Visualization
Isosurface Volume Visualization
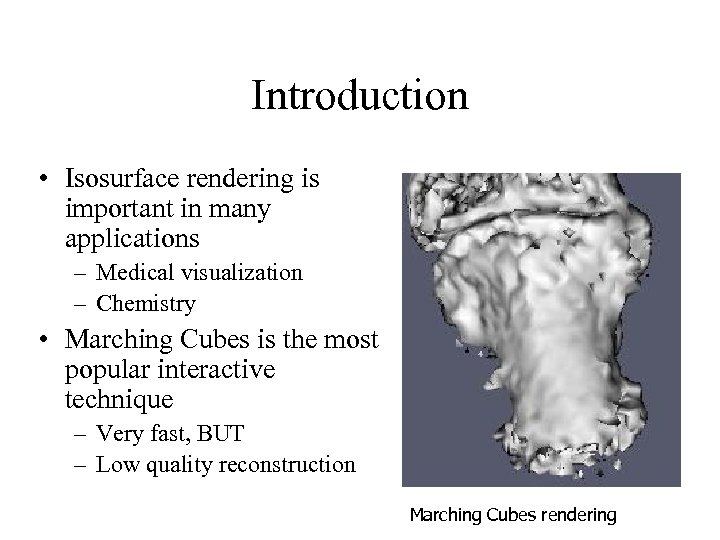 Introduction • Isosurface rendering is important in many applications – Medical visualization – Chemistry • Marching Cubes is the most popular interactive technique – Very fast, BUT – Low quality reconstruction Marching Cubes rendering
Introduction • Isosurface rendering is important in many applications – Medical visualization – Chemistry • Marching Cubes is the most popular interactive technique – Very fast, BUT – Low quality reconstruction Marching Cubes rendering
 Introduction (cont) • BT Volumes can do better than MC – Interactive frame rates – Isosurface level changed on the fly – High-quality reconstruction – Many filters possible BT Volume rendering
Introduction (cont) • BT Volumes can do better than MC – Interactive frame rates – Isosurface level changed on the fly – High-quality reconstruction – Many filters possible BT Volume rendering
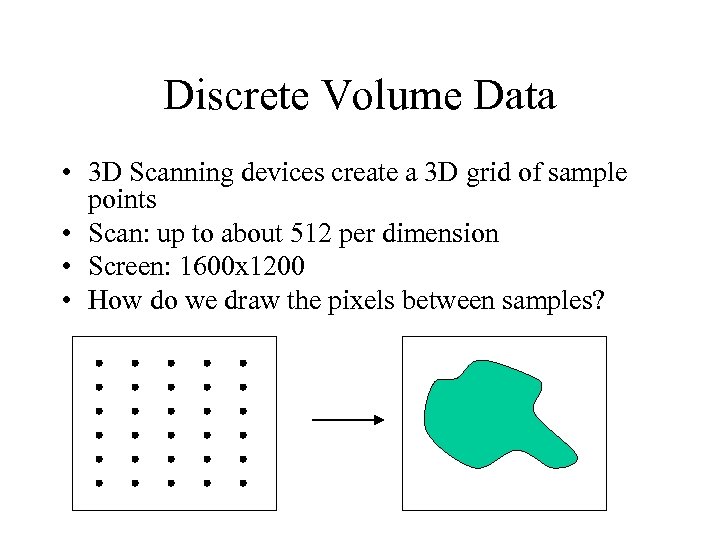 Discrete Volume Data • 3 D Scanning devices create a 3 D grid of sample points • Scan: up to about 512 per dimension • Screen: 1600 x 1200 • How do we draw the pixels between samples?
Discrete Volume Data • 3 D Scanning devices create a 3 D grid of sample points • Scan: up to about 512 per dimension • Screen: 1600 x 1200 • How do we draw the pixels between samples?
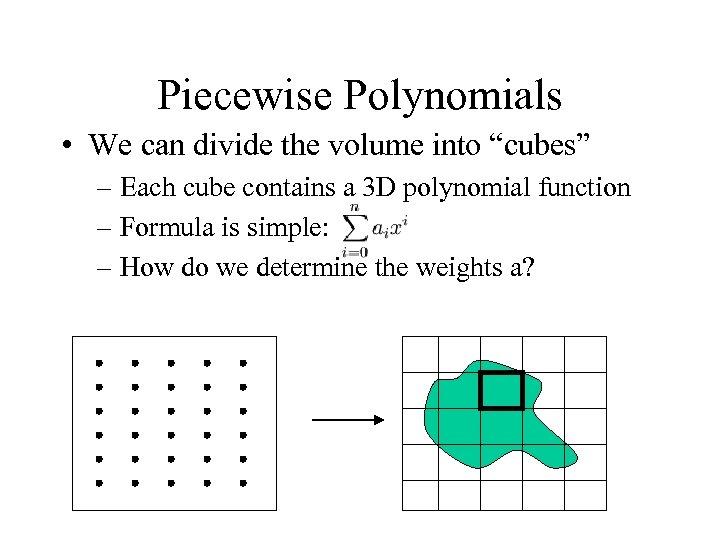 Piecewise Polynomials • We can divide the volume into “cubes” – Each cube contains a 3 D polynomial function – Formula is simple: – How do we determine the weights a?
Piecewise Polynomials • We can divide the volume into “cubes” – Each cube contains a 3 D polynomial function – Formula is simple: – How do we determine the weights a?
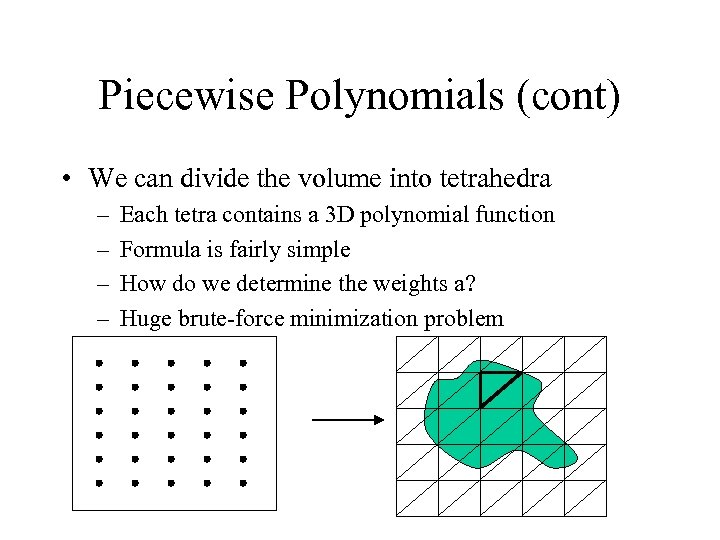 Piecewise Polynomials (cont) • We can divide the volume into tetrahedra – – Each tetra contains a 3 D polynomial function Formula is fairly simple How do we determine the weights a? Huge brute-force minimization problem
Piecewise Polynomials (cont) • We can divide the volume into tetrahedra – – Each tetra contains a 3 D polynomial function Formula is fairly simple How do we determine the weights a? Huge brute-force minimization problem
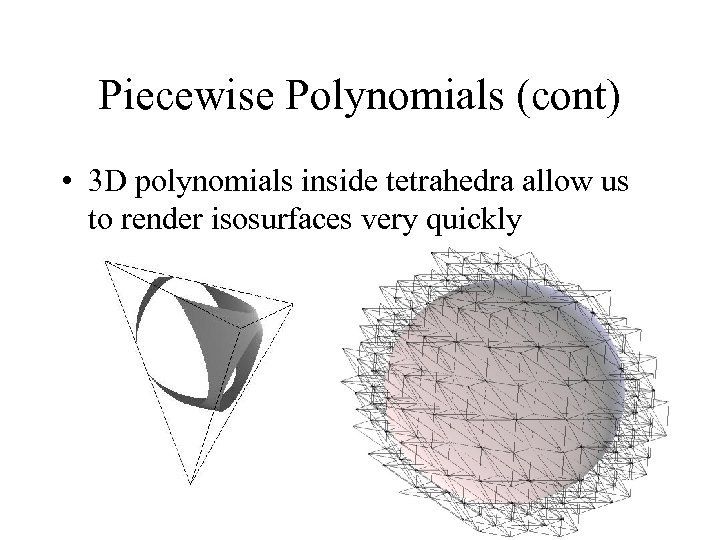 Piecewise Polynomials (cont) • 3 D polynomials inside tetrahedra allow us to render isosurfaces very quickly
Piecewise Polynomials (cont) • 3 D polynomials inside tetrahedra allow us to render isosurfaces very quickly
 Contributions • Our main contribution is an elegant method for finding the weights for each polynomial • We also presented a real-time rendering algorithm which can display ANY isosurface level • Our algorithm is robust, automatic, and produces high-quality volume rendering
Contributions • Our main contribution is an elegant method for finding the weights for each polynomial • We also presented a real-time rendering algorithm which can display ANY isosurface level • Our algorithm is robust, automatic, and produces high-quality volume rendering
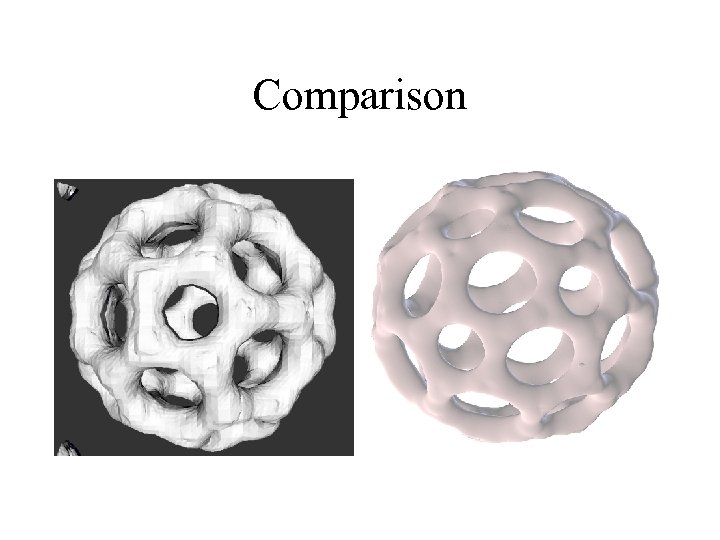 Comparison
Comparison
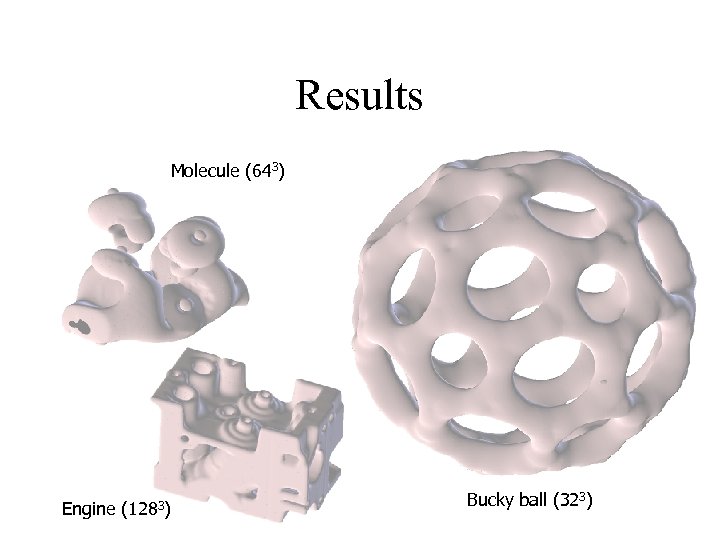 Results Molecule (643) Engine (1283) Bucky ball (323)
Results Molecule (643) Engine (1283) Bucky ball (323)
 Video
Video
 Research Questions? • Part 2: Game Development – A Case Study in Game Development problems
Research Questions? • Part 2: Game Development – A Case Study in Game Development problems
 Game Development • I have always wanted to be a game developer • Started at Firaxis part-time in summer 2006 – Sid Meiers Railroads! –worked on city system – Civilization Revolution • It really is that much fun!
Game Development • I have always wanted to be a game developer • Started at Firaxis part-time in summer 2006 – Sid Meiers Railroads! –worked on city system – Civilization Revolution • It really is that much fun!
 Railroads! • Railroad simulator • Player controls – – – Laying track Buying trains Creating cargo routes between cities/industries Buy/Sell stock Buyout opponent • Typical game development problem: City building placement algorithm
Railroads! • Railroad simulator • Player controls – – – Laying track Buying trains Creating cargo routes between cities/industries Buy/Sell stock Buyout opponent • Typical game development problem: City building placement algorithm

 What about Cities?
What about Cities?
 City Requirements • Iconic representation of a city – Big buildings in the middle – Small buildings outside – Different size cities • Buildings should not self -intersect • City should not follow “pattern”
City Requirements • Iconic representation of a city – Big buildings in the middle – Small buildings outside – Different size cities • Buildings should not self -intersect • City should not follow “pattern”
 City Requirements (2) • Cities cannot get in the way! • Player can build track through a city – How should the city react?
City Requirements (2) • Cities cannot get in the way! • Player can build track through a city – How should the city react?
 City Requirements (2) • Cities cannot get in the way! • Player can build track through a city – How should the city react? – Our take: City should “move” around track – How can this be done?
City Requirements (2) • Cities cannot get in the way! • Player can build track through a city – How should the city react? – Our take: City should “move” around track – How can this be done?
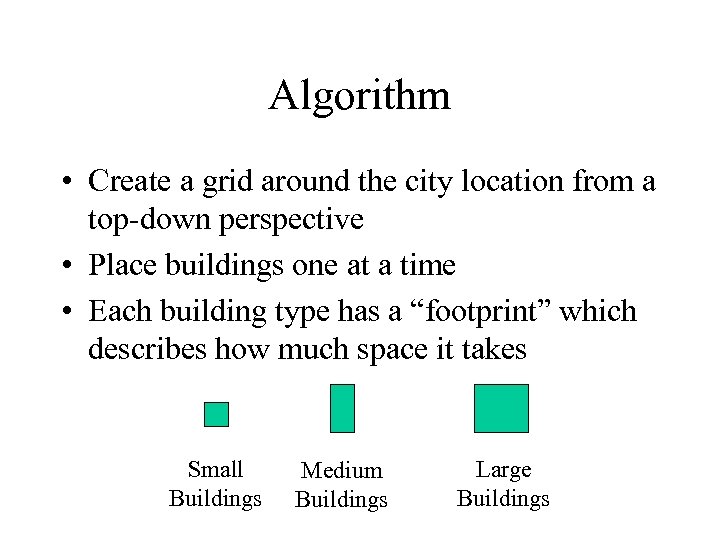 Algorithm • Create a grid around the city location from a top-down perspective • Place buildings one at a time • Each building type has a “footprint” which describes how much space it takes Small Buildings Medium Buildings Large Buildings
Algorithm • Create a grid around the city location from a top-down perspective • Place buildings one at a time • Each building type has a “footprint” which describes how much space it takes Small Buildings Medium Buildings Large Buildings
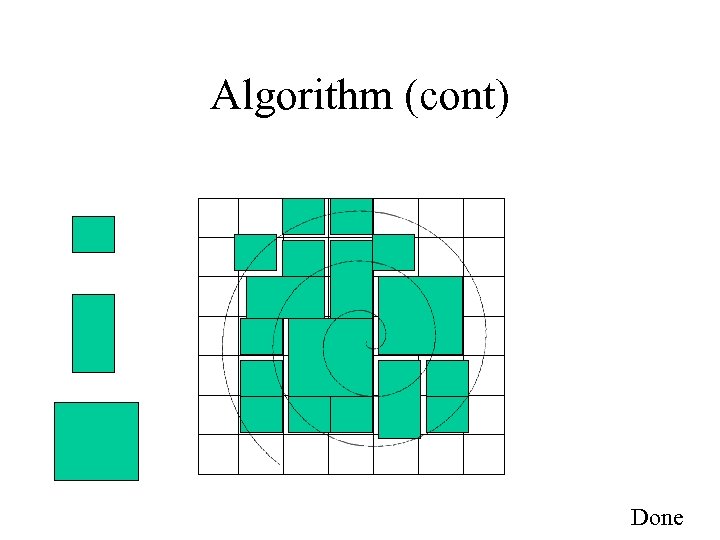 Algorithm (cont) Done
Algorithm (cont) Done
 Algorithm (cont) • Draw the city by randomly choosing a building model from each building type • This will give basic city shape BUT… – What about terrain? (steep/rivers) – What about the tracks? • Solution: Before building city, mark grid cells which are “blocked” by terrain or track – Then create the city in the same way
Algorithm (cont) • Draw the city by randomly choosing a building model from each building type • This will give basic city shape BUT… – What about terrain? (steep/rivers) – What about the tracks? • Solution: Before building city, mark grid cells which are “blocked” by terrain or track – Then create the city in the same way
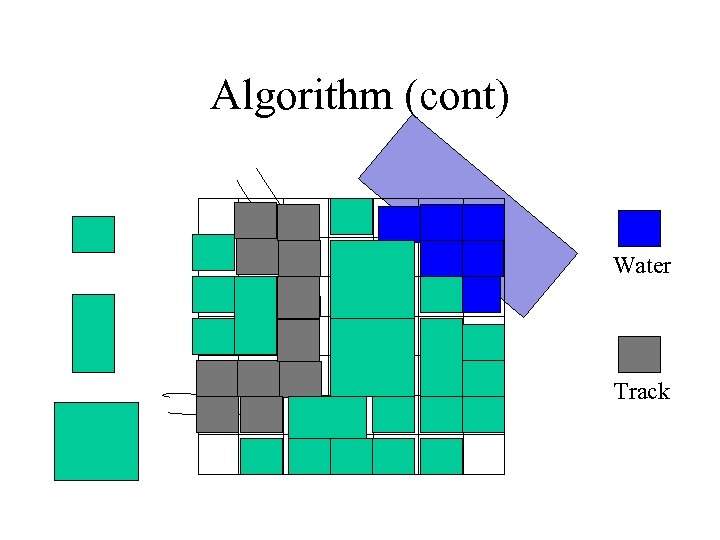 Algorithm (cont) Water Track
Algorithm (cont) Water Track

 Results • Advantages: – Works around all obstacles – Fast enough to re-run per frame – Maintains city “pyramid” shape
Results • Advantages: – Works around all obstacles – Fast enough to re-run per frame – Maintains city “pyramid” shape
 Results (cont) • Disadvantages: – Building types can change when the city is rebuilt – Can be jarring (this can be fixed somewhat by fixing the number and type of large buildings)
Results (cont) • Disadvantages: – Building types can change when the city is rebuilt – Can be jarring (this can be fixed somewhat by fixing the number and type of large buildings)
 Recommendations • If you want to do research… – PAY ATTENTION to algorithms! – Don’t be afraid of MATH • If you want to be a game developer… – Learn C/C++ COMPLETELY – Know how to write low-level code – Know memory management
Recommendations • If you want to do research… – PAY ATTENTION to algorithms! – Don’t be afraid of MATH • If you want to be a game developer… – Learn C/C++ COMPLETELY – Know how to write low-level code – Know memory management


