c86017fe1caa97df8dc0f421a751dd86.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 76

 Me on the first “Pink Thursday”
Me on the first “Pink Thursday”
 Review • What is definition of Economics • What are needs • What is the difference between universal and nonuniversal needs • What are wants • What is difference between Micro and Macro economics? • What is the difference between scarcity and shortage? • What is basic economic truth?
Review • What is definition of Economics • What are needs • What is the difference between universal and nonuniversal needs • What are wants • What is difference between Micro and Macro economics? • What is the difference between scarcity and shortage? • What is basic economic truth?
 The Toilet Crisis • What is the nature of the toilet crisis in the third world? • What are some of the results of this crisis? • What were facts cited in this video? • What is being done to address this issue?
The Toilet Crisis • What is the nature of the toilet crisis in the third world? • What are some of the results of this crisis? • What were facts cited in this video? • What is being done to address this issue?
 New Key Terms • Trade offs: All the possible choices or options sacrificed when a choice is made • Opportunity Cost: The next best alternative sacrificed when a choice is made • Guns or Butter: The choice that the government makes between allocating scarce resources to satisfying either the military or the non-military needs and wants of our society (nation).
New Key Terms • Trade offs: All the possible choices or options sacrificed when a choice is made • Opportunity Cost: The next best alternative sacrificed when a choice is made • Guns or Butter: The choice that the government makes between allocating scarce resources to satisfying either the military or the non-military needs and wants of our society (nation).
 Additional key terms • Standard of Living: A measure of how well a society satisfies the needs and wants of its people. • GDP: The value of all the products (goods and services) produced in a nation. • Per-capita GDP: A measurement determined by the GDP of a nation divided by its population. • Sunk Costs: Cost which have already been incurred.
Additional key terms • Standard of Living: A measure of how well a society satisfies the needs and wants of its people. • GDP: The value of all the products (goods and services) produced in a nation. • Per-capita GDP: A measurement determined by the GDP of a nation divided by its population. • Sunk Costs: Cost which have already been incurred.

 The Road Not Taken” by Robert Frost Every choice has a cost because choosing to do one thing means giving up the opportunity to do something else.
The Road Not Taken” by Robert Frost Every choice has a cost because choosing to do one thing means giving up the opportunity to do something else.
 We recognize that… • Faced with the same option, different people often make different choices because they put different values on each alternative’ s costs and expected outcomes
We recognize that… • Faced with the same option, different people often make different choices because they put different values on each alternative’ s costs and expected outcomes

 What are tradeoffs? • Think of all the choices that you had with regards to eating breakfast this morning.
What are tradeoffs? • Think of all the choices that you had with regards to eating breakfast this morning.
 OR… • Think of all the items you could buy with $50 at the mall this afternoon
OR… • Think of all the items you could buy with $50 at the mall this afternoon
 OR… • Think of all the choices of what you could be doing if you were not in this classroom right now?
OR… • Think of all the choices of what you could be doing if you were not in this classroom right now?
 Trade offs • Tradeoffs are all the REALISTIC choices that we have when allocating scarce resources such as our time or money
Trade offs • Tradeoffs are all the REALISTIC choices that we have when allocating scarce resources such as our time or money
 Opportunity cost and trade offs
Opportunity cost and trade offs
 Brad had to pick between two different women • Actually he had millions of women to choose from but it came down to just these two
Brad had to pick between two different women • Actually he had millions of women to choose from but it came down to just these two
 His choice
His choice
 Lopez’s Choice
Lopez’s Choice
 Difficult Choice….
Difficult Choice….
 Trade Offs • Think about the alternatives of how you could spend $100 at the mall • The way the government could use $1, 000 • The options we have in Brentwood for eating “junk food”
Trade Offs • Think about the alternatives of how you could spend $100 at the mall • The way the government could use $1, 000 • The options we have in Brentwood for eating “junk food”
 Opportunity cost • You decide to go shopping with your friends this weekend.
Opportunity cost • You decide to go shopping with your friends this weekend.
 At the mall you go to your favorite store
At the mall you go to your favorite store
 Where your boyfriend used to work
Where your boyfriend used to work
 You need to buy him cologne as a gift and you narrow it down to either…
You need to buy him cologne as a gift and you narrow it down to either…
 “Fierce”
“Fierce”
 Or “Proof”
Or “Proof”
 You decide to get the “Fierce”
You decide to get the “Fierce”
 What was the opportunity cost of your decision? • The “Proof”
What was the opportunity cost of your decision? • The “Proof”
 You decide to continue shopping • You still have a few extra $20 s in your purse • You go over to the women’s clothing • After considering all the options (“trade offs) • You settle on one of two polo shirts
You decide to continue shopping • You still have a few extra $20 s in your purse • You go over to the women’s clothing • After considering all the options (“trade offs) • You settle on one of two polo shirts
 A blue shirt to match your eyes
A blue shirt to match your eyes
 Or a new shirt to wear in Lopez’s class next Thursday
Or a new shirt to wear in Lopez’s class next Thursday
 • You decide to accept the opportunity cost of the blue shirt so that you can be more fashionable in Econ Class so you buy the pink polo
• You decide to accept the opportunity cost of the blue shirt so that you can be more fashionable in Econ Class so you buy the pink polo

 Guns versus Butter
Guns versus Butter
 SUNK COSTS ACTIVITY • Why so difficult to end the war? • Why we never discontinue government programs? • Why people sometimes stay in bad relationships?
SUNK COSTS ACTIVITY • Why so difficult to end the war? • Why we never discontinue government programs? • Why people sometimes stay in bad relationships?

 Super Sweet 16 Party
Super Sweet 16 Party


 Homeland Security • It is the first responsibility of any government to protect its citizens from enemies both foreign and domestic?
Homeland Security • It is the first responsibility of any government to protect its citizens from enemies both foreign and domestic?
 What is the price of this “protection” • Financially • In terms of tolerating “certain actions” like “torture” • Racial Profiling? • Civil Rights, like privacy
What is the price of this “protection” • Financially • In terms of tolerating “certain actions” like “torture” • Racial Profiling? • Civil Rights, like privacy
 Special Powers for Pres? • • National Security and Homeland Security Presidential Directive White House News NATIONAL SECURITY PRESIDENTIAL DIRECTIVE/NSPD 51 HOMELAND SECURITY PRESIDENTIAL DIRECTIVE/HSPD-20 Subject: National Continuity Policy Purpose (1) This directive establishes a comprehensive national policy on the continuity of Federal Government structures and operations and a single National Continuity Coordinator responsible for coordinating the development and implementation of Federal continuity policies. This policy establishes "National Essential Functions, " prescribes continuity requirements for all executive departments and agencies, and provides guidance for State, local, territorial, and tribal governments, and private sector organizations in order to ensure a comprehensive and integrated national continuity program that will enhance the credibility of our national security posture and enable a more rapid and effective response to and recovery from a national emergency.
Special Powers for Pres? • • National Security and Homeland Security Presidential Directive White House News NATIONAL SECURITY PRESIDENTIAL DIRECTIVE/NSPD 51 HOMELAND SECURITY PRESIDENTIAL DIRECTIVE/HSPD-20 Subject: National Continuity Policy Purpose (1) This directive establishes a comprehensive national policy on the continuity of Federal Government structures and operations and a single National Continuity Coordinator responsible for coordinating the development and implementation of Federal continuity policies. This policy establishes "National Essential Functions, " prescribes continuity requirements for all executive departments and agencies, and provides guidance for State, local, territorial, and tribal governments, and private sector organizations in order to ensure a comprehensive and integrated national continuity program that will enhance the credibility of our national security posture and enable a more rapid and effective response to and recovery from a national emergency.




 El Principe de Asturias • Spain’s aircraft carrier which carriers twelve Harrier jets and 16 helicopters.
El Principe de Asturias • Spain’s aircraft carrier which carriers twelve Harrier jets and 16 helicopters.
 Spraying Strawberries • Jose has a strawberry patch
Spraying Strawberries • Jose has a strawberry patch
 Spraying Strawberries • Jose owns a small strawberry farm
Spraying Strawberries • Jose owns a small strawberry farm
 The sale of the strawberries supports his entire family
The sale of the strawberries supports his entire family
 One day…. • Jose discovers that there are bugs eating his strawberries
One day…. • Jose discovers that there are bugs eating his strawberries
 He was worried • He picture his little son, Emilio going hungry because they had no strawberries to sell
He was worried • He picture his little son, Emilio going hungry because they had no strawberries to sell
 He called his friend Paco • Paco had a small plane that he used for crop dusting
He called his friend Paco • Paco had a small plane that he used for crop dusting
 Paco’s plane was just what Jose needed to save his crop and poor Emilio
Paco’s plane was just what Jose needed to save his crop and poor Emilio
 Jose offered to fly over the farm and dust the fields • He agreed to charge just $50. 00 for each dusting
Jose offered to fly over the farm and dust the fields • He agreed to charge just $50. 00 for each dusting
 Jose was once in Mr. Lopez’s Econ Class. • Jose knew that he needed to calculate the marginal net benefit for each dusting in order to determine how many times Paco should dust the crops
Jose was once in Mr. Lopez’s Econ Class. • Jose knew that he needed to calculate the marginal net benefit for each dusting in order to determine how many times Paco should dust the crops
 His objective • Jose wanted to maximize the amount of strawberries saved but he did not want to pay more than was necessary • Since he never was truant in Lopez’s class, he knew that at some point the marginal cost would exceed the marginal benefit.
His objective • Jose wanted to maximize the amount of strawberries saved but he did not want to pay more than was necessary • Since he never was truant in Lopez’s class, he knew that at some point the marginal cost would exceed the marginal benefit.
 Page 1. 28 • We are going to use the table on page 1. 28 to calculate how many times Jose should have Paco dust the strawberry fields.
Page 1. 28 • We are going to use the table on page 1. 28 to calculate how many times Jose should have Paco dust the strawberry fields.

 Production Possibilities • Remember Opportunity cost? • While there are sometimes many tradeoffs to a choice there is always one opportunity cost. • That being the best alternative to the choice we make
Production Possibilities • Remember Opportunity cost? • While there are sometimes many tradeoffs to a choice there is always one opportunity cost. • That being the best alternative to the choice we make
 If you own a factory • Whatever you choose to produce using the resources of your factory there is always an opportunity cost (best alternative) to this choice.
If you own a factory • Whatever you choose to produce using the resources of your factory there is always an opportunity cost (best alternative) to this choice.
 Lets assume • We have a factory that can produce either Watermelons or Flip Flops • What are our production possibilities?
Lets assume • We have a factory that can produce either Watermelons or Flip Flops • What are our production possibilities?
 First Option • We can produce all watermelons
First Option • We can produce all watermelons
 Second Option • We can produce all flip flops
Second Option • We can produce all flip flops
 Third Option • We can produce some combination of both watermelons and flip flops
Third Option • We can produce some combination of both watermelons and flip flops
 The options again • 50 watermelons and 0 flip flops • 100 flip flops and 0 watermelons • Some combination of both
The options again • 50 watermelons and 0 flip flops • 100 flip flops and 0 watermelons • Some combination of both
 The combinations • Assume we start are producing 100 flip flops and 0 watermelons. • Knowing our maximum potential is for 50 watermelons in lieu of the 100 flip flops, what is the trade off for each watermelon we produce.
The combinations • Assume we start are producing 100 flip flops and 0 watermelons. • Knowing our maximum potential is for 50 watermelons in lieu of the 100 flip flops, what is the trade off for each watermelon we produce.
 Producing Watermelons • So for every watermelon we produce we forgo 2 pairs of flip flops.
Producing Watermelons • So for every watermelon we produce we forgo 2 pairs of flip flops.
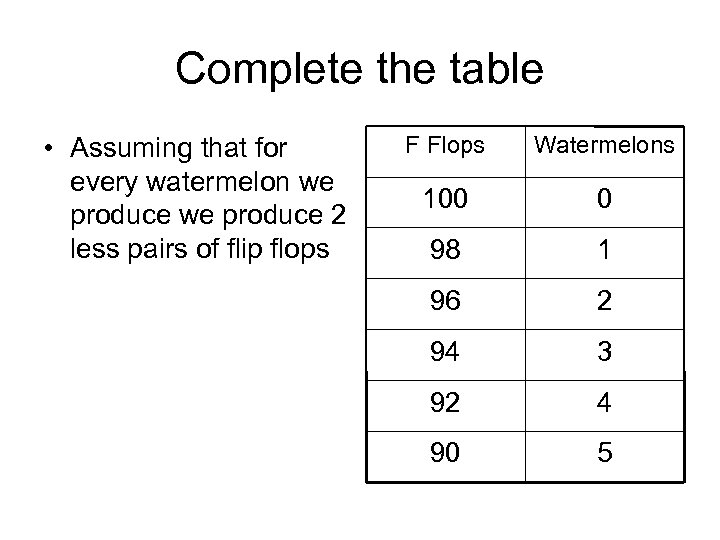 Complete the table • Assuming that for every watermelon we produce 2 less pairs of flip flops F Flops Watermelons 100 0 98 1 96 2 94 3 92 4 90 5
Complete the table • Assuming that for every watermelon we produce 2 less pairs of flip flops F Flops Watermelons 100 0 98 1 96 2 94 3 92 4 90 5
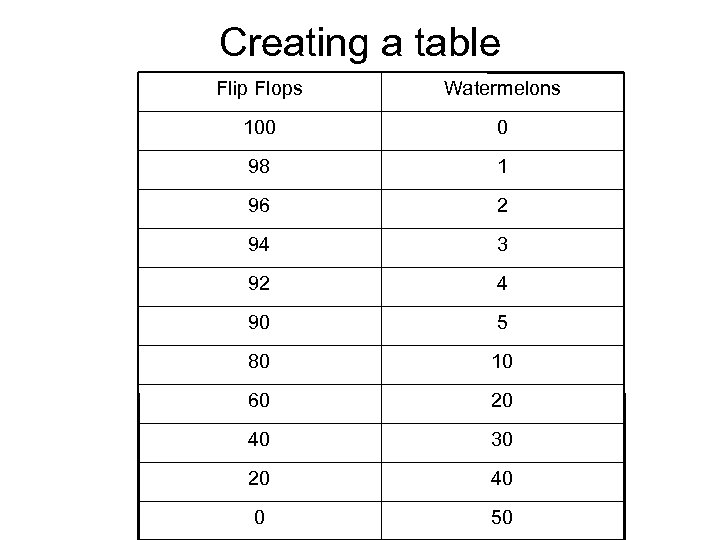 Creating a table Flip Flops Watermelons 100 0 98 1 96 2 94 3 92 4 90 5 80 10 60 20 40 30 20 40 0 50
Creating a table Flip Flops Watermelons 100 0 98 1 96 2 94 3 92 4 90 5 80 10 60 20 40 30 20 40 0 50
 Law of Increasing costs • How many flip flops do we have to forego to make one watermelon? • Two watermelons? • Three watermelons? • As we increase the production of one item we must give up increasing amounts of a second item
Law of Increasing costs • How many flip flops do we have to forego to make one watermelon? • Two watermelons? • Three watermelons? • As we increase the production of one item we must give up increasing amounts of a second item
 For example… • If you make shoes, it takes more leather to make two pairs of shoes than it does to make just one pair. • The more shoes we produce the more leather we require. • Therefore we are giving up increasing quantities of an alternative produce as we increase our production of shoes.
For example… • If you make shoes, it takes more leather to make two pairs of shoes than it does to make just one pair. • The more shoes we produce the more leather we require. • Therefore we are giving up increasing quantities of an alternative produce as we increase our production of shoes.
 Key terms • • • Factors of Production Land Labor Capital Physical Capital Human Capital
Key terms • • • Factors of Production Land Labor Capital Physical Capital Human Capital
 Definitions • Factors of Production: Resources used to make all goods and service. • Land: Natural resources • Labor: Efforts of a person towards a task • Capital: Human made resources • Physical Capital: Buildings and tools • Human Capital: Knowledge, skills, and experience
Definitions • Factors of Production: Resources used to make all goods and service. • Land: Natural resources • Labor: Efforts of a person towards a task • Capital: Human made resources • Physical Capital: Buildings and tools • Human Capital: Knowledge, skills, and experience
 For example • • • Land: Property on Oak Street, natural gas Labor: Digging a ditch Capital: Assets of this school Physical Capital: The desks and chairs Human Capital: Knowledge in Mr. Lopez’s brain
For example • • • Land: Property on Oak Street, natural gas Labor: Digging a ditch Capital: Assets of this school Physical Capital: The desks and chairs Human Capital: Knowledge in Mr. Lopez’s brain
 Key Terms • Thinking at the Margin: Decision making my units or increments on the use of resources. • Marginal benefit: The benefit from the allocation of an additional unit of a resource. • Marginal cost: The cost of allocating an addition unit of an increment. • Law of Diminishing Returns: The tendency of the marginal benefit to diminish as additional units of a resource are allocated.
Key Terms • Thinking at the Margin: Decision making my units or increments on the use of resources. • Marginal benefit: The benefit from the allocation of an additional unit of a resource. • Marginal cost: The cost of allocating an addition unit of an increment. • Law of Diminishing Returns: The tendency of the marginal benefit to diminish as additional units of a resource are allocated.


