d21bd9a9b6a6be60cfd93be1d58091c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 ME 59700 Fall 2014 Introduction to Systems Engineering Session 1 Dr. Dan C. Surber, ESEP © Copyright 2013 1
ME 59700 Fall 2014 Introduction to Systems Engineering Session 1 Dr. Dan C. Surber, ESEP © Copyright 2013 1
 Agenda • • • Introductions (5 minutes) “Formalities” (15 minutes) Introduce systems & engineering (20 minutes) Wasson’s construct (10 minutes) Concept Exploration (15 minutes) Web sites (5 minutes) 2
Agenda • • • Introductions (5 minutes) “Formalities” (15 minutes) Introduce systems & engineering (20 minutes) Wasson’s construct (10 minutes) Concept Exploration (15 minutes) Web sites (5 minutes) 2
 Introductions • Introductions – Instructor’s Bio is posted on Blackboard site – Guest Lecturer’s may join us during semester • Required information on all written submissions for grade: – Full name – Name of assignment : (CP-01, HW-01, Test-01) – Date 3
Introductions • Introductions – Instructor’s Bio is posted on Blackboard site – Guest Lecturer’s may join us during semester • Required information on all written submissions for grade: – Full name – Name of assignment : (CP-01, HW-01, Test-01) – Date 3
 “Formalities” • Required paperwork • ATTENDANCE – Travel is understood: let me know ahead of time – Make arrangements to submit assignments on time • OFFICE HOURS – By appointment dsurber@iupui. edu – Cell phone: 317. 989. 7974 4
“Formalities” • Required paperwork • ATTENDANCE – Travel is understood: let me know ahead of time – Make arrangements to submit assignments on time • OFFICE HOURS – By appointment dsurber@iupui. edu – Cell phone: 317. 989. 7974 4
 “Our CONTRACT” • Knowledge is made available – but YOU must do the learning: – Lecture notes are in Power Point – sent to students by email PRIOR to the class sessions – Syllabus - posted On. Course website – Weekly Plan – sent to students on On. Course • • • Quizzes (8) Homework (8) Class Project Briefings (5) Examinations (2 section tests & Final Exam) (3) ON LINE RESOURCE – Assignments: get them from WEEKLY PLAN, and turn them in for grade to On. Course – Quizzes and Tests: taken IN-CLASS (timed, open book, open notes) – FINAL EXAM (IN-CLASS, timed, open book, open notes) • ATTENDANCE – – notify instructor BEFORE absence – Submit ASSIGNMENTS are due on the date they are due (LATE submittals = 0 points) IN CLASS or submitted to On. Course as directed by Instructor • COURSE GRADE – straight line percentage, as stated in syllabus (attendance & participation will affect border line grades) – (NO CURVE) • “NO Bonus Points or EXTRA POINTS” • PLEASE DO NOT BE LATE SUBMITTING ASSIGNMENTS 5
“Our CONTRACT” • Knowledge is made available – but YOU must do the learning: – Lecture notes are in Power Point – sent to students by email PRIOR to the class sessions – Syllabus - posted On. Course website – Weekly Plan – sent to students on On. Course • • • Quizzes (8) Homework (8) Class Project Briefings (5) Examinations (2 section tests & Final Exam) (3) ON LINE RESOURCE – Assignments: get them from WEEKLY PLAN, and turn them in for grade to On. Course – Quizzes and Tests: taken IN-CLASS (timed, open book, open notes) – FINAL EXAM (IN-CLASS, timed, open book, open notes) • ATTENDANCE – – notify instructor BEFORE absence – Submit ASSIGNMENTS are due on the date they are due (LATE submittals = 0 points) IN CLASS or submitted to On. Course as directed by Instructor • COURSE GRADE – straight line percentage, as stated in syllabus (attendance & participation will affect border line grades) – (NO CURVE) • “NO Bonus Points or EXTRA POINTS” • PLEASE DO NOT BE LATE SUBMITTING ASSIGNMENTS 5
 Reading/Studying Technical Material • Editors are tough “task masters”; there is a format to a good book, and to a good text book • Use the 3 -Step Method – Skim • Get the “big” picture • See the outline/structure – Sweep (First and Last) • Intro & Summary • Paragraphs of a section • Sentences of a paragraph Quizzes, Tests, & Final Exam are all open book and open notes. – Synthesize (Re-visit for the “good stuff”) • • BOLD items Italicized items Lists Figures, Tables, Footnotes • Make notes in the margin, highlight, write questions in pencil, mark up the lectures • Draw pictures & Capture “relationships” amongst concepts 6
Reading/Studying Technical Material • Editors are tough “task masters”; there is a format to a good book, and to a good text book • Use the 3 -Step Method – Skim • Get the “big” picture • See the outline/structure – Sweep (First and Last) • Intro & Summary • Paragraphs of a section • Sentences of a paragraph Quizzes, Tests, & Final Exam are all open book and open notes. – Synthesize (Re-visit for the “good stuff”) • • BOLD items Italicized items Lists Figures, Tables, Footnotes • Make notes in the margin, highlight, write questions in pencil, mark up the lectures • Draw pictures & Capture “relationships” amongst concepts 6
 Homework, Tests & Final • OPEN BOOK & OPEN NOTES • NO COLLABORATION (Quizzes, Tests, or FINAL) • QUIZZES – All QUIZZES in class (10 minutes each) • Tests 1 & 2 – Take in class (1 hour each) SO WHAT’S TESTABLE? • anything in the text book section intro & chapters • everything from the lectures • FINAL EXAMS – Students take as scheduled in class room (2 hours) – Talk to instructor about other arrangements • HOMEWORK – Submit PRINTED artifact by the start of class on date due – Submit by the due date on the WEEKLY PLAN 7
Homework, Tests & Final • OPEN BOOK & OPEN NOTES • NO COLLABORATION (Quizzes, Tests, or FINAL) • QUIZZES – All QUIZZES in class (10 minutes each) • Tests 1 & 2 – Take in class (1 hour each) SO WHAT’S TESTABLE? • anything in the text book section intro & chapters • everything from the lectures • FINAL EXAMS – Students take as scheduled in class room (2 hours) – Talk to instructor about other arrangements • HOMEWORK – Submit PRINTED artifact by the start of class on date due – Submit by the due date on the WEEKLY PLAN 7
 Class Project Briefings • CP-01 through CP-05 • Design Review/Phase Gates (submitted individually) • In-class Briefings – Each student briefs 5 minutes – Instructor will give each briefer a critique (GRADED – 10 pts) – ALL students will submit a written version (GRADED – 50 pts) • Each briefing has 5 key topics that must be covered • ALL of the CLASS will LEARN from one another – Varieties of system perspectives – Varieties of approaches to decomposition & definition – Students may question each other in class after each briefing • Briefing order will be alphabetical, one-half on 1 st session and the other half on 2 nd session (noted in WEEKLY PLAN) 8
Class Project Briefings • CP-01 through CP-05 • Design Review/Phase Gates (submitted individually) • In-class Briefings – Each student briefs 5 minutes – Instructor will give each briefer a critique (GRADED – 10 pts) – ALL students will submit a written version (GRADED – 50 pts) • Each briefing has 5 key topics that must be covered • ALL of the CLASS will LEARN from one another – Varieties of system perspectives – Varieties of approaches to decomposition & definition – Students may question each other in class after each briefing • Briefing order will be alphabetical, one-half on 1 st session and the other half on 2 nd session (noted in WEEKLY PLAN) 8
 End of “administrivia” • Text book (mandatory & testable): – Systems Engineering and Analysis, 5 th ed. , by Ben Blanchard & Wolter Fabrycky, 2011. • Useful References (NOT REQUIRED or testable) – Defense Acquisition University, Systems Engineering Fundamentals, 2001 – System Analysis, Design, and Development, by Charles S. Wasson, 2006. – INCOSE, Systems Engineering Handbook, ver. 3. 2 • List of NASA ISS websites useful for information about assigned space station element for class project. – Provided by instructor on Blackboard 9
End of “administrivia” • Text book (mandatory & testable): – Systems Engineering and Analysis, 5 th ed. , by Ben Blanchard & Wolter Fabrycky, 2011. • Useful References (NOT REQUIRED or testable) – Defense Acquisition University, Systems Engineering Fundamentals, 2001 – System Analysis, Design, and Development, by Charles S. Wasson, 2006. – INCOSE, Systems Engineering Handbook, ver. 3. 2 • List of NASA ISS websites useful for information about assigned space station element for class project. – Provided by instructor on Blackboard 9
 Introduce Systems Engineering • • • System Life Cycle Product Development Life Cycle Define a System Define Systems Engineering The “Vee” Diagram as a general representation Other life cycle models 10
Introduce Systems Engineering • • • System Life Cycle Product Development Life Cycle Define a System Define Systems Engineering The “Vee” Diagram as a general representation Other life cycle models 10
 Two Basic Types of Systems • Man-made systems for this course • Precedented Systems – Extant, pre-existing, built, defined • Defined interfaces • Solution architecture • Product breakdown structure – Possess a CONOPS & a System CONTEXT – Have at least ONE mission event time line defined • Unprecedented Systems – – Conceptual (at best, may not even be conceived) Need can be expressed Must develop CONOPS, define mission(s), & Context Describe FUNCTIONS, INTERFACES, and TESTING 11
Two Basic Types of Systems • Man-made systems for this course • Precedented Systems – Extant, pre-existing, built, defined • Defined interfaces • Solution architecture • Product breakdown structure – Possess a CONOPS & a System CONTEXT – Have at least ONE mission event time line defined • Unprecedented Systems – – Conceptual (at best, may not even be conceived) Need can be expressed Must develop CONOPS, define mission(s), & Context Describe FUNCTIONS, INTERFACES, and TESTING 11
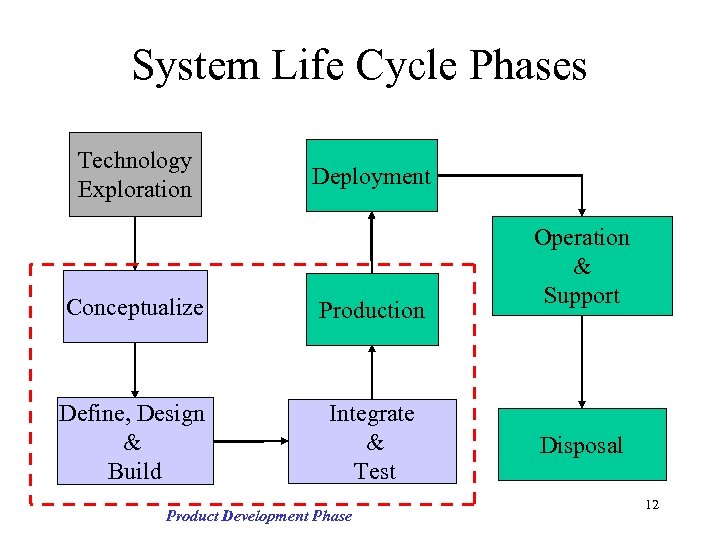 System Life Cycle Phases Technology Exploration Deployment Conceptualize Production Define, Design & Build Integrate & Test Product Development Phase Operation & Support Disposal 12
System Life Cycle Phases Technology Exploration Deployment Conceptualize Production Define, Design & Build Integrate & Test Product Development Phase Operation & Support Disposal 12
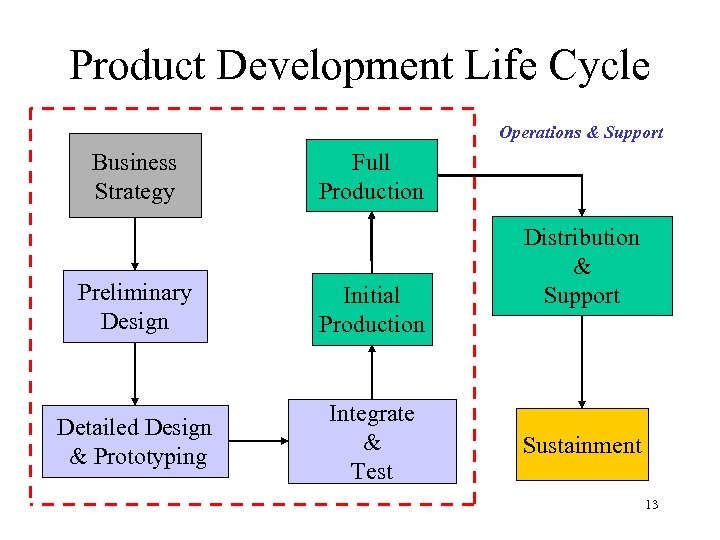 Product Development Life Cycle Operations & Support Business Strategy Full Production Preliminary Design Initial Production Detailed Design & Prototyping Integrate & Test Distribution & Support Sustainment 13
Product Development Life Cycle Operations & Support Business Strategy Full Production Preliminary Design Initial Production Detailed Design & Prototyping Integrate & Test Distribution & Support Sustainment 13
 Systems • What is a system? – “A collection of things that work together to perform a useful purpose that none of them can do alone. ” ** – “A functional grouping of hardware, software, and human interfaces that work together to meet the mission need expressed by the end user. ” • What is a system of systems? – “A group of dissimilar systems that interoperate to achieve a mission purpose none of them can perform alone. ” – May possess unplanned, emergent behavior that is not visible by the architecture or design teams. ** this is the INSTRUCTOR’s preferred definition Credit to: INCOSE Handbook; Forsberg & Moor; Ben Blanchard & Wolter Fabrycky; J. O. Grady 14
Systems • What is a system? – “A collection of things that work together to perform a useful purpose that none of them can do alone. ” ** – “A functional grouping of hardware, software, and human interfaces that work together to meet the mission need expressed by the end user. ” • What is a system of systems? – “A group of dissimilar systems that interoperate to achieve a mission purpose none of them can perform alone. ” – May possess unplanned, emergent behavior that is not visible by the architecture or design teams. ** this is the INSTRUCTOR’s preferred definition Credit to: INCOSE Handbook; Forsberg & Moor; Ben Blanchard & Wolter Fabrycky; J. O. Grady 14
 Define Systems Engineering • Blanchard, p. 18, bottom. ‘SE is good engineering with special areas of emphasis. ’ • Wasson: “SE is a problem solving - solution development discipline that requires a fundamental understanding in how to think about and analyze systems. ” • DSMC: “SE is an interdisciplinary engineering management process that evolves and verifies an integrated, life-cycle balanced set of system solutions that satisfy customer needs. ” • INCOSE definition: an interdisciplinary approach and means to enable the realization of success systems. ** SEHbk, v 3, p. 2. 1. ** this is the INSTRUCTOR’s preferred definition 15
Define Systems Engineering • Blanchard, p. 18, bottom. ‘SE is good engineering with special areas of emphasis. ’ • Wasson: “SE is a problem solving - solution development discipline that requires a fundamental understanding in how to think about and analyze systems. ” • DSMC: “SE is an interdisciplinary engineering management process that evolves and verifies an integrated, life-cycle balanced set of system solutions that satisfy customer needs. ” • INCOSE definition: an interdisciplinary approach and means to enable the realization of success systems. ** SEHbk, v 3, p. 2. 1. ** this is the INSTRUCTOR’s preferred definition 15
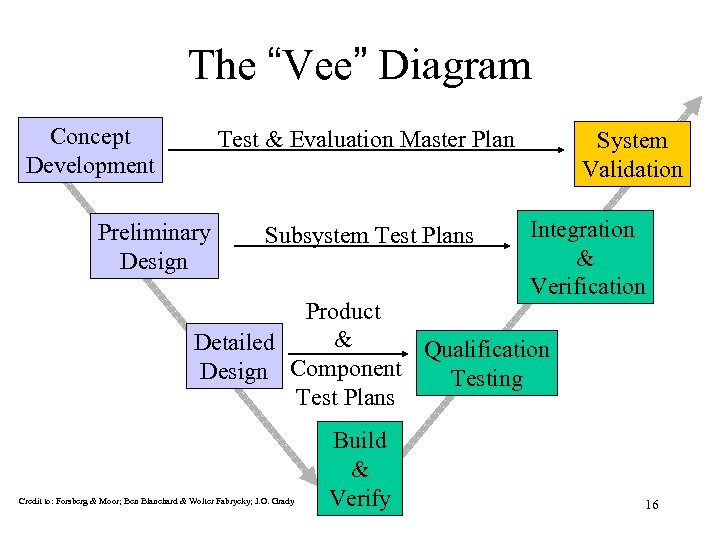 The “Vee” Diagram Concept Development Test & Evaluation Master Plan Preliminary Design Subsystem Test Plans System Validation Integration & Verification Product & Detailed Qualification Design Component Testing Test Plans Credit to: Forsberg & Moor; Ben Blanchard & Wolter Fabrycky; J. O. Grady Build & Verify 16
The “Vee” Diagram Concept Development Test & Evaluation Master Plan Preliminary Design Subsystem Test Plans System Validation Integration & Verification Product & Detailed Qualification Design Component Testing Test Plans Credit to: Forsberg & Moor; Ben Blanchard & Wolter Fabrycky; J. O. Grady Build & Verify 16
 PMTE • People – Right knowledge, skills, abilities? = Training Plan – Right people at the right time? = Staffing Plan – Key Stakeholders? = Stakeholder Involvement Plan & Artifacts • Methods – Proven Processes? = Process Tailoring & Support, Stakeholders – Key Events, Activities, Criteria? = IMP, IMS, SEMP/SEP • Tools – Company standard? = Templates, Enablers, Checklists, Work Instructions – Standards? = Project/Engineering Notebook, Reference Architectures • Environment – Leadership buy-in & support? = Senior Management Reviews – Metrics? = Earned Value Measurement, Measurement Analysis, – Decision Making? = Trade offs, Technical Performance Measures, Risk & Opportunity Management 17
PMTE • People – Right knowledge, skills, abilities? = Training Plan – Right people at the right time? = Staffing Plan – Key Stakeholders? = Stakeholder Involvement Plan & Artifacts • Methods – Proven Processes? = Process Tailoring & Support, Stakeholders – Key Events, Activities, Criteria? = IMP, IMS, SEMP/SEP • Tools – Company standard? = Templates, Enablers, Checklists, Work Instructions – Standards? = Project/Engineering Notebook, Reference Architectures • Environment – Leadership buy-in & support? = Senior Management Reviews – Metrics? = Earned Value Measurement, Measurement Analysis, – Decision Making? = Trade offs, Technical Performance Measures, Risk & Opportunity Management 17
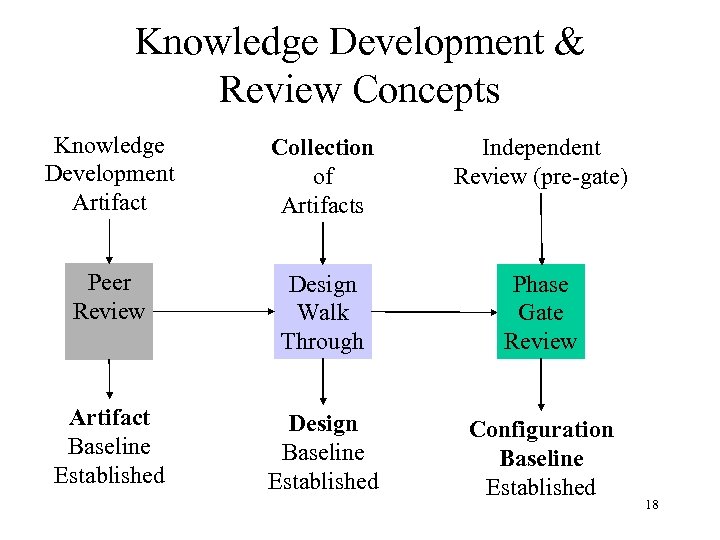 Knowledge Development & Review Concepts Knowledge Development Artifact Collection of Artifacts Independent Review (pre-gate) Peer Review Design Walk Through Phase Gate Review Artifact Baseline Established Design Baseline Established Configuration Baseline Established 18
Knowledge Development & Review Concepts Knowledge Development Artifact Collection of Artifacts Independent Review (pre-gate) Peer Review Design Walk Through Phase Gate Review Artifact Baseline Established Design Baseline Established Configuration Baseline Established 18
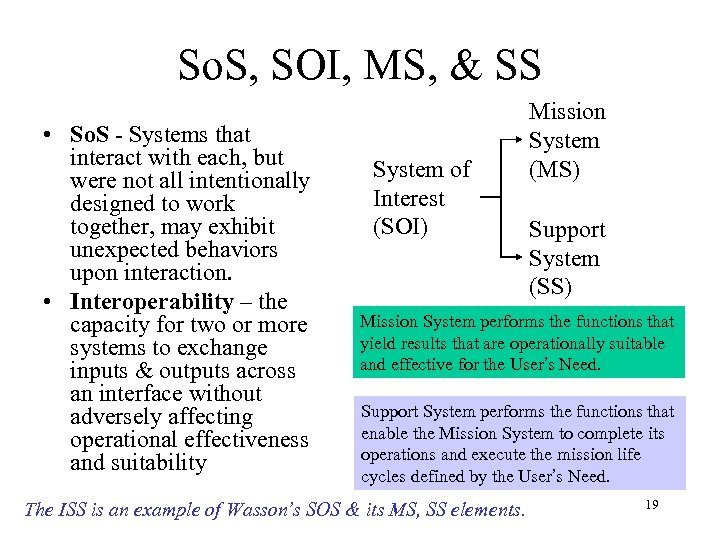 So. S, SOI, MS, & SS • So. S - Systems that interact with each, but were not all intentionally designed to work together, may exhibit unexpected behaviors upon interaction. • Interoperability – the capacity for two or more systems to exchange inputs & outputs across an interface without adversely affecting operational effectiveness and suitability System of Interest (SOI) Mission System (MS) Support System (SS) Mission System performs the functions that yield results that are operationally suitable and effective for the User’s Need. Support System performs the functions that enable the Mission System to complete its operations and execute the mission life cycles defined by the User’s Need. The ISS is an example of Wasson’s SOS & its MS, SS elements. 19
So. S, SOI, MS, & SS • So. S - Systems that interact with each, but were not all intentionally designed to work together, may exhibit unexpected behaviors upon interaction. • Interoperability – the capacity for two or more systems to exchange inputs & outputs across an interface without adversely affecting operational effectiveness and suitability System of Interest (SOI) Mission System (MS) Support System (SS) Mission System performs the functions that yield results that are operationally suitable and effective for the User’s Need. Support System performs the functions that enable the Mission System to complete its operations and execute the mission life cycles defined by the User’s Need. The ISS is an example of Wasson’s SOS & its MS, SS elements. 19
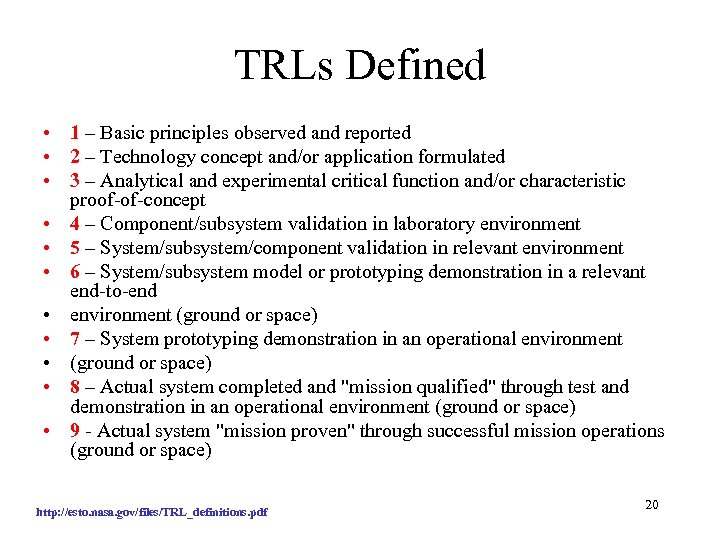 TRLs Defined • 1 – Basic principles observed and reported • 2 – Technology concept and/or application formulated • 3 – Analytical and experimental critical function and/or characteristic proof-of-concept • 4 – Component/subsystem validation in laboratory environment • 5 – System/subsystem/component validation in relevant environment • 6 – System/subsystem model or prototyping demonstration in a relevant end-to-end • environment (ground or space) • 7 – System prototyping demonstration in an operational environment • (ground or space) • 8 – Actual system completed and "mission qualified" through test and demonstration in an operational environment (ground or space) • 9 - Actual system "mission proven" through successful mission operations (ground or space) http: //esto. nasa. gov/files/TRL_definitions. pdf 20
TRLs Defined • 1 – Basic principles observed and reported • 2 – Technology concept and/or application formulated • 3 – Analytical and experimental critical function and/or characteristic proof-of-concept • 4 – Component/subsystem validation in laboratory environment • 5 – System/subsystem/component validation in relevant environment • 6 – System/subsystem model or prototyping demonstration in a relevant end-to-end • environment (ground or space) • 7 – System prototyping demonstration in an operational environment • (ground or space) • 8 – Actual system completed and "mission qualified" through test and demonstration in an operational environment (ground or space) • 9 - Actual system "mission proven" through successful mission operations (ground or space) http: //esto. nasa. gov/files/TRL_definitions. pdf 20
 PD Life Cycle Models • • Waterfall Incremental Evolutionary Spiral See Figure 2. 5 in text. 21
PD Life Cycle Models • • Waterfall Incremental Evolutionary Spiral See Figure 2. 5 in text. 21
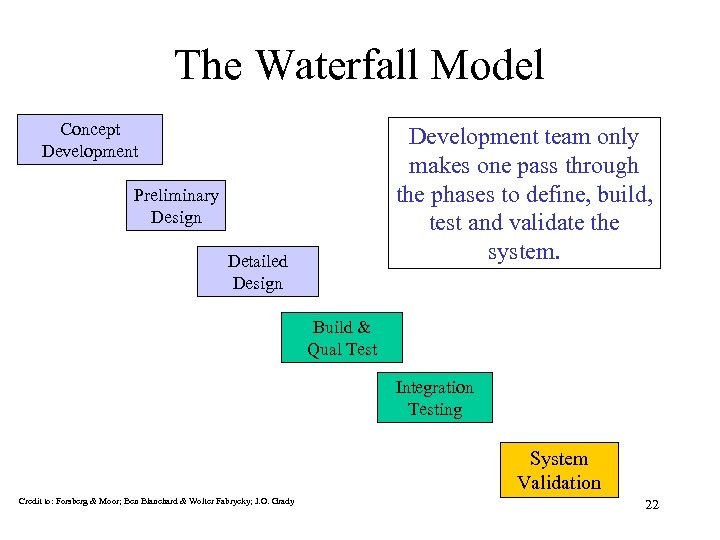 The Waterfall Model Concept Development team only makes one pass through the phases to define, build, test and validate the system. Preliminary Design Detailed Design Build & Qual Test Integration Testing System Validation Credit to: Forsberg & Moor; Ben Blanchard & Wolter Fabrycky; J. O. Grady 22
The Waterfall Model Concept Development team only makes one pass through the phases to define, build, test and validate the system. Preliminary Design Detailed Design Build & Qual Test Integration Testing System Validation Credit to: Forsberg & Moor; Ben Blanchard & Wolter Fabrycky; J. O. Grady 22
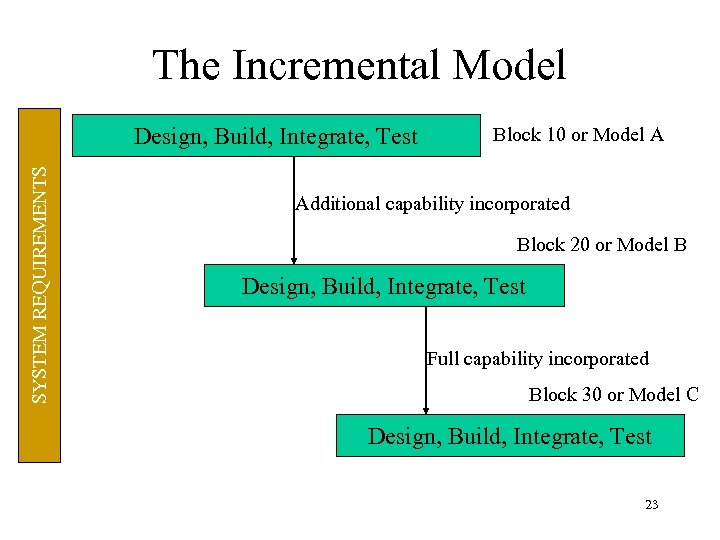 The Incremental Model SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Design, Build, Integrate, Test Block 10 or Model A Additional capability incorporated Block 20 or Model B Design, Build, Integrate, Test Full capability incorporated Block 30 or Model C Design, Build, Integrate, Test 23
The Incremental Model SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Design, Build, Integrate, Test Block 10 or Model A Additional capability incorporated Block 20 or Model B Design, Build, Integrate, Test Full capability incorporated Block 30 or Model C Design, Build, Integrate, Test 23
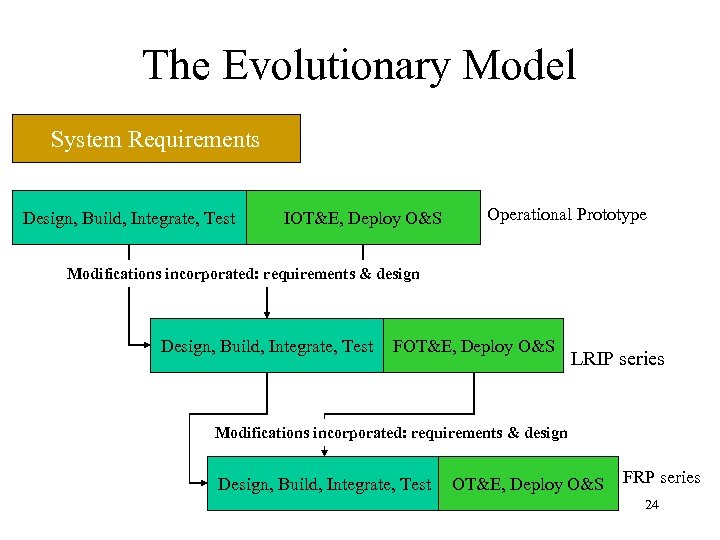 The Evolutionary Model System Requirements Design, Build, Integrate, Test IOT&E, Deploy O&S Operational Prototype Modifications incorporated: requirements & design Design, Build, Integrate, Test FOT&E, Deploy O&S LRIP series Modifications incorporated: requirements & design Design, Build, Integrate, Test OT&E, Deploy O&S FRP series 24
The Evolutionary Model System Requirements Design, Build, Integrate, Test IOT&E, Deploy O&S Operational Prototype Modifications incorporated: requirements & design Design, Build, Integrate, Test FOT&E, Deploy O&S LRIP series Modifications incorporated: requirements & design Design, Build, Integrate, Test OT&E, Deploy O&S FRP series 24
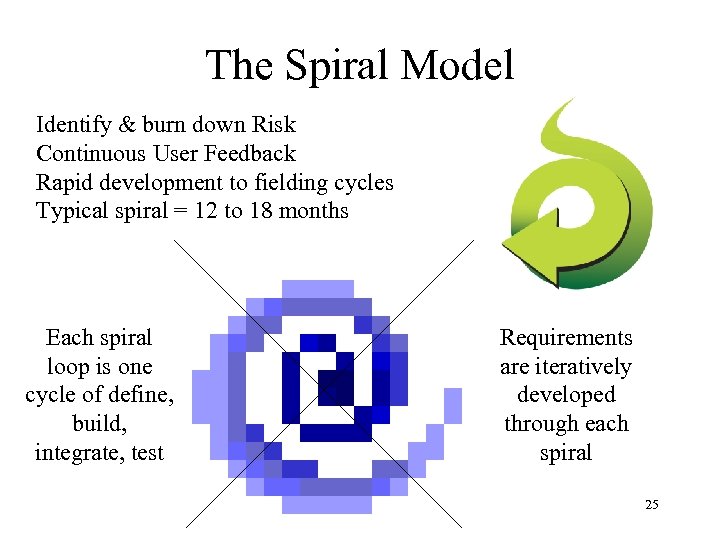 The Spiral Model Identify & burn down Risk Continuous User Feedback Rapid development to fielding cycles Typical spiral = 12 to 18 months Each spiral loop is one cycle of define, build, integrate, test Requirements are iteratively developed through each spiral 25
The Spiral Model Identify & burn down Risk Continuous User Feedback Rapid development to fielding cycles Typical spiral = 12 to 18 months Each spiral loop is one cycle of define, build, integrate, test Requirements are iteratively developed through each spiral 25
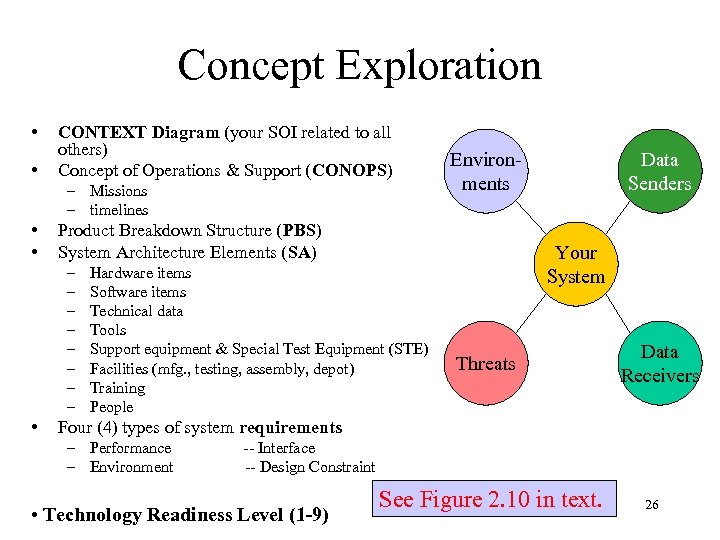 Concept Exploration • • CONTEXT Diagram (your SOI related to all others) Concept of Operations & Support (CONOPS) – Missions – timelines • • Product Breakdown Structure (PBS) System Architecture Elements (SA) – – – – • Environments Hardware items Software items Technical data Tools Support equipment & Special Test Equipment (STE) Facilities (mfg. , testing, assembly, depot) Training People Data Senders Your System Threats Data Receivers Four (4) types of system requirements – Performance – Environment -- Interface -- Design Constraint • Technology Readiness Level (1 -9) See Figure 2. 10 in text. 26
Concept Exploration • • CONTEXT Diagram (your SOI related to all others) Concept of Operations & Support (CONOPS) – Missions – timelines • • Product Breakdown Structure (PBS) System Architecture Elements (SA) – – – – • Environments Hardware items Software items Technical data Tools Support equipment & Special Test Equipment (STE) Facilities (mfg. , testing, assembly, depot) Training People Data Senders Your System Threats Data Receivers Four (4) types of system requirements – Performance – Environment -- Interface -- Design Constraint • Technology Readiness Level (1 -9) See Figure 2. 10 in text. 26
 PICK a System • Each student will research an ISS system (on-orbit module) – as assigned by the Instructor • Use LIST of URLs, GOOGLE, WIKI PEDIA, Aviation Week & Space Technology, NASA Tech Briefs, SAE Journals, IEEE Journals • DO NOT use information from any source without permission and understanding of IP, EAR/ITAR, trademarks, and copyrights – give credit to your sources from URLs, journals – Get permission to use if site claims IP or rights 27
PICK a System • Each student will research an ISS system (on-orbit module) – as assigned by the Instructor • Use LIST of URLs, GOOGLE, WIKI PEDIA, Aviation Week & Space Technology, NASA Tech Briefs, SAE Journals, IEEE Journals • DO NOT use information from any source without permission and understanding of IP, EAR/ITAR, trademarks, and copyrights – give credit to your sources from URLs, journals – Get permission to use if site claims IP or rights 27
 Web Sites • INCOSE (home page, members have access to SE Handbook, Metrics Primer, IPAL): http: //www. incose. org/ • Defense Acquisition University: http: //www. dau. mil/ • AW&ST online: http: //www. aviationweek. com/aw/ • Defense Daily Network: http: //www. defensedaily. com • NASA Tech Briefs: http: //www. techbriefs. com • SAE International: http: //www. sae. org/servlets/index • Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State Univ. • Carneghie Mellon & SEI (CMMI for Systems) • Google = “systems engineering” http: //www. google. com/ • Wiki-pedia “systems engineering” http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/main_page • See the list of INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION web sites in the RESOURCES section of COURSE web site 28
Web Sites • INCOSE (home page, members have access to SE Handbook, Metrics Primer, IPAL): http: //www. incose. org/ • Defense Acquisition University: http: //www. dau. mil/ • AW&ST online: http: //www. aviationweek. com/aw/ • Defense Daily Network: http: //www. defensedaily. com • NASA Tech Briefs: http: //www. techbriefs. com • SAE International: http: //www. sae. org/servlets/index • Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State Univ. • Carneghie Mellon & SEI (CMMI for Systems) • Google = “systems engineering” http: //www. google. com/ • Wiki-pedia “systems engineering” http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/main_page • See the list of INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION web sites in the RESOURCES section of COURSE web site 28


