34d6fe1ce01aab076bc03951d63e4341.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 74
 MDSS Training For Health Care Providers
MDSS Training For Health Care Providers
 The Michigan Disease Surveillance System Why we’re launching a new tool for public health surveillance in Michigan • Makes reporting of diseases/conditions easier, more efficient and closer to real-time so public health interventions can be implemented • Reduces delays in initiation of public health follow-up by correctly reporting to county of residence rather than county of diagnosis • Allows reporting 24 hours/day from your PC • Clarifies whether the case reported involves multiple providers/facilities • Provides documentation of facility’s role in reporting for regulatory and accreditation agencies • Allows instantaneous retrieval of summary reports of diseases • Reduces volume of necessary telephone communications for additional information between LHD and facility-based ICP 2
The Michigan Disease Surveillance System Why we’re launching a new tool for public health surveillance in Michigan • Makes reporting of diseases/conditions easier, more efficient and closer to real-time so public health interventions can be implemented • Reduces delays in initiation of public health follow-up by correctly reporting to county of residence rather than county of diagnosis • Allows reporting 24 hours/day from your PC • Clarifies whether the case reported involves multiple providers/facilities • Provides documentation of facility’s role in reporting for regulatory and accreditation agencies • Allows instantaneous retrieval of summary reports of diseases • Reduces volume of necessary telephone communications for additional information between LHD and facility-based ICP 2
 MDSS Healthcare Provider (HCP) Responsibilities • Confidentiality – The MDSS will contain confidential medical information on individuals reported into the system. Data is protected by system security and role defined access, but participants will continue to be bound by rules of confidentiality while accessing system information. MDSS is compliant with HIPAA regulations. • Participation – To realize the goals of this system, patient information must be entered in a timely manner. – HCP reporting responsibilities remain unchanged with this new, electronic method of reporting (Communicable Disease Rules R 325. 171 et al. ). – Your enthusiastic support will make the MDSS a more productive and effective method of communicable disease surveillance 3
MDSS Healthcare Provider (HCP) Responsibilities • Confidentiality – The MDSS will contain confidential medical information on individuals reported into the system. Data is protected by system security and role defined access, but participants will continue to be bound by rules of confidentiality while accessing system information. MDSS is compliant with HIPAA regulations. • Participation – To realize the goals of this system, patient information must be entered in a timely manner. – HCP reporting responsibilities remain unchanged with this new, electronic method of reporting (Communicable Disease Rules R 325. 171 et al. ). – Your enthusiastic support will make the MDSS a more productive and effective method of communicable disease surveillance 3
 Accessing the MDSS • Software and System Requirements – Internet Access – Internet Browser (Internet Explorer 6. 0 recommended) – Adobe Reader 5. 1 or higher (www. adobe. com) • Single Sign-on (SSO) User ID and Password • Authorization to use the MDSS • Healthcare providers should partner with their local health department to register and utilize MDSS 4
Accessing the MDSS • Software and System Requirements – Internet Access – Internet Browser (Internet Explorer 6. 0 recommended) – Adobe Reader 5. 1 or higher (www. adobe. com) • Single Sign-on (SSO) User ID and Password • Authorization to use the MDSS • Healthcare providers should partner with their local health department to register and utilize MDSS 4
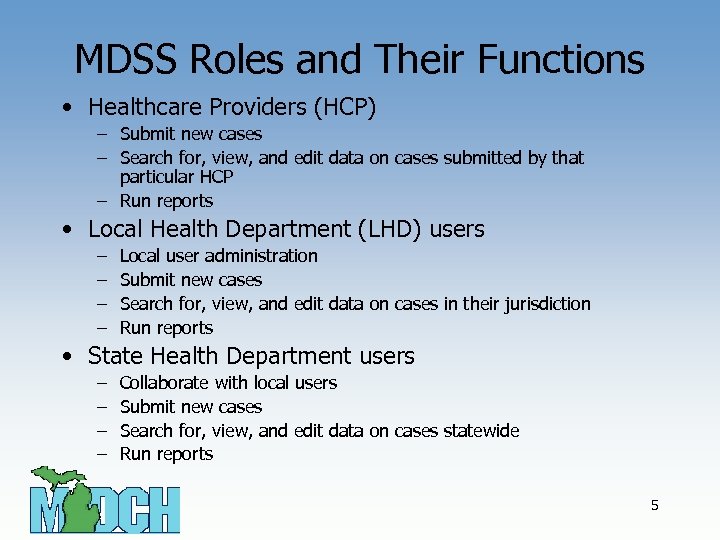 MDSS Roles and Their Functions • Healthcare Providers (HCP) – Submit new cases – Search for, view, and edit data on cases submitted by that particular HCP – Run reports • Local Health Department (LHD) users – – Local user administration Submit new cases Search for, view, and edit data on cases in their jurisdiction Run reports • State Health Department users – – Collaborate with local users Submit new cases Search for, view, and edit data on cases statewide Run reports 5
MDSS Roles and Their Functions • Healthcare Providers (HCP) – Submit new cases – Search for, view, and edit data on cases submitted by that particular HCP – Run reports • Local Health Department (LHD) users – – Local user administration Submit new cases Search for, view, and edit data on cases in their jurisdiction Run reports • State Health Department users – – Collaborate with local users Submit new cases Search for, view, and edit data on cases statewide Run reports 5
 How to access, navigate in, and exit the MDSS
How to access, navigate in, and exit the MDSS
 Entering the MDSS • Point browser to https: //sso. state. mi. us/ • Log In with SSO User ID and Password 7
Entering the MDSS • Point browser to https: //sso. state. mi. us/ • Log In with SSO User ID and Password 7
 The Top Navigation Bar consists of links to different modules: ö Case Investigation: Contains all of the functions to enter and manage cases. You can add, change, and search the communicable disease information stored within MDSS. ö Reports: Contains all of the reports available on MDSS. You can specify the type of report you wish to create and what information you would like to include on the report. ö Logout: Terminates your session and returns you to the State of Michigan Department of Community Health Application Portal. 8
The Top Navigation Bar consists of links to different modules: ö Case Investigation: Contains all of the functions to enter and manage cases. You can add, change, and search the communicable disease information stored within MDSS. ö Reports: Contains all of the reports available on MDSS. You can specify the type of report you wish to create and what information you would like to include on the report. ö Logout: Terminates your session and returns you to the State of Michigan Department of Community Health Application Portal. 8
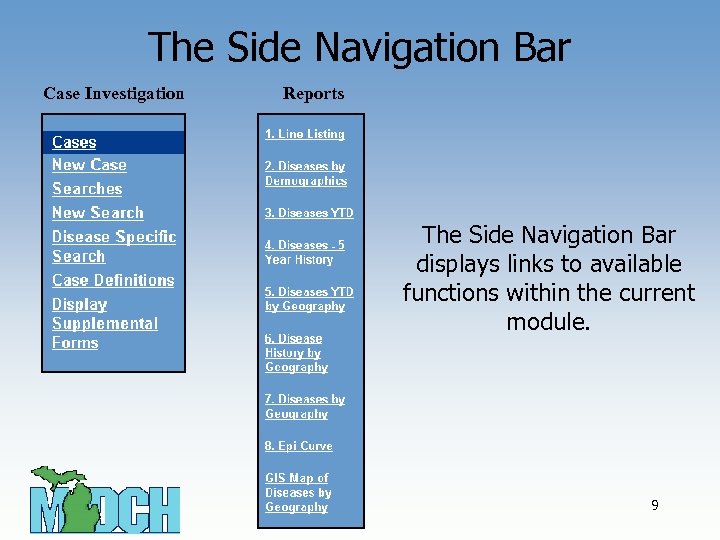 The Side Navigation Bar Case Investigation Reports The Side Navigation Bar displays links to available functions within the current module. 9
The Side Navigation Bar Case Investigation Reports The Side Navigation Bar displays links to available functions within the current module. 9
 On Line Help • The User Guide is accessible on-line. It can be searched by the table of contents, by the index, or by keyword. • Click the HELP buttons throughout the application for assistance relative to your current screen. • Appendix C of the User Guide offers helpful data entry tips. 10
On Line Help • The User Guide is accessible on-line. It can be searched by the table of contents, by the index, or by keyword. • Click the HELP buttons throughout the application for assistance relative to your current screen. • Appendix C of the User Guide offers helpful data entry tips. 10
 MDSS Security • Browser buttons (Back, Forward, Refresh, etc. ) are not available for use in MDSS. • For security, MDSS and SSO will automatically log you out if your session remains inactive for more than 60 minutes. – Save your work frequently – Always save your work and log out of MDSS and the SSO portal if you leave your computer – You will lose unsaved work if you’re automatically logged out 11
MDSS Security • Browser buttons (Back, Forward, Refresh, etc. ) are not available for use in MDSS. • For security, MDSS and SSO will automatically log you out if your session remains inactive for more than 60 minutes. – Save your work frequently – Always save your work and log out of MDSS and the SSO portal if you leave your computer – You will lose unsaved work if you’re automatically logged out 11
 Logging Out 1) Click Logout in MDSS, AND 2) Click Sign Off in the SSO Portal 12
Logging Out 1) Click Logout in MDSS, AND 2) Click Sign Off in the SSO Portal 12
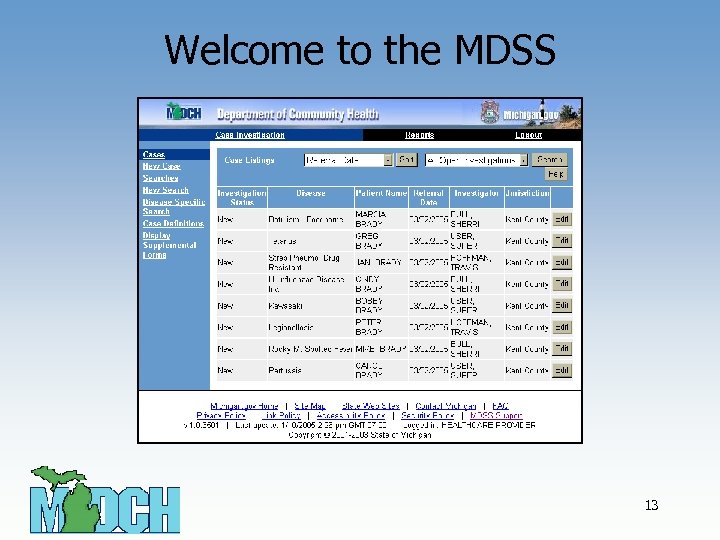 Welcome to the MDSS 13
Welcome to the MDSS 13
 How to Enter a Case into the MDSS
How to Enter a Case into the MDSS
 New Case Entry • The New Case function allows new cases to be manually added to MDSS. • The New Case entry process is divided into three sections. 15
New Case Entry • The New Case function allows new cases to be manually added to MDSS. • The New Case entry process is divided into three sections. 15
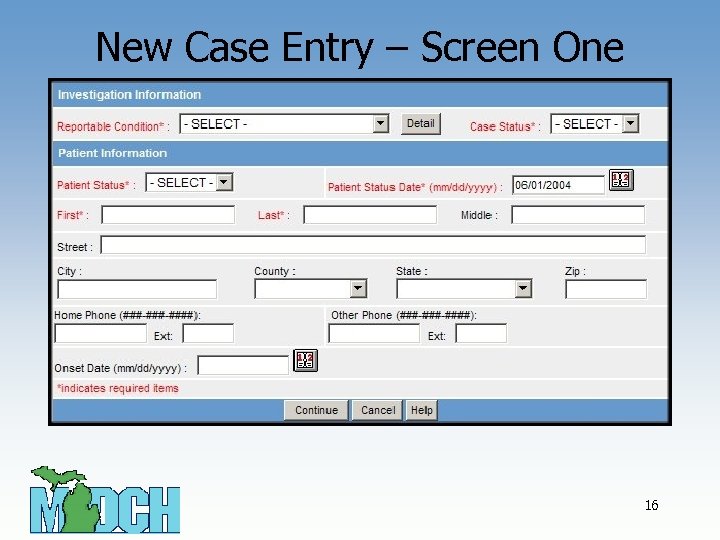 New Case Entry – Screen One 16
New Case Entry – Screen One 16
 Screen One Key Field Definitions • Fields in Red with * are required fields. Case entry will not proceed unless they are completed (Unknown is generally an option). • Case Status – refers to the case definition criteria (Confirmed, Suspect, Not a Case, Probable, Unknown). • Patient Status - This field is used to indicate the present condition of the patient. • Patient Status Date - Automatically set to current date during case entry and updated when a change is made to the “Patient Status”. Can also be entered directly. • Refer to the section New Case in Chapter 4 of User Guide or view Online Help for more details. 17
Screen One Key Field Definitions • Fields in Red with * are required fields. Case entry will not proceed unless they are completed (Unknown is generally an option). • Case Status – refers to the case definition criteria (Confirmed, Suspect, Not a Case, Probable, Unknown). • Patient Status - This field is used to indicate the present condition of the patient. • Patient Status Date - Automatically set to current date during case entry and updated when a change is made to the “Patient Status”. Can also be entered directly. • Refer to the section New Case in Chapter 4 of User Guide or view Online Help for more details. 17
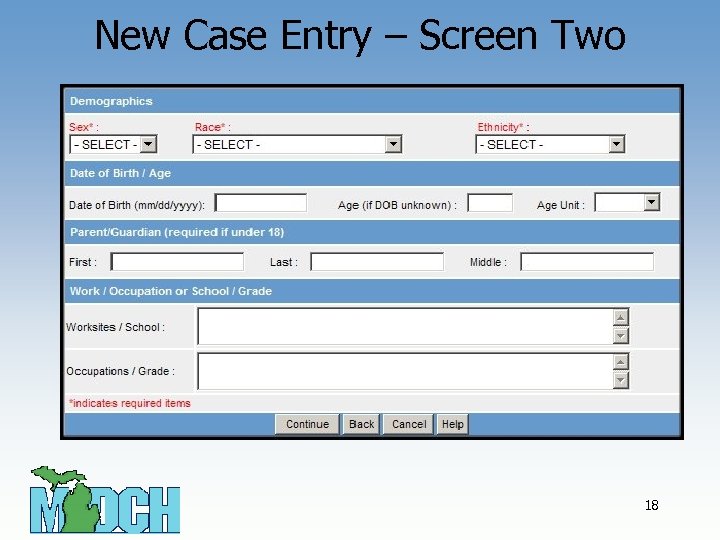 New Case Entry – Screen Two 18
New Case Entry – Screen Two 18
 Screen Two Key Field Definitions • Age - Reflects the age at illness onset by subtracting Onset Date from Date of Birth (when available). Referral Date is used if no Onset Date is available. • Age Unit: Pertains to the measurement of the age of the patient at illness onset (in days, months, or years). • If Date of Birth is not available, Age and Age Units can be entered directly. Age units should be: – Days if Age is less than or equal to 30 days – Months if Age is less than 2 years – Years if Age is greater than or equal to 2 years 19
Screen Two Key Field Definitions • Age - Reflects the age at illness onset by subtracting Onset Date from Date of Birth (when available). Referral Date is used if no Onset Date is available. • Age Unit: Pertains to the measurement of the age of the patient at illness onset (in days, months, or years). • If Date of Birth is not available, Age and Age Units can be entered directly. Age units should be: – Days if Age is less than or equal to 30 days – Months if Age is less than 2 years – Years if Age is greater than or equal to 2 years 19
 New Case Entry – Screen Three 20
New Case Entry – Screen Three 20
 Entering Lab Data for Referrals • Laboratory data is vital to most public health investigations. • There are two options for entering laboratory data during the New Case Entry process: – In the “Notes” section – Or the “Enter Lab Data” section 21
Entering Lab Data for Referrals • Laboratory data is vital to most public health investigations. • There are two options for entering laboratory data during the New Case Entry process: – In the “Notes” section – Or the “Enter Lab Data” section 21
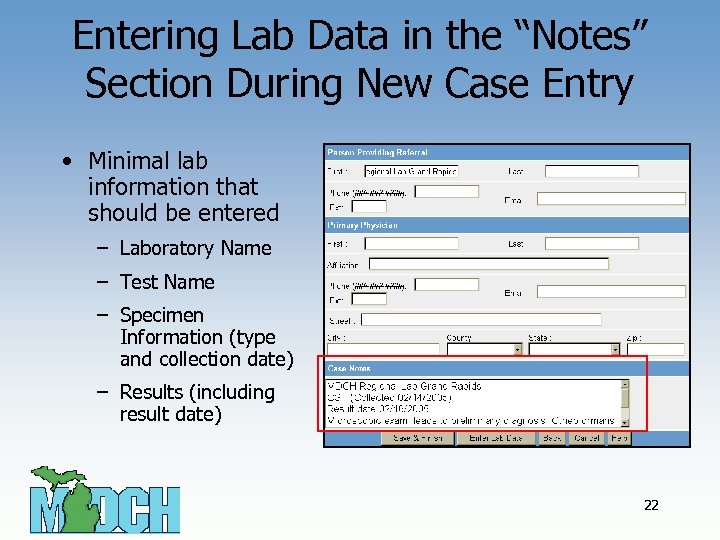 Entering Lab Data in the “Notes” Section During New Case Entry • Minimal lab information that should be entered – Laboratory Name – Test Name – Specimen Information (type and collection date) – Results (including result date) 22
Entering Lab Data in the “Notes” Section During New Case Entry • Minimal lab information that should be entered – Laboratory Name – Test Name – Specimen Information (type and collection date) – Results (including result date) 22
 Choosing “Enter Lab Data” During New Case Entry • You may choose to enter lab data through the “Enter Lab Data” option on the third screen of New Case Entry 23
Choosing “Enter Lab Data” During New Case Entry • You may choose to enter lab data through the “Enter Lab Data” option on the third screen of New Case Entry 23
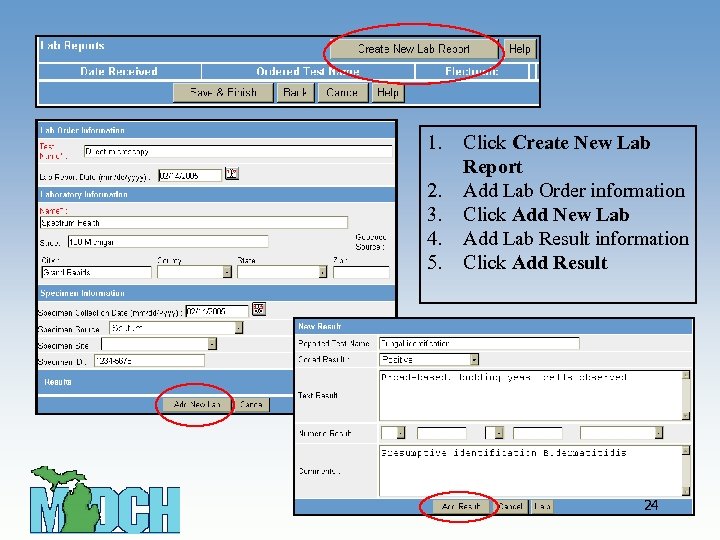 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Click Create New Lab Report Add Lab Order information Click Add New Lab Add Lab Result information Click Add Result 24
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Click Create New Lab Report Add Lab Order information Click Add New Lab Add Lab Result information Click Add Result 24
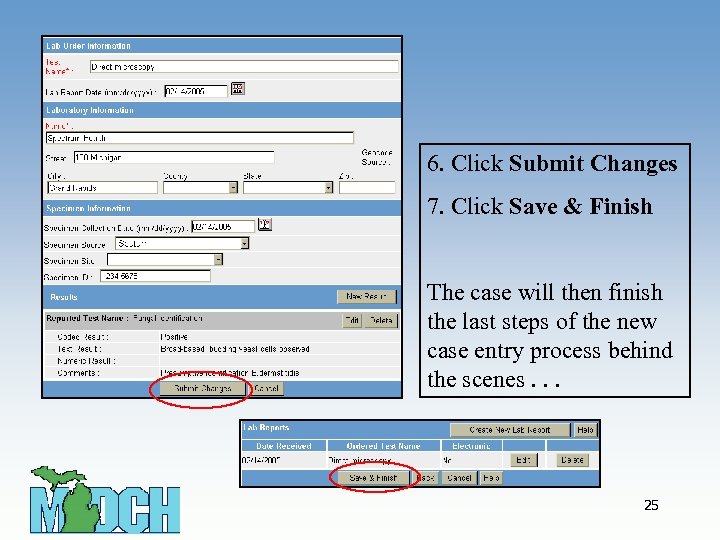 6. Click Submit Changes 7. Click Save & Finish The case will then finish the last steps of the new case entry process behind the scenes. . . 25
6. Click Submit Changes 7. Click Save & Finish The case will then finish the last steps of the new case entry process behind the scenes. . . 25
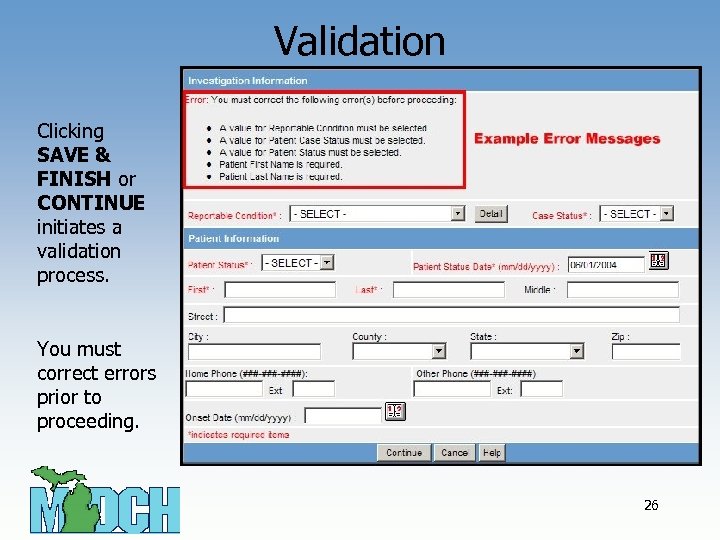 Validation Clicking SAVE & FINISH or CONTINUE initiates a validation process. You must correct errors prior to proceeding. 26
Validation Clicking SAVE & FINISH or CONTINUE initiates a validation process. You must correct errors prior to proceeding. 26
 Background Processing Once a case is entered, the following processes occur behind the scenes: • Geocoding: Validates address, assigns coordinates to map address, supports LHJ referral. • De-Duplication: The process of identifying and merging duplicate patients and case reports. This can result in the case not being immediately available to view. • Case Referral: Determines the referral LHJ based on the Investigation Address (case address if available, otherwise provider or lab address), and assigns the case to the LHJ Administrator to initiate follow-up. More information about these processes can be found in the section Background Processing in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or by viewing Online Help. 27
Background Processing Once a case is entered, the following processes occur behind the scenes: • Geocoding: Validates address, assigns coordinates to map address, supports LHJ referral. • De-Duplication: The process of identifying and merging duplicate patients and case reports. This can result in the case not being immediately available to view. • Case Referral: Determines the referral LHJ based on the Investigation Address (case address if available, otherwise provider or lab address), and assigns the case to the LHJ Administrator to initiate follow-up. More information about these processes can be found in the section Background Processing in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or by viewing Online Help. 27
 Exercise - New Case Entries • Instructor Example • Student Exercise – Log in to the MDSS at https: //sso. state. mi. us/ – Enter a New Laboratory Confirmed Case • Choose Salmonellosis as the Reportable Condition • Complete three screens of new case entry including adding lab results in the case notes area – Enter New Case of Meningitis with suspected viral etiology • Choose “Meningitis-Aseptic” as the reportable condition • Add negative bacterial cultures, symptoms and CSF study results into the case notes area 28
Exercise - New Case Entries • Instructor Example • Student Exercise – Log in to the MDSS at https: //sso. state. mi. us/ – Enter a New Laboratory Confirmed Case • Choose Salmonellosis as the Reportable Condition • Complete three screens of new case entry including adding lab results in the case notes area – Enter New Case of Meningitis with suspected viral etiology • Choose “Meningitis-Aseptic” as the reportable condition • Add negative bacterial cultures, symptoms and CSF study results into the case notes area 28
 Welcome Back to the MDSS 29
Welcome Back to the MDSS 29
 How to View and Edit a Case in the MDSS
How to View and Edit a Case in the MDSS
 Case Listings Overview 31
Case Listings Overview 31
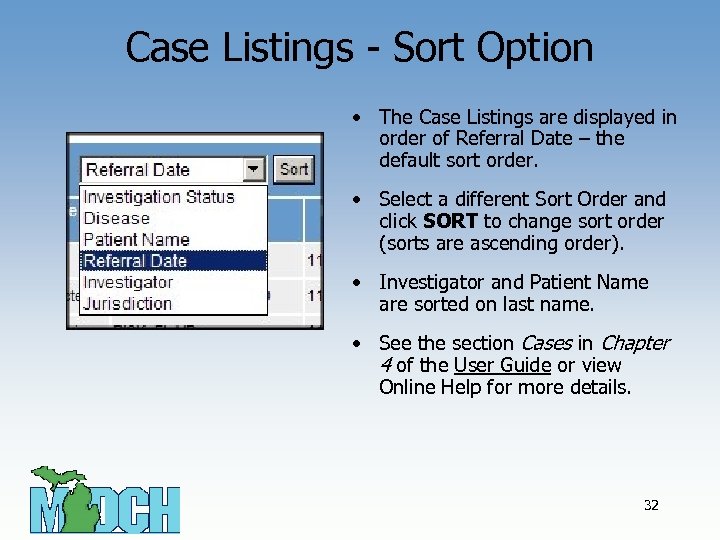 Case Listings - Sort Option • The Case Listings are displayed in order of Referral Date – the default sort order. • Select a different Sort Order and click SORT to change sort order (sorts are ascending order). • Investigator and Patient Name are sorted on last name. • See the section Cases in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or view Online Help for more details. 32
Case Listings - Sort Option • The Case Listings are displayed in order of Referral Date – the default sort order. • Select a different Sort Order and click SORT to change sort order (sorts are ascending order). • Investigator and Patient Name are sorted on last name. • See the section Cases in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or view Online Help for more details. 32
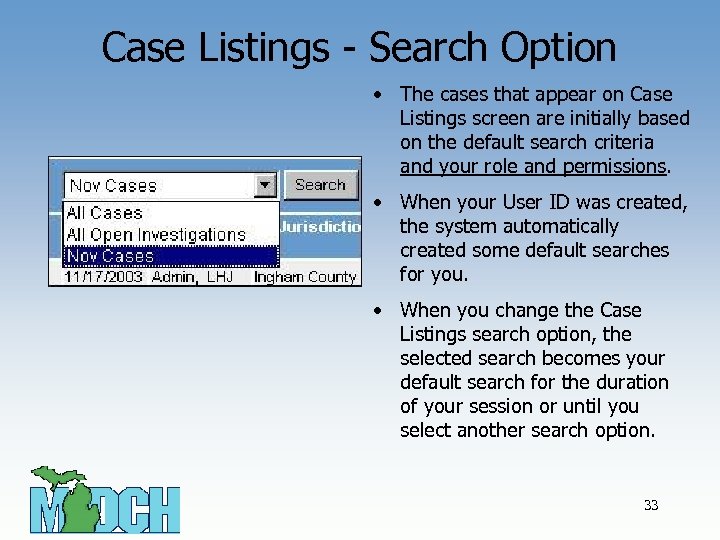 Case Listings - Search Option • The cases that appear on Case Listings screen are initially based on the default search criteria and your role and permissions. • When your User ID was created, the system automatically created some default searches for you. • When you change the Case Listings search option, the selected search becomes your default search for the duration of your session or until you select another search option. 33
Case Listings - Search Option • The cases that appear on Case Listings screen are initially based on the default search criteria and your role and permissions. • When your User ID was created, the system automatically created some default searches for you. • When you change the Case Listings search option, the selected search becomes your default search for the duration of your session or until you select another search option. 33
 Accessing the Case Details 1. Locate the specific case you want to access. 2. Click the EDIT button and the "Case Detail" screens will appear. Note: When you select a case, all cases associated with that patient will be un-editable. 34
Accessing the Case Details 1. Locate the specific case you want to access. 2. Click the EDIT button and the "Case Detail" screens will appear. Note: When you select a case, all cases associated with that patient will be un-editable. 34
 Case Locking • When a case is selected for editing or viewing, all cases for the associated patient are locked by the user who first accesses the record. • All of the screens within “Case Details” will indicate that the case is locked and by which user. 35
Case Locking • When a case is selected for editing or viewing, all cases for the associated patient are locked by the user who first accesses the record. • All of the screens within “Case Details” will indicate that the case is locked and by which user. 35
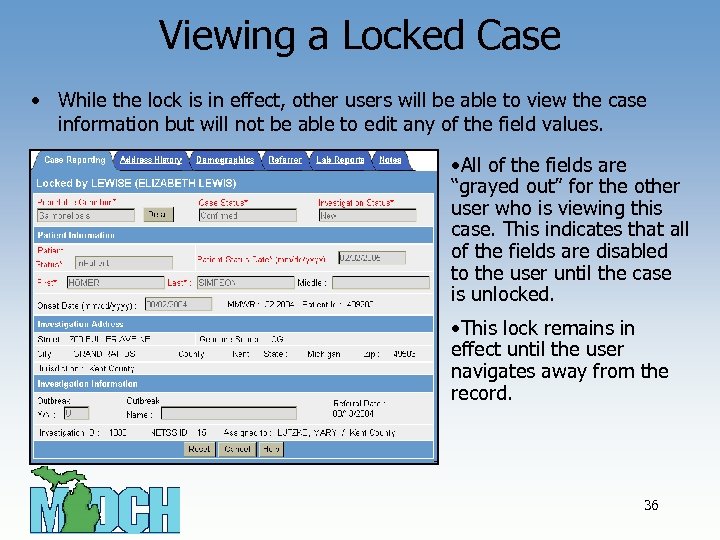 Viewing a Locked Case • While the lock is in effect, other users will be able to view the case information but will not be able to edit any of the field values. • All of the fields are “grayed out” for the other user who is viewing this case. This indicates that all of the fields are disabled to the user until the case is unlocked. • This lock remains in effect until the user navigates away from the record. 36
Viewing a Locked Case • While the lock is in effect, other users will be able to view the case information but will not be able to edit any of the field values. • All of the fields are “grayed out” for the other user who is viewing this case. This indicates that all of the fields are disabled to the user until the case is unlocked. • This lock remains in effect until the user navigates away from the record. 36
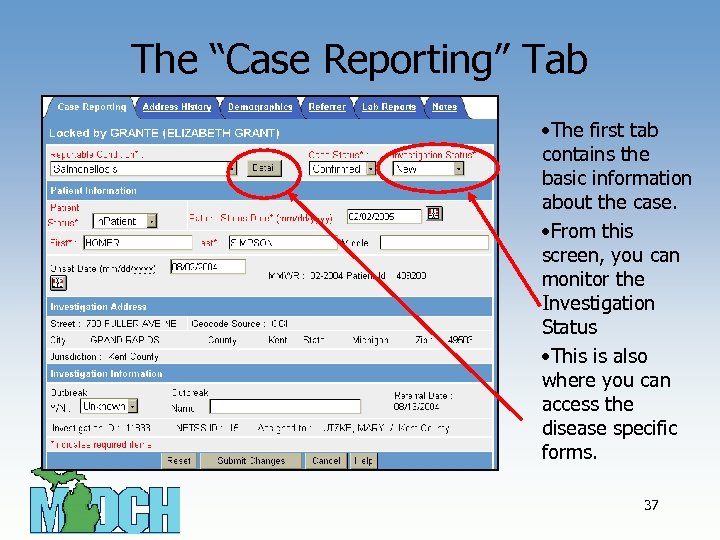 The “Case Reporting” Tab • The first tab contains the basic information about the case. • From this screen, you can monitor the Investigation Status • This is also where you can access the disease specific forms. 37
The “Case Reporting” Tab • The first tab contains the basic information about the case. • From this screen, you can monitor the Investigation Status • This is also where you can access the disease specific forms. 37
 Case Investigation Status • Investigation Status – refers to the stage of the LHD investigation (New, Active, Completed, Cancelled, Superceded). This is the responsibility of LHD. • Resolved cases are marked “Confirmed” or “Not a Case” for Case Status and “Completed” or “Probable” for Investigation Status. • If duplicate cases are entered, all but one are marked “Superceded” for Investigation Status with one case investigated to resolution. • “Cancelled” is selected if the case cannot be investigated to resolution (e. g. , patient or provider can not be reached). 38
Case Investigation Status • Investigation Status – refers to the stage of the LHD investigation (New, Active, Completed, Cancelled, Superceded). This is the responsibility of LHD. • Resolved cases are marked “Confirmed” or “Not a Case” for Case Status and “Completed” or “Probable” for Investigation Status. • If duplicate cases are entered, all but one are marked “Superceded” for Investigation Status with one case investigated to resolution. • “Cancelled” is selected if the case cannot be investigated to resolution (e. g. , patient or provider can not be reached). 38
 Disease Specific Forms • Disease Specific Forms provide: – A place to record supplemental data for reportable conditions requiring more detailed information – A common format for handwritten and computer data entry – A substitute for mailing in case investigation forms • The Disease Specific Forms are based on the communicable disease forms used for case investigations • These forms can be saved, retrieved, and printed at any stage in the case investigation • All Web interface information entered, except Notes and Laboratory Reports, are automatically transferred to the Disease Specific Form when the form is Activated. 39
Disease Specific Forms • Disease Specific Forms provide: – A place to record supplemental data for reportable conditions requiring more detailed information – A common format for handwritten and computer data entry – A substitute for mailing in case investigation forms • The Disease Specific Forms are based on the communicable disease forms used for case investigations • These forms can be saved, retrieved, and printed at any stage in the case investigation • All Web interface information entered, except Notes and Laboratory Reports, are automatically transferred to the Disease Specific Form when the form is Activated. 39
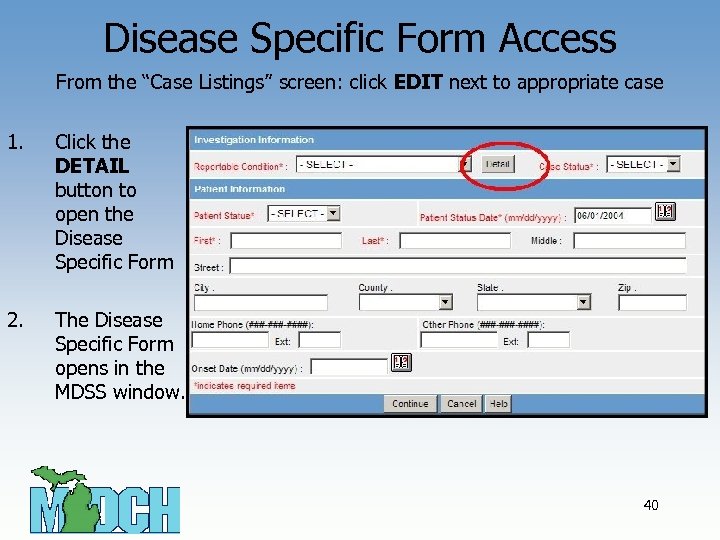 Disease Specific Form Access From the “Case Listings” screen: click EDIT next to appropriate case 1. Click the DETAIL button to open the Disease Specific Form 2. The Disease Specific Form opens in the MDSS window. 40
Disease Specific Form Access From the “Case Listings” screen: click EDIT next to appropriate case 1. Click the DETAIL button to open the Disease Specific Form 2. The Disease Specific Form opens in the MDSS window. 40
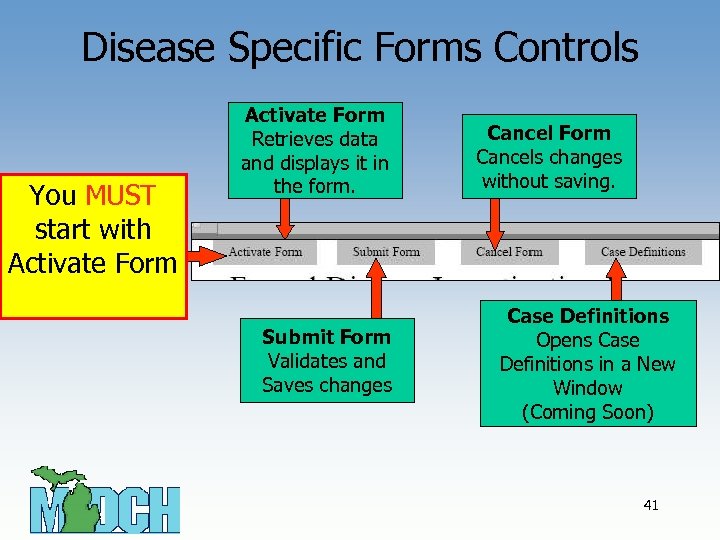 Disease Specific Forms Controls You MUST start with Activate Form Retrieves data and displays it in the form. Submit Form Validates and Saves changes Cancel Form Cancels changes without saving. Case Definitions Opens Case Definitions in a New Window (Coming Soon) 41
Disease Specific Forms Controls You MUST start with Activate Form Retrieves data and displays it in the form. Submit Form Validates and Saves changes Cancel Form Cancels changes without saving. Case Definitions Opens Case Definitions in a New Window (Coming Soon) 41
 Working With Disease Specific Forms 1. After opening form, always start by clicking the ACTIVATE button. This retrieves the form data from the database. 2. Add or edit data to form as required 3. Click the SUBMIT FORM button to save changes 4. Save changes frequently 5. Click the printer icon in the upper left corner to print partially or fully completed forms 6. Details are provided in the section Disease Specific Forms in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or by viewing Online Help. 42
Working With Disease Specific Forms 1. After opening form, always start by clicking the ACTIVATE button. This retrieves the form data from the database. 2. Add or edit data to form as required 3. Click the SUBMIT FORM button to save changes 4. Save changes frequently 5. Click the printer icon in the upper left corner to print partially or fully completed forms 6. Details are provided in the section Disease Specific Forms in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or by viewing Online Help. 42
 Exercise – Disease Specific Forms • • Instructor Example Student Exercise 1. Create a new case (using a different name and demographic information) with “Meningococcal Disease” as the reportable condition 2. Find the new case in your case listings, open the Disease Specific Form and click ACTIVATE 3. Add laboratory, epidemiologic and other information including the following data: a. Bacterial species Neisseria meningitidis of serogroup W 135. b. Symptoms: confusion/memory loss and stiff neck/back c. Muscle paralysis in the “neck” muscles d. Fever of 101 degrees Fahrenheit 4. Save the new information by clicking SUBMIT FORM 43
Exercise – Disease Specific Forms • • Instructor Example Student Exercise 1. Create a new case (using a different name and demographic information) with “Meningococcal Disease” as the reportable condition 2. Find the new case in your case listings, open the Disease Specific Form and click ACTIVATE 3. Add laboratory, epidemiologic and other information including the following data: a. Bacterial species Neisseria meningitidis of serogroup W 135. b. Symptoms: confusion/memory loss and stiff neck/back c. Muscle paralysis in the “neck” muscles d. Fever of 101 degrees Fahrenheit 4. Save the new information by clicking SUBMIT FORM 43
 Welcome Back to the MDSS 44
Welcome Back to the MDSS 44
 Editing Address Information • Address information can be edited in the “Address History” tab • Refer to the section Cases in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or view Online Help for more details. 45
Editing Address Information • Address information can be edited in the “Address History” tab • Refer to the section Cases in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or view Online Help for more details. 45
 Change of Jurisdiction Warning The Change in Jurisdiction Warning occurs if you change the Onset Date, Investigation Address, or Home Address “From and To Dates” because the Address dates and Onset Date determine LHJ referral. 46
Change of Jurisdiction Warning The Change in Jurisdiction Warning occurs if you change the Onset Date, Investigation Address, or Home Address “From and To Dates” because the Address dates and Onset Date determine LHJ referral. 46
 The “Lab Reports” Tab • The Lab Reports tab is where you can view electronic lab reports (ELRs). • “Electronic” value of “Yes” means it was received by automated referral. • Electronic lab reports cannot be modified. • Click CREATE NEW LAB REPORT button to manually add a lab report. • Click EDIT to view or edit an existing lab report. • Use DELETE only if an entered report is not supposed to be associated with the patient. • The Lab Reports tab lists all labs associated with a patient and not just the particular case you are viewing. 47
The “Lab Reports” Tab • The Lab Reports tab is where you can view electronic lab reports (ELRs). • “Electronic” value of “Yes” means it was received by automated referral. • Electronic lab reports cannot be modified. • Click CREATE NEW LAB REPORT button to manually add a lab report. • Click EDIT to view or edit an existing lab report. • Use DELETE only if an entered report is not supposed to be associated with the patient. • The Lab Reports tab lists all labs associated with a patient and not just the particular case you are viewing. 47
 Other Case Detail Tabs • Demographics - provides information regarding the patient and collects important demographic information. • Referrer - provides information regarding the case reporting and who made the referral. Referrer information has two major sections: o Person Providing Referral o Primary Physician • Notes - provides a free form entry of text notes that are associated with a case investigation. • Refer to the section Cases in Chapter 4 of User Guide or view Online Help for more details about these sections. 48
Other Case Detail Tabs • Demographics - provides information regarding the patient and collects important demographic information. • Referrer - provides information regarding the case reporting and who made the referral. Referrer information has two major sections: o Person Providing Referral o Primary Physician • Notes - provides a free form entry of text notes that are associated with a case investigation. • Refer to the section Cases in Chapter 4 of User Guide or view Online Help for more details about these sections. 48
 How to Search in the MDSS
How to Search in the MDSS
 New Searches The New Search function allows you to create a new search. 50
New Searches The New Search function allows you to create a new search. 50
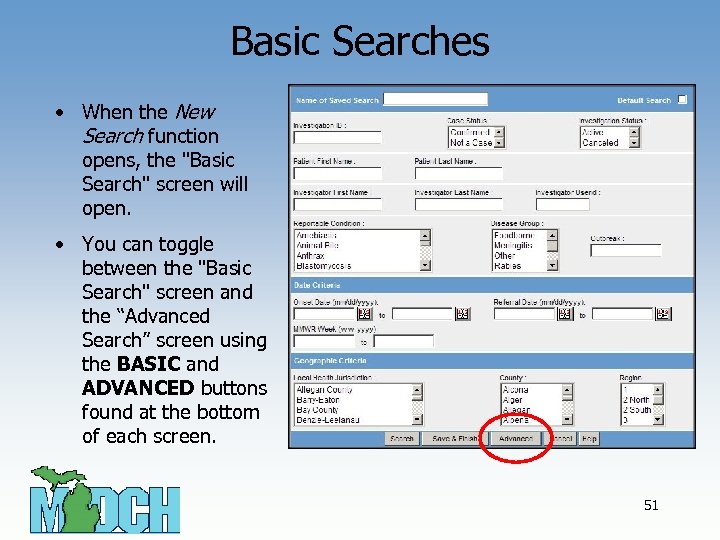 Basic Searches • When the New Search function opens, the "Basic Search" screen will open. • You can toggle between the "Basic Search" screen and the “Advanced Search” screen using the BASIC and ADVANCED buttons found at the bottom of each screen. 51
Basic Searches • When the New Search function opens, the "Basic Search" screen will open. • You can toggle between the "Basic Search" screen and the “Advanced Search” screen using the BASIC and ADVANCED buttons found at the bottom of each screen. 51
 General Notes on Searching • You are only able to search on cases that you have entered. • Text Searches use an asterisk (*) as a “wild card” • L* gives all entries that start with L • Date searches: • Enter only “From Date” for all cases after and including a certain date • Enter only “To Date” for all cases before and including a certain date • Each new variable added operates like an “and”; the search becomes more restrictive (i. e. , Male and 2 -6 YOA and Salmonella) • Each selection within a variable operates like an “or”; the search becomes less restrictive (i. e. , Detroit or Jackson or Alpena) 52
General Notes on Searching • You are only able to search on cases that you have entered. • Text Searches use an asterisk (*) as a “wild card” • L* gives all entries that start with L • Date searches: • Enter only “From Date” for all cases after and including a certain date • Enter only “To Date” for all cases before and including a certain date • Each new variable added operates like an “and”; the search becomes more restrictive (i. e. , Male and 2 -6 YOA and Salmonella) • Each selection within a variable operates like an “or”; the search becomes less restrictive (i. e. , Detroit or Jackson or Alpena) 52
 Selecting and De-selecting Multiple Options Selecting Multiple Sequential Options 1. 2. Move the mouse cursor to first desired option on the list and click left mouse button. Move the mouse cursor to the last desired option of the list and hold down the SHIFT key while clicking the left mouse button. Selecting Multiple Non-Consecutive Options 1. 2. Move the mouse cursor to first desired option on the list and click left mouse button. Move the mouse cursor to the next desired option on the list and hold down the CTRL key while clicking the left mouse button. Repeat #2 until all desired options selected. De-Selecting Options 1. Move the mouse cursor to option you want to de-select and hold down the CTRL key while clicking the left mouse button See Appendix C for more details 53
Selecting and De-selecting Multiple Options Selecting Multiple Sequential Options 1. 2. Move the mouse cursor to first desired option on the list and click left mouse button. Move the mouse cursor to the last desired option of the list and hold down the SHIFT key while clicking the left mouse button. Selecting Multiple Non-Consecutive Options 1. 2. Move the mouse cursor to first desired option on the list and click left mouse button. Move the mouse cursor to the next desired option on the list and hold down the CTRL key while clicking the left mouse button. Repeat #2 until all desired options selected. De-Selecting Options 1. Move the mouse cursor to option you want to de-select and hold down the CTRL key while clicking the left mouse button See Appendix C for more details 53
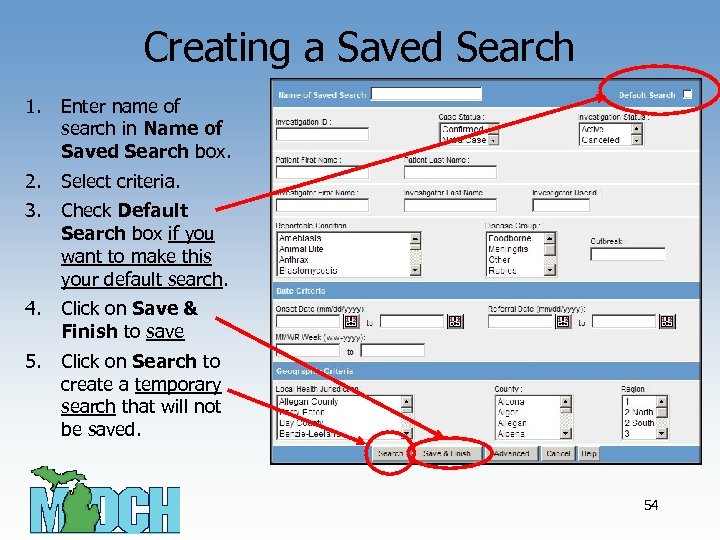 Creating a Saved Search 1. Enter name of search in Name of Saved Search box. 2. Select criteria. 3. Check Default Search box if you want to make this your default search. 4. Click on Save & Finish to save 5. Click on Search to create a temporary search that will not be saved. 54
Creating a Saved Search 1. Enter name of search in Name of Saved Search box. 2. Select criteria. 3. Check Default Search box if you want to make this your default search. 4. Click on Save & Finish to save 5. Click on Search to create a temporary search that will not be saved. 54
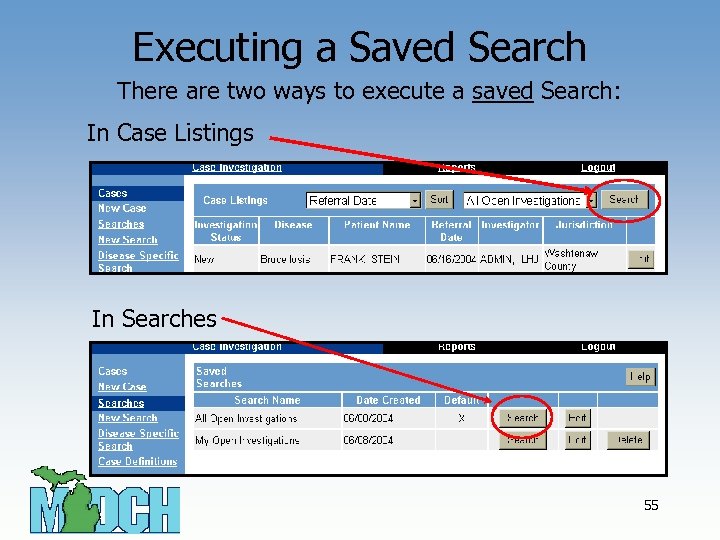 Executing a Saved Search There are two ways to execute a saved Search: In Case Listings In Searches 55
Executing a Saved Search There are two ways to execute a saved Search: In Case Listings In Searches 55
 Editing and Deleting Saved Searches The Searches function provides access to your saved searches to execute, edit, or delete existing searches. • You cannot delete your default search, but Edit allows you to select a new default search. • EDIT search works just like New Search but starts with the existing search criteria. 56
Editing and Deleting Saved Searches The Searches function provides access to your saved searches to execute, edit, or delete existing searches. • You cannot delete your default search, but Edit allows you to select a new default search. • EDIT search works just like New Search but starts with the existing search criteria. 56
 Disease Specific Search • The Search and New Search functions limit the selectable criteria to basic case information - information that is common to all diseases such as the patient last name and allows you to search across multiple diseases. • The Disease Specific Search expands the selectable criteria to include all of the data collected for a particular reportable condition but you can only search one disease at a time. 57
Disease Specific Search • The Search and New Search functions limit the selectable criteria to basic case information - information that is common to all diseases such as the patient last name and allows you to search across multiple diseases. • The Disease Specific Search expands the selectable criteria to include all of the data collected for a particular reportable condition but you can only search one disease at a time. 57
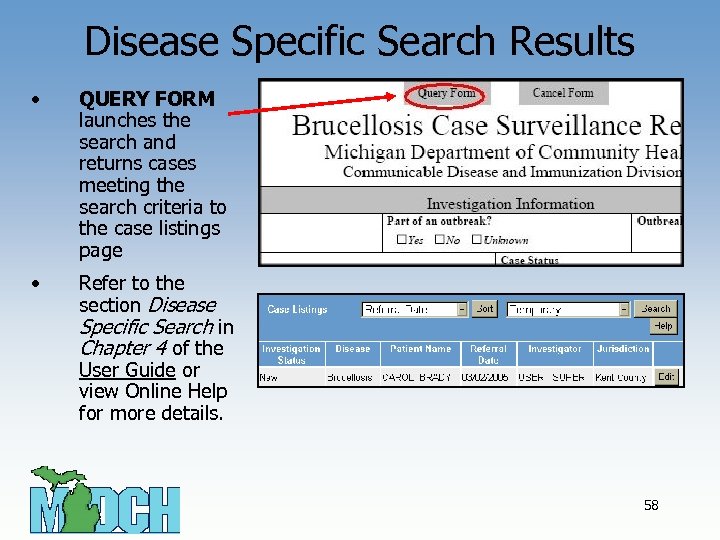 Disease Specific Search Results • QUERY FORM launches the search and returns cases meeting the search criteria to the case listings page • Refer to the section Disease Specific Search in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or view Online Help for more details. 58
Disease Specific Search Results • QUERY FORM launches the search and returns cases meeting the search criteria to the case listings page • Refer to the section Disease Specific Search in Chapter 4 of the User Guide or view Online Help for more details. 58
 Exercise – Creating a New Search and Modifying a Search • Instructor Example • Student Exercise – Create search for all current (Investigation Status of “New” or “Active”) cases of Salmonellosis in the last six months – Save as “Salmonella” and then execute – Open your “Salmonella” search from your saved searches – Add “Meningococcal Disease” from the Reportable Condition list – Save as “Salmonella and N. Meningitidis” and then execute 59
Exercise – Creating a New Search and Modifying a Search • Instructor Example • Student Exercise – Create search for all current (Investigation Status of “New” or “Active”) cases of Salmonellosis in the last six months – Save as “Salmonella” and then execute – Open your “Salmonella” search from your saved searches – Add “Meningococcal Disease” from the Reportable Condition list – Save as “Salmonella and N. Meningitidis” and then execute 59
 Exercise – Disease Specific Search • Instructor Example • Student Exercise – Use the Disease Specific Search to find cases of Meningococcal Disease that match the following criteria: • W 135 is the serotype • And the case had muscle paralysis in the neck muscles 60
Exercise – Disease Specific Search • Instructor Example • Student Exercise – Use the Disease Specific Search to find cases of Meningococcal Disease that match the following criteria: • W 135 is the serotype • And the case had muscle paralysis in the neck muscles 60
 Welcome Back to the MDSS 61
Welcome Back to the MDSS 61
 Closing a Case and Reporting to CDC • Only LHJ Administrators and State staff may close a case • Only cases with Case Status “Confirmed” and Investigation Status “Completed” or “Probably” are reported to the CDC • Changes made to cases that have been reported to the CDC will be resolved during annual data cleaning 62
Closing a Case and Reporting to CDC • Only LHJ Administrators and State staff may close a case • Only cases with Case Status “Confirmed” and Investigation Status “Completed” or “Probably” are reported to the CDC • Changes made to cases that have been reported to the CDC will be resolved during annual data cleaning 62
 Print Investigation • Currently, the Print Investigation feature within the “Case Detail” tabs has been disabled within MDSS. • For now, use the Disease Specific Form to print case investigation information. 1) Open the form, 2) click Activate Form, and then 3) click the Printer icon in the toolbar. 63
Print Investigation • Currently, the Print Investigation feature within the “Case Detail” tabs has been disabled within MDSS. • For now, use the Disease Specific Form to print case investigation information. 1) Open the form, 2) click Activate Form, and then 3) click the Printer icon in the toolbar. 63
 Display the Supplemental Forms MDSS offers a method for printing and displaying blank Disease Specific Forms. 1. From the Side Navigation bar, point and click the DISPLAY SUPPLEMENTAL FORMS link. The “Supplemental Forms” screen will appear. 2. Click the VIEW button. The Disease Specific form will open. 3. Click the Close Form button to close the form and return to the form list. 64
Display the Supplemental Forms MDSS offers a method for printing and displaying blank Disease Specific Forms. 1. From the Side Navigation bar, point and click the DISPLAY SUPPLEMENTAL FORMS link. The “Supplemental Forms” screen will appear. 2. Click the VIEW button. The Disease Specific form will open. 3. Click the Close Form button to close the form and return to the form list. 64
 How to Run a Report in the MDSS
How to Run a Report in the MDSS
 Reports There are several reports formats available within the MDSS Reports module: • • • Report Report Report 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - Line Listing Disease by Demographics Diseases YTD Diseases – 5 Year History Diseases YTD by Geography Disease History by Geography Diseases by Geography Epi Curve GIS Reports 66
Reports There are several reports formats available within the MDSS Reports module: • • • Report Report Report 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - Line Listing Disease by Demographics Diseases YTD Diseases – 5 Year History Diseases YTD by Geography Disease History by Geography Diseases by Geography Epi Curve GIS Reports 66
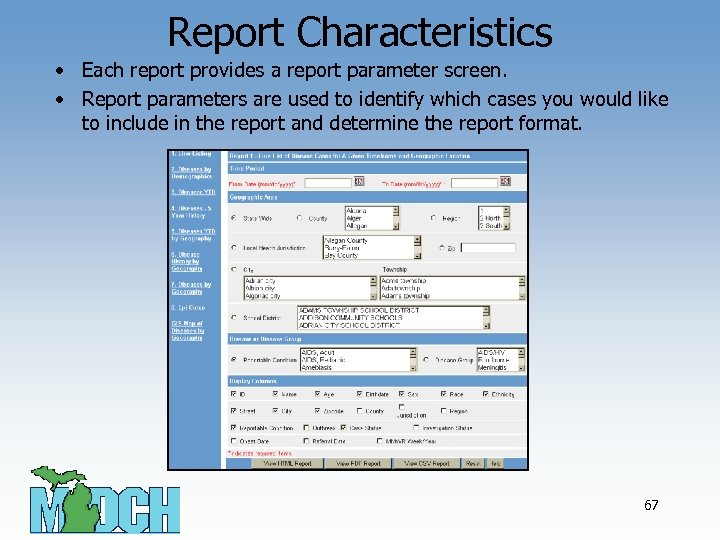 Report Characteristics • Each report provides a report parameter screen. • Report parameters are used to identify which cases you would like to include in the report and determine the report format. 67
Report Characteristics • Each report provides a report parameter screen. • Report parameters are used to identify which cases you would like to include in the report and determine the report format. 67
 Notes about MDSS Reports • Reports contain data for cases that are: –Identified as "Suspected", "Confirmed“, "Probable”, or “Unknown” in the Case Status field, AND –Identified as “New, ” “Active, ” or “Completed” in the Investigation Status field. –(“Not A Case, ” “Canceled, ” and “Superceded” cases are excluded from Reports. ) • When you enter a date range as the “Time Period” parameter, MDSS selects cases with Onset Dates that fall within that range. If Onset Date is unavailable (missing), MDSS will use Referral Date instead. • “Report 1 – Line Listing” presents patient-level data. This report is limited to what is available to that user in the case listings. • The rest of the reports presents counts or rates for all the cases in the state (no identifying data); therefore, there are no userassociated restrictions. 68
Notes about MDSS Reports • Reports contain data for cases that are: –Identified as "Suspected", "Confirmed“, "Probable”, or “Unknown” in the Case Status field, AND –Identified as “New, ” “Active, ” or “Completed” in the Investigation Status field. –(“Not A Case, ” “Canceled, ” and “Superceded” cases are excluded from Reports. ) • When you enter a date range as the “Time Period” parameter, MDSS selects cases with Onset Dates that fall within that range. If Onset Date is unavailable (missing), MDSS will use Referral Date instead. • “Report 1 – Line Listing” presents patient-level data. This report is limited to what is available to that user in the case listings. • The rest of the reports presents counts or rates for all the cases in the state (no identifying data); therefore, there are no userassociated restrictions. 68
 Exercise – Epi Curve Report • Instructor Example • Student Exercise 1. Go into the Reports module by clicking Reports link at the top of the screen 2. Select Report 8 – Epi Curve 3. Create a graph with the following properties: a. All the cases of salmonella in the entire state since the beginning of the year grouped by week 4. Display the report in PDF format and save it to your desktop 69
Exercise – Epi Curve Report • Instructor Example • Student Exercise 1. Go into the Reports module by clicking Reports link at the top of the screen 2. Select Report 8 – Epi Curve 3. Create a graph with the following properties: a. All the cases of salmonella in the entire state since the beginning of the year grouped by week 4. Display the report in PDF format and save it to your desktop 69
 Welcome Back to the MDSS 70
Welcome Back to the MDSS 70
 Support and Help Contacts • For browser and connectivity issues contact your local IT support • Your Local Health Department is the primary point of contact for MDSS issues • If your Local Health Department is unavailable – Contact a MDCH Regional Epidemiologist (see next slide for info), or – Contact the CD & Immunization Division of MDCH at (517) 335 -8165 or mdch_mdss@michigan. gov 71
Support and Help Contacts • For browser and connectivity issues contact your local IT support • Your Local Health Department is the primary point of contact for MDSS issues • If your Local Health Department is unavailable – Contact a MDCH Regional Epidemiologist (see next slide for info), or – Contact the CD & Immunization Division of MDCH at (517) 335 -8165 or mdch_mdss@michigan. gov 71
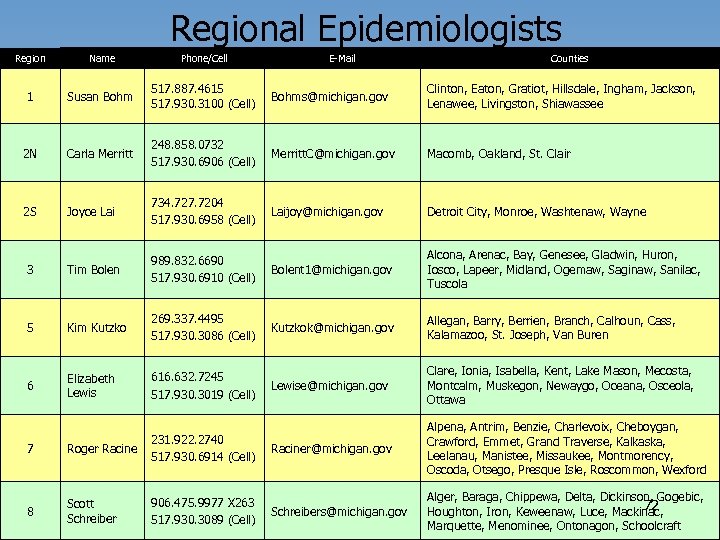 Regional Epidemiologists Region Name Phone/Cell E-Mail Counties 1 Susan Bohm 517. 887. 4615 517. 930. 3100 (Cell) Bohms@michigan. gov Clinton, Eaton, Gratiot, Hillsdale, Ingham, Jackson, Lenawee, Livingston, Shiawassee 2 N Carla Merritt 248. 858. 0732 517. 930. 6906 (Cell) Merritt. C@michigan. gov Macomb, Oakland, St. Clair 2 S Joyce Lai 734. 727. 7204 517. 930. 6958 (Cell) Laijoy@michigan. gov Detroit City, Monroe, Washtenaw, Wayne 3 Tim Bolen 989. 832. 6690 517. 930. 6910 (Cell) Bolent 1@michigan. gov Alcona, Arenac, Bay, Genesee, Gladwin, Huron, Iosco, Lapeer, Midland, Ogemaw, Saginaw, Sanilac, Tuscola 5 Kim Kutzko 269. 337. 4495 517. 930. 3086 (Cell) Kutzkok@michigan. gov Allegan, Barry, Berrien, Branch, Calhoun, Cass, Kalamazoo, St. Joseph, Van Buren 6 Elizabeth Lewis 616. 632. 7245 517. 930. 3019 (Cell) Lewise@michigan. gov Clare, Ionia, Isabella, Kent, Lake Mason, Mecosta, Montcalm, Muskegon, Newaygo, Oceana, Osceola, Ottawa 7 Roger Racine 231. 922. 2740 517. 930. 6914 (Cell) Raciner@michigan. gov Alpena, Antrim, Benzie, Charlevoix, Cheboygan, Crawford, Emmet, Grand Traverse, Kalkaska, Leelanau, Manistee, Missaukee, Montmorency, Oscoda, Otsego, Presque Isle, Roscommon, Wexford 8 Scott Schreiber 906. 475. 9977 X 263 517. 930. 3089 (Cell) Schreibers@michigan. gov Alger, Baraga, Chippewa, Delta, Dickinson, Gogebic, 72 Houghton, Iron, Keweenaw, Luce, Mackinac, Marquette, Menominee, Ontonagon, Schoolcraft
Regional Epidemiologists Region Name Phone/Cell E-Mail Counties 1 Susan Bohm 517. 887. 4615 517. 930. 3100 (Cell) Bohms@michigan. gov Clinton, Eaton, Gratiot, Hillsdale, Ingham, Jackson, Lenawee, Livingston, Shiawassee 2 N Carla Merritt 248. 858. 0732 517. 930. 6906 (Cell) Merritt. C@michigan. gov Macomb, Oakland, St. Clair 2 S Joyce Lai 734. 727. 7204 517. 930. 6958 (Cell) Laijoy@michigan. gov Detroit City, Monroe, Washtenaw, Wayne 3 Tim Bolen 989. 832. 6690 517. 930. 6910 (Cell) Bolent 1@michigan. gov Alcona, Arenac, Bay, Genesee, Gladwin, Huron, Iosco, Lapeer, Midland, Ogemaw, Saginaw, Sanilac, Tuscola 5 Kim Kutzko 269. 337. 4495 517. 930. 3086 (Cell) Kutzkok@michigan. gov Allegan, Barry, Berrien, Branch, Calhoun, Cass, Kalamazoo, St. Joseph, Van Buren 6 Elizabeth Lewis 616. 632. 7245 517. 930. 3019 (Cell) Lewise@michigan. gov Clare, Ionia, Isabella, Kent, Lake Mason, Mecosta, Montcalm, Muskegon, Newaygo, Oceana, Osceola, Ottawa 7 Roger Racine 231. 922. 2740 517. 930. 6914 (Cell) Raciner@michigan. gov Alpena, Antrim, Benzie, Charlevoix, Cheboygan, Crawford, Emmet, Grand Traverse, Kalkaska, Leelanau, Manistee, Missaukee, Montmorency, Oscoda, Otsego, Presque Isle, Roscommon, Wexford 8 Scott Schreiber 906. 475. 9977 X 263 517. 930. 3089 (Cell) Schreibers@michigan. gov Alger, Baraga, Chippewa, Delta, Dickinson, Gogebic, 72 Houghton, Iron, Keweenaw, Luce, Mackinac, Marquette, Menominee, Ontonagon, Schoolcraft
 Acknowledgements • Michigan Department of Community Health – Bureau of Epidemiology – Bureau of Laboratories – Office of Public Health Preparedness • Michigan Department of Information Technology • Altarum Institute • Scientific Technologies Corporation • MDSS Pilot Jurisdictions – Macomb, Kent, Washtenaw, Marquette and Central Michigan • MDSS Steering Committee Members – Matthew Boulton, Bill Colville, Frances Downes, John Dyke, Jim Lee, Pamela Masur, Whitney Mauer, Linda Myers, John Petrasky, Girish Salpekar, Bill Schneider, Melinda Wilkins 73
Acknowledgements • Michigan Department of Community Health – Bureau of Epidemiology – Bureau of Laboratories – Office of Public Health Preparedness • Michigan Department of Information Technology • Altarum Institute • Scientific Technologies Corporation • MDSS Pilot Jurisdictions – Macomb, Kent, Washtenaw, Marquette and Central Michigan • MDSS Steering Committee Members – Matthew Boulton, Bill Colville, Frances Downes, John Dyke, Jim Lee, Pamela Masur, Whitney Mauer, Linda Myers, John Petrasky, Girish Salpekar, Bill Schneider, Melinda Wilkins 73
 Thank you! Any questions? 74
Thank you! Any questions? 74


