c74979aa0889fcff0d43a0079d623079.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 MDG COUNTDOWN: CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT PROGRAM FOR MIDWIVES ON MATERNAL AND NEWBORN CARE
MDG COUNTDOWN: CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT PROGRAM FOR MIDWIVES ON MATERNAL AND NEWBORN CARE
 Presentation Overview 1. Maternal and Newborn deaths in the 2. 3. 4. 5. Philippines “Three delays” Millennium Development Goals Interventions to lessen maternal & newborn mortality (SBA, Em. OC, FP) Philippine Midwifery Law and Midwifery Ethics
Presentation Overview 1. Maternal and Newborn deaths in the 2. 3. 4. 5. Philippines “Three delays” Millennium Development Goals Interventions to lessen maternal & newborn mortality (SBA, Em. OC, FP) Philippine Midwifery Law and Midwifery Ethics
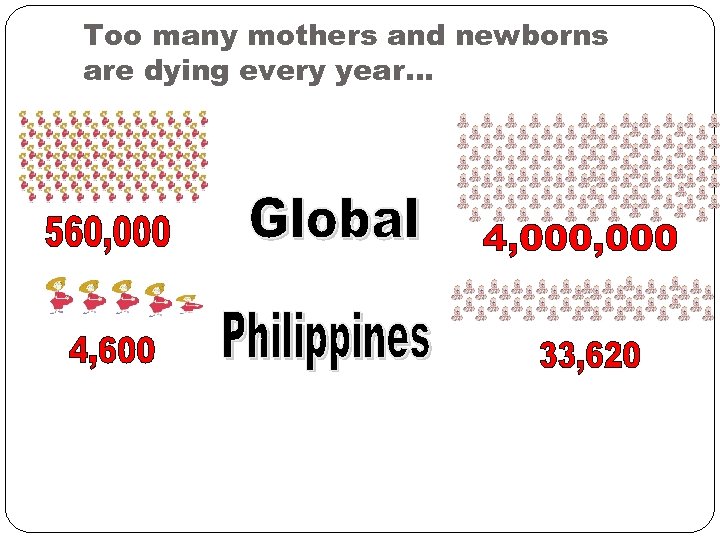 Too many mothers and newborns are dying every year…
Too many mothers and newborns are dying every year…
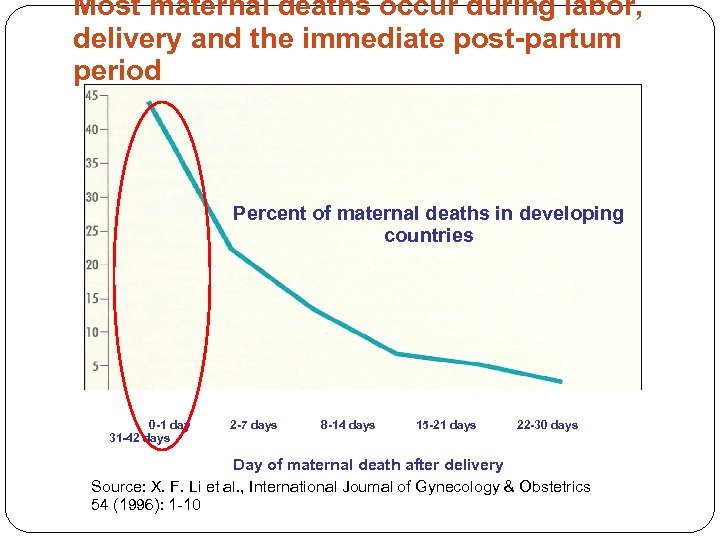 Most maternal deaths occur during labor, delivery and the immediate post-partum period Percent of maternal deaths in developing countries 0 -1 day 31 -42 days 2 -7 days 8 -14 days 15 -21 days 22 -30 days Day of maternal death after delivery Source: X. F. Li et al. , International Joumal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 54 (1996): 1 -10
Most maternal deaths occur during labor, delivery and the immediate post-partum period Percent of maternal deaths in developing countries 0 -1 day 31 -42 days 2 -7 days 8 -14 days 15 -21 days 22 -30 days Day of maternal death after delivery Source: X. F. Li et al. , International Joumal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 54 (1996): 1 -10
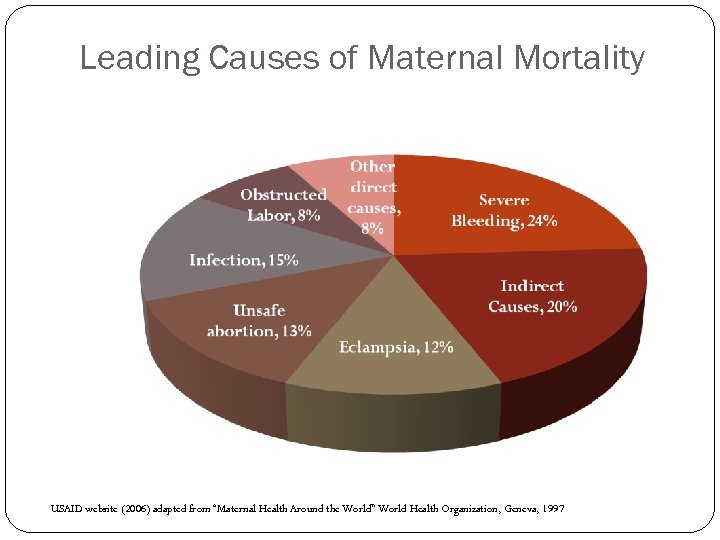 Leading Causes of Maternal Mortality USAID website (2006) adapted from “Maternal Health Around the World” World Health Organization, Geneva, 1997
Leading Causes of Maternal Mortality USAID website (2006) adapted from “Maternal Health Around the World” World Health Organization, Geneva, 1997
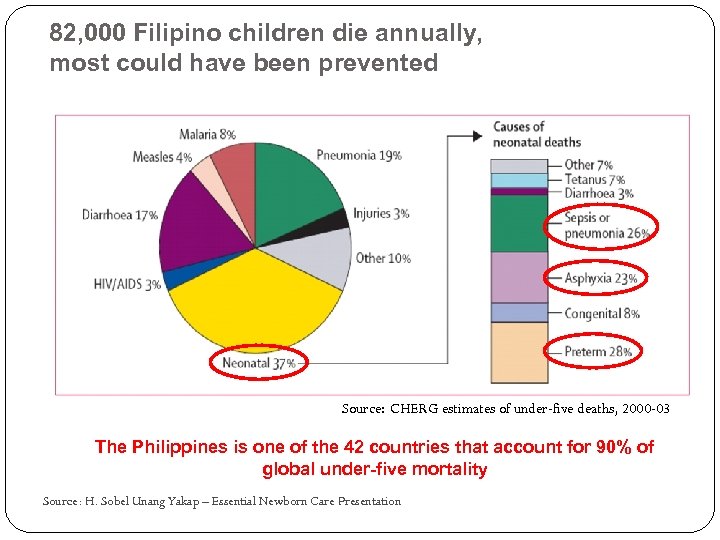 82, 000 Filipino children die annually, most could have been prevented Source: CHERG estimates of under-five deaths, 2000 -03 The Philippines is one of the 42 countries that account for 90% of global under-five mortality Source: H. Sobel Unang Yakap – Essential Newborn Care Presentation
82, 000 Filipino children die annually, most could have been prevented Source: CHERG estimates of under-five deaths, 2000 -03 The Philippines is one of the 42 countries that account for 90% of global under-five mortality Source: H. Sobel Unang Yakap – Essential Newborn Care Presentation
 Reasons for High Maternal and Newborn Mortality Rate • Young age at marriage & first pregnancy • Domestic violence and gender inequality • Poor maternal health • Poor hygiene during and after delivery • Lack of/poor newborn care • The three delays
Reasons for High Maternal and Newborn Mortality Rate • Young age at marriage & first pregnancy • Domestic violence and gender inequality • Poor maternal health • Poor hygiene during and after delivery • Lack of/poor newborn care • The three delays
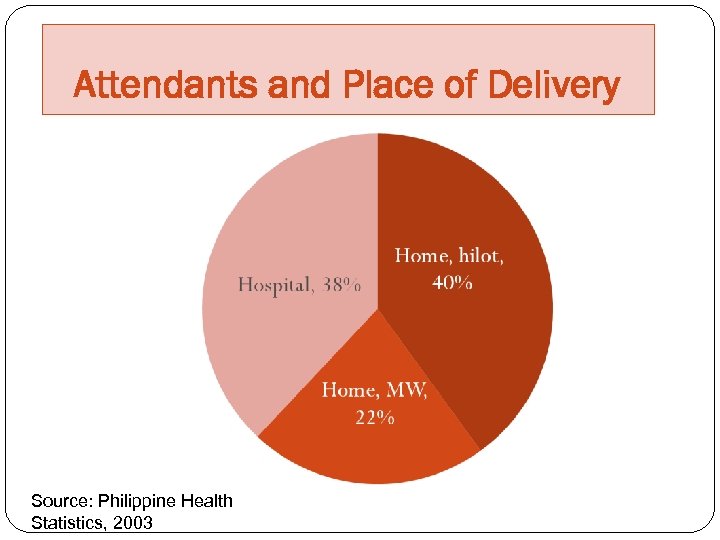 Attendants and Place of Delivery Source: Philippine Health Statistics, 2003
Attendants and Place of Delivery Source: Philippine Health Statistics, 2003
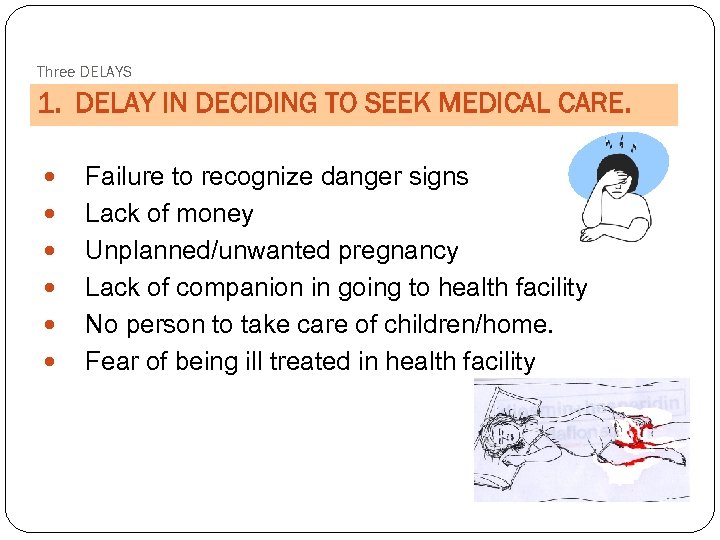 Three DELAYS 1. DELAY IN DECIDING TO SEEK MEDICAL CARE. Failure to recognize danger signs Lack of money Unplanned/unwanted pregnancy Lack of companion in going to health facility No person to take care of children/home. Fear of being ill treated in health facility
Three DELAYS 1. DELAY IN DECIDING TO SEEK MEDICAL CARE. Failure to recognize danger signs Lack of money Unplanned/unwanted pregnancy Lack of companion in going to health facility No person to take care of children/home. Fear of being ill treated in health facility
 Three DELAYS 2. DELAY IN IDENTIFYING and REACHING THE APPROPRIATE FACILITY Distance from a woman’s home to health facility/provider Lack of/poor condition of roads Lack of emergency transportation Lack of awareness of existing services Lack of community support
Three DELAYS 2. DELAY IN IDENTIFYING and REACHING THE APPROPRIATE FACILITY Distance from a woman’s home to health facility/provider Lack of/poor condition of roads Lack of emergency transportation Lack of awareness of existing services Lack of community support
 Three DELAYS 3. DELAY IN RECEIVING APPROPRIATE and ADEQUATE CARE AT HEALTH FACILITY Lack of health care providers Shortage of supplies Lack of equipments Lack of competence of health providers Weak referral system
Three DELAYS 3. DELAY IN RECEIVING APPROPRIATE and ADEQUATE CARE AT HEALTH FACILITY Lack of health care providers Shortage of supplies Lack of equipments Lack of competence of health providers Weak referral system

 MDG 4: Reduce Child Mortality Reduce Under 5 -mortality rate from 80. 0 to 26. 7 (per 1, 000 LB) Reduce Infant mortality rate from 57. 0 to 19. 0 (per 1, 000 LB)
MDG 4: Reduce Child Mortality Reduce Under 5 -mortality rate from 80. 0 to 26. 7 (per 1, 000 LB) Reduce Infant mortality rate from 57. 0 to 19. 0 (per 1, 000 LB)
 MDG 5: Improve Maternal Health To accomplish MDG 5: Reduce maternal mortality by 75% by 2015 (for the Philippines the target is to reduce MMR from 209 to 52 deaths per 100, 000 live births).
MDG 5: Improve Maternal Health To accomplish MDG 5: Reduce maternal mortality by 75% by 2015 (for the Philippines the target is to reduce MMR from 209 to 52 deaths per 100, 000 live births).
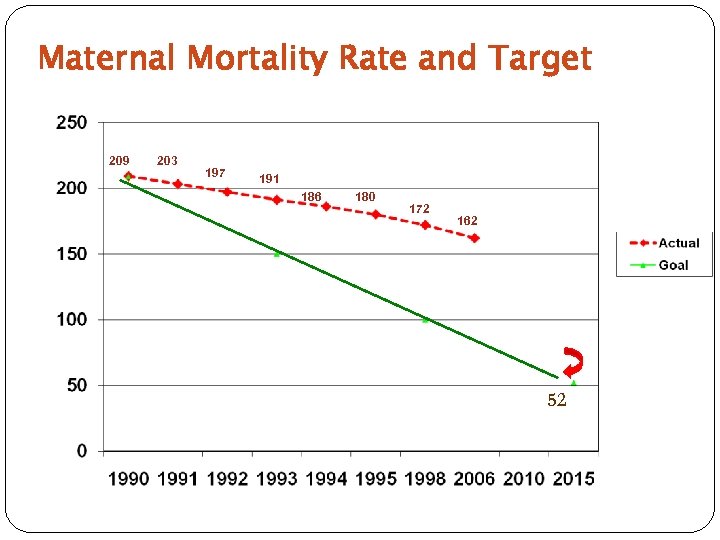 Maternal Mortality Rate and Target 209 203 197 191 186 180 172 162 52
Maternal Mortality Rate and Target 209 203 197 191 186 180 172 162 52
 How will we make it happen? (Current tools to avert maternal death and disability) • A skilled health care professional attends every childbirth • Every woman has access to Emergency Obstetric and Newborn Care (Em. ONC) • Family planning services to help women space their pregnancies Source: Averting Maternal Death and Disability Program
How will we make it happen? (Current tools to avert maternal death and disability) • A skilled health care professional attends every childbirth • Every woman has access to Emergency Obstetric and Newborn Care (Em. ONC) • Family planning services to help women space their pregnancies Source: Averting Maternal Death and Disability Program
 Skilled Care During Childbirth The single most important way to reduce maternal deaths is to ensure that a skilled attendant is present at every birth. Source: A Joint WHO/UNFPA/UNICEF/World Bank Statement on Reduction of Maternal Mortality, 1999.
Skilled Care During Childbirth The single most important way to reduce maternal deaths is to ensure that a skilled attendant is present at every birth. Source: A Joint WHO/UNFPA/UNICEF/World Bank Statement on Reduction of Maternal Mortality, 1999.
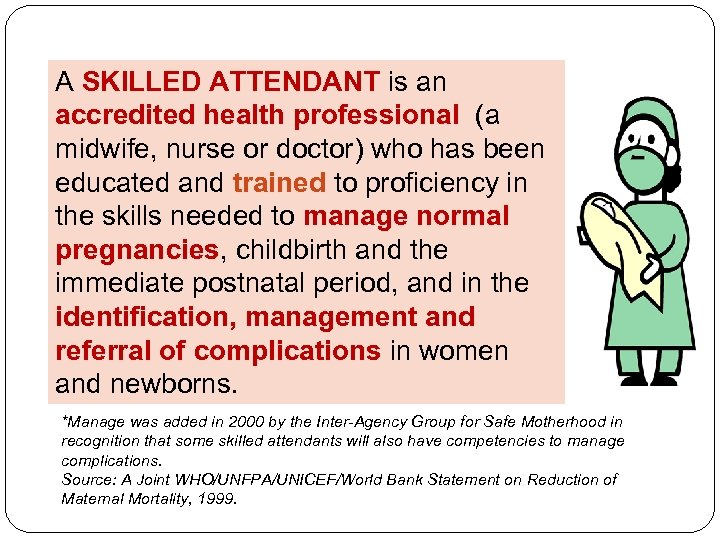 A SKILLED ATTENDANT is an accredited health professional (a midwife, nurse or doctor) who has been educated and trained to proficiency in the skills needed to manage normal pregnancies, childbirth and the immediate postnatal period, and in the identification, management and referral of complications in women and newborns. *Manage was added in 2000 by the Inter-Agency Group for Safe Motherhood in recognition that some skilled attendants will also have competencies to manage complications. Source: A Joint WHO/UNFPA/UNICEF/World Bank Statement on Reduction of Maternal Mortality, 1999.
A SKILLED ATTENDANT is an accredited health professional (a midwife, nurse or doctor) who has been educated and trained to proficiency in the skills needed to manage normal pregnancies, childbirth and the immediate postnatal period, and in the identification, management and referral of complications in women and newborns. *Manage was added in 2000 by the Inter-Agency Group for Safe Motherhood in recognition that some skilled attendants will also have competencies to manage complications. Source: A Joint WHO/UNFPA/UNICEF/World Bank Statement on Reduction of Maternal Mortality, 1999.
 EMERGENCY OBSTETRIC and NEWBORN CARE (Em. ONC) … the elements of obstetric & newborn care needed for the management of normal and complicated pregnancy, delivery, postpartum periods and the newborn. Early detection and treatment of problem pregnancies to prevent progression to an emergency. Management of emergency complications* Definition BEm. ONC CEm. ONC
EMERGENCY OBSTETRIC and NEWBORN CARE (Em. ONC) … the elements of obstetric & newborn care needed for the management of normal and complicated pregnancy, delivery, postpartum periods and the newborn. Early detection and treatment of problem pregnancies to prevent progression to an emergency. Management of emergency complications* Definition BEm. ONC CEm. ONC
 Em. ONC Key Functions Parenteral (IV or IM) administration of Antibiotics Oxytocin Anticonvulsants Manual Removal of Placenta Removal of Retained Products of conception Assisted Vaginal Delivery Administration of corticosteroid for preterm labor Essential Newborn Care Surgery (Cesarean Section) Blood Transfusion
Em. ONC Key Functions Parenteral (IV or IM) administration of Antibiotics Oxytocin Anticonvulsants Manual Removal of Placenta Removal of Retained Products of conception Assisted Vaginal Delivery Administration of corticosteroid for preterm labor Essential Newborn Care Surgery (Cesarean Section) Blood Transfusion
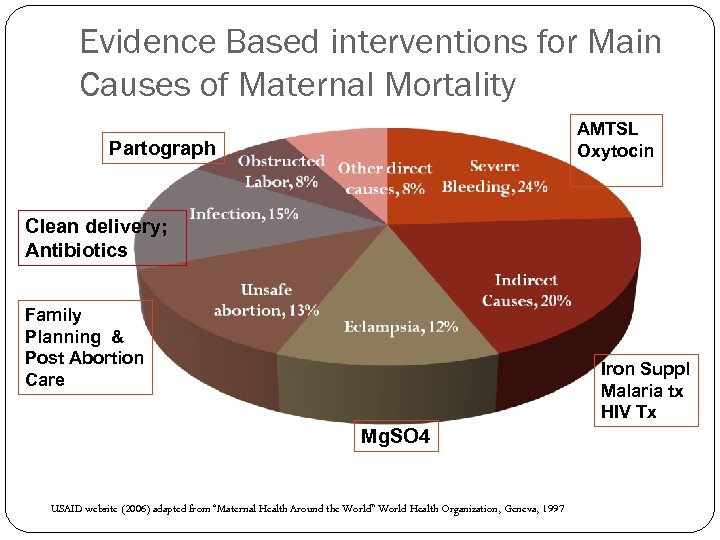 Evidence Based interventions for Main Causes of Maternal Mortality AMTSL Oxytocin Partograph Clean delivery; Antibiotics Family Planning & Post Abortion Care Iron Suppl Malaria tx HIV Tx Mg. SO 4 USAID website (2006) adapted from “Maternal Health Around the World” World Health Organization, Geneva, 1997
Evidence Based interventions for Main Causes of Maternal Mortality AMTSL Oxytocin Partograph Clean delivery; Antibiotics Family Planning & Post Abortion Care Iron Suppl Malaria tx HIV Tx Mg. SO 4 USAID website (2006) adapted from “Maternal Health Around the World” World Health Organization, Geneva, 1997
 Functioning referral system
Functioning referral system
 The Midwifery Act of 1992 Practice of Midwifery defined 1. care of women during pregnancy, labor and puerperium; management of normal deliveries 2. health education of the patient, family and community; 3. primary health care in the community, including nutrition and family planning 4. carrying out the written order of physician with regard to antenatal, intranatal and postnatal of the normal pregnant mother, 5. giving immunization
The Midwifery Act of 1992 Practice of Midwifery defined 1. care of women during pregnancy, labor and puerperium; management of normal deliveries 2. health education of the patient, family and community; 3. primary health care in the community, including nutrition and family planning 4. carrying out the written order of physician with regard to antenatal, intranatal and postnatal of the normal pregnant mother, 5. giving immunization
 Skills required by R. A. 7392 PInternal examination during labor PRepair of obstetric perineal lacerations PIntravenous fluid insertion POxytocics after delivery of placenta PVitamin K for newborn
Skills required by R. A. 7392 PInternal examination during labor PRepair of obstetric perineal lacerations PIntravenous fluid insertion POxytocics after delivery of placenta PVitamin K for newborn
 Principles of Professional Conduct In providing professional services, a certain level of competence is necessary. Professionals shall undertake only those services that they can reasonably deliver with professional competence. Keep up with new knowledge and techniques in their field, continually improve their skills and upgrade their level of competence, and take part in a lifelong continuing education program. Source: Code of Good Governance for the Professions in the Philippines signed June 23, 2003.
Principles of Professional Conduct In providing professional services, a certain level of competence is necessary. Professionals shall undertake only those services that they can reasonably deliver with professional competence. Keep up with new knowledge and techniques in their field, continually improve their skills and upgrade their level of competence, and take part in a lifelong continuing education program. Source: Code of Good Governance for the Professions in the Philippines signed June 23, 2003.
 The Way Forward 1. Recognize signs & symptoms of obstetric complications 2. Know when & where to seek care if complications arise 3. Invest in community education: • Eliminate delays 4. Create women friendly policies
The Way Forward 1. Recognize signs & symptoms of obstetric complications 2. Know when & where to seek care if complications arise 3. Invest in community education: • Eliminate delays 4. Create women friendly policies
 References 7. National Demographic and Health Survey 2008 National Statistic Office (NSO) Philippines and ORC Macro Making Pregnancy Safer World Health Organization Geneva 2002 Averting Maternal Death and Disability Program materials Columbia University New York Managing Complications in Pregnancy and Childbirth World Health Organization Geneva 2003 Pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and newborn care: A guide for essential practice - Updated second edition: Pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and newborn care 2003 World Health Organization Promoting Quality Maternal and Newborn Care: A Reference Manual for Program Managers. Copyright © 1998 Cooperative for Assistance and Relief Everywhere, Inc. (CARE). The Millennium Project Background Paper Task Force on Child Health and 8. Linangan ng Kababaihan (Likhaan) Safe Motherhood poster 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Maternal Health March 2003, Freedman Lynn et al Thank you!!!
References 7. National Demographic and Health Survey 2008 National Statistic Office (NSO) Philippines and ORC Macro Making Pregnancy Safer World Health Organization Geneva 2002 Averting Maternal Death and Disability Program materials Columbia University New York Managing Complications in Pregnancy and Childbirth World Health Organization Geneva 2003 Pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and newborn care: A guide for essential practice - Updated second edition: Pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and newborn care 2003 World Health Organization Promoting Quality Maternal and Newborn Care: A Reference Manual for Program Managers. Copyright © 1998 Cooperative for Assistance and Relief Everywhere, Inc. (CARE). The Millennium Project Background Paper Task Force on Child Health and 8. Linangan ng Kababaihan (Likhaan) Safe Motherhood poster 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Maternal Health March 2003, Freedman Lynn et al Thank you!!!


