ad4a51962a6c47307c2f41e9f8cb1957.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.

CHAPTER 14 Antitrust and Trade Regulation 14 -2

Learning Objectives v v v v v Describe the federal regulation of antitrust law Discuss the importance of the Sherman Antitrust Act Explain the state antitrust enforcement system Describe the difference between per se and rule of reason approaches Discuss the different antitrust violations Describe the special problems with antitrust enforcement groups Describe monopolistic behavior Discuss mergers and acquisitions antitrust laws Explain the impact on the U. S. of international antitrust laws 14 -3
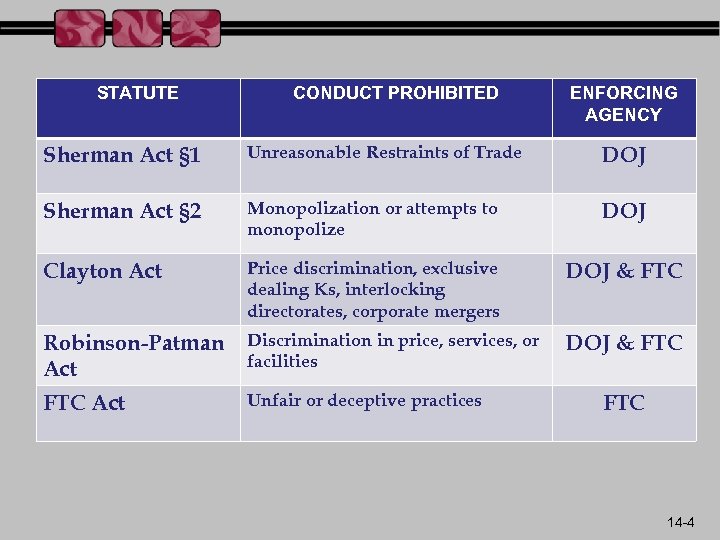
STATUTE CONDUCT PROHIBITED ENFORCING AGENCY Sherman Act § 1 Unreasonable Restraints of Trade DOJ Sherman Act § 2 Monopolization or attempts to monopolize DOJ Clayton Act Price discrimination, exclusive dealing Ks, interlocking directorates, corporate mergers DOJ & FTC Robinson-Patman Act Discrimination in price, services, or facilities DOJ & FTC Act Unfair or deceptive practices FTC 14 -4

State Antitrust laws v National Association of Attorneys General (NAAG) v. Multistate Antitrust Task Force v. Uniform approach to antitrust law among states v. May bring action if they think a company is taking anti-competitive measures Ø APPLE Ø MICROSOFT 14 -5
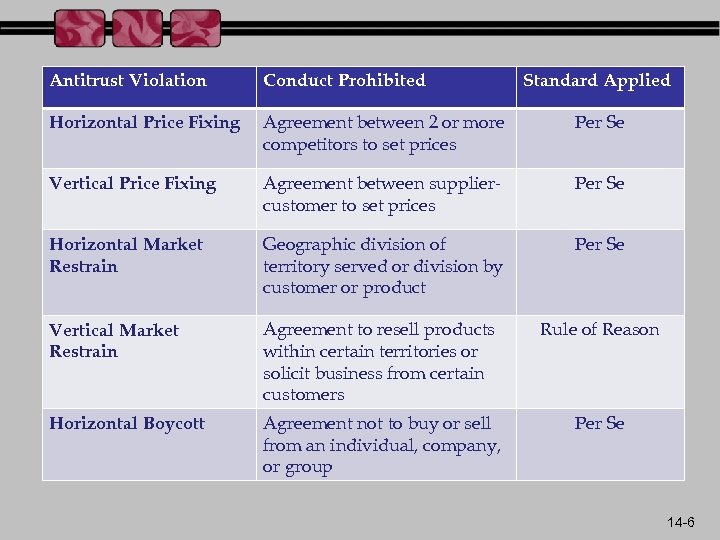
Antitrust Violation Conduct Prohibited Standard Applied Horizontal Price Fixing Agreement between 2 or more competitors to set prices Per Se Vertical Price Fixing Agreement between suppliercustomer to set prices Per Se Horizontal Market Restrain Geographic division of territory served or division by customer or product Per Se Vertical Market Restrain Agreement to resell products within certain territories or solicit business from certain customers Rule of Reason Horizontal Boycott Agreement not to buy or sell from an individual, company, or group Per Se 14 -6
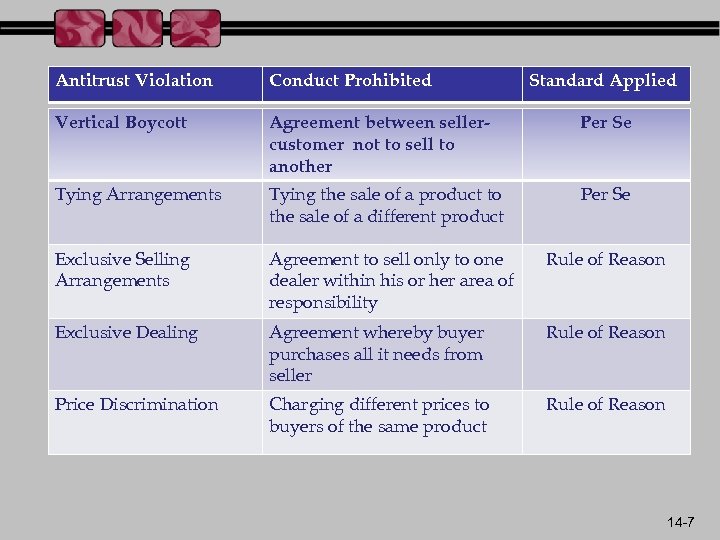
Antitrust Violation Conduct Prohibited Standard Applied Vertical Boycott Agreement between sellercustomer not to sell to another Per Se Tying Arrangements Tying the sale of a product to the sale of a different product Per Se Exclusive Selling Arrangements Agreement to sell only to one dealer within his or her area of responsibility Rule of Reason Exclusive Dealing Agreement whereby buyer purchases all it needs from seller Rule of Reason Price Discrimination Charging different prices to buyers of the same product Rule of Reason 14 -7
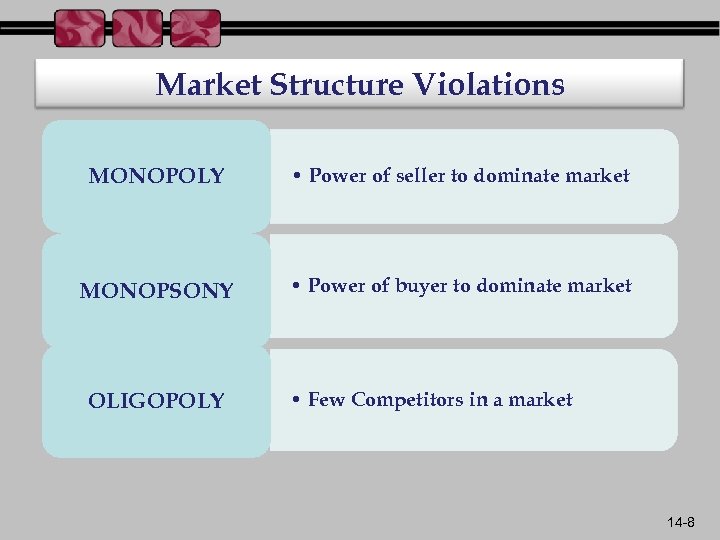
Market Structure Violations MONOPOLY • Power of seller to dominate market MONOPSONY • Power of buyer to dominate market OLIGOPOLY • Few Competitors in a market 14 -8
Types of Mergers Ø HORIZONTAL Ø VERTICAL Ø CONGLOMERATE 14 -9

Horizontal Mergers v. Mergers involving companies selling same or similar products in the same geographic markets Ø Courts balance the market size and power with the consequences of the merger Ø Antitrust concerns Ø DOJ may approve even if only two companies in the market q. XM Satellite Radio - Sirius Satellite Radio 14 -10

Vertical Mergers v. Mergers involving a company purchasing a customer or supplier in order to expand into new markets ØUpstream ØDownstream ØAlso created by acquiring a license 14 -11

Conglomerate Mergers v. Merging firms had no prior relationship v. May have been competitors ØClosely-related products ØDifferent Geographic Markets ØAntitrust Concerns ØReciprocity ØEntrenchment 14 -12

International Antitrust Enforcement v. U. S. companies selling their products oversees must not violate international trade rules v. European Union Trade Regulation v The New Chinese Anti-Monopoly law - 2007 14 -13
ad4a51962a6c47307c2f41e9f8cb1957.ppt