8ca1fc42bcad1e482572d35de62b95a1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2008, The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2008, The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2008, The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 8 Enterprise Business Systems Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2008, The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Learning Objectives • Identify and give examples to illustrate the following aspects of customer relationship, enterprise research, and supply chain management systems • Business processes supported • Customer and business value provided • Potential challenges and trends 3
Learning Objectives • Identify and give examples to illustrate the following aspects of customer relationship, enterprise research, and supply chain management systems • Business processes supported • Customer and business value provided • Potential challenges and trends 3
 Customer Relationship Management • A customer-centric focus • Customer relationships have become a company’s most valued asset • Every company’s strategy should be to find and retain the most profitable customers possible 4
Customer Relationship Management • A customer-centric focus • Customer relationships have become a company’s most valued asset • Every company’s strategy should be to find and retain the most profitable customers possible 4
 Case 1: Business Benefits of CRM • Forex Capital Markets trades $20 billion worth of currency per month • 12, 000 clients in 70 countries • Tracking sales leads and prospects • Began with Excel spreadsheets • Switched to Access database • Volume forced move to CRM system • Access controlled through data security and information sharing privileges 5
Case 1: Business Benefits of CRM • Forex Capital Markets trades $20 billion worth of currency per month • 12, 000 clients in 70 countries • Tracking sales leads and prospects • Began with Excel spreadsheets • Switched to Access database • Volume forced move to CRM system • Access controlled through data security and information sharing privileges 5
 Case 1: Business Benefits of CRM • Wyse Technology • World leader in thin-client computing • Revenues in excess of $180 million • Doubled sales within 12 months of installing CRM system • No additional staff needed 6
Case 1: Business Benefits of CRM • Wyse Technology • World leader in thin-client computing • Revenues in excess of $180 million • Doubled sales within 12 months of installing CRM system • No additional staff needed 6
 Case Study Questions • Why can’t Microsoft Excel spreadsheets and Access database software handle the customer relationship needs of companies like FXCM? • What functions do CRM systems like Salesforce provide to a company that these software packages do not? • What business benefits has the Salesforce CRM system provided to FXCM? • To Wyse Technology? 7
Case Study Questions • Why can’t Microsoft Excel spreadsheets and Access database software handle the customer relationship needs of companies like FXCM? • What functions do CRM systems like Salesforce provide to a company that these software packages do not? • What business benefits has the Salesforce CRM system provided to FXCM? • To Wyse Technology? 7
 Case Study Questions • Salesforce. com is an example of an ASP (application service provider), which was discussed in Chapter 4. • What benefits do you see in this case for that method of providing a CRM system to a company versus installing a CRM software package? • What disadvantages might arise? • Which method would you prefer? 8
Case Study Questions • Salesforce. com is an example of an ASP (application service provider), which was discussed in Chapter 4. • What benefits do you see in this case for that method of providing a CRM system to a company versus installing a CRM software package? • What disadvantages might arise? • Which method would you prefer? 8
 What is CRM? • Managing the full range of the customer relationship involves • Providing customer-facing employees with a single, complete view of every customer at every touch point and across all channels • Providing the customer with a single, complete view of the company and its extended channels • CRM uses IT to create a cross-functional enterprise system that integrates and automates many of the customer-serving processes 9
What is CRM? • Managing the full range of the customer relationship involves • Providing customer-facing employees with a single, complete view of every customer at every touch point and across all channels • Providing the customer with a single, complete view of the company and its extended channels • CRM uses IT to create a cross-functional enterprise system that integrates and automates many of the customer-serving processes 9
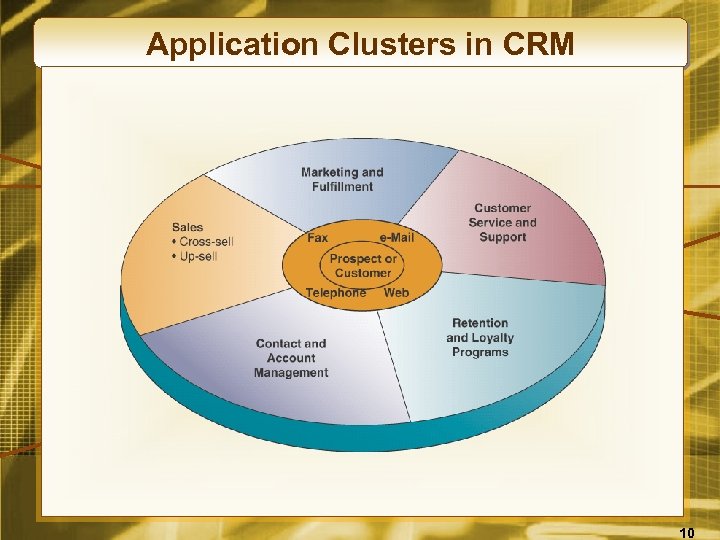 Application Clusters in CRM 10
Application Clusters in CRM 10
 Contact and Account Management • CRM helps sales, marketing, and service professionals capture and track relevant data about • Every past and planned contact with prospects and customers • Other business and life cycle events of customers • Data are captured through customer touchpoints • Telephone, fax, e-mail • Websites, retail stores, kiosks • Personal contact 11
Contact and Account Management • CRM helps sales, marketing, and service professionals capture and track relevant data about • Every past and planned contact with prospects and customers • Other business and life cycle events of customers • Data are captured through customer touchpoints • Telephone, fax, e-mail • Websites, retail stores, kiosks • Personal contact 11
 Sales • A CRM system provides sales reps with the tools and data resources they need to • Support and manage their sales activities • Optimize cross- and up-selling • CRM also provides the means to check on a customer’s account status and history before scheduling a sales call 12
Sales • A CRM system provides sales reps with the tools and data resources they need to • Support and manage their sales activities • Optimize cross- and up-selling • CRM also provides the means to check on a customer’s account status and history before scheduling a sales call 12
 Marketing and Fulfillment • CRM systems help with direct marketing campaigns by automatic such tasks as • • • Qualifying leads for targeted marketing Scheduling and tracking mailings Capturing and managing responses Analyzing the business value of the campaign Fulfilling responses and requests 13
Marketing and Fulfillment • CRM systems help with direct marketing campaigns by automatic such tasks as • • • Qualifying leads for targeted marketing Scheduling and tracking mailings Capturing and managing responses Analyzing the business value of the campaign Fulfilling responses and requests 13
 Customer Service and Support • A CRM system gives service reps real-time access to the same database used by sales and marketing • Requests for service are created, assigned, and managed • Call center software routes calls to agents • Help desk software provides service data and suggestions for solving problems • Web-based self-service enables customers to access personalized support information 14
Customer Service and Support • A CRM system gives service reps real-time access to the same database used by sales and marketing • Requests for service are created, assigned, and managed • Call center software routes calls to agents • Help desk software provides service data and suggestions for solving problems • Web-based self-service enables customers to access personalized support information 14
 Retention and Loyalty Programs • It costs 6 times more to sell to a new customer • An unhappy customer will tell 8 -10 others • Boosting customer retention by 5 percent can boost profits by 85 percent • The odds of selling to an existing customer are 50 percent; a new one 15 percent • About 70 percent of customers will do business with the company again if a problem is quickly taken care of 15
Retention and Loyalty Programs • It costs 6 times more to sell to a new customer • An unhappy customer will tell 8 -10 others • Boosting customer retention by 5 percent can boost profits by 85 percent • The odds of selling to an existing customer are 50 percent; a new one 15 percent • About 70 percent of customers will do business with the company again if a problem is quickly taken care of 15
 Retention and Loyalty Programs • Enhancing and optimizing customer retention and loyalty is a primary objective of CRM • Identify, reward, and market to the most loyal and profitable customers • Evaluate targeted marketing and relationship programs 16
Retention and Loyalty Programs • Enhancing and optimizing customer retention and loyalty is a primary objective of CRM • Identify, reward, and market to the most loyal and profitable customers • Evaluate targeted marketing and relationship programs 16
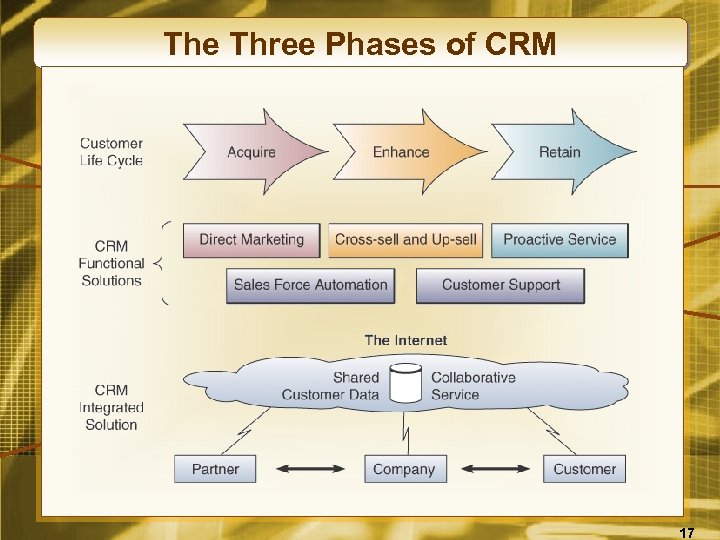 The Three Phases of CRM 17
The Three Phases of CRM 17
 Benefits of CRM • Identify and target the best customers • Real-time customization and personalization of products and services • Track when and how a customer contacts the company • Provide a consistent customer experience • Provide superior service and support across all customer contact points 18
Benefits of CRM • Identify and target the best customers • Real-time customization and personalization of products and services • Track when and how a customer contacts the company • Provide a consistent customer experience • Provide superior service and support across all customer contact points 18
 CRM Failures • Business benefits of CRM are not guaranteed • 50 percent of CRM projects did not produce promised results • 20 percent damaged customer relationships • Reasons for failure • Lack of understanding and preparation • Not solving business process problems first • No participation on part of business stakeholders involved 19
CRM Failures • Business benefits of CRM are not guaranteed • 50 percent of CRM projects did not produce promised results • 20 percent damaged customer relationships • Reasons for failure • Lack of understanding and preparation • Not solving business process problems first • No participation on part of business stakeholders involved 19
 Trends in CRM • Operational CRM • Supports customer interaction with greater convenience through a variety of channels • Synchronizes customer interactions consistently across all channels • Makes the company easier to do business with 20
Trends in CRM • Operational CRM • Supports customer interaction with greater convenience through a variety of channels • Synchronizes customer interactions consistently across all channels • Makes the company easier to do business with 20
 Trends in CRM • Analytical CRM • Extracts in-depth customer history, preferences, and profitability from databases • Allows prediction of customer value and behavior • Allows forecast of demand • Helps tailor information and offers to customer needs 21
Trends in CRM • Analytical CRM • Extracts in-depth customer history, preferences, and profitability from databases • Allows prediction of customer value and behavior • Allows forecast of demand • Helps tailor information and offers to customer needs 21
 Trends in CRM • Collaborative CRM • Easy collaboration with customers, suppliers, and partners • Improves efficiency and integration throughout supply chain • Greater responsiveness to customer needs through outside sourcing of products and services 22
Trends in CRM • Collaborative CRM • Easy collaboration with customers, suppliers, and partners • Improves efficiency and integration throughout supply chain • Greater responsiveness to customer needs through outside sourcing of products and services 22
 Trends in CRM • Portal-based CRM • Provides users with tools and information that fit their needs • Empowers employees to respond to customer demands more quickly • Helps reps become truly customer-faced • Provides instant access to all internal and external customer information 23
Trends in CRM • Portal-based CRM • Provides users with tools and information that fit their needs • Empowers employees to respond to customer demands more quickly • Helps reps become truly customer-faced • Provides instant access to all internal and external customer information 23
 ERP: The Business Backbone • ERP is a cross-functional enterprise backbone that integrates and automates processes within • • • Manufacturing Logistics Distribution Accounting Finance Human resources 24
ERP: The Business Backbone • ERP is a cross-functional enterprise backbone that integrates and automates processes within • • • Manufacturing Logistics Distribution Accounting Finance Human resources 24
 Case 2: Business Value of ERP • Autosystems produces headlamps for major automobile manufacturers • Until a few years ago, the manufacturing process was managed with paper documents • An ERP system was installed, but did not extend to the shop floor • Significant research was done before deciding to add the shop floor reporting module 25
Case 2: Business Value of ERP • Autosystems produces headlamps for major automobile manufacturers • Until a few years ago, the manufacturing process was managed with paper documents • An ERP system was installed, but did not extend to the shop floor • Significant research was done before deciding to add the shop floor reporting module 25
 Case 2: Business Value of ERP • Installing PCs and ERP software on the shop floor allows Autosystems to • Enter timely, accurate information • Plan more efficiently • Make production changes in order to avoid labor or scrap problems • Discuss these issues with employees while they are still current and meaningful 26
Case 2: Business Value of ERP • Installing PCs and ERP software on the shop floor allows Autosystems to • Enter timely, accurate information • Plan more efficiently • Make production changes in order to avoid labor or scrap problems • Discuss these issues with employees while they are still current and meaningful 26
 Case Study Questions • Why did Autosystems decide to install the Activ. Entry system? • Why did they feel it necessary to integrate it with their TRANS 4 M ERP system? • Which three business benefits of the use of Activ. Entry provided the most business value? • What changes are already being planned to improve the use of Activ. Entry? • What other improvements should the company consider? 27
Case Study Questions • Why did Autosystems decide to install the Activ. Entry system? • Why did they feel it necessary to integrate it with their TRANS 4 M ERP system? • Which three business benefits of the use of Activ. Entry provided the most business value? • What changes are already being planned to improve the use of Activ. Entry? • What other improvements should the company consider? 27
 What is ERP? • Enterprise resource planning is a cross-functional enterprise system • An integrated suite of software modules • Supports basic internal business processes • Facilitates business, supplier, and customer information flows 28
What is ERP? • Enterprise resource planning is a cross-functional enterprise system • An integrated suite of software modules • Supports basic internal business processes • Facilitates business, supplier, and customer information flows 28
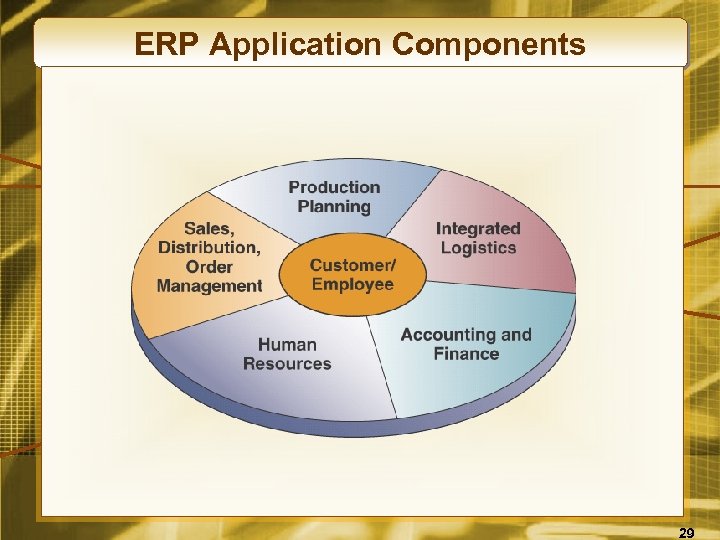 ERP Application Components 29
ERP Application Components 29
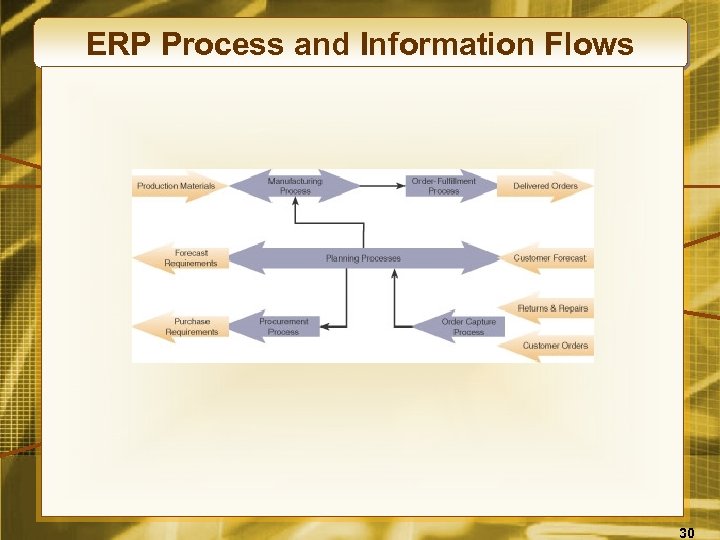 ERP Process and Information Flows 30
ERP Process and Information Flows 30
 Benefits and Challenges of ERP • ERP Business Benefits • • Quality and efficiency Decreased costs Decision support Enterprise agility • ERP Costs • Risks and costs are considerable • Hardware and software a small part of total costs • Failure can cripple or kill a business 31
Benefits and Challenges of ERP • ERP Business Benefits • • Quality and efficiency Decreased costs Decision support Enterprise agility • ERP Costs • Risks and costs are considerable • Hardware and software a small part of total costs • Failure can cripple or kill a business 31
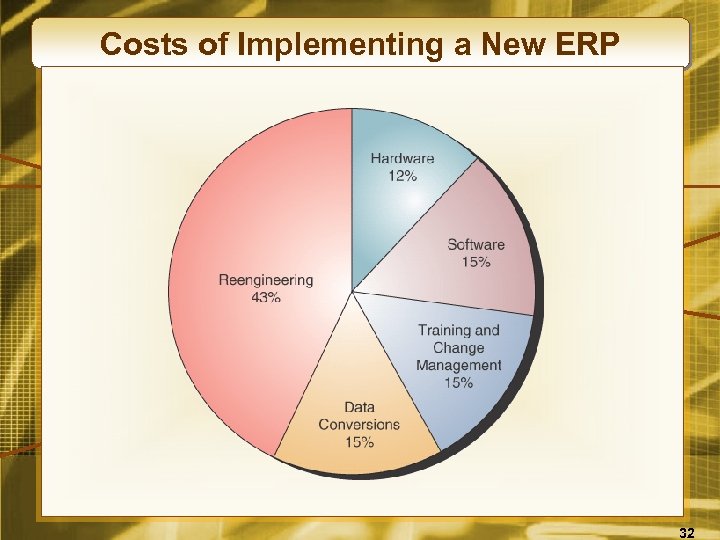 Costs of Implementing a New ERP 32
Costs of Implementing a New ERP 32
 Causes of ERP Failures • Most common causes of ERP failure • Under-estimating the complexity of planning, development, training • Failure to involve affected employees in planning and development • Trying to do too much too fast • Insufficient training • Insufficient data conversion and testing • Over-reliance on ERP vendor or consultants 33
Causes of ERP Failures • Most common causes of ERP failure • Under-estimating the complexity of planning, development, training • Failure to involve affected employees in planning and development • Trying to do too much too fast • Insufficient training • Insufficient data conversion and testing • Over-reliance on ERP vendor or consultants 33
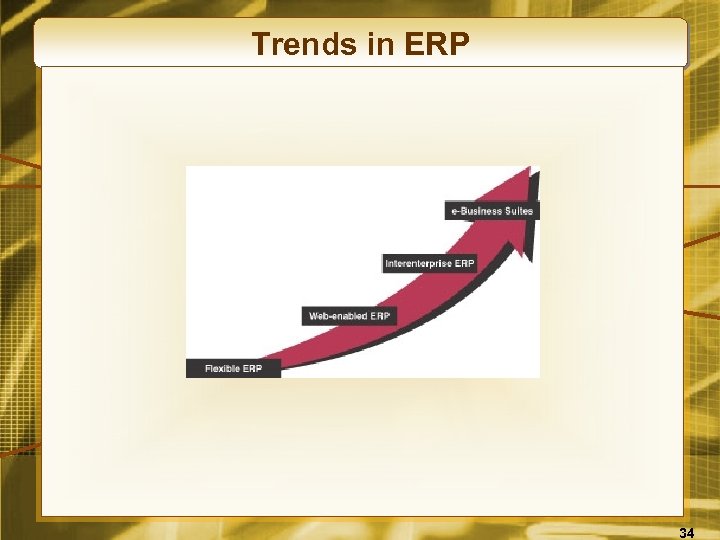 Trends in ERP 34
Trends in ERP 34
 Supply Chain Management (SCM) • Fundamentally, supply chain management helps a company • • • Get the right products To the right place At the right time In the proper quantity At an acceptable cost 35
Supply Chain Management (SCM) • Fundamentally, supply chain management helps a company • • • Get the right products To the right place At the right time In the proper quantity At an acceptable cost 35
 Goals of SCM • The goal of SCM is to efficiently • Forecast demand • Control inventory • Enhance relationships with customers, suppliers, distributors, and others • Receive feedback on the status of every link in the supply chain 36
Goals of SCM • The goal of SCM is to efficiently • Forecast demand • Control inventory • Enhance relationships with customers, suppliers, distributors, and others • Receive feedback on the status of every link in the supply chain 36
 Case 3: Applying Lean Logistics to SCM • The Tesco supermarket chain is a pioneer in retailing • Used SCM to overcome disadvantage of weak supplier leverage and expensive logistics • Changed product distribution methods to reduce labor costs and inventory levels • Got suppliers to ship in smaller quantities, preconfigured for sales display • Reduced total product “touches” from 150 to 50 • Reduced throughput time from 20 days to 5 37
Case 3: Applying Lean Logistics to SCM • The Tesco supermarket chain is a pioneer in retailing • Used SCM to overcome disadvantage of weak supplier leverage and expensive logistics • Changed product distribution methods to reduce labor costs and inventory levels • Got suppliers to ship in smaller quantities, preconfigured for sales display • Reduced total product “touches” from 150 to 50 • Reduced throughput time from 20 days to 5 37
 Case Study Questions • What key insights of Tesco’s SCM direction Graham Booth helped revolutionize Tesco’s supply chain and range of retail store formats? • Can these insights be applied to any kind of retail business? • How did Dan Jones and the Cardiff Business School of Wales demonstrate the inefficiencies of the Tesco and Britvic supply chains? • Can this methodology be applied to the supply chain of any kind of business? 38
Case Study Questions • What key insights of Tesco’s SCM direction Graham Booth helped revolutionize Tesco’s supply chain and range of retail store formats? • Can these insights be applied to any kind of retail business? • How did Dan Jones and the Cardiff Business School of Wales demonstrate the inefficiencies of the Tesco and Britvic supply chains? • Can this methodology be applied to the supply chain of any kind of business? 38
 Case Study Questions • What are the major business and competitive benefits gained by Tesco as the result of its supply chain initiatives? • Can other retail chains and retail stores achieve some or all of the same results? • Defend your position with examples of actual retail chains and stores you know. 39
Case Study Questions • What are the major business and competitive benefits gained by Tesco as the result of its supply chain initiatives? • Can other retail chains and retail stores achieve some or all of the same results? • Defend your position with examples of actual retail chains and stores you know. 39
 What is a Supply Chain? • The interrelationships • With suppliers, customers, distributors, and other businesses • Needed to design, build, and sell a product • Each supply chain process should add value to the products or services a company produces • Frequently called a value chain 40
What is a Supply Chain? • The interrelationships • With suppliers, customers, distributors, and other businesses • Needed to design, build, and sell a product • Each supply chain process should add value to the products or services a company produces • Frequently called a value chain 40
 Supply Chain Life Cycle 41
Supply Chain Life Cycle 41
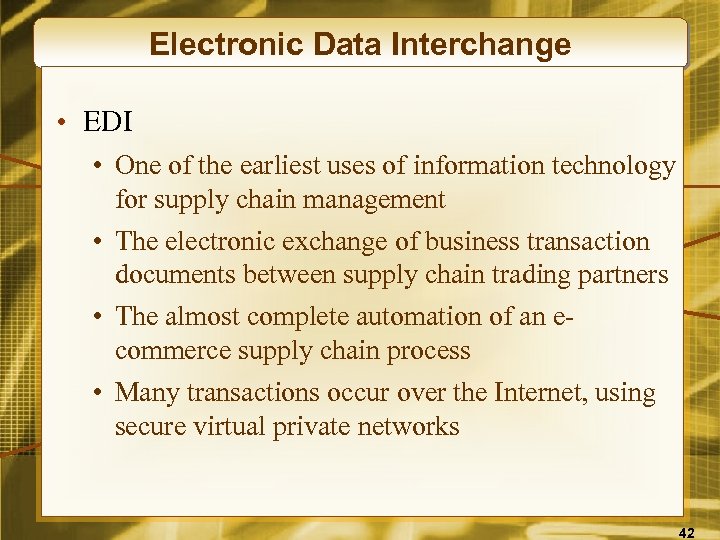 Electronic Data Interchange • EDI • One of the earliest uses of information technology for supply chain management • The electronic exchange of business transaction documents between supply chain trading partners • The almost complete automation of an ecommerce supply chain process • Many transactions occur over the Internet, using secure virtual private networks 42
Electronic Data Interchange • EDI • One of the earliest uses of information technology for supply chain management • The electronic exchange of business transaction documents between supply chain trading partners • The almost complete automation of an ecommerce supply chain process • Many transactions occur over the Internet, using secure virtual private networks 42
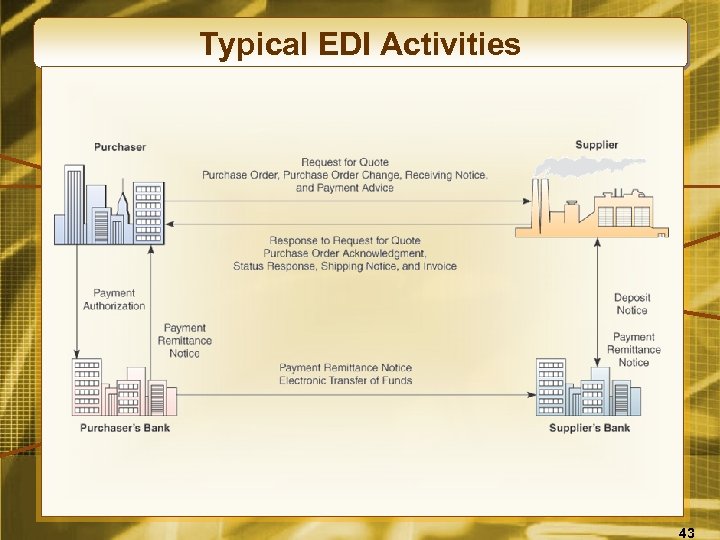 Typical EDI Activities 43
Typical EDI Activities 43
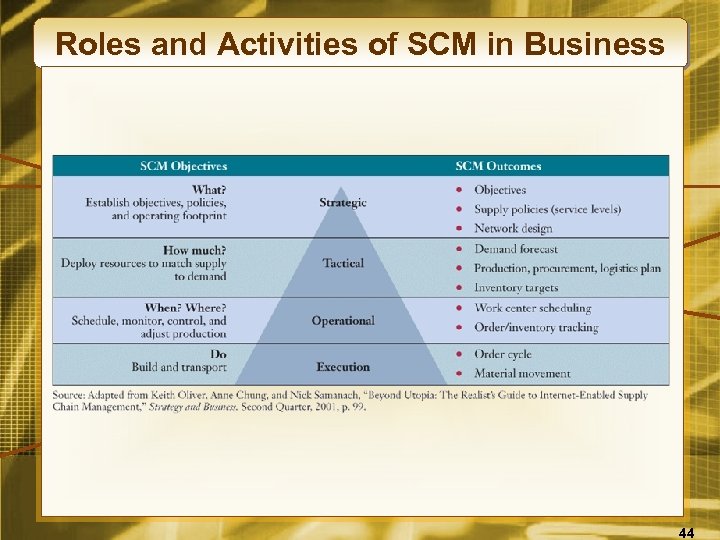 Roles and Activities of SCM in Business 44
Roles and Activities of SCM in Business 44
 Planning & Execution Functions of SCM • Planning • Supply chain design • Collaborative demand supply planning • Execution • • • Materials management Collaborative manufacturing Collaborative fulfillment Supply chain event management Supply chain performance management 45
Planning & Execution Functions of SCM • Planning • Supply chain design • Collaborative demand supply planning • Execution • • • Materials management Collaborative manufacturing Collaborative fulfillment Supply chain event management Supply chain performance management 45
 Benefits and Challenges of SCM • Key Benefits • • • Faster, more accurate order processing Reductions in inventory levels Quicker times to market Lower transaction and materials costs Strategic relationships with supplier 46
Benefits and Challenges of SCM • Key Benefits • • • Faster, more accurate order processing Reductions in inventory levels Quicker times to market Lower transaction and materials costs Strategic relationships with supplier 46
 Goals and Objectives of SCM 47
Goals and Objectives of SCM 47
 Benefits and Challenges of SCM • Key Challenges • Lack of demand planning knowledge, tools, and guidelines • Inaccurate data provided by other information systems • Lack of collaboration among marketing, production, and inventory management • SCM tools are immature, incomplete, and hard to implement 48
Benefits and Challenges of SCM • Key Challenges • Lack of demand planning knowledge, tools, and guidelines • Inaccurate data provided by other information systems • Lack of collaboration among marketing, production, and inventory management • SCM tools are immature, incomplete, and hard to implement 48
 Trends in SCM 49
Trends in SCM 49
 Case 4: Consequences of ERP Failure • The goal Agilent Technologies Inc. specializes in measurement and technology • Its goal is to enable customers to speed their time to market • Achieve volume production • Obtain high-quality precision manufacturing • Consequences of a new ERP system • One year to stabilize system • $105 million in lost revenue • $70 million in lost profits 50
Case 4: Consequences of ERP Failure • The goal Agilent Technologies Inc. specializes in measurement and technology • Its goal is to enable customers to speed their time to market • Achieve volume production • Obtain high-quality precision manufacturing • Consequences of a new ERP system • One year to stabilize system • $105 million in lost revenue • $70 million in lost profits 50
 Case 4: Consequences of ERP Failure • Lessons Learned • • Disruptions can be more extensive than expected Enterprise resource planning is very complex ERP implementations are more than software People, process, policies, the company’s culture should all be taken into consideration • According to Enterprise Applications Consulting • 99 percent of rollout fiascoes are caused by management’s inability to spec requirements, and the implementer’s inability to implement specs 51
Case 4: Consequences of ERP Failure • Lessons Learned • • Disruptions can be more extensive than expected Enterprise resource planning is very complex ERP implementations are more than software People, process, policies, the company’s culture should all be taken into consideration • According to Enterprise Applications Consulting • 99 percent of rollout fiascoes are caused by management’s inability to spec requirements, and the implementer’s inability to implement specs 51
 Case 4: Consequences of ERP Failure • Russ Berrie and Company • First ERP implementation attempt took three years and cost $10. 3 million • Litigation is pending between Russ Berrie and SAP • Second attempt • Uses new applications • Is being implement department by department • Uses stand-alone systems 52
Case 4: Consequences of ERP Failure • Russ Berrie and Company • First ERP implementation attempt took three years and cost $10. 3 million • Litigation is pending between Russ Berrie and SAP • Second attempt • Uses new applications • Is being implement department by department • Uses stand-alone systems 52
 Case Study Questions • What are the main reasons companies experience failures in implementing ERP systems? • What are several key things companies should do to avoid ERP systems failures? • Why do you think ERP system in particular are often cited as examples of failures in IT systems development, implementation, or management? 53
Case Study Questions • What are the main reasons companies experience failures in implementing ERP systems? • What are several key things companies should do to avoid ERP systems failures? • Why do you think ERP system in particular are often cited as examples of failures in IT systems development, implementation, or management? 53


