05889a8e660949029b754f2d706fe97c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
 CHAPTER 10 Global Strategy Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
CHAPTER 10 Global Strategy Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
 Key Issues • What is the concept of strategy? • How can firms profit from global expansion? • What are the different strategies to compete globally? • How do cost pressures and country differences influence global strategy? • How can firms use strategic alliances to support their global strategy? Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Key Issues • What is the concept of strategy? • How can firms profit from global expansion? • What are the different strategies to compete globally? • How do cost pressures and country differences influence global strategy? • How can firms use strategic alliances to support their global strategy? Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
 Slide 10 -1 Global Strategy • Strategy: “the action managers take to attain the goals of a firm” – General purpose: maximize/make profit • Differentiate products, increase price: add value, features, quality, service • Achieve low cost – Key means: allocation of scarce resources to attain goals Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -1 Global Strategy • Strategy: “the action managers take to attain the goals of a firm” – General purpose: maximize/make profit • Differentiate products, increase price: add value, features, quality, service • Achieve low cost – Key means: allocation of scarce resources to attain goals Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
 Slide 10 -2 Activity Value Chain • Firm as a chain of discrete value creating activities – Primary • upstream activities, manufacturing • downstream activities: marketing, sales, after sales service – Support • infrastructure (general and administrative) • human resources • research and development Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -2 Activity Value Chain • Firm as a chain of discrete value creating activities – Primary • upstream activities, manufacturing • downstream activities: marketing, sales, after sales service – Support • infrastructure (general and administrative) • human resources • research and development Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
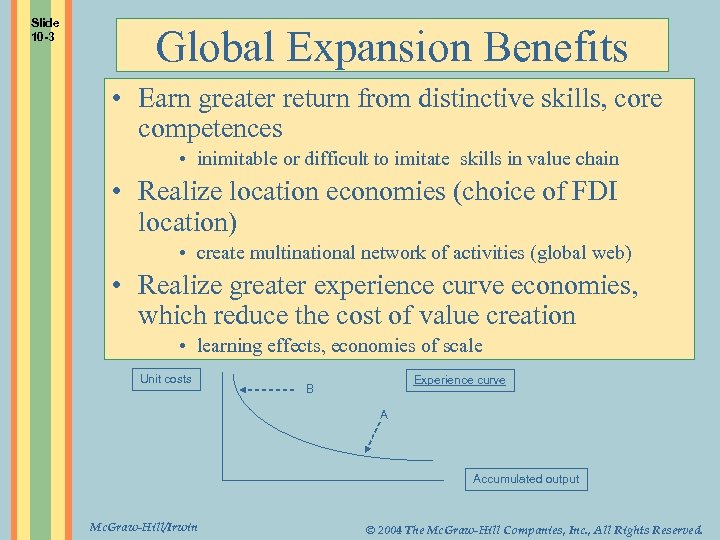 Slide 10 -3 Global Expansion Benefits • Earn greater return from distinctive skills, core competences • inimitable or difficult to imitate skills in value chain • Realize location economies (choice of FDI location) • create multinational network of activities (global web) • Realize greater experience curve economies, which reduce the cost of value creation • learning effects, economies of scale Unit costs Experience curve B A Accumulated output Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -3 Global Expansion Benefits • Earn greater return from distinctive skills, core competences • inimitable or difficult to imitate skills in value chain • Realize location economies (choice of FDI location) • create multinational network of activities (global web) • Realize greater experience curve economies, which reduce the cost of value creation • learning effects, economies of scale Unit costs Experience curve B A Accumulated output Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
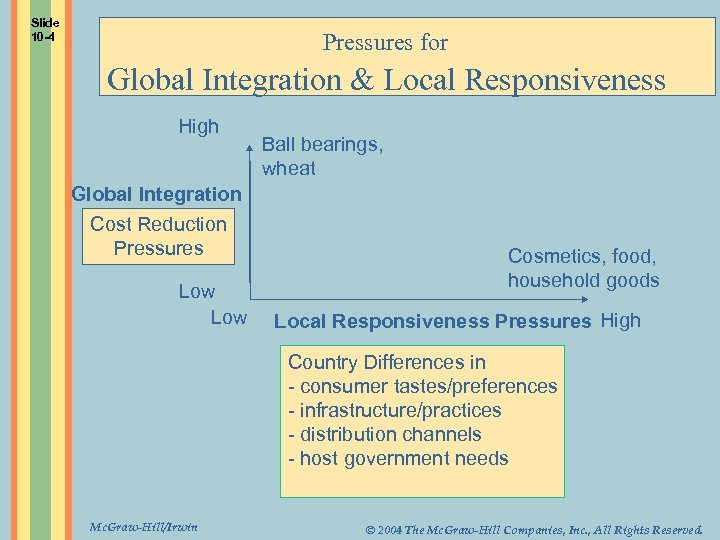 Slide 10 -4 Pressures for Global Integration & Local Responsiveness High Global Integration Cost Reduction Pressures Low Ball bearings, wheat Cosmetics, food, household goods Local Responsiveness Pressures High Country Differences in - consumer tastes/preferences - infrastructure/practices - distribution channels - host government needs Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -4 Pressures for Global Integration & Local Responsiveness High Global Integration Cost Reduction Pressures Low Ball bearings, wheat Cosmetics, food, household goods Local Responsiveness Pressures High Country Differences in - consumer tastes/preferences - infrastructure/practices - distribution channels - host government needs Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
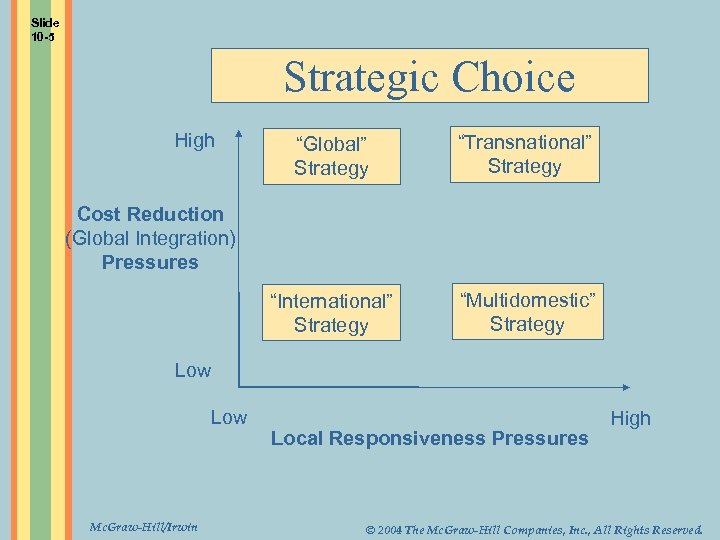 Slide 10 -5 Strategic Choice High “Global” Strategy “Transnational” Strategy “International” Strategy “Multidomestic” Strategy Cost Reduction (Global Integration) Pressures Low Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Local Responsiveness Pressures High © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -5 Strategic Choice High “Global” Strategy “Transnational” Strategy “International” Strategy “Multidomestic” Strategy Cost Reduction (Global Integration) Pressures Low Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Local Responsiveness Pressures High © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
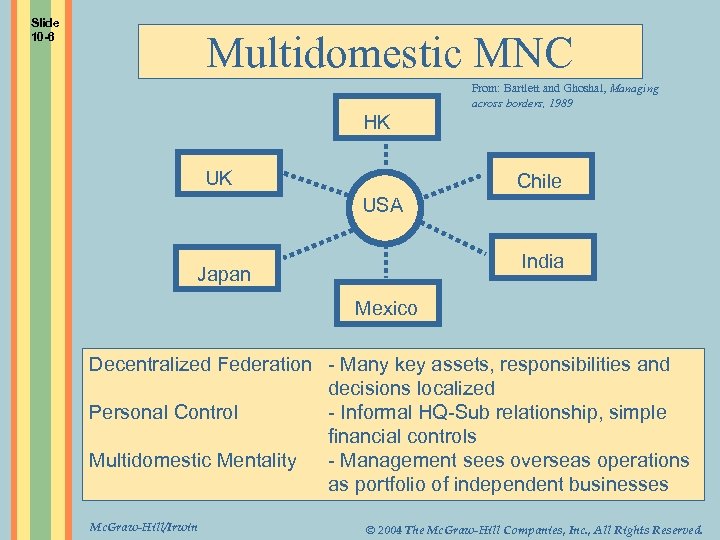 Slide 10 -6 Multidomestic MNC From: Bartlett and Ghoshal, Managing across borders, 1989 HK UK Chile USA India Japan Mexico Decentralized Federation - Many key assets, responsibilities and decisions localized Personal Control - Informal HQ-Sub relationship, simple financial controls Multidomestic Mentality - Management sees overseas operations as portfolio of independent businesses Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -6 Multidomestic MNC From: Bartlett and Ghoshal, Managing across borders, 1989 HK UK Chile USA India Japan Mexico Decentralized Federation - Many key assets, responsibilities and decisions localized Personal Control - Informal HQ-Sub relationship, simple financial controls Multidomestic Mentality - Management sees overseas operations as portfolio of independent businesses Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
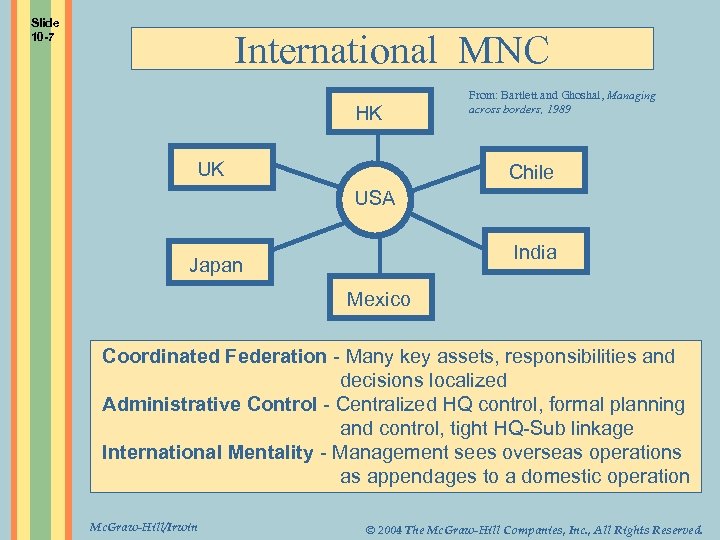 Slide 10 -7 International MNC HK UK From: Bartlett and Ghoshal, Managing across borders, 1989 Chile USA India Japan Mexico Coordinated Federation - Many key assets, responsibilities and decisions localized Administrative Control - Centralized HQ control, formal planning and control, tight HQ-Sub linkage International Mentality - Management sees overseas operations as appendages to a domestic operation Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -7 International MNC HK UK From: Bartlett and Ghoshal, Managing across borders, 1989 Chile USA India Japan Mexico Coordinated Federation - Many key assets, responsibilities and decisions localized Administrative Control - Centralized HQ control, formal planning and control, tight HQ-Sub linkage International Mentality - Management sees overseas operations as appendages to a domestic operation Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
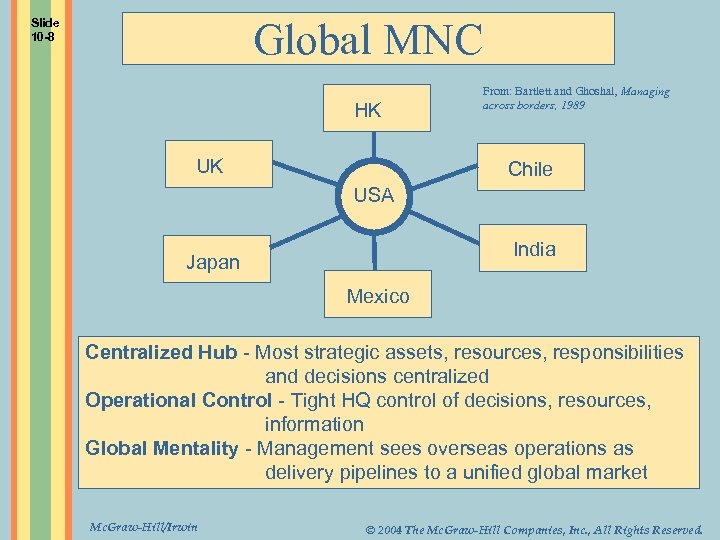 Global MNC Slide 10 -8 HK UK From: Bartlett and Ghoshal, Managing across borders, 1989 Chile USA India Japan Mexico Centralized Hub - Most strategic assets, resources, responsibilities and decisions centralized Operational Control - Tight HQ control of decisions, resources, information Global Mentality - Management sees overseas operations as delivery pipelines to a unified global market Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Global MNC Slide 10 -8 HK UK From: Bartlett and Ghoshal, Managing across borders, 1989 Chile USA India Japan Mexico Centralized Hub - Most strategic assets, resources, responsibilities and decisions centralized Operational Control - Tight HQ control of decisions, resources, information Global Mentality - Management sees overseas operations as delivery pipelines to a unified global market Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
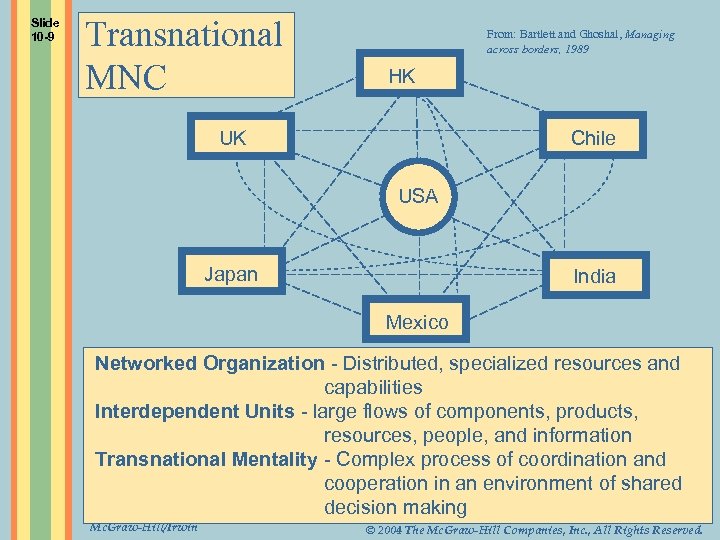 Slide 10 -9 Transnational MNC From: Bartlett and Ghoshal, Managing across borders, 1989 HK Chile UK USA Japan India Mexico Networked Organization - Distributed, specialized resources and capabilities Interdependent Units - large flows of components, products, resources, people, and information Transnational Mentality - Complex process of coordination and cooperation in an environment of shared decision making Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -9 Transnational MNC From: Bartlett and Ghoshal, Managing across borders, 1989 HK Chile UK USA Japan India Mexico Networked Organization - Distributed, specialized resources and capabilities Interdependent Units - large flows of components, products, resources, people, and information Transnational Mentality - Complex process of coordination and cooperation in an environment of shared decision making Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
 Slide 10 -10 International Strategic Alliances • Cooperative agreements among competitors from different countries • Advantages – Facilitate entry into a foreign country – Allow sharing of fixed costs of new products/processes – Bring together complementary skills and assets that can not easily be developed independently – Help establish industry standards in technology – Reduce operating costs, e. g. , shared training, purchasing • Disadvantages – Give competitors new technology / markets at low cost – Disproportional benefit accrual to partners Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -10 International Strategic Alliances • Cooperative agreements among competitors from different countries • Advantages – Facilitate entry into a foreign country – Allow sharing of fixed costs of new products/processes – Bring together complementary skills and assets that can not easily be developed independently – Help establish industry standards in technology – Reduce operating costs, e. g. , shared training, purchasing • Disadvantages – Give competitors new technology / markets at low cost – Disproportional benefit accrual to partners Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
 Slide 10 -11 Making alliances work Which partner? • A suitable partner – Helps achieve strategic goals; brings needed, valuable capabilities – Shares the firm’s vision for the alliance’s purpose – Is not likely to exploit the alliance to its own ends • To select a partner – Do thorough background check from public sources – Collect information from third parties who have personal experience with the likely partner(s) – Spend a lot of face-to-face time with likely partner(s) Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -11 Making alliances work Which partner? • A suitable partner – Helps achieve strategic goals; brings needed, valuable capabilities – Shares the firm’s vision for the alliance’s purpose – Is not likely to exploit the alliance to its own ends • To select a partner – Do thorough background check from public sources – Collect information from third parties who have personal experience with the likely partner(s) – Spend a lot of face-to-face time with likely partner(s) Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
 Slide 10 -12 Making alliances work What Structure? • Protect technology/know-how that is not intended to be transferred • Draw a solid contract with safeguards against opportunism • Achieve equitable gain through agreed swaps of technology the other wants • Seek creditable, clearly articulated commitment to partner “behavior” a-priori Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -12 Making alliances work What Structure? • Protect technology/know-how that is not intended to be transferred • Draw a solid contract with safeguards against opportunism • Achieve equitable gain through agreed swaps of technology the other wants • Seek creditable, clearly articulated commitment to partner “behavior” a-priori Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
 Slide 10 -13 Making alliances work How to manage? • Show sensitivity to cultural differences that explain different managerial styles • Build trust – Set up framework formal and informal face-to-face meetings to create the opportunity for a common value system to emerge – Build an informal network of personal relationships • Learn from partners – Apply the knowledge within your own organization – Brief your employees on partner strengths Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.
Slide 10 -13 Making alliances work How to manage? • Show sensitivity to cultural differences that explain different managerial styles • Build trust – Set up framework formal and informal face-to-face meetings to create the opportunity for a common value system to emerge – Build an informal network of personal relationships • Learn from partners – Apply the knowledge within your own organization – Brief your employees on partner strengths Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , All Rights Reserved.


