766775972c0db57bd85705cdc2b3cc7d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

MBA 669 Special Topics: IT-enabled organizational Forms Dave Salisbury salisbury@udayton. edu (email) http: //www. davesalisbury. com/ (web site)

This Week’s Fun Stuff n n IT for competitive advantage The power of virtual integration n n Dell TAL & JC Penney Synchronizing your firm ERP and the control of information/decision-making How fast does one have to be?

Strategic Issues n Strategic Advantage n n If you’re first, a novel technology creates an advantage Strategic Necessity n Eventually, technology-based gains are lost because they are easily replicable

Information Resource Advantages n n n What makes it valuable? Who gets the value? Is it equally distributed? Is it mobile? How quickly does it depreciate?

Sustainable Competitive Advantage n The Environment n n Foundation Factors n n What happens “out there” Something unique to leverage Action & Strategy n What you do with the situation

Intra-Organizational Coordination n Vertical Control n n n Flattening hierarchy Technology control replaces human management Horizontal Control n n Electronic workflow Concurrent engineering Stockless production Virtual organization

Intra-Organizational Coordination n Organization and unit size n n Reduction in size Not vertical integration, but virtual integration Outsourcing Coupling n n Spin-off entrepreneurial Federation

Intra-Organizational Coordination n Core product n n Communication protocols n n Information Learning and innovation Influence rather than fiat Weak ties Ownership/control n From hierarchies to markets (Dell in week 5)

Inter-organizational forms n Inter-organizational coupling n n Again, from hierarchies to markets (Dell in week 5) Electronic integration Integration in terms of strategic alliances enabled by IT Interstitial links

Supply Chain Management n Network of facilities and distribution options n n Procurement Transformation Distribution IT is obviously heavily involved

Supply Chain Management (SCM) Cross-functional interenterprise system that uses IT to help support & manage the links between some of a company’s key business processes and those of its suppliers, customers, & business partners n Goal is to create a fast, efficient, & lowcost network of business relationships n
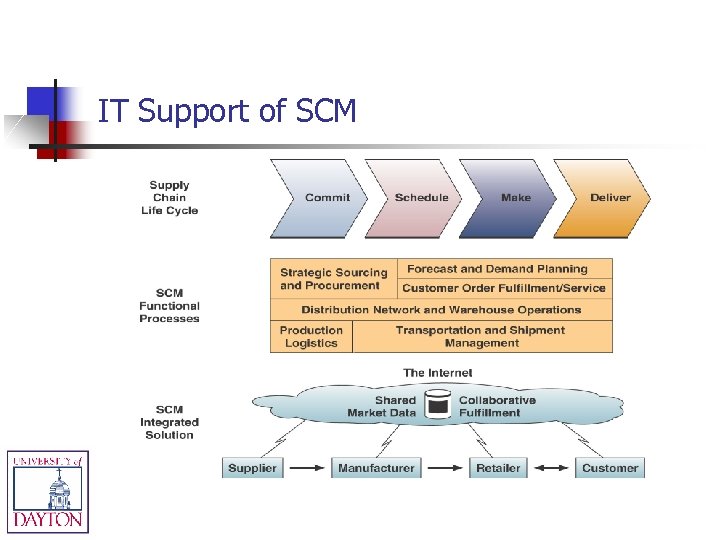
IT Support of SCM

Customer Relationship Management n n n Customer-facing employees get a single, complete view of customers at each touch point & across all channels Customers get a single, complete view of the company and its extended channels Integrates & automates customer service processes IT framework of software & databases that integrates this with the rest of the company’s business operations Enhances employee ability to interact with customer Allows businesses to identify their best customers, and makes possible real-time product & service customization (e. g. Amazon. com’s suggestion lists)

Major CRM Application Components
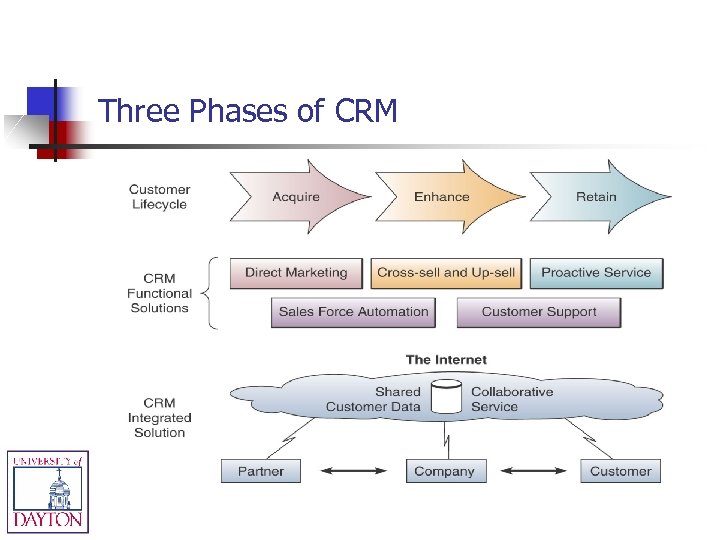
Three Phases of CRM
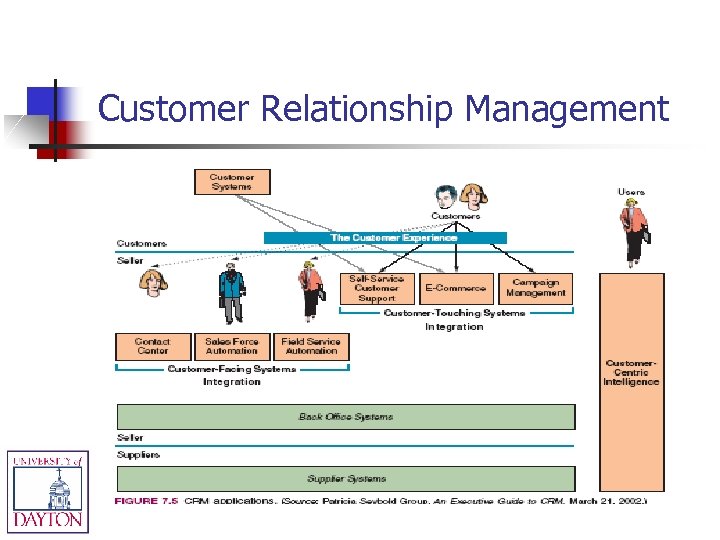
Customer Relationship Management

Customer Relationship Management n n n CRM has been practiced manually by corporations for generations. E-crm emerged in the mid-1990’s, when customers began using electronic touchpoints. Three service levels n n n Foundational service. This includes the minimum necessary services such as Web site responsiveness (e. g. , how quickly and accurately the service is provided), site effectiveness, and order fulfillment. Customer-centered services. These services include order tracking, product configuration and customization, and security/trust. These are the services that matter the most to customers. Value-added services. These are extra services such as online auctions and online training and education.

Customer Relationship Management CRM Activities n n n Customer Service on the Web Search and Comparison Capabilities Free Products and Services Technical and Other Information and Service Allowing Customers to Order Products and Services Online Letting Customers Track Accounts or Order Status n n n n Tools for Customer Service Personalized Web Pages FAQs Chat Rooms E-Mail and Automated Response Call Centers Troubleshooting Tools Wireless CRM

Customer Resource Life Cycle n n n Establish Requirements Specify Select Source Order Authorize/Pay for Acquire n n n n Test and Accept Integrate Monitor Upgrade Maintain Transfer/Dispose Account for

Processes v. Functions n n Marketing, Finance, etc. Processes n n Things that get done Tend to cross functional barriers

IT & Business Processes n n IT as an enabler of change Reengineering Total quality management Cross functional and crossorganizational integration

Breaking Business Barriers n n Time barriers Geographic barriers Cost barriers Structural barriers
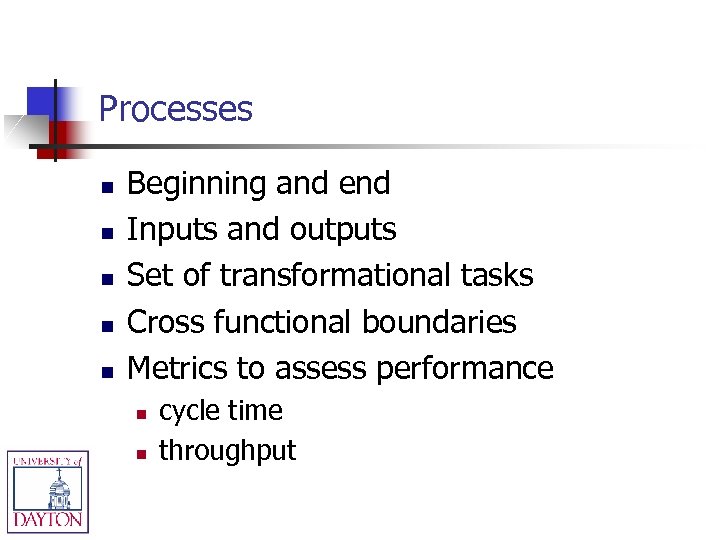
Processes n n n Beginning and end Inputs and outputs Set of transformational tasks Cross functional boundaries Metrics to assess performance n n cycle time throughput

Dell n n n Direct business model Bypass the dealer channel Inventory velocity Technology navigator Virtual integration

Dell n n n Partnerships and trust Affiliation with the customer Fast-cycle segmentation Trading inventory for information Using IT to stay close to the customer

Ford and Virtual Integration n n Ford has attempted a Dell-like transformation Radical business process redesign It works for Dell; will it work at Ford? What are the similarities between the two businesses? What are the differences between the supply chains at Dell and Ford?

Enterprise Resource Planning n n n SAP, People. Soft, etc. A means to pull together scattered and fragmented IS Modules for various operations activities n n Manufacturing Accounting Human Resources Sales

Enterprise Resource Planning n n Require fundamental changes to business processes If you have no processes in place, no biggie If you do have existing processes, and they are a source of advantage, EIS are not appropriate When you are out of time, it’s a canned package that works

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) n n Cross-functional enterprise backbone that integrates & automates internal business processes and IS Helps companies gain enhance their efficiency, agility, & responsiveness Gives a company an integrated real-time view of its core business processes ERP software suites typically consist of integrated modules: n n n Manufacturing Distribution Sales Accounting Human Resource Management

Major Application Components of ERP
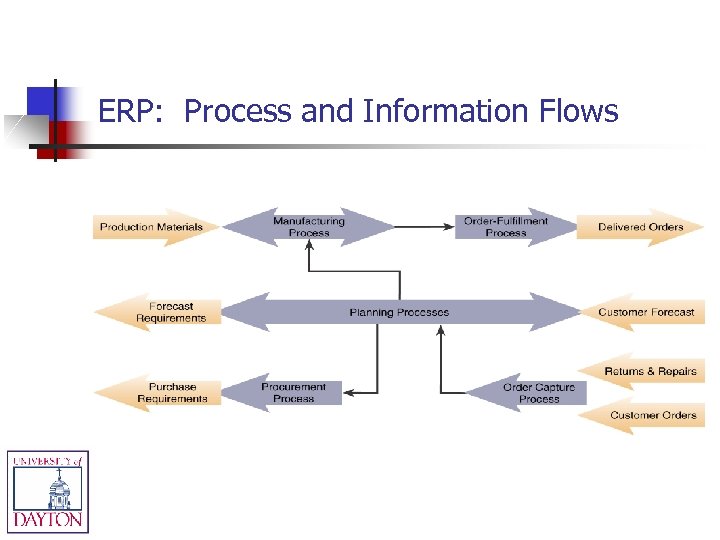
ERP: Process and Information Flows

Costs of ERP
Supply Chain Management (SCM) n n A cross-functional interenterprise system that uses IT to help support & manage the links between some of a company’s key business processes and those of its suppliers, customers, & business partners. Goal is to create a fast, efficient, & low-cost network of business relationships.
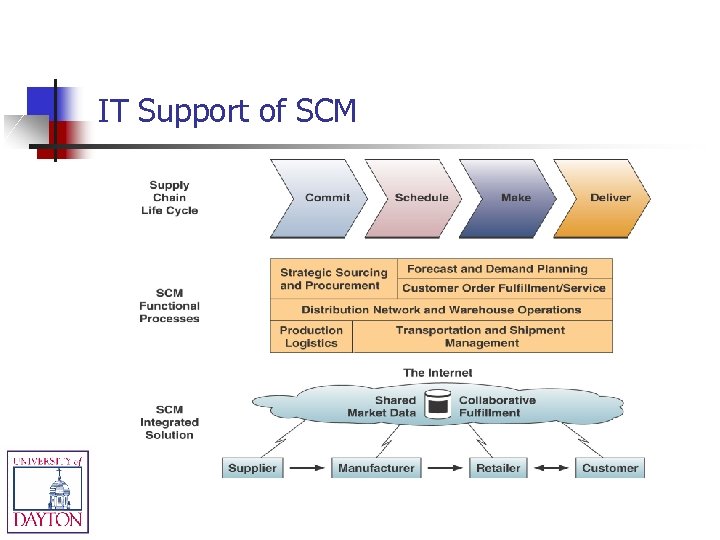
IT Support of SCM

Synchronization n n Having a “hot-synch” button Three dimensions n n n Offerings Technology Organization

ERP and locus of control n n n Some cases used to push decisionmaking to lower levels Some cases used to get control What is the effect of advanced IT in organizations? n n Liberating or constraining? Autonomy or top-down control?

More isomorphism and globalization n n Infrastructure Standards Legal systems Systems
766775972c0db57bd85705cdc2b3cc7d.ppt