5f3f584f4f69300e37d730d9347a133f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

MBA 201 a: Economic Costs

Economic versus accounting costs – We will discuss how economists and accountants have different motives in thinking about costs. • • – Accountants are trying to keep track of them; Economists are trying to make sound strategic decisions on the basis of them. Economic costs include opportunity costs & exclude sunk costs. Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 1

Opportunity costs – Payoffs from an action must be judged against the best alternative action. – Make sure you think of all the possible alternatives at a decision node, – … and think through the implications of each node. – Acquisition costs are irrelevant to opportunity costs. – Economic costs include opportunity costs. Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 2

Opportunity cost examples – What are the major costs associated with attending Haas for you? – What is the cost to Hertz of a car that is returned late? – What is the value of your frequent flyer miles? Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 3

Opportunity cost example: airline fuel hedges – A number of the airlines buy hedges on jet fuel costs. • For instance, if jet fuel prices are trading at $1/gallon, an airline may hedge possible price increases by purchasing a financial option that allows it to buy 500 million gallons of fuel at that price in the future. • If the jet fuel price falls below $1/gallon, the airline is out what they paid for the hedge and they buy fuel at the lower spot price. • If the jet fuel price goes above $1/gallon, they can purchase 500 million gallons at $1/gallon. Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 4

Airline jet fuel hedge example – Southwest Airlines currently holds options allowing them to purchase jet fuel at a price of $1. 25/gallon. – Imagine that it has a route for which its net revenue is equivalent to $1. 25/gallon. * In other words, the route is only profitable if the jet fuel price is at or below $1. 25. – Should Southwest’s decision to fly that route depend on whether or not it has hedged its fuel costs? * For instance, imagine a route where SWA has non-fuel costs of $5, 000 per flight. Its planes get roughly. 25 miles/gallon, so if the route is 500 miles, it’s using 4*500 = 2000 gallons of fuel at a cost of $1. 25*2000=$2, 500. If it usually carries 100 passengers who generate net revenue of $75 apiece, its passengers are paying $7, 500. Net revenues on the route are negative unless fuel is less than or equal to $1. 25/gallon. Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 5
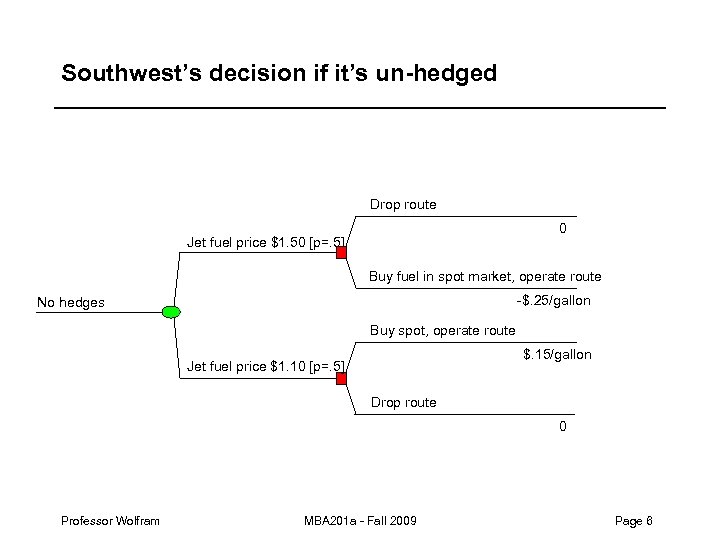
Southwest’s decision if it’s un-hedged Drop route 0 Jet fuel price $1. 50 [p=. 5] Buy fuel in spot market, operate route -$. 25/gallon No hedges Buy spot, operate route $. 15/gallon Jet fuel price $1. 10 [p=. 5] Drop route 0 Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 6
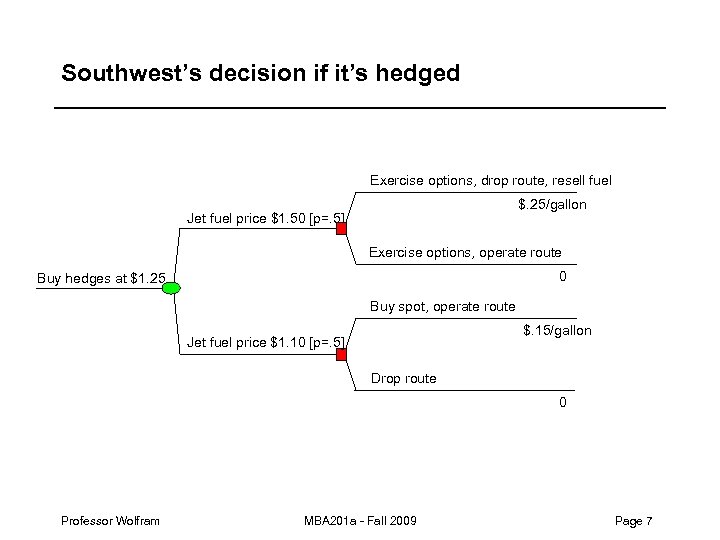
Southwest’s decision if it’s hedged Exercise options, drop route, resell fuel $. 25/gallon Jet fuel price $1. 50 [p=. 5] Exercise options, operate route 0 Buy hedges at $1. 25 Buy spot, operate route $. 15/gallon Jet fuel price $1. 10 [p=. 5] Drop route 0 Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 7
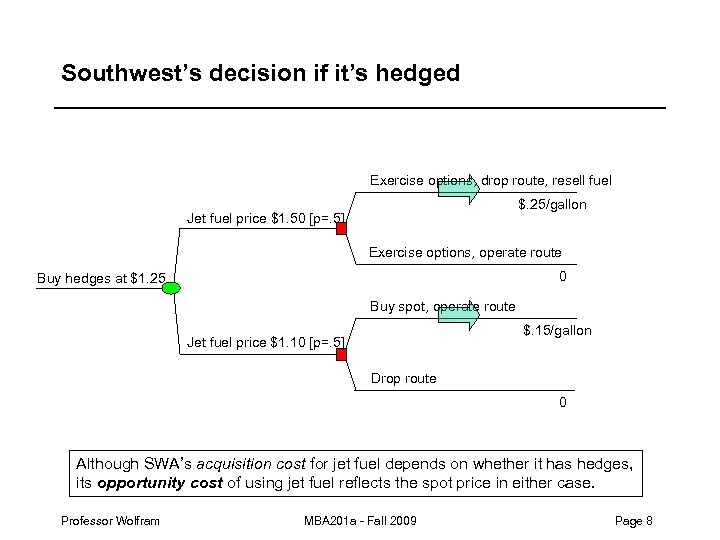
Southwest’s decision if it’s hedged Exercise options, drop route, resell fuel $. 25/gallon Jet fuel price $1. 50 [p=. 5] Exercise options, operate route 0 Buy hedges at $1. 25 Buy spot, operate route $. 15/gallon Jet fuel price $1. 10 [p=. 5] Drop route 0 Although SWA’s acquisition cost for jet fuel depends on whether it has hedges, its opportunity cost of using jet fuel reflects the spot price in either case. Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 8
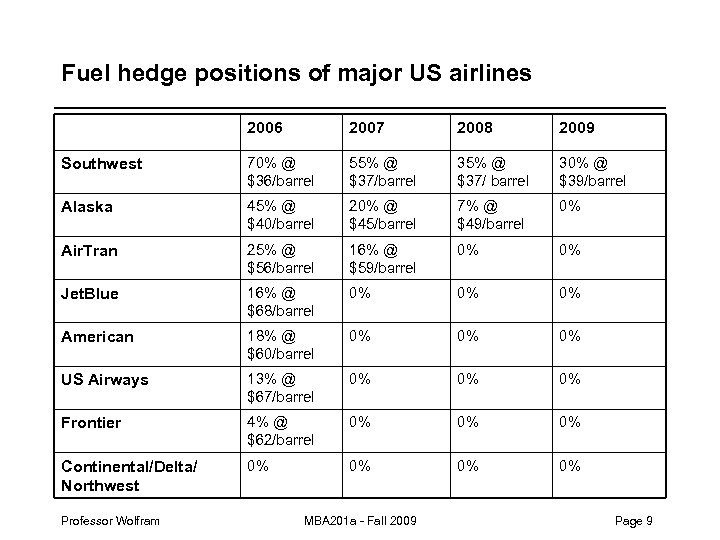
Fuel hedge positions of major US airlines 2006 2007 2008 2009 Southwest 70% @ $36/barrel 55% @ $37/barrel 35% @ $37/ barrel 30% @ $39/barrel Alaska 45% @ $40/barrel 20% @ $45/barrel 7% @ $49/barrel 0% Air. Tran 25% @ $56/barrel 16% @ $59/barrel 0% 0% Jet. Blue 16% @ $68/barrel 0% 0% 0% American 18% @ $60/barrel 0% 0% 0% US Airways 13% @ $67/barrel 0% 0% 0% Frontier 4% @ $62/barrel 0% 0% 0% Continental/Delta/ Northwest 0% 0% Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 9
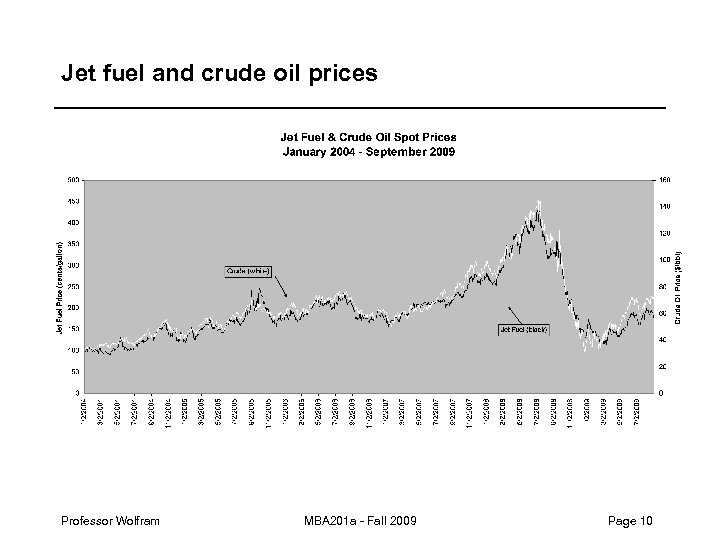
Jet fuel and crude oil prices Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 10

Southwest hedging: what’s the lesson? – Southwest’s accounting profits have been hugely affected by it’s hedging position. – But it’s economic decisions most likely have not been influenced. Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 11
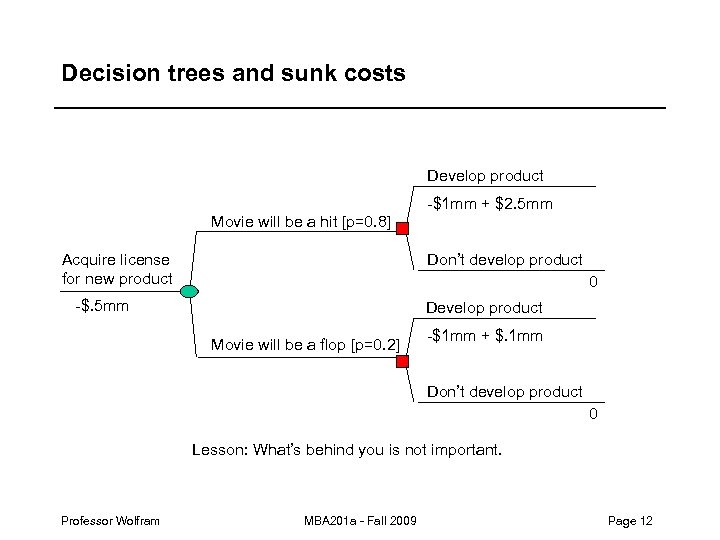
Decision trees and sunk costs Develop product -$1 mm + $2. 5 mm Movie will be a hit [p=0. 8] Acquire license for new product Don’t develop product 0 -$. 5 mm Develop product Movie will be a flop [p=0. 2] -$1 mm + $. 1 mm Don’t develop product 0 Lesson: What’s behind you is not important. Professor Wolfram MBA 201 a - Fall 2009 Page 12
5f3f584f4f69300e37d730d9347a133f.ppt