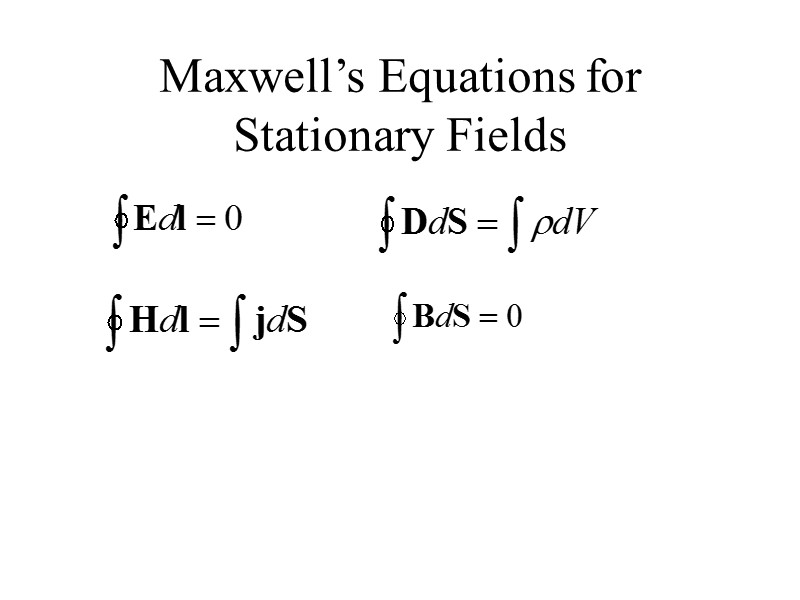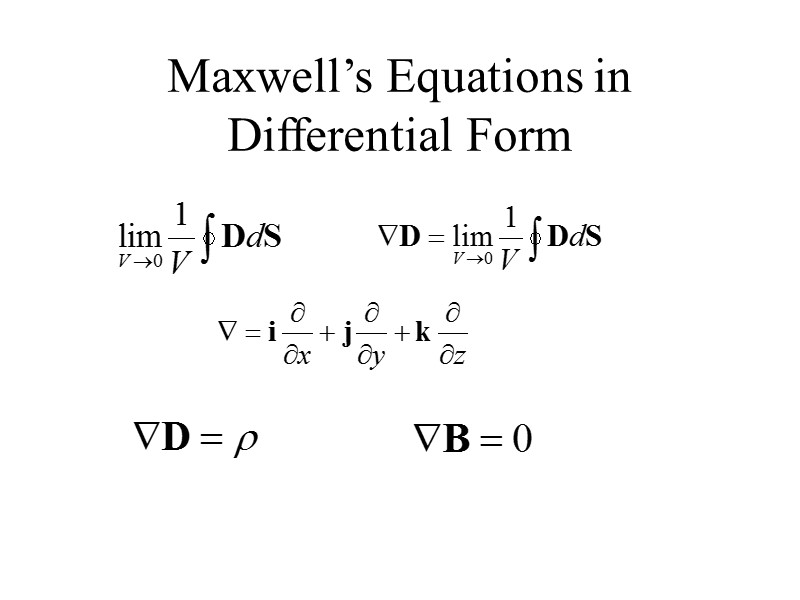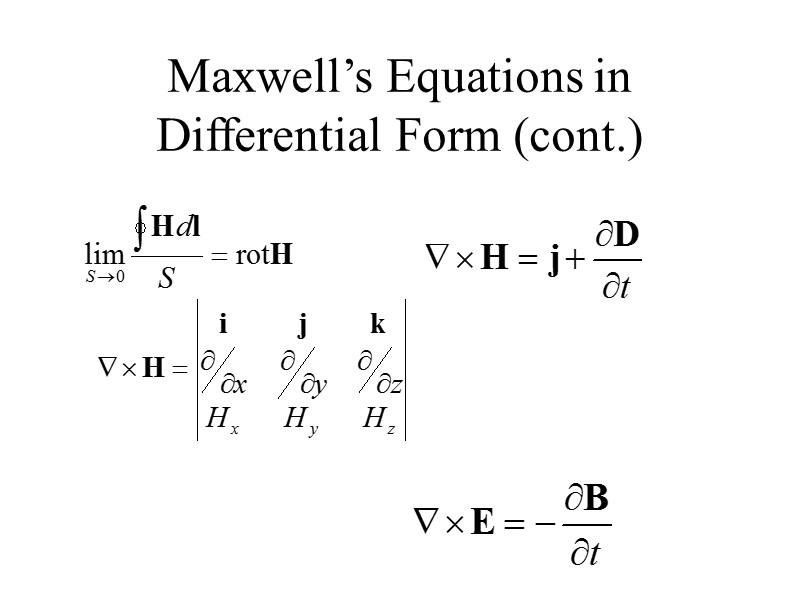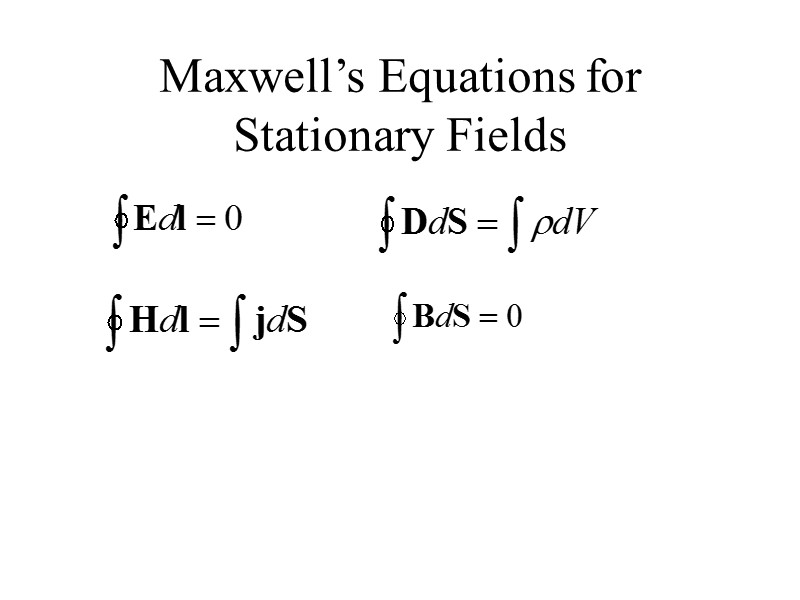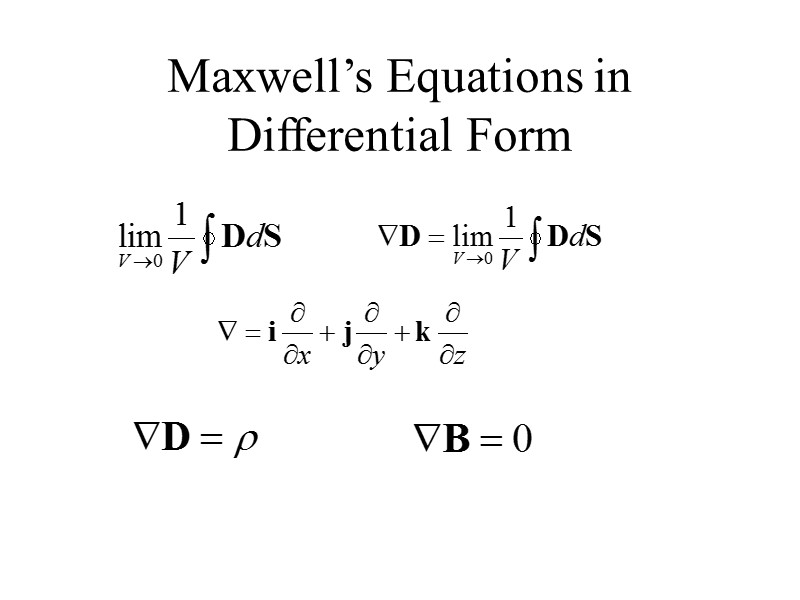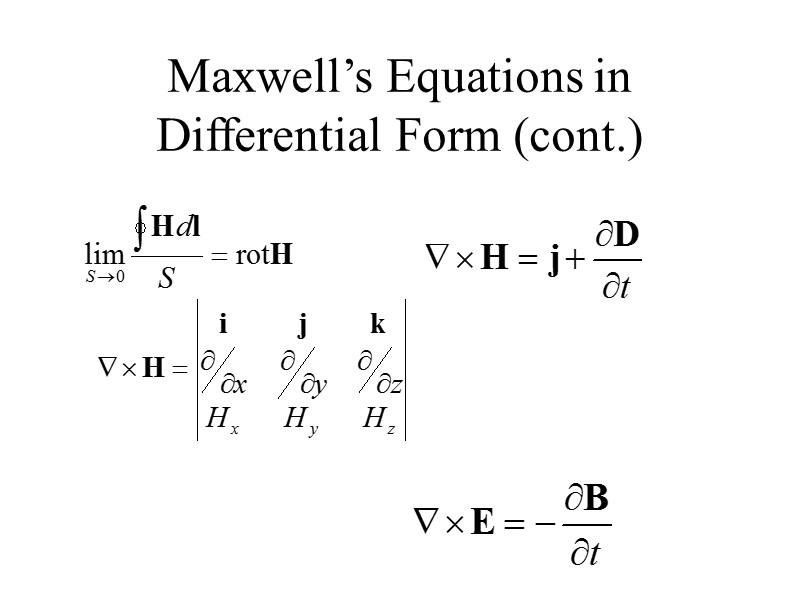 Maxwell’s Equations Equivalent Currents Maxwell’s Equations in Integral Form Maxwell’s Equations for Stationary Fields Maxwell’s Equations in Differential Form Material Equations Properties of Maxwell’s Equations Energy of Electromagnetic Field
Maxwell’s Equations Equivalent Currents Maxwell’s Equations in Integral Form Maxwell’s Equations for Stationary Fields Maxwell’s Equations in Differential Form Material Equations Properties of Maxwell’s Equations Energy of Electromagnetic Field
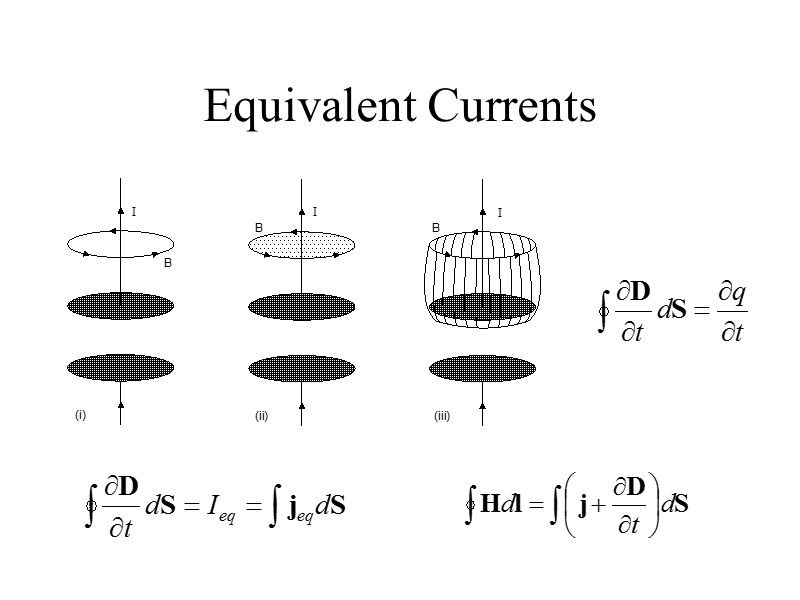 Equivalent Currents
Equivalent Currents
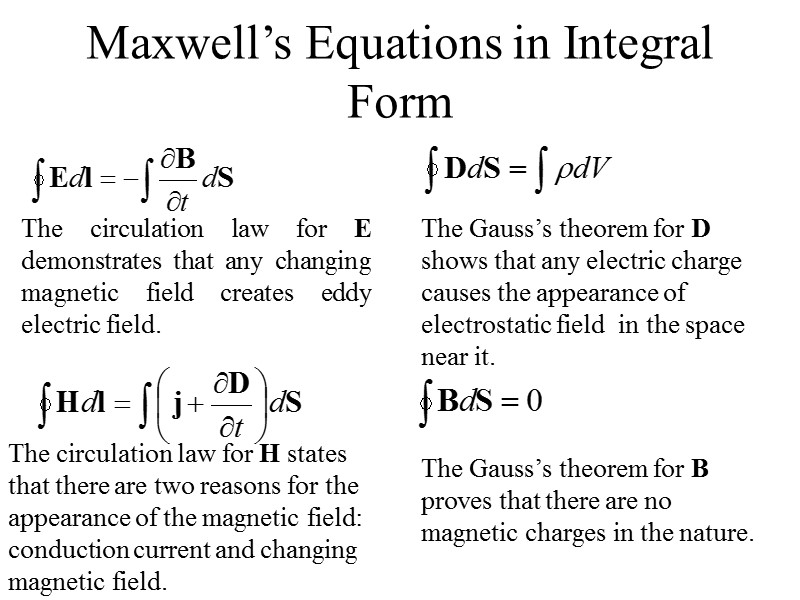 Maxwell’s Equations in Integral Form The circulation law for E demonstrates that any changing magnetic field creates eddy electric field. The Gauss’s theorem for D shows that any electric charge causes the appearance of electrostatic field in the space near it. The circulation law for H states that there are two reasons for the appearance of the magnetic field: conduction current and changing magnetic field. The Gauss’s theorem for B proves that there are no magnetic charges in the nature.
Maxwell’s Equations in Integral Form The circulation law for E demonstrates that any changing magnetic field creates eddy electric field. The Gauss’s theorem for D shows that any electric charge causes the appearance of electrostatic field in the space near it. The circulation law for H states that there are two reasons for the appearance of the magnetic field: conduction current and changing magnetic field. The Gauss’s theorem for B proves that there are no magnetic charges in the nature.
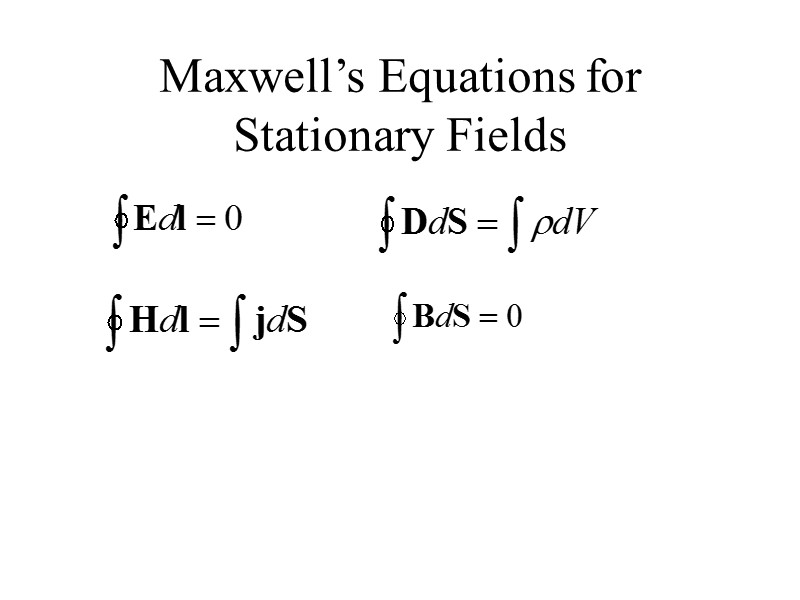 Maxwell’s Equations for Stationary Fields
Maxwell’s Equations for Stationary Fields
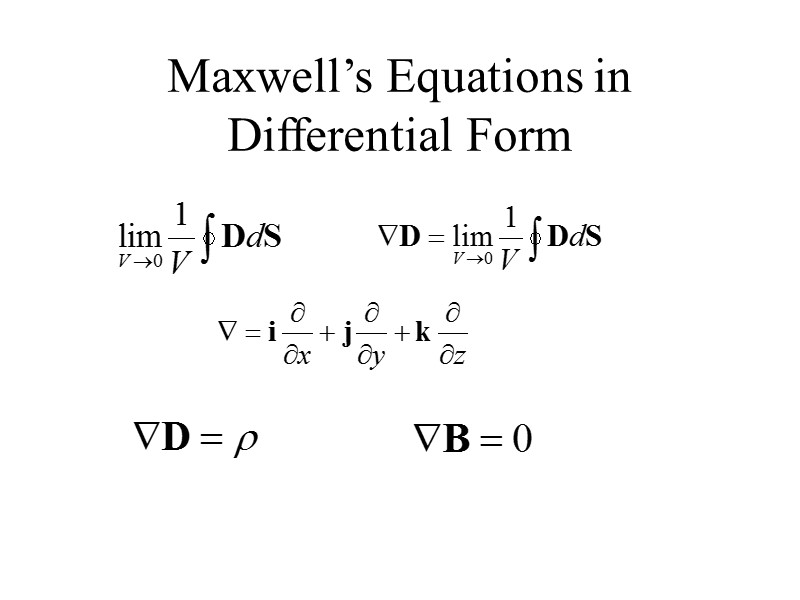 Maxwell’s Equations in Differential Form
Maxwell’s Equations in Differential Form
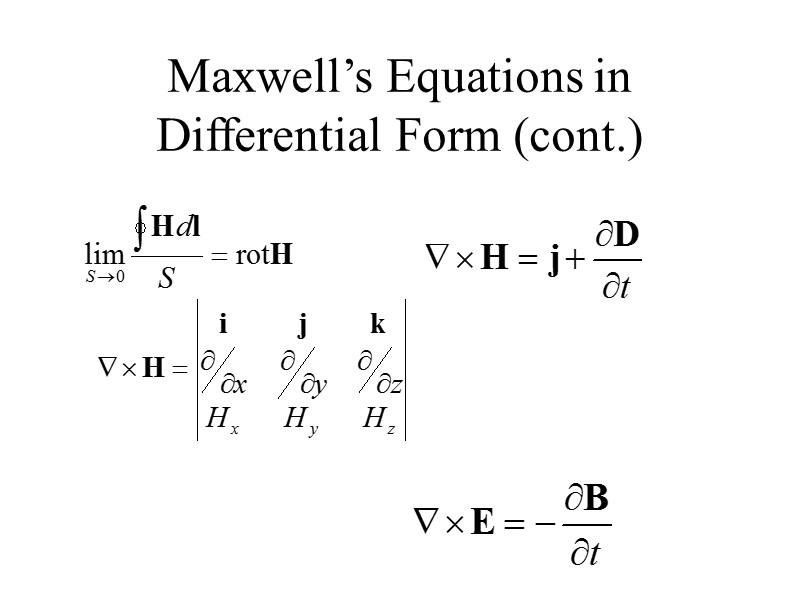 Maxwell’s Equations in Differential Form (cont.)
Maxwell’s Equations in Differential Form (cont.)
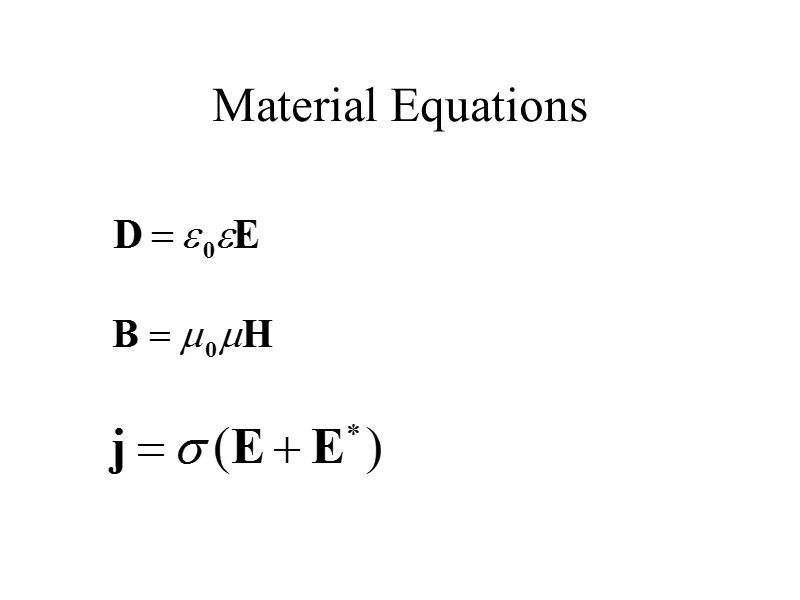 Material Equations
Material Equations
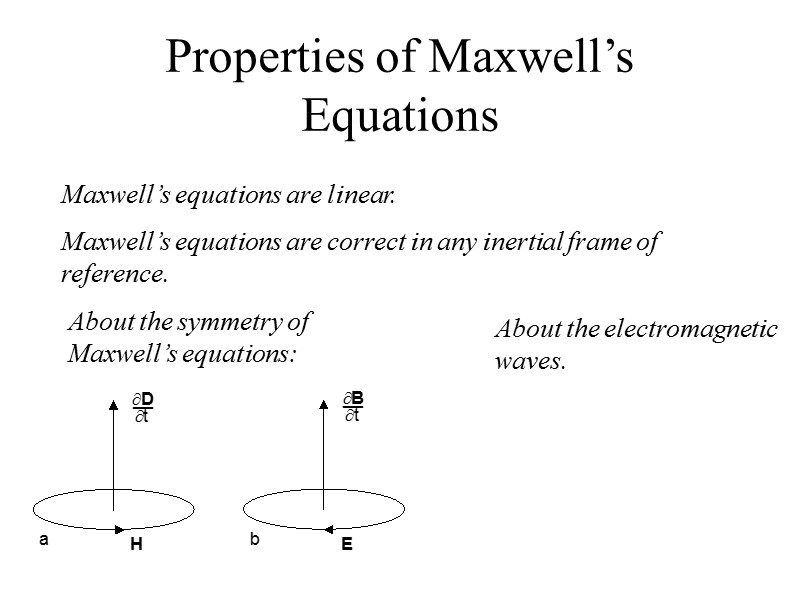 Properties of Maxwell’s Equations Maxwell’s equations are linear. Maxwell’s equations are correct in any inertial frame of reference. About the symmetry of Maxwell’s equations: About the electromagnetic waves.
Properties of Maxwell’s Equations Maxwell’s equations are linear. Maxwell’s equations are correct in any inertial frame of reference. About the symmetry of Maxwell’s equations: About the electromagnetic waves.
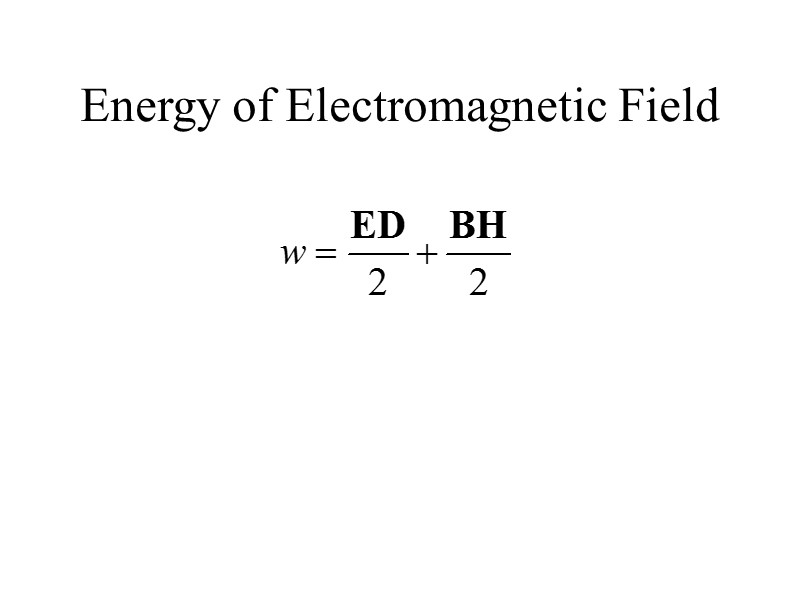 Energy of Electromagnetic Field
Energy of Electromagnetic Field