ba4f6b03bf0aef2a3a4be768872c40b7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Maximum volume/space or minimum materials Design your own assignment
Maximum volume/space or minimum materials Design your own assignment
 Let’s look at a couple of ideas
Let’s look at a couple of ideas
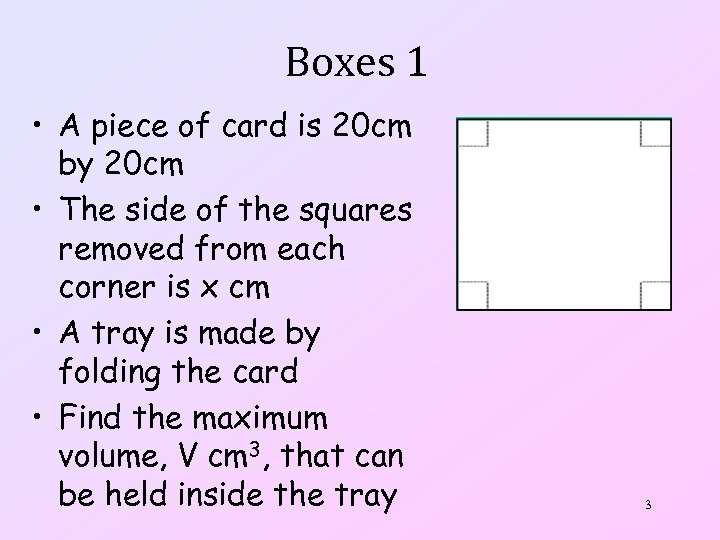 Boxes 1 • A piece of card is 20 cm by 20 cm • The side of the squares removed from each corner is x cm • A tray is made by folding the card • Find the maximum volume, V cm 3, that can be held inside the tray 3
Boxes 1 • A piece of card is 20 cm by 20 cm • The side of the squares removed from each corner is x cm • A tray is made by folding the card • Find the maximum volume, V cm 3, that can be held inside the tray 3
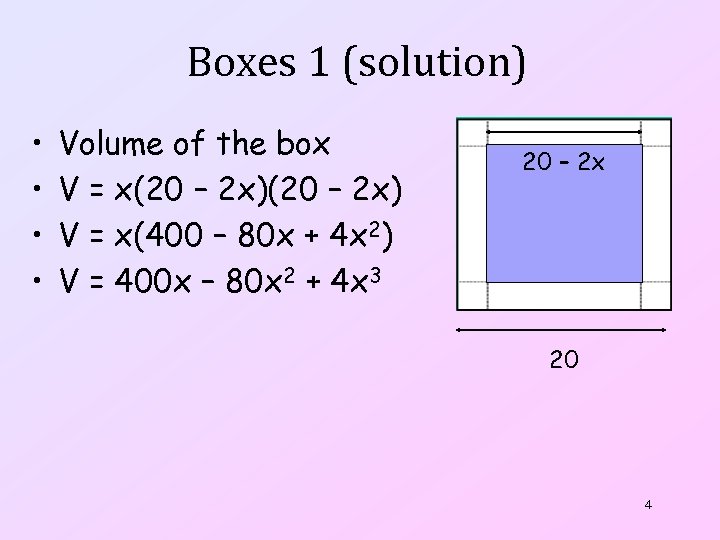 Boxes 1 (solution) • • Volume of the box V = x(20 – 2 x) V = x(400 – 80 x + 4 x 2) V = 400 x – 80 x 2 + 4 x 3 20 – 2 x 20 4
Boxes 1 (solution) • • Volume of the box V = x(20 – 2 x) V = x(400 – 80 x + 4 x 2) V = 400 x – 80 x 2 + 4 x 3 20 – 2 x 20 4
 Boxes 2 • Find d. V/dx and the 2 nd derivative • Solve the equation when d. V/dx = 0 • Hence find the values of x for which the function V has turning points • and establish the maximum volume for the box that can be made from the sheet of card 5
Boxes 2 • Find d. V/dx and the 2 nd derivative • Solve the equation when d. V/dx = 0 • Hence find the values of x for which the function V has turning points • and establish the maximum volume for the box that can be made from the sheet of card 5
 • • • Boxes 2 (solution 1) V = 400 x – 80 x 2 + 4 x 3 Let V = V(x), So d. V/dx = V ’(x) and the 2 nd derivative = V ’’(x) V ’(x) = 400 – 160 x + 12 x 2 V ’’(x) = -160 + 24 x V will have turning points where V ’(x) = 0 So 400 – 160 x + 12 x 2 = 0 100 – 40 x + 3 x 2 = 0 6
• • • Boxes 2 (solution 1) V = 400 x – 80 x 2 + 4 x 3 Let V = V(x), So d. V/dx = V ’(x) and the 2 nd derivative = V ’’(x) V ’(x) = 400 – 160 x + 12 x 2 V ’’(x) = -160 + 24 x V will have turning points where V ’(x) = 0 So 400 – 160 x + 12 x 2 = 0 100 – 40 x + 3 x 2 = 0 6
 Boxes 2 (solution 2) • • 100 – 40 x + 3 x 2 = 0 Is this solved by formula or factorisation? The determinant, b 2 – 4 ac = (-40)2 – 4. 3. (100) = 1600 – 1200 = 400 = 202, a square number So factorise: 100 – 40 x + 3 x 2 = (10 – x)(10 – 3 x) = 0 x = 10 or 10/3 But given x < 10 (half the width) x = 10 is not a reasonable solution for this situation 7
Boxes 2 (solution 2) • • 100 – 40 x + 3 x 2 = 0 Is this solved by formula or factorisation? The determinant, b 2 – 4 ac = (-40)2 – 4. 3. (100) = 1600 – 1200 = 400 = 202, a square number So factorise: 100 – 40 x + 3 x 2 = (10 – x)(10 – 3 x) = 0 x = 10 or 10/3 But given x < 10 (half the width) x = 10 is not a reasonable solution for this situation 7
 Boxes 2 (solution 3) • • x = 10/3 – is it a maximum? V’’(x) = -160 + 24 x When x = 10/3 V’’(10/3) = - 160 + 24 x 10/3 < 0 maximum Vmax = 400(10/3) – 80(10/3)2 + 4(10/3)3 Vmax = 593 cm 3 (3 sf) 8
Boxes 2 (solution 3) • • x = 10/3 – is it a maximum? V’’(x) = -160 + 24 x When x = 10/3 V’’(10/3) = - 160 + 24 x 10/3 < 0 maximum Vmax = 400(10/3) – 80(10/3)2 + 4(10/3)3 Vmax = 593 cm 3 (3 sf) 8
 Start to think about assignments • Devise a packaging problem that will either use the least materials or hold the most volume 9
Start to think about assignments • Devise a packaging problem that will either use the least materials or hold the most volume 9
 Start to think about assignments • It could be a tin can, in which case you would have 2 variables (radius and height) + one fixed quantity (volume) • So you would find an expression for calculating the fixed quantity and then use this expression to get rid of either the height or the radius 10
Start to think about assignments • It could be a tin can, in which case you would have 2 variables (radius and height) + one fixed quantity (volume) • So you would find an expression for calculating the fixed quantity and then use this expression to get rid of either the height or the radius 10
 Start to think about assignments • Then form an expression for the quantity you want to make as small (or as large) as possible • Differentiate it, put = 0 and find the value of x that will give the minimum (or maximum) • Hence find the other dimension and the value of the material or volume that you require 11
Start to think about assignments • Then form an expression for the quantity you want to make as small (or as large) as possible • Differentiate it, put = 0 and find the value of x that will give the minimum (or maximum) • Hence find the other dimension and the value of the material or volume that you require 11
 Let me demonstrate • Say I want to use the minimum metal to make a can to hold 500 ml ( which is the same as 500 cm 3) • If r cm is the radius and h cm is the height, the volume V = r 2 h • and the metal used M = 2 r 2 + 2 rh • So if V = 500 then r 2 h = 500 • I will eliminate h (its easier than a squared term) so h = 500/ r 2 12
Let me demonstrate • Say I want to use the minimum metal to make a can to hold 500 ml ( which is the same as 500 cm 3) • If r cm is the radius and h cm is the height, the volume V = r 2 h • and the metal used M = 2 r 2 + 2 rh • So if V = 500 then r 2 h = 500 • I will eliminate h (its easier than a squared term) so h = 500/ r 2 12
 Let me demonstrate • • Using h = 500/ r 2 M = 2 r 2 + 2 rh = 2 r 2 + 2 r x 500/ r 2 M = 2 r 2 + 2 x 500/ r = 2 r 2 + 1000 r-1 So d. M/dr = 4 r - 1000 r-2 When d. M/dr = 0 we will have turning point So 4 r - 1000 r-2 = 0 4 r = 1000 r-2 4 r 3 = 1000 r 3 = 250/ r = 4. 30(3 sf) 13
Let me demonstrate • • Using h = 500/ r 2 M = 2 r 2 + 2 rh = 2 r 2 + 2 r x 500/ r 2 M = 2 r 2 + 2 x 500/ r = 2 r 2 + 1000 r-1 So d. M/dr = 4 r - 1000 r-2 When d. M/dr = 0 we will have turning point So 4 r - 1000 r-2 = 0 4 r = 1000 r-2 4 r 3 = 1000 r 3 = 250/ r = 4. 30(3 sf) 13
 Let me demonstrate • • r = 4. 30(3 sf) Is this a minimum? M’’(x) = 4 + 2000 r-3 At r = 4. 30 M’’(4. 30) = 4 + 2000/(4. 30)3 > 0 a minimum So h = 500 (18. 5 ) =8. 60 (3 sf) M= 2 x 18. 5 + 2 x 4. 3 x 8. 6 = 349 cm 2 (3 sf) 14
Let me demonstrate • • r = 4. 30(3 sf) Is this a minimum? M’’(x) = 4 + 2000 r-3 At r = 4. 30 M’’(4. 30) = 4 + 2000/(4. 30)3 > 0 a minimum So h = 500 (18. 5 ) =8. 60 (3 sf) M= 2 x 18. 5 + 2 x 4. 3 x 8. 6 = 349 cm 2 (3 sf) 14
 Don’t think you can do that one! • If you did a can, I would expect for instance that you would decide the base and the top would be double thickness, so you would end up with different answers • or that 2 different metals would be used with a different unit cost for each 15
Don’t think you can do that one! • If you did a can, I would expect for instance that you would decide the base and the top would be double thickness, so you would end up with different answers • or that 2 different metals would be used with a different unit cost for each 15
 But there are dozens of others • Boxes of all shapes, with and without lids • What about a Toblerone box? • Or how about swimming pools, with a shallow end a deep end? Would the cement be equally thick all over? • What about ice cream cone packaging? • What about a wooden play house? (remember the door!) 16
But there are dozens of others • Boxes of all shapes, with and without lids • What about a Toblerone box? • Or how about swimming pools, with a shallow end a deep end? Would the cement be equally thick all over? • What about ice cream cone packaging? • What about a wooden play house? (remember the door!) 16
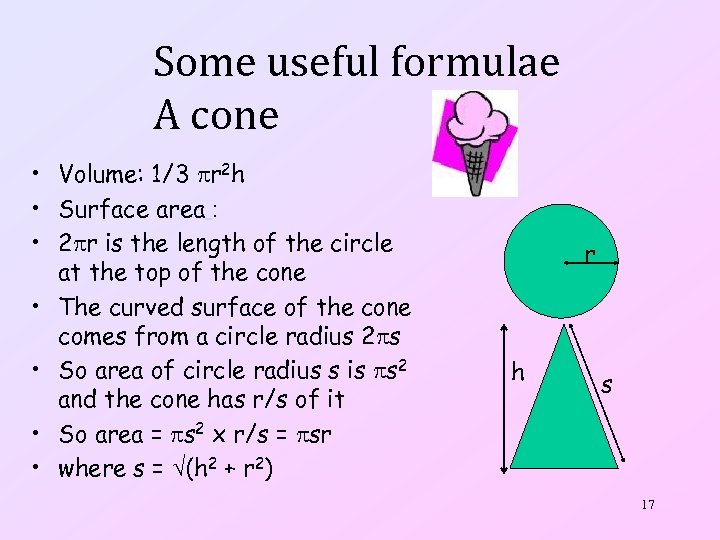 Some useful formulae A cone • Volume: 1/3 r 2 h • Surface area : • 2 r is the length of the circle at the top of the cone • The curved surface of the cone comes from a circle radius 2 s • So area of circle radius s is s 2 and the cone has r/s of it • So area = s 2 x r/s = sr • where s = (h 2 + r 2) r h s 17
Some useful formulae A cone • Volume: 1/3 r 2 h • Surface area : • 2 r is the length of the circle at the top of the cone • The curved surface of the cone comes from a circle radius 2 s • So area of circle radius s is s 2 and the cone has r/s of it • So area = s 2 x r/s = sr • where s = (h 2 + r 2) r h s 17
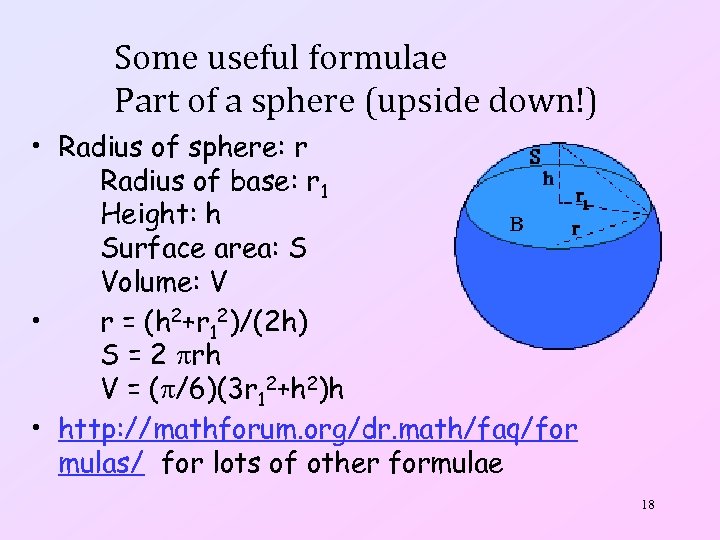 Some useful formulae Part of a sphere (upside down!) • Radius of sphere: r Radius of base: r 1 Height: h Surface area: S Volume: V • r = (h 2+r 12)/(2 h) S = 2 rh V = ( /6)(3 r 12+h 2)h • http: //mathforum. org/dr. math/faq/for mulas/ for lots of other formulae 18
Some useful formulae Part of a sphere (upside down!) • Radius of sphere: r Radius of base: r 1 Height: h Surface area: S Volume: V • r = (h 2+r 12)/(2 h) S = 2 rh V = ( /6)(3 r 12+h 2)h • http: //mathforum. org/dr. math/faq/for mulas/ for lots of other formulae 18


