175f42a8887ed61d8c51e73492e33181.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9
 Maxim Pathfinder Prework 16 August 1999
Maxim Pathfinder Prework 16 August 1999
 Maxim Pathfinder Prework Topics 6 6 6 General Orbit and Pointing Data Acquisition Concepts Operations Concepts Suggestions for Study Work Style this Week
Maxim Pathfinder Prework Topics 6 6 6 General Orbit and Pointing Data Acquisition Concepts Operations Concepts Suggestions for Study Work Style this Week
 General 6 Maxim Pathfinder is an X-ray telescope, preparing for a larger X-ray telescope - the “real” Maxim 6 Chandra and Constellation-X are precursors to Maxim 6 NGST, LISA and SIM are missions, active or proposed, which will employ technology applicable to Maxim
General 6 Maxim Pathfinder is an X-ray telescope, preparing for a larger X-ray telescope - the “real” Maxim 6 Chandra and Constellation-X are precursors to Maxim 6 NGST, LISA and SIM are missions, active or proposed, which will employ technology applicable to Maxim
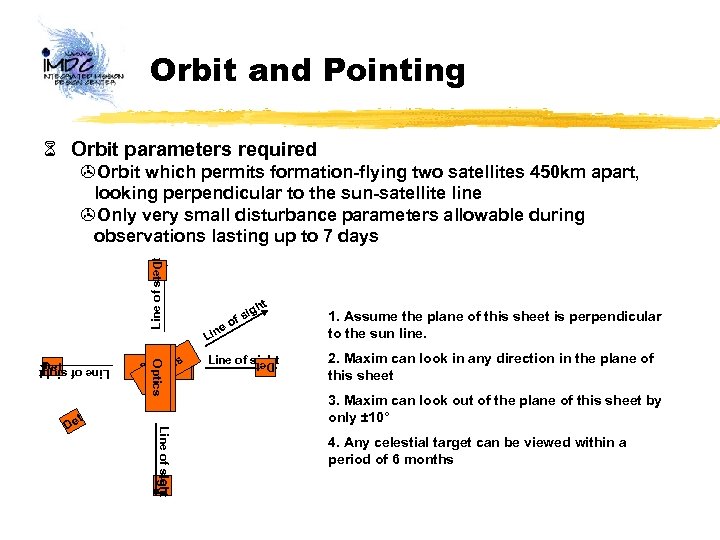 Orbit and Pointing 6 Orbit parameters required Det Line of sight >Orbit which permits formation-flying two satellites 450 km apart, looking perpendicular to the sun-satellite line >Only very small disturbance parameters allowable during observations lasting up to 7 days Optics Line of sight t Det Line of sight De e Lin o Line of sight Det Opticss tic Op Optics Det ht ig fs 1. Assume the plane of this sheet is perpendicular to the sun line. 2. Maxim can look in any direction in the plane of this sheet 3. Maxim can look out of the plane of this sheet by only ± 10° 4. Any celestial target can be viewed within a period of 6 months
Orbit and Pointing 6 Orbit parameters required Det Line of sight >Orbit which permits formation-flying two satellites 450 km apart, looking perpendicular to the sun-satellite line >Only very small disturbance parameters allowable during observations lasting up to 7 days Optics Line of sight t Det Line of sight De e Lin o Line of sight Det Opticss tic Op Optics Det ht ig fs 1. Assume the plane of this sheet is perpendicular to the sun line. 2. Maxim can look in any direction in the plane of this sheet 3. Maxim can look out of the plane of this sheet by only ± 10° 4. Any celestial target can be viewed within a period of 6 months
 Data Acquisition Concepts 6 Observations may last several days, but data probably should be downlinked at intervals as the observation progresses 6 Instrumentation on optics spacecraft will produce ~10 kbps + spacecraft engineering data 6 Instrumentation on detector spacecraft will produce ~10 kbps + spacecraft engineering data 6 Recommend whether each spacecraft should downlink separately, or one should relay data from both satellites
Data Acquisition Concepts 6 Observations may last several days, but data probably should be downlinked at intervals as the observation progresses 6 Instrumentation on optics spacecraft will produce ~10 kbps + spacecraft engineering data 6 Instrumentation on detector spacecraft will produce ~10 kbps + spacecraft engineering data 6 Recommend whether each spacecraft should downlink separately, or one should relay data from both satellites
 Operations Concepts 6 Early orbit operations will require adjustment of the 64 flat mirrors. This implies either an onboard automated process or real-time ground interaction. 6 Target acquisition also may be either automated onboard or accomplished with real-time ground interaction (potential trade study). 6 Rapid slew from target to target is not required.
Operations Concepts 6 Early orbit operations will require adjustment of the 64 flat mirrors. This implies either an onboard automated process or real-time ground interaction. 6 Target acquisition also may be either automated onboard or accomplished with real-time ground interaction (potential trade study). 6 Rapid slew from target to target is not required.
 Suggestions for Study > Recommend the type of orbit or trajectory best suited to this mission. > Compare the pros and cons of having independent data links from each satellite to ground vs. having one satellite collect all the data for both and relay that to the ground. > Does each satellite have independent data storage or does that function get combined in one or the other of the satellites. > Determine the best means of pointing the satellites and maintaining pointing during observations. > Determine whether data should be stored and dumped at intervals or maintain continuous contact, and whether ground antennas should be shared with other missions or dedicated to this mission. > Perform analysis of thermal problems, recommend and size radiators and other cooling devices.
Suggestions for Study > Recommend the type of orbit or trajectory best suited to this mission. > Compare the pros and cons of having independent data links from each satellite to ground vs. having one satellite collect all the data for both and relay that to the ground. > Does each satellite have independent data storage or does that function get combined in one or the other of the satellites. > Determine the best means of pointing the satellites and maintaining pointing during observations. > Determine whether data should be stored and dumped at intervals or maintain continuous contact, and whether ground antennas should be shared with other missions or dedicated to this mission. > Perform analysis of thermal problems, recommend and size radiators and other cooling devices.
 More Suggestions for Study > Recommend placement of spacecraft subsystems on both satellites, determining mass and momentum properties. > Recommend a power subsystem for each satellite. > Consider radiation precautions needed and recommend necessary protection. > Recommend propulsion needed to achieve the mission orbit (once we determine what it should be) and recommend propulsion which may be needed if pointing and stabilization cannot be accomplished with wheels or other means. > Analyze potential effects of solar wind and how that may affect pointing control of the satellites. > Identify technology developments needed to enable accomplishing the mission. Identify the expected technology developments benefiting this mission starting 10 years in the future.
More Suggestions for Study > Recommend placement of spacecraft subsystems on both satellites, determining mass and momentum properties. > Recommend a power subsystem for each satellite. > Consider radiation precautions needed and recommend necessary protection. > Recommend propulsion needed to achieve the mission orbit (once we determine what it should be) and recommend propulsion which may be needed if pointing and stabilization cannot be accomplished with wheels or other means. > Analyze potential effects of solar wind and how that may affect pointing control of the satellites. > Identify technology developments needed to enable accomplishing the mission. Identify the expected technology developments benefiting this mission starting 10 years in the future.
 Work Style this Week 6 Emphasize a collaborative approach > Many of the parameters the DET needs (mass, size, power) will require a negotiated agreement between affected parties > Maxim team and DET personnel need frequent interaction 6 Scorecard of agreed parameters for reference by all 6 Morning meeting each day at 9: 30 to synchronize everybody for the day 6 Informal splinter meetings of affected parties
Work Style this Week 6 Emphasize a collaborative approach > Many of the parameters the DET needs (mass, size, power) will require a negotiated agreement between affected parties > Maxim team and DET personnel need frequent interaction 6 Scorecard of agreed parameters for reference by all 6 Morning meeting each day at 9: 30 to synchronize everybody for the day 6 Informal splinter meetings of affected parties


