537b4f48f36e6e46888122f87829da40.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Mauritius Customs Trade Facilitation Implementation Sooryadev Singh PURMAH, MBA Team Leader, Customs (Trade Facilitation & Customs Cooperation) Joined Customs & Excise Dept in Feb 1972
Mauritius Customs Trade Facilitation Implementation Sooryadev Singh PURMAH, MBA Team Leader, Customs (Trade Facilitation & Customs Cooperation) Joined Customs & Excise Dept in Feb 1972
 Republic of Mauritius §Total area: 67× 46 = 2040 sq km §Population: 1. 3 million (est) §Mono-crop economy to a diversified one: sugar, industrial manufacturing, tourism, financial services, freeport activities, ICT, sea food hub § 87% of tariff lines at zero rate §Island state with no natural resources
Republic of Mauritius §Total area: 67× 46 = 2040 sq km §Population: 1. 3 million (est) §Mono-crop economy to a diversified one: sugar, industrial manufacturing, tourism, financial services, freeport activities, ICT, sea food hub § 87% of tariff lines at zero rate §Island state with no natural resources
 World Bank Doing Business 2012 Out of 183 countries: • Ease of Doing Business - 23 rd • Trading Across Borders - 21 st • Paying Taxes: 11 th
World Bank Doing Business 2012 Out of 183 countries: • Ease of Doing Business - 23 rd • Trading Across Borders - 21 st • Paying Taxes: 11 th
 MRA-Customs Department Collects 34 % state revenues 670 customs officers 1 Seaport and 1 International Airport 350, 000 declarations per year (total)
MRA-Customs Department Collects 34 % state revenues 670 customs officers 1 Seaport and 1 International Airport 350, 000 declarations per year (total)
 Triggers for Change: Trade Facilitation v/s Control Limited resources in contrast with dramatic increase in volume of trade & travel Globalization: Liberalization of governmental policies on cross-border movement of trade and resources Technological development Development of institutions to support and facilitate international trade Increased global competition Protection of society & terrorism Public criticism
Triggers for Change: Trade Facilitation v/s Control Limited resources in contrast with dramatic increase in volume of trade & travel Globalization: Liberalization of governmental policies on cross-border movement of trade and resources Technological development Development of institutions to support and facilitate international trade Increased global competition Protection of society & terrorism Public criticism
 Objectives of Customs Trade Facilitation Programme Attain revenue targets Implement Government economic policies Reduce economic distortions associated with smuggling and commercial fraud Create a ‘level playing field’ for traders Facilitate honest traders while targeting high risk ones Promote transparency Promote voluntary compliance Ensure predictability Reduce discretion and corruption
Objectives of Customs Trade Facilitation Programme Attain revenue targets Implement Government economic policies Reduce economic distortions associated with smuggling and commercial fraud Create a ‘level playing field’ for traders Facilitate honest traders while targeting high risk ones Promote transparency Promote voluntary compliance Ensure predictability Reduce discretion and corruption
 Managing Change at Mauritius Customs • WCO Customs Reform & Modernization Programme (CRMP) as from 1998 and Project Management Concept as from end of 2002 • CRMP : Orientation Meeting with policy makers → Diagnosis & Planning: Team of Facilitators - WCO, HM Customs, Revenue Canada: Data Collection, Diagnosis & Report: 3 Workshops • Project Management Concept: Team constituted & Strategic planning approach
Managing Change at Mauritius Customs • WCO Customs Reform & Modernization Programme (CRMP) as from 1998 and Project Management Concept as from end of 2002 • CRMP : Orientation Meeting with policy makers → Diagnosis & Planning: Team of Facilitators - WCO, HM Customs, Revenue Canada: Data Collection, Diagnosis & Report: 3 Workshops • Project Management Concept: Team constituted & Strategic planning approach
 Outcomes of Diagnosis Mission & Implementation Strategy • • • 1. Outcomes Vision: Towards a clean & efficient Customs Mission: Fiscal, Economic, Protective, Business Support Strategic plans: Based on 6 Primary Functions 2. Implementation Steering Committee Change Management Team (+ consultants) Implementation Teams in 6 priority areas • Work Improvement Teams • Evaluation • Recruitment of expatriates in Oct 2006 & Feb 2009 to boost ongoing reforms
Outcomes of Diagnosis Mission & Implementation Strategy • • • 1. Outcomes Vision: Towards a clean & efficient Customs Mission: Fiscal, Economic, Protective, Business Support Strategic plans: Based on 6 Primary Functions 2. Implementation Steering Committee Change Management Team (+ consultants) Implementation Teams in 6 priority areas • Work Improvement Teams • Evaluation • Recruitment of expatriates in Oct 2006 & Feb 2009 to boost ongoing reforms
 Major Changes Over The Years 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Paradigm shift: gatekeeper to facilitator Partnership with business Automation - Customs Management System (CMS/EDI). Implementation of WTO Valuation Agreement, Post Clearance Control System Schedule of duties/SOP manuals for officers Redeployment of staff and creation of various enforcement units Code of ethics for officers and customer charter for stakeholders Complaints Bureau Tariff Information Unit Autonomous unit for air-freighted goods Customs Investigation and Intelligence Unit including a drug cell Non-Intrusive Inspection Techniques (NII): Scanners Centralized Risk Management Section
Major Changes Over The Years 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Paradigm shift: gatekeeper to facilitator Partnership with business Automation - Customs Management System (CMS/EDI). Implementation of WTO Valuation Agreement, Post Clearance Control System Schedule of duties/SOP manuals for officers Redeployment of staff and creation of various enforcement units Code of ethics for officers and customer charter for stakeholders Complaints Bureau Tariff Information Unit Autonomous unit for air-freighted goods Customs Investigation and Intelligence Unit including a drug cell Non-Intrusive Inspection Techniques (NII): Scanners Centralized Risk Management Section
 Other Trade Facilitation Initiatives Single Window office for Cargo Inspection Single Window office for Exporters Ecertificate of origin CARGO FAST TRACK Program - AEO project Cargo Community System – Electronic platform for tracking & tracing of containers Express Courier Hub Project Integrated Tariff and Tariff Classification Rulings databases on web-site Rules, regulations, procedures, SOP manual for stakeholders & administrative forms available on website Intranet system for officers Appeal Mechanism
Other Trade Facilitation Initiatives Single Window office for Cargo Inspection Single Window office for Exporters Ecertificate of origin CARGO FAST TRACK Program - AEO project Cargo Community System – Electronic platform for tracking & tracing of containers Express Courier Hub Project Integrated Tariff and Tariff Classification Rulings databases on web-site Rules, regulations, procedures, SOP manual for stakeholders & administrative forms available on website Intranet system for officers Appeal Mechanism
 Requisites for Capacity Building in Customs WCO definition: ‘Developing or acquiring skills, competencies, tools, processes and resources needed to improve the capacity of the administration to carry out its allotted functions and achieve its objectives. ’ Sustained Political Will & Commitment Leadership & Stakeholder Support Ownership & Participation of Customs Personnel Adequate Human and Financial Resources Effective Human Resource Management Practices Paradigm shift: Gatekeeper Mentality to Facilitator Partnership with Business Community Communication Strategy Strategic Management Approach & Change Management Model
Requisites for Capacity Building in Customs WCO definition: ‘Developing or acquiring skills, competencies, tools, processes and resources needed to improve the capacity of the administration to carry out its allotted functions and achieve its objectives. ’ Sustained Political Will & Commitment Leadership & Stakeholder Support Ownership & Participation of Customs Personnel Adequate Human and Financial Resources Effective Human Resource Management Practices Paradigm shift: Gatekeeper Mentality to Facilitator Partnership with Business Community Communication Strategy Strategic Management Approach & Change Management Model
 Strategies to create a “World Class” Customs Service Institutional Infrastructural Technology Technical assistance/consultants Apply international Customs conventions , best practices and control techniques (e. g. , risk management & postclearance controls) Modernize Customs law and regulations Simplify, standardize & harmonise customs procedures Effective Human Resource Management Practices
Strategies to create a “World Class” Customs Service Institutional Infrastructural Technology Technical assistance/consultants Apply international Customs conventions , best practices and control techniques (e. g. , risk management & postclearance controls) Modernize Customs law and regulations Simplify, standardize & harmonise customs procedures Effective Human Resource Management Practices
 WCO & WTO Trade Facilitation Instruments HS Convention RKC Arusha Declaration Customs Reform & Modernization Programme Columbus Programme – WCO Framework of Standards WTO Valuation Agreement Time Release Study WCO Data Model Rules of origin
WCO & WTO Trade Facilitation Instruments HS Convention RKC Arusha Declaration Customs Reform & Modernization Programme Columbus Programme – WCO Framework of Standards WTO Valuation Agreement Time Release Study WCO Data Model Rules of origin
 Institutional Change - 1 July 2006 Mauritius Revenue Authority (MRA): revenue depts under one umbrella as a corporate body to act as agent of government: q. Vision: World Class Revenue Service q. Mission: Continually reform and modernize in order to achieve effectiveness and efficiency comprising with highly motivated and skilled staff. q. Core Values: Integrity, Responsiveness, Fairness, Transparency, Accountability
Institutional Change - 1 July 2006 Mauritius Revenue Authority (MRA): revenue depts under one umbrella as a corporate body to act as agent of government: q. Vision: World Class Revenue Service q. Mission: Continually reform and modernize in order to achieve effectiveness and efficiency comprising with highly motivated and skilled staff. q. Core Values: Integrity, Responsiveness, Fairness, Transparency, Accountability
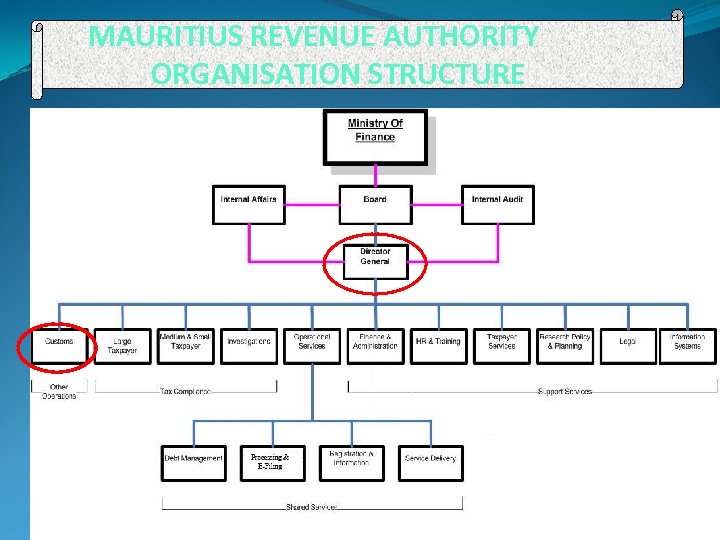 MAURITIUS REVENUE AUTHORITY ORGANISATION STRUCTURE
MAURITIUS REVENUE AUTHORITY ORGANISATION STRUCTURE
 Existing Offices Renovated to Improve Customer Service ‘One Stop Shop’ @ Dragon House Customer Counters @ SSR Air Cargo Open Concept Offices @ IKS Building ‘RED/GREEN’ Channel @ SSR
Existing Offices Renovated to Improve Customer Service ‘One Stop Shop’ @ Dragon House Customer Counters @ SSR Air Cargo Open Concept Offices @ IKS Building ‘RED/GREEN’ Channel @ SSR
 “Single Window” Cargo Inspection Office at Port
“Single Window” Cargo Inspection Office at Port

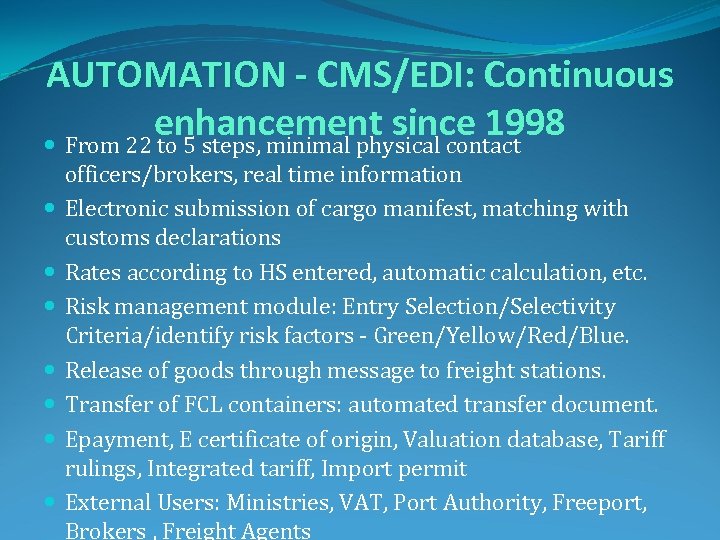 AUTOMATION - CMS/EDI: Continuous enhancement since 1998 From 22 to 5 steps, minimal physical contact officers/brokers, real time information Electronic submission of cargo manifest, matching with customs declarations Rates according to HS entered, automatic calculation, etc. Risk management module: Entry Selection/Selectivity Criteria/identify risk factors - Green/Yellow/Red/Blue. Release of goods through message to freight stations. Transfer of FCL containers: automated transfer document. Epayment, E certificate of origin, Valuation database, Tariff rulings, Integrated tariff, Import permit External Users: Ministries, VAT, Port Authority, Freeport, Brokers , Freight Agents
AUTOMATION - CMS/EDI: Continuous enhancement since 1998 From 22 to 5 steps, minimal physical contact officers/brokers, real time information Electronic submission of cargo manifest, matching with customs declarations Rates according to HS entered, automatic calculation, etc. Risk management module: Entry Selection/Selectivity Criteria/identify risk factors - Green/Yellow/Red/Blue. Release of goods through message to freight stations. Transfer of FCL containers: automated transfer document. Epayment, E certificate of origin, Valuation database, Tariff rulings, Integrated tariff, Import permit External Users: Ministries, VAT, Port Authority, Freeport, Brokers , Freight Agents
 Port Nuctech X-Ray Scanners Airport (operational since Feb 2006)
Port Nuctech X-Ray Scanners Airport (operational since Feb 2006)
 Training and Development Initiatives • Management Development , Project Management , Investigative & Control Techniques, Risk Management • Post clearance auditing • Laws & Regulations, Processes & Procedures • ICT & Integrity • Customer Care, Performance Management System
Training and Development Initiatives • Management Development , Project Management , Investigative & Control Techniques, Risk Management • Post clearance auditing • Laws & Regulations, Processes & Procedures • ICT & Integrity • Customer Care, Performance Management System
 Staff and Stakeholder Training
Staff and Stakeholder Training
 K 9 Drug Detector Dogs
K 9 Drug Detector Dogs
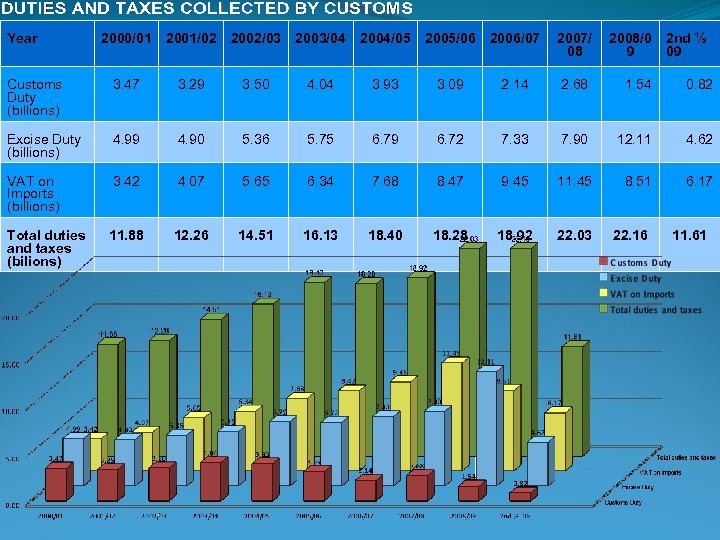 Year 2000/01 2001/02 2002/03 2003/04 2004/05 2005/06 2006/07 2007/ 08 2008/0 9 2 nd ½ 09 Customs Duty (billions) 3. 47 3. 29 3. 50 4. 04 3. 93 3. 09 2. 14 2. 68 1. 54 0. 82 Excise Duty (billions) 4. 99 4. 90 5. 36 5. 75 6. 79 6. 72 7. 33 7. 90 12. 11 4. 62 VAT on Imports (billions) 3. 42 4. 07 5. 65 6. 34 7. 68 8. 47 9. 45 11. 45 8. 51 6. 17 Total duties and taxes (bilions) 11. 88 12. 26 14. 51 16. 13 18. 40 18. 28 18. 92 22. 03 22. 16 11. 61
Year 2000/01 2001/02 2002/03 2003/04 2004/05 2005/06 2006/07 2007/ 08 2008/0 9 2 nd ½ 09 Customs Duty (billions) 3. 47 3. 29 3. 50 4. 04 3. 93 3. 09 2. 14 2. 68 1. 54 0. 82 Excise Duty (billions) 4. 99 4. 90 5. 36 5. 75 6. 79 6. 72 7. 33 7. 90 12. 11 4. 62 VAT on Imports (billions) 3. 42 4. 07 5. 65 6. 34 7. 68 8. 47 9. 45 11. 45 8. 51 6. 17 Total duties and taxes (bilions) 11. 88 12. 26 14. 51 16. 13 18. 40 18. 28 18. 92 22. 03 22. 16 11. 61
 Integrity Internal Affairs & Internal Audit Divisions within MRA 2006: Customs Department awarded by ICAC the Best Anti-Corruption Framework Award in the Public Service and the most improved public sector institution. 2010: Integrity Risk Assessment conducted for whole MRA: MRA awarded Best Anti-Corruption Framework & ranked first in Management Commitment and Integrity Management
Integrity Internal Affairs & Internal Audit Divisions within MRA 2006: Customs Department awarded by ICAC the Best Anti-Corruption Framework Award in the Public Service and the most improved public sector institution. 2010: Integrity Risk Assessment conducted for whole MRA: MRA awarded Best Anti-Corruption Framework & ranked first in Management Commitment and Integrity Management
 Projects in the pipeline Mauritius Trade Portal based on the Single Window Concept Paperless Customs Internal Appeal Mechanism & Prescribed Administrative Penalties Accounts Manager.
Projects in the pipeline Mauritius Trade Portal based on the Single Window Concept Paperless Customs Internal Appeal Mechanism & Prescribed Administrative Penalties Accounts Manager.
 End Note • In today’s world, the only constant is change - Need for continuous improvement • For change to be sustainable - Need for trust and commitment through leadership, employee participation, communication & motivation • Comment from a change agent: ‘Customs reform is like pregnancy. It is often fun and easy to conceive, but delivery is long and painful. ’
End Note • In today’s world, the only constant is change - Need for continuous improvement • For change to be sustainable - Need for trust and commitment through leadership, employee participation, communication & motivation • Comment from a change agent: ‘Customs reform is like pregnancy. It is often fun and easy to conceive, but delivery is long and painful. ’


