667615d331eb82411ca9da9c6658888e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 106

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd 12 -hour clock notation
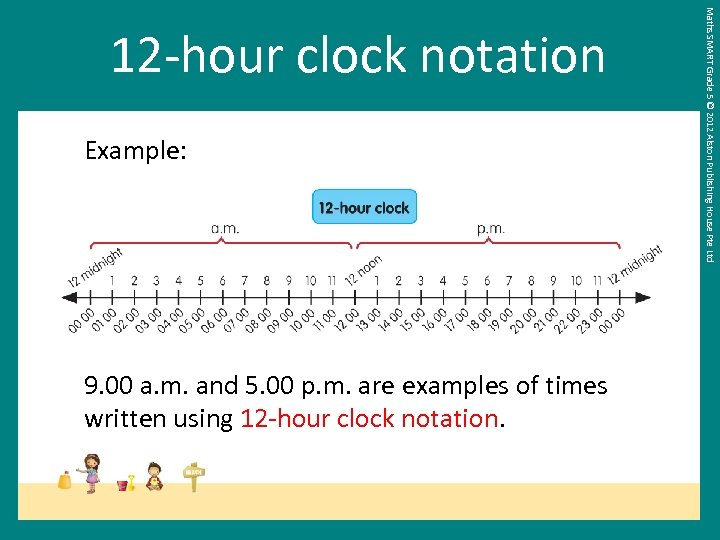
Example: 9. 00 a. m. and 5. 00 p. m. are examples of times written using 12 -hour clock notation. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd 12 -hour clock notation

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd 24 -hour clock notation
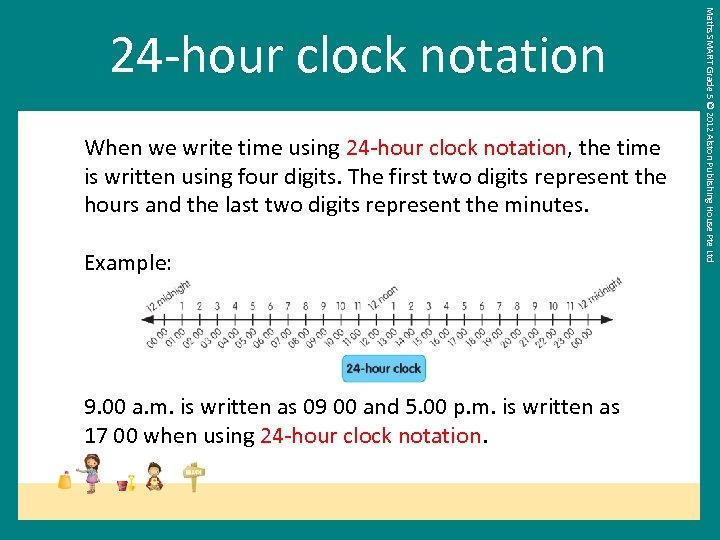
When we write time using 24 -hour clock notation, the time is written using four digits. The first two digits represent the hours and the last two digits represent the minutes. Example: 9. 00 a. m. is written as 09 00 and 5. 00 p. m. is written as 17 00 when using 24 -hour clock notation. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd 24 -hour clock notation

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Acute angle
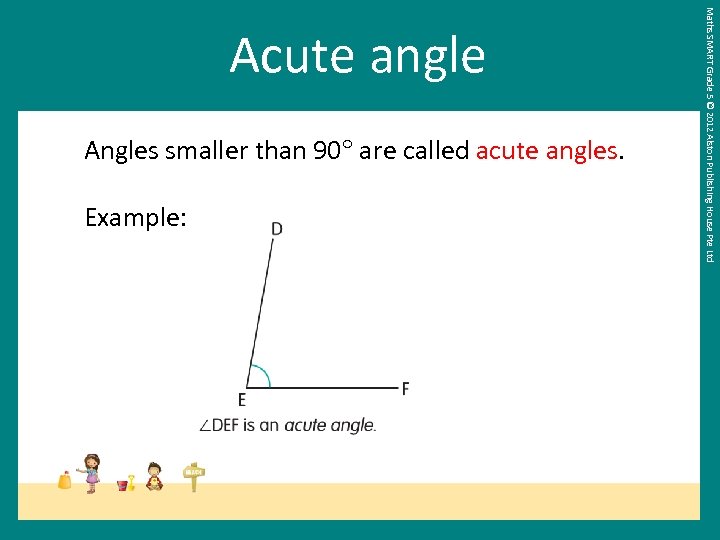
Angles smaller than 90 are called acute angles. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Acute angle

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Adjacent
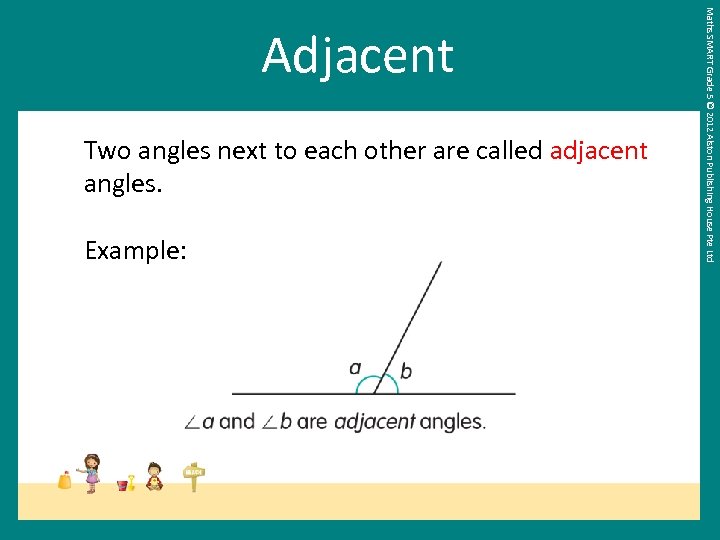
Two angles next to each other are called adjacent angles. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Adjacent

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Angles at a point
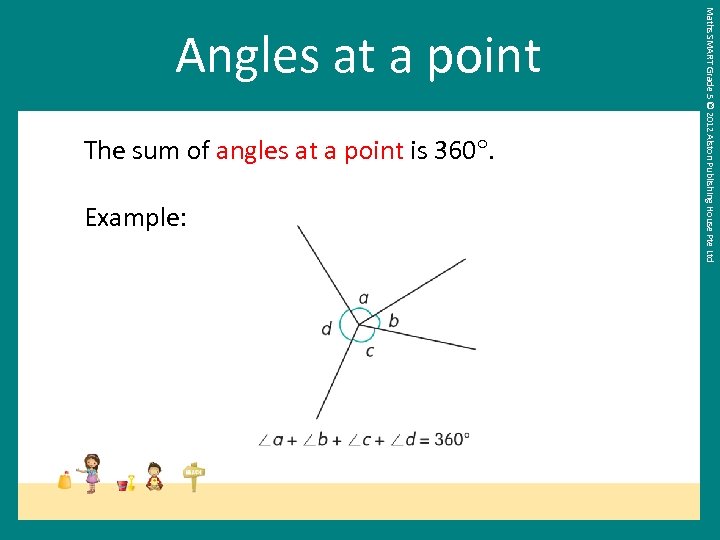
The sum of angles at a point is 360. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Angles at a point
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Angles in a triangle
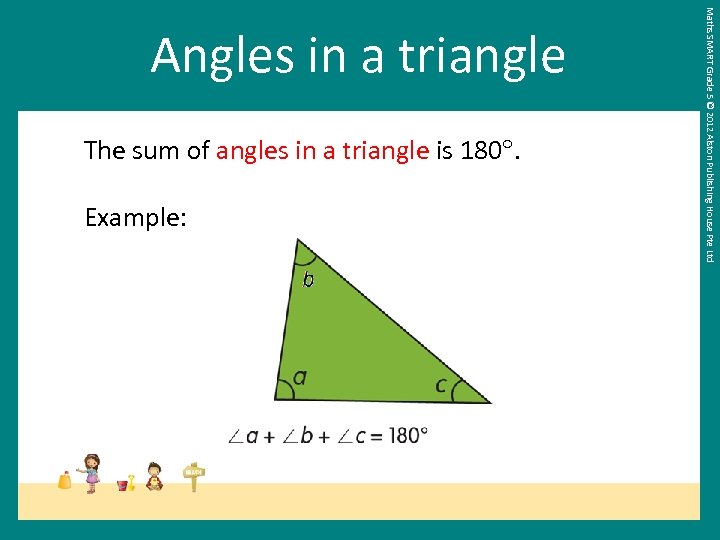
The sum of angles in a triangle is 180. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Angles in a triangle

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Angles on a straight line
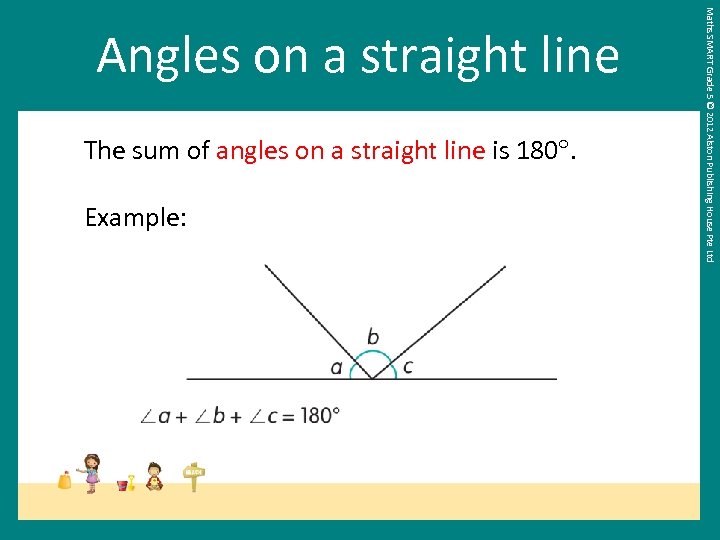
The sum of angles on a straight line is 180. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Angles on a straight line

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Area
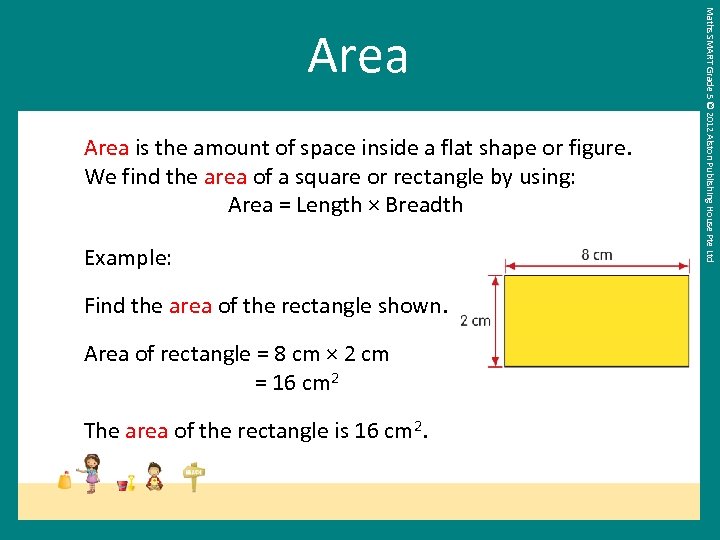
Area is the amount of space inside a flat shape or figure. We find the area of a square or rectangle by using: Area = Length × Breadth Example: Find the area of the rectangle shown. Area of rectangle = 8 cm × 2 cm = 16 cm 2 The area of the rectangle is 16 cm 2. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Area

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Breadth
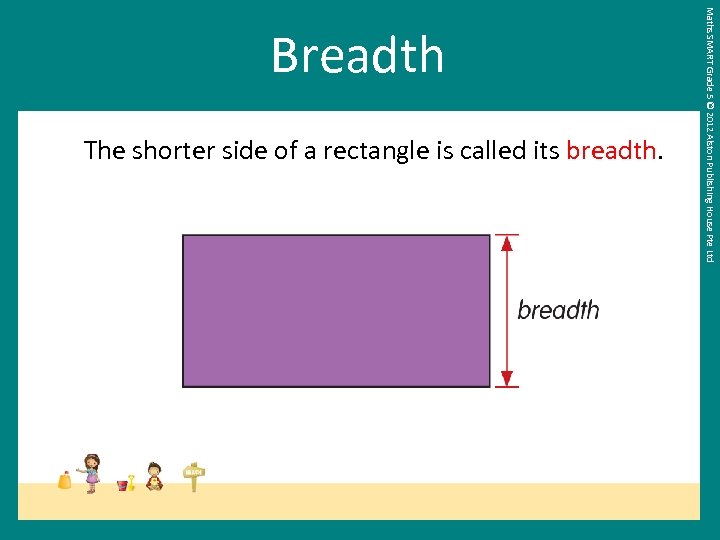
The shorter side of a rectangle is called its breadth. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Breadth

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Centre mark
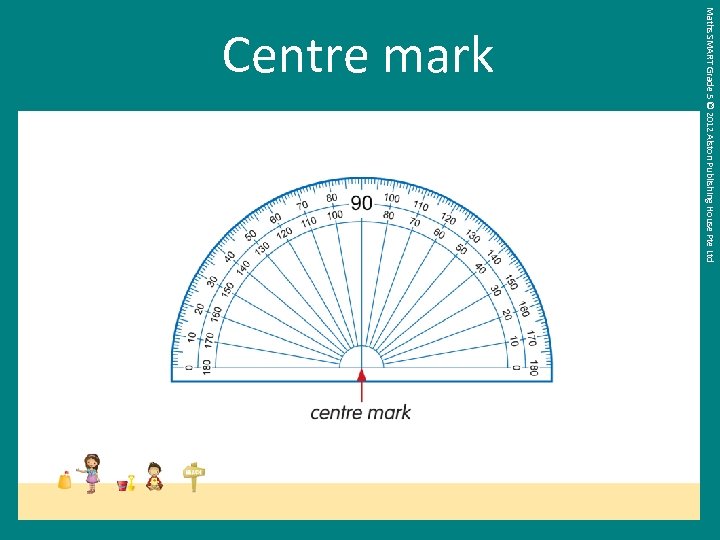
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Centre mark

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Certain
An event is certain if it will always happen. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Certain
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Chance

The probability of an event is the chance or likelihood of it happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Chance
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Convert
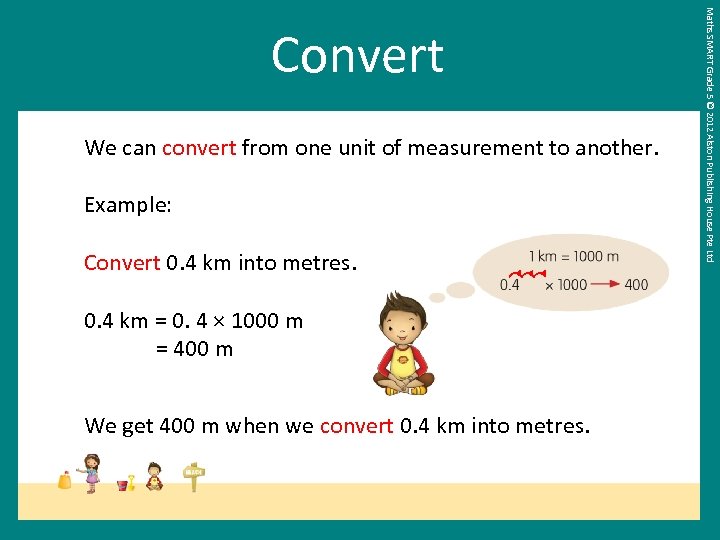
We can convert from one unit of measurement to another. Example: Convert 0. 4 km into metres. 0. 4 km = 0. 4 × 1000 m = 400 m We get 400 m when we convert 0. 4 km into metres. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Convert

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Coordinate grid
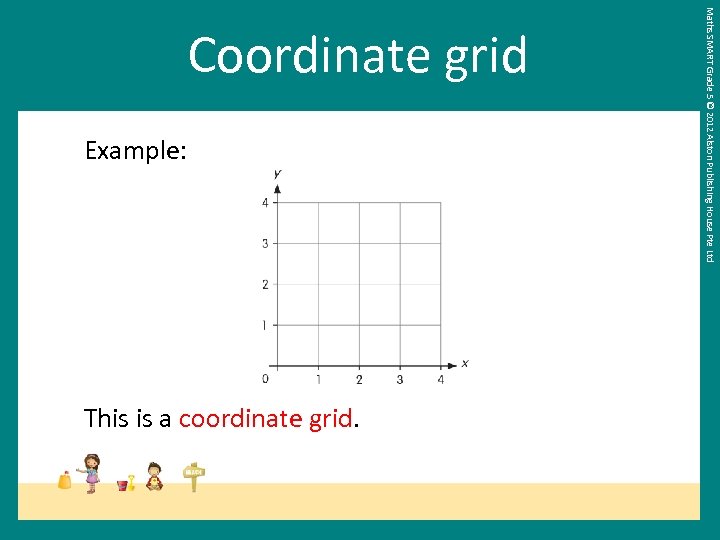
Example: This is a coordinate grid. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Coordinate grid

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Duration

Example: A ballet performance lasted for 1 h 45 min. We can also say that the duration of the ballet performance was 1 h 45 min. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Duration

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Equally likely

An event is equally likely if it has an even chance of happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Equally likely

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Even chance

An event is equally likely if it has an even chance of happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Even chance

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Event
An event is something that happens. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Event

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Good chance

An event is likely if it has a good chance of happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Good chance

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Image

The figure formed after a transformation is known as an image. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Image

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Impossible

An event is impossible if it will never happen, or has no chance of happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Impossible
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Inner scale
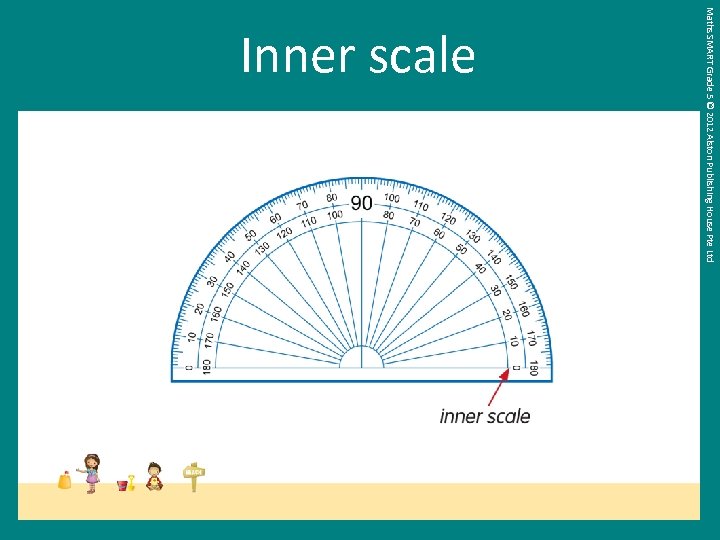
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Inner scale
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Length
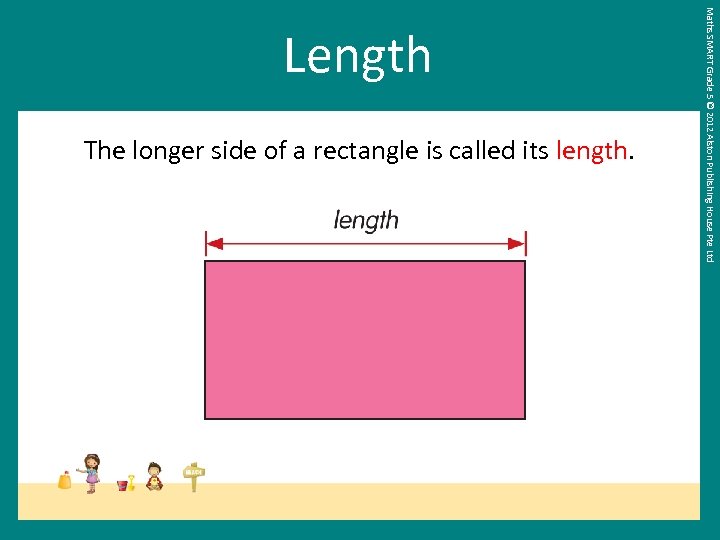
The longer side of a rectangle is called its length. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Length

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Likelihood

The probability of an event is the chance or likelihood of it happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Likelihood

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Likely

An event is likely if it has a good chance of happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Likely
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Line graph
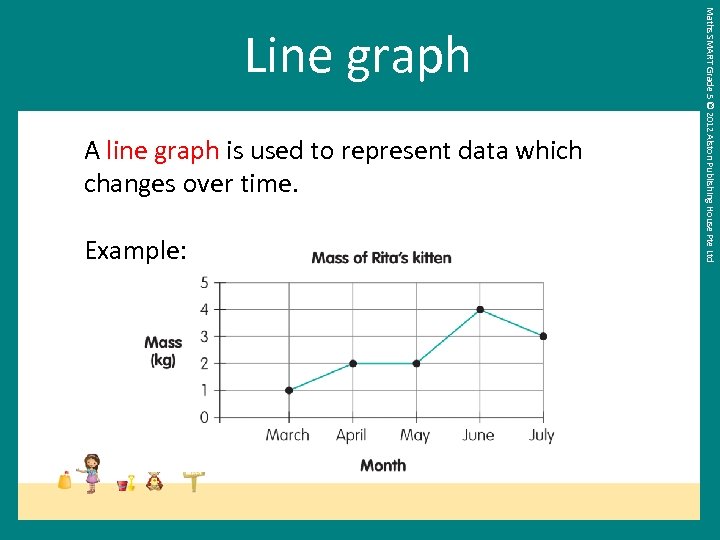
A line graph is used to represent data which changes over time. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Line graph

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Mirror image
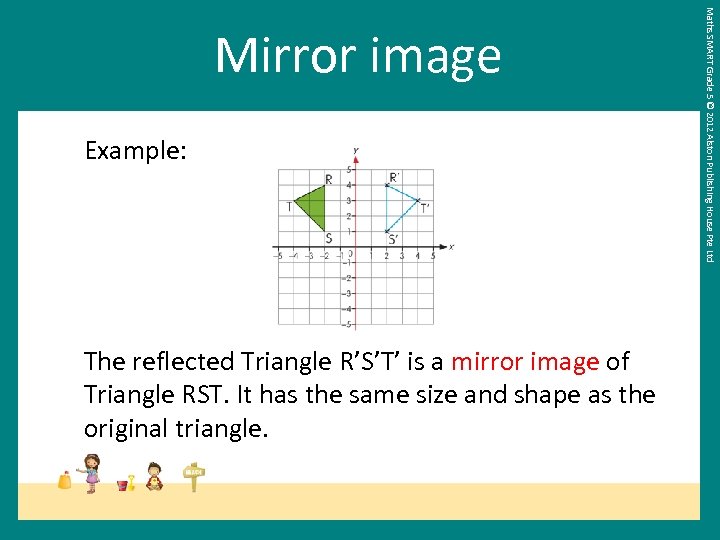
Example: The reflected Triangle R’S’T’ is a mirror image of Triangle RST. It has the same size and shape as the original triangle. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Mirror image

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Mirror line
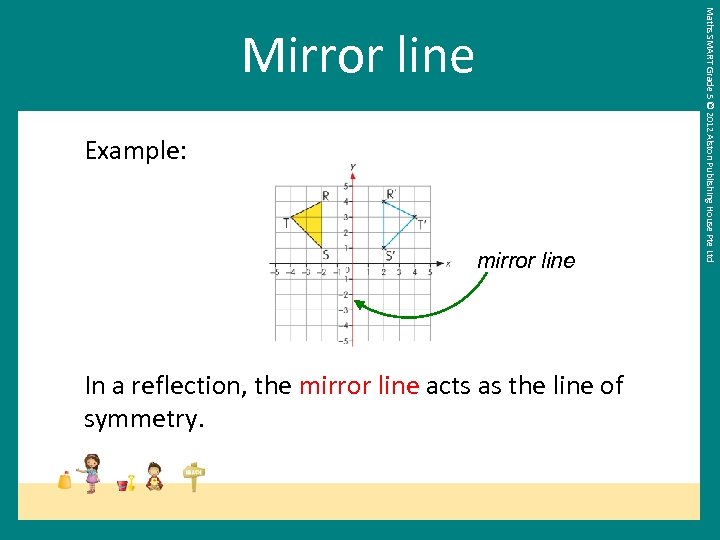
Example: mirror line In a reflection, the mirror line acts as the line of symmetry. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Mirror line

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd No chance

An event is impossible if it will never happen, or has no chance of happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd No chance
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Obtuse angle
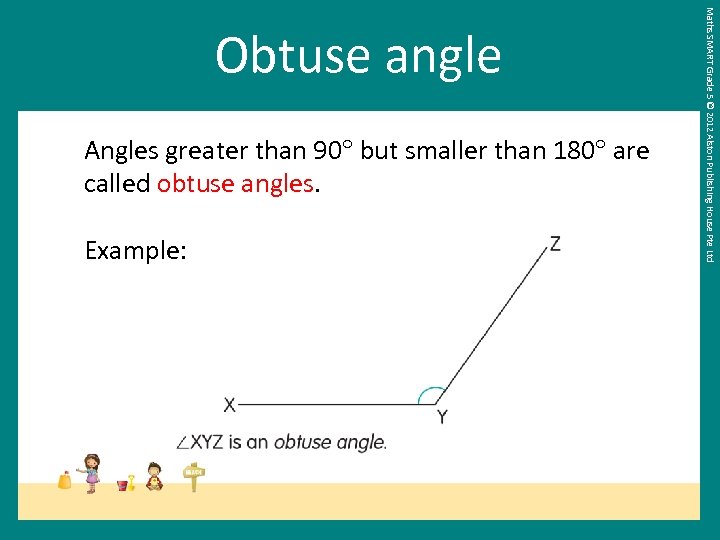
Angles greater than 90 but smaller than 180 are called obtuse angles. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Obtuse angle

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Outcome

An outcome is a result. Example: When we throw a die, the possible outcomes are the numbers 1 to 6. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Outcome
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Outer scale
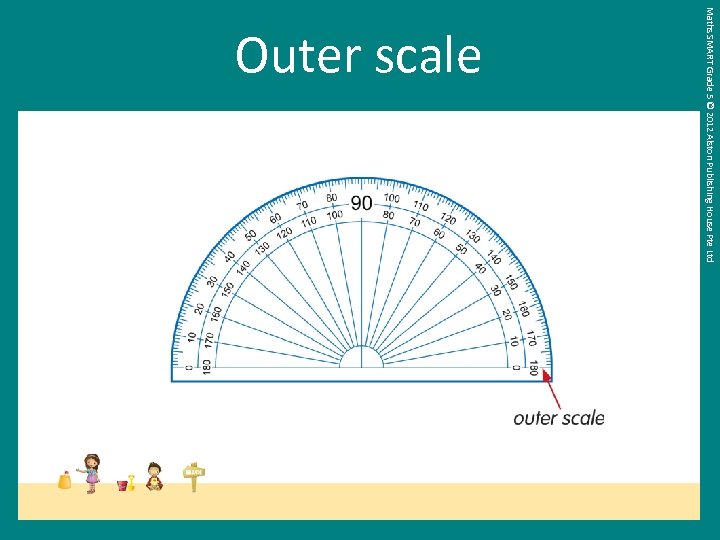
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Outer scale
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Percent (%)
Percent (%) means out of 100. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Percent (%)
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Perimeter
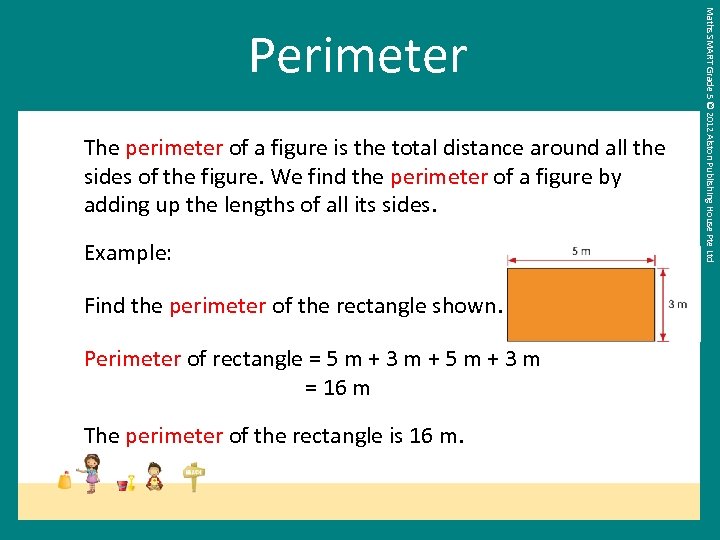
The perimeter of a figure is the total distance around all the sides of the figure. We find the perimeter of a figure by adding up the lengths of all its sides. Example: Find the perimeter of the rectangle shown. Perimeter of rectangle = 5 m + 3 m + 5 m + 3 m = 16 m The perimeter of the rectangle is 16 m. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Perimeter

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Poor chance

An event is unlikely if it has a poor chance of happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Poor chance

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Probability

The probability of an event is the chance or likelihood of it happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Probability

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Probability line
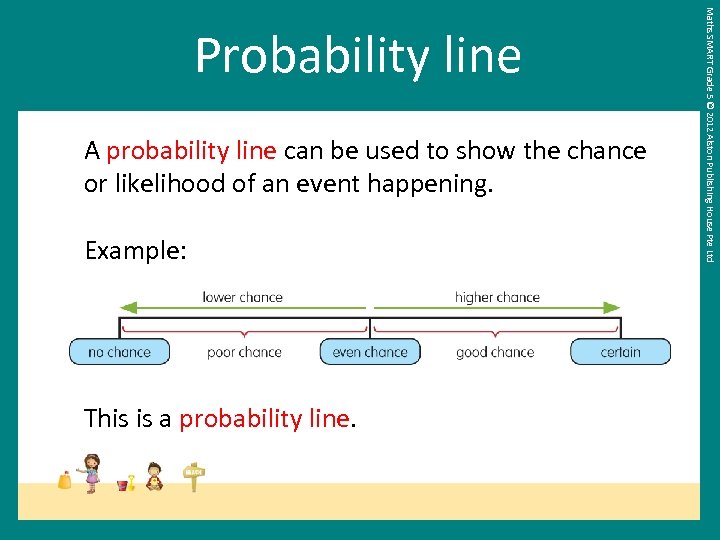
A probability line can be used to show the chance or likelihood of an event happening. Example: This is a probability line. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Probability line
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Protractor
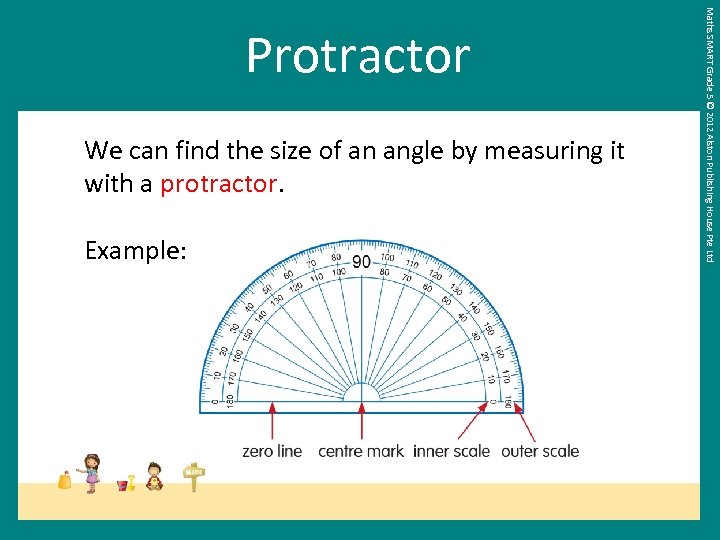
We can find the size of an angle by measuring it with a protractor. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Protractor

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Quadrant
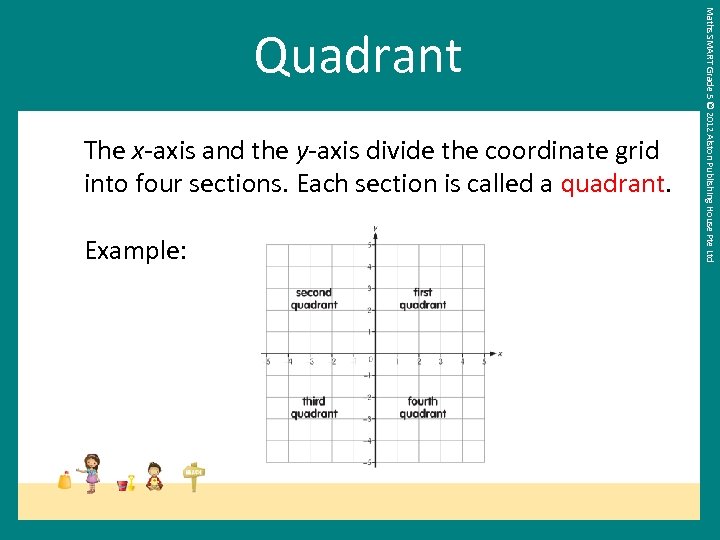
The x-axis and the y-axis divide the coordinate grid into four sections. Each section is called a quadrant. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Quadrant

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Reflection
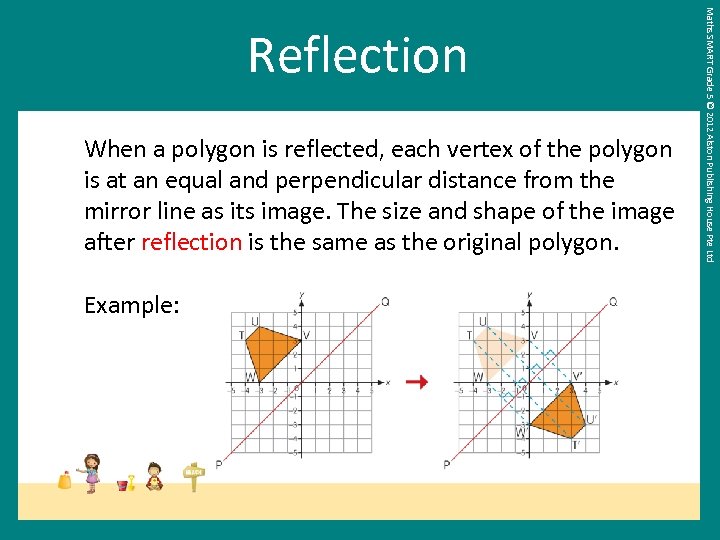
When a polygon is reflected, each vertex of the polygon is at an equal and perpendicular distance from the mirror line as its image. The size and shape of the image after reflection is the same as the original polygon. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Reflection
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Scale
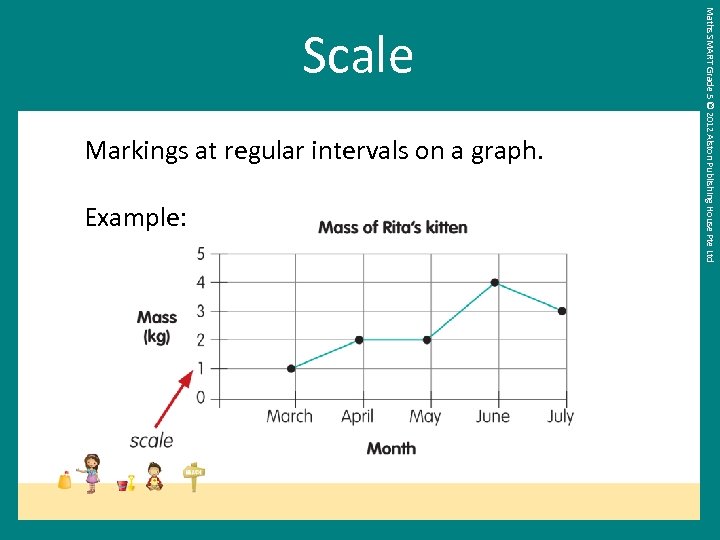
Markings at regular intervals on a graph. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Scale
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Second (s)

A unit of measurement for time. Example: 1 minute = 60 seconds Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Second (s)

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Second hand

A clock has an hour hand, a minute hand a second hand. The second hand shows us the number of seconds that has passed in one minute. second hand Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Second hand

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Stopwatch

A stopwatch measures duration in minutes and seconds. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Stopwatch

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Time line

A time line can be used to calculate duration. Example: This time line shows the duration from 20 15 to 22 20. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Time line
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Translation
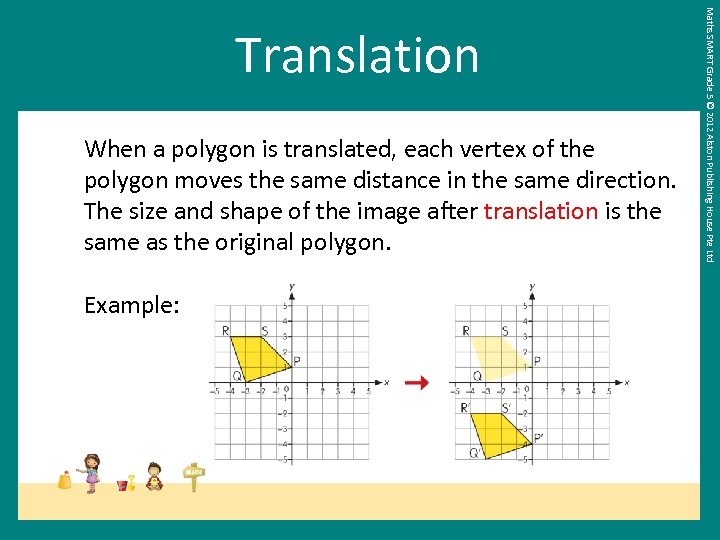
When a polygon is translated, each vertex of the polygon moves the same distance in the same direction. The size and shape of the image after translation is the same as the original polygon. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Translation

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Transformation
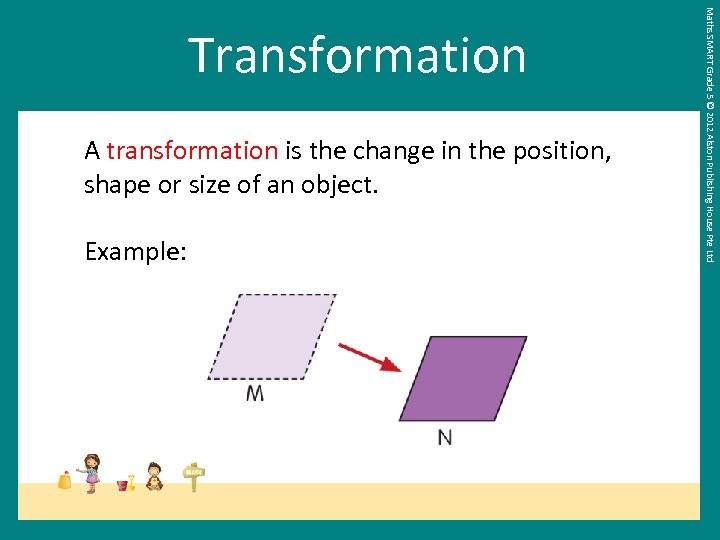
A transformation is the change in the position, shape or size of an object. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Transformation

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Unlikely

An event is unlikely if it has a poor chance of happening. Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Unlikely

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Vertically opposite angles
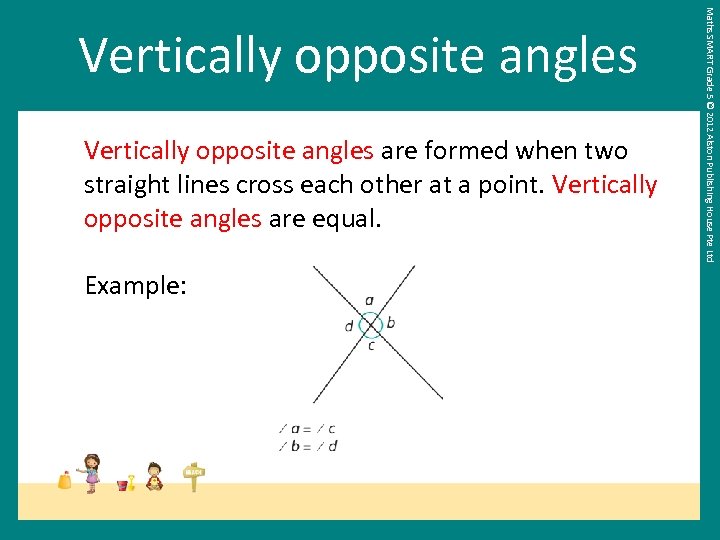
Vertically opposite angles are formed when two straight lines cross each other at a point. Vertically opposite angles are equal. Example: Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Vertically opposite angles

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd X-axis
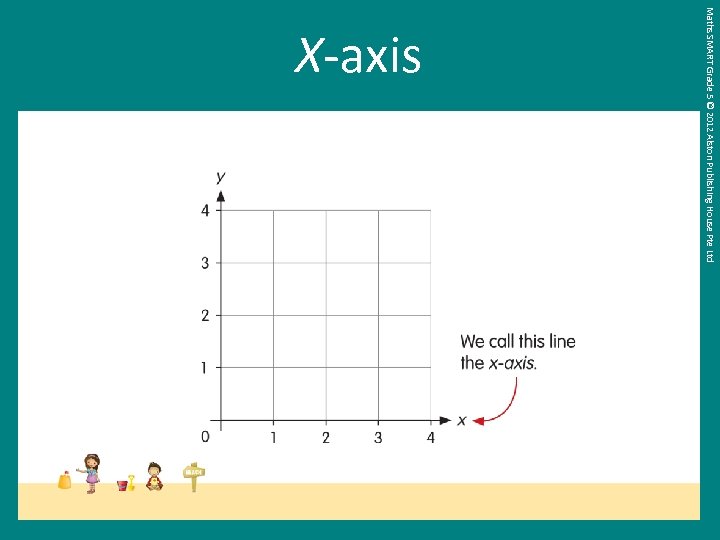
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd X-axis

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd X-coordinate
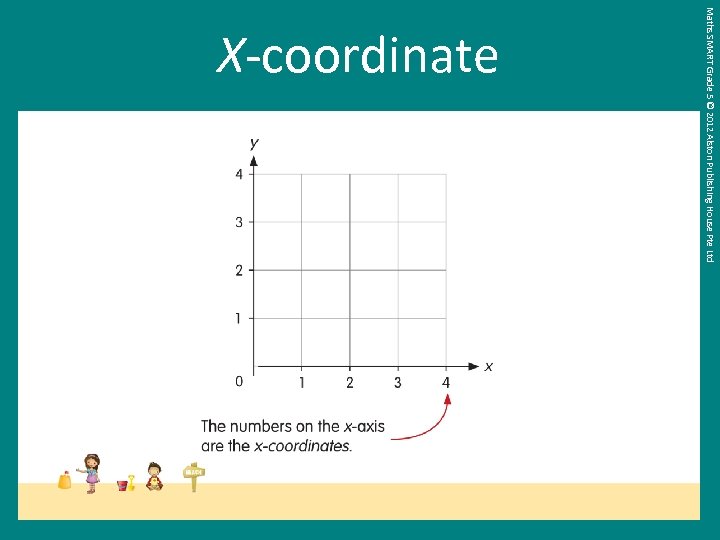
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd X-coordinate

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Y-axis
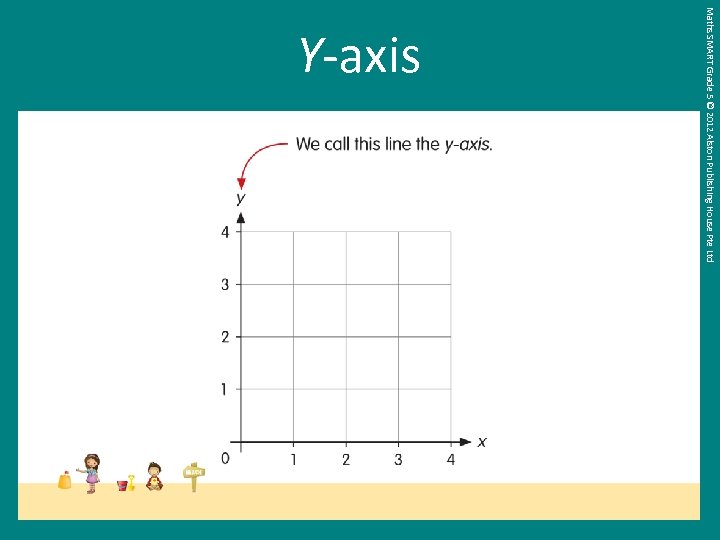
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Y-axis

Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Y-coordinate
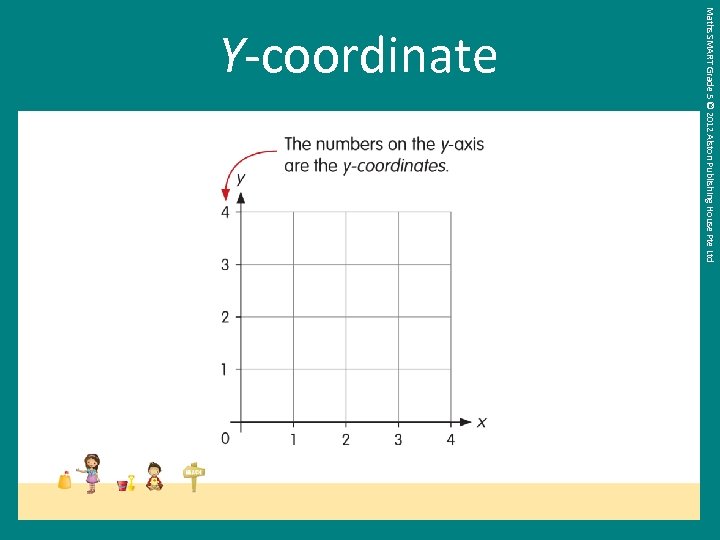
Maths SMART Grade 5 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Y-coordinate
667615d331eb82411ca9da9c6658888e.ppt