e42534153b32cf40ddf724c94d73d89d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

Mathematical modelling in biomedical fluid dynamics Dr David Smith 1

• Ph. D, applied mathematics, Birmingham (2001 -2005) – Prof John Blake, Dr Eamonn Gaffney – Mucus transport fluid mechanics • MRC training fellowship (2006 -2009), Medicine / Maths – Sperm motility imaging and modelling, with Dr Jackson Kirkman. Brown, Birmingham Women’s Hospital • Science City IT Theme Research fellow (December 2009 – November 2012): ‘High performance computing and novel imaging for fluid mechanics in reproduction’, Mathematics, Birmingham – Joint-appointment with Warwick Engineering and Centre for Scientific Computing: Prof Bryanston-Cross, Dr Timmerman, Daniel Claus, Dr Denissenko – Interactions with TM (sperm imaging and modelling, also cancer metabolomics) – Interactions with AM (drug delivery, characterisation of biofluids and cells)

Centre for Human Reproductive Science • An international network, based at Birmingham Women’s Hospital and the University • Research lead: Dr Jackson Kirkman-Brown (TM Reproduction) • Based in an IVF clinic, Ch. RS provides unique access to: – human material (sperm, eggs, reproductive tract) – clinical experience – what really works – ethical permissions to work with human material – new infrastructure through Science City 3

• Subfertility affects 1 in 6 couples in the UK; male factors are present in around half of all cases • Motility, the ability of sperm to swim, is the most common problem • Treatments for male subfertility such as IVF/ICSI are invasive for the female and resulting embryo and carry risk • Unplanned pregnancy • Half of all pregnancies are unplanned • In the developing world, this carries a significant health risk (1 death in the world per minute from pregnancy-related causes) • Motility is a potential contraceptive target 4

Fluid mechanics underlying new medicine • Fertell: this test is effective because it utilises the correct fluid viscosity • New developments will require more sophisticated understanding. Examples include: – screening of drug treatments and selecting high quality sperm for IVF – optimising intra-uterine insemination and embryo transfer – delivery vehicles for new drugs 5
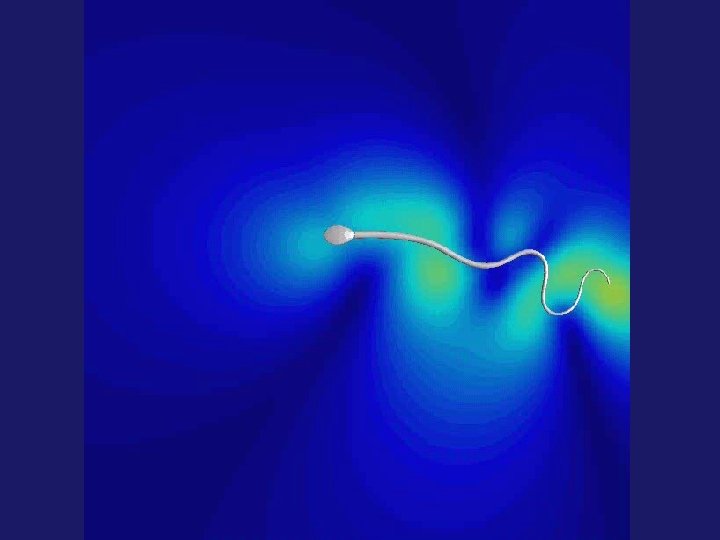
Integrated research • Imaging: high-speed 2 D and 3 D imaging of how the flagellum propels the cell, in normal progressive state, and when stimulated by hormones and aromatics • Fluid properties: physiological viscosity and viscoelasticity have radical effects on flagellar movement, progression and behaviour • Mechanics: through fluid mechanical models we can interpret – energy consumption & energy pathways – how intracellular signals cause changes in behaviour through flagellum movement – this requires computational modelling
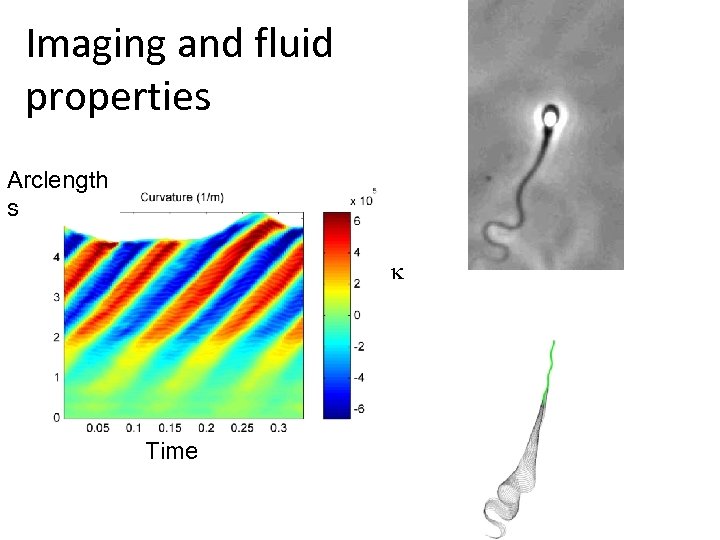
Imaging and fluid properties Arclength s k Time
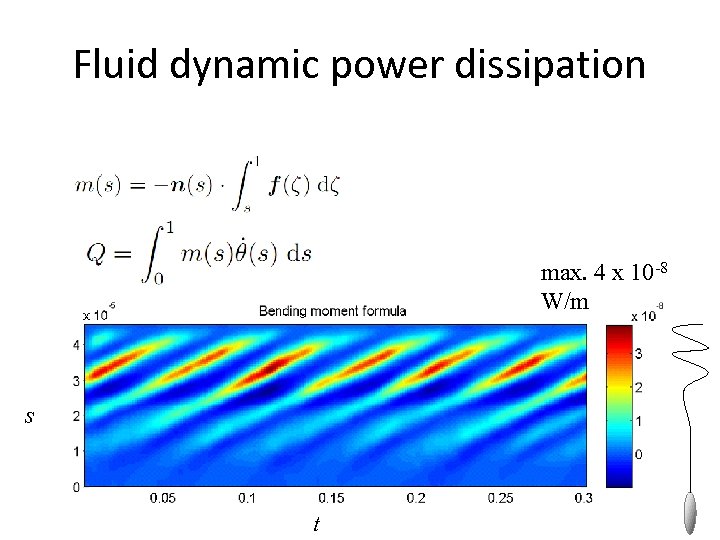
Fluid dynamic power dissipation max. 4 x 10 -8 W/m s t

Funding • MRC and Wellcome trust fellowships • EPSRC studentships • Brazilian govt. funding & Hester Cordelia Parsons Fund – Hermes Gadêlha • Nuffield Undergraduate Bursaries – Tom Johnson • KAUST funding to Dr Eamonn Gaffney • STFC • MRC Biomarker Strategic Call • Science City: Reproduction Infrastructure • Thanks to Birmingham Women’s for supporting our research 11
e42534153b32cf40ddf724c94d73d89d.ppt