14f34d348c2b141006c1a84d239f928a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 198

Math Word Problems Helpful Tips and Strategies

What are the challenges? • To know how to translate word problems into a workable mathematical equation. • To know where to start and how to go about figuring out the answer. • To know the strategies needed to break down a word problem so it is clear and easy to solve.

6 Steps for Solving Math Word Problems

Step 1 Convert the words into an equation. • Read through the entire problem first. • Don’t try to solve it when you’ve only read one sentence. • Read the problem completely in order to get the whole picture. • Effectively translate and solve the problem.

Step 2 Go back to the beginning. • Reread the first sentence. • Write down what you know and what you don’t know. • Use variables to stand for the unknowns and clearly label what they stand for. • Do the same for the second sentence and each following sentence.

Step 3 Look for Signal Words that mean certain mathematical operations.

Signal Words Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division Equals

Step 4 Perform the required operations.

Step 5 Make sure you are answering the question that is being asked of you. • One step may seem like it’s the answer, but it may take several steps to arrive at the final answer. • Don’t lose sight of what the word problem is asking for or asking you to do. • Label the answer with the unit of measurement or with the object the question is requesting.

Step 6 Mentally or on paper check your answer to make sure it is correct and makes sense. • Replace the variable in each step with your answer. • Calculate the equation with the now known variable to see if it satisfies the equation. If it does, then you’re done!

Practice, Practice! Mastering word problems requires practice!

Understanding Algebra Word Problems *Represent a given situation using algebraic expressions or equations in one variable. *Simplify and evaluate algebraic expressions.

The biggest challenge to solving word problems is figuring out whether to add, subtract, multiply or divide. Words Meaning Addition Words Meaning Subtraction Words Meaning Multiplication Division and increased more than plus sum total decreased difference less than left lower than minus double half (× ½) product times triple twice divide into half (÷ 2) divide by divide among quotient
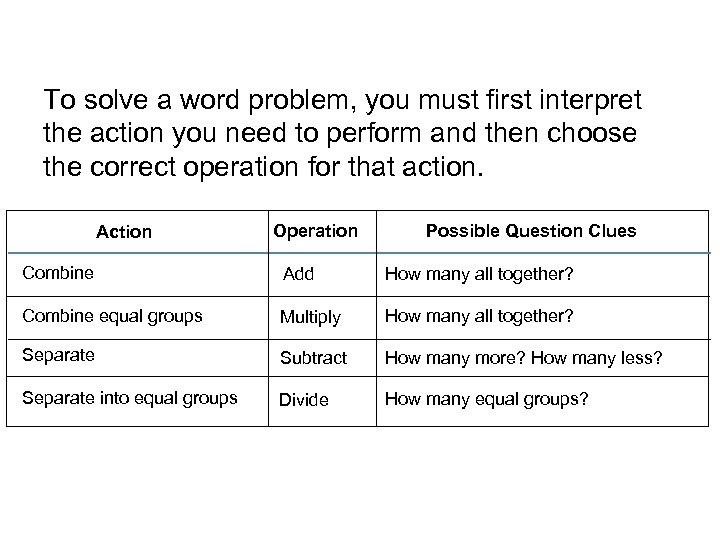
To solve a word problem, you must first interpret the action you need to perform and then choose the correct operation for that action. Action Operation Possible Question Clues Combine Add How many all together? Combine equal groups Multiply How many all together? Separate Subtract How many more? How many less? Separate into equal groups Divide How many equal groups?
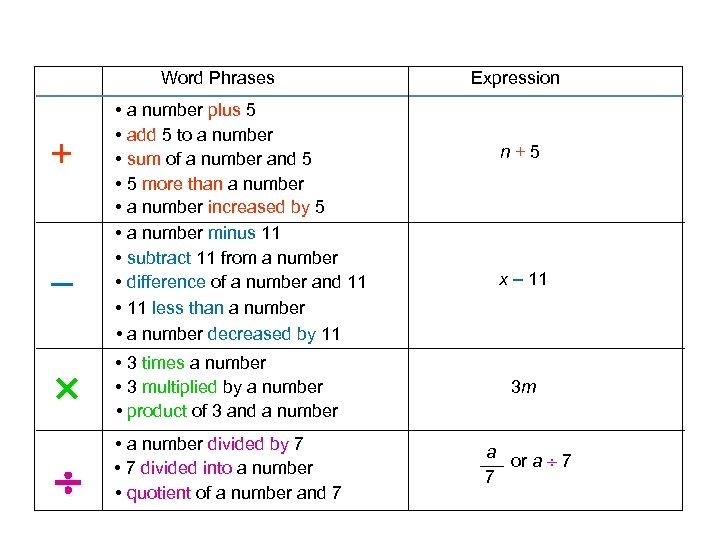
Word Phrases + – • a number plus 5 • add 5 to a number • sum of a number and 5 • 5 more than a number • a number increased by 5 • a number minus 11 • subtract 11 from a number • difference of a number and 11 • 11 less than a number • a number decreased by 11 Expression n+5 x 11 • 3 times a number • 3 multiplied by a number • product of 3 and a number 3 m • a number divided by 7 • 7 divided into a number • quotient of a number and 7 a or a 7 7

TEST YOUR SKILL!! Match the phrase with the correct algebraic expression.
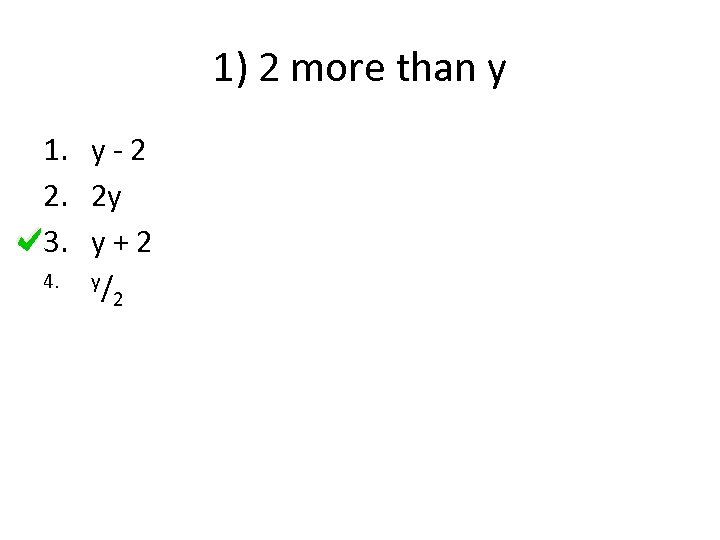
1) 2 more than y 1. y - 2 2. 2 y 3. y + 2 4. y/ 2

2) 16 divided into m 1. 16 - m 2. 16 m 3. m + 16 4. m/ 16
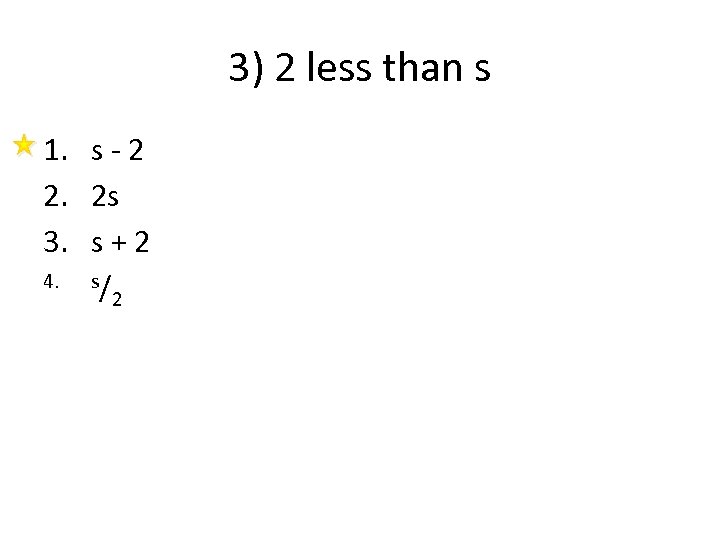
3) 2 less than s 1. s - 2 2. 2 s 3. s + 2 4. s/ 2

4) Triple John’s age j 1. 2. 3. 4. 3+j j-3 3 j j÷ 3
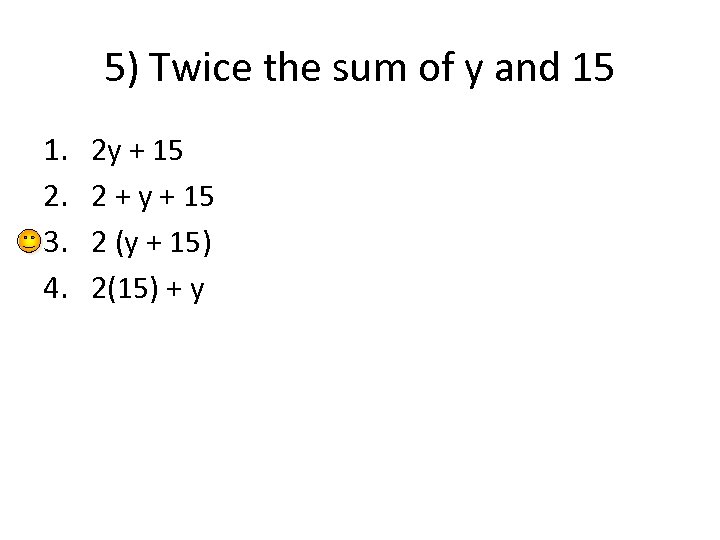
5) Twice the sum of y and 15 1. 2. 3. 4. 2 y + 15 2 + y + 15 2 (y + 15) 2(15) + y

6) n feet lower than 10 1. 10 - n 2. n - 10 3. n + 10 4. 10 + n

7) The quotient t and 4 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 goes into t t goes into 4 Multiply 4 by t Add 4 and t

8) 18 divided by a number, g 1. 2. 3. 4. 18 - g 18 ÷ g g + 18 18 × g

Setting Up Algebra Word Problems

To set up algebra word problems: 1. To complete an algebra problem, an equal sign must be added. 2. The words is or are as well as equals tell you that you should add an equal sign. Double Jake’s age, x, minus 4 is 22. 2 x - 4 = 22

Translate the word problem into an equation. DO NOT find the solution yet. 1. Triple the original number, n, is 2, 700. 3 n = 2700 2. The product of a number, y, and 5 is equal to 15. 5 y = 15 3. Four times the difference of a number, x, and 2 is 20. 4(x – 2) = 20 4. The total, t, divided into 5 groups is 45. t ÷ 5 = 45

Translate the word problem into an equation. DO NOT find the solution yet. 1. The number of pants in the store, p, minus 54 pants sold today is 320. p – 54 = 320 2. One-half an amount, x, added to $50 is $262. x/2 + 50 = 262 3. One hundred plants, divided by 5 rows, equals n number of plants per row. 100 ÷ 5 = n 4. A number, y, less than 50 is 82. y - 50 = 82

Translate the word problem into an equation. DO NOT find the solution yet. 1. Seventeen more than half a number, h, is 35. h/2 + 17 = 35 2. The quotient of a number, w, and 4 is 32. w ÷ 4 = 32 3. Six less a number, d, is 12. d – 6 = 12 4. Four times the sum of a number, y, and 10 is 48. 4(y + 10) = 48
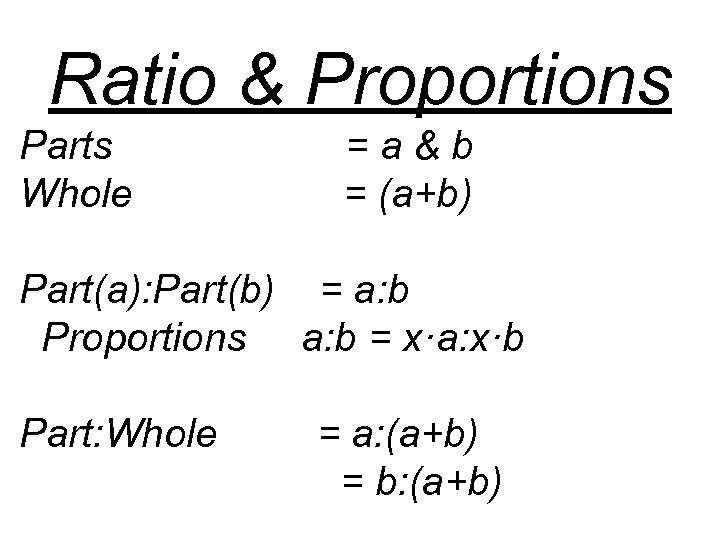
Ratio & Proportions Parts Whole =a&b = (a+b) Part(a): Part(b) = a: b Proportions a: b = x·a: x·b Part: Whole = a: (a+b) = b: (a+b)
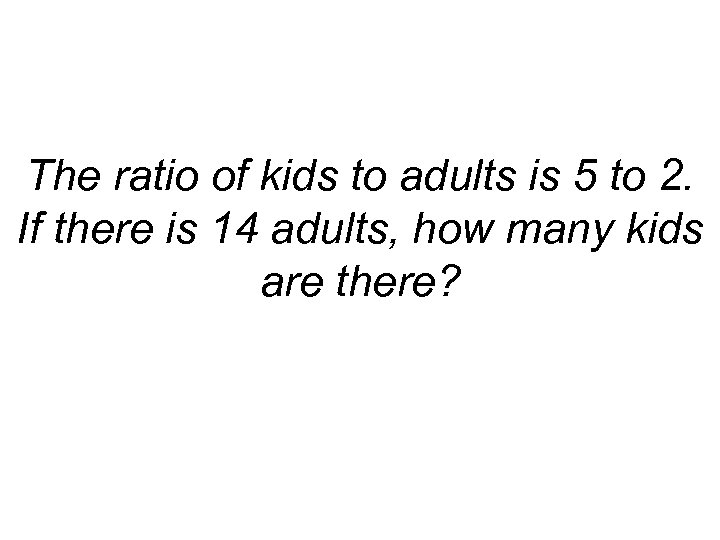
The ratio of kids to adults is 5 to 2. If there is 14 adults, how many kids are there?
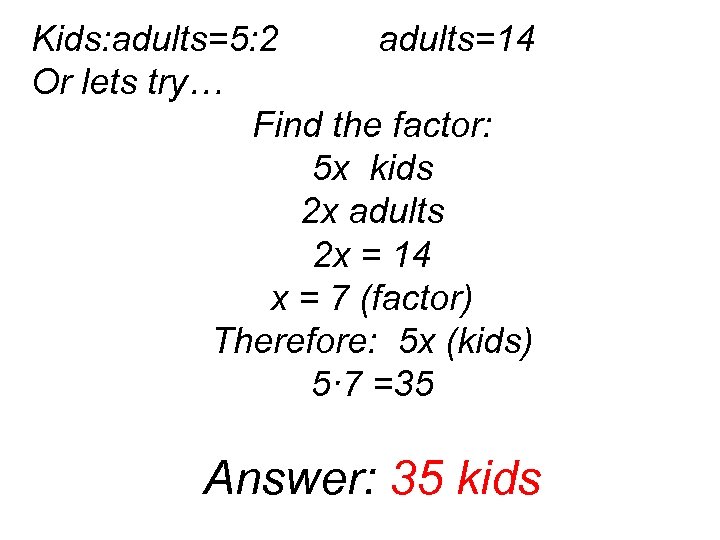
Kids: adults=5: 2 adults=14 Or lets try… Find the factor: 5 x kids 2 x adults 2 x = 14 x = 7 (factor) Therefore: 5 x (kids) 5· 7 =35 Answer: 35 kids

The ratio of kids to adults is 3 to 5. If there are 26 more adults than kids, how many kids are there?
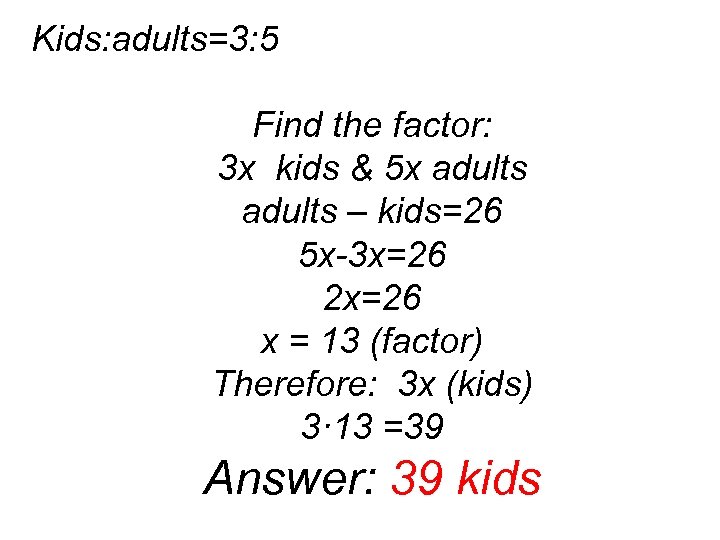
Kids: adults=3: 5 Find the factor: 3 x kids & 5 x adults – kids=26 5 x-3 x=26 2 x=26 x = 13 (factor) Therefore: 3 x (kids) 3· 13 =39 Answer: 39 kids

30 boys and girls are planning for a picnic. There a ratio of 3 girls to 7 boys. How many boys are there?
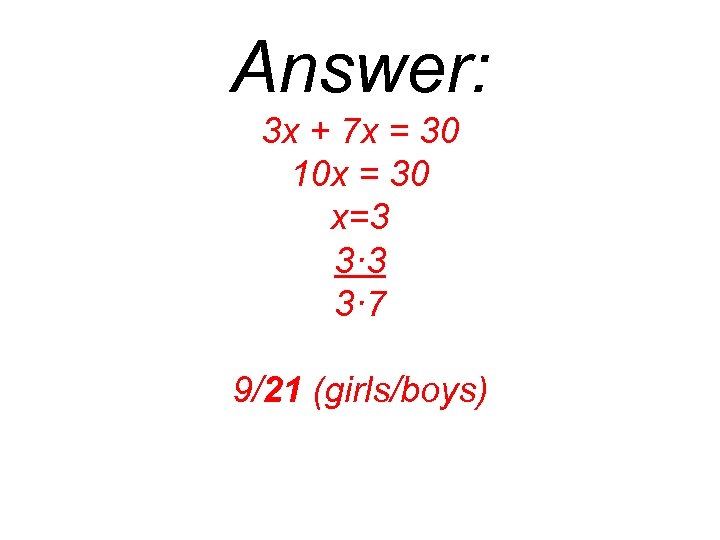
Answer: 3 x + 7 x = 30 10 x = 30 x=3 3· 7 9/21 (girls/boys)
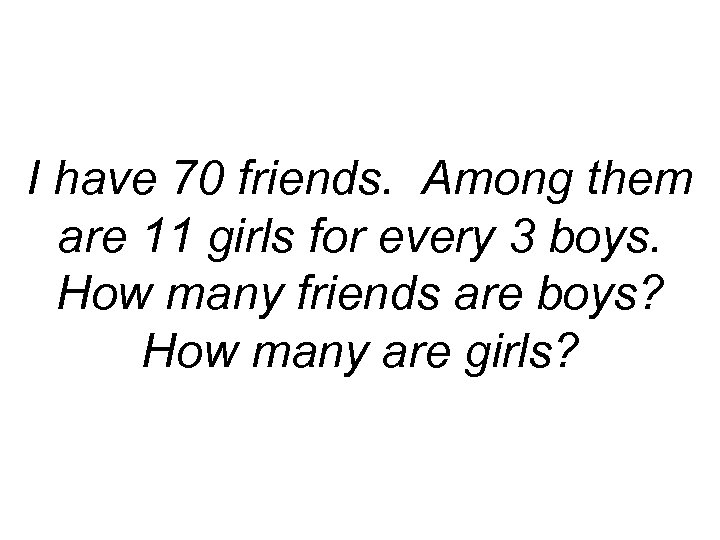
I have 70 friends. Among them are 11 girls for every 3 boys. How many friends are boys? How many are girls?
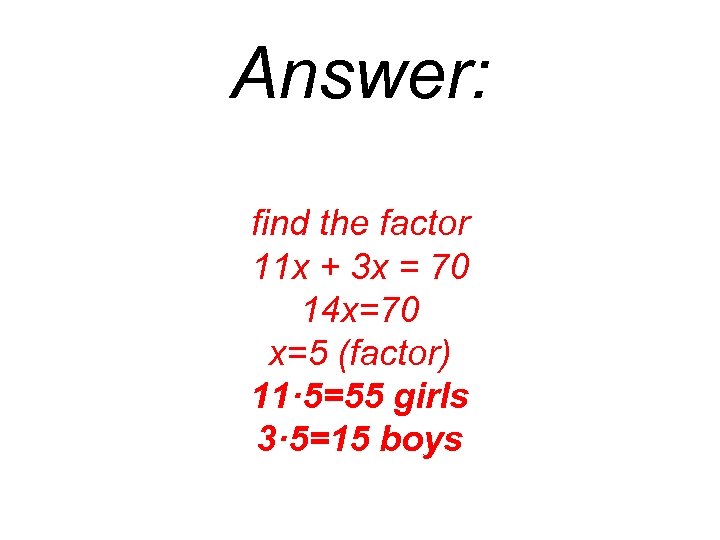
Answer: find the factor 11 x + 3 x = 70 14 x=70 x=5 (factor) 11· 5=55 girls 3· 5=15 boys

The ratio of dogs to cats is 9 to 2. If there are 72 dogs, how many total dogs and cats are there?

Answer: 88

To get a shade of orange paint, we mix white, red, & yellow in the ratio 2: 5: 4. If we need 6 gallons of orange paint, then how many gallons of each color do we need?

Answer: White=2 x, red=5 x, yellow=4 x 2 x+5 x+4 x=6 X=6/11 White=12/11, red=30/11, yellow=24/11

The top 3 cash prizes in the math tournament are in the ratio 5: 2: 1. The 1 st place prize is rd place $20, 000 more than the 3 prize. How much is the second place prize?
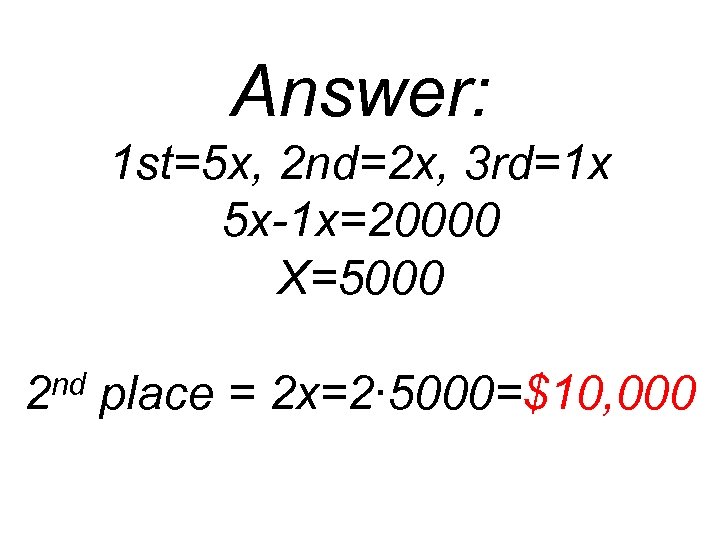
Answer: 1 st=5 x, 2 nd=2 x, 3 rd=1 x 5 x-1 x=20000 X=5000 nd 2 place = 2 x=2∙ 5000=$10, 000
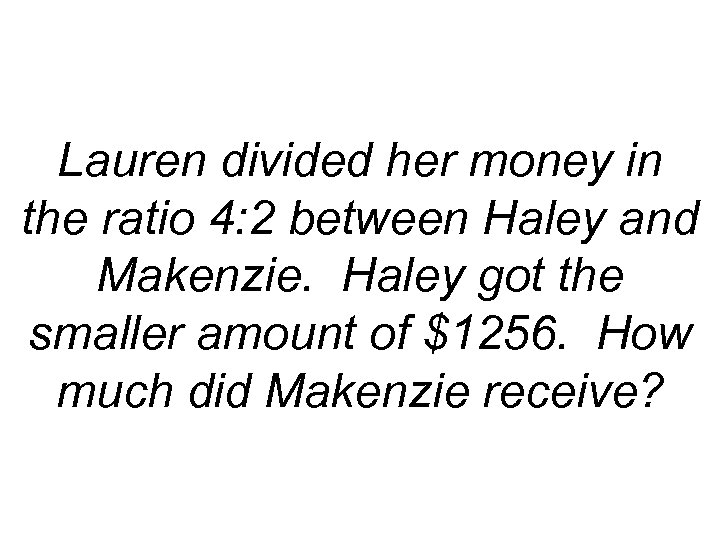
Lauren divided her money in the ratio 4: 2 between Haley and Makenzie. Haley got the smaller amount of $1256. How much did Makenzie receive?

4/2 = M/1256 2 M = 4· 1256 M =2512

12 miles is approximately equal to 6 km. How many miles are equal to 42 km?
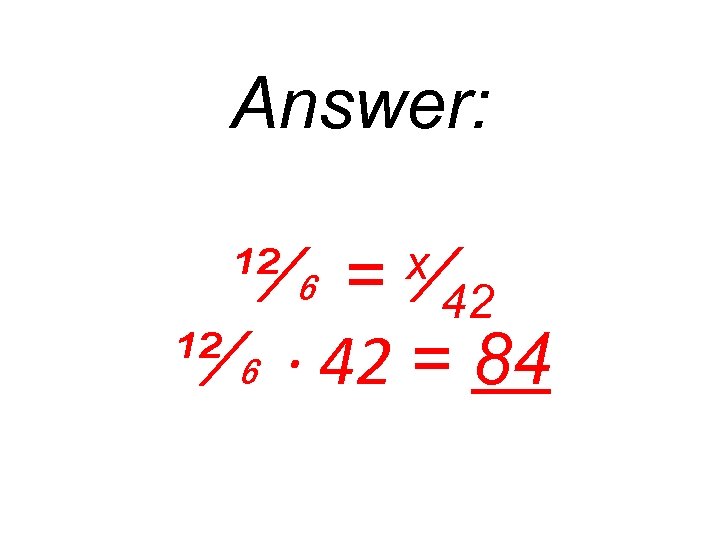
Answer: ¹²⁄₆ = 42 ¹²⁄₆ ∙ 42 = 84 x⁄

12 miles is approximately equal to 6 km. How many km are equal to 18 miles?

Answer: 9

Direct and Inverse Variations

Direct Variation When we talk about a direct variation, we are talking about a relationship where as x increases, y increases or decreases at a CONSTANT RATE.
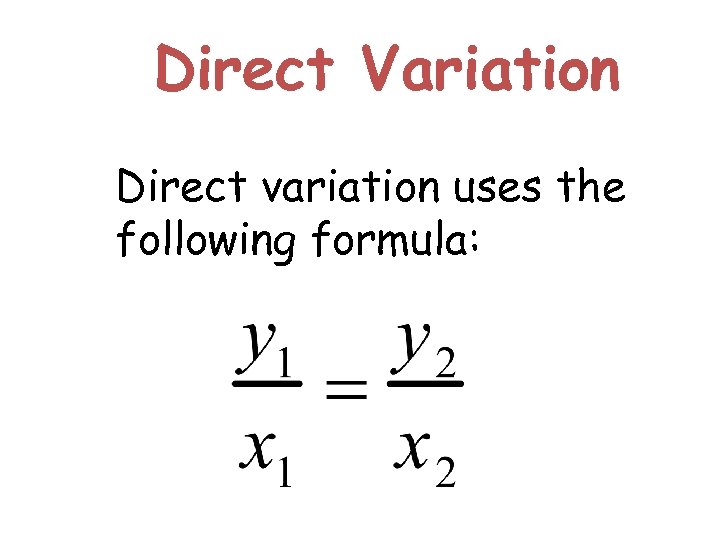
Direct Variation Direct variation uses the following formula:

Direct Variation example: if y varies directly as x and y = 10 as x = 2. 4, find x when y =15. what x and y go together?

Direct Variation If y varies directly as x and y = 10 find x when y =15. y = 10, x = 2. 4 make these y 1 and x 1 y = 15, and x = ? make these y 2 and x 2
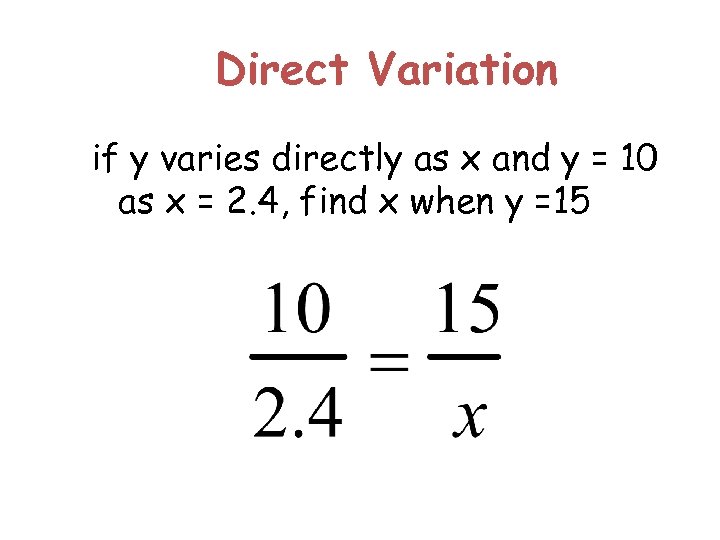
Direct Variation if y varies directly as x and y = 10 as x = 2. 4, find x when y =15
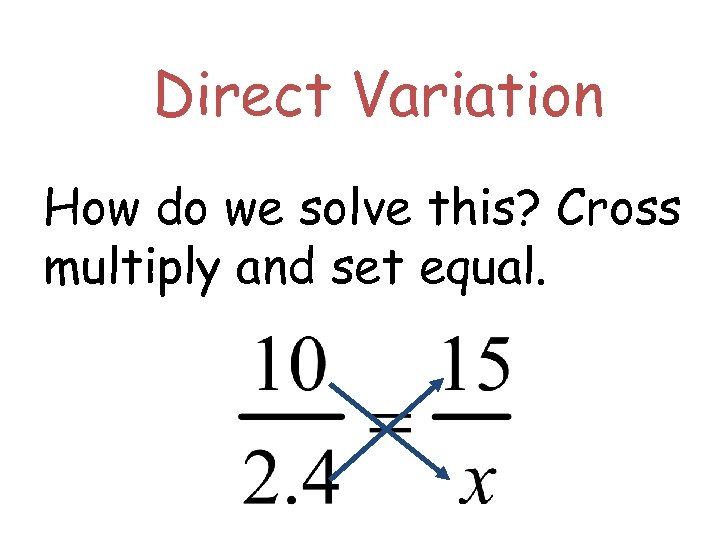
Direct Variation How do we solve this? Cross multiply and set equal.

Direct Variation We get: 10 x = 36 Solve for x by diving both sides by 10. We get x = 3. 6

Direct Variation Let’s do another. If y varies directly with x and y = 12 when x = 2, find y when x = 8. Set up your equation.

Direct Variation If y varies directly with x and y = 12 when x = 2, find y when x = 8.
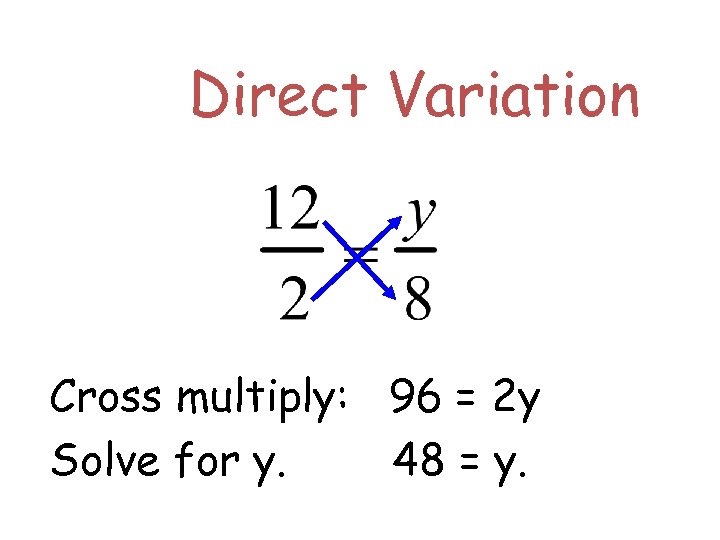
Direct Variation Cross multiply: 96 = 2 y Solve for y. 48 = y.

Inverse Variation Inverse is very similar to direct, but in an inverse relationship as one value goes up, the other goes down. There is not necessarily a constant rate.

Inverse Variation With Direct variation we Divide our x’s and y’s. In Inverse variation we will Multiply them. x 1 y 1 = x 2 y 2

Inverse Variation If y varies inversely with x and y = 12 when x = 2, find y when x = 8. x 1 y 1 = x 2 y 2 2(12) = 8 y 24 = 8 y y=3

Inverse Variation If y varies inversely as x and x = 18 when y = 6, find y when x = 8. 18(6) = 8 y 108 = 8 y y = 13. 5

Joint Variation Joint variation occurs when a quantity varies directly as the product of two or more other quantities. For instance, if z=kxy where k does not equal zero, then z varies jointly with x and y.

Joint Variation Example • The variable z varies jointly with x and y. Write an equation relating x, y and z. Then find z when x = -4 and y = 7. Use z = kxy x = 3, y = 8, z = 6

You Try The variable z varies jointly with x and y. Write an equation relating x, y and z. Then find z when x = -4 and y = 7. Use z = kxy (x = -12, y = 4, z = 2)
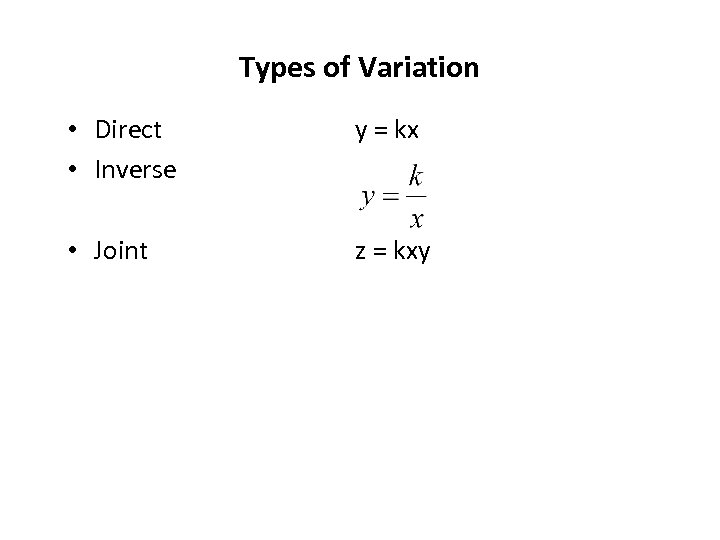
Types of Variation • Direct • Inverse y = kx • Joint z = kxy

Rate, Time, & Distance

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems If an object such as an automobile or an airplane travels at a r constant, or uniform, rate of speed, “ ” , then the distance traveled by the object, “ t period of time, “ ” d”, during a

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems is given by the “distance, rate, time” formula: d = rt.

Distance = Rate x Time D = RT (dirt) Rate x Time = Distance 50 mph x 2 hours = 100 miles

D/T = R Distance / Time = Rate 100 miles / 2 hours = 50 mph

D/R = T Distance /Rate = Time 100 miles / 50 mph = 2 hours

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems Example 1 You ride your bike for 7 hours. If you travel 36. 75 miles, what is your average speed?

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems Example 1 The quantities in this problem are: • distance (constant at 36. 75 miles), • time (constant at 7 hours), • and rate, or speed (unknown variable).

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems Example 1 Represent the variable rate with r. You can use the distance, rate, time formula. d = rt

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems Example 1 But since you know the distance and time, and wish to solve for rate, it would be helpful to solve the equation for r first.

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems Example 1 is our mathematical model. Some mathematical models can be easy!

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems Example 1 Now we can solve for the rate, time. r , by dividing the distance by the 5. 25 miles per hour

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems When you read a word problem that involves rate, time, and distance, note whether the problem situation involves • motion in the same direction; • motion in opposite directions; • a round trip.

Solving Word Problems 1. Draw a sketch 2. Identify Unknowns 3. Assign Variable 4. Make a Chart 5. Write and solve an equation

Motion in Same Directions

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems Jason and Le. Roy are entered in a 26 -mile marathon race. Jason’s average pace is 6 miles per hour (mph) and Le. Roy’s average pace is 8 mph. Both runners start at the same time. How far from the finish line will Jason be when Le. Roy crosses the finish line?

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems What are the known constants? • Jason’s rate of 6 mph • Le. Roy’s rate of 8 mph • Race distance of 26 miles

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems What are the unknowns? • The amount of time it takes Le. Roy to finish the race • The distance Jason has to run when Le. Roy finishes

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems Let Le. Roy’s time be t. What is the distance, rate, time, model for Leroy in this problem? 8 t = 26 What is the solution for t? t = 3. 25 hours

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems At the time that Le. Roy crosses the finish line, Jason has run for the same amount of time, t. What is the model for how far Jason is from the finish line at that time? d = 26 - 6(3. 25) d = 6. 5 miles

Equation for Motion in Opposite Directions Add distance for both objects and set equal to the total distance apart.

Example • Bike riders Brent and Jane started at noon from points 60 km apart and rode toward each other, meeting at 1: 30 pm. Brent’s speed was 4 km/h greater than Jane’s speed. • Find their speeds.

Start riding at 12 pm & meet at 1: 30 pm r r+4 60 km

Unknown Jane and Brent’s speed.

Variables Let r = Jane’s rate Let r + 4 = Brent rate Make a chart and use the information to label your diagram
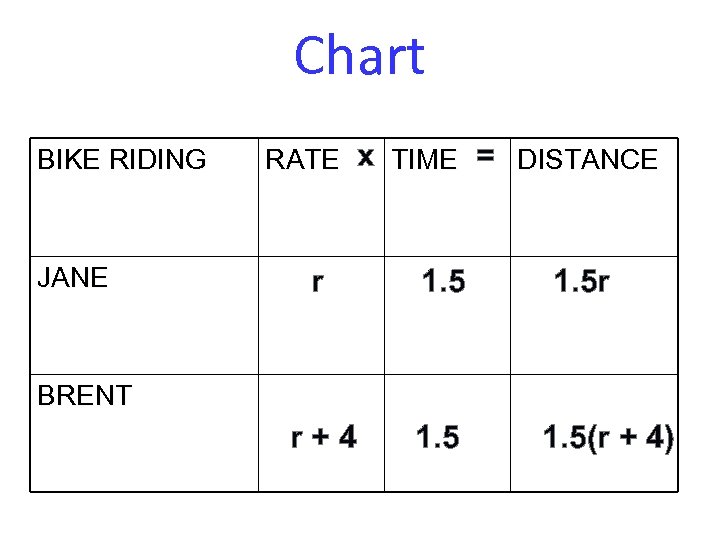
Chart BIKE RIDING JANE RATE x TIME = DISTANCE r 1. 5 r+4 1. 5 r BRENT 1. 5(r + 4)

Equation • 1. 5 ( r + 4) + 1. 5 r = 60 • r = 18 Jane’s speed • r + 4 = 22 Brent’s speed was 22 km/h and Jane’s speed was 18 km/h

Try This • At noon a private plane left Austin for Los Angeles, 2100 km away, flying at 500 km/h. One hour later a jet left Los Angeles for Austin at 700 km/h. At what time did they pass each other?
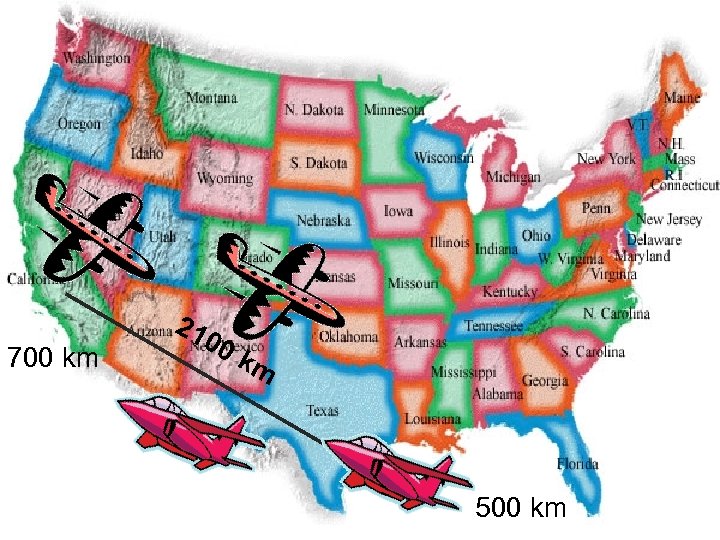
700 km 21 00 km 500 km
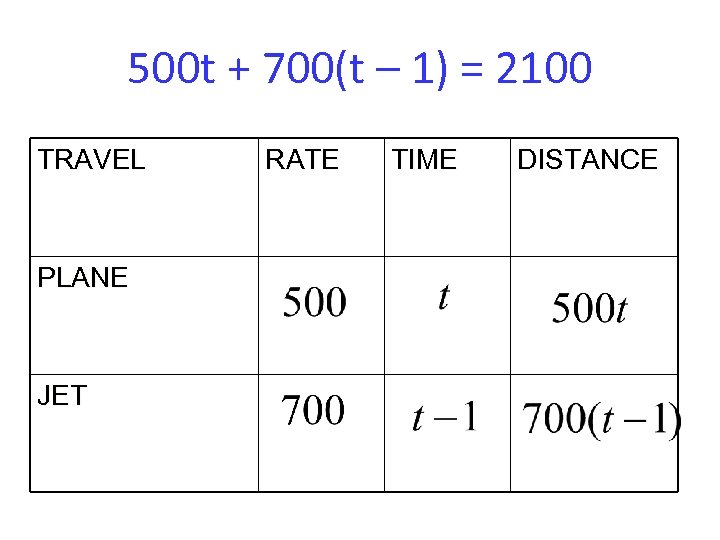
500 t + 700(t – 1) = 2100 TRAVEL PLANE JET RATE TIME DISTANCE

500 t + 700(t – 1) = 2100 500 t +700 t – 700 = 2100 1200 t – 700 = 2100 +700 =+700 1200 t = 2800 1200 t/1200 =2800/1200 T=2 1/3 hrs is 2 hrs 20 min WHATS THE QUESTION Airplane took 2 hours and 20 min before meeting with Jet that took t – 1 =2 hr 20 min – 1 = 1 hr and 20 min Time is 12: 00 + 2 hr and 20 min. They jet passed the plane at 2: 20

Rate, Time, and Distance Dan and Emily are truck drivers. Dan, averaging 55 miles per hour (mph), begins a 280 -mile trip from their company’s Norfolk warehouse to Charlotte, NC at 7 AM. Emily sets out from the Charlotte warehouse at 8 AM on the same day as Dan and travels at 45 mph in the opposite direction as the route taken by Dan.

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems How many hours will Emily have been driving when she and Dan pass each other? How will you start to set up a model for solving this problem?

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems What is the variable that you must solve for? time Is the length of time traveled the same for Dan and Emily when they pass each other? No.

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems Why is the time different for the two drivers? • Dan started at 7 AM and • Emily started at 8 AM. • Dan averaged 55 mph and • Emily averaged 45 mph.

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems t Let represent the amount of time that Emily travels until the trucks pass each other. t In terms of , how long will Dan have been on the road when the trucks pass each other? One hour longer or. . . t+1

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems The mathematical model for this problem is: Dan’s Distance + Emily’s Distance = 280 miles Dan’s rate*Dan’s time + Emily’s rate*Emily’s time = 280 55(t+1) + 45 t = 280

Rate, Time, and Distance Problems 55(t+1) + 45 t = 280 55 t+55 + 45 t = 280 100 t + 55 = 280 100 t = 225 t = 2. 25 hours

Let’s work some problems! Distance=Rate·Time Rate=distance/time Time=distance/rate

I ride my bike 18 mph and it takes 40 minutes to get to work. How far is work from my house?

Answer: D=R·T D =18 mph· 40 min ∙ 1 hr/60 min 12 miles

My house is 12 miles from work. How fast do I have to drive (in miles per hour) to get to work in 15 minutes?

Answer: Rate = distance/time R =12 mi/15 min ∙ 60 min/1 hr= 48 mph

My house is 12 miles from work. I drove 40 mph today and was 8 minutes late. How fast should I have drove to get to work on time?

Answer: T = D/R T =12 mi/40 mph =18 min To be on time: 18 min-8 min=10 min R=D/T=12 mi/10 min · 60 min/1 hr = 72 mph !!!

A tortoise and hare have a 400 foot race. The tortoise crawls 5 feet per minute the entire time. st half of the The hare runs the 1 distance at 200 feet per minute and walks the rest of the race at 2 feet per minute. Who wins?

Tortoise T = D/R = 400 ft/(5 ft/min) T=80 minutes Hare 1 st Half T=200 ft/(200 ft/min) = 1 minute Hare 2 nd Half T=200 ft/(2 ft/min) = 100 minutes Hare =1 min + 100 min= 101 min Tortoise wins!

A tortoise and hare have a 400 foot race. The tortoise crawls 5 feet per minute the entire time. The hare runs the 1 st half of the distance at 200 feet per minute and walks the rest of the race at 2 feet per minute. How many minutes after the start of the race does the tortoise catch the hare?

After 1 minute: Tortoise D= R·T = (5 ft/min) · 1 min = 5 ft Hare D= R·T = (200 ft/min) · 1 min = 200 ft Therefore the hare is 195 ft ahead at 1 minute. At this point the hare is moving at 2 feet per minute and the tortoise is moving at 5 feet per minute. So the tortoise is catching up at 3 feet per minute. T= D/R = 195 ft/(3 ft/min) = 65 minutes The tortoise catches the hare at 1 min + 65 min 66 minutes

Lets move on to a different type of word problem.

Work Word Problems

"Work" problems involve situations such as two people working together to paint a house. You are usually told how long each person takes to paint a similarly-sized house, and you are asked how long it will take the two of them to paint the house when they work together. Many of these problems are not terribly realistic (since when do two laser printers work together on printing one report? ), but it's the technique that they want you to learn, not the applicability to "real life". The method of solution for work problems is not obvious, so don't feel bad if you're totally lost at the moment. There is a "trick" to doing work problems: you have to think of the problem in terms of how much each person / machine / whatever does in a given unit of time.
Example:

Working alone, Ryan can dig a 10 ft by 10 ft hole in five hours. Castel can dig the same hole in six hours. How long would it take them if they worked together?

Ryan = 1 room/5 hours Castel = 1 room/6 hours Together = (room/hr) 1/5 +1/6 =1/t 11/30 = 1t hour 11 t = 30/11 = 2. 73 hours

Shawna can pour a large concrete driveway in six hours. Dan can pour the same driveway in seven hours. Find how long it would take them if they worked together.

Shawna = 1 room/6 hours Dan = 1 room/7 hours Together = (room/hr) 1/6 +1/7 =1/t 13/42 = 1t hour 13 t = 42/13 = 3. 23 hours

It takes Trevon ten hours to clean an attic. Cody can clean the same attic in seven hours. Find how long it would take them if they worked together.

Trevon = 1 room/10 hours Cody = 1 room/7 hours Together = (room/hr) 1/10 +1/7 =1/t 17/70 = 1t hour 17 t = 70/17 = 4. 12 hours

Working together, Paul and Daniel can pick forty bushels of apples in 4. 95 hours. Had he done it alone it would have taken Daniel 9 hours. Find how long it would take Paul to do it alone.

Paul = 1 job/t hours Daniel = 1 job/9 hours Together = 1 job/ 4. 95 hours 1/t +1/9 =1/4. 95 1/t = 1/4. 95 - 1/9 1/t = (9 - 4. 95)/(4. 95· 9) 1/t = 4. 05/44. 55 4. 05 t = 44. 55/4. 05 = 11 hours

Working together, Jenny and Natalie can mop a warehouse in 5. 14 hours. Had she done it alone it would have taken Natalie 12 hours. How long would it take Jenny to do it alone?

Jenny = 1 job/t hours Natalie = 1 job/12 hours Together = 1 job/ 5. 14 hours 1/t +1/12 =1/5. 14 1/t = 1/5. 14 - 1/12 1/t = (12 – 5. 14)/(5. 14· 12) 1/t = 6. 86/61. 68 6. 86 t = 61. 68/6. 86 = 8. 99 hours

Lauren can paint the whole classroom alone in 8 hours. Micah can paint the whole classroom alone in 6 hours. How long will it take them to paint the classroom working together?

Lauren = 1 room/8 hours Micah = 1 room/6 hours Together= 1/8 +1/6 =7/24 (room/hr) 1/8 +1/6 = 1/t 7/24 = 1/t 7 t = 24/7 3 3/7 (3. 43) hours

It took 24 minutes for my bathtub to fill when both the faucet was on and the drain was open. After the tub filled, I turned off the faucet and the tub drained in 8 minutes. How long would it have taken to fill the tub if I had plugged the drain in the beginning?

Drain= 1 tub/8 min Tub= 1 tub/tmin 1/t – 1/8 = 1/24 1/t =1/24 + 1/8 1/t = 1/6 t = 6 minutes
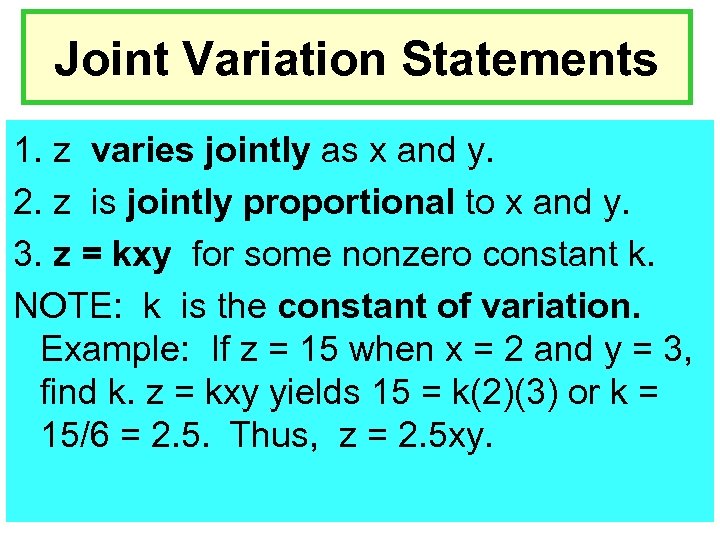
Joint Variation Statements 1. z varies jointly as x and y. 2. z is jointly proportional to x and y. 3. z = kxy for some nonzero constant k. NOTE: k is the constant of variation. Example: If z = 15 when x = 2 and y = 3, find k. z = kxy yields 15 = k(2)(3) or k = 15/6 = 2. 5. Thus, z = 2. 5 xy.

Four electric grinders can grind 9 pounds of flour in 5 hours. How many pounds of flour would 10 grinders grind in 10 hours?

Answer: Joint Proportion 9 lbs 5 hrs· 4 grinders = X lbs 10 hrs· 10 grinders Answer = 45 lbs

Mixture Problems

Creating a Mixture • A mixture is a combination of several elements that together, make a whole. Ø To represent the total amount of mixture: Mixture = Part 1 + Part 2 Ø To represent the amount of a part: Part 1 = Mixture – Part 2 or Part 2 = Mixture – Part 1 v. Note: This is how you assign the variable!

Organizing the Problem Think of putting together a puzzle. How did you start? - Did you take one piece out of the box at a time? - Did you dump all the pieces out and start with the corners? Using a chart to solve a word problem is like putting together a puzzle: you’ve got to organize the pieces first!
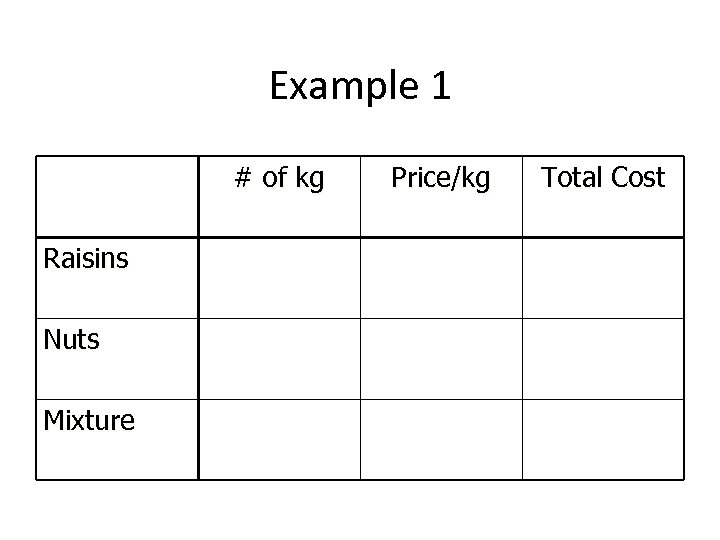
Example 1 # of kg Raisins Nuts Mixture Price/kg Total Cost
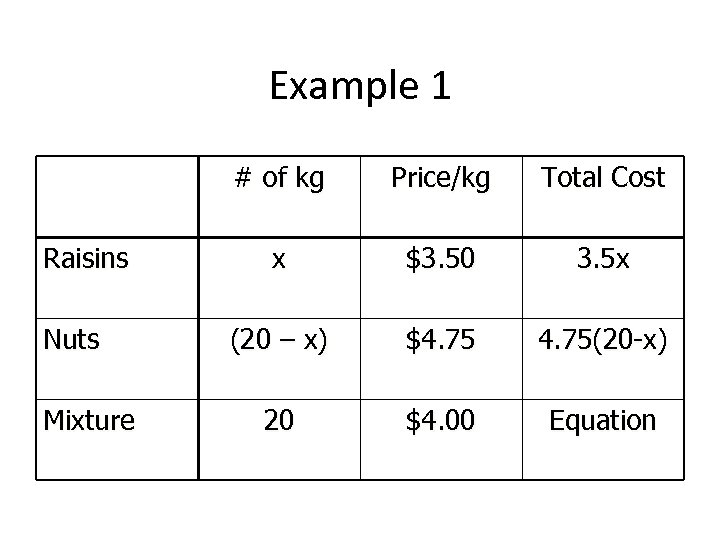
Example 1 # of kg Raisins Nuts Mixture Price/kg Total Cost x $3. 50 3. 5 x (20 – x) $4. 75(20 -x) 20 $4. 00 Equation
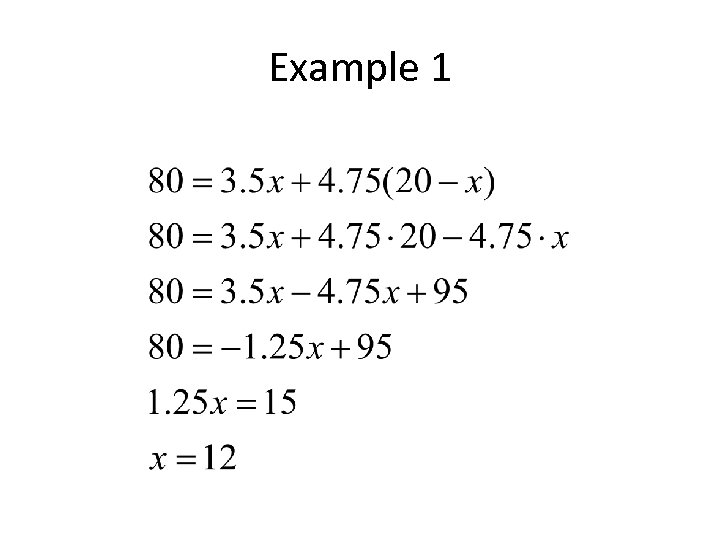
Example 1

Example 1 So there are 12 kg of Raisins and 20 - 12 = 8 kg of Nuts in this mixture.

Solving Mixture Problems One variable equations

The Problem • A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid?

Identify key words • A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? How much guides us to the question: How much 15% solution? To get guides us to where = will go.
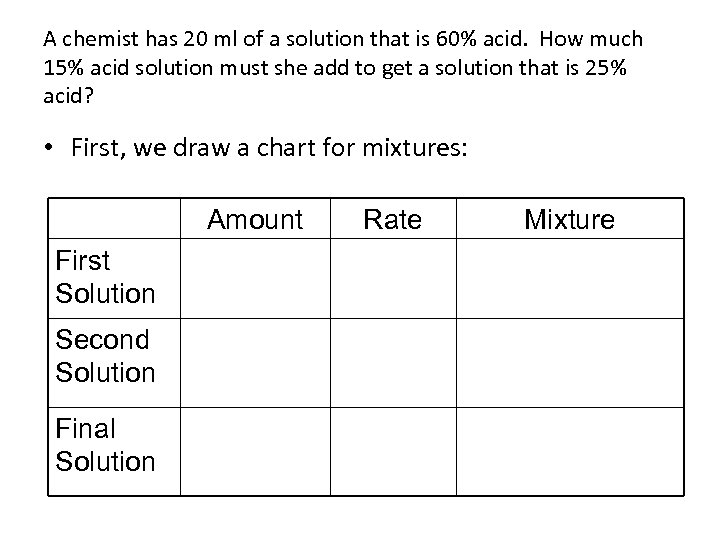
A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? • First, we draw a chart for mixtures: Amount First Solution Second Solution Final Solution Rate Mixture
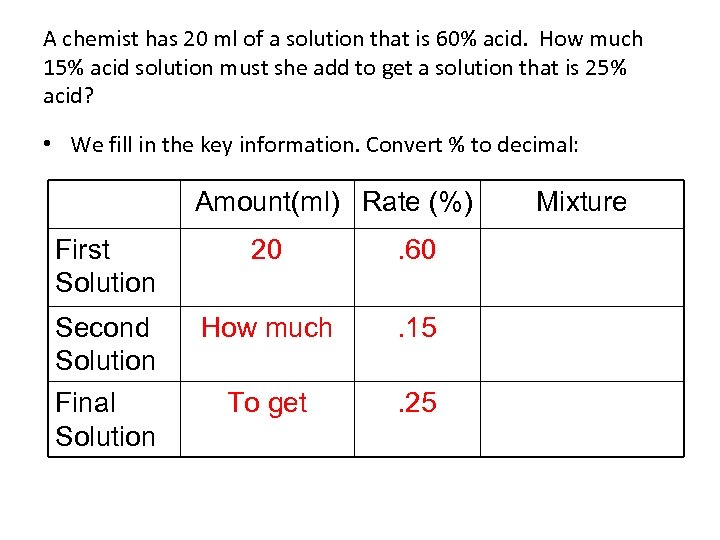
A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? • We fill in the key information. Convert % to decimal: Amount(ml) Rate (%) First Solution 20 . 60 Second Solution Final Solution How much . 15 To get . 25 Mixture

A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? • The first column is added down. 20 + “how much” = “to get” • We have two unknowns! The question words are x, so now we have 20 + x = “to get” • 20 + x = “to get” Because we have an equation, 20 + x means the same amount as “to get. ” Until you can use two variables, you must use the 20 + x in place of “to get”
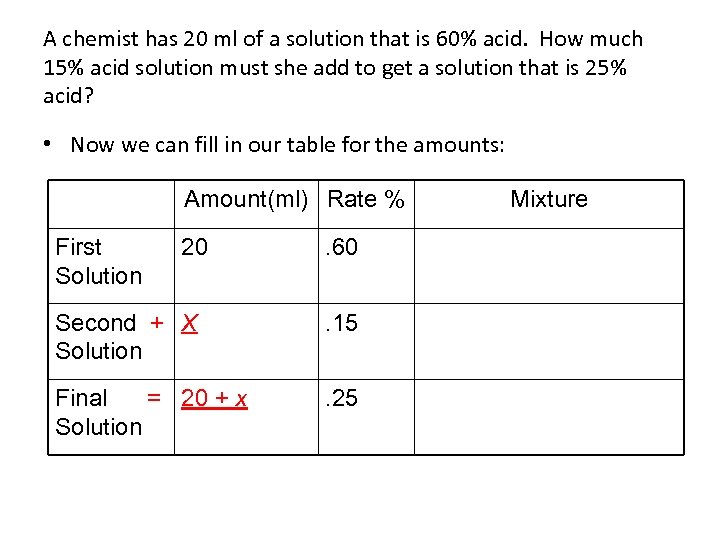
A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? • Now we can fill in our table for the amounts: Amount(ml) Rate % First Solution 20 . 60 Second + X Solution . 15 Final = 20 + x Solution . 25 Mixture

A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? • Now we multiply each row across. It’s better to write the mixture as “rate * amount” even though the columns are in the opposite order. (remember, 3*4 is the same as 4*3). Amount(ml) * Rate % = Mixture First Solution 20 *. 60 =. 60(20) Second Solution X *. 15 =. 15 x Final Solution (20 + x) * =. 25(20 + x) . 25
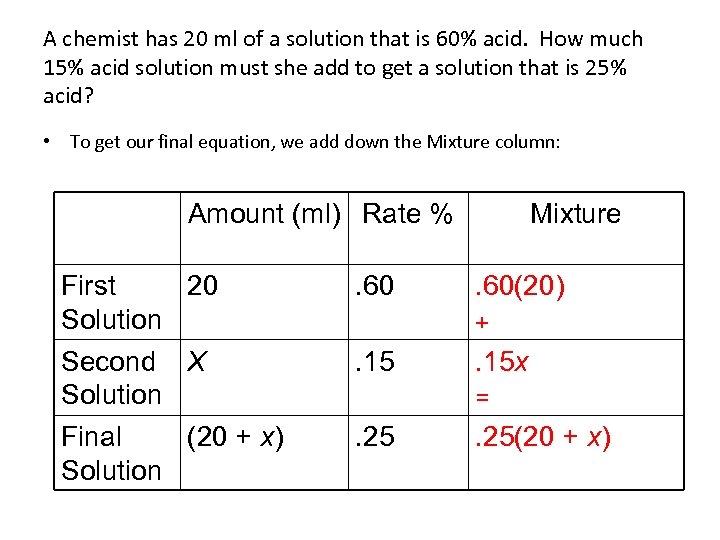
A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? • To get our final equation, we add down the Mixture column: Amount (ml) Rate % First 20 Solution Second X Solution Final (20 + x) Solution . 60 Mixture. 60(20) + . 15 x = . 25(20 + x)
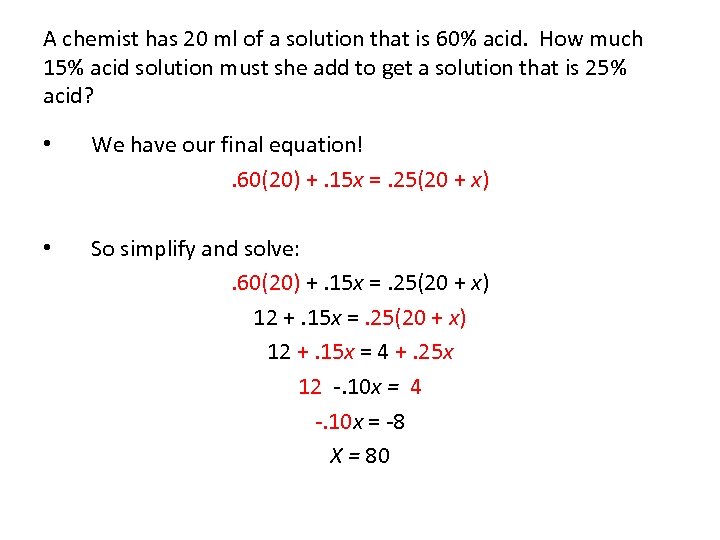
A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? • We have our final equation!. 60(20) +. 15 x =. 25(20 + x) • So simplify and solve: . 60(20) +. 15 x =. 25(20 + x) 12 +. 15 x = 4 +. 25 x 12 -. 10 x = 4 -. 10 x = -8 X = 80

A chemist has 20 ml of a solution that is 60% acid. How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? • Now we know that x = 80. Did we answer the question? How much 15% acid solution must she add to get a solution that is 25% acid? Remember, “how much” was an amount measured in ml. She must add 80 ml.
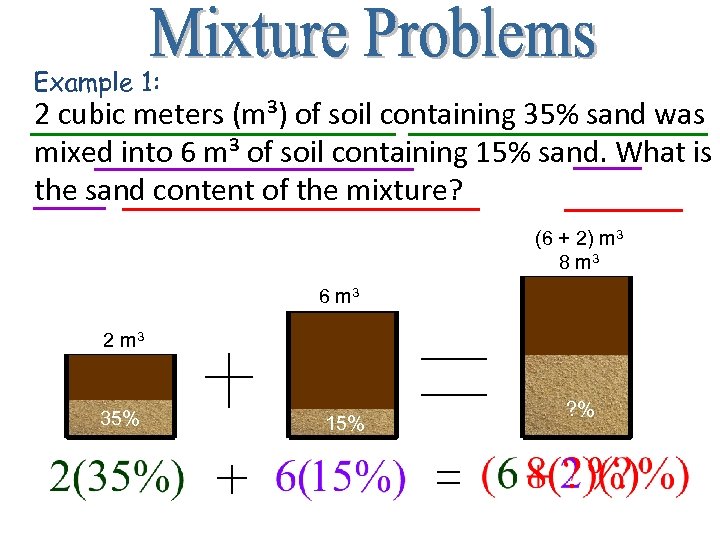
Example 1: 2 cubic meters (m³) of soil containing 35% sand was mixed into 6 m³ of soil containing 15% sand. What is the sand content of the mixture? (6 + 2) m 3 8 m 3 6 m 3 2 m 3 35% 15% ? %
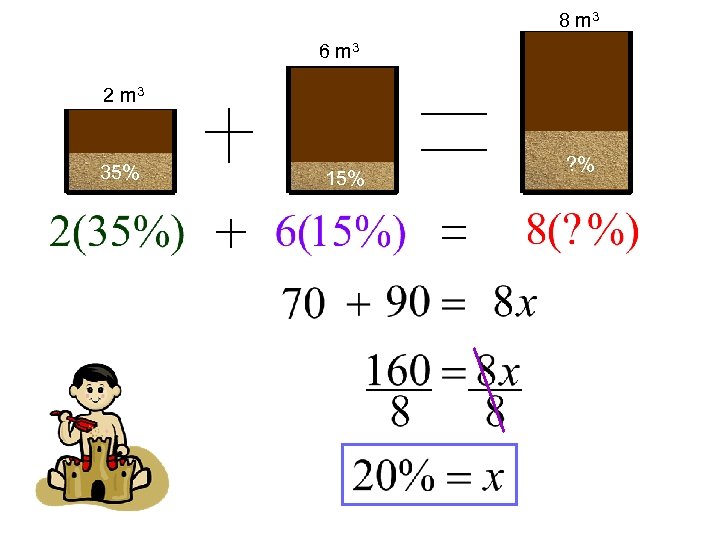
8 m 3 6 m 3 2 m 3 35% 15% ? %
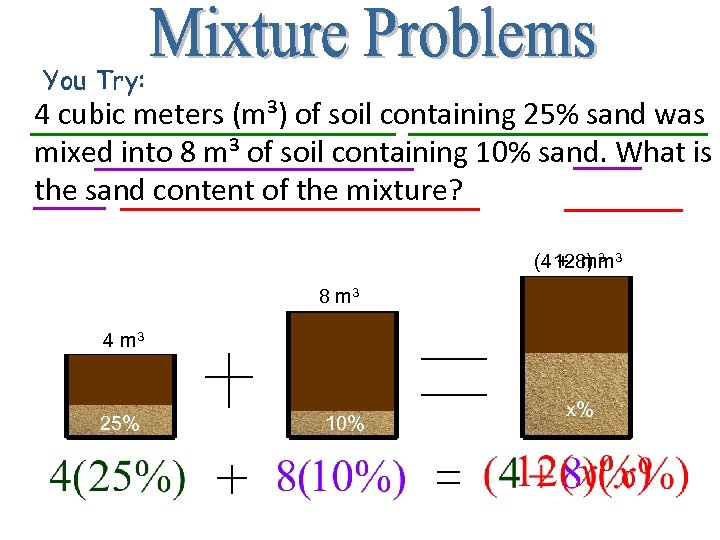
You Try: 4 cubic meters (m³) of soil containing 25% sand was mixed into 8 m³ of soil containing 10% sand. What is the sand content of the mixture? (4 128) 3 3 + mm 8 m 3 4 m 3 25% 10% x%
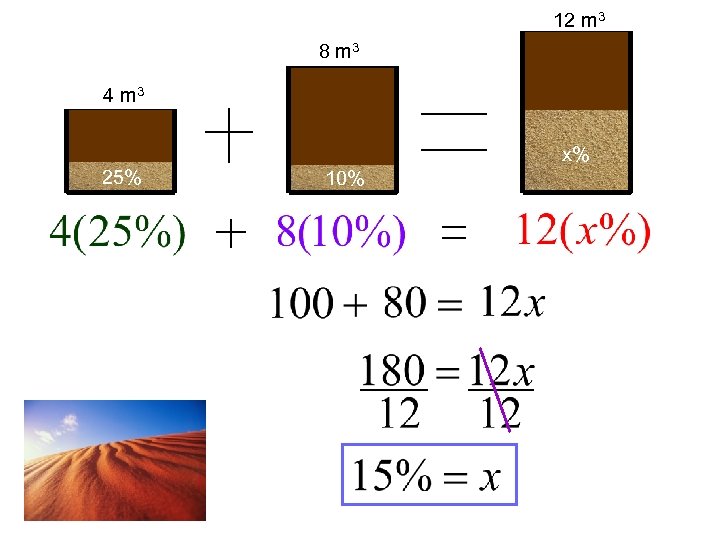
12 m 3 8 m 3 4 m 3 x% 25% 10%

Example 2: How many pounds of only blue m&m’s must be added to an 11 pound bag containing 35% blue to make a bag that is 45% blue? x + 11 pounds x pounds 11 pounds 100% 45% 35%
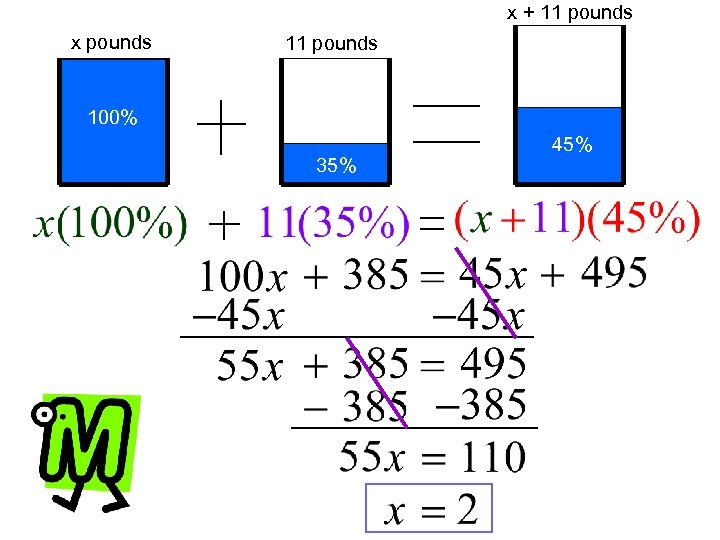
x + 11 pounds x pounds 11 pounds 100% 35% 45%

Competition Problems
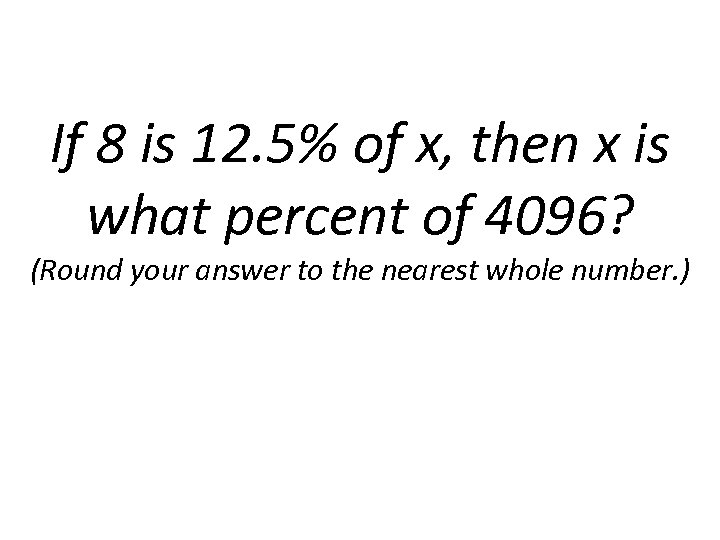
If 8 is 12. 5% of x, then x is what percent of 4096? (Round your answer to the nearest whole number. )
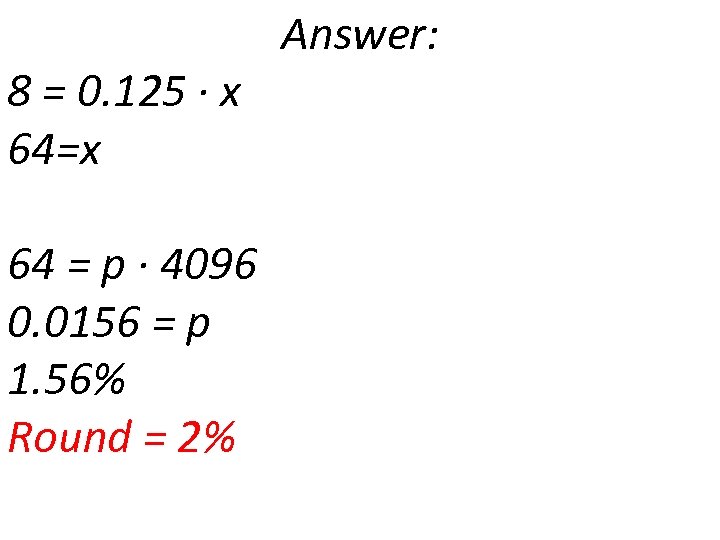
8 = 0. 125 ∙ x 64=x 64 = p ∙ 4096 0. 0156 = p 1. 56% Round = 2% Answer:
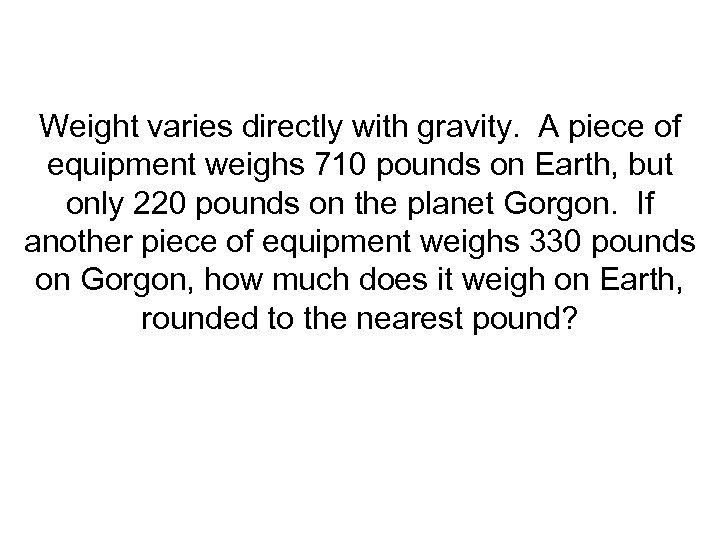
Weight varies directly with gravity. A piece of equipment weighs 710 pounds on Earth, but only 220 pounds on the planet Gorgon. If another piece of equipment weighs 330 pounds on Gorgon, how much does it weigh on Earth, rounded to the nearest pound?

Answer: (Direct Variation) y 1/x 1 = y 2/x 2 710/220 = x/330 X=1065 pounds

The length of a violin string varies inversely as the frequency of its vibrations. If a 10 -inch long string vibrates at a frequency of 512 cycles per second, find the frequency of an 8 -inch string.

Answer: 640 cycles per second

A photo 3 inches wide and 5 inches long is being enlarged. The new photo is 12 inches long. How many inches wide will it be?

Answer: 7. 2
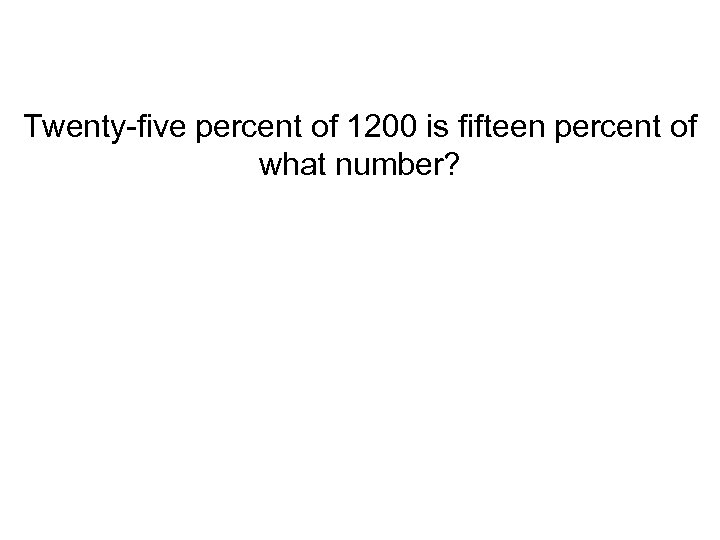
Twenty-five percent of 1200 is fifteen percent of what number?

Answer: 2000

A kavu purse is discounted 25% of it’s original price of $60, during the weekend sale. At the reduced price the store will make a profit of 20% over cost. What was the cost of the purse to the store?

Answer: . 75(60)=45 Cost + profit = $45 C + 0. 2(C) = 45 1. 2 C =45 C=37. 5 $37. 50

The ratio of Auburn to Alabama fans at Cedar Ridge Middle School is 2: 5. There are 840 Alabama fans in attendance. How many more Auburn fans would need to enroll to make the ratio of Auburn to Alabama 1: 2.
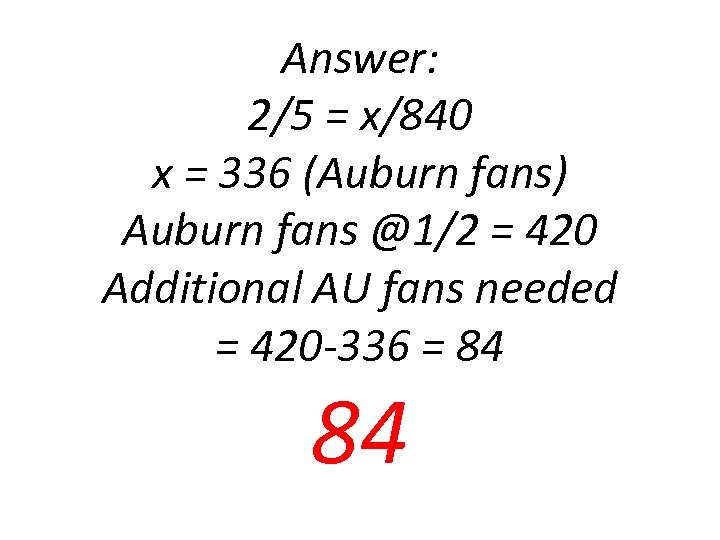
Answer: 2/5 = x/840 x = 336 (Auburn fans) Auburn fans @1/2 = 420 Additional AU fans needed = 420 -336 = 84 84

A 42 -in flat screen television originally cost $1200. What was its total cost after a 15% discount and an 8% tax rate were applied?

Answer: $1101. 60

The solution in a 9 liter radiator system is 25% antifreeze. How much solution must be drained and replaced by 100% antifreeze to obtain a 50% solution?

Answer: New A. F. + Surviving A. F. = Total A. F. 1 x +. 25(9 -x) = 0. 5(9) x + 9/4 – x/4 = 9/2 ¾ x = 9/2 – 9/4 ¾ x = 9/4 3 x = 9 x=3 3 liters

A 50 m. L solution of acid in water contains 25% acid. How many m. L of water would you add in order to make a 10% acid solution?

Answer: New water + old Water = Total water 1 x + 0. 75(50) = 0. 9(50+x) x + 37. 5 = 45 + 0. 9 x 0. 1 x = 7. 5 x = 75 75 ml
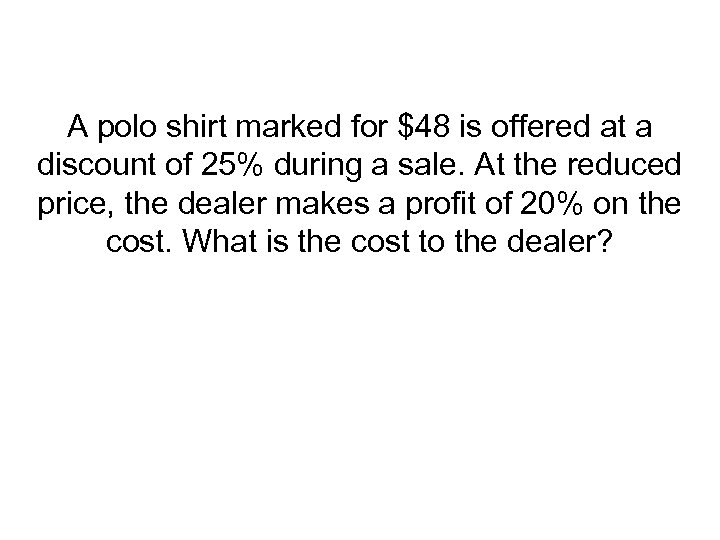
A polo shirt marked for $48 is offered at a discount of 25% during a sale. At the reduced price, the dealer makes a profit of 20% on the cost. What is the cost to the dealer?

Answer: $30

The ratio of Auburn to Alabama fans at Cedar Ridge Middle School is 2: 5. There are 840 Alabama or Auburn fans in attendance. How many more Auburn fans would need to attend to make the ratio (of Auburn to Alabama fans ) 1: 2?

Answer: 60

Lucy paints a room in 7 hours. Katie could paint the same room in 5 hours. How long will it take them to paint the room together? Answer in hours and minutes.

Answer: 1/7 +1/5 =1/x X=35/12 2 hours 55 minutes

Louise can trim the shrubbery in 6 hours working alone. Her father can do it in 5 hours. They worked together until dinner but trimmed only 11/ 15 of the shrubbery. How long did they work?
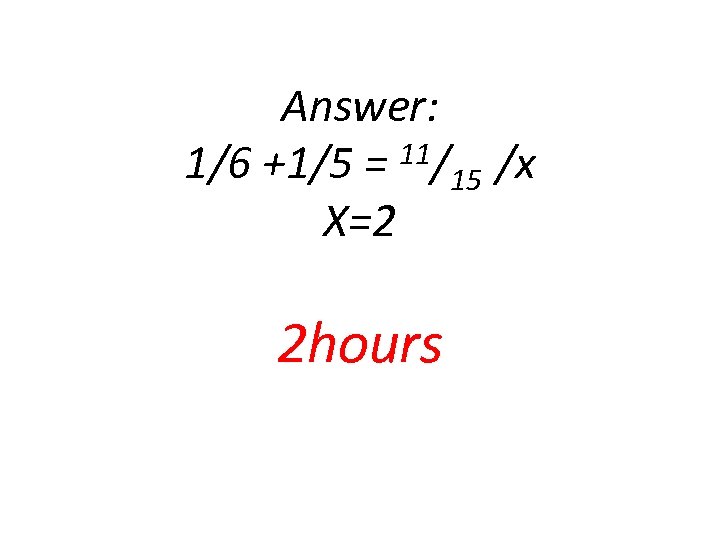
Answer: 11/ /x 1/6 +1/5 = 15 X=2 2 hours

The denominator of a fraction is 3 more than the numerator. If 25 is added to each, the resulting fraction is equivalent to 0. 9. Find the original fraction.
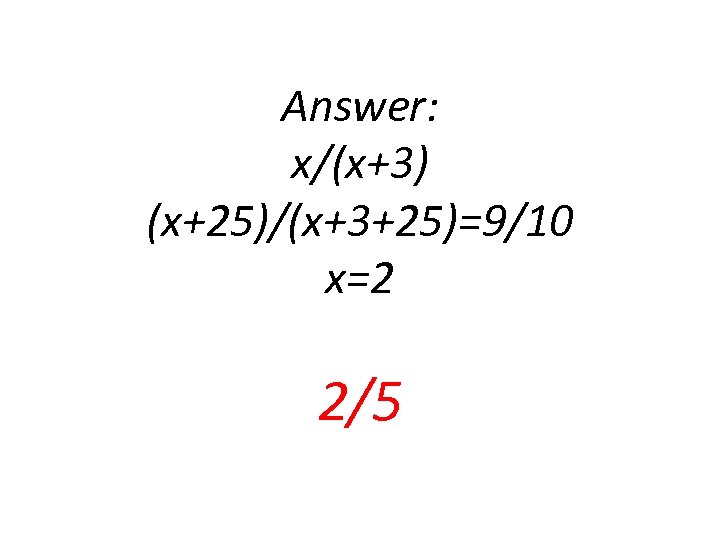
Answer: x/(x+3) (x+25)/(x+3+25)=9/10 x=2 2/5

If Chloe can make three Christmas ornaments an hour & Isaac can make 2 each hour, how many hours would it take them to make 45 ornaments working together?

Answer: 1 hour x hour = 5 orn 1 hour 5 orn 45 orn ∙ 45 orn = x hours x = 9 hours

2 students are writing math questions. If Levi writes 10 questions every 30 minutes and Ben writes 5 questions every 20 minutes, how many hours will it take them to write 100 questions?

Answer: Rate 30 minutes = 1 hour 10 questions 20 minutes 5 questions 1 hour 15 questions 1 hour 35 questions = ∙ 100 questions = 20/7 hours x = 20/7 hours
14f34d348c2b141006c1a84d239f928a.ppt