b617061d90944cd2c067cde767562d8e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61
 Materials Management • Planning and controlling the flow of materials • Objectives: – Maximize the use of the firms resources – Provide the required level of customer service
Materials Management • Planning and controlling the flow of materials • Objectives: – Maximize the use of the firms resources – Provide the required level of customer service
 Company Objectives Income = Revenue - Expense • Need to increase income with: – Best customer service – Lowest production costs – Lowest inventory investment – Lowest distribution costs
Company Objectives Income = Revenue - Expense • Need to increase income with: – Best customer service – Lowest production costs – Lowest inventory investment – Lowest distribution costs
 Manufacturing Planning and Control • Planning and controlling the flow of materials through the manufacturing process through: – Production Planning – Implementation and Control – Inventory Management
Manufacturing Planning and Control • Planning and controlling the flow of materials through the manufacturing process through: – Production Planning – Implementation and Control – Inventory Management
 Production Planning • To meet the demands of the marketplace • Establish priorities • Ensure capacity • Activities – Forecasting – Master Planning – Materials Requirements Planning – Capacity Planning
Production Planning • To meet the demands of the marketplace • Establish priorities • Ensure capacity • Activities – Forecasting – Master Planning – Materials Requirements Planning – Capacity Planning
 Implementation and Control • Putting into action and achieving the plans – (made by production planning) • Purchasing
Implementation and Control • Putting into action and achieving the plans – (made by production planning) • Purchasing
 Inputs to the Manufacturing Planning and Control System 1. Product description 2. Process specifications 3. Time needed 4. Available facilities 5. Quantity required
Inputs to the Manufacturing Planning and Control System 1. Product description 2. Process specifications 3. Time needed 4. Available facilities 5. Quantity required
 • Bill of Material – Components used to make the product
• Bill of Material – Components used to make the product
 Process Specifications • Recorded on a Route Sheet • Describe how the product is made – Operations required to make the product – Sequence of operations – Equipment and accessories required – Standard time to perform each operation
Process Specifications • Recorded on a Route Sheet • Describe how the product is made – Operations required to make the product – Sequence of operations – Equipment and accessories required – Standard time to perform each operation
 Quantities Required • Information from – Forecasts – Customer Orders – Production Planning
Quantities Required • Information from – Forecasts – Customer Orders – Production Planning
 Physical Supply / Distribution • All the activities involved in moving goods – from the supplier to the beginning of the production process – from the end of the process to the customer • Transportation • Distribution Inventory • Warehousing • Packaging • Materials Handling
Physical Supply / Distribution • All the activities involved in moving goods – from the supplier to the beginning of the production process – from the end of the process to the customer • Transportation • Distribution Inventory • Warehousing • Packaging • Materials Handling
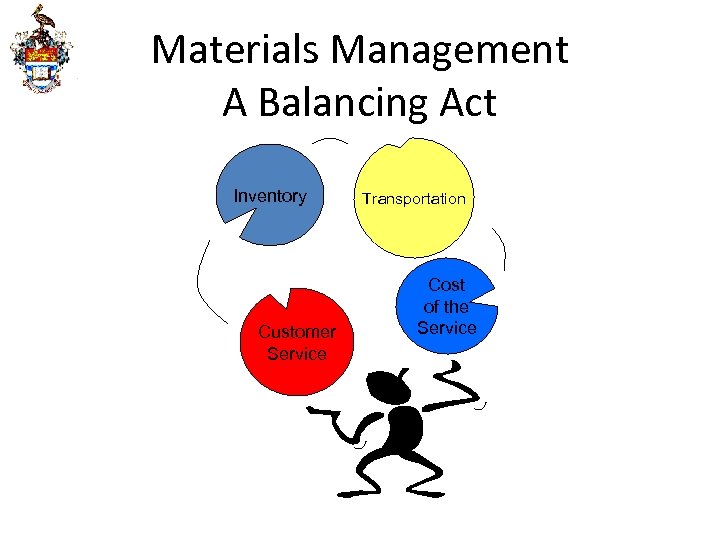 Materials Management A Balancing Act Inventory Customer Service Transportation Cost of the Service
Materials Management A Balancing Act Inventory Customer Service Transportation Cost of the Service
 Materials ä ä ä 12 | : Packaging materials Finished products Rejected and recovered materials Recalled products Returned goods Waste materials Artemisinin based combined medicines February 23 -27, 2009, Kampala, Uganda
Materials ä ä ä 12 | : Packaging materials Finished products Rejected and recovered materials Recalled products Returned goods Waste materials Artemisinin based combined medicines February 23 -27, 2009, Kampala, Uganda
 Definition It is concerned with planning, organizing and controlling the flow of materials from their initial purchase through internal operations to the service point through distribution.
Definition It is concerned with planning, organizing and controlling the flow of materials from their initial purchase through internal operations to the service point through distribution.
 AIM OF MATERIAL MANAGEMENT To get 1. The Right quality 2. Right quantity of supplies 3. At the Right time 4. At the Right place 5. For the Right cost
AIM OF MATERIAL MANAGEMENT To get 1. The Right quality 2. Right quantity of supplies 3. At the Right time 4. At the Right place 5. For the Right cost
 PURPOSE OF MATERIAL MANAGEMENT • To gain economy in purchasing • To satisfy the demand during period of replenishment • To carry reserve stock to avoid stock out • To stabilize fluctuations in consumption • To provide reasonable level of client services
PURPOSE OF MATERIAL MANAGEMENT • To gain economy in purchasing • To satisfy the demand during period of replenishment • To carry reserve stock to avoid stock out • To stabilize fluctuations in consumption • To provide reasonable level of client services
 Objective of material management Primary • Right price • Low procurement & storage cost • Continuity of supply • Consistency in quality • Good supplier relations • Development of personnel • Good information system Secondary • Forecasting • Inter-departmental harmony • Product improvement • Standardization • Make or buy decision • New materials & products
Objective of material management Primary • Right price • Low procurement & storage cost • Continuity of supply • Consistency in quality • Good supplier relations • Development of personnel • Good information system Secondary • Forecasting • Inter-departmental harmony • Product improvement • Standardization • Make or buy decision • New materials & products
 Economy in material management • Containing the costs • Instilling efficiency in all activities
Economy in material management • Containing the costs • Instilling efficiency in all activities
 Four basic needs of Material management 1. To have adequate materials on hand when needed 2. To pay the lowest possible prices, consistent with quality and value requirement for purchases materials 3. To minimize the inventory investment 4. To operate efficiently
Four basic needs of Material management 1. To have adequate materials on hand when needed 2. To pay the lowest possible prices, consistent with quality and value requirement for purchases materials 3. To minimize the inventory investment 4. To operate efficiently
 Basic principles of material management Effective management & supervision It depends on managerial functions of • Planning • Organizing • Staffing • Directing • Controlling • Reporting • Budgeting Skillful & hard poised negotiations Effective purchase system Should be simple Must not increase other costs Inventory control
Basic principles of material management Effective management & supervision It depends on managerial functions of • Planning • Organizing • Staffing • Directing • Controlling • Reporting • Budgeting Skillful & hard poised negotiations Effective purchase system Should be simple Must not increase other costs Inventory control
 Elements of material management 1. Demand estimation 2. Identify the needed items 3. Calculate from the trends in Consumption. 4. Review with resource constraints
Elements of material management 1. Demand estimation 2. Identify the needed items 3. Calculate from the trends in Consumption. 4. Review with resource constraints
 Objectives of procurement system • Acquire needed supplies as inexpensively as possible • Obtain high quality supplies • Assure prompt & dependable delivery • Distribute the procurement workload to avoid period of idleness & overwork
Objectives of procurement system • Acquire needed supplies as inexpensively as possible • Obtain high quality supplies • Assure prompt & dependable delivery • Distribute the procurement workload to avoid period of idleness & overwork
 Points to remember while purchasing • Proper specification • Invite quotations from reputed firms • Comparison of offers based on basic price, freight & insurance, taxes and levies • Quantity & payment discounts • Payment terms • Delivery period, guarantee • Vendor reputation (reliability, technical capabilities, Convenience, Availability, aftersales service, sales assistance)
Points to remember while purchasing • Proper specification • Invite quotations from reputed firms • Comparison of offers based on basic price, freight & insurance, taxes and levies • Quantity & payment discounts • Payment terms • Delivery period, guarantee • Vendor reputation (reliability, technical capabilities, Convenience, Availability, aftersales service, sales assistance)
 Storage • Store must be of adequate space • Materials must be stored in an appropriate place in a correct way • Group wise & alphabetical arrangement helps in identification & retrieval • First-in, first-out principle to be followed OR. . • Monitor expiry date
Storage • Store must be of adequate space • Materials must be stored in an appropriate place in a correct way • Group wise & alphabetical arrangement helps in identification & retrieval • First-in, first-out principle to be followed OR. . • Monitor expiry date
 Inventory control It means stocking adequate number and kind of stores, so that the materials are available whenever required and wherever required.
Inventory control It means stocking adequate number and kind of stores, so that the materials are available whenever required and wherever required.
 Functions of inventory control • To provide maximum supply service, consistent with maximum efficiency & optimum investment. • To provide cushion between forecasted & actual demand for a material
Functions of inventory control • To provide maximum supply service, consistent with maximum efficiency & optimum investment. • To provide cushion between forecasted & actual demand for a material
 • Re-order level: stock level at which fresh order is placed. • Average consumption per day. lead time. buffer stock • Lead time: Duration time between placing an order & receipt of material
• Re-order level: stock level at which fresh order is placed. • Average consumption per day. lead time. buffer stock • Lead time: Duration time between placing an order & receipt of material
 PROCURMENT OF EQUIPMENT Points to be noted before purchase of an equipment: • Latest technology • Availability of maintenance & repair facility, with minimum down time • Post warranty repair at reasonable cost • Upgradeability • Reputed manufacturer • Low operating costs • Installation
PROCURMENT OF EQUIPMENT Points to be noted before purchase of an equipment: • Latest technology • Availability of maintenance & repair facility, with minimum down time • Post warranty repair at reasonable cost • Upgradeability • Reputed manufacturer • Low operating costs • Installation
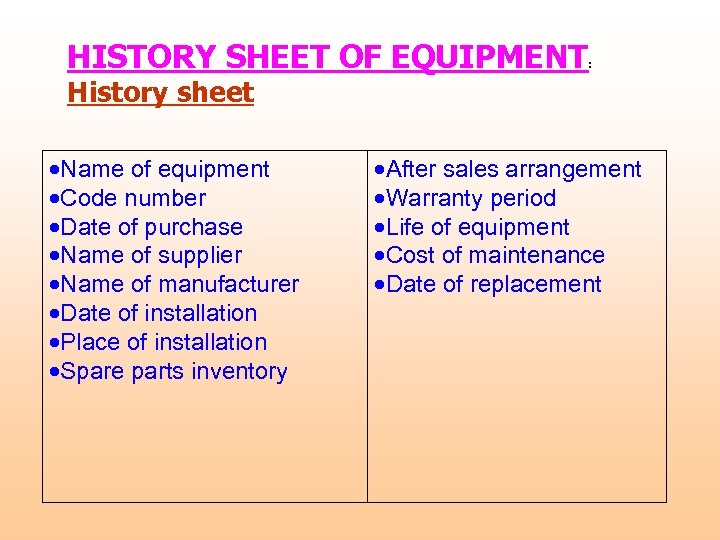 HISTORY SHEET OF EQUIPMENT : History sheet Name of equipment Code number Date of purchase Name of supplier Name of manufacturer Date of installation Place of installation Spare parts inventory After sales arrangement Warranty period Life of equipment Cost of maintenance Date of replacement
HISTORY SHEET OF EQUIPMENT : History sheet Name of equipment Code number Date of purchase Name of supplier Name of manufacturer Date of installation Place of installation Spare parts inventory After sales arrangement Warranty period Life of equipment Cost of maintenance Date of replacement
![Maintenance sheet: Annual maintenance contract [AMC] Starting date Expiry date Service / repair description Maintenance sheet: Annual maintenance contract [AMC] Starting date Expiry date Service / repair description](https://present5.com/presentation/b617061d90944cd2c067cde767562d8e/image-29.jpg) Maintenance sheet: Annual maintenance contract [AMC] Starting date Expiry date Service / repair description Materials / spares used Cost of repairs In-house Outside agency
Maintenance sheet: Annual maintenance contract [AMC] Starting date Expiry date Service / repair description Materials / spares used Cost of repairs In-house Outside agency
 EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE & CONDEMNATION Maintenance & repairs: Preventive maintenance Master maintenance plan Repair of equipment
EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE & CONDEMNATION Maintenance & repairs: Preventive maintenance Master maintenance plan Repair of equipment
 PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE • Purchase with warranty & spares. • Safeguard the electronic equipments with: (as per guidelines) • Voltage stabilizer, UPS • Automatic switch over generator • Requirement of electricity, water, space, atmospheric conditions, etc. Must be taken into consideration • Well equipped maintenance cell must be available • All equipment must be operated as per instructions with trained staff • Maintenance cell • Communications between maintenance cell & suppliers of the equipment. • Follow-up of maintenance & repair services • Repair of equipment • Outside agencies • In-house facility
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE • Purchase with warranty & spares. • Safeguard the electronic equipments with: (as per guidelines) • Voltage stabilizer, UPS • Automatic switch over generator • Requirement of electricity, water, space, atmospheric conditions, etc. Must be taken into consideration • Well equipped maintenance cell must be available • All equipment must be operated as per instructions with trained staff • Maintenance cell • Communications between maintenance cell & suppliers of the equipment. • Follow-up of maintenance & repair services • Repair of equipment • Outside agencies • In-house facility
 DISPOSAL 1. Circulate to other units, where it is needed 2. Return to the vendor, if willing to accept 3. Sell to agencies, scrap dealers, etc 4. Auction 5. Local destruction
DISPOSAL 1. Circulate to other units, where it is needed 2. Return to the vendor, if willing to accept 3. Sell to agencies, scrap dealers, etc 4. Auction 5. Local destruction
 Material handling system q Right Definition : Material handling uses the right method to provide the right amount of the right material at the right place, at the right time, in the right sequence, in the right position, in the right condition, and at the right cost. 19 July 2012 KLE College of Pharmacy, Nipani. 33
Material handling system q Right Definition : Material handling uses the right method to provide the right amount of the right material at the right place, at the right time, in the right sequence, in the right position, in the right condition, and at the right cost. 19 July 2012 KLE College of Pharmacy, Nipani. 33
 Value Analysis Defined… • Value Analysis is defined as a cross-functional objective evaluation used to improve and analyze the value of a product, system or service. The overriding goal of a Value Analysis program is to decrease cost while improving performance and/or quality. • Value Analysis is effective because it is the analysis of both function and cost.
Value Analysis Defined… • Value Analysis is defined as a cross-functional objective evaluation used to improve and analyze the value of a product, system or service. The overriding goal of a Value Analysis program is to decrease cost while improving performance and/or quality. • Value Analysis is effective because it is the analysis of both function and cost.
 Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 35
Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 35
 Materials Management n n Definition - Materials management is the planning and control of the flow of materials that are part of the inbound logistics system. Materials Management Activities (procurement, warehousing, production planning, inbound transportation, receiving, materials quality control, inventory management, and salvage and scrap disposal) Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 36
Materials Management n n Definition - Materials management is the planning and control of the flow of materials that are part of the inbound logistics system. Materials Management Activities (procurement, warehousing, production planning, inbound transportation, receiving, materials quality control, inventory management, and salvage and scrap disposal) Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 36
 Materials Management: 1. Procurement n n Buying goods and services for a firm, a process of obtaining goods and services for the firm Importance n Contributes to the competitive advantage of the firm n Significant portion of the logistics costs Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 37
Materials Management: 1. Procurement n n Buying goods and services for a firm, a process of obtaining goods and services for the firm Importance n Contributes to the competitive advantage of the firm n Significant portion of the logistics costs Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 37
 Materials Management: 1. Procurement n Definition of Procurement 12 Activities 1. Identify or reevaluate needs 2. Define and evaluate user requirements 3. Decide whether to make or buy 4. Identify the type of purchase 5. Conduct a market analysis 6. Identify all possible suppliers Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 38
Materials Management: 1. Procurement n Definition of Procurement 12 Activities 1. Identify or reevaluate needs 2. Define and evaluate user requirements 3. Decide whether to make or buy 4. Identify the type of purchase 5. Conduct a market analysis 6. Identify all possible suppliers Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 38
 Materials Management: 1. Procurement n Definition of Procurement Activities… 8. Prescreen all possible sources 9. Evaluate the remaining supplier base 10. Choose a supplier 11. Receive delivery of the product or service 12. Make a post purchase performance evaluation Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 39
Materials Management: 1. Procurement n Definition of Procurement Activities… 8. Prescreen all possible sources 9. Evaluate the remaining supplier base 10. Choose a supplier 11. Receive delivery of the product or service 12. Make a post purchase performance evaluation Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 39
 Materials Management: 2. Importance of Item and Service Purchased n Products and services purchased by a company are not all the same. Some are more important than others and require greater procurement attention. Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 40
Materials Management: 2. Importance of Item and Service Purchased n Products and services purchased by a company are not all the same. Some are more important than others and require greater procurement attention. Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 40
 Materials Management: 2. Managing the Procurement Process in 4 Steps n 1. Determine the type of purchase New purchase n Straight rebuy n Modified rebuy n Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 41
Materials Management: 2. Managing the Procurement Process in 4 Steps n 1. Determine the type of purchase New purchase n Straight rebuy n Modified rebuy n Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 41
 Materials Management: 2. Managing the Procurement Process in 4 Steps n 2. Identify levels of investment n n Determine the necessary levels of investment of time and information. The more complex the purchase, the more time needs to be spent and more information needs to be gathered to get it right the first time. Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 42
Materials Management: 2. Managing the Procurement Process in 4 Steps n 2. Identify levels of investment n n Determine the necessary levels of investment of time and information. The more complex the purchase, the more time needs to be spent and more information needs to be gathered to get it right the first time. Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 42
 Materials Management: Managing the Procurement Process in 4 Steps n n 3. Perform the procurement process n Do those activities that are necessary to effectively make a purchase and satisfy the user’s requirements. 4. Evaluate the effectiveness of the procurement process n Were the user’s needs satisfied? Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 43
Materials Management: Managing the Procurement Process in 4 Steps n n 3. Perform the procurement process n Do those activities that are necessary to effectively make a purchase and satisfy the user’s requirements. 4. Evaluate the effectiveness of the procurement process n Were the user’s needs satisfied? Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 43
 Materials Management: 2. Managing the Procurement Process n Supplier/Vendor Evaluation and Relationships n Maintaining a healthy vendor relationship is a critical part of a successful supply chain. n Developing a true partnership relationship with a firm’s vendors. n TQM begins with the vendors. Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 44
Materials Management: 2. Managing the Procurement Process n Supplier/Vendor Evaluation and Relationships n Maintaining a healthy vendor relationship is a critical part of a successful supply chain. n Developing a true partnership relationship with a firm’s vendors. n TQM begins with the vendors. Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 44
 Materials Management: 2. Managing the Procurement Process n Vendor Selection Criteria 1. Quality 2. Reliability 3. Capability 4. Financial 5. Vendor Location Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 45
Materials Management: 2. Managing the Procurement Process n Vendor Selection Criteria 1. Quality 2. Reliability 3. Capability 4. Financial 5. Vendor Location Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 45
 Materials Management: 4. Other Materials Management 5 Activities 1. Warehousing n Type of facilities required 2. Production Planning and Control n Coordinating product supply with product demand (such as open air …Chapt 8) (forecasting, see Figure 4 -7) Chapter 4 3. Transportation n Vendor control n Modal choice n Rush shipments n Inspection n Damage claims Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. (rail, water. . ) 46
Materials Management: 4. Other Materials Management 5 Activities 1. Warehousing n Type of facilities required 2. Production Planning and Control n Coordinating product supply with product demand (such as open air …Chapt 8) (forecasting, see Figure 4 -7) Chapter 4 3. Transportation n Vendor control n Modal choice n Rush shipments n Inspection n Damage claims Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. (rail, water. . ) 46
 Materials Management: Other Materials Management Activities n 4. Quality Control n Quality standards n did customer receive what was ordered? n Sample inspection n statistical QC from vendor to assure 100% quality Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 47
Materials Management: Other Materials Management Activities n 4. Quality Control n Quality standards n did customer receive what was ordered? n Sample inspection n statistical QC from vendor to assure 100% quality Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 47
 Materials Management: Other Materials Management Activities n 5. Salvage and Scrap Disposal n Value of scrap may be income to the firm. n Disposal must adhere to environmental regulations. Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 48
Materials Management: Other Materials Management Activities n 5. Salvage and Scrap Disposal n Value of scrap may be income to the firm. n Disposal must adhere to environmental regulations. Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 48
 Electronic Procurement n Disadvantages n Security of electronic messages n Lack of face-to-face contact Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 49
Electronic Procurement n Disadvantages n Security of electronic messages n Lack of face-to-face contact Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 49
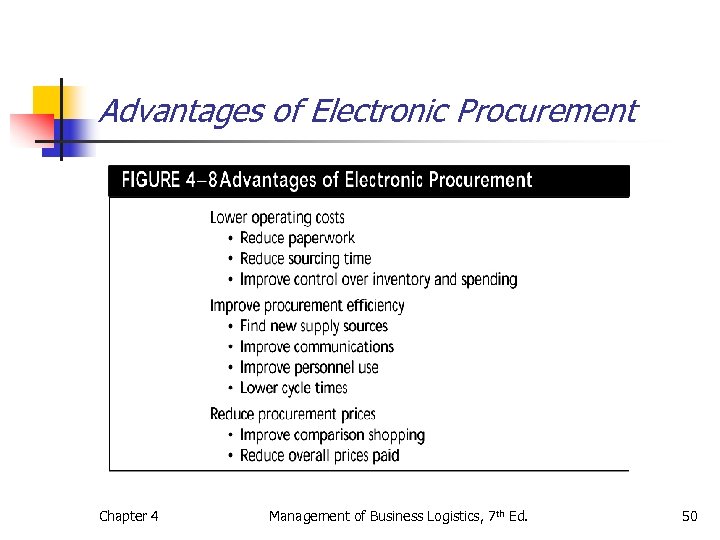 Advantages of Electronic Procurement Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 50
Advantages of Electronic Procurement Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 50
 GHS Pictograms
GHS Pictograms
 Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 52
Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 52
 Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 53
Chapter 4 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 53
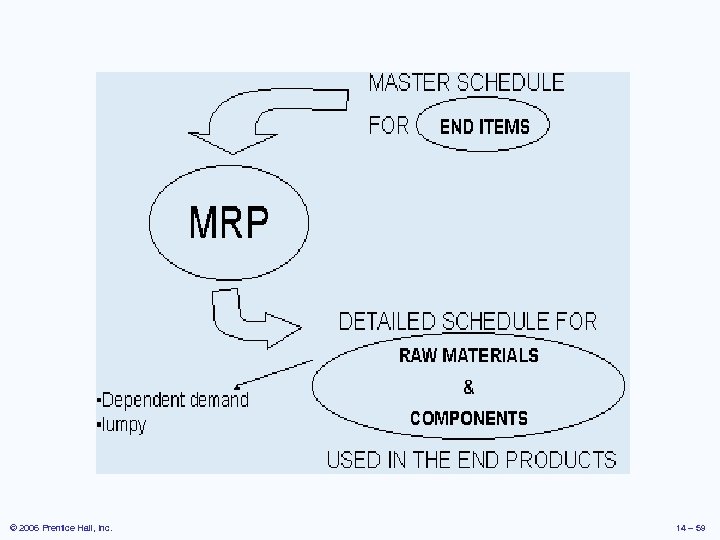
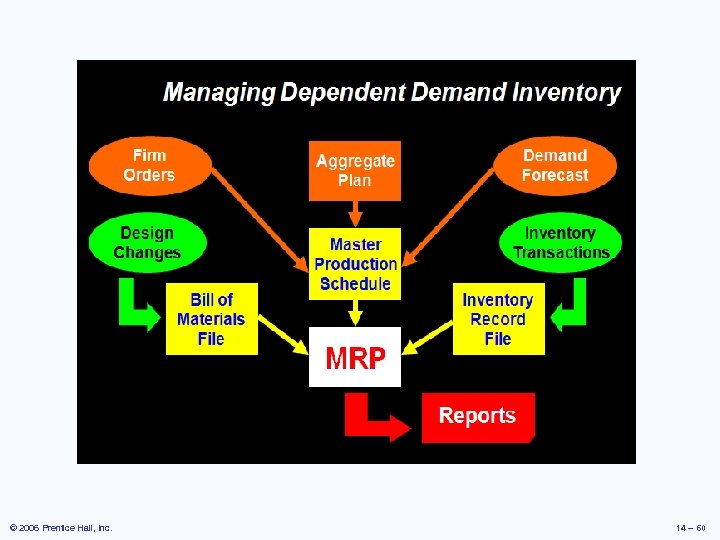
 Master Production Schedule (MPS) þ þ Specifies what is to be made and when Must be in accordance with the aggregate production plan þ Aggregate production plan sets the overall level of output in broad terms þ As the process moves from planning to execution, each step must be tested for feasibility þ The MPS is the result of the production planning process © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 54
Master Production Schedule (MPS) þ þ Specifies what is to be made and when Must be in accordance with the aggregate production plan þ Aggregate production plan sets the overall level of output in broad terms þ As the process moves from planning to execution, each step must be tested for feasibility þ The MPS is the result of the production planning process © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 54
 Bills of Material þ List of components, ingredients, and materials needed to make product þ Provides product structure þ Items above given level are called parents þ Items below given level are called children © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 55
Bills of Material þ List of components, ingredients, and materials needed to make product þ Provides product structure þ Items above given level are called parents þ Items below given level are called children © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 55
 © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 56
© 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 56
 © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 57
© 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 57
 © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 58
© 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 58
 © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 59
© 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 59
 © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 60
© 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 60
 • MM – Don’t run out of material. • Understand the process from which material will pass. Initial price of material might be less but it might have to go through expensive process before that material can be used. • Value Analysis – Cost reduction by changing material. Changing material/process that can decrease the cost without compromising quality. © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 61
• MM – Don’t run out of material. • Understand the process from which material will pass. Initial price of material might be less but it might have to go through expensive process before that material can be used. • Value Analysis – Cost reduction by changing material. Changing material/process that can decrease the cost without compromising quality. © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc. 14 – 61


