83e574465d336b04574045abd979481b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 Material Management (MM) Master Data & Records EGS 5622 Enterprise Systems Integration Spring, 2018
Material Management (MM) Master Data & Records EGS 5622 Enterprise Systems Integration Spring, 2018
 MM Master Data & Records SAP MM Master Data and Records
MM Master Data & Records SAP MM Master Data and Records
 Material Data Definition Generic classification(material types) : ◦ Physical objects to buy, transform into other product (e. g. manufacture), sell, maintain other resources, or use in support for business activities. ◦ Trading goods ◦ Raw materials ◦ Semi-finished products (WIPs) ◦ Finished products ◦ Consumables (e. g. , stationery, production tools) ◦ Spare parts (for maintenance)
Material Data Definition Generic classification(material types) : ◦ Physical objects to buy, transform into other product (e. g. manufacture), sell, maintain other resources, or use in support for business activities. ◦ Trading goods ◦ Raw materials ◦ Semi-finished products (WIPs) ◦ Finished products ◦ Consumables (e. g. , stationery, production tools) ◦ Spare parts (for maintenance)
 Material Data Typical material attributes (views), by business functions: • Industry sector (All materials) • Basic (All materials) • Purchase (Procurement) • Sales (Sales) • Work scheduling (Production) • MRP (Production Planning) • Accounting (All materials) • Costing (Production)
Material Data Typical material attributes (views), by business functions: • Industry sector (All materials) • Basic (All materials) • Purchase (Procurement) • Sales (Sales) • Work scheduling (Production) • MRP (Production Planning) • Accounting (All materials) • Costing (Production)
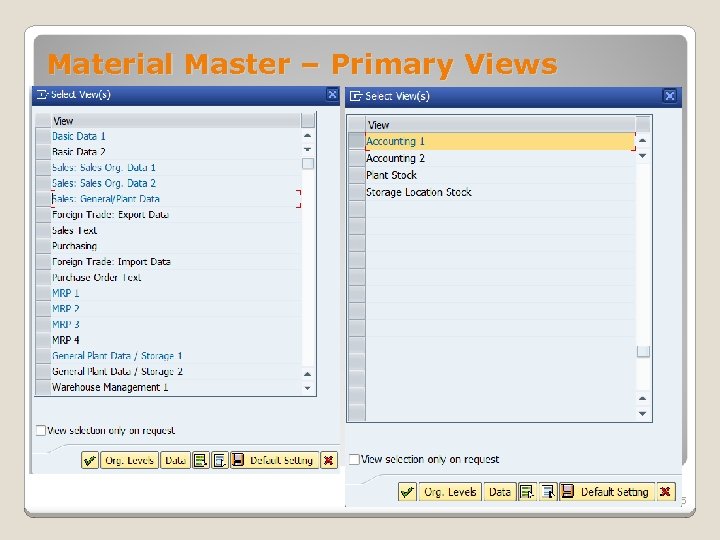 Material Master – Primary Views 5
Material Master – Primary Views 5
 MM Master Data MM
MM Master Data MM
 MM Master Data (review) Material master data are part of SAP master data, which are relatively fixed. Organizational structure must be completed before creating the master data
MM Master Data (review) Material master data are part of SAP master data, which are relatively fixed. Organizational structure must be completed before creating the master data
 Master Data records (review) Each master data record is unique Master data records are usually created or converted (from a legacy system) at the beginning of SAP deployment Material master records are maintained by various organization units such as sales, purchasing, production, & accounting, etc.
Master Data records (review) Each master data record is unique Master data records are usually created or converted (from a legacy system) at the beginning of SAP deployment Material master records are maintained by various organization units such as sales, purchasing, production, & accounting, etc.
 Material Master Data Modeling Material attributes are used to sufficiently differentiate their: • Industry sector • Material type • organizational levels • various business views
Material Master Data Modeling Material attributes are used to sufficiently differentiate their: • Industry sector • Material type • organizational levels • various business views
 Material Master – Industry Sector Industry sector is used to group records It determines industry-specific data that will appear on the master record Industry sector examples: • Chemical industry (C ), • Mechanical engineering (M), • Pharmaceuticals (P), • Plant Eng. /Construction (A), • Retail, and so on.
Material Master – Industry Sector Industry sector is used to group records It determines industry-specific data that will appear on the master record Industry sector examples: • Chemical industry (C ), • Mechanical engineering (M), • Pharmaceuticals (P), • Plant Eng. /Construction (A), • Retail, and so on.
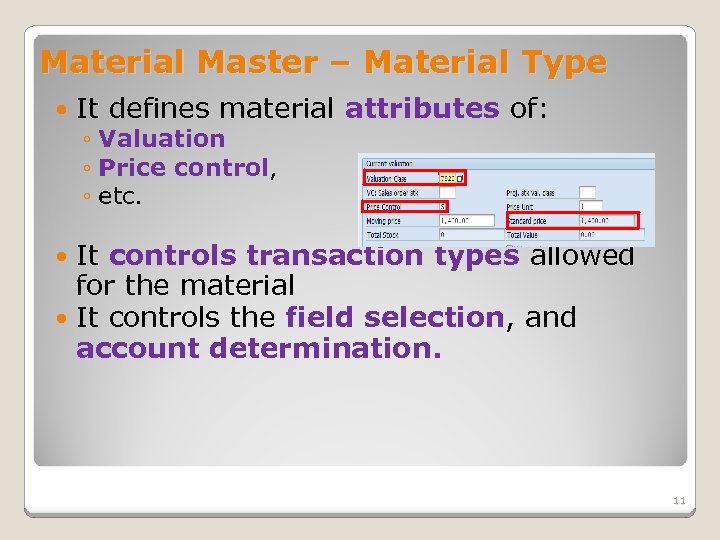 Material Master – Material Type It defines material attributes of: ◦ Valuation ◦ Price control, ◦ etc. It controls transaction types allowed for the material It controls the field selection, and account determination. 11
Material Master – Material Type It defines material attributes of: ◦ Valuation ◦ Price control, ◦ etc. It controls transaction types allowed for the material It controls the field selection, and account determination. 11
 Material Master – Material Type (continued) Material type information is used to determines: • What views are maintained • Whether internal or external procurement is allowed • Whether changes in material quantity need to be updated
Material Master – Material Type (continued) Material type information is used to determines: • What views are maintained • Whether internal or external procurement is allowed • Whether changes in material quantity need to be updated
 Material Master – Material Types (continued) SAP standard material types (used in all industries): ◦ ROH (Raw Materials) Purchased externally only No sales view ◦ HAWA (Trading Goods) Always purchased externally Sold without any change to the material No manufacturing views exist ◦ FERT (Finished Products) Are produced internally Normally no purchasing views exist ◦ HALB (Semi-Finished Products) Are produced internally Normally no purchasing and sales views exist January 2008 13
Material Master – Material Types (continued) SAP standard material types (used in all industries): ◦ ROH (Raw Materials) Purchased externally only No sales view ◦ HAWA (Trading Goods) Always purchased externally Sold without any change to the material No manufacturing views exist ◦ FERT (Finished Products) Are produced internally Normally no purchasing views exist ◦ HALB (Semi-Finished Products) Are produced internally Normally no purchasing and sales views exist January 2008 13
 Material Master – More Material Types (-continued) HIBE (Operating Supplies) VERP (Customer returnable packaging) LEER (Empty containers) KMAT(Configurable material) ERSA (Spare parts) DIEN (Services) NLAG (Non-stock, non-valuated material) UNBW (Non-valuated, stocked material) FHMI (Production resources/tools) WETT (Competitive products) PROD (Product group) IBAU (Maintenance assembly, plant maintenance)
Material Master – More Material Types (-continued) HIBE (Operating Supplies) VERP (Customer returnable packaging) LEER (Empty containers) KMAT(Configurable material) ERSA (Spare parts) DIEN (Services) NLAG (Non-stock, non-valuated material) UNBW (Non-valuated, stocked material) FHMI (Production resources/tools) WETT (Competitive products) PROD (Product group) IBAU (Maintenance assembly, plant maintenance)
 Material Master – Organization Levels Material master data can be related to all organizational levels General information of material master records defined in “Basic View”, such as description, number, base unit of measure has to be related to the highest level of organization (i. e. , at client level) Other material master records are tailored at the plant or lower levels
Material Master – Organization Levels Material master data can be related to all organizational levels General information of material master records defined in “Basic View”, such as description, number, base unit of measure has to be related to the highest level of organization (i. e. , at client level) Other material master records are tailored at the plant or lower levels
 Material Master – at Various Organization Levels (-continued) Data are visible ◦ At client level: Material number Description Units of measure ◦ At plant level: Planning data Manufacturing data Purchasing data ◦ At storage location ◦ level: Stock quantities 16
Material Master – at Various Organization Levels (-continued) Data are visible ◦ At client level: Material number Description Units of measure ◦ At plant level: Planning data Manufacturing data Purchasing data ◦ At storage location ◦ level: Stock quantities 16
 Material Master – Primary Views Basic data 1 (for all materials) Sales: sales organization data 1 (for trading and finished goods) Sales: sales organization data 2 (for trading and finished goods) Sales: general/plant data (for trading and finished goods) Purchasing (for trading and raw materials) Forecasting MRP: 1 MRP: 2 MRP: 3 Work scheduling (for finished and semi-finished goods) General Plant Data/Storage (for all materials) Accounting 1 (for all materials) Costing 1 (for raw, semi-finished, and finished goods)
Material Master – Primary Views Basic data 1 (for all materials) Sales: sales organization data 1 (for trading and finished goods) Sales: sales organization data 2 (for trading and finished goods) Sales: general/plant data (for trading and finished goods) Purchasing (for trading and raw materials) Forecasting MRP: 1 MRP: 2 MRP: 3 Work scheduling (for finished and semi-finished goods) General Plant Data/Storage (for all materials) Accounting 1 (for all materials) Costing 1 (for raw, semi-finished, and finished goods)
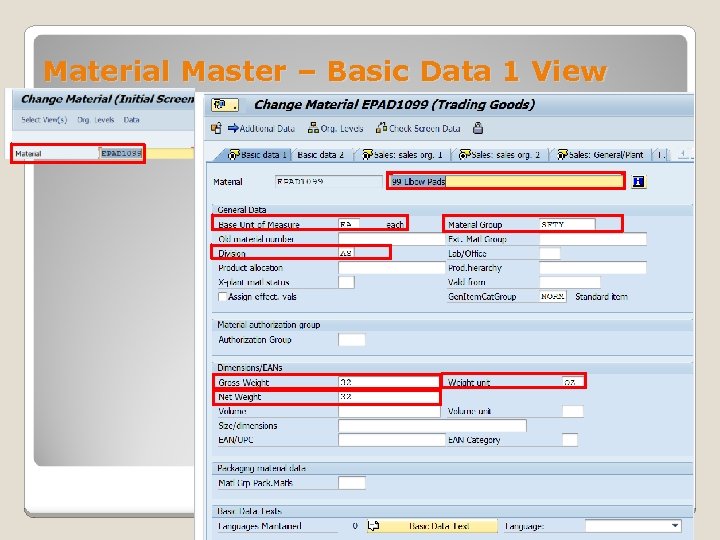
 Material Master – Basic Data 1 View General data Dimensions/EANs ◦ Material (ID) and Description ◦ Basic Unit of Measure Unit of measure in which stocks of the material are managed ◦ Material Group Used to group together several materials or services with the same attributes ◦ Division Used to determine the sales area and the business area for a material, product, or service ◦ Gross weight Used to check storage capacity in warehouse ◦ Net weight Weight excluding packaging and extras – this is needed for sales and distribution ◦ Weight Unit of Measure for weight ◦ Volume The space that the material occupies per unit of volume
Material Master – Basic Data 1 View General data Dimensions/EANs ◦ Material (ID) and Description ◦ Basic Unit of Measure Unit of measure in which stocks of the material are managed ◦ Material Group Used to group together several materials or services with the same attributes ◦ Division Used to determine the sales area and the business area for a material, product, or service ◦ Gross weight Used to check storage capacity in warehouse ◦ Net weight Weight excluding packaging and extras – this is needed for sales and distribution ◦ Weight Unit of Measure for weight ◦ Volume The space that the material occupies per unit of volume
 Material Master – Basic Data 1 View 19
Material Master – Basic Data 1 View 19
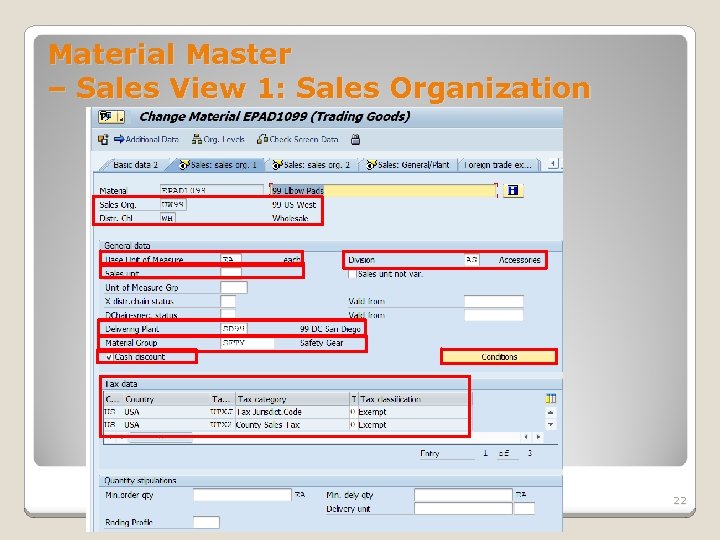
 Material Master – Sales View 1: Sales Organization General Data ◦ Base Unit of Measure The Base Unit of Measure is the unit of measure in which stocks are managed within your company. ◦ Division You may enter the Division which your product is in for sales (defaults if entered in the Basic data screen). ◦ Material Group A key that’s used to group several materials or services for analysis/reporting as well as search by match code. ◦ Sales Unit (optional) The unit of measure in which the material is sold, if left blank then uses the base unit of measure.
Material Master – Sales View 1: Sales Organization General Data ◦ Base Unit of Measure The Base Unit of Measure is the unit of measure in which stocks are managed within your company. ◦ Division You may enter the Division which your product is in for sales (defaults if entered in the Basic data screen). ◦ Material Group A key that’s used to group several materials or services for analysis/reporting as well as search by match code. ◦ Sales Unit (optional) The unit of measure in which the material is sold, if left blank then uses the base unit of measure.
 Material Master – Sales View 1: Sales Organization ◦ Delivering Plant where the material is available for sale. ◦ Cash discount Indicator used for a cash discount of the material. ◦ Conditions Pricing procedure for the material Tax Data ◦ Tax classification material The indicator used for system to determine output tax for the material when processing sales and distribution-specific documents
Material Master – Sales View 1: Sales Organization ◦ Delivering Plant where the material is available for sale. ◦ Cash discount Indicator used for a cash discount of the material. ◦ Conditions Pricing procedure for the material Tax Data ◦ Tax classification material The indicator used for system to determine output tax for the material when processing sales and distribution-specific documents
 Material Master – Sales View 1: Sales Organization 22
Material Master – Sales View 1: Sales Organization 22
 Material Master – Sales View 2: Sales Organization Grouping Terms ◦ Material Statistics Group Determine which data the system updates in the logistics information system ◦ Material Pricing Group materials to apply the same conditions ◦ Volume Rebate Group for rebate settlement. ◦ General Item Category Group Determine item categories during sales document processing. ◦ Commission Group Commission group to which the material is assigned.
Material Master – Sales View 2: Sales Organization Grouping Terms ◦ Material Statistics Group Determine which data the system updates in the logistics information system ◦ Material Pricing Group materials to apply the same conditions ◦ Volume Rebate Group for rebate settlement. ◦ General Item Category Group Determine item categories during sales document processing. ◦ Commission Group Commission group to which the material is assigned.
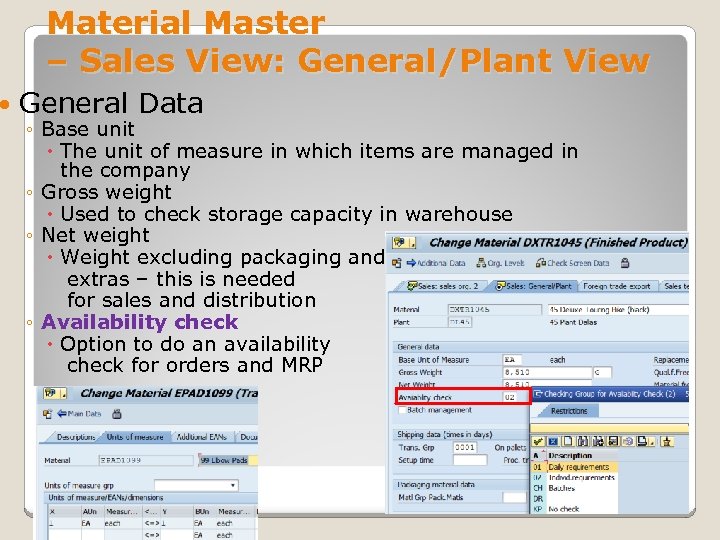 Material Master – Sales View: General/Plant View General Data ◦ Base unit The unit of measure in which items are managed in the company ◦ Gross weight Used to check storage capacity in warehouse ◦ Net weight Weight excluding packaging and extras – this is needed for sales and distribution ◦ Availability check Option to do an availability check for orders and MRP January 2008 © SAP AG - University Alliances and The Rushmore Group, LLC 2008. All rights reserved. 24
Material Master – Sales View: General/Plant View General Data ◦ Base unit The unit of measure in which items are managed in the company ◦ Gross weight Used to check storage capacity in warehouse ◦ Net weight Weight excluding packaging and extras – this is needed for sales and distribution ◦ Availability check Option to do an availability check for orders and MRP January 2008 © SAP AG - University Alliances and The Rushmore Group, LLC 2008. All rights reserved. 24
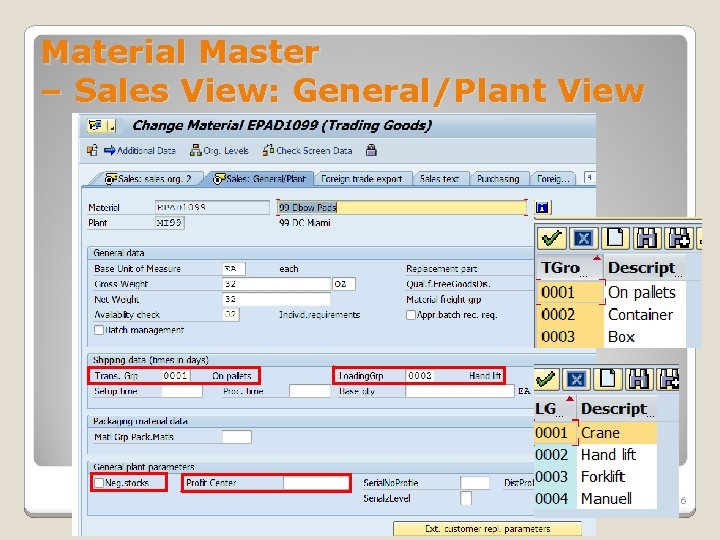
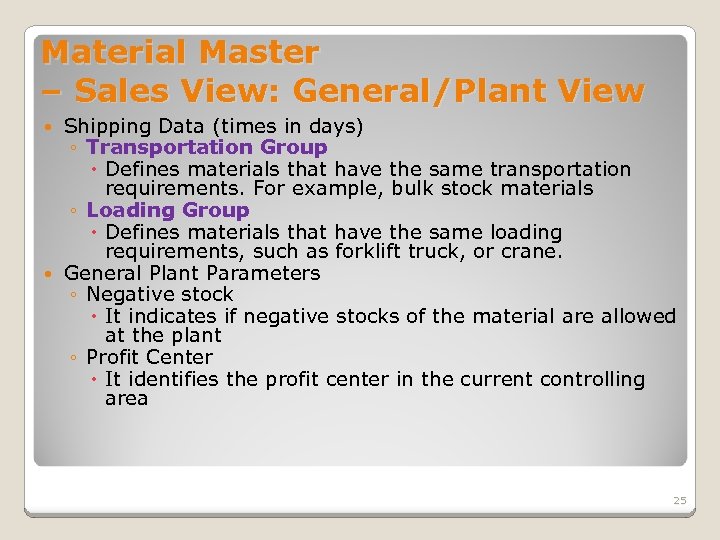 Material Master – Sales View: General/Plant View Shipping Data (times in days) ◦ Transportation Group Defines materials that have the same transportation requirements. For example, bulk stock materials ◦ Loading Group Defines materials that have the same loading requirements, such as forklift truck, or crane. General Plant Parameters ◦ Negative stock It indicates if negative stocks of the material are allowed at the plant ◦ Profit Center It identifies the profit center in the current controlling area 25
Material Master – Sales View: General/Plant View Shipping Data (times in days) ◦ Transportation Group Defines materials that have the same transportation requirements. For example, bulk stock materials ◦ Loading Group Defines materials that have the same loading requirements, such as forklift truck, or crane. General Plant Parameters ◦ Negative stock It indicates if negative stocks of the material are allowed at the plant ◦ Profit Center It identifies the profit center in the current controlling area 25
 Material Master – Sales View: General/Plant View 26
Material Master – Sales View: General/Plant View 26
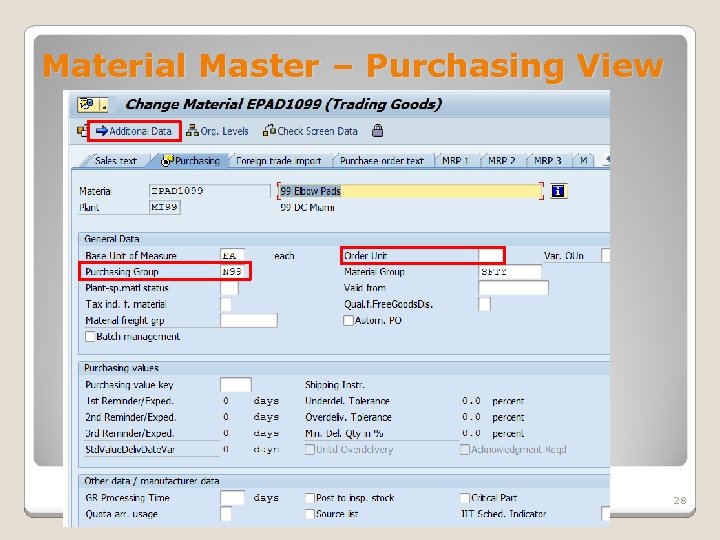
 Material Master – Purchasing View General Data • Order Unit • The unit of measure in which a company purchases the product • Purchasing Group • Key for a buyer or a group of buyers, who is/are responsible for certain purchasing activities. Purchasing Values • Purchasing Value Key • It defines the reminder days and tolerance limits for purchasing
Material Master – Purchasing View General Data • Order Unit • The unit of measure in which a company purchases the product • Purchasing Group • Key for a buyer or a group of buyers, who is/are responsible for certain purchasing activities. Purchasing Values • Purchasing Value Key • It defines the reminder days and tolerance limits for purchasing
 Material Master – Purchasing View 28
Material Master – Purchasing View 28
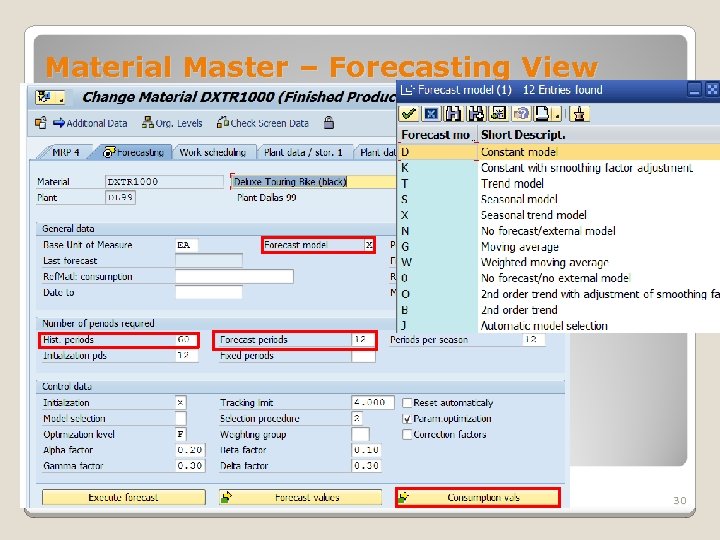
 Material Master – Forecasting View Number of Periods Required ◦ Historical Periods The number of historical values the system uses for the forecast ◦ Forecast Periods Number of period splits for which a forecast should be created Forecast Model o Used for system to calculate future requirements of the material. Consumption Values ◦ The sum of planned and unplanned consumption 29
Material Master – Forecasting View Number of Periods Required ◦ Historical Periods The number of historical values the system uses for the forecast ◦ Forecast Periods Number of period splits for which a forecast should be created Forecast Model o Used for system to calculate future requirements of the material. Consumption Values ◦ The sum of planned and unplanned consumption 29
 Material Master – Forecasting View 30
Material Master – Forecasting View 30
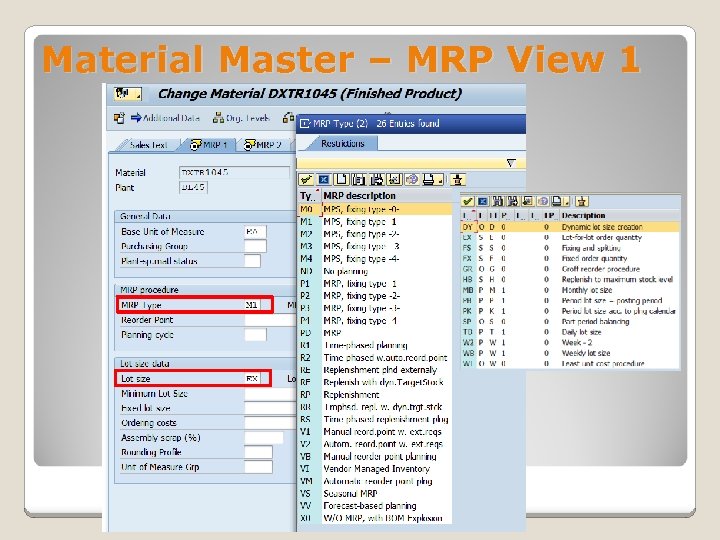
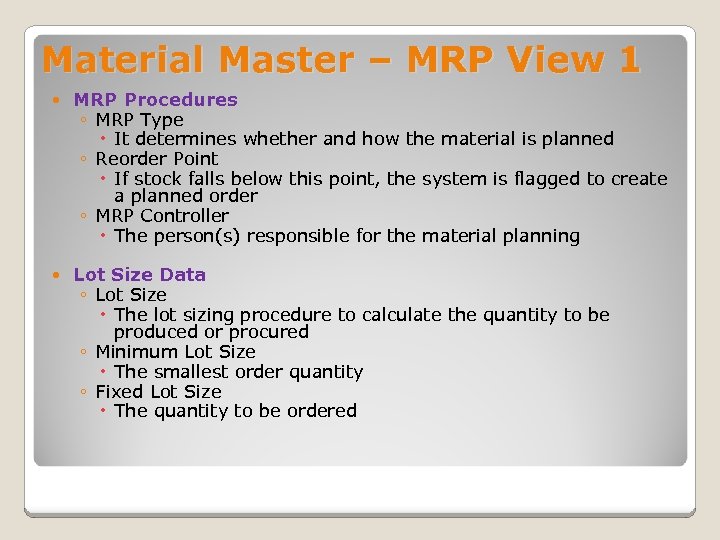 Material Master – MRP View 1 MRP Procedures ◦ MRP Type It determines whether and how the material is planned ◦ Reorder Point If stock falls below this point, the system is flagged to create a planned order ◦ MRP Controller The person(s) responsible for the material planning Lot Size Data ◦ Lot Size The lot sizing procedure to calculate the quantity to be produced or procured ◦ Minimum Lot Size The smallest order quantity ◦ Fixed Lot Size The quantity to be ordered
Material Master – MRP View 1 MRP Procedures ◦ MRP Type It determines whether and how the material is planned ◦ Reorder Point If stock falls below this point, the system is flagged to create a planned order ◦ MRP Controller The person(s) responsible for the material planning Lot Size Data ◦ Lot Size The lot sizing procedure to calculate the quantity to be produced or procured ◦ Minimum Lot Size The smallest order quantity ◦ Fixed Lot Size The quantity to be ordered
 Material Master – MRP View 1 January 2008
Material Master – MRP View 1 January 2008
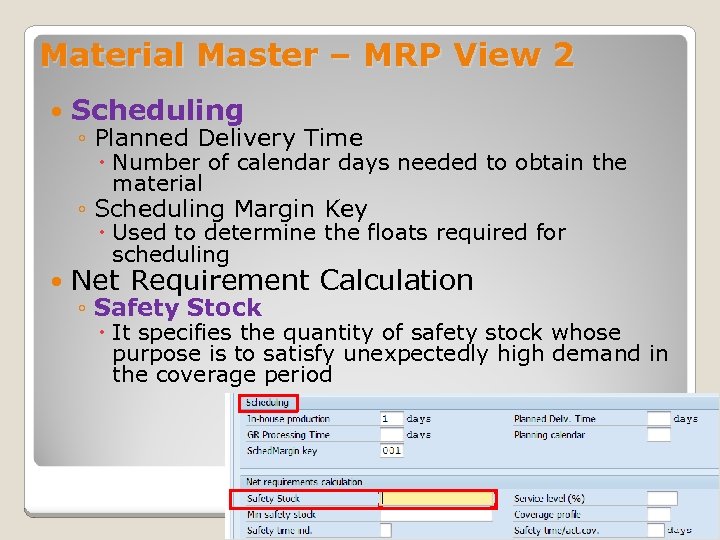 Material Master – MRP View 2 Scheduling ◦ Planned Delivery Time Number of calendar days needed to obtain the material ◦ Scheduling Margin Key Used to determine the floats required for scheduling Net Requirement Calculation ◦ Safety Stock It specifies the quantity of safety stock whose purpose is to satisfy unexpectedly high demand in the coverage period January 2008 © SAP AG - University Alliances and The Rushmore Group, LLC 2008. All rights reserved. 33
Material Master – MRP View 2 Scheduling ◦ Planned Delivery Time Number of calendar days needed to obtain the material ◦ Scheduling Margin Key Used to determine the floats required for scheduling Net Requirement Calculation ◦ Safety Stock It specifies the quantity of safety stock whose purpose is to satisfy unexpectedly high demand in the coverage period January 2008 © SAP AG - University Alliances and The Rushmore Group, LLC 2008. All rights reserved. 33
 Material Master – MRP View 3 Availability Check ◦ It specifies whether and how the system checks availability and generates requirements for materials planning
Material Master – MRP View 3 Availability Check ◦ It specifies whether and how the system checks availability and generates requirements for materials planning
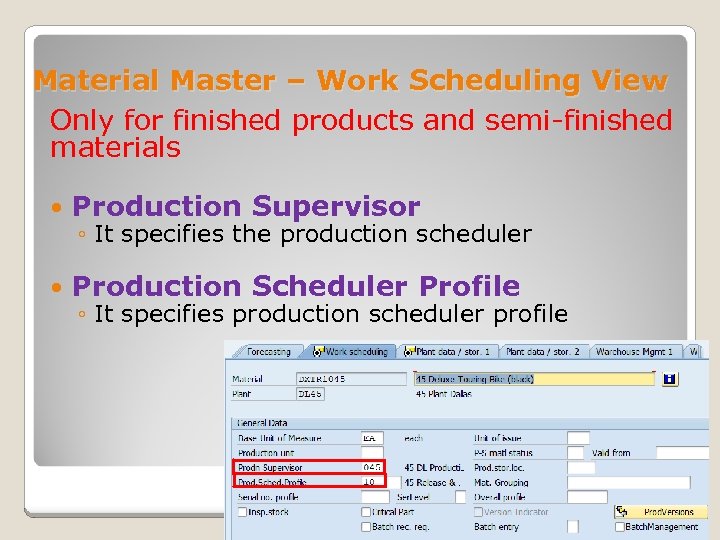 Material Master – Work Scheduling View Only for finished products and semi-finished materials Production Supervisor Production Scheduler Profile ◦ It specifies the production scheduler ◦ It specifies production scheduler profile January 2008 © SAP AG - University Alliances and The Rushmore Group, LLC 2008. All rights reserved. 35
Material Master – Work Scheduling View Only for finished products and semi-finished materials Production Supervisor Production Scheduler Profile ◦ It specifies the production scheduler ◦ It specifies production scheduler profile January 2008 © SAP AG - University Alliances and The Rushmore Group, LLC 2008. All rights reserved. 35
 Material Master – Plant Data/Storage View 1 General Data ◦ Container Requirements Defines which type of container the material must be stored and shipped in ◦ Storage Conditions Defines the conditions on how a material must be stored or warehoused Shelf Life Data ◦ Minimum remaining shelf life Minimum time the material must keep upon goods receipt for the goods receipt to be accepted by the system ◦ Total Shelf Life Period of time the material will keep in total, from the date of production or receipt to the shelf life expiration date
Material Master – Plant Data/Storage View 1 General Data ◦ Container Requirements Defines which type of container the material must be stored and shipped in ◦ Storage Conditions Defines the conditions on how a material must be stored or warehoused Shelf Life Data ◦ Minimum remaining shelf life Minimum time the material must keep upon goods receipt for the goods receipt to be accepted by the system ◦ Total Shelf Life Period of time the material will keep in total, from the date of production or receipt to the shelf life expiration date
 Material Master – Accounting View 1 Current Valuation ◦ Valuation Class • It allows the stock values of materials of the same material type to be posted to different G/L accounts. • It allows the stock values of materials of different material types to be posted to the same G/L account. • It determines together with other factors the G/L accounts updated for a valuation-relevant transaction (Material Movements) ◦ Price Unit • Number of units to which the price refers
Material Master – Accounting View 1 Current Valuation ◦ Valuation Class • It allows the stock values of materials of the same material type to be posted to different G/L accounts. • It allows the stock values of materials of different material types to be posted to the same G/L account. • It determines together with other factors the G/L accounts updated for a valuation-relevant transaction (Material Movements) ◦ Price Unit • Number of units to which the price refers
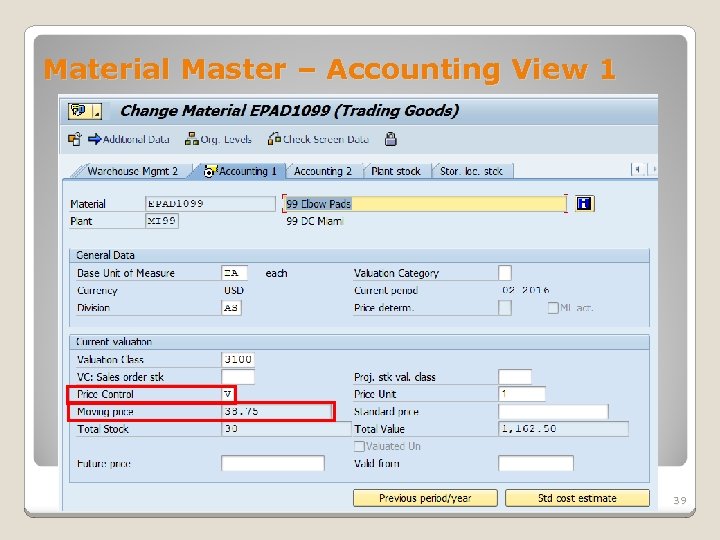
 Material Master – Accounting View 1 Current Valuation ◦ Price Control Indicator • The price control used to valuate the stock of a material (e. g. , Standard or Moving Average Price) ◦ Standard Price • The valuation of material stocks at standard prices means that all goods movements are valuated at the same price over an extended period ◦ Moving Average Price • The system calculates the moving average price automatically by dividing the material value in the stock account by the total of all storage location stocks in the plant concerned
Material Master – Accounting View 1 Current Valuation ◦ Price Control Indicator • The price control used to valuate the stock of a material (e. g. , Standard or Moving Average Price) ◦ Standard Price • The valuation of material stocks at standard prices means that all goods movements are valuated at the same price over an extended period ◦ Moving Average Price • The system calculates the moving average price automatically by dividing the material value in the stock account by the total of all storage location stocks in the plant concerned
 Material Master – Accounting View 1 39
Material Master – Accounting View 1 39
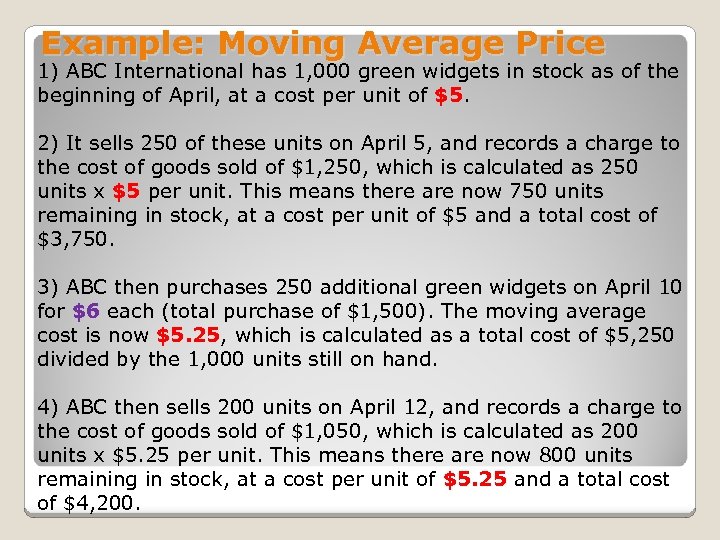 Example: Moving Average Price 1) ABC International has 1, 000 green widgets in stock as of the beginning of April, at a cost per unit of $5. 2) It sells 250 of these units on April 5, and records a charge to the cost of goods sold of $1, 250, which is calculated as 250 units x $5 per unit. This means there are now 750 units remaining in stock, at a cost per unit of $5 and a total cost of $3, 750. 3) ABC then purchases 250 additional green widgets on April 10 for $6 each (total purchase of $1, 500). The moving average cost is now $5. 25, which is calculated as a total cost of $5, 250 divided by the 1, 000 units still on hand. 4) ABC then sells 200 units on April 12, and records a charge to the cost of goods sold of $1, 050, which is calculated as 200 units x $5. 25 per unit. This means there are now 800 units remaining in stock, at a cost per unit of $5. 25 and a total cost of $4, 200.
Example: Moving Average Price 1) ABC International has 1, 000 green widgets in stock as of the beginning of April, at a cost per unit of $5. 2) It sells 250 of these units on April 5, and records a charge to the cost of goods sold of $1, 250, which is calculated as 250 units x $5 per unit. This means there are now 750 units remaining in stock, at a cost per unit of $5 and a total cost of $3, 750. 3) ABC then purchases 250 additional green widgets on April 10 for $6 each (total purchase of $1, 500). The moving average cost is now $5. 25, which is calculated as a total cost of $5, 250 divided by the 1, 000 units still on hand. 4) ABC then sells 200 units on April 12, and records a charge to the cost of goods sold of $1, 050, which is calculated as 200 units x $5. 25 per unit. This means there are now 800 units remaining in stock, at a cost per unit of $5. 25 and a total cost of $4, 200.
 Material Master – Costing 1 View General Data ◦ Overhead Group It assigns same overhead rate to group Material is costed with quantity structure ◦ indicator determines whether the material is costed using costing with or without a quantity structure. Material-related origin ◦ If this indicator is set, the material number will be written to the cost element itemization in the Controlling module. 41
Material Master – Costing 1 View General Data ◦ Overhead Group It assigns same overhead rate to group Material is costed with quantity structure ◦ indicator determines whether the material is costed using costing with or without a quantity structure. Material-related origin ◦ If this indicator is set, the material number will be written to the cost element itemization in the Controlling module. 41
 Material Master – Costing View For raw, semi- and finished materials 42
Material Master – Costing View For raw, semi- and finished materials 42
 GBI MM Master Data and Records
GBI MM Master Data and Records
 Trading Goods Material Type Materials Views required HAWA EPAD 10## Basic data 1 (Trading Goods) KPAD 10## Purchasing OHMT 10## MRP 1, 2, 3 (optional) RHMT 10## General Plant data/Storage 1 RKIT 10## Accounting 1 Sales: Sales Org. Dta 1 Sales: Sales Org. Data 2 Sales: General/Plant data Valuation class 3100
Trading Goods Material Type Materials Views required HAWA EPAD 10## Basic data 1 (Trading Goods) KPAD 10## Purchasing OHMT 10## MRP 1, 2, 3 (optional) RHMT 10## General Plant data/Storage 1 RKIT 10## Accounting 1 Sales: Sales Org. Dta 1 Sales: Sales Org. Data 2 Sales: General/Plant data Valuation class 3100
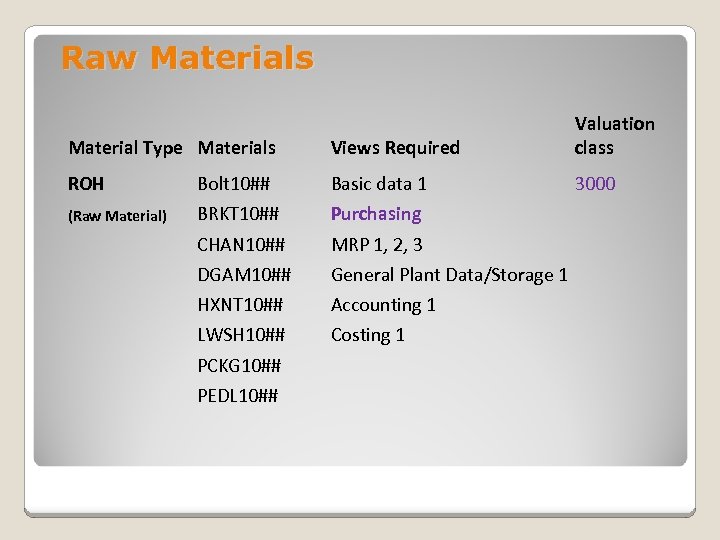 Raw Materials Material Type Materials Views Required Valuation class ROH Bolt 10## Basic data 1 3000 (Raw Material) BRKT 10## Purchasing CHAN 10## MRP 1, 2, 3 DGAM 10## General Plant Data/Storage 1 HXNT 10## Accounting 1 LWSH 10## Costing 1 PCKG 10## PEDL 10##
Raw Materials Material Type Materials Views Required Valuation class ROH Bolt 10## Basic data 1 3000 (Raw Material) BRKT 10## Purchasing CHAN 10## MRP 1, 2, 3 DGAM 10## General Plant Data/Storage 1 HXNT 10## Accounting 1 LWSH 10## Costing 1 PCKG 10## PEDL 10##
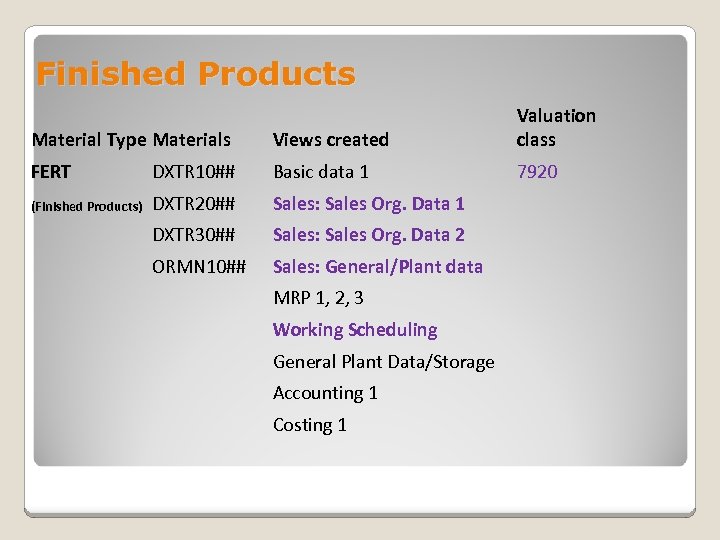 Finished Products Material Type Materials Views created Valuation class FERT DXTR 10## Basic data 1 7920 (Finished Products) DXTR 20## Sales: Sales Org. Data 1 DXTR 30## Sales: Sales Org. Data 2 ORMN 10## Sales: General/Plant data MRP 1, 2, 3 Working Scheduling General Plant Data/Storage Accounting 1 Costing 1
Finished Products Material Type Materials Views created Valuation class FERT DXTR 10## Basic data 1 7920 (Finished Products) DXTR 20## Sales: Sales Org. Data 1 DXTR 30## Sales: Sales Org. Data 2 ORMN 10## Sales: General/Plant data MRP 1, 2, 3 Working Scheduling General Plant Data/Storage Accounting 1 Costing 1
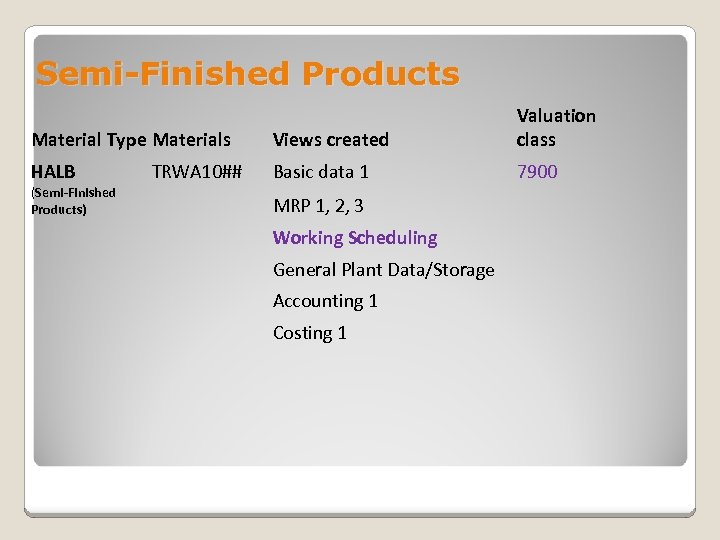 Semi-Finished Products Material Type Materials Views created Valuation class HALB Basic data 1 7900 (Semi-Finished Products) TRWA 10## MRP 1, 2, 3 Working Scheduling General Plant Data/Storage Accounting 1 Costing 1
Semi-Finished Products Material Type Materials Views created Valuation class HALB Basic data 1 7900 (Semi-Finished Products) TRWA 10## MRP 1, 2, 3 Working Scheduling General Plant Data/Storage Accounting 1 Costing 1
 Exercises: (Due date 1/31/2018) 1. Create primary cost elements 2. Create secondary cost elements 3. Create cost element groups 4. Open period for variant 5. Close period 6. Review accounts 7. Display balance I 8. Enter G/L account posting 9. Display balance II 10. Determine tax version 11. Define tax accounts 12. Configure automatic posting for materials 13. Maintain default values for tax codes 14. Set tolerance limits for price variance 15. Set tolerance limits for goods receipt 16. Set tolerance limits for invoice
Exercises: (Due date 1/31/2018) 1. Create primary cost elements 2. Create secondary cost elements 3. Create cost element groups 4. Open period for variant 5. Close period 6. Review accounts 7. Display balance I 8. Enter G/L account posting 9. Display balance II 10. Determine tax version 11. Define tax accounts 12. Configure automatic posting for materials 13. Maintain default values for tax codes 14. Set tolerance limits for price variance 15. Set tolerance limits for goods receipt 16. Set tolerance limits for invoice
 Exercises: 17. Define tolerances (vendors) 18. Default values for inventory 19. Default values foe plants 20. Define attributes of material types 21. Create trading goods
Exercises: 17. Define tolerances (vendors) 18. Default values for inventory 19. Default values foe plants 20. Define attributes of material types 21. Create trading goods


