cc85e5323c3ca53a15a96761cec3ee83.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Matakuliah Tahun Versi : T 0604 -Pengantar Teknologi Informasi : 2008 : 2. 0/0. 0 Pertemuan 18 Basisdata (Databases) (Lanjutan) Sumber: Chapter 8. Databases & Information Systems: Digital engines for today’s economy, p. 407 Williams, B. K, Stacy C. Sawyer (2007). Using Information Technology: A Practical Introduction to Computers & Communications. Seventh Edition, Mc. Graw-Hill, New York. ISBN-13: 978 -0 -07 -110768 -6 1
Matakuliah Tahun Versi : T 0604 -Pengantar Teknologi Informasi : 2008 : 2. 0/0. 0 Pertemuan 18 Basisdata (Databases) (Lanjutan) Sumber: Chapter 8. Databases & Information Systems: Digital engines for today’s economy, p. 407 Williams, B. K, Stacy C. Sawyer (2007). Using Information Technology: A Practical Introduction to Computers & Communications. Seventh Edition, Mc. Graw-Hill, New York. ISBN-13: 978 -0 -07 -110768 -6 1
 Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • menjelaskan: jenis-jenis model basisdata, manfaat dan cara kerja data mining; etika dalam penggunaan basisdata (C 2) 2
Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • menjelaskan: jenis-jenis model basisdata, manfaat dan cara kerja data mining; etika dalam penggunaan basisdata (C 2) 2
 Outline Materi • Database Models • Data Mining • The Ethics of Using Databases 3
Outline Materi • Database Models • Data Mining • The Ethics of Using Databases 3
 Database Models • Fields or records are arranged in a family tree, with child records subordinate to parent or higher-level records • Like a hierarchical database, but each child • Network database record can have more than one parent record • Relates, or connects, data in different files • Relational database through the use of a key, or common data element • Uses objects (software written in small, • Object-oriented reusable chunks) as elements within database files • Models data as facts, dimensions, or • Multidimensional numerical measures for use in the interactive analysis of large amounts of database • Hierarchical database 8 -4
Database Models • Fields or records are arranged in a family tree, with child records subordinate to parent or higher-level records • Like a hierarchical database, but each child • Network database record can have more than one parent record • Relates, or connects, data in different files • Relational database through the use of a key, or common data element • Uses objects (software written in small, • Object-oriented reusable chunks) as elements within database files • Models data as facts, dimensions, or • Multidimensional numerical measures for use in the interactive analysis of large amounts of database • Hierarchical database 8 -4
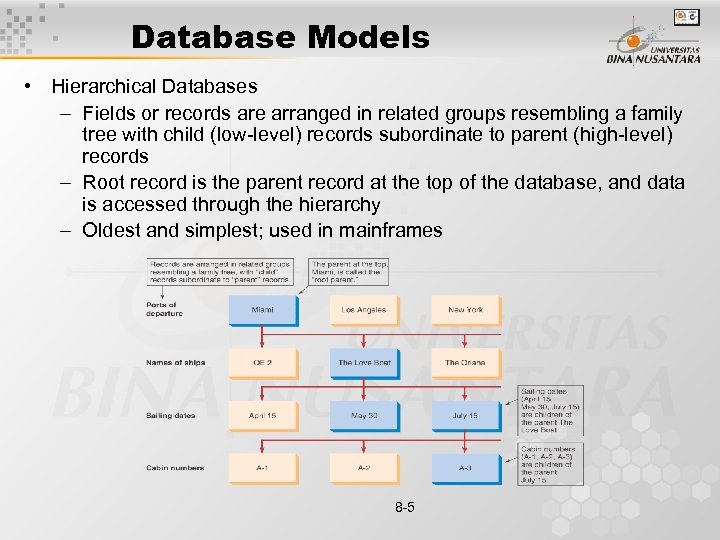 Database Models • Hierarchical Databases – Fields or records are arranged in related groups resembling a family tree with child (low-level) records subordinate to parent (high-level) records – Root record is the parent record at the top of the database, and data is accessed through the hierarchy – Oldest and simplest; used in mainframes 8 -5
Database Models • Hierarchical Databases – Fields or records are arranged in related groups resembling a family tree with child (low-level) records subordinate to parent (high-level) records – Root record is the parent record at the top of the database, and data is accessed through the hierarchy – Oldest and simplest; used in mainframes 8 -5
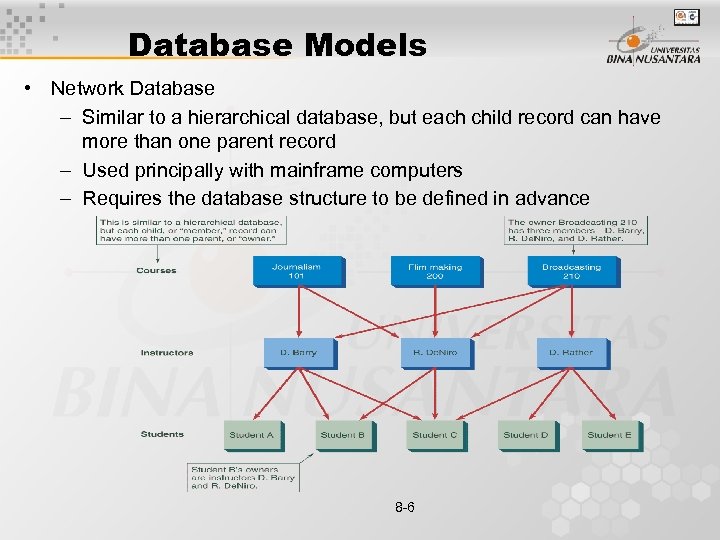 Database Models • Network Database – Similar to a hierarchical database, but each child record can have more than one parent record – Used principally with mainframe computers – Requires the database structure to be defined in advance 8 -6
Database Models • Network Database – Similar to a hierarchical database, but each child record can have more than one parent record – Used principally with mainframe computers – Requires the database structure to be defined in advance 8 -6
 Database Models • Relational Database – Relates or connects data in different files through the use of a key, or common data element – Examples are Oracle, Informix, Sybase – Data exists independently of how it is physically stored – Users don’t need to know data structure to use the database – Uses SQL (structured query language) to create, modify, maintain, and query the data – Query by Example uses sample records or forms to allow users to define the qualifications for choosing records 8 -7
Database Models • Relational Database – Relates or connects data in different files through the use of a key, or common data element – Examples are Oracle, Informix, Sybase – Data exists independently of how it is physically stored – Users don’t need to know data structure to use the database – Uses SQL (structured query language) to create, modify, maintain, and query the data – Query by Example uses sample records or forms to allow users to define the qualifications for choosing records 8 -7
 Database Models • Object-oriented Databases – Use “objects”, software written in small, manageable chunks, as elements within data files – An object consists of • Data in any form, including audio, graphics, and video • Instructions on the action to be taken with the data – Examples include Fast. Objects, Gem. Stone, Objectivity DB, Jasmine Object Database, and KE Express – Types include • Web database • Hypermedia database 8 -8
Database Models • Object-oriented Databases – Use “objects”, software written in small, manageable chunks, as elements within data files – An object consists of • Data in any form, including audio, graphics, and video • Instructions on the action to be taken with the data – Examples include Fast. Objects, Gem. Stone, Objectivity DB, Jasmine Object Database, and KE Express – Types include • Web database • Hypermedia database 8 -8
 Database Models • Multidimensional Database – Models data as facts, dimensions, or numerical answers for use in the interactive analysis of large amounts of data for decisionmaking purposes – Allows users to ask questions in colloquial English – Use OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) software to provide answers to complex database queries 8 -9
Database Models • Multidimensional Database – Models data as facts, dimensions, or numerical answers for use in the interactive analysis of large amounts of data for decisionmaking purposes – Allows users to ask questions in colloquial English – Use OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) software to provide answers to complex database queries 8 -9
 Data Mining • Is the computer-assisted process of sifting through and analyzing vast amounts of data to extract hidden patterns and meaning and to discover new knowledge • Data is fed into a Data Warehouse through the following steps – – Identify and connect to data sources Perform data fusion and data cleansing Obtain both data and meta-data (data about the data) Transport data and meta-data to the Data Warehouse • Data Warehouse is a special database that shows detailed and summary data from multiple sources 8 -10
Data Mining • Is the computer-assisted process of sifting through and analyzing vast amounts of data to extract hidden patterns and meaning and to discover new knowledge • Data is fed into a Data Warehouse through the following steps – – Identify and connect to data sources Perform data fusion and data cleansing Obtain both data and meta-data (data about the data) Transport data and meta-data to the Data Warehouse • Data Warehouse is a special database that shows detailed and summary data from multiple sources 8 -10
 Data Mining • Methods for searching for patterns in the data and interpreting the results – Regression analysis • Develops a formula to fit patterns in the data that has been extracted • Formula is applied to other data sets to predict future trends – Classification analysis • A statistical pattern recognition process that is applied to data sets with more than just numerical data 8 -11
Data Mining • Methods for searching for patterns in the data and interpreting the results – Regression analysis • Develops a formula to fit patterns in the data that has been extracted • Formula is applied to other data sets to predict future trends – Classification analysis • A statistical pattern recognition process that is applied to data sets with more than just numerical data 8 -11
 Data Mining • Applications include – A phone company identifying customers with large bills, who were really small businesses trying to pay the cheaper residential rate – A coach in the Gymnastics Federation used it to discover what long-term factors contributed to athletes’ performance – Retail stores use it to predict future purchase patterns to help them choose which products to stock for the future 8 -12
Data Mining • Applications include – A phone company identifying customers with large bills, who were really small businesses trying to pay the cheaper residential rate – A coach in the Gymnastics Federation used it to discover what long-term factors contributed to athletes’ performance – Retail stores use it to predict future purchase patterns to help them choose which products to stock for the future 8 -12
 The Ethics of Using Databases • Identity Theft concerns – A crime in which thieves hijack your identity and use your good credit rating to get cash, take out loans, order credit cards, and buy things in your name • Privacy concerns – Name migration: getting endless junk mail and telemarketing calls – Résumé rustling and online snooping – Government prying and spying Discussion Question: Has any one had their identity stolen? How long did it take you to get it straightened out? 8 -13
The Ethics of Using Databases • Identity Theft concerns – A crime in which thieves hijack your identity and use your good credit rating to get cash, take out loans, order credit cards, and buy things in your name • Privacy concerns – Name migration: getting endless junk mail and telemarketing calls – Résumé rustling and online snooping – Government prying and spying Discussion Question: Has any one had their identity stolen? How long did it take you to get it straightened out? 8 -13
 Kesimpulan 14
Kesimpulan 14


