54c760f7d2ae3209da01735ca028dcb3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Masterclasses - best practice with authentic data from particle physics Michael Kobel TU Dresden kobel@physik. tu-dresden. de

What is a particle physics masterclass? • As in a masterclass in the arts, students work with an expert. • Expert = particle physicist. • Instead of, say, a violin, the subject is particle physics data analysis. Kickoff: Discover the Cosmos 02. 09. 2011 CERN 2

Motivation • Idea from UK 1996 (R. Barlow et al. ) – Students (16 -19 year-olds) spend 1 day with researchers – Listen to scientists‘ introduction to particle physics – Work like and with scientists („masters“): measurements with real particle physics data • Why Masterclasses? – Make modern particle physics data available to students – Let students explore fundamental forces and building blocks of nature – Demonstrate the scientific research process – Stimulate interest in science (proven in refereed evaluation Physics Education 42 (2007) 636 -644 )

Two Formats 1. International masterclasses – – Organized by E/IPPOG since 2005 Once / year, daily for 4 -5 weeks Students come to institutes worldwide Video Conference at the end of the day 2. Local masterclasses at schools – – National activities (Germany, I 2 U 2, etc) Netzwerk Teilchenwelt (Germany): > 100 masterclasses / year Researchers bring data to schools Also stand-alone by teacher possible Kickoff: Discover the Cosmos 02. 09. 2011 CERN 4

Participation I/EPPOG international masterclasses US (Quarknet) adding -Canada -Columbia -China -Japan Brazil South Africa Israel 5

Introductory Talk(s) Measurements Collection of Results Interpretation

Video conference (int. Masterclass only) – – 16: 30 – 17: 30 2 Moderators at CERN 5 institutes Agenda • • • Introduction What´s going on at the LHC? Combination of results Student Q & A Discussion Quiz with prizes Kickoff: Discover the Cosmos 02. 09. 2011 CERN 7
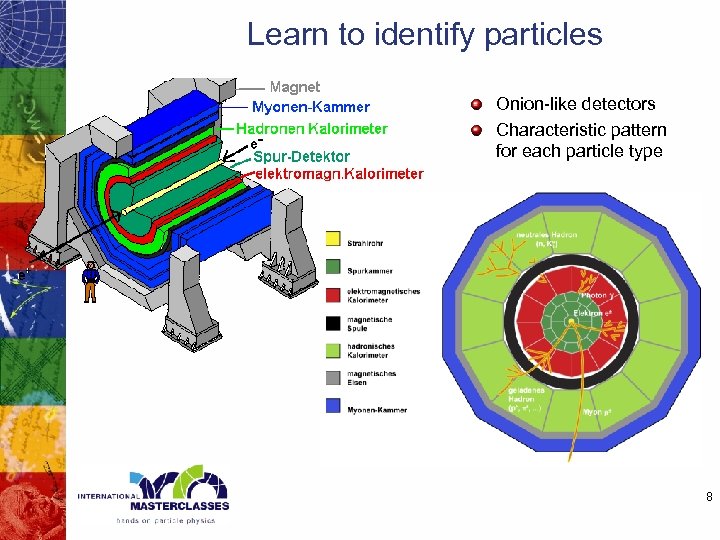
Learn to identify particles Onion-like detectors Characteristic pattern for each particle type 8
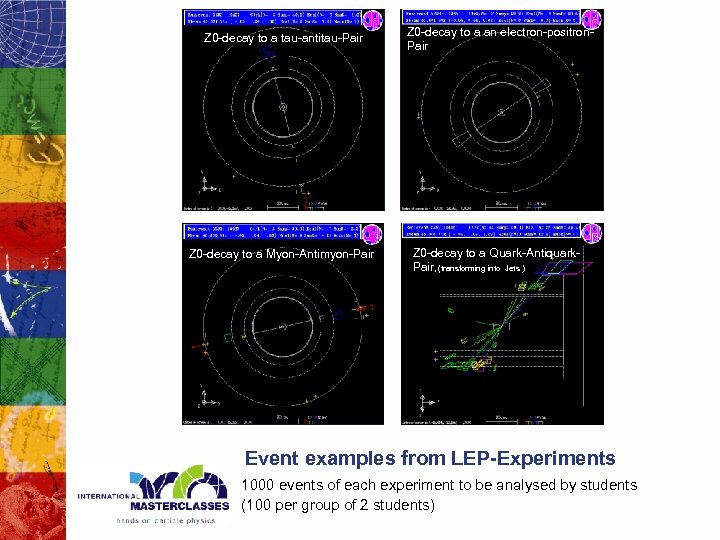
Z 0 -decay to a tau-antitau-Pair Z 0 -decay to a Myon-Antimyon-Pair Z 0 -decay to a an electron-positron. Pair Z 0 -decay to a Quark-Antiquark. Pair, (transforming into Jets ) Event examples from LEP-Experiments 1000 events of each experiment to be analysed by students (100 per group of 2 students)
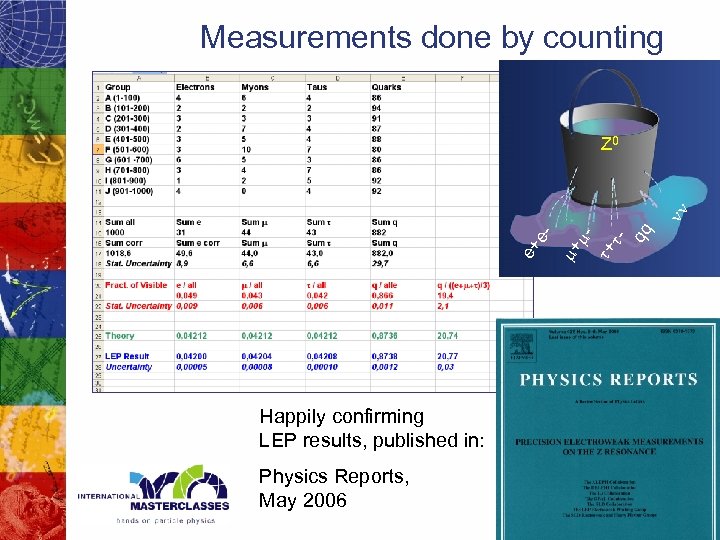
Measurements done by counting Happily confirming LEP results, published in: Physics Reports, May 2006 tqq t+ mm+ e+ e- nn Z 0
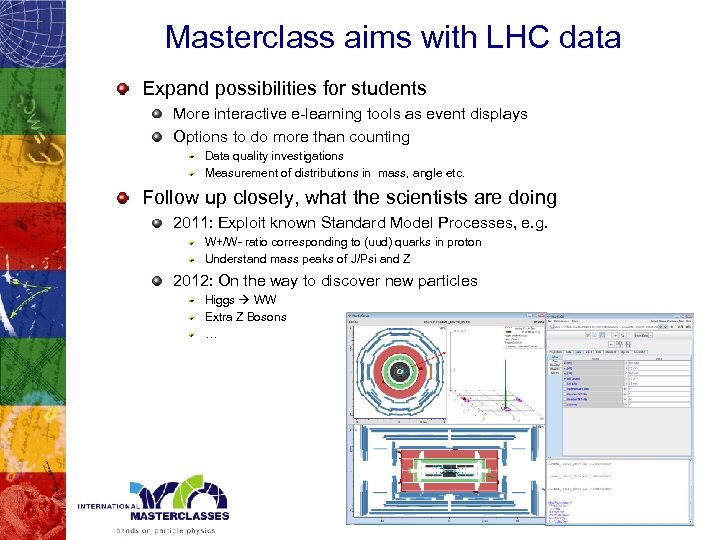
Masterclass aims with LHC data Expand possibilities for students More interactive e-learning tools as event displays Options to do more than counting Data quality investigations Measurement of distributions in mass, angle etc. Follow up closely, what the scientists are doing 2011: Exploit known Standard Model Processes, e. g. W+/W- ratio corresponding to (uud) quarks in proton Understand mass peaks of J/Psi and Z 2012: On the way to discover new particles Higgs WW Extra Z Bosons …
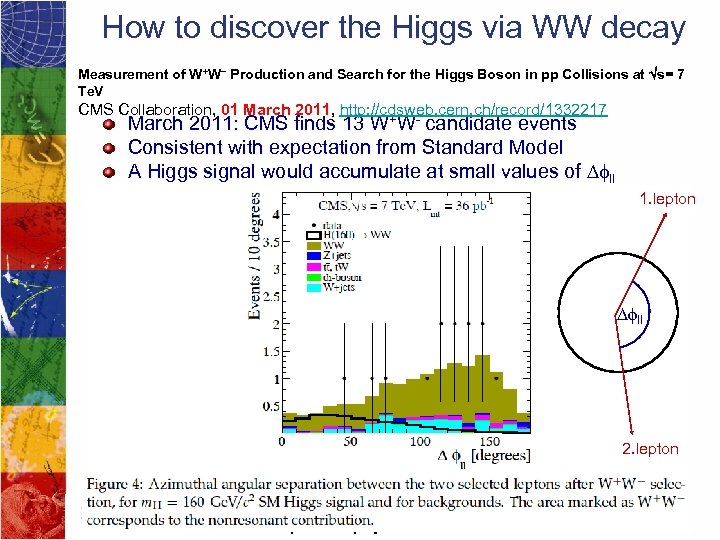
How to discover the Higgs via WW decay Measurement of W+W− Production and Search for the Higgs Boson in pp Collisions at Ös= 7 Te. V CMS Collaboration, 01 March 2011, http: //cdsweb. cern. ch/record/1332217 March 2011: CMS finds 13 W+W- candidate events Consistent with expectation from Standard Model A Higgs signal would accumulate at small values of Dfll 1. lepton Dfll 2. lepton International particle physics masterclasses 2011 12
E-learning Platforms and Tools used ATLAS Minerva (M. Wielers, P. Watkins, T. Mc. Laughlan et al) based on ATLANTIS http: //atlas-minerva. web. cern. ch Hypatia (C. Kourkoumelis et al. ) based on ATLANTIS http: //hypatia. phys. uoa. gr Under construction: Amelia (M. Barnett, J. Pequenao) http: //amelia. sourceforge. net CMS i. Spy online (M. Hategan, K. Cecire et al. ) in collaboration with Quarknet (US) www 12. i 2 u 2. org/elab/cms/event-display ALICE masterclass application (P. Debski, Y. Foka et al. ) simplified ALICE event display in ROOT environment http: //aliceinfo. cern. ch/static/Pictures/pictures_High_Resolution/Master. Class. Webpage. html 13

Refereed evaluation in Physics Education 42 (2007) 636 -644 severity: just right success independent of a-priori knowledge and gender 14
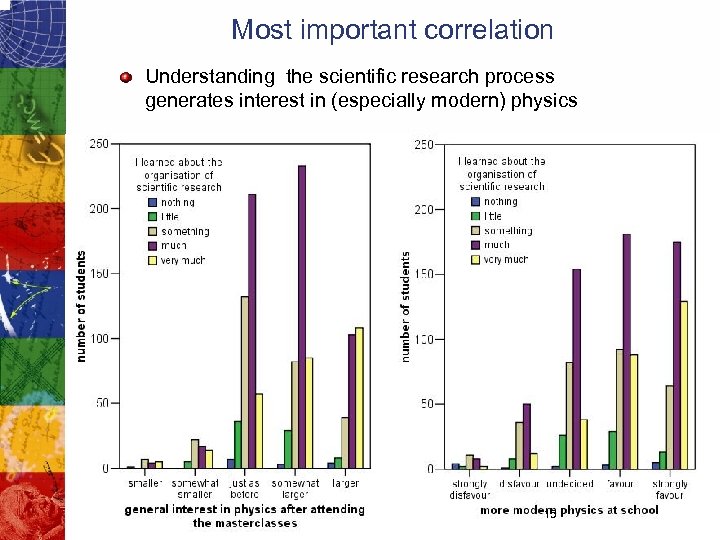
Most important correlation Understanding the scientific research process generates interest in (especially modern) physics 15

Organisation and funding • International masterclasses – Coordinated in Dresden for I/EPPOG by MK (project leader), Uta Bilow (coordinator) – Contributions from • • • Dresden didactics (Gesche Pospiech (chair) , Konrad Jende (Ph. D. student)) Oslo University (Farid Ould Saada, Maiken Pedersen et al) Quarknet (K. Cecire et al) ALICE … • Netzwerk Teilchenwelt (Germany) – Lead in Dresden for 23 German Institutes by MK (project leader), Anne Glück (coordinator), Gesche Pospiech (evaluation) – Cooperations with • • • DESY Zeuthen (measurement of cosmic rays) Würzburg University (context materials for schools) CERN (workshops for students and teachers) Funded by: Kickoff: Discover the Cosmos 02. 09. 2011 CERN 16
54c760f7d2ae3209da01735ca028dcb3.ppt