 MASTER EQUATION OF MANY-PARTICLE SYSTEMS IN A FUNCTIONAL FORM Wipsar Sunu Brams Dwandaru Matthias Schmidt CORNWALL, 6 -8 MARCH 2009
MASTER EQUATION OF MANY-PARTICLE SYSTEMS IN A FUNCTIONAL FORM Wipsar Sunu Brams Dwandaru Matthias Schmidt CORNWALL, 6 -8 MARCH 2009
 What will be discussed in the talk? A special many-particle system: totally asymmetric exclusion process (TASEP). Motivation: why study the TASEP? The master equation of the TASEP. conclusion outlook
What will be discussed in the talk? A special many-particle system: totally asymmetric exclusion process (TASEP). Motivation: why study the TASEP? The master equation of the TASEP. conclusion outlook
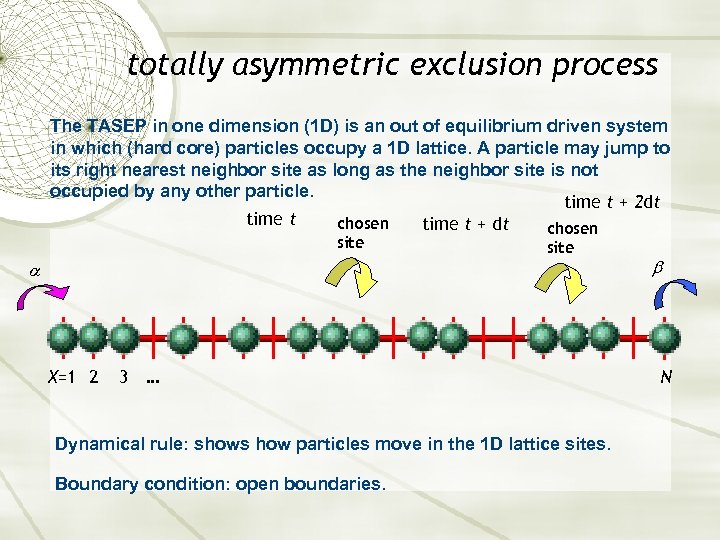 totally asymmetric exclusion process The TASEP in one dimension (1 D) is an out of equilibrium driven system in which (hard core) particles occupy a 1 D lattice. A particle may jump to its right nearest neighbor site as long as the neighbor site is not occupied by any other particle. time t + 2 dt time t chosen time t + dt chosen site X=1 2 3 … Dynamical rule: shows how particles move in the 1 D lattice sites. Boundary condition: open boundaries. N
totally asymmetric exclusion process The TASEP in one dimension (1 D) is an out of equilibrium driven system in which (hard core) particles occupy a 1 D lattice. A particle may jump to its right nearest neighbor site as long as the neighbor site is not occupied by any other particle. time t + 2 dt time t chosen time t + dt chosen site X=1 2 3 … Dynamical rule: shows how particles move in the 1 D lattice sites. Boundary condition: open boundaries. N
 motivation: everyday life motor protein
motivation: everyday life motor protein
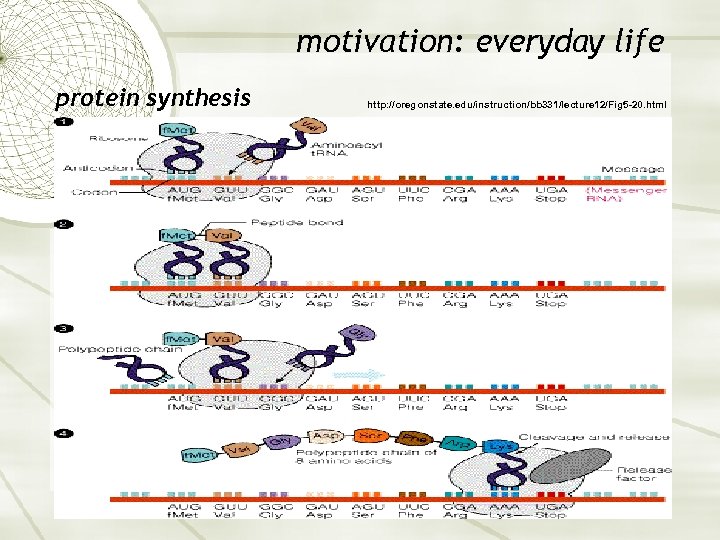 motivation: everyday life protein synthesis http: //oregonstate. edu/instruction/bb 331/lecture 12/Fig 5 -20. html
motivation: everyday life protein synthesis http: //oregonstate. edu/instruction/bb 331/lecture 12/Fig 5 -20. html
 motivation: everyday life Yogyakarta, Indonesia Jakarta, Indonesia
motivation: everyday life Yogyakarta, Indonesia Jakarta, Indonesia
 Prof. David Mukamel, Weizmann Institute, Israel Dr. Debasish Chowdhury, Physics Dept. , IIT, India Prof. Royce K. P. Zia, Virgina Tech. , US Prof. Beate Schmittmann, Virgina Tech. , US Prof. Dr. Joachim Krug, Universitat zu Koln, Germany Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Gunter M. Schutz, Universitat Bonn, Germany
Prof. David Mukamel, Weizmann Institute, Israel Dr. Debasish Chowdhury, Physics Dept. , IIT, India Prof. Royce K. P. Zia, Virgina Tech. , US Prof. Beate Schmittmann, Virgina Tech. , US Prof. Dr. Joachim Krug, Universitat zu Koln, Germany Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Gunter M. Schutz, Universitat Bonn, Germany
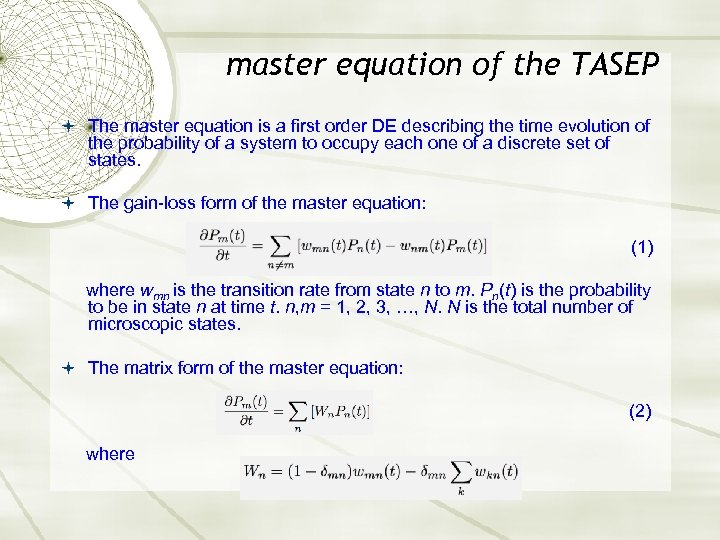 master equation of the TASEP The master equation is a first order DE describing the time evolution of the probability of a system to occupy each one of a discrete set of states. The gain-loss form of the master equation: (1) where wmn is the transition rate from state n to m. Pn(t) is the probability to be in state n at time t. n, m = 1, 2, 3, …, N. N is the total number of microscopic states. The matrix form of the master equation: (2) where
master equation of the TASEP The master equation is a first order DE describing the time evolution of the probability of a system to occupy each one of a discrete set of states. The gain-loss form of the master equation: (1) where wmn is the transition rate from state n to m. Pn(t) is the probability to be in state n at time t. n, m = 1, 2, 3, …, N. N is the total number of microscopic states. The matrix form of the master equation: (2) where
 acknowledgement Prof. Matthias Schmidt Prof. R. Evans Morgan, Jon, Gavin, Tom, and Paul Overseas Research Student (ORS) All of you for listening
acknowledgement Prof. Matthias Schmidt Prof. R. Evans Morgan, Jon, Gavin, Tom, and Paul Overseas Research Student (ORS) All of you for listening
 relationship between TASEP and the lattice fluid mixture 1. Identify TASEP particles and their movements as species in the lattice fluid mixture, hence the relationship. 2. Do calculations in the static lattice fluid mixture via DFT. 3. Apply the correspondence to obtain the desired TASEP properties. [Dwandaru W S B and Schmidt M 2007 J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 40 13209 -13215]
relationship between TASEP and the lattice fluid mixture 1. Identify TASEP particles and their movements as species in the lattice fluid mixture, hence the relationship. 2. Do calculations in the static lattice fluid mixture via DFT. 3. Apply the correspondence to obtain the desired TASEP properties. [Dwandaru W S B and Schmidt M 2007 J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 40 13209 -13215]
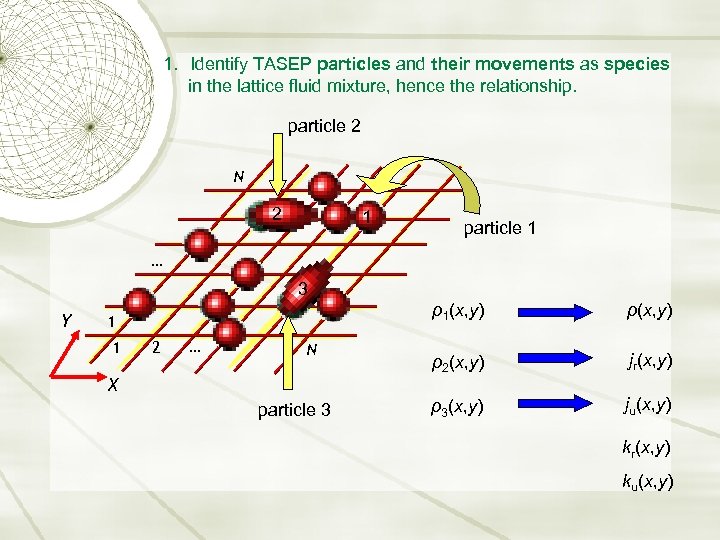 1. Identify TASEP particles and their movements as species in the lattice fluid mixture, hence the relationship. particle 2 N 2 1 particle 1 … 3 Y ρ1(x, y) 1 1 2 … N X particle 3 ρ(x, y) ρ2(x, y) jr(x, y) ρ3(x, y) ju(x, y) kr(x, y) ku(x, y)
1. Identify TASEP particles and their movements as species in the lattice fluid mixture, hence the relationship. particle 2 N 2 1 particle 1 … 3 Y ρ1(x, y) 1 1 2 … N X particle 3 ρ(x, y) ρ2(x, y) jr(x, y) ρ3(x, y) ju(x, y) kr(x, y) ku(x, y)
 A correspondence between the fluids mixture and the TASEP in 2 D: i = 1, 2.
A correspondence between the fluids mixture and the TASEP in 2 D: i = 1, 2.
 2. Calculations in the static lattice fluid mixture, yields: The linearized density profiles, i. e. 3. Apply the correspondence to get into the TASEP.
2. Calculations in the static lattice fluid mixture, yields: The linearized density profiles, i. e. 3. Apply the correspondence to get into the TASEP.
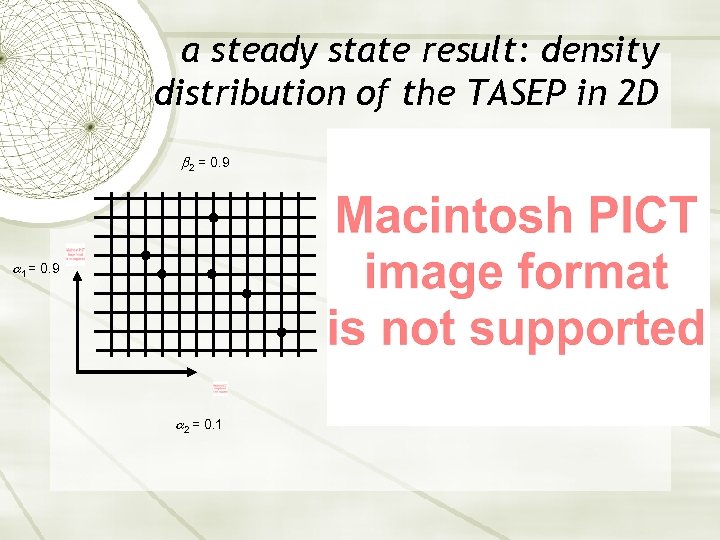 a steady state result: density distribution of the TASEP in 2 D 2 = 0. 9 1 = 0. 9 2 = 0. 1
a steady state result: density distribution of the TASEP in 2 D 2 = 0. 9 1 = 0. 9 2 = 0. 1
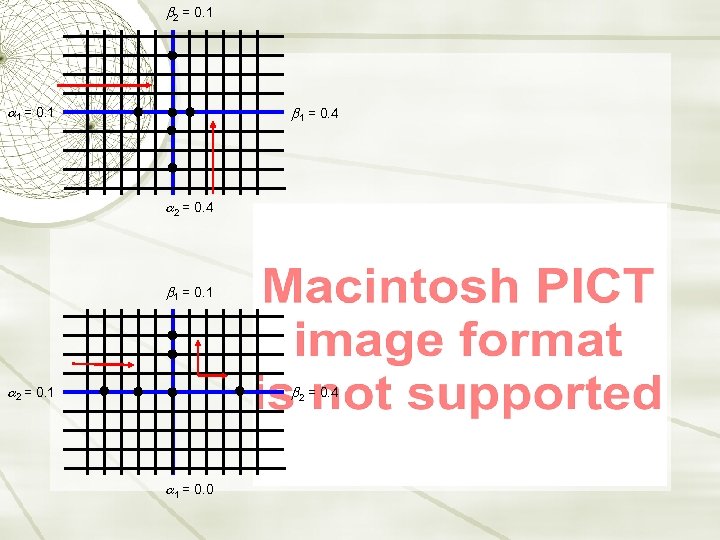 2 = 0. 1 1 = 0. 4 2 = 0. 4 1 = 0. 1 2 = 0. 4 1 = 0. 0
2 = 0. 1 1 = 0. 4 2 = 0. 4 1 = 0. 1 2 = 0. 4 1 = 0. 0